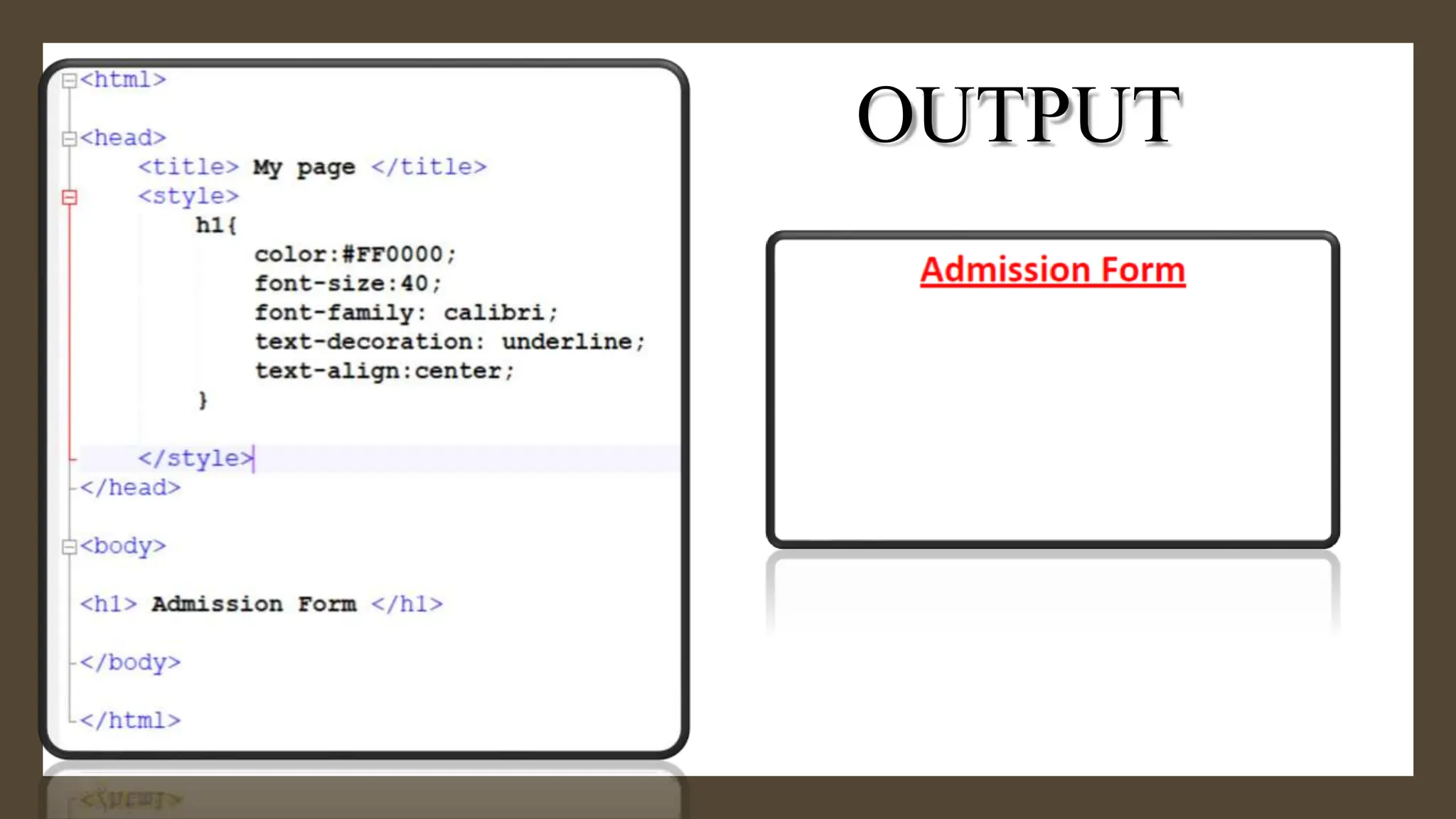
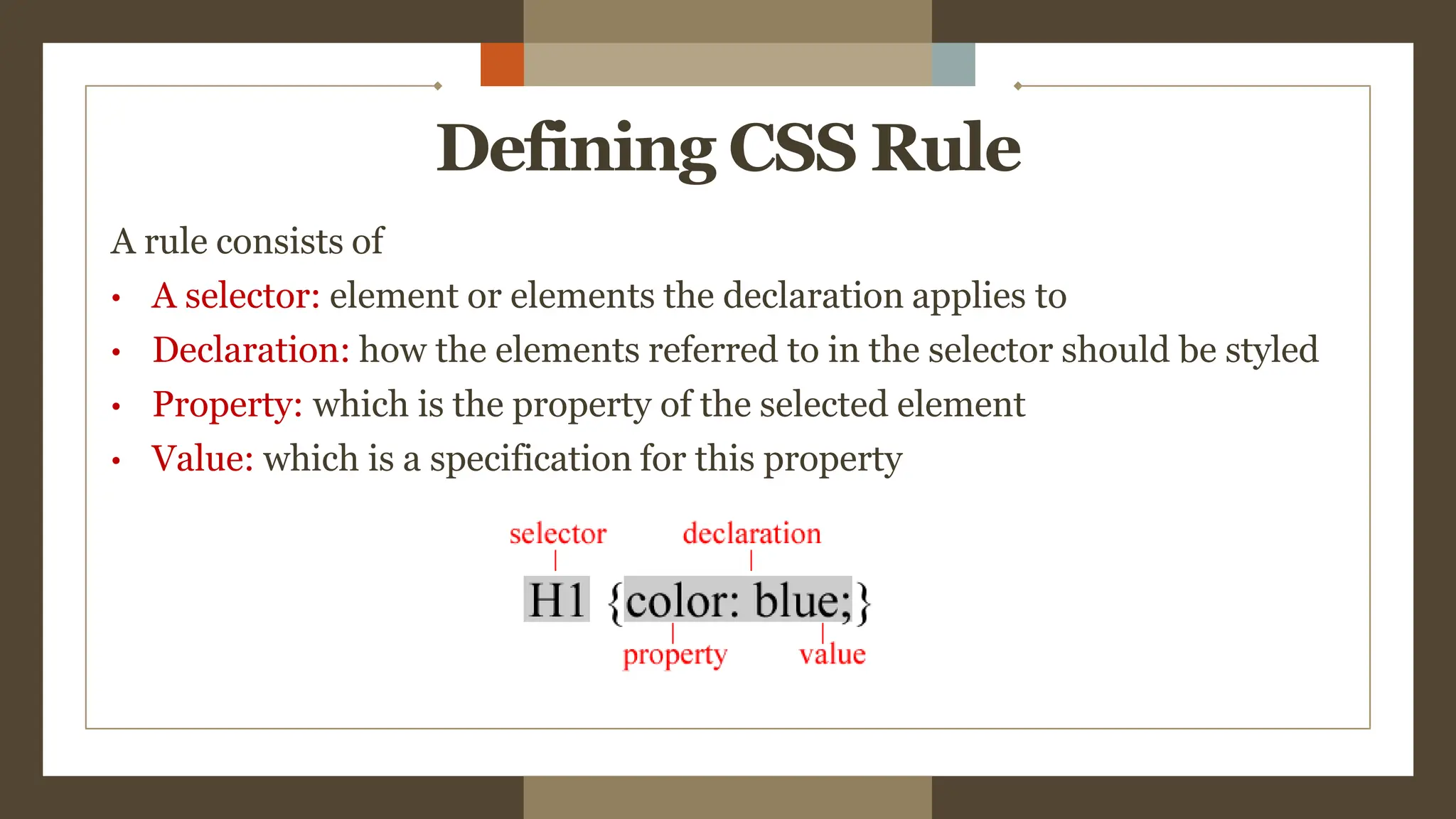
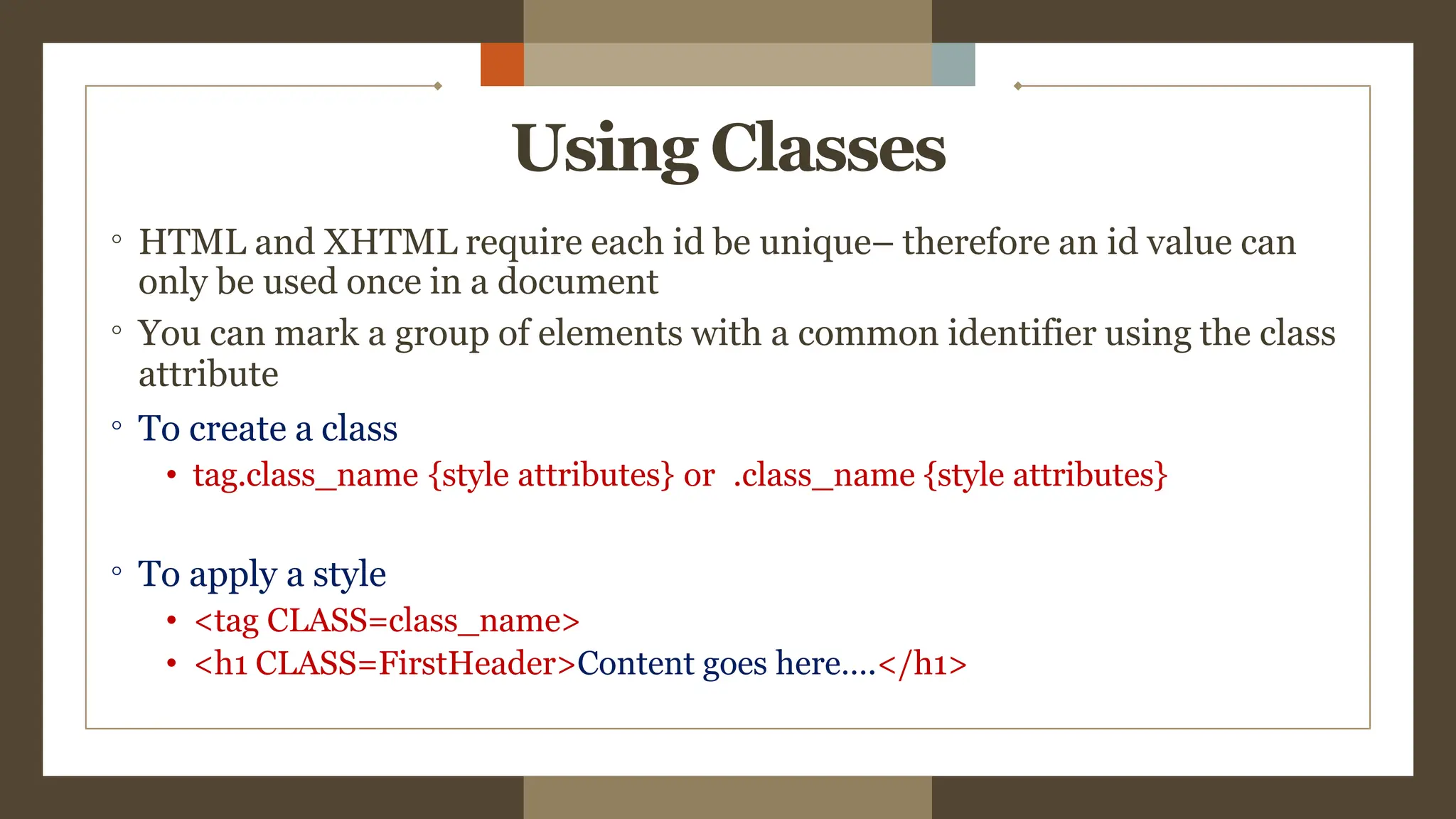
