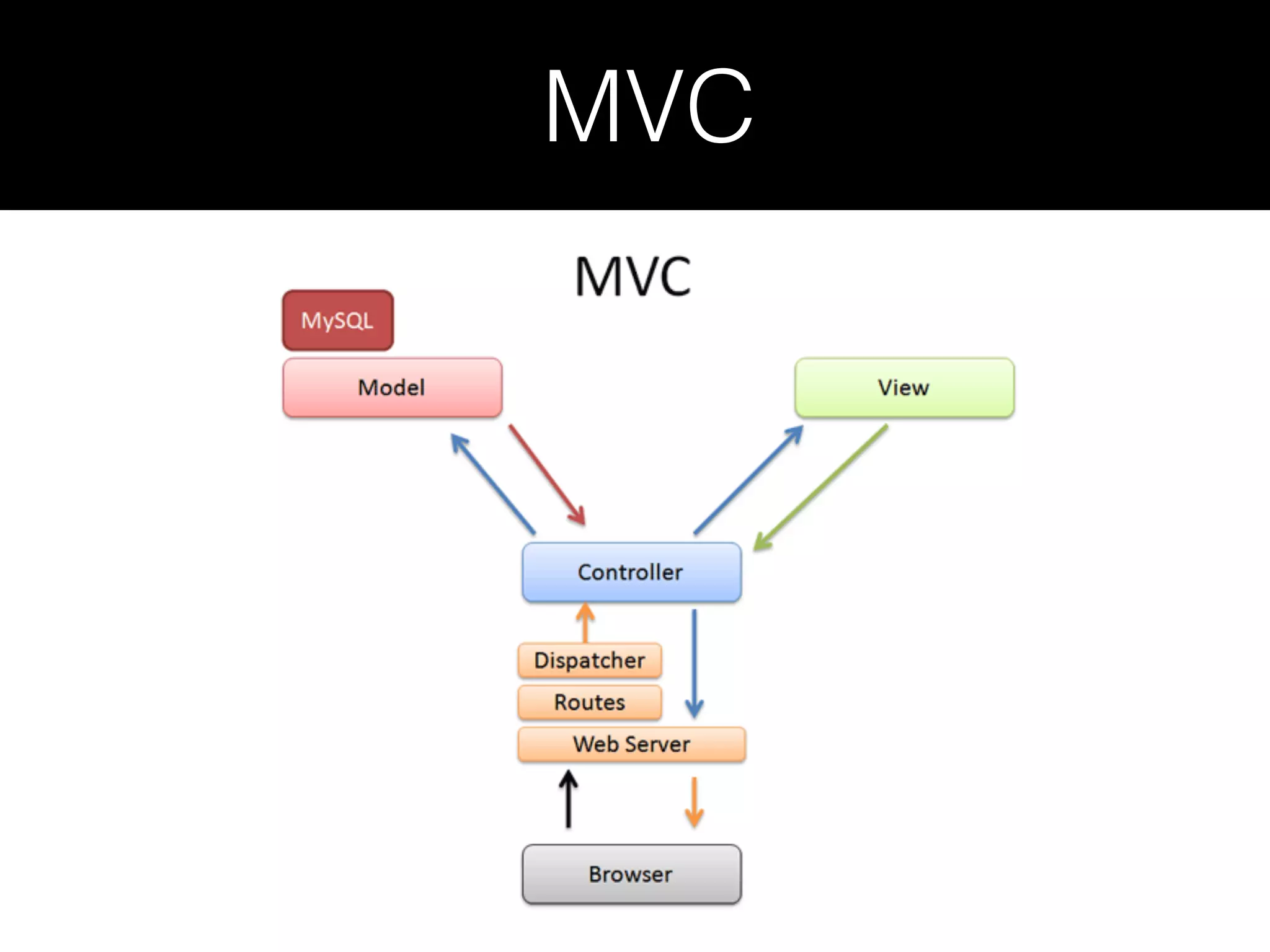
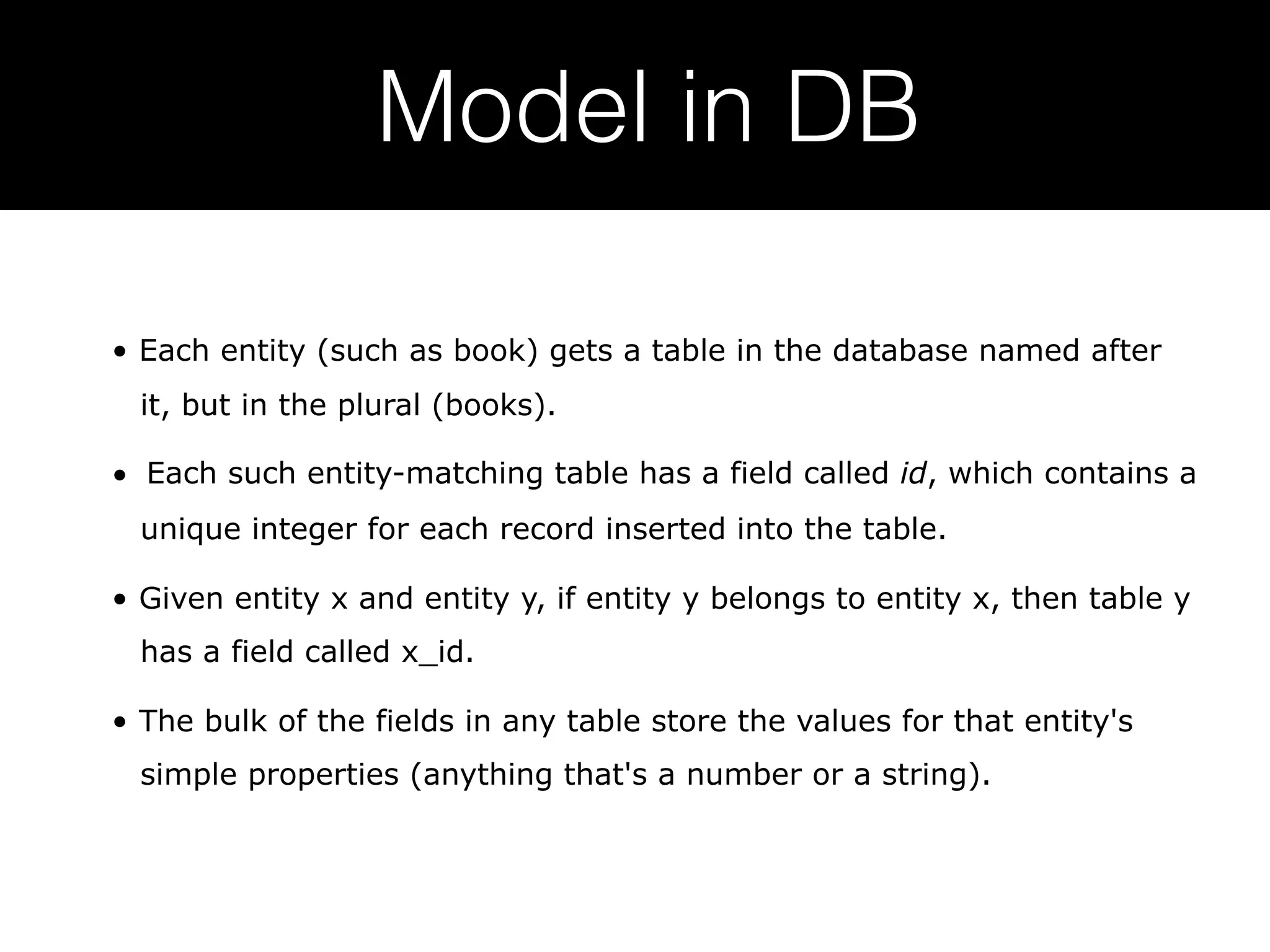
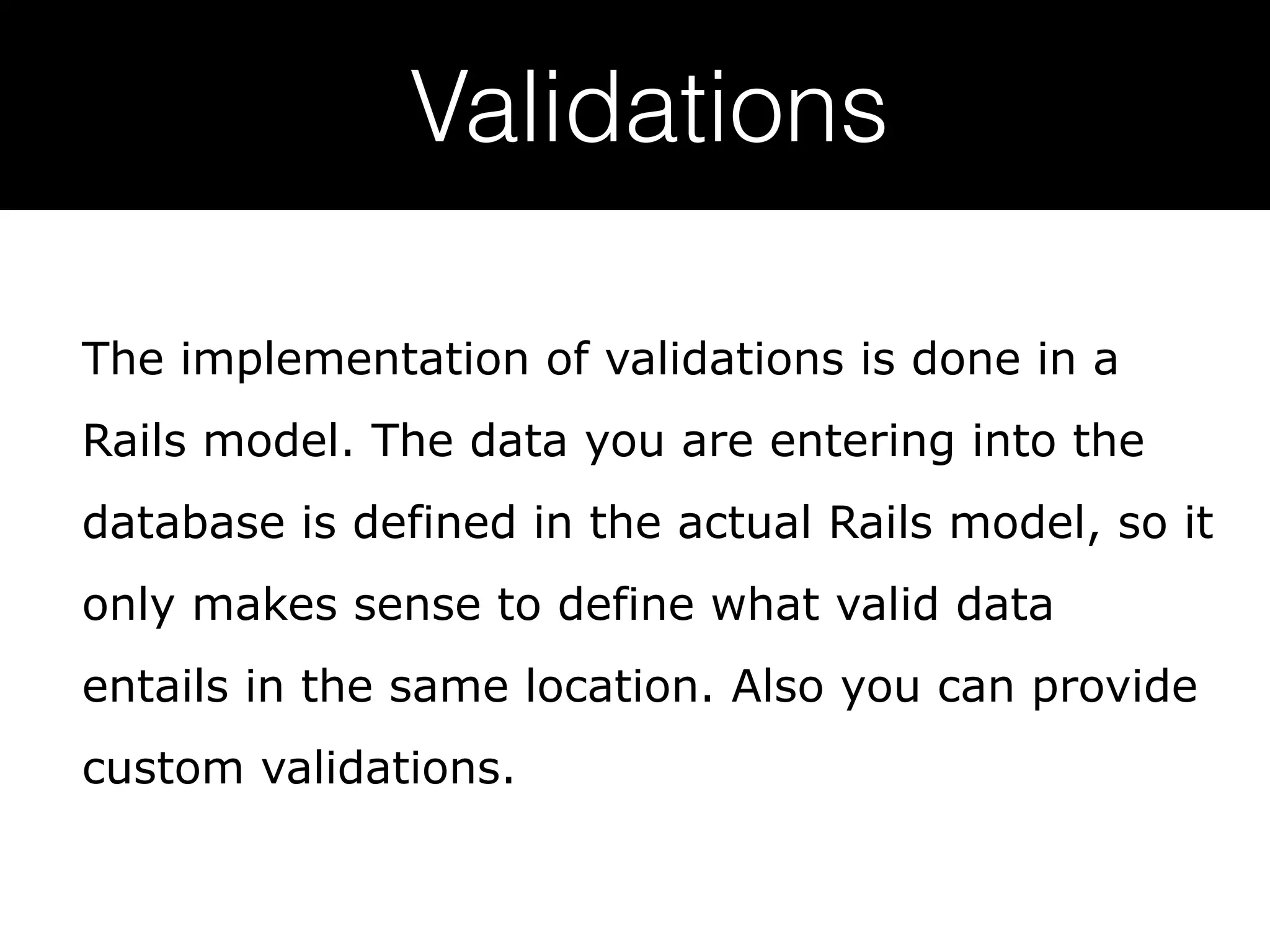
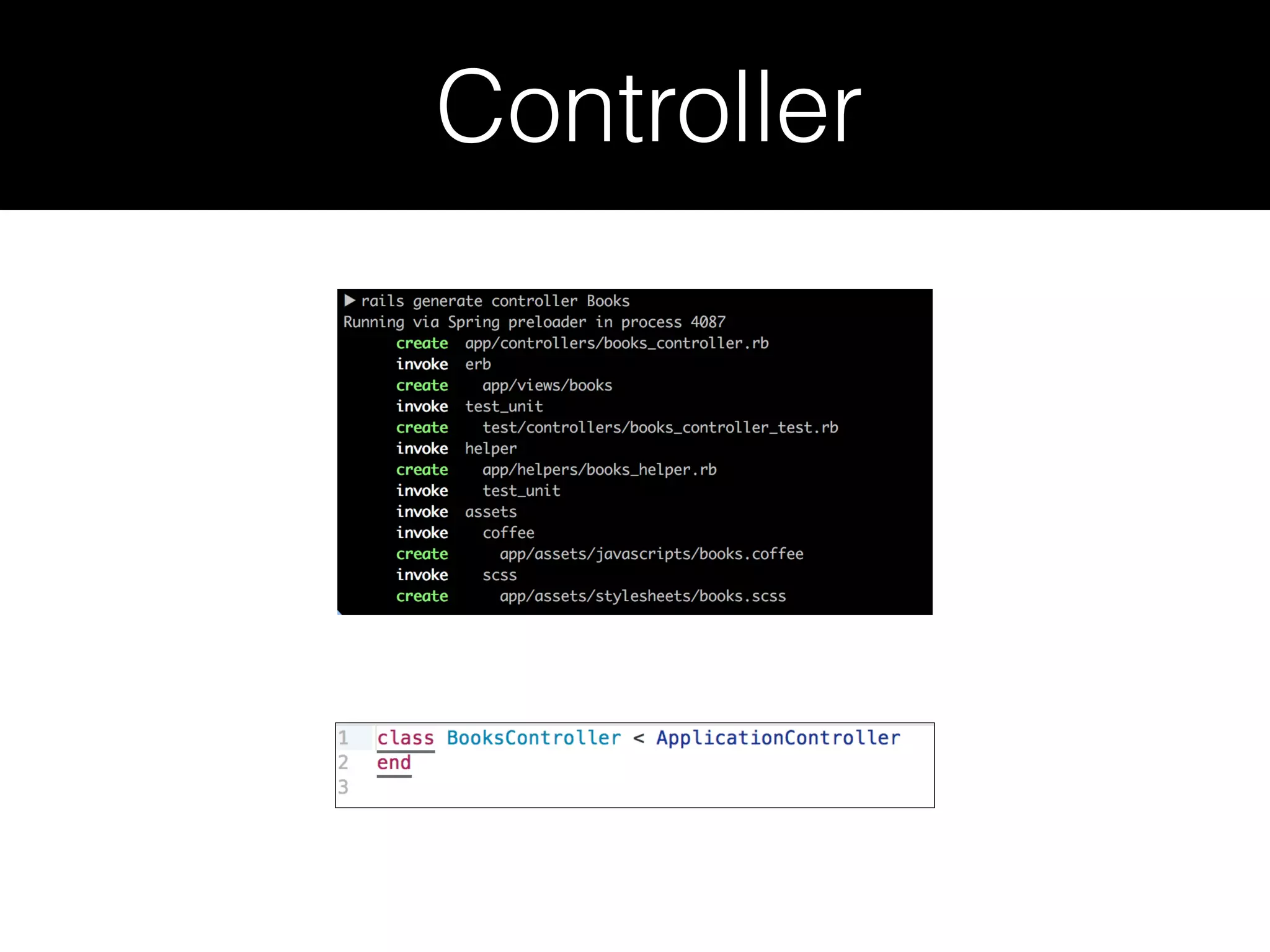
Ruby on Rails is a full-stack web application framework written in Ruby. It uses the MVC pattern and convention over configuration principles. Rails makes it possible to develop database-backed web applications rapidly by minimizing configuration through conventions and providing scaffolding. Key Rails concepts include Active Record for ORM, migrations for schema changes, routing for URLs, controllers for application logic, views for presentation, and testing frameworks. Rails emphasizes productivity through conventions that reduce configuration overhead.