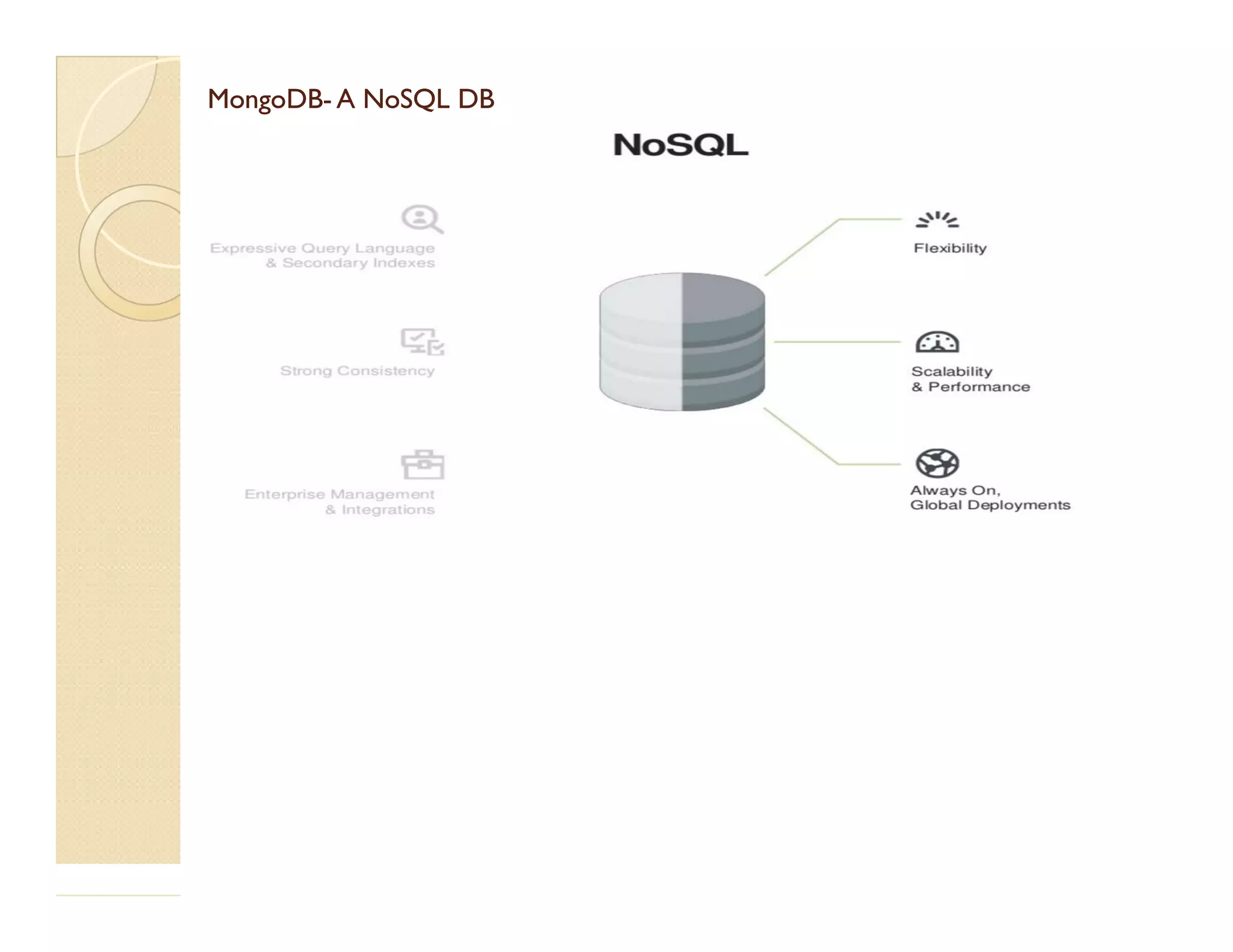
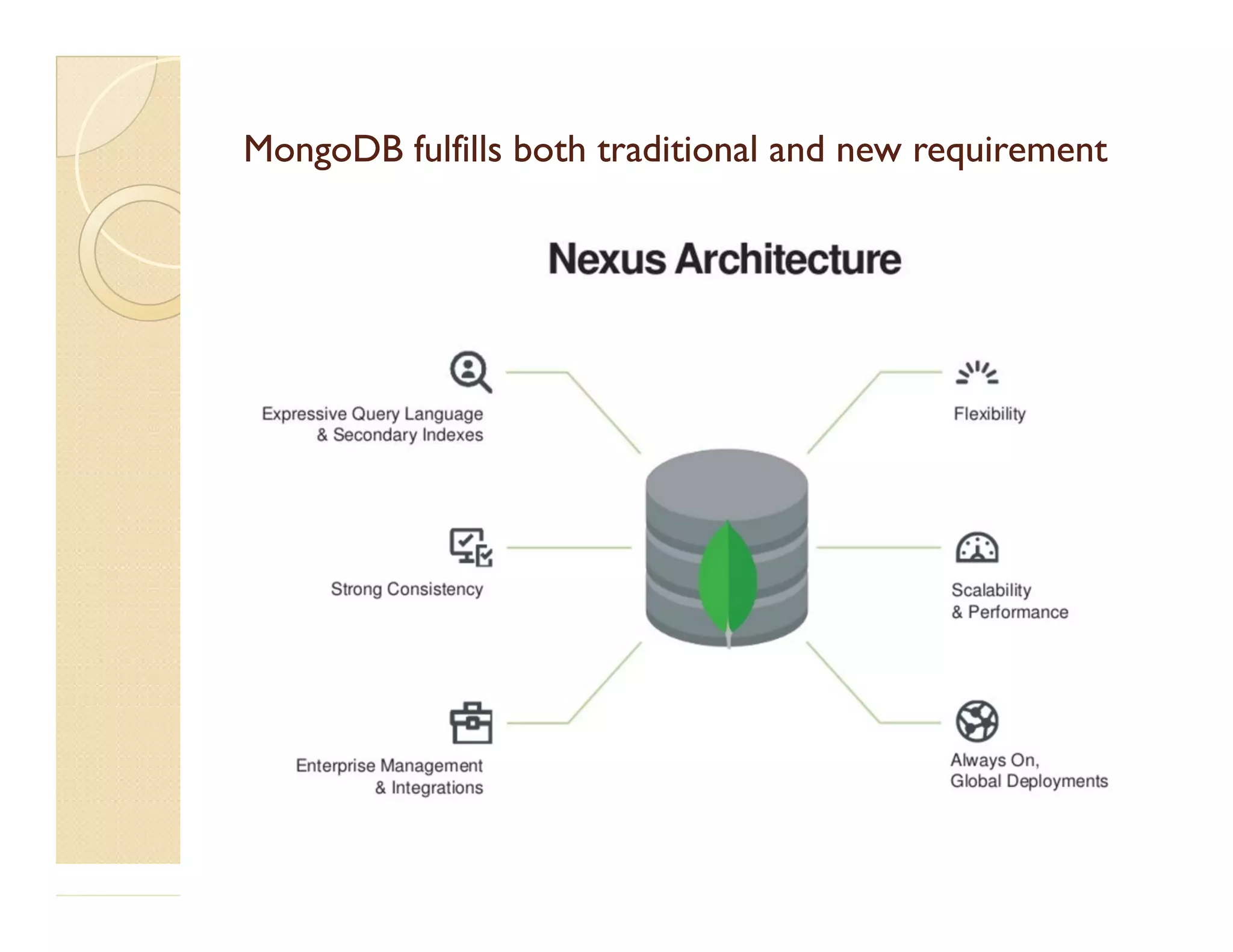
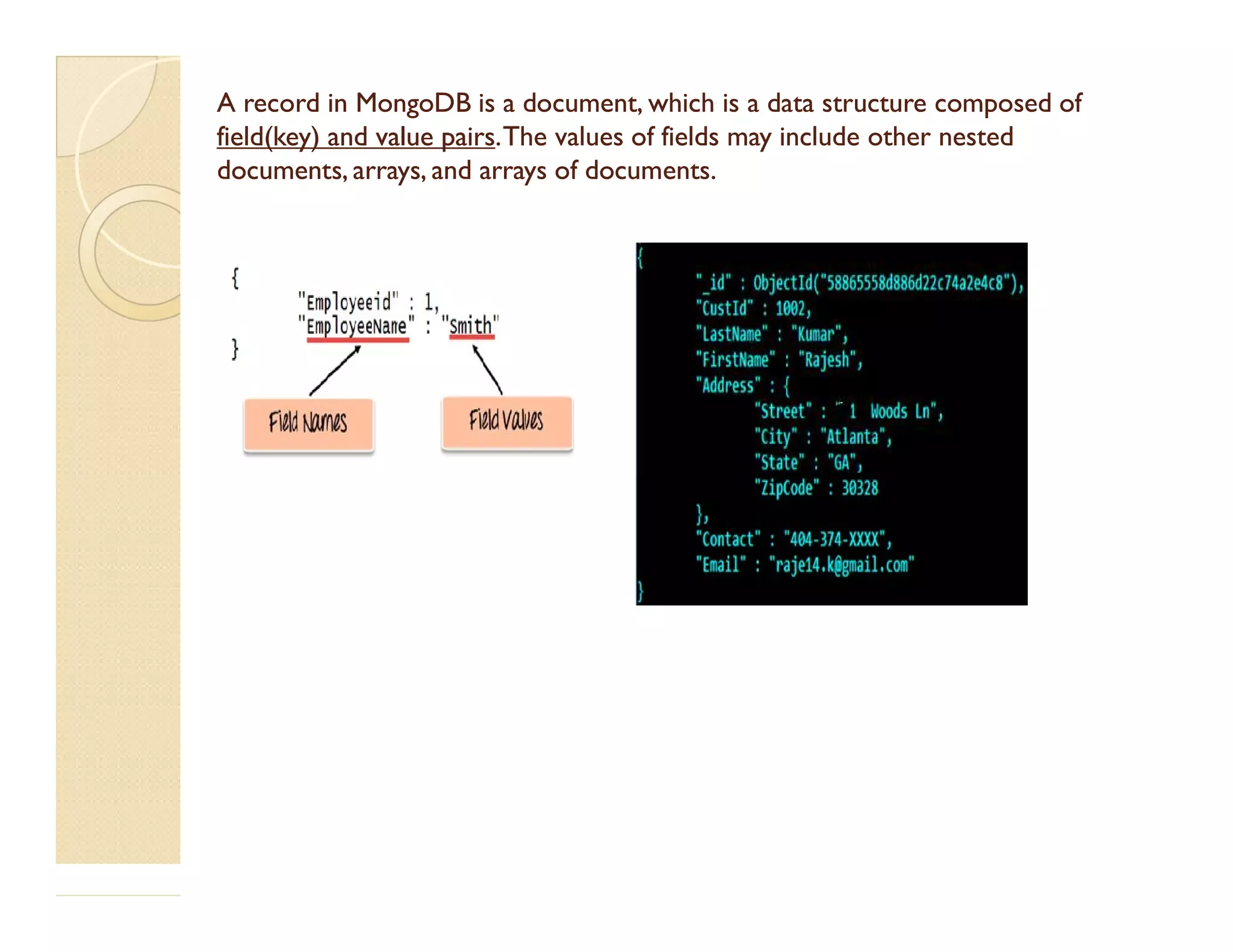
