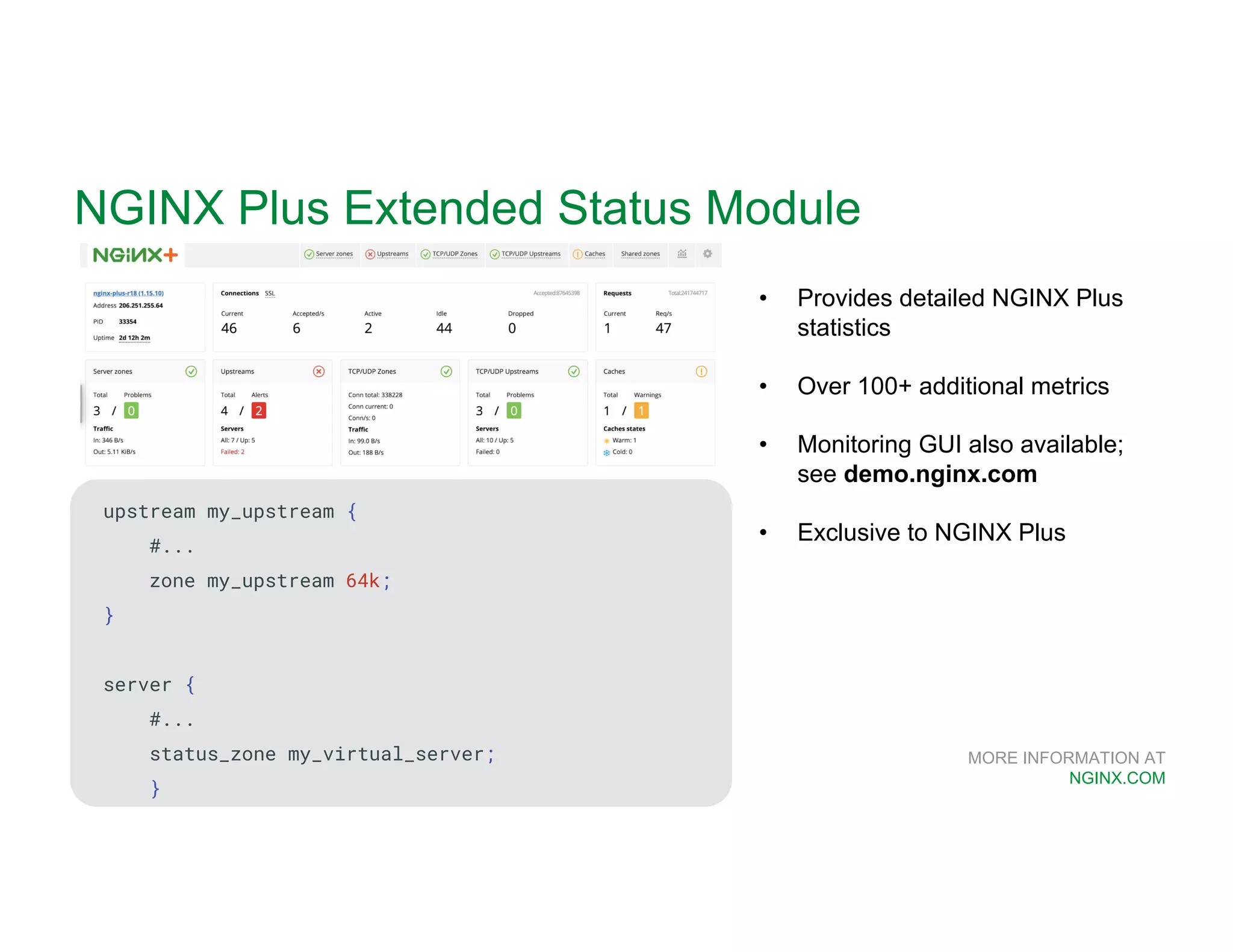
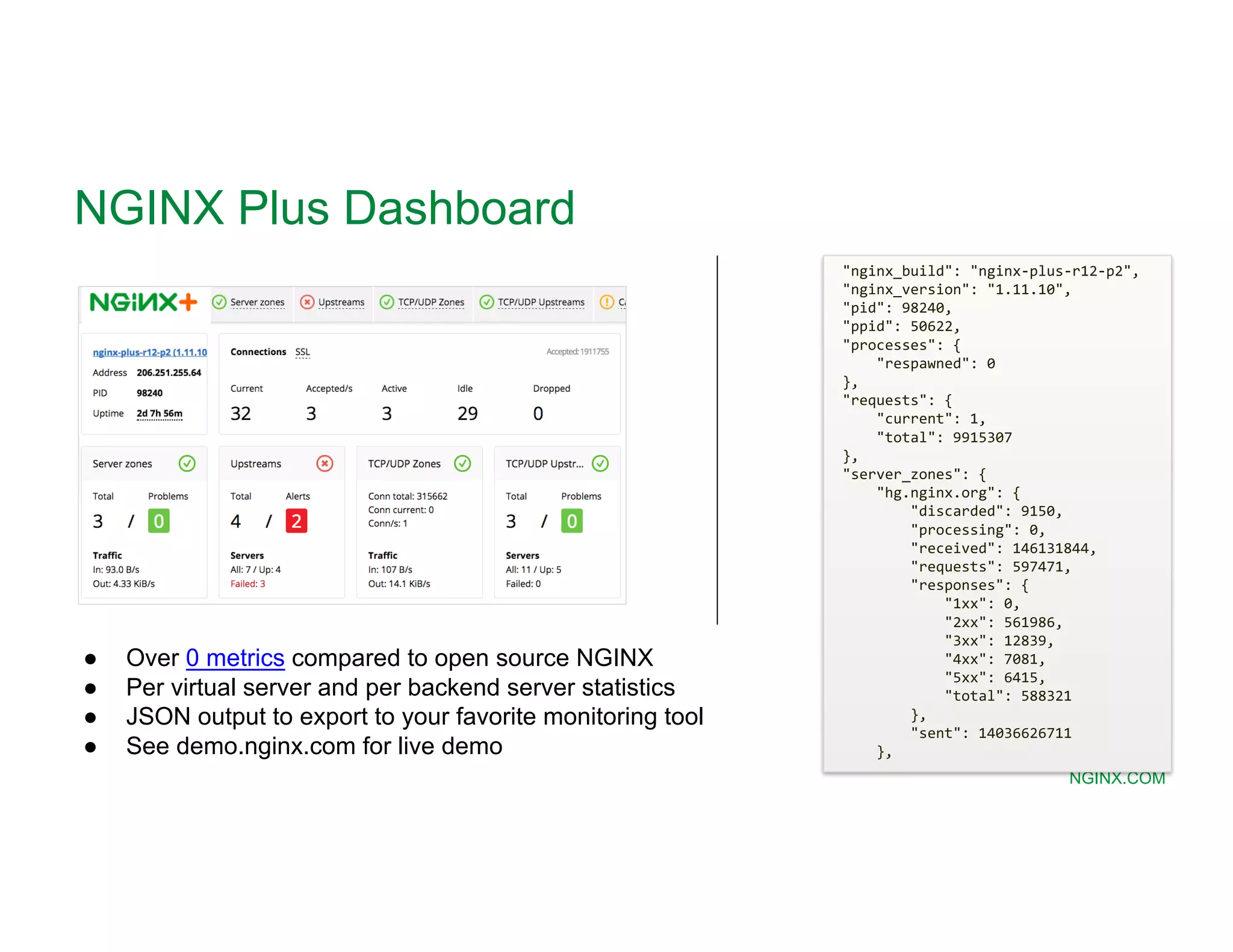
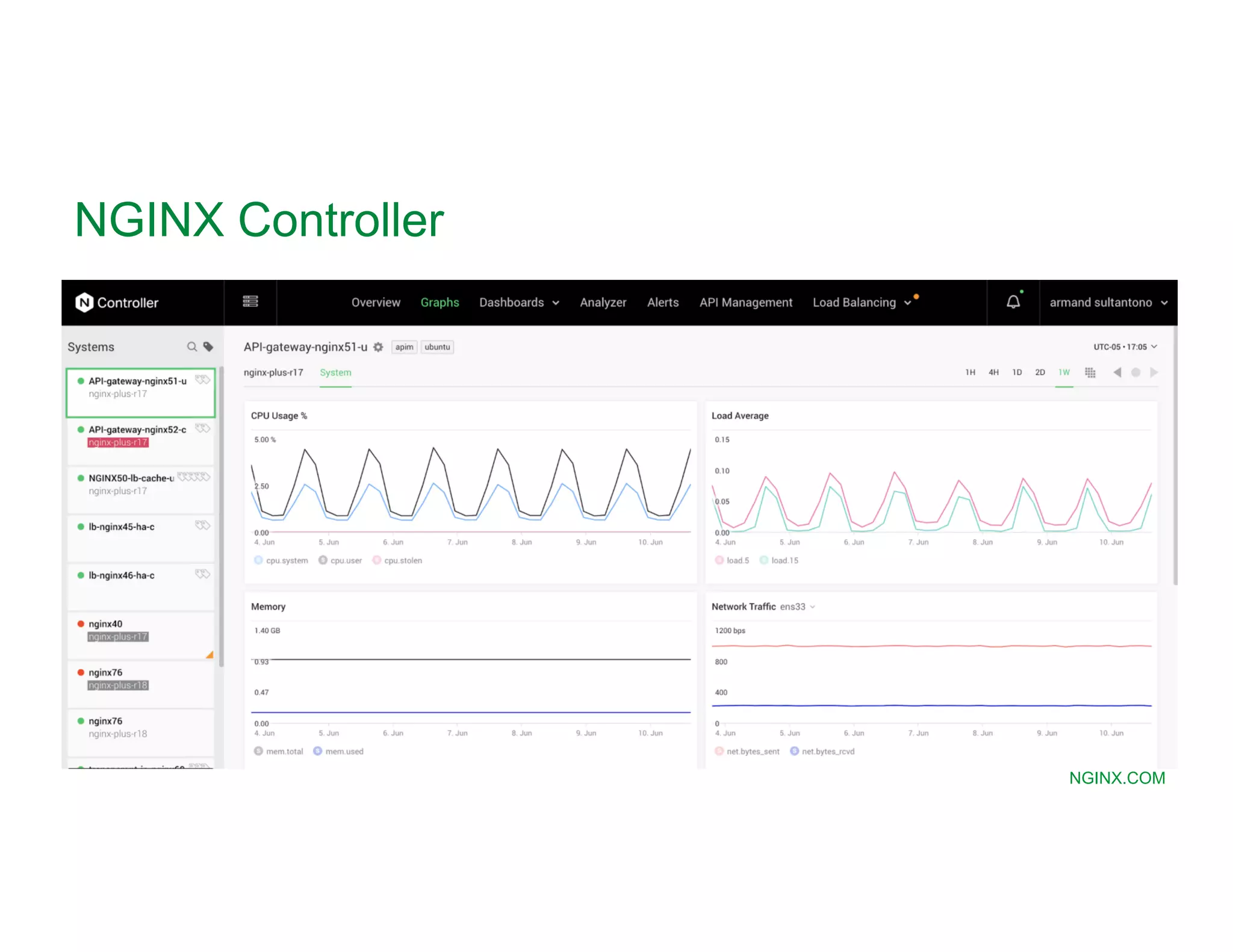
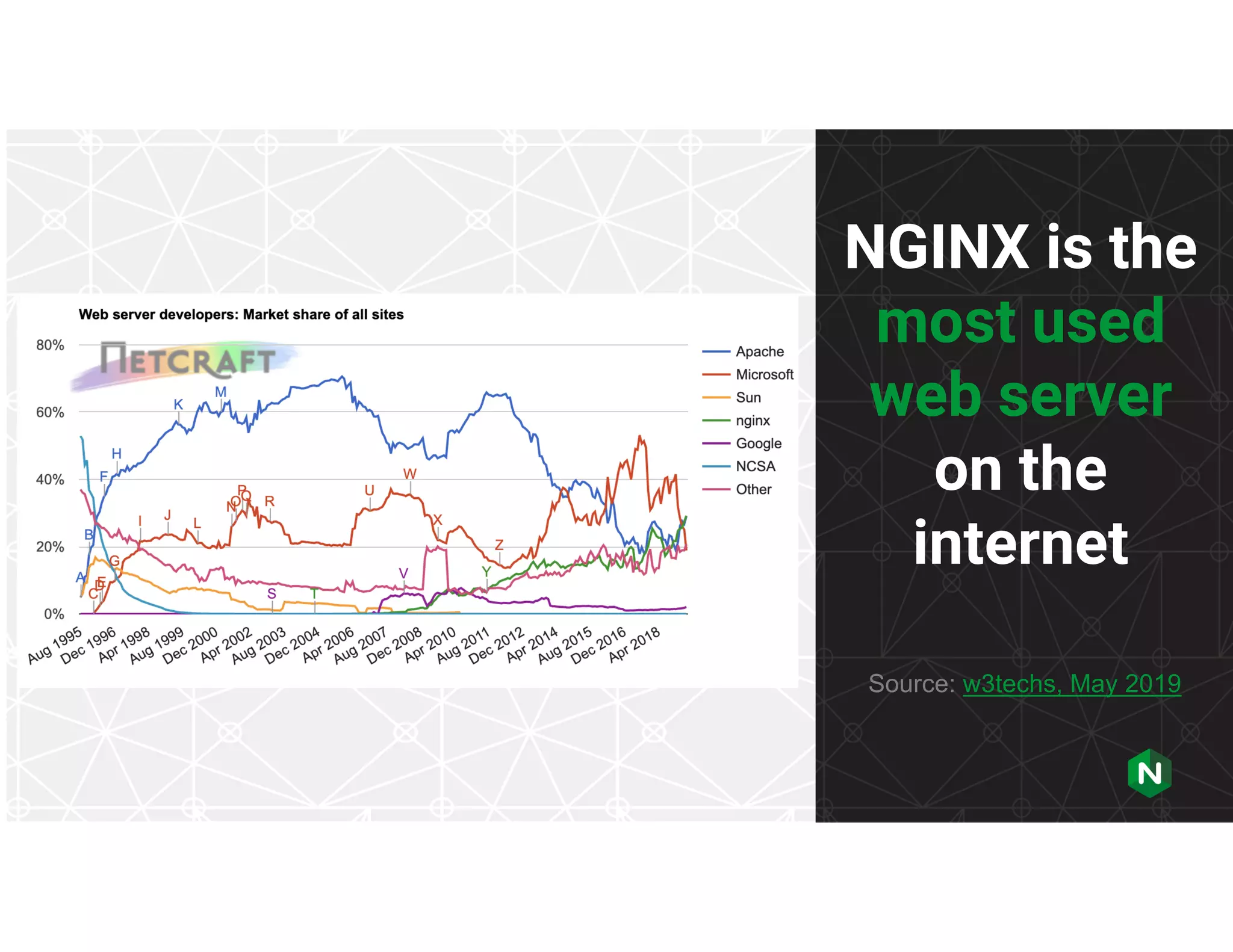
The document provides a comprehensive guide on NGINX, detailing its functionalities as a web server, load balancer, reverse proxy, and API gateway, alongside installation, configuration, and monitoring processes. It covers basic and advanced configurations including SSL settings, caching, and load balancing, as well as integration with modern application architectures like Kubernetes and multi-cloud environments. Additionally, it highlights essential commands, directories, and file structures associated with NGINX for effective management and optimization.








