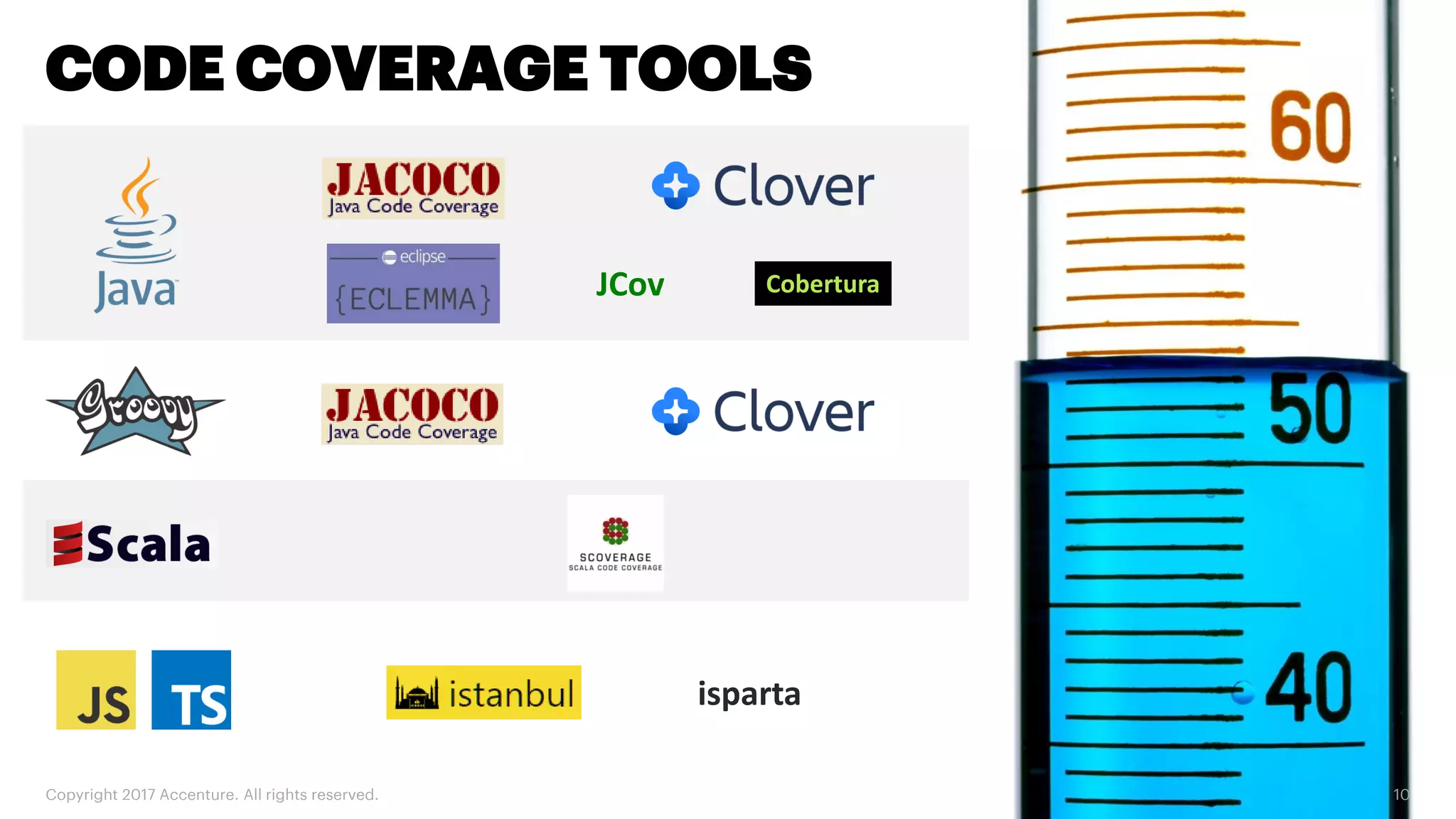