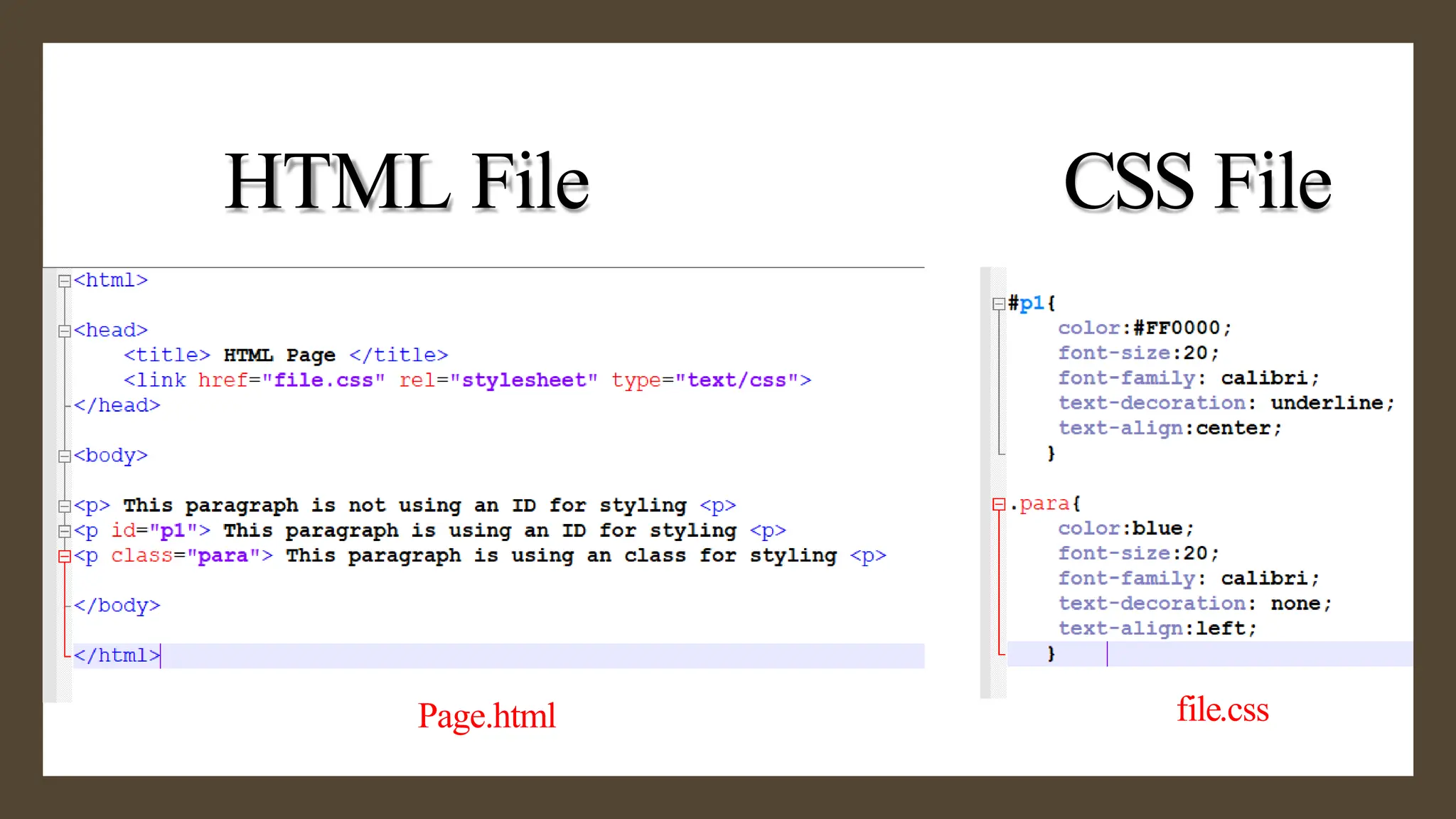
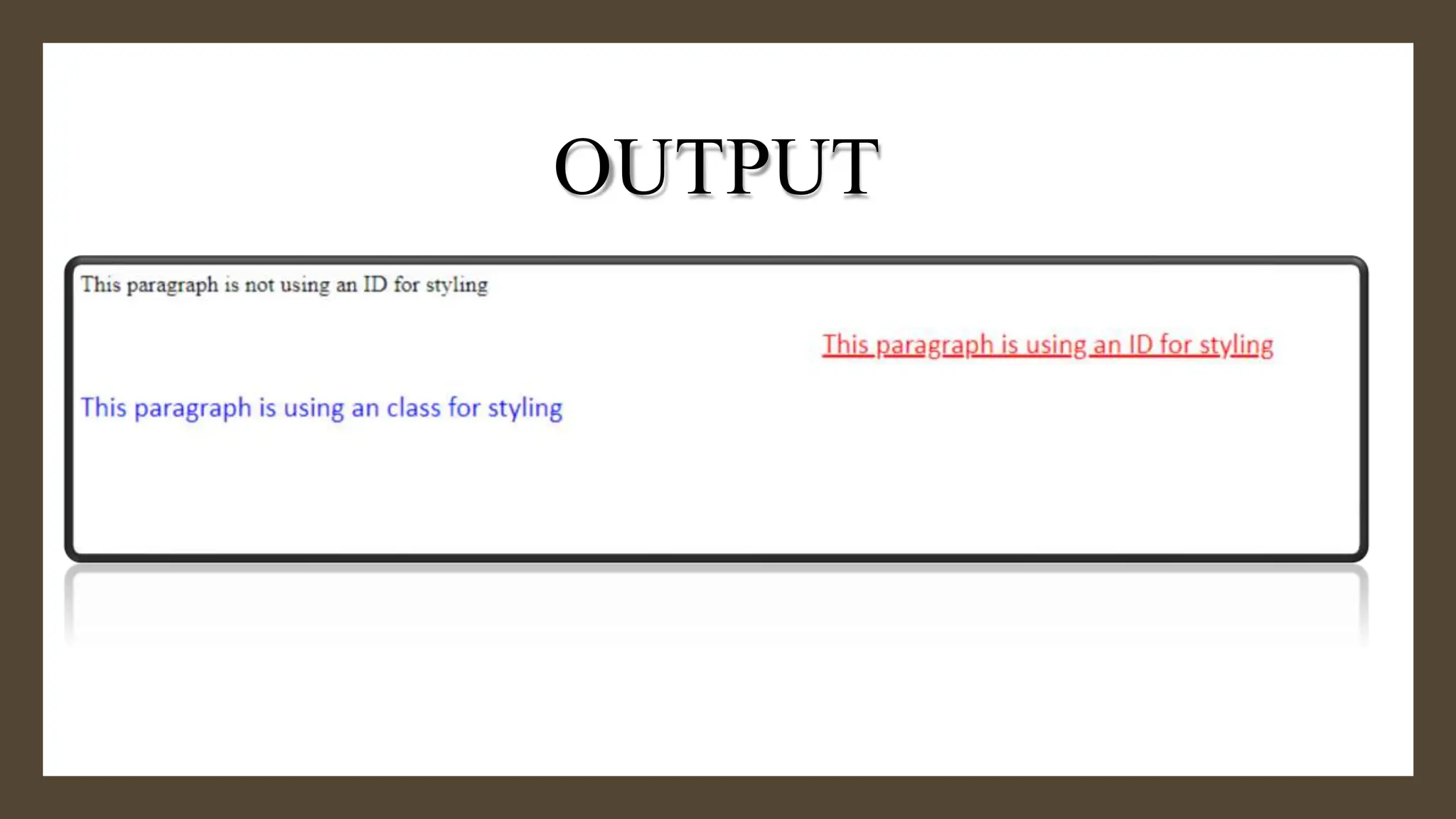
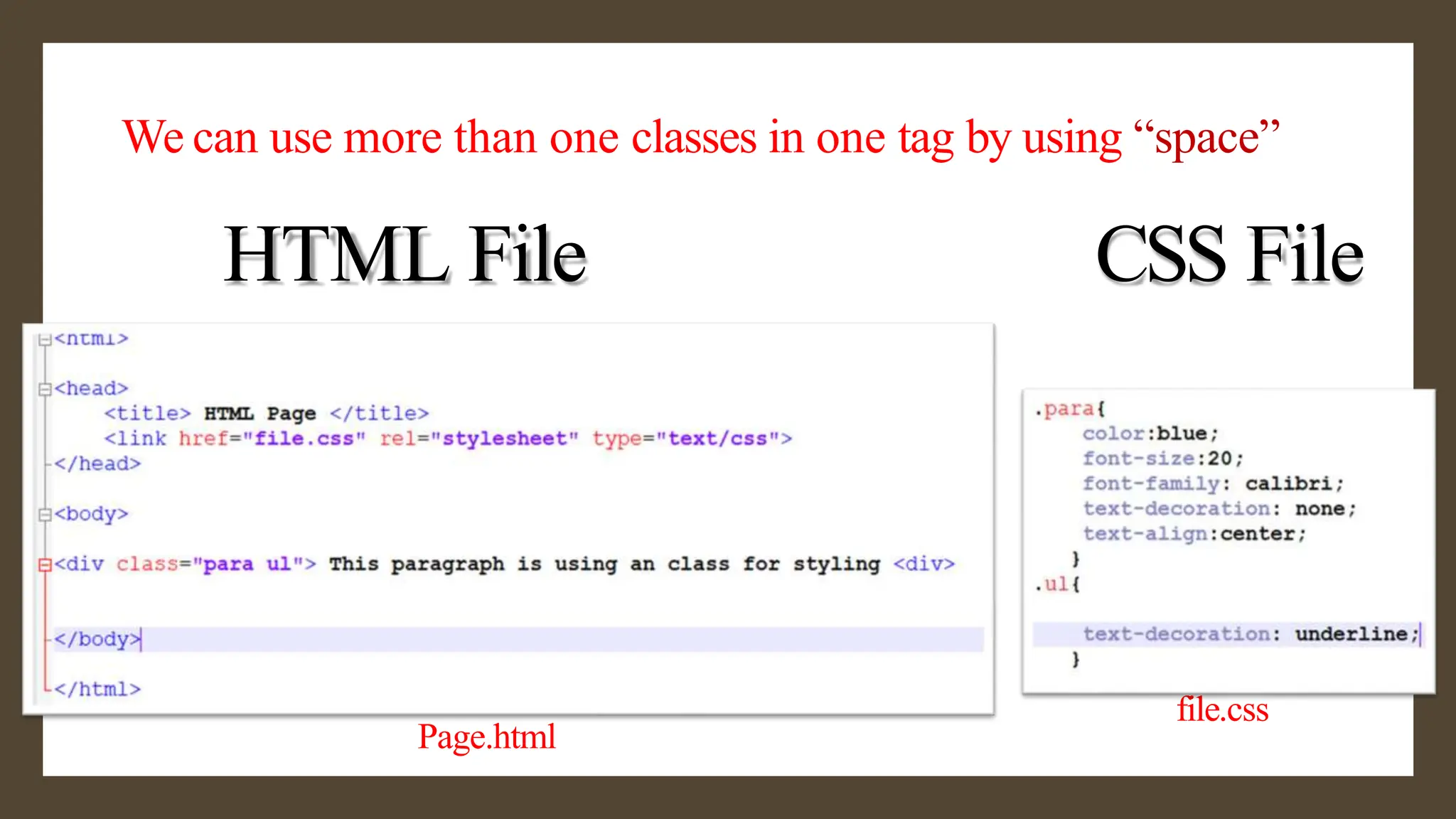
The document provides an overview of the <div> tag in HTML and its styling using CSS, which was created by Hakon Lie in 1994 and has become a W3C standard for web page presentation. It explains various types of style sheets, including inline, embedded, and external styles, along with how to define CSS rules, properties, and the differences between IDs and classes. Additionally, it covers font, text, background, border, padding properties, and how to style hyperlinks using CSS pseudo-classes.