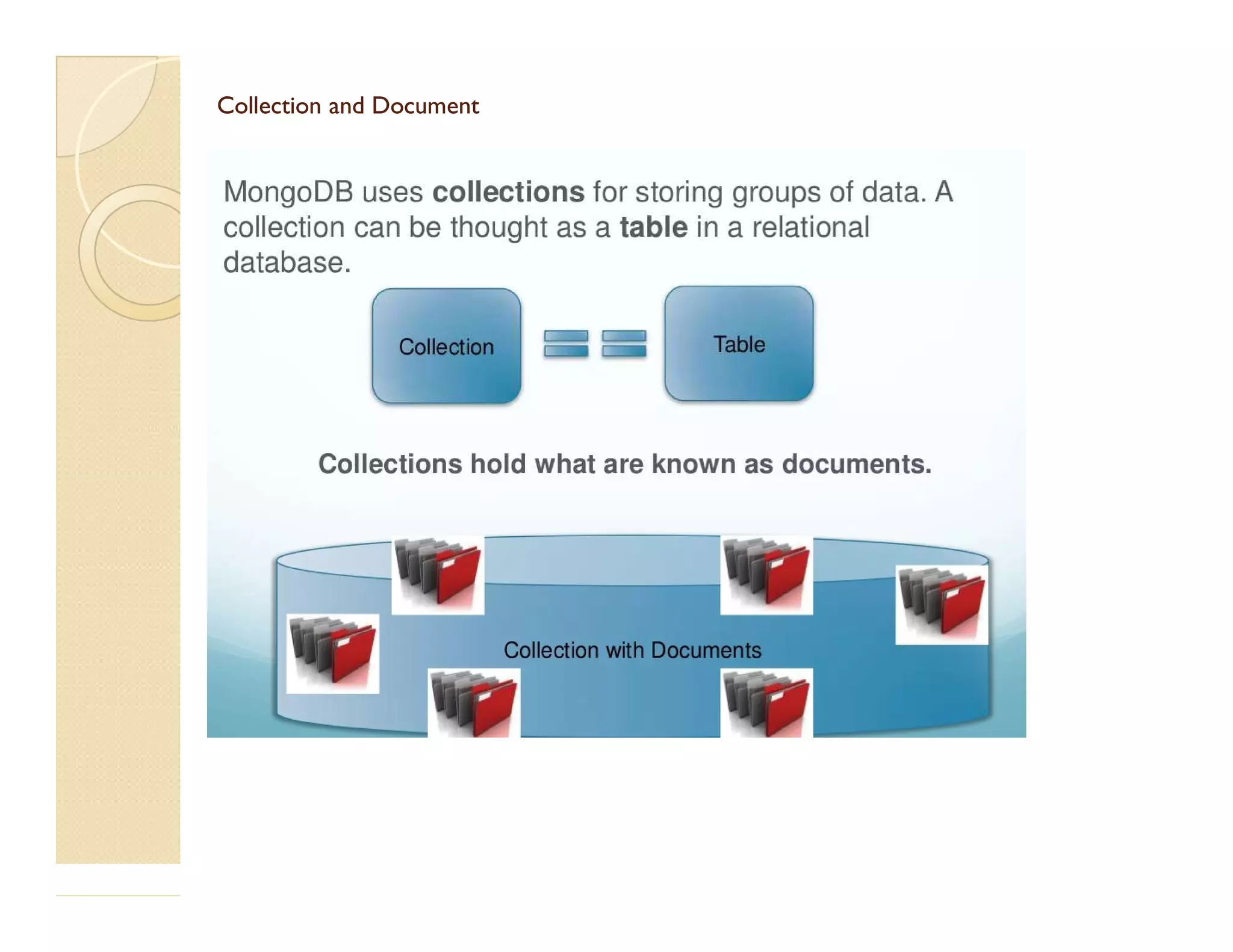
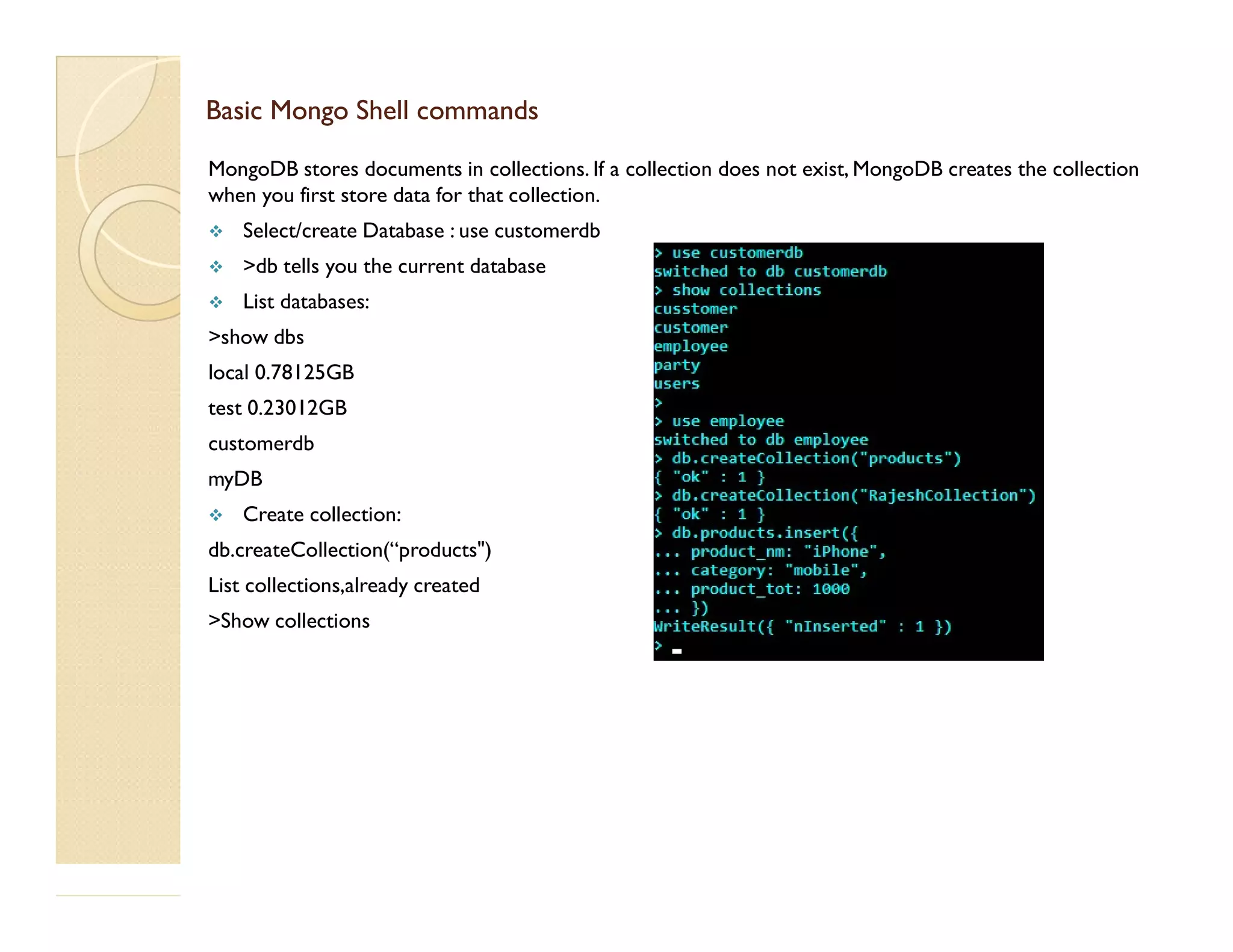
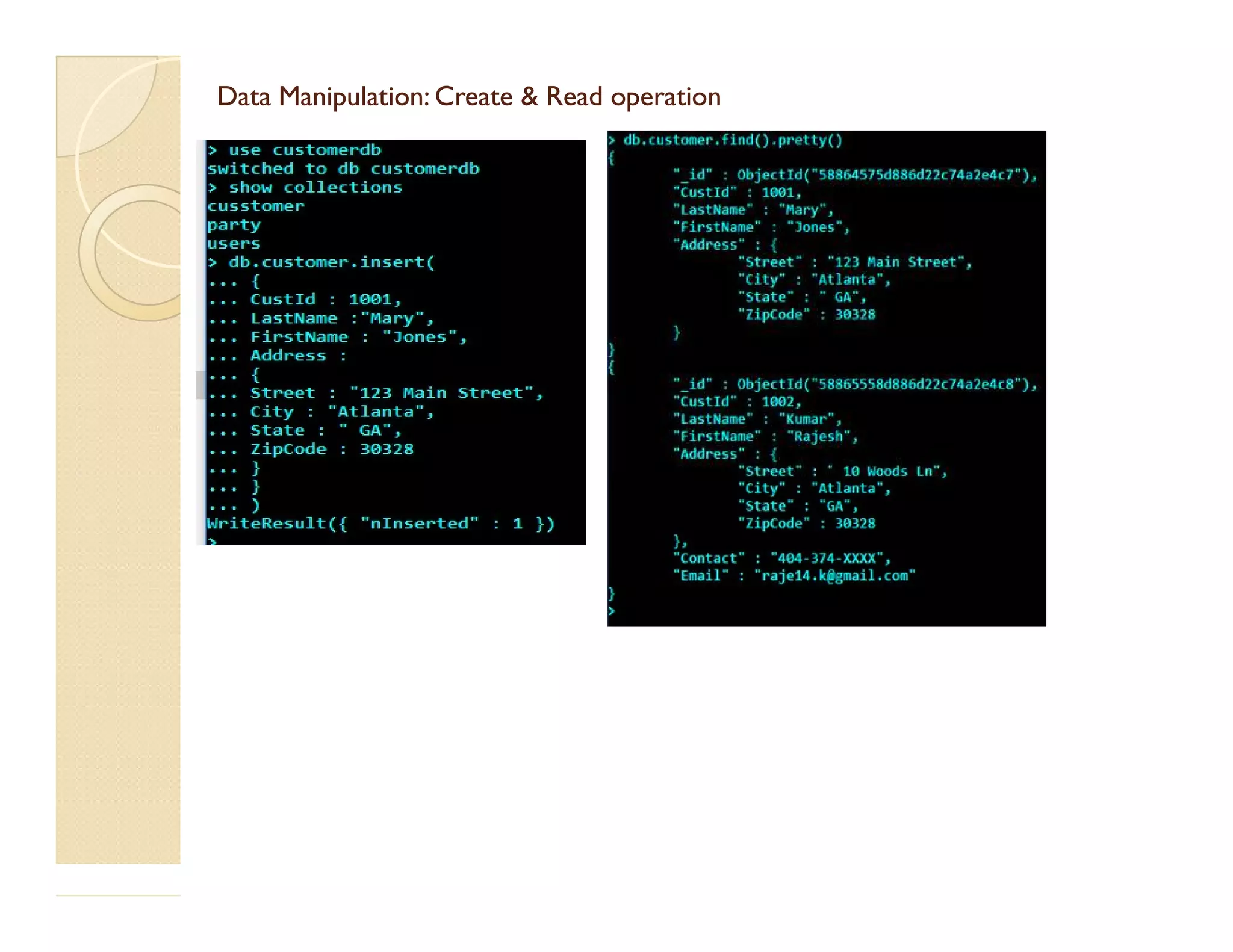