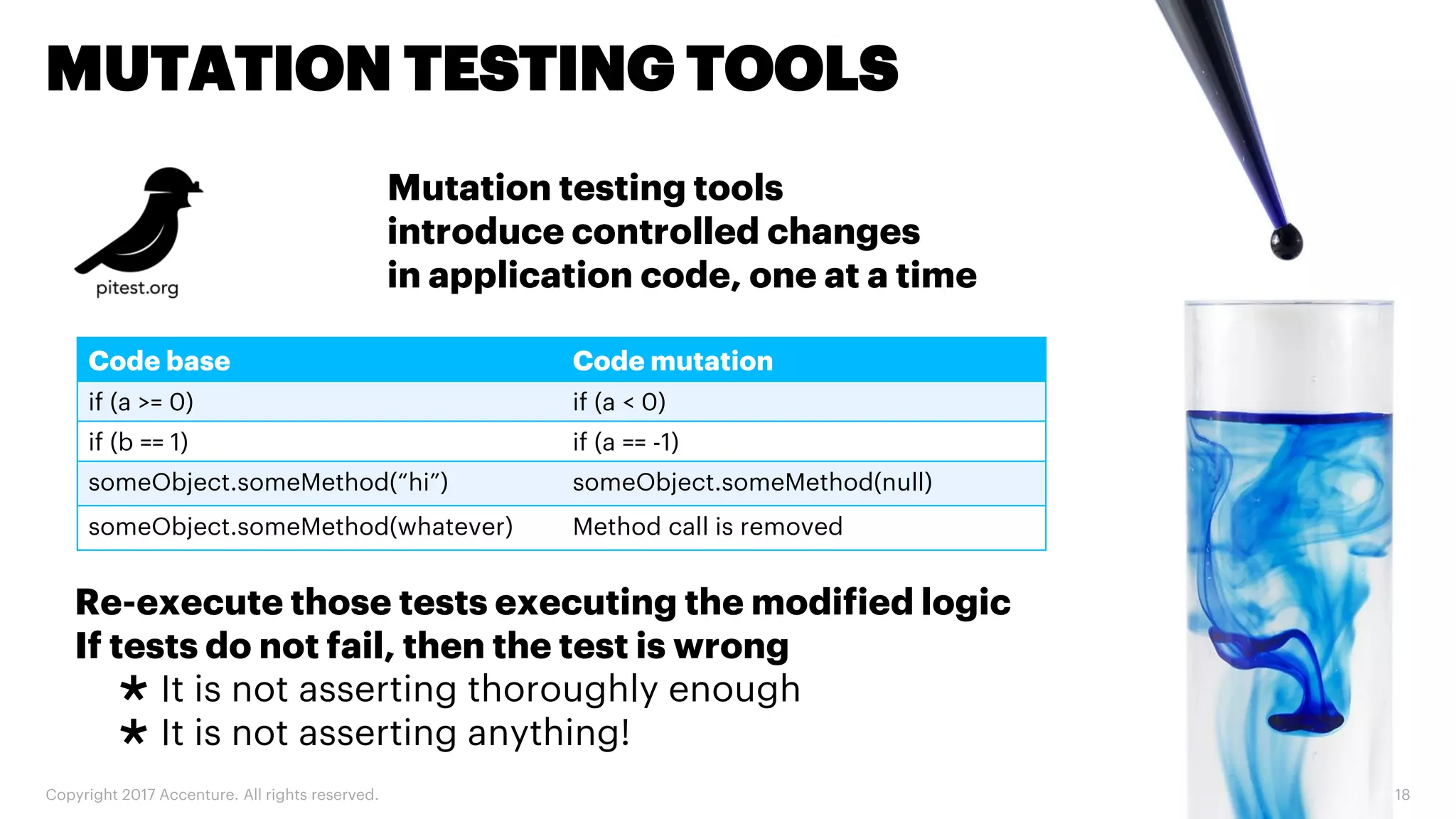
