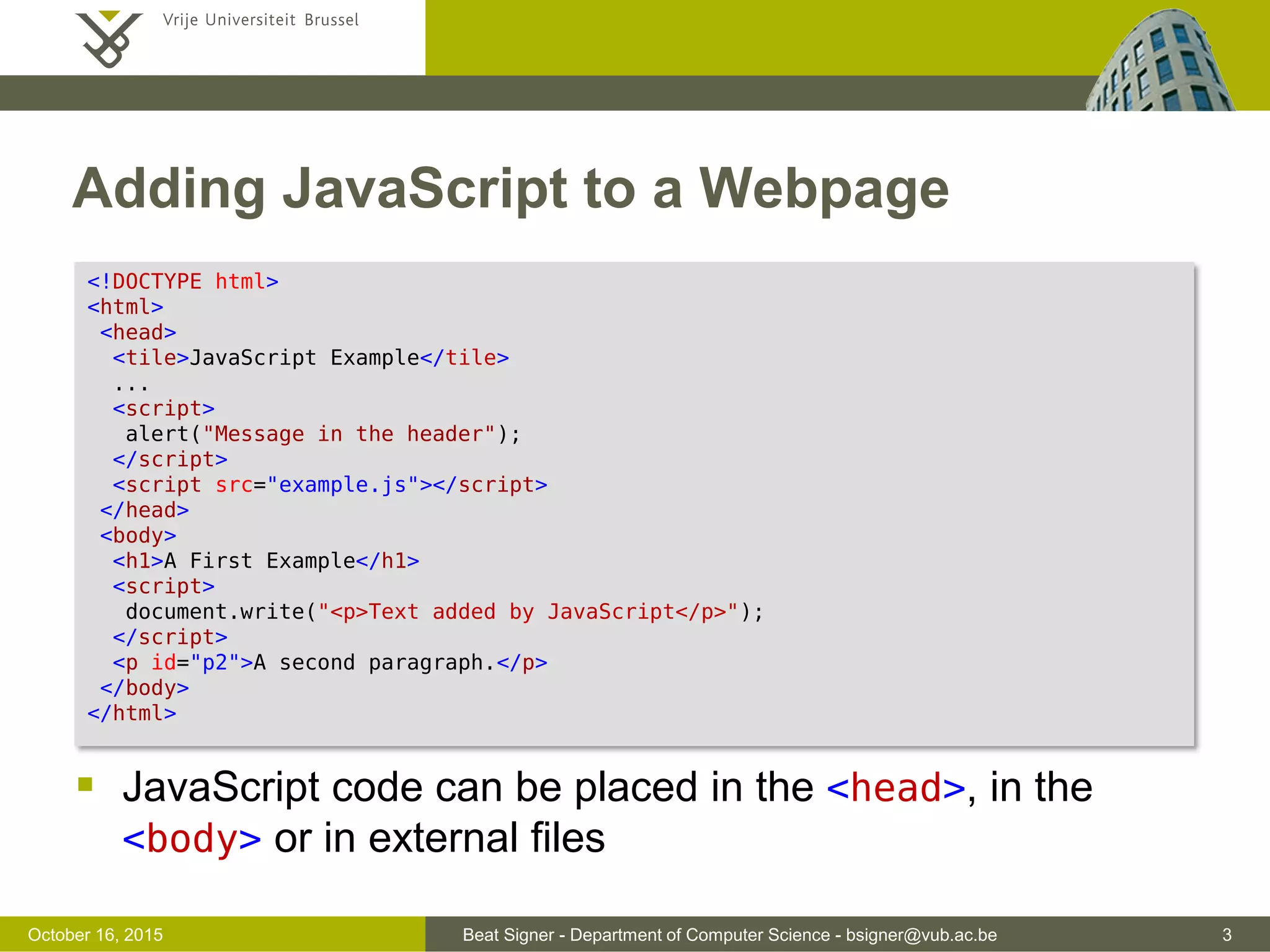
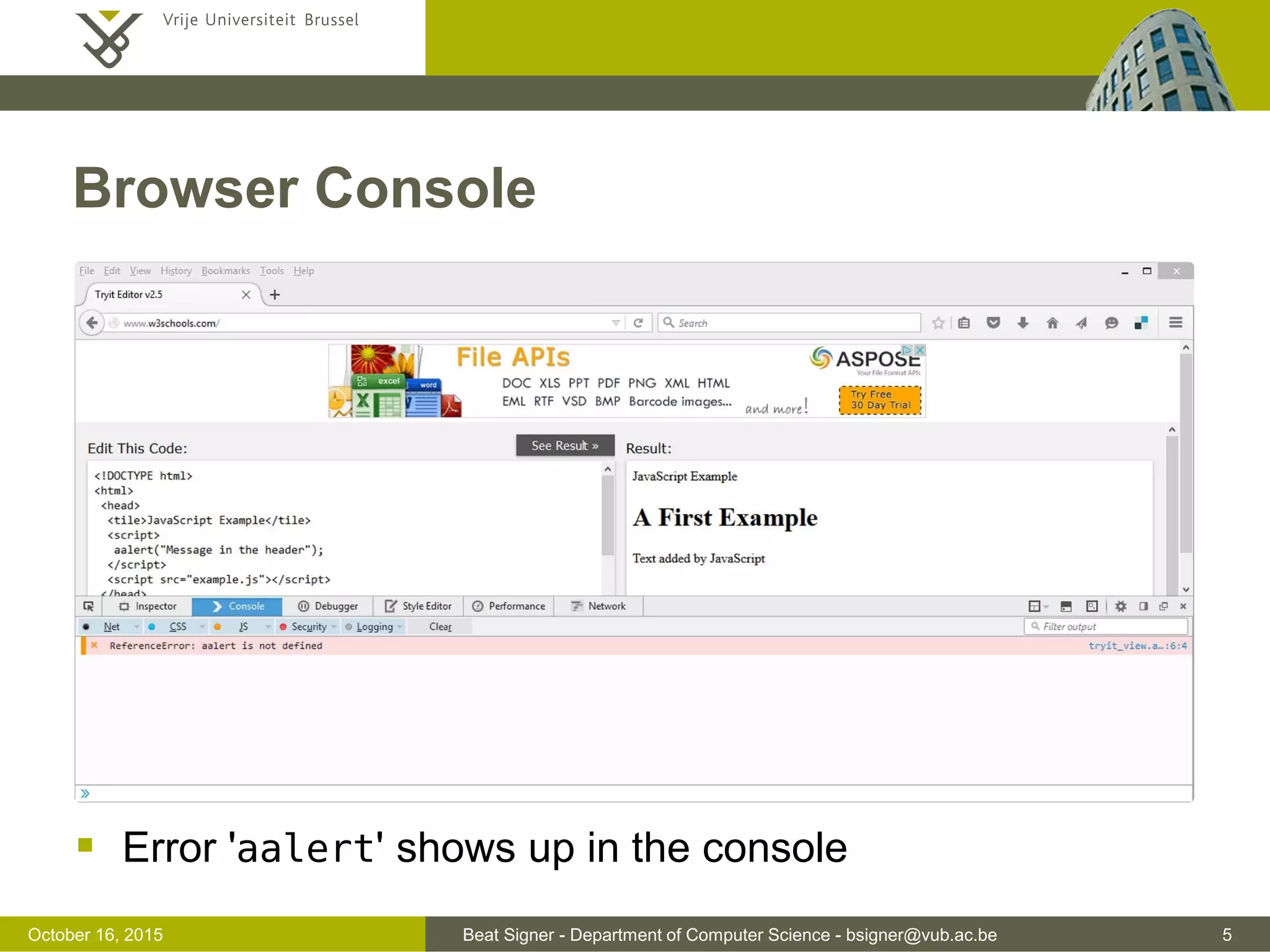
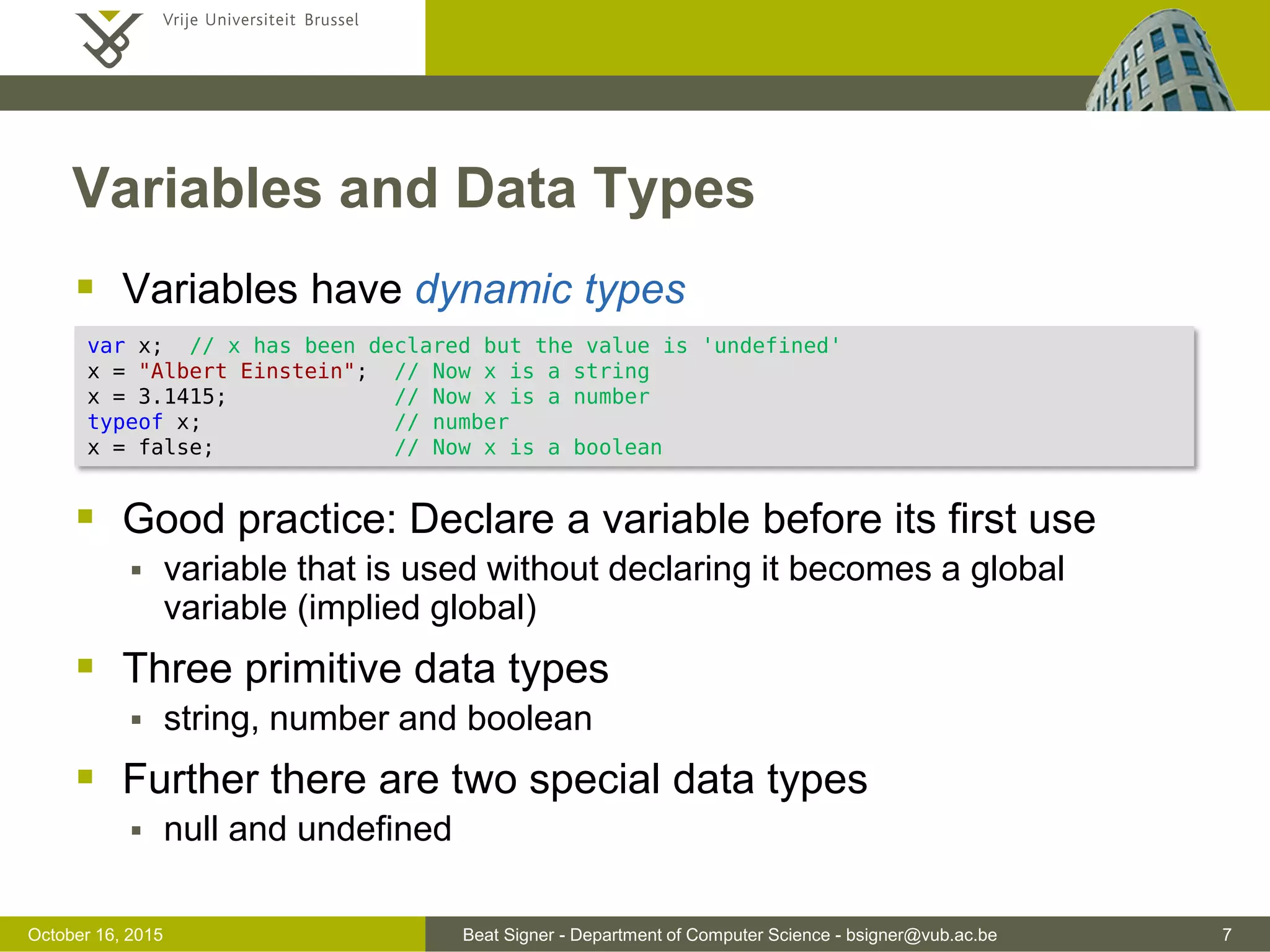
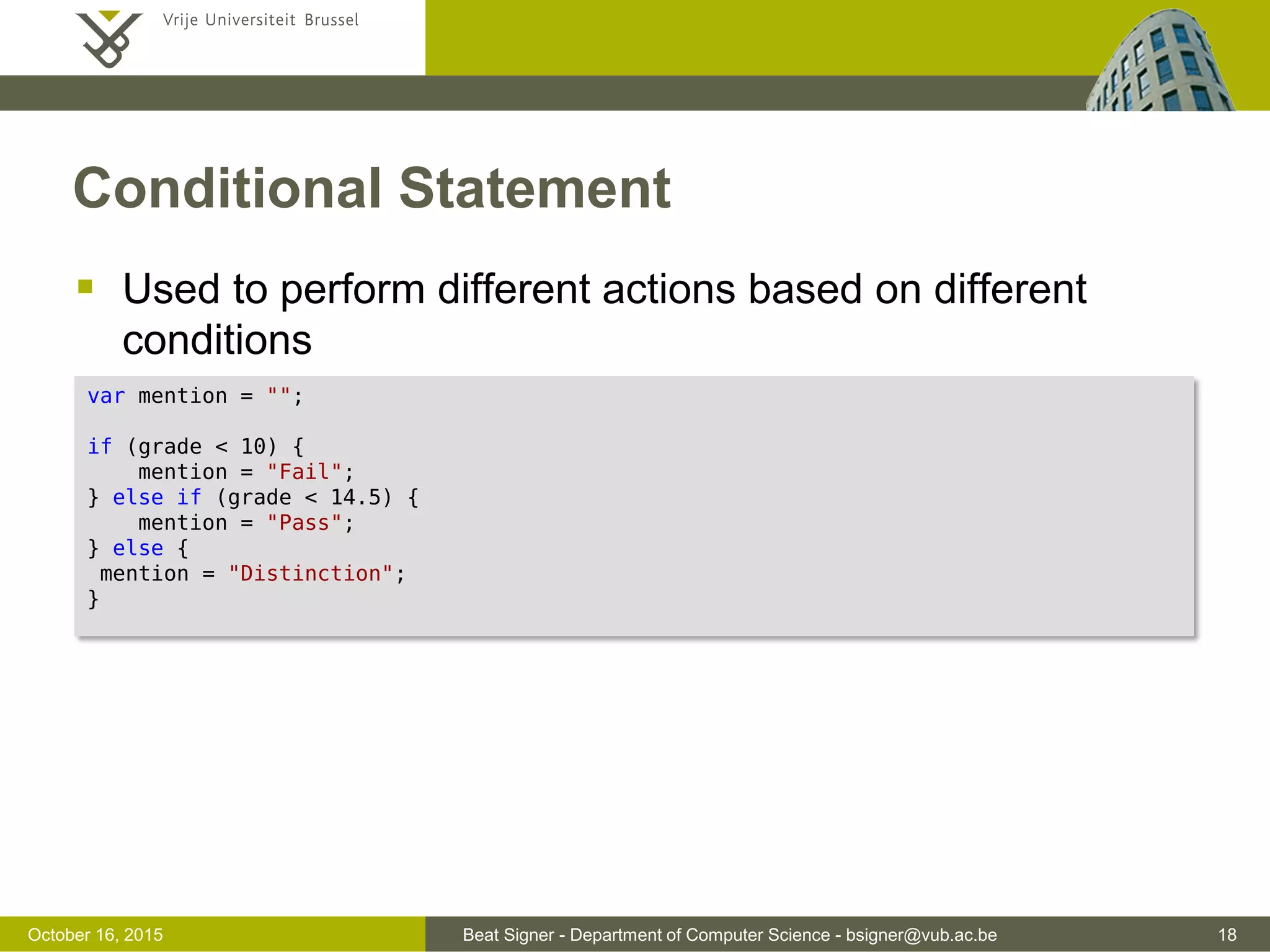
This document discusses JavaScript and jQuery. It provides an overview of JavaScript, including its history, uses, data types, variables, operators, and functions. It also discusses how to add JavaScript to webpages and troubleshoot issues. The document then covers jQuery, a popular JavaScript library, and how it simplifies DOM traversal, event handling, animations and more. It provides examples of basic jQuery syntax and selecting and manipulating HTML elements.

![Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - bsigner@vub.ac.be 2November 4, 2016 JavaScript High-level loosely typed dynamic language Introduced by Netscape in 1995 lightweight interpreted client-side programming Supports imperative, object-oriented and functional programming styles Nowadays also used in non-web-based environments PDF, Microsoft Office, … JavaScript implements the ECMAScript specification current version is ECMAScript 2016 [http://stackoverflow.com/research/developer-survey-2016]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04javascript-160311142716/75/JavaScript-and-jQuery-Web-Technologies-1019888BNR-2-2048.jpg)







![Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - bsigner@vub.ac.be 13November 4, 2016 Objects Container of properties (name/value) where a value can be any JavaScript value (including other objects) Two possibilities to retrieve object values second option only works for legal JavaScript names and non-reserved words var student = { firstName: "John", lastName: "Harper", height: 182 }; student["firstName"]; student.lastName;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04javascript-160311142716/75/JavaScript-and-jQuery-Web-Technologies-1019888BNR-13-2048.jpg)

![Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - bsigner@vub.ac.be 15November 4, 2016 Arrays An array is a variable that can hold multiple values which can be accessed via an integer offest values of different types might be mixed Other methods to sort arrays, combine arrays etc. var points = [10, 5, 17, 42]; points.length; // number of elements (4) points[1]; // accesses the element with the given offset (5) points[points.length] = 13; // adds 13 to the end of the array [10, 5, 17, 42, 13] var last = points.pop(); // removes the last element [10, 5 , 17 , 42] var l = points.push(2); // adds 2 at the end and returns the length (5) var first = points.shift(); // removes the first element [5, 17, 42, 2] l = points.unshift(7); // adds 7 to the beginning and returns the length (5) delete points[2]; // the third element will be undefined var matrix = [[3, 1, 2], [9, 6, 4], [5, 7, 8]]; // array of arrays ("2D" array) matrix [1][2]; // 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04javascript-160311142716/75/JavaScript-and-jQuery-Web-Technologies-1019888BNR-15-2048.jpg)


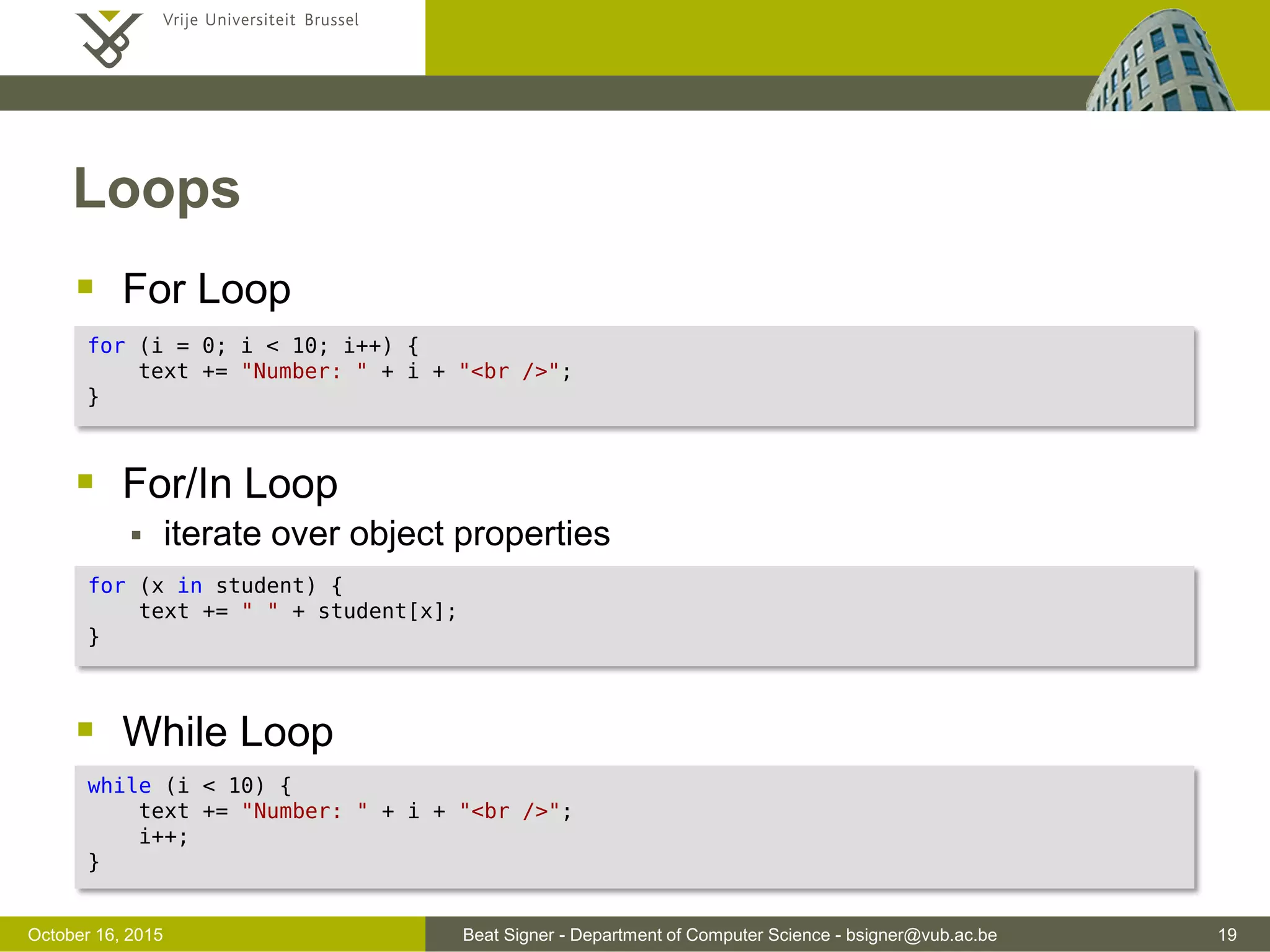
![Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - bsigner@vub.ac.be 20November 4, 2016 Loops For Loop For/In Loop iterate over object properties While Loop for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { text += "Number: " + i + "<br />"; } for (x in student) { text += " " + student[x]; // Add all properties of 'student' to text string } while (i < 10) { text += "Number: " + i + "<br />"; i++; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04javascript-160311142716/75/JavaScript-and-jQuery-Web-Technologies-1019888BNR-20-2048.jpg)


![Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - bsigner@vub.ac.be 23November 4, 2016 JavaScript Best Practices ... Always use the === and !== equality operators == and != do some automatic type coercion (with complicated rules) if the types are not equal Do not use the typed wrappers new Boolean(), new Number() and new String() also use {} instead of new Object() and [] instead of new Array() Avoid block-less if, while, do or for statements Avoid the use of eval() runs text as code and leads to performance and security issues if (x > 10) { t = true; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04javascript-160311142716/75/JavaScript-and-jQuery-Web-Technologies-1019888BNR-23-2048.jpg)
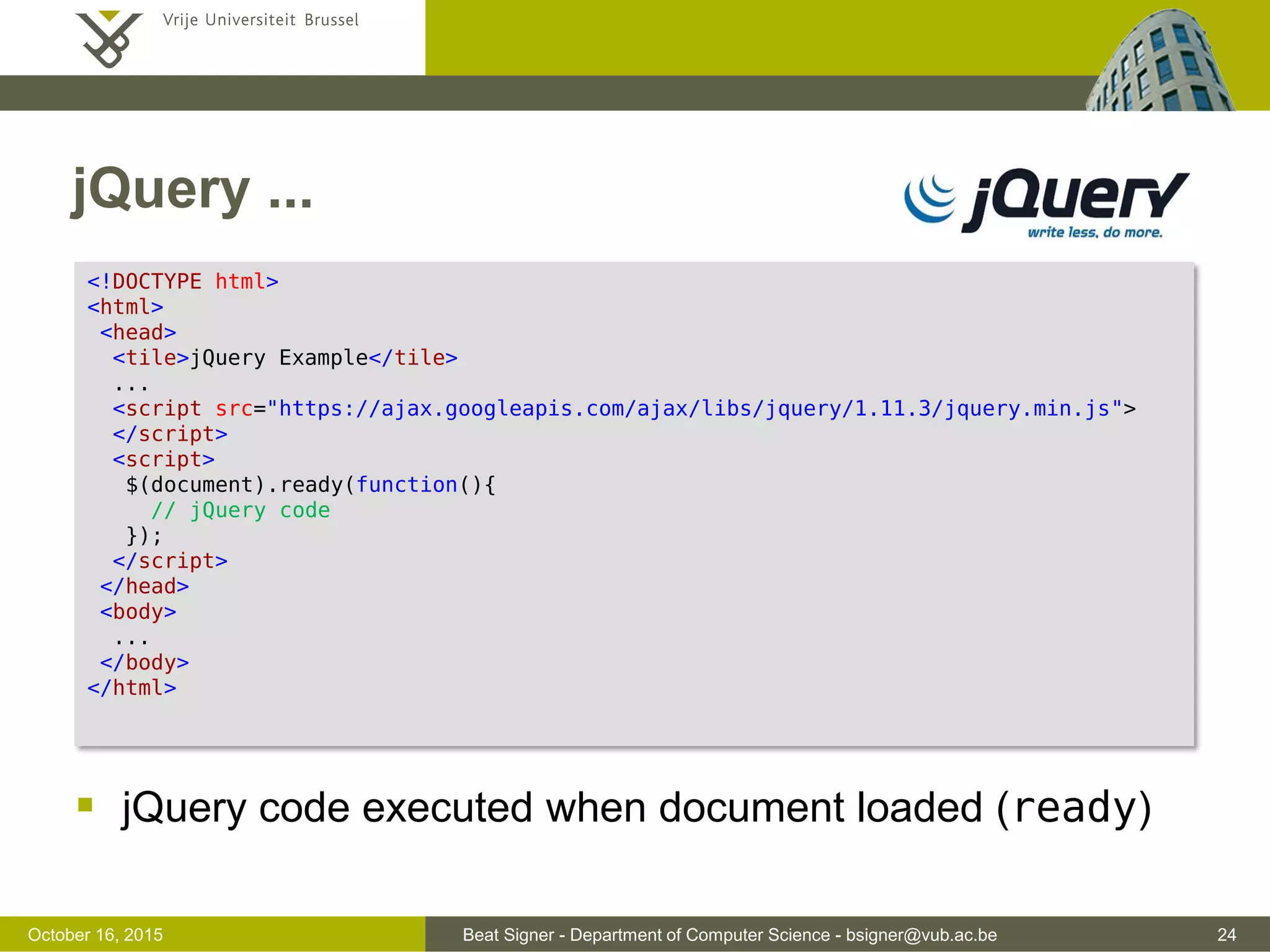
