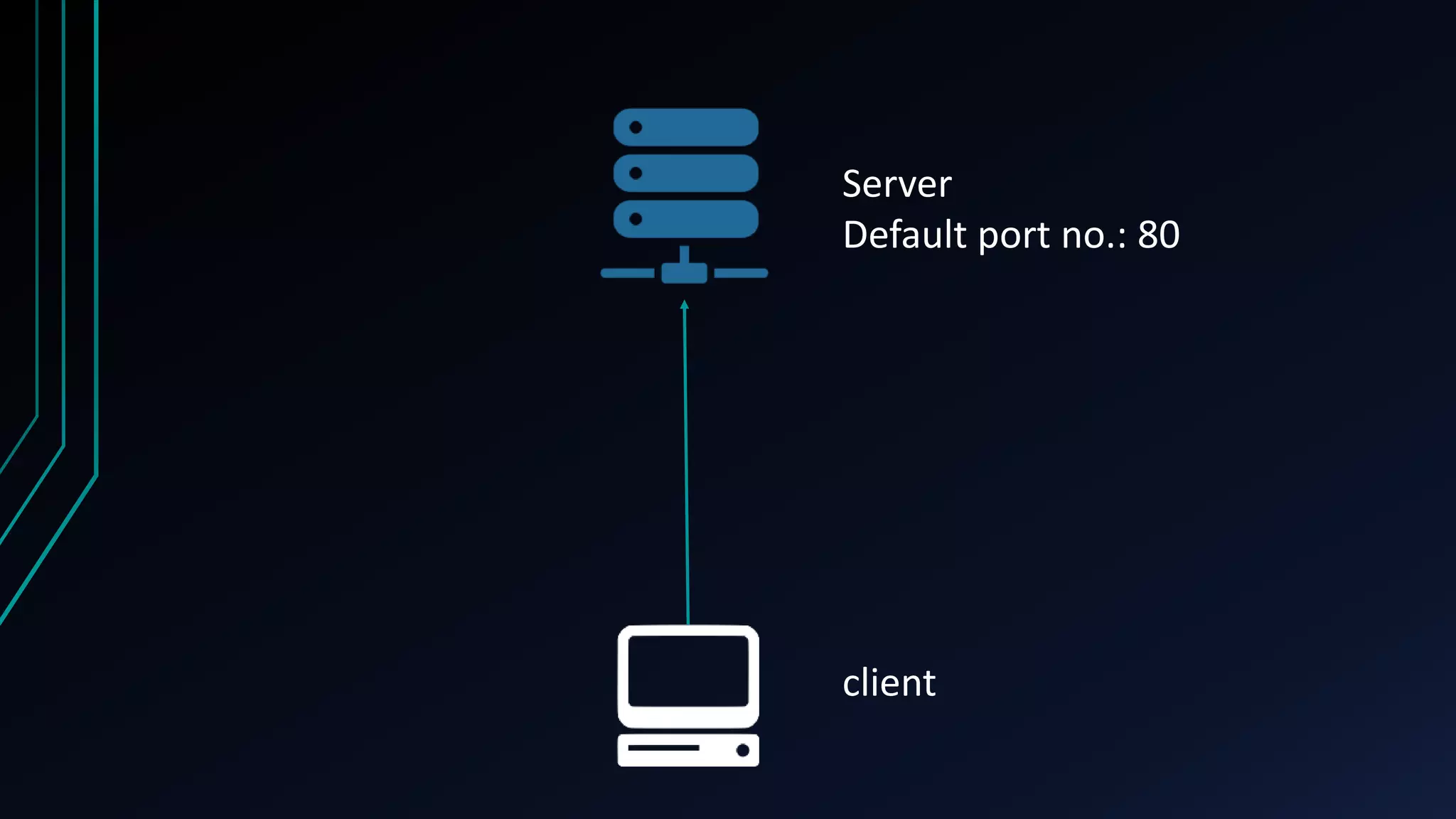
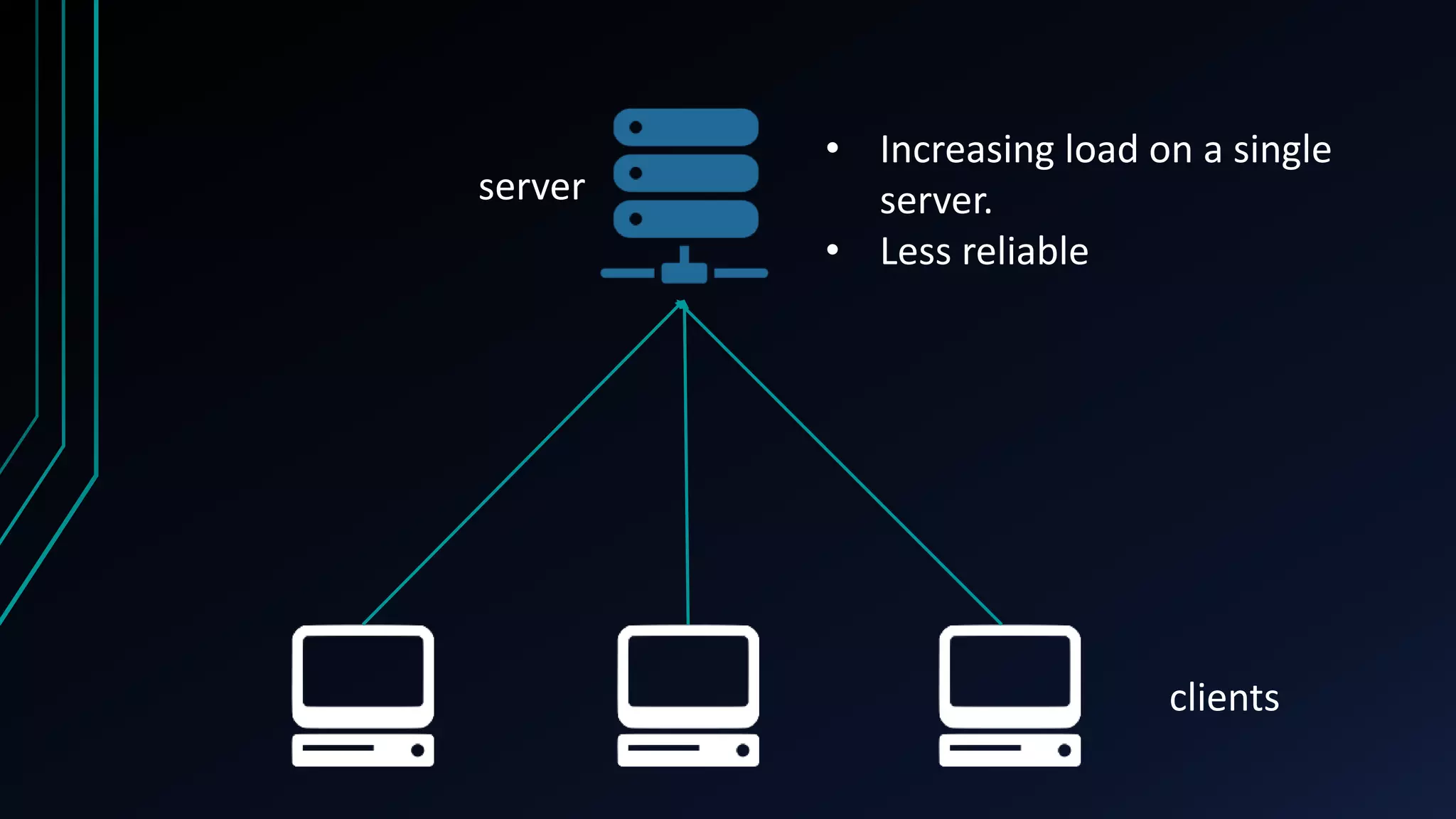
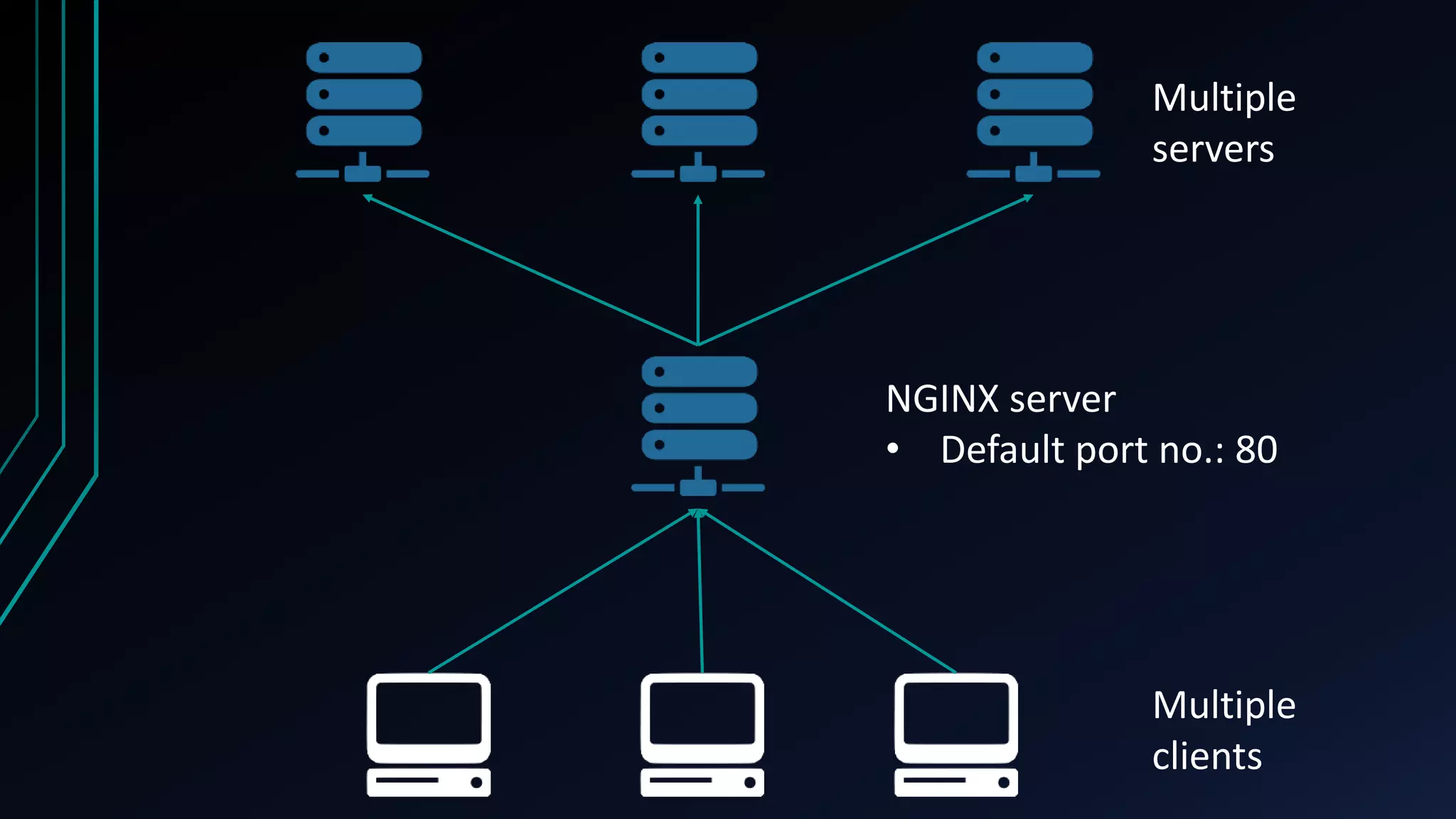
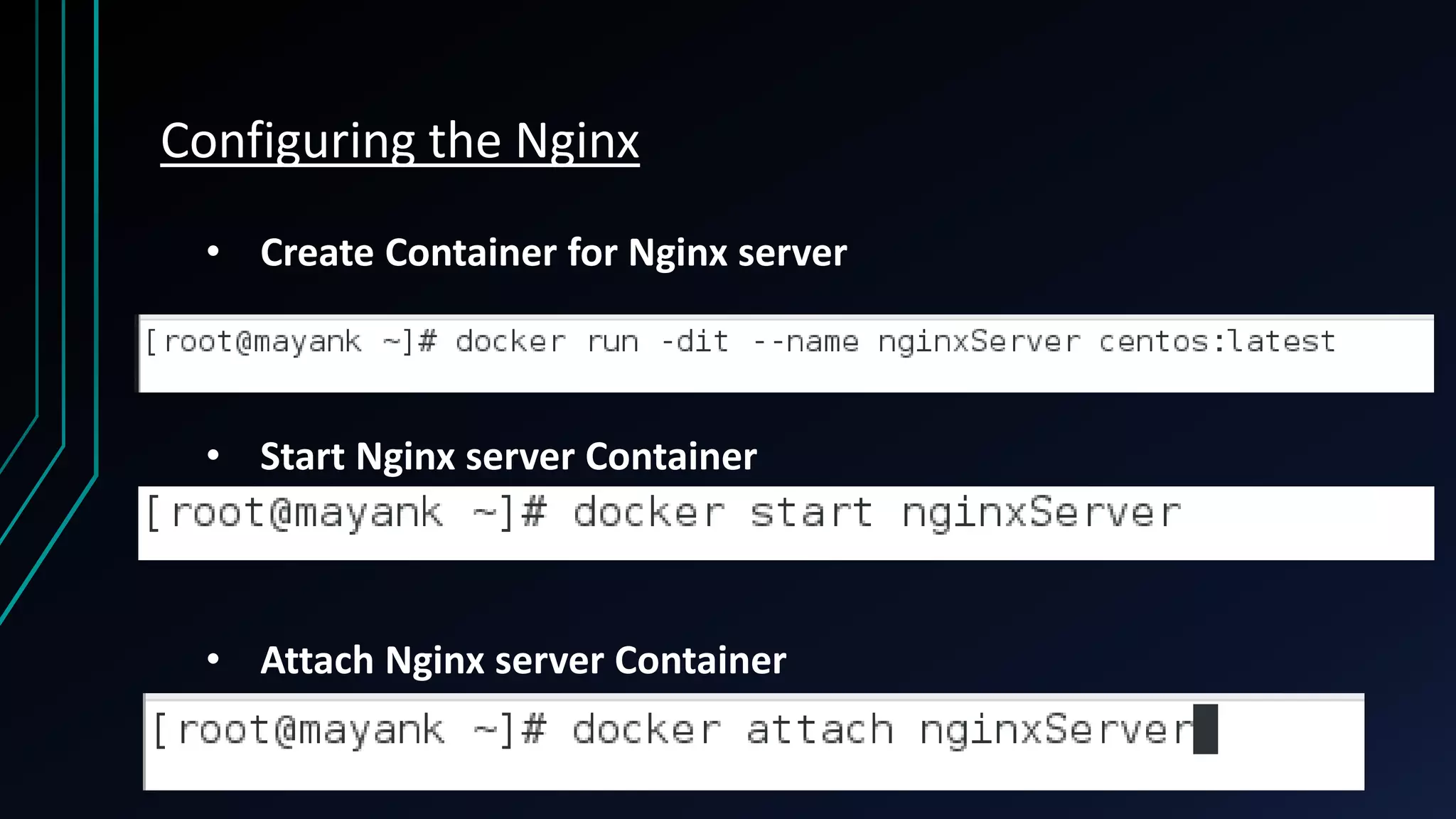
The document presents an overview of load balancing with Nginx, focusing on its implementation in containerized environments for handling HTTP requests. It discusses Nginx's capabilities as a software-based load balancer that efficiently distributes traffic across multiple backend servers while ensuring high availability. Key features include various load balancing methods, its popularity among high-traffic websites, and the advantages of containerization in managing applications.