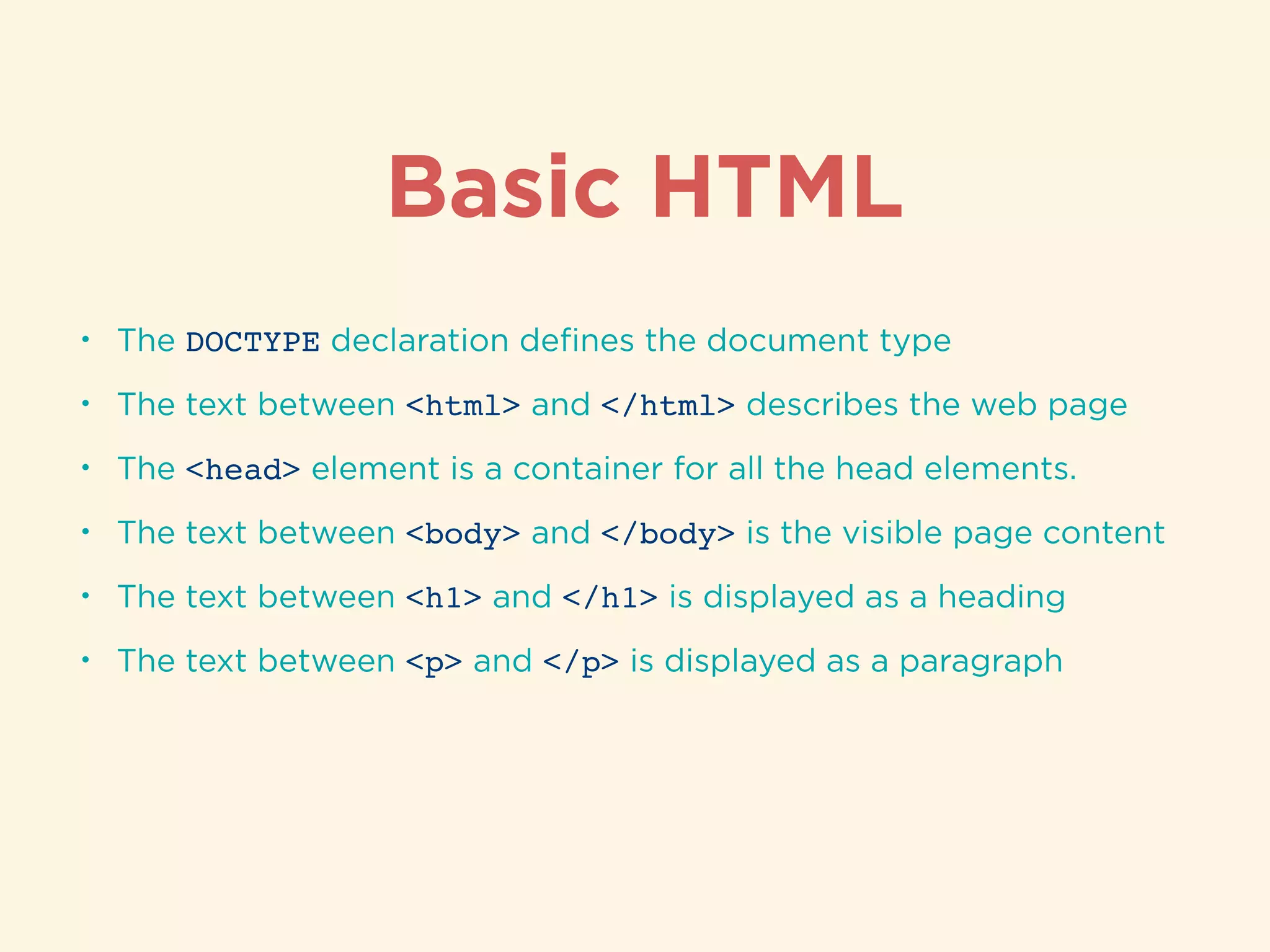
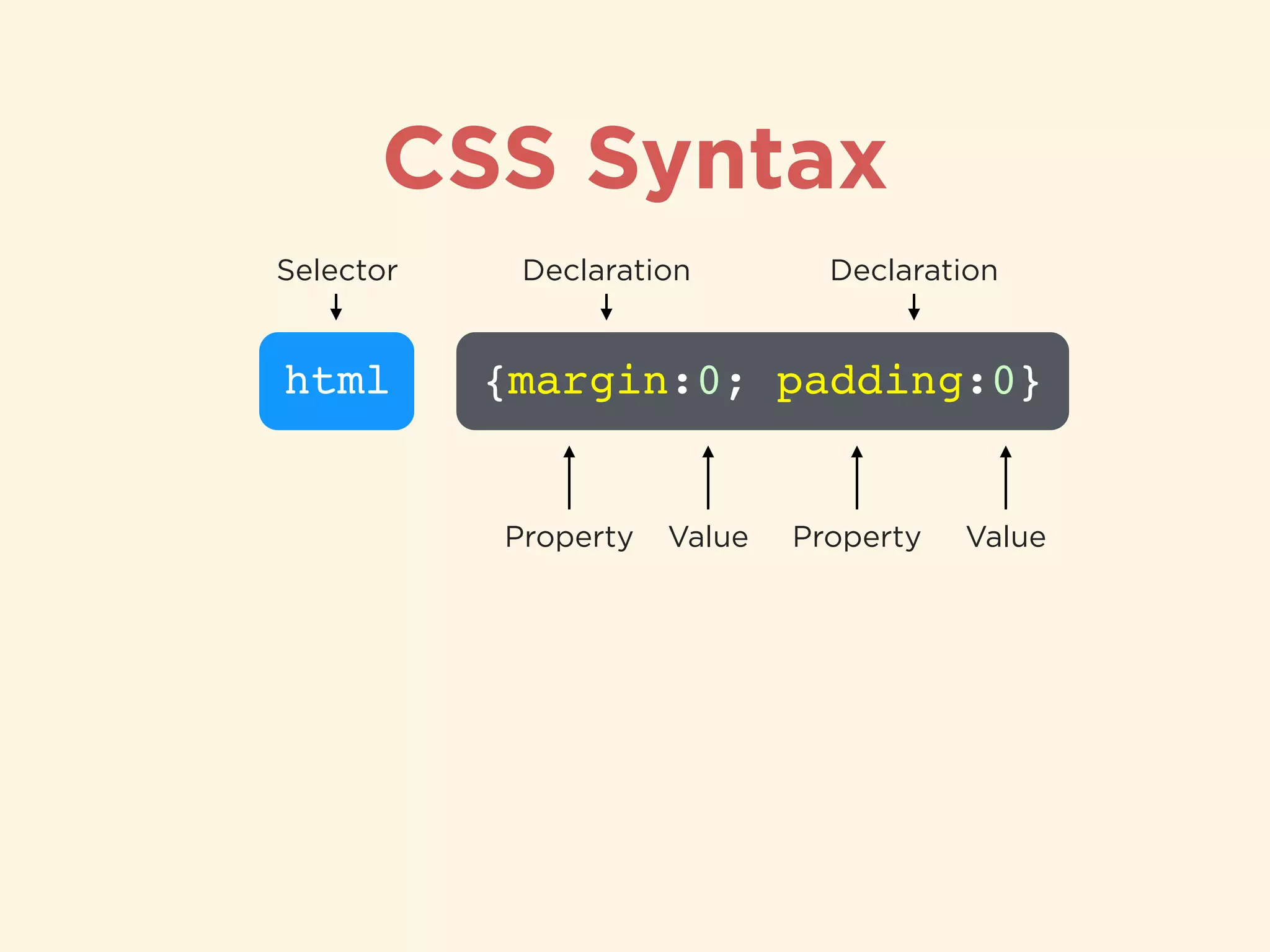
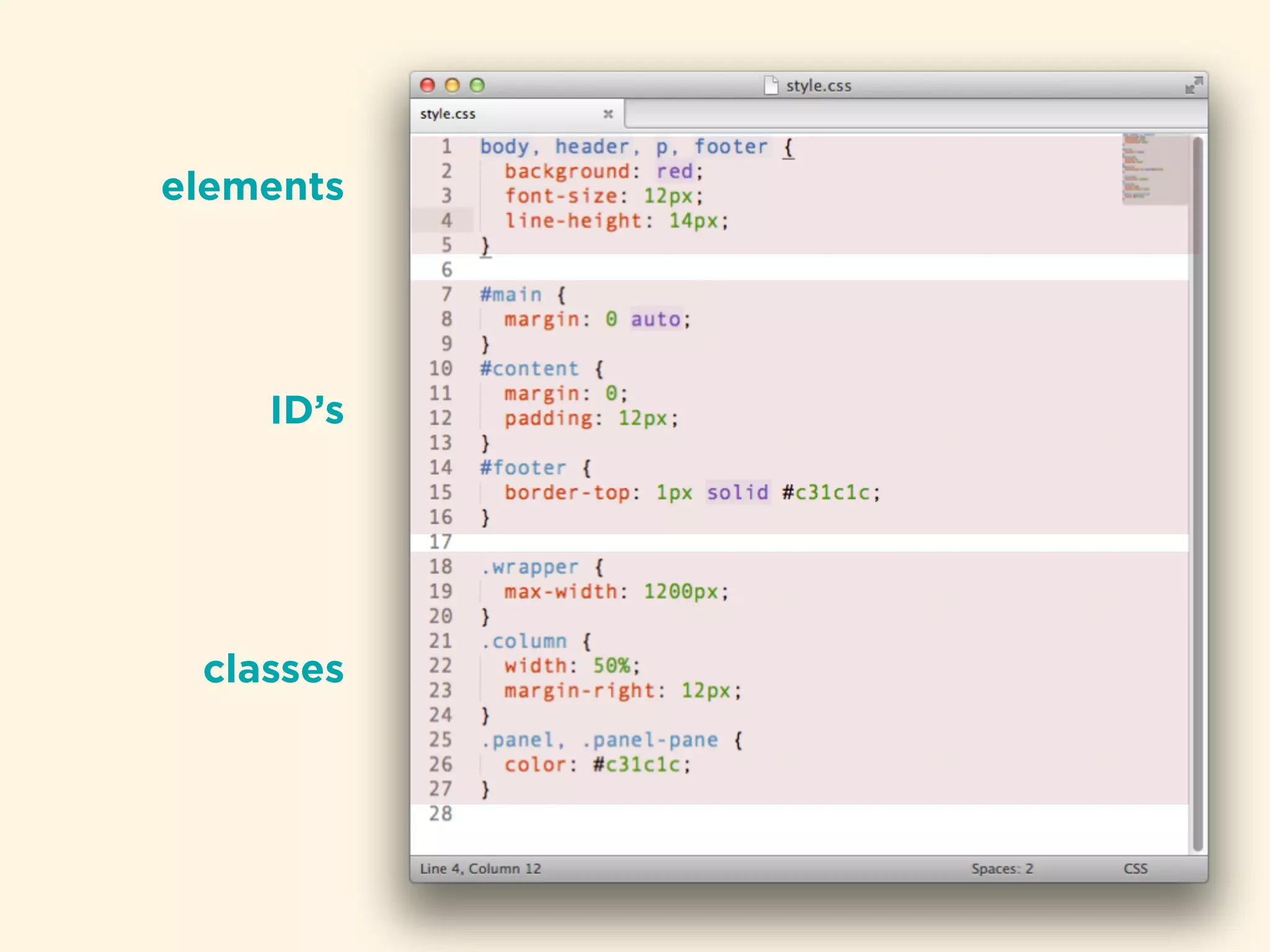