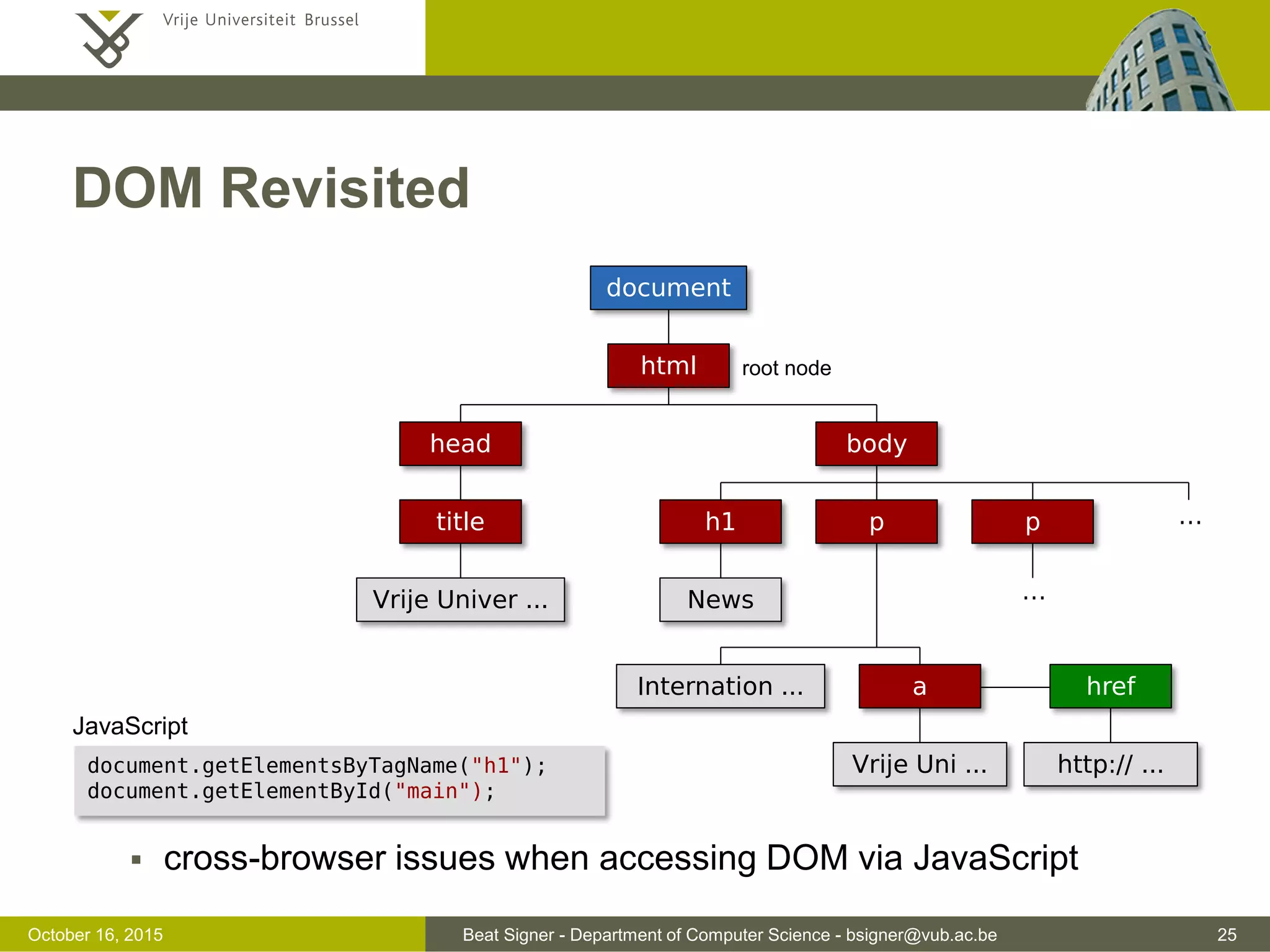
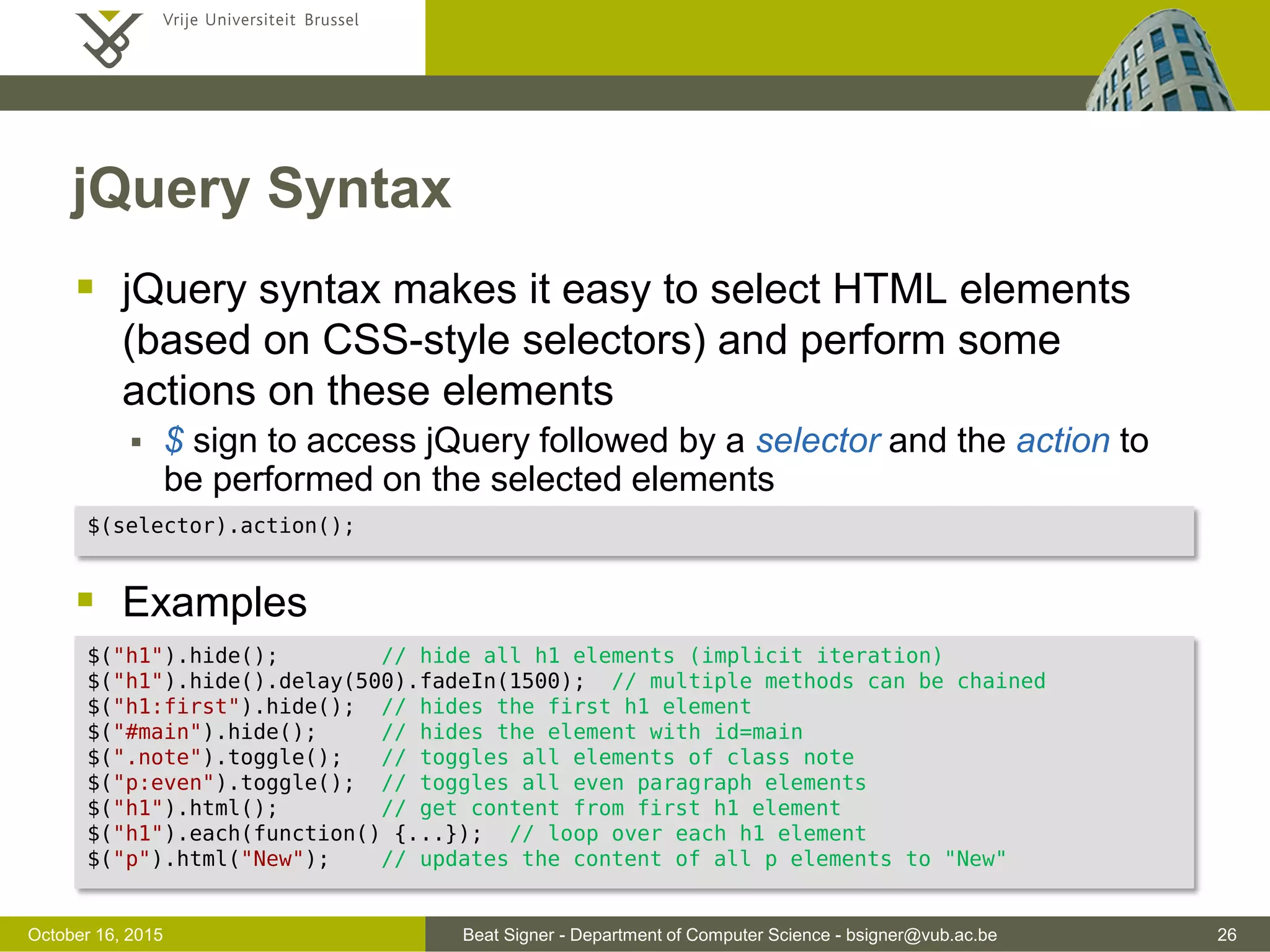








![Beat Signer - Department of Computer Science - bsigner@vub.ac.be 37November 4, 2016 JSON Example { "surname": "Signer", "forename": "Beat", "address": { "street": "Pleinlaan 2", "city": "Brussels", "postalCode": 1050, "country": "Belgium" }, "phoneNumbers": [ { "type": "office", "number": "123 456 789" }, { "type": "fax", "number": "987 654 321" } ] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture04javascript-160311142716/75/JavaScript-and-jQuery-Web-Technologies-1019888BNR-37-2048.jpg)