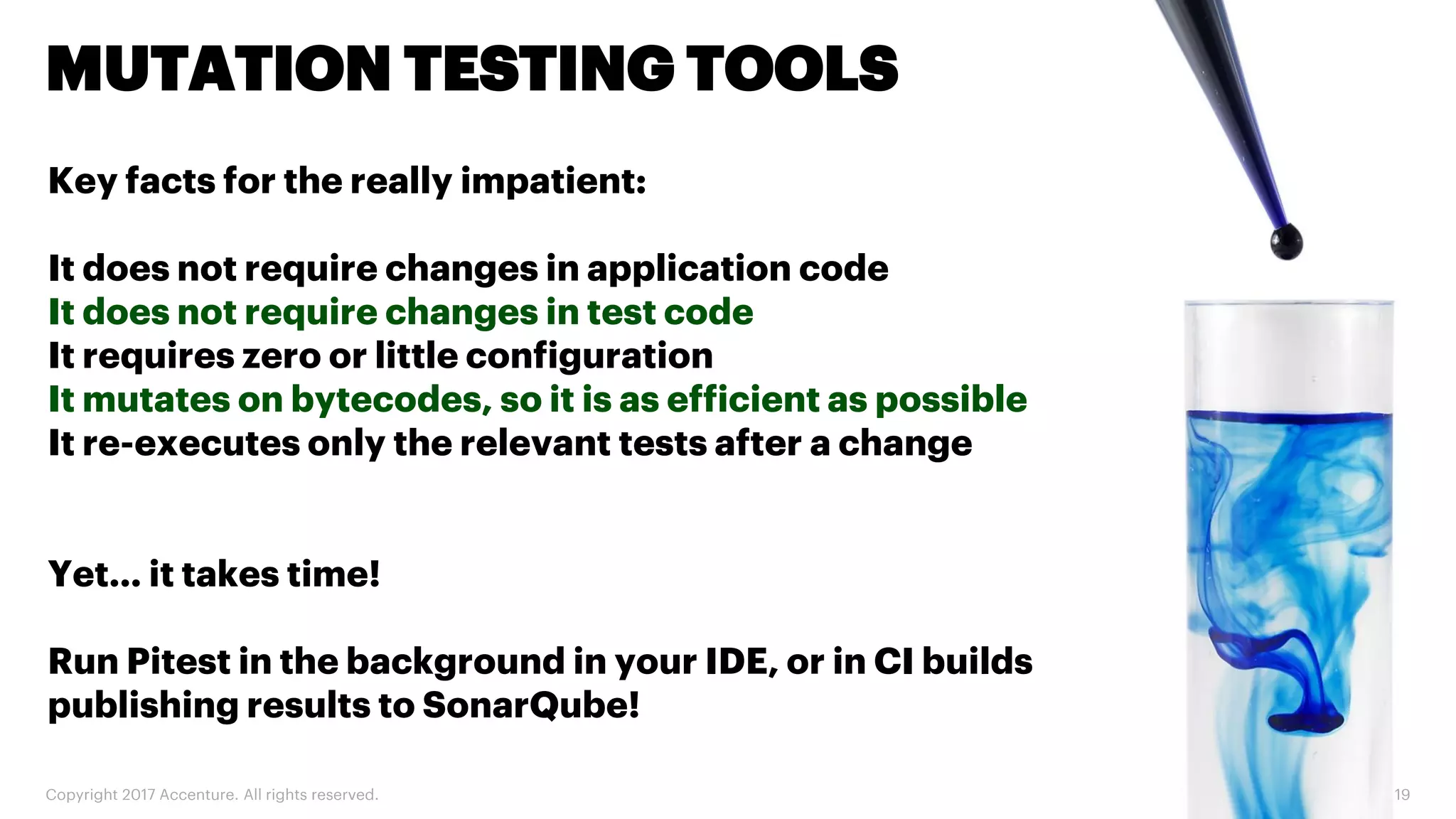