![NGINX Installation: CentOS/Red Hat [nginx] name=nginx repo baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/mainline/OS/OSRELEASE/$basearch/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1 Create /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo with the following contents: • OS -- rhel or centos depending on your distro • OSRELEASE -- 6 or 7 for 6.x or 7.x versions, respectively $ yum –y install nginx $ systemctl enable nginx $ systemctl start nginx $ firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp $ firewall-cmd --reload](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nginx-basicsandbestpractices-190612234919/75/NGINX-ADC-Basics-and-Best-Practices-17-2048.jpg)













![MORE INFORMATION AT NGINX.COM NGINX Access Logs 192.168.179.1 - - [15/May/2017:16:36:25 -0700] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 612 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.110 Safari/537.36" "-" 192.168.179.1 - - [15/May/2017:16:36:26 -0700] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 571 "http://fmemon-redhat.local/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.110 Safari/537.36" "-" 192.168.179.1 - - [15/May/2017:16:36:31 -0700] "GET /basic_status HTTP/1.1" 200 100 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.110 Safari/537.36" "-" ● Enabled by default. Can be disabled with the access_log off directive. ● Nginx uses the combined log format (also used by Apache) and includes IP address, date, request , referrer, user agent, etc. You can add additional NGINX variables, e.g. timing and a Log format configurable with the log_format directive ● Can enable access logs at a virtual server scope access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nginx-basicsandbestpractices-190612234919/75/NGINX-ADC-Basics-and-Best-Practices-46-2048.jpg)
![MORE INFORMATION AT NGINX.COM NGINX Error Logs 2018/03/22 11:29:08 [error] 12696#12696: upstream timed out (110: Connection timed out) while connecting to upstream, health check "" of peer 10.70.88.24:8832 in upstream "Dev.InternalApi" 2018/03/22 11:29:23 [error] 12696#12696: upstream timed out (110: Connection timed out) while connecting to upstream, health check "" of peer 10.70.88.15:8832 in upstream "Dev.InternalApi" 2018/03/23 15:25:35 [error] 19997#0: *1 open() "/var/www/nginx-default/phpmy-admin/scripts/setup.php" failed (2: No such file or directory), client: 80.154.42.54, server: localhost, request: "GET /phpmy-admin/scripts/setup.php HTTP/1.1", host: "www.example.com" • Enabled by default. Can be disabled with the error_log off directive. • Can enable access logs at a virtual server scope • Log to file, stderr, syslog or memory • Option to log for selected clients error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log [level];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nginx-basicsandbestpractices-190612234919/75/NGINX-ADC-Basics-and-Best-Practices-47-2048.jpg)
![MORE INFORMATION AT NGINX.COM Error Log Levels debug Detailed Trace info General Info notice Something Normal warn Something Strange error Unsuccessful crit Important Issue(s) alert Fix Now! emerg Unusable error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log [level];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nginx-basicsandbestpractices-190612234919/75/NGINX-ADC-Basics-and-Best-Practices-48-2048.jpg)
![MORE INFORMATION AT NGINX.COM Extra examples log_format simple escape=json '{"timestamp":"$time_iso8601","client":"$remote_addr","uri":"$uri","status":"$status"}'; server { server_name www.example.com; access_log /var/log/nginx/example.log simple; error_log syslog:server=192.168.1.1 debug; } server { server_name www.example2.com; map $status $condition { ~^[23] 0; default 1; } access_log /var/log/nginx/example2.log simple custom if=$condition; error_log /var/log/nginx/example2_error.log info; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nginx-basicsandbestpractices-190612234919/75/NGINX-ADC-Basics-and-Best-Practices-49-2048.jpg)