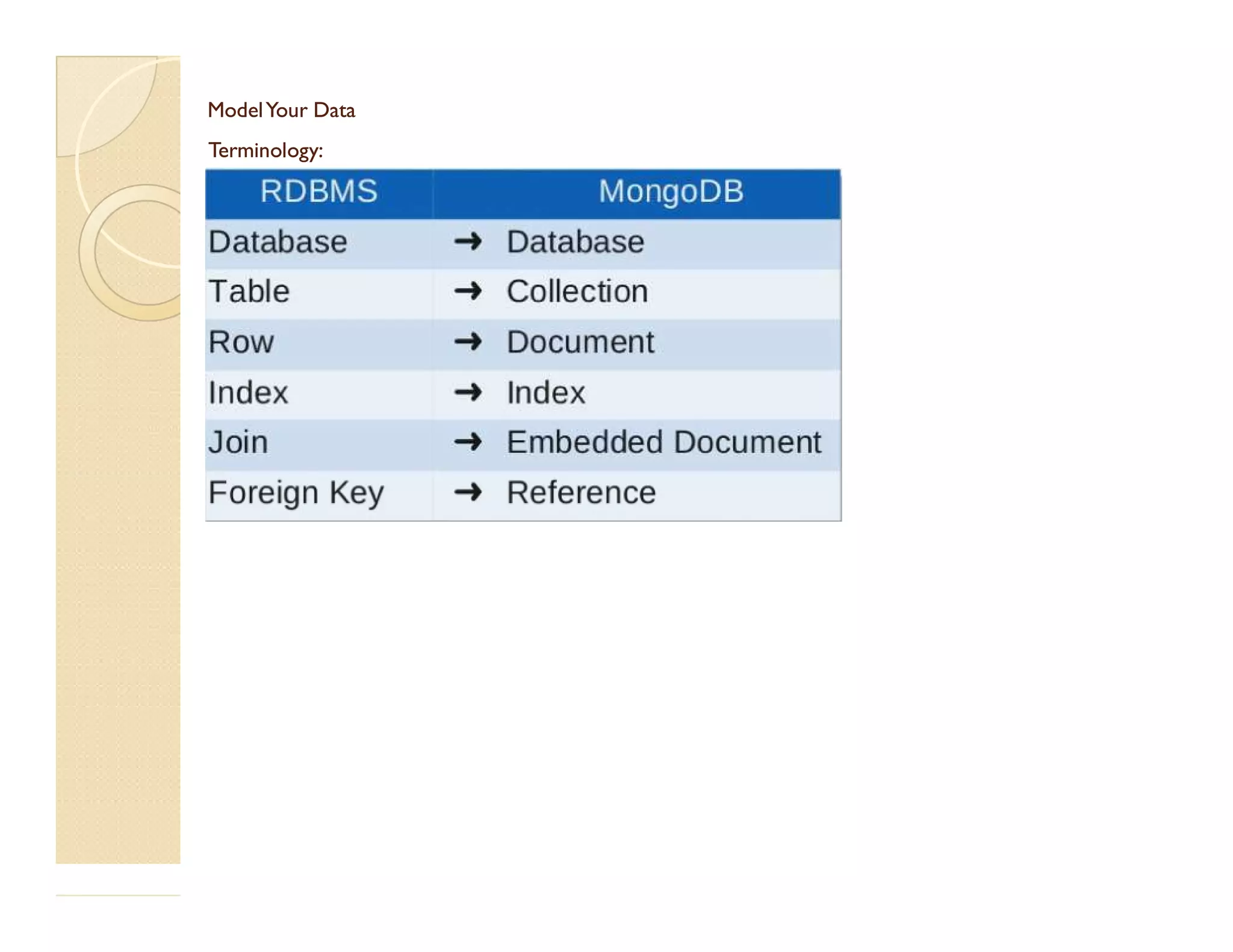
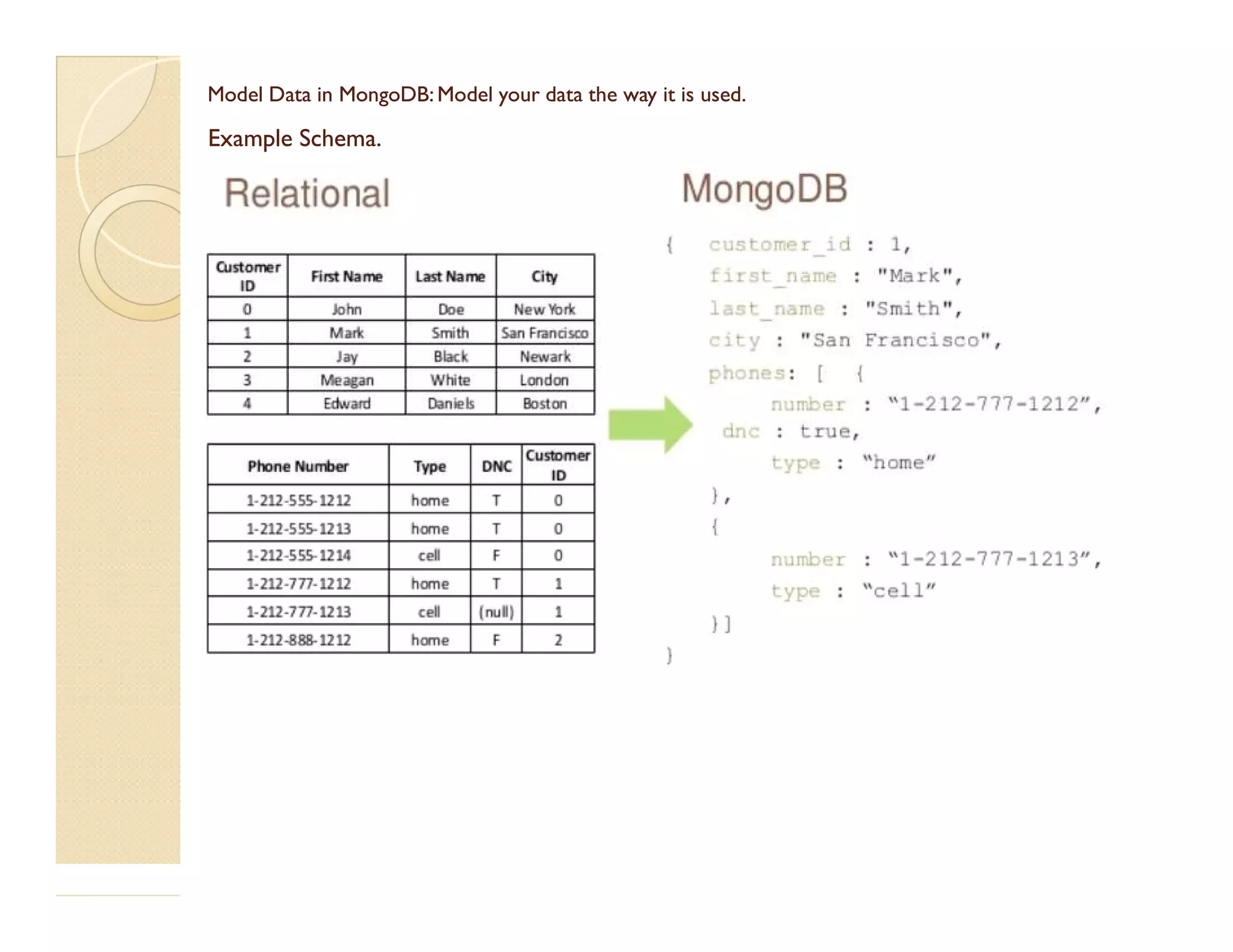
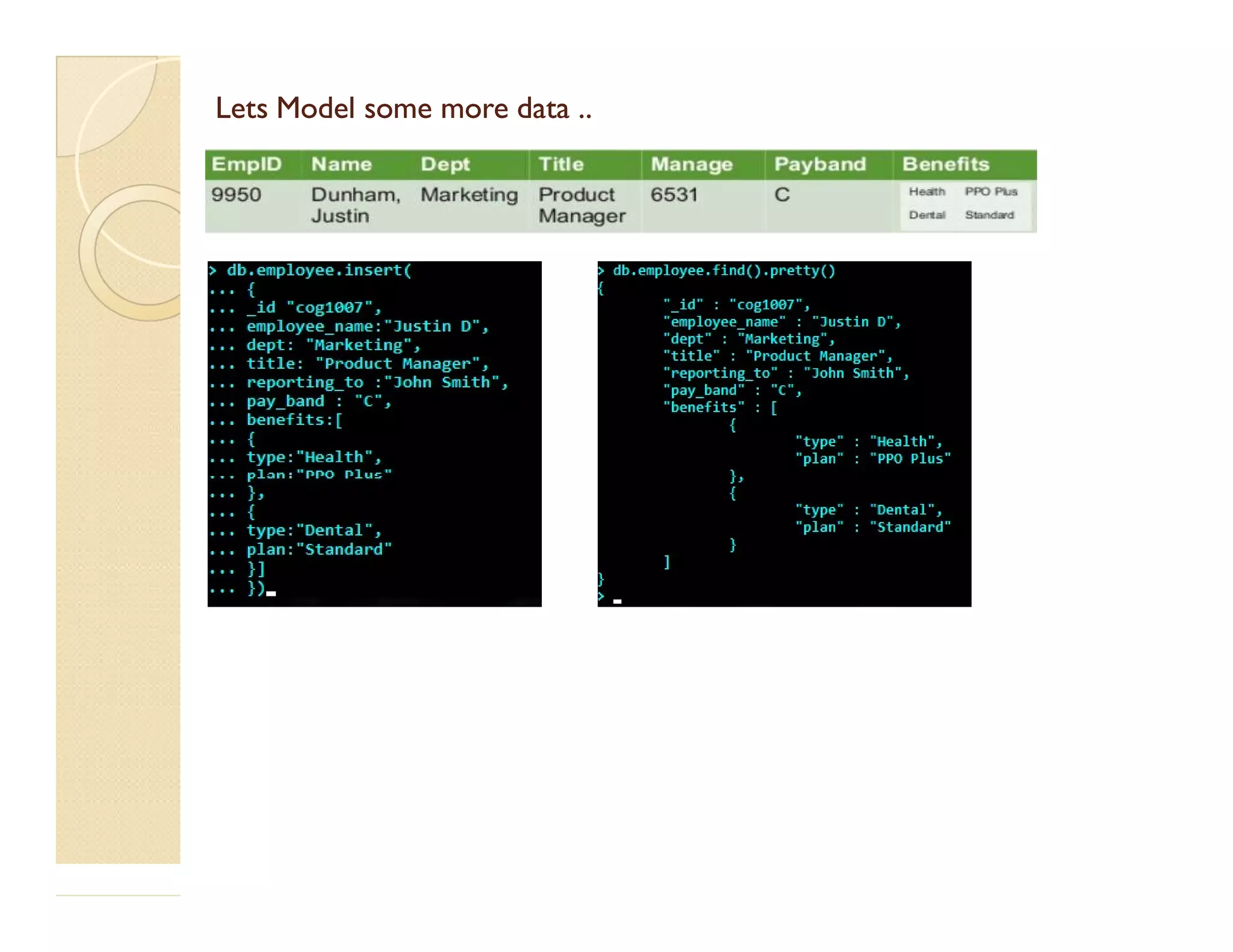
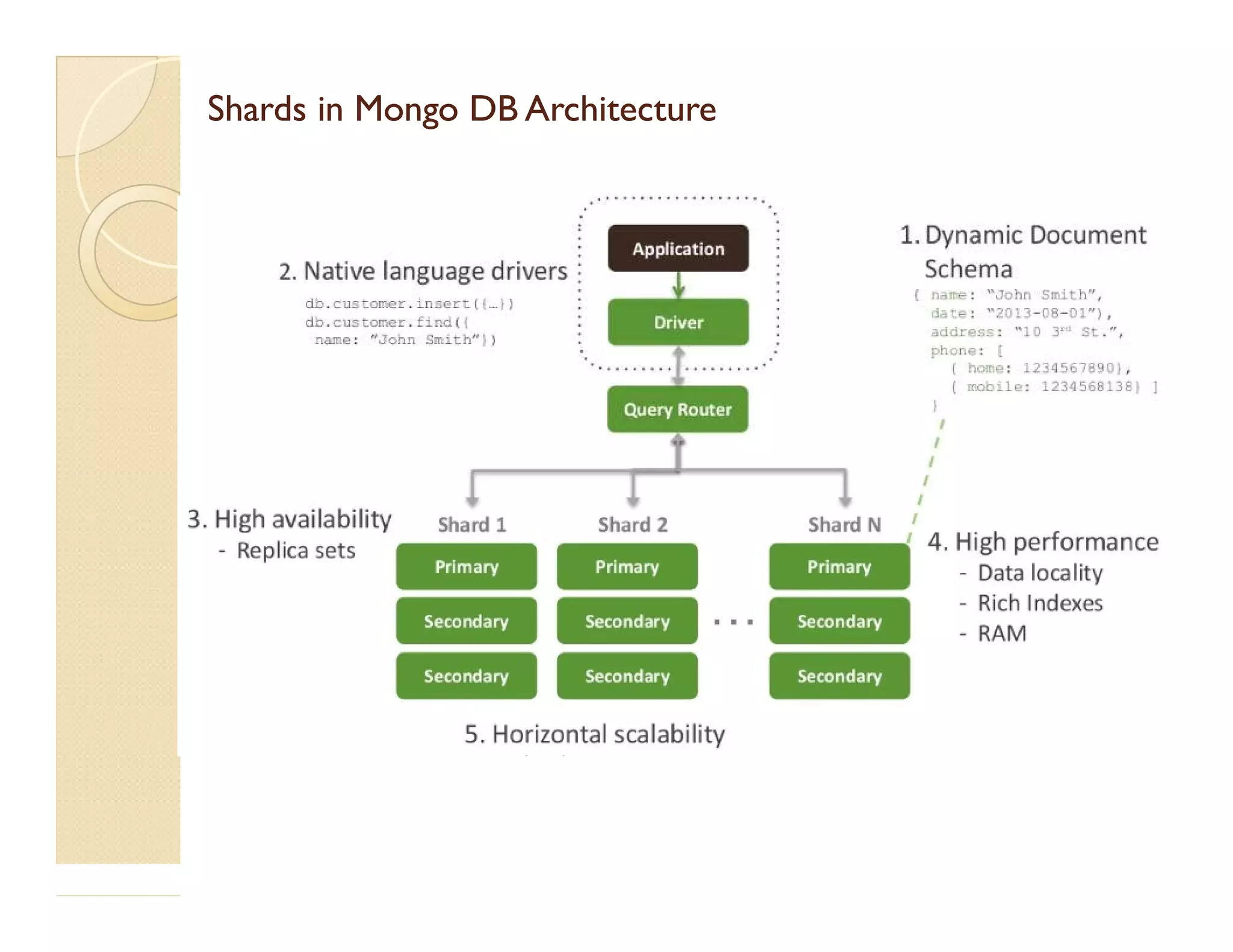