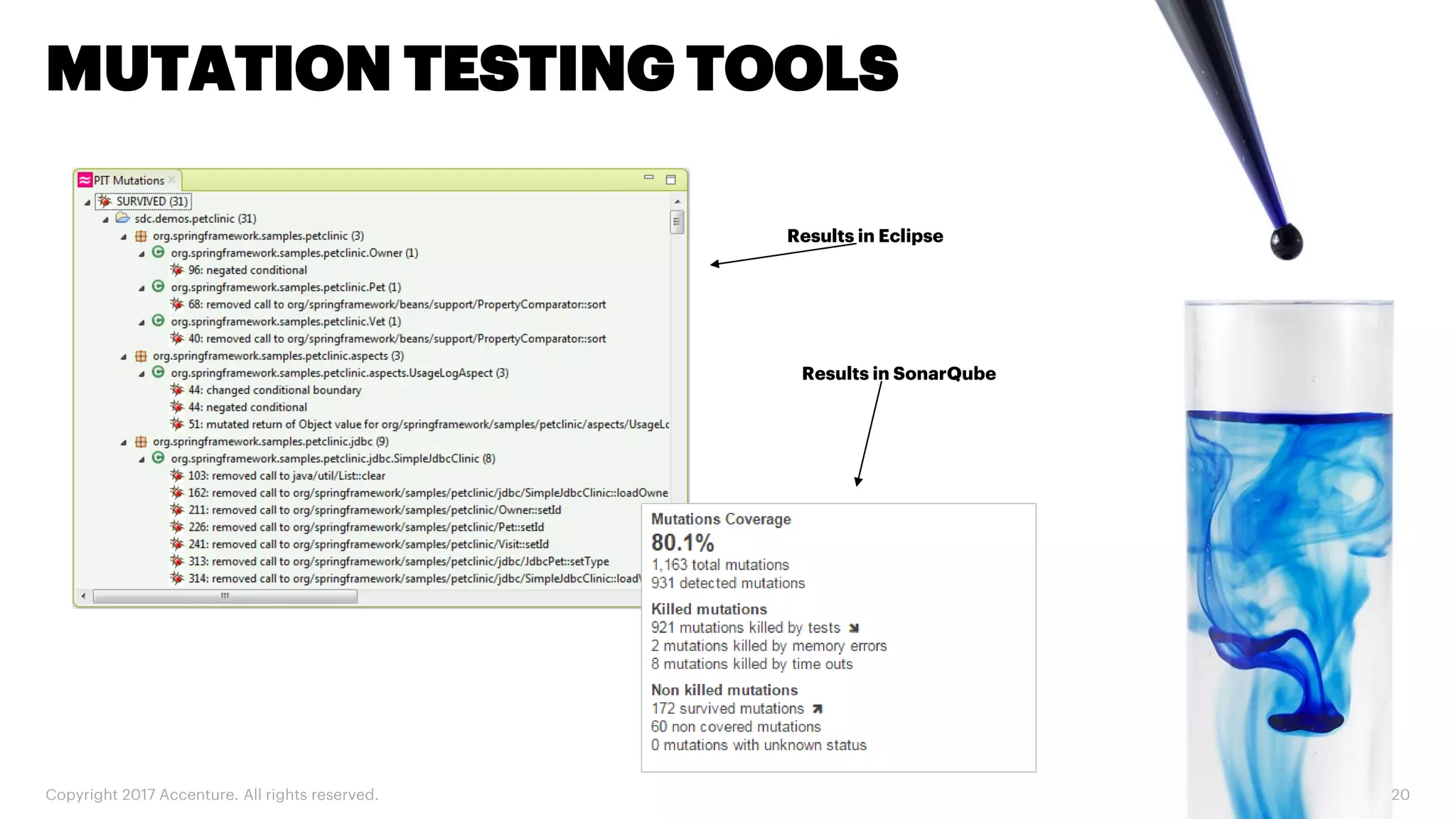
