The document provides an overview of arrays and stacks in programming. It defines arrays as collections of homogeneous elements stored in consecutive memory, discusses their types, initialization, and basic operations, and explains stacks as a last-in-first-out (LIFO) structure with operations like push and pop. Additionally, it highlights stack applications such as expression evaluation and function calls.
![Introduction to Array An array is defined as a set of finite number of homogeneous elements or same data items. It means an array can contain one type of data only, either all integer, all float-point number or all character. Simply, declaration of array is as follows: int arr[10] ; Where int specifies the data type or type of elements arrays stores. “arr” is the name of array & the number specified inside the square brackets is the number of elements an array can store, this is also called sized or length of array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lineardatastructures-240918082700-3dbd75a1/75/Linear-Data-Structures-array-stack-queue-2-2048.jpg)
![Introduction to Array The elements of array will always be stored in the consecutive (continues) memory location. The number of elements that can be stored in an array, that is the size of array or its length is given by the following equation: (Upperbound-lowerbound)+1 For the above array it would be (9-0)+1=10,where 0 is the lower bound of array and 9 is the upper bound of array. Array can always be read or written through loop. for(i=0;i<=9;i++) { scanf(“%d”,&arr[i]); printf(“%d”,arr[i]); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lineardatastructures-240918082700-3dbd75a1/75/Linear-Data-Structures-array-stack-queue-3-2048.jpg)
![Representation of One Dimensional Array An array with only one row or column is called one-dimensional array. It is finite collection of n number of elements of same type such that: ◦ can be referred by indexing. ◦ The Elements are stored in continuous locations. Syntax: Datatype Array_Name [Size]; Where, Datatype : Type of value it can store (Example: int, char, float) Array_Name: To identify the array. Size : The maximum number of elements that an array can hold.