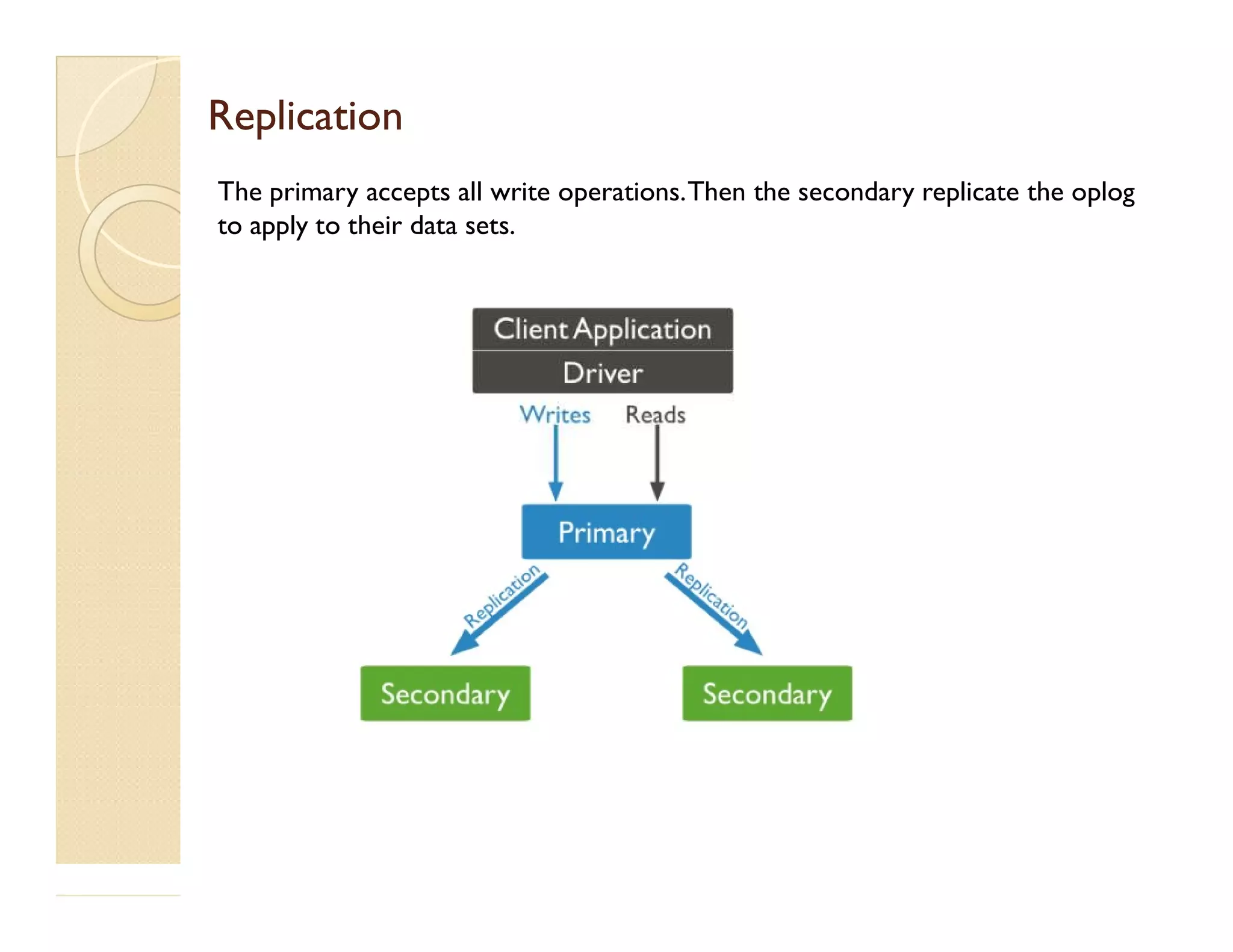
This document provides an overview of MongoDB, a popular NoSQL database. It discusses why NoSQL databases were created, the different types of NoSQL databases, and focuses on MongoDB. MongoDB is a document-oriented database that stores data in JSON-like documents with dynamic schemas. It provides horizontal scaling, high performance, and flexible data models. The presentation covers MongoDB concepts like databases, collections, documents, CRUD operations, indexing, sharding, replication, and use cases. It provides examples of modeling data in MongoDB and considerations for data and schema design.