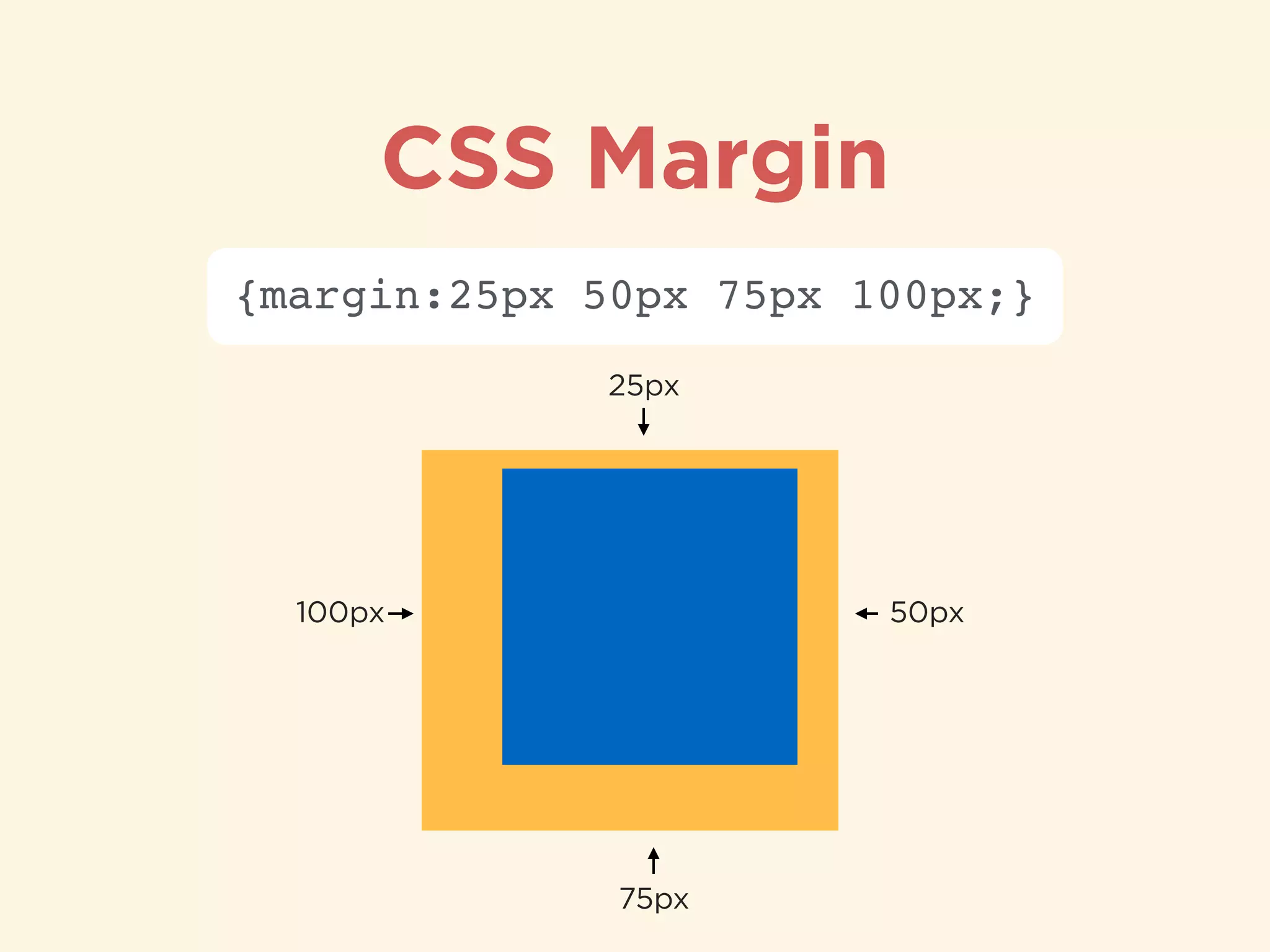
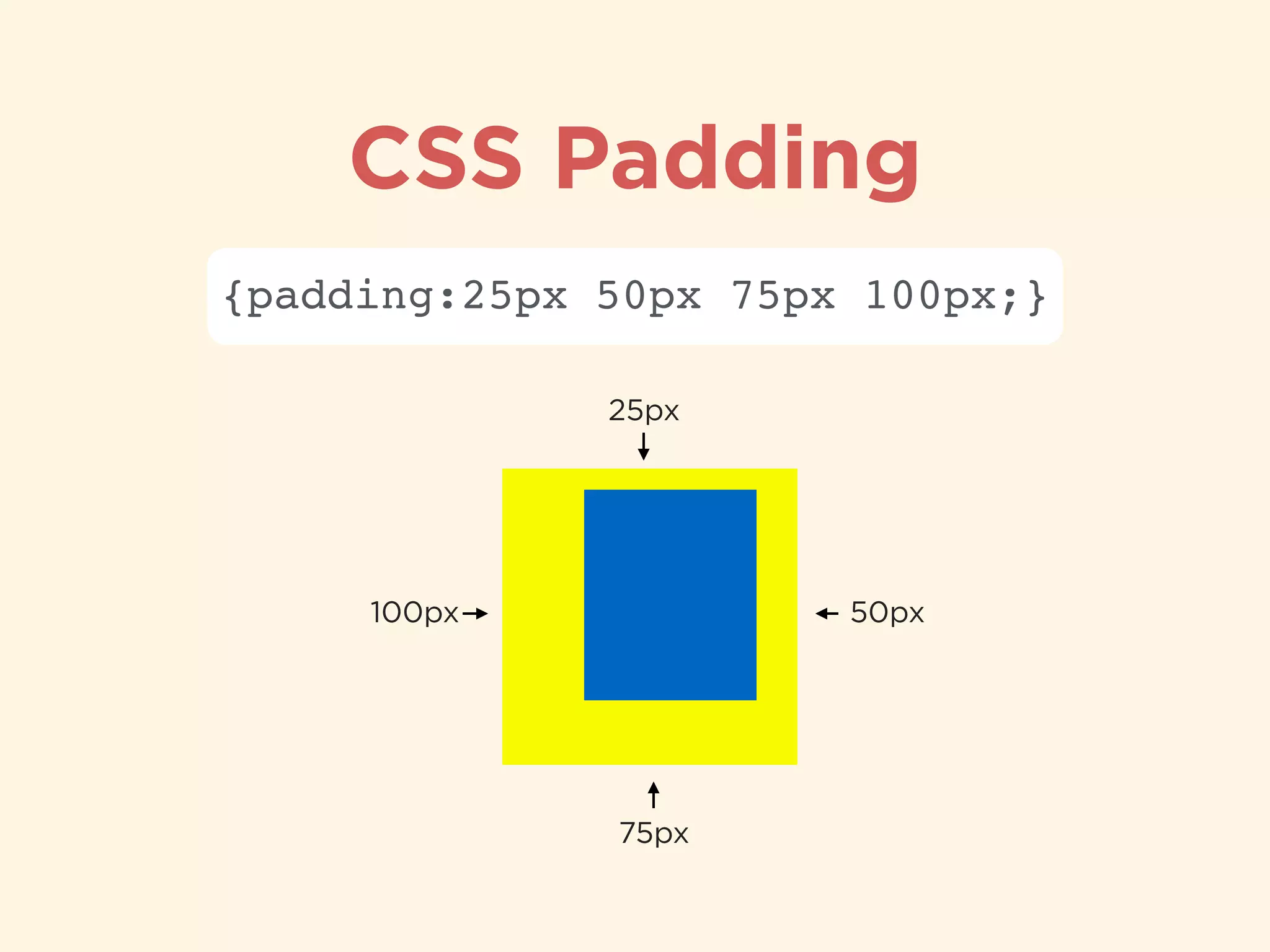
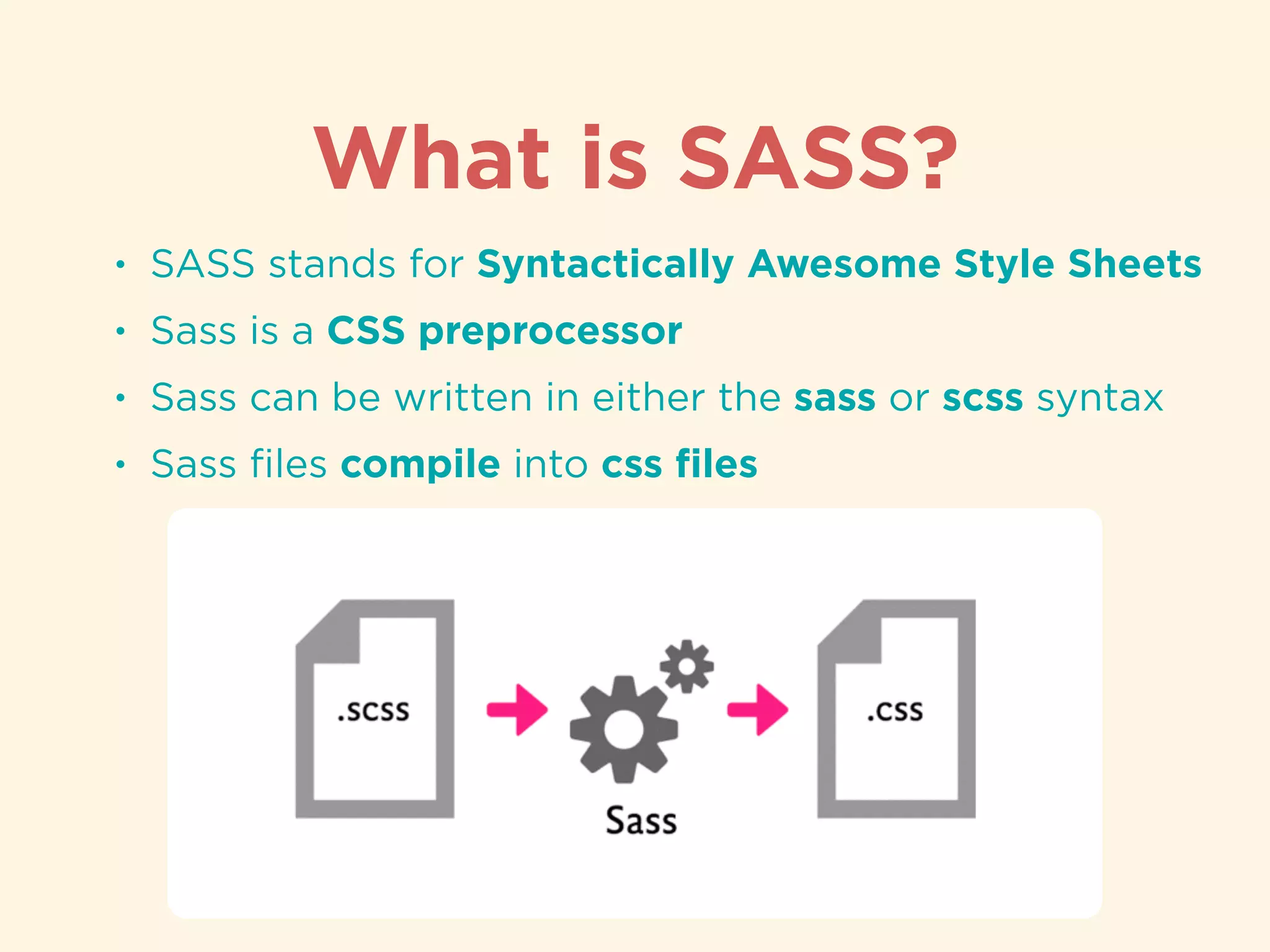