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lineardatastructures-240918082700-3dbd75a1/75/Linear-Data-Structures-array-stack-queue-4-2048.jpg)
![Initializing One Dimensional Array An array can also be created by specifying the size and assigning array elements at the time of declaration. Syntax for initialization: int arr[10]= {2,4,6,7,5,8}; char word[5]= {‘h’, ‘e’, ‘l’, ‘l’, ‘o’}; Write program to show use of initializers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lineardatastructures-240918082700-3dbd75a1/75/Linear-Data-Structures-array-stack-queue-5-2048.jpg)
![Accessing One Dimensional Array Elements Individual element of array can be accessed using the following syntax: array_name[index]; e.g., to assign a value to second location of the array, arr[1]=90; Similarly to read a particular value, scanf(“%d”, &arr[2]); Above statement reads a value from keyboard and assigns it to third location of the array. Write a program to illustrate reading and writing of the array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lineardatastructures-240918082700-3dbd75a1/75/Linear-Data-Structures-array-stack-queue-6-2048.jpg)
![Memory Allocation of Array The elements of linear array are stored in consecutive memory locations. It is shown below: Address of element a[k]=B + w * k](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lineardatastructures-240918082700-3dbd75a1/75/Linear-Data-Structures-array-stack-queue-7-2048.jpg)

![Initializing Two Dimensional Array An array can also be created by specifying the size and assigning array elements at the time of declaration. Syntax for initialization: int arr[3][3]= {2,4,6,7,5,8,9,3,1}; Write program to show use of initializers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lineardatastructures-240918082700-3dbd75a1/75/Linear-Data-Structures-array-stack-queue-9-2048.jpg)
![Accessing Two Dimensional Array Elements Individual element of array can be accessed using the following syntax: array_name[row_index][col_index]; e.g., to assign a value to first row and first column