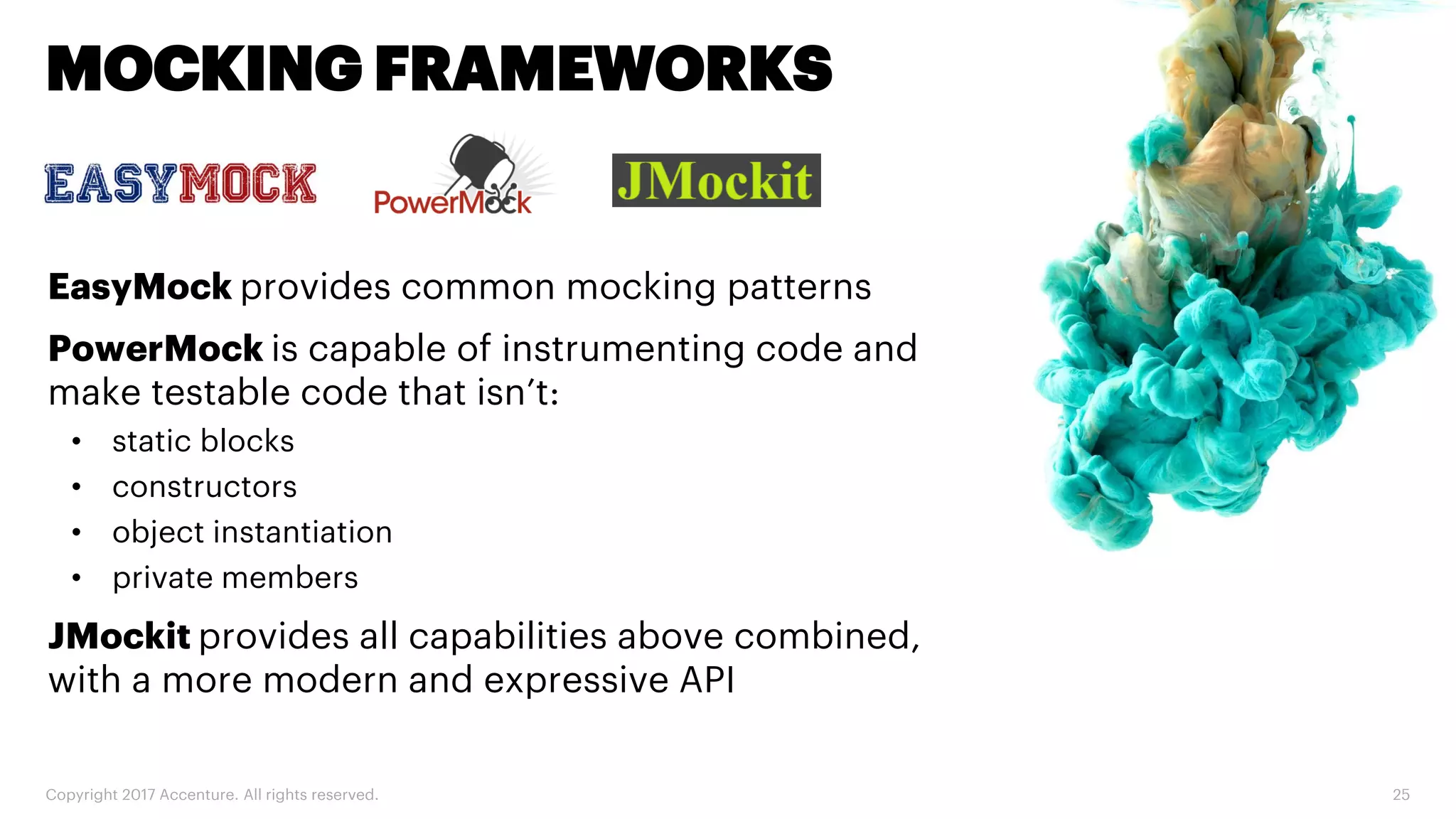