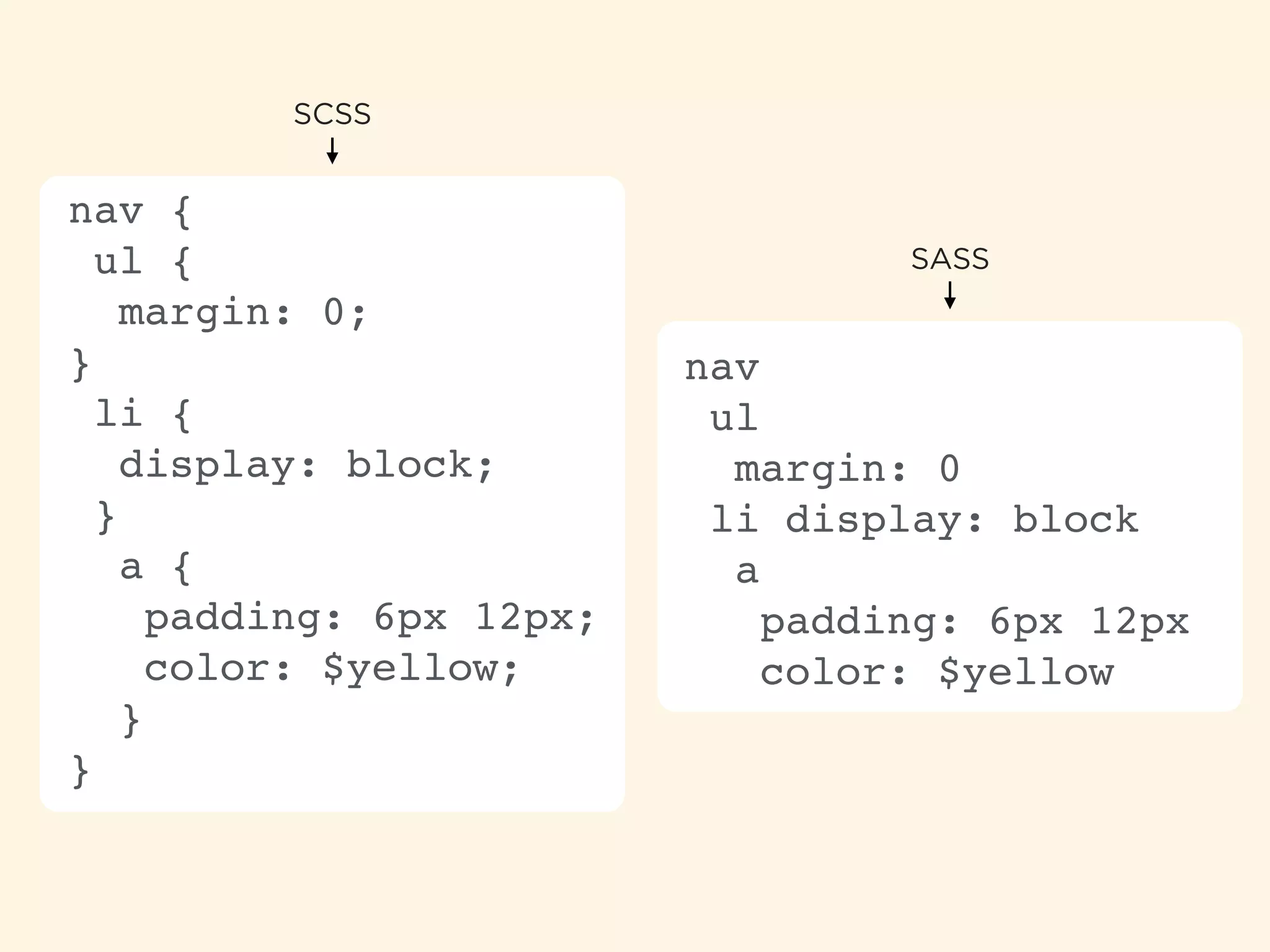
The document provides an introduction to HTML, CSS, and SASS. It discusses what each technology is, how they are used together, and some of their key features. It explains that HTML is a markup language used to define the structure and content of web pages, CSS is used to style and lay out HTML elements, and SASS is a CSS preprocessor that adds powerful features like variables, nesting, and mixins to make CSS more efficient to write and maintain. It then provides overviews of important HTML tags, CSS properties and selectors, and features of SASS like mixins and extends.