location of the array, arr[0][0]=9; Similarly to read a particular value, scanf(“%d”, &arr[1][0]); Above statement reads a value from keyboard and assigns it to second row and first column location of the array. Write a program to illustrate reading and writing of the 2-D array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lineardatastructures-240918082700-3dbd75a1/75/Linear-Data-Structures-array-stack-queue-10-2048.jpg)


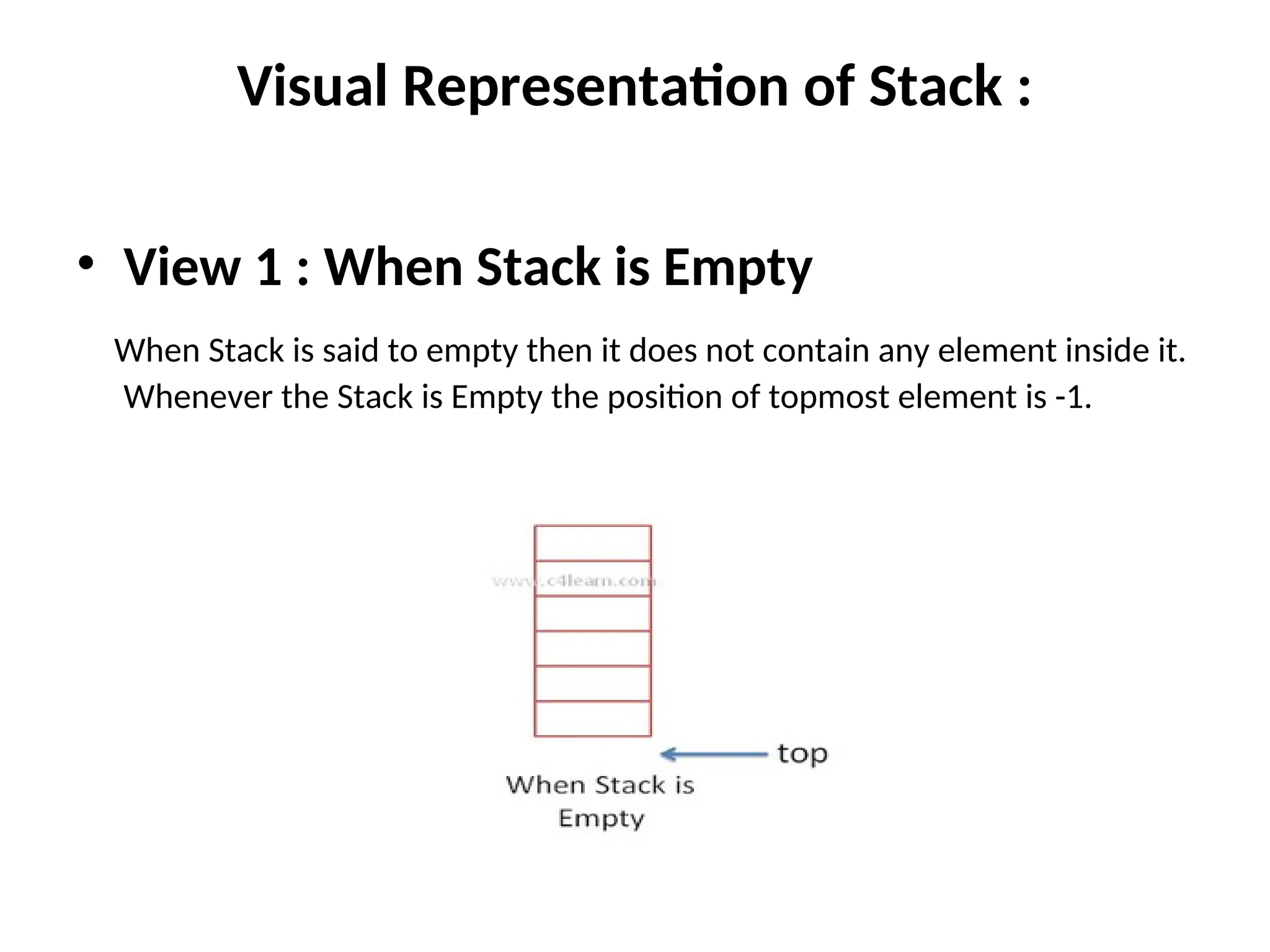
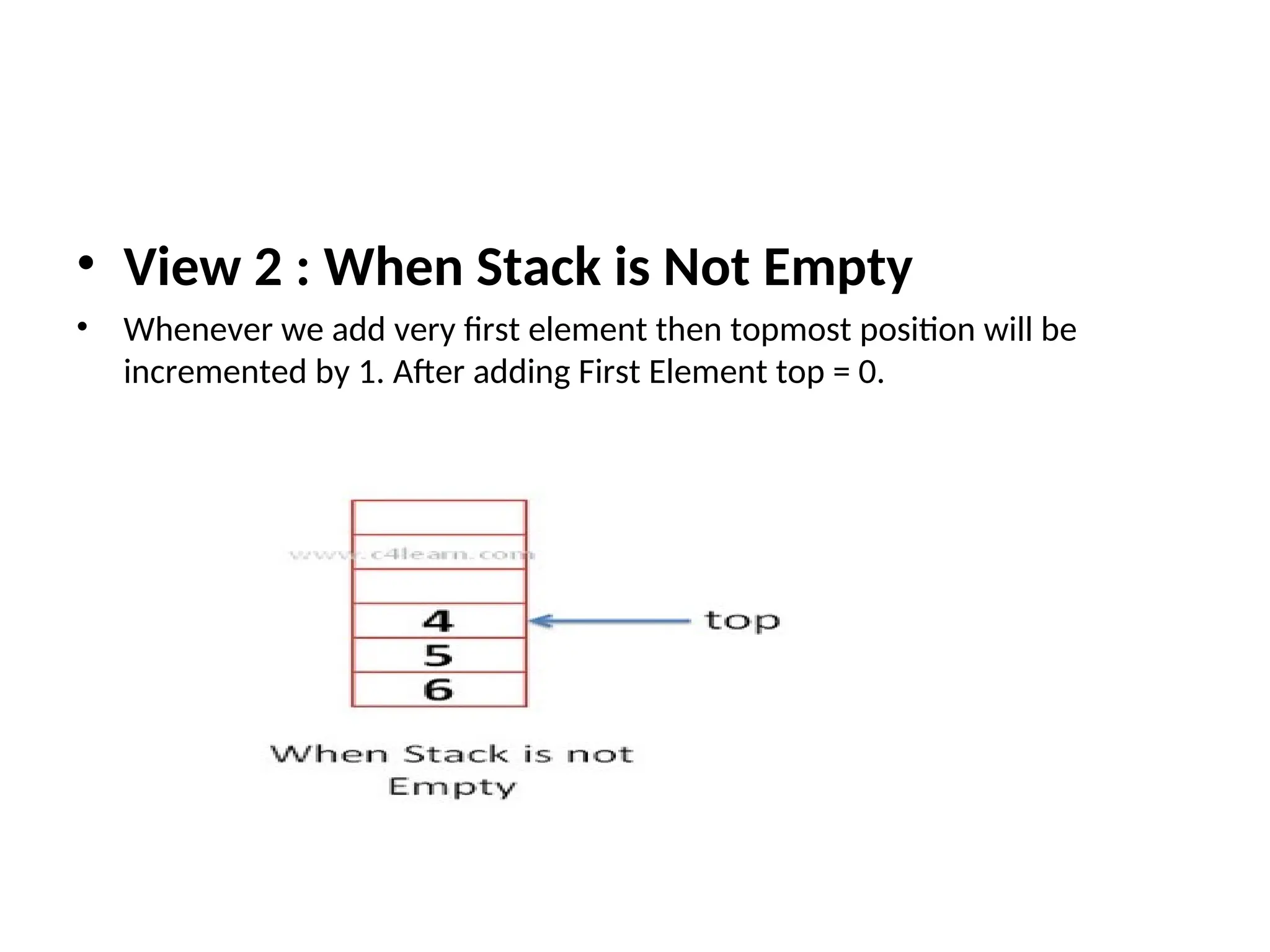
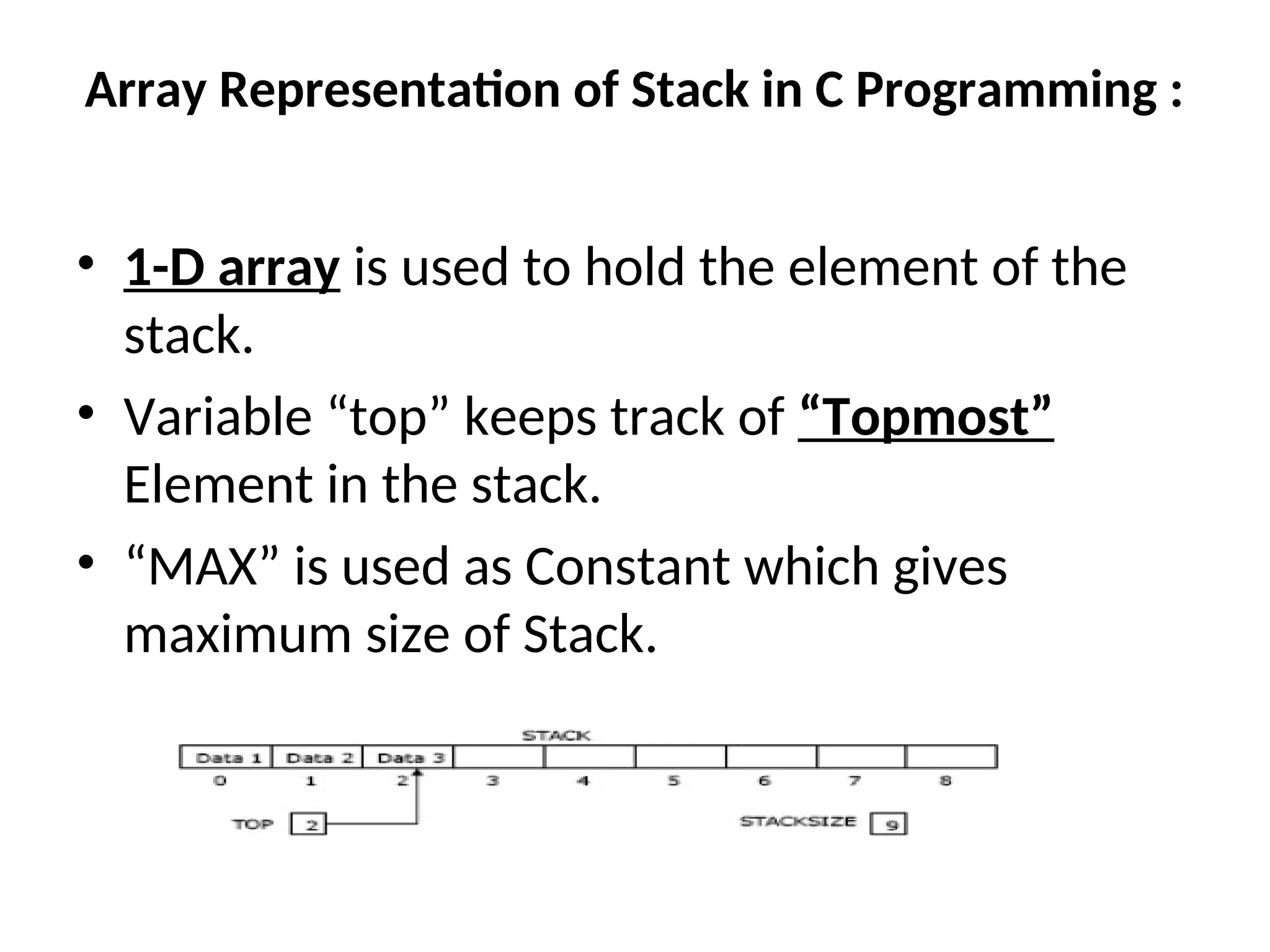
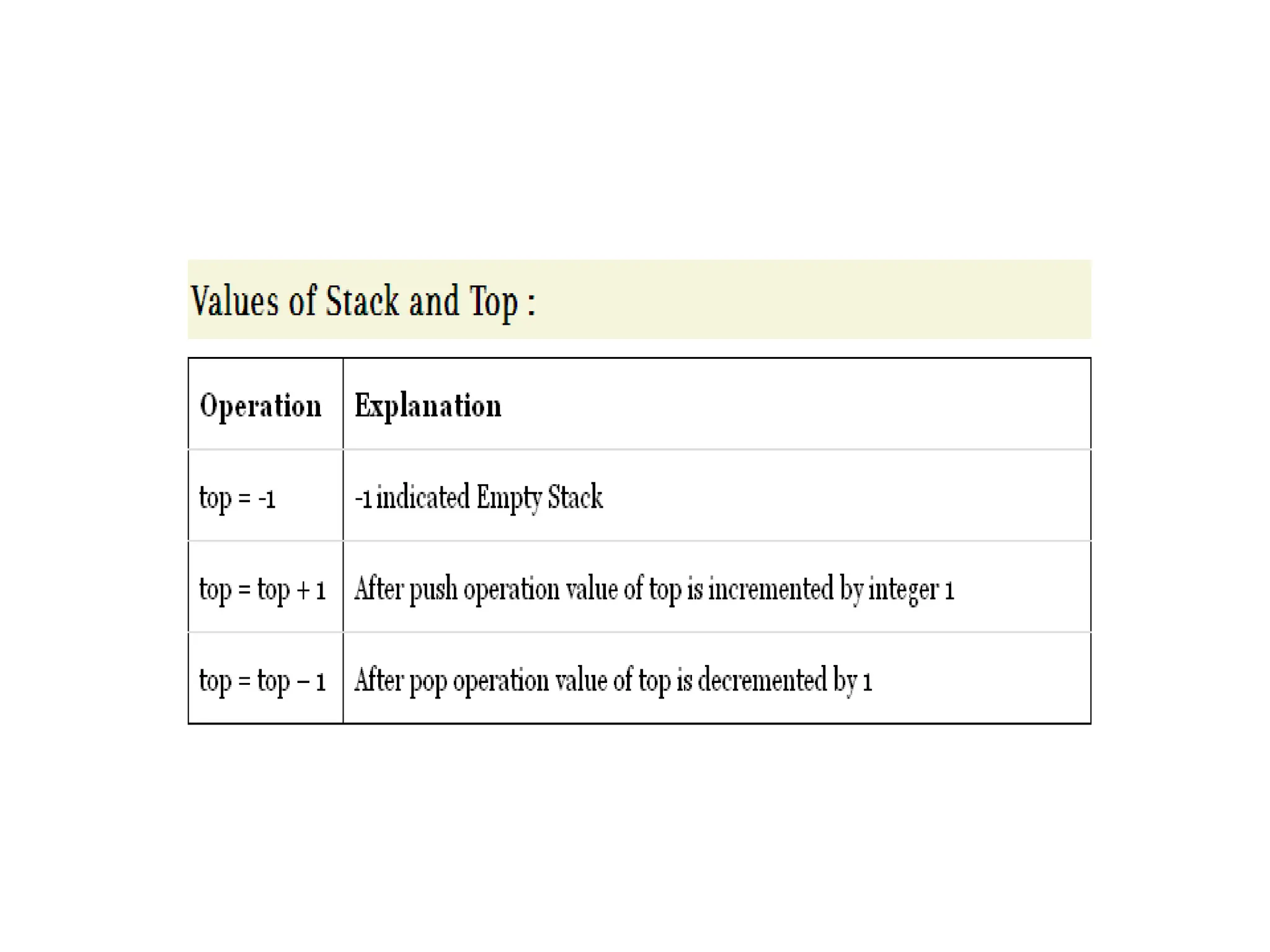
![What is Stack ? • Stack is used as Linear data structure which can be accessed from only one end . • Stack is LIFO Structure [ Last in First Out ] • Stack is Ordered List of Elements of Same Type. • Stack is Linear List • In Stack all Operations such as Insertion and Deletion are permitted at only one end called Top](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lineardatastructures-240918082700-3dbd75a1/75/Linear-Data-Structures-array-stack-queue-13-2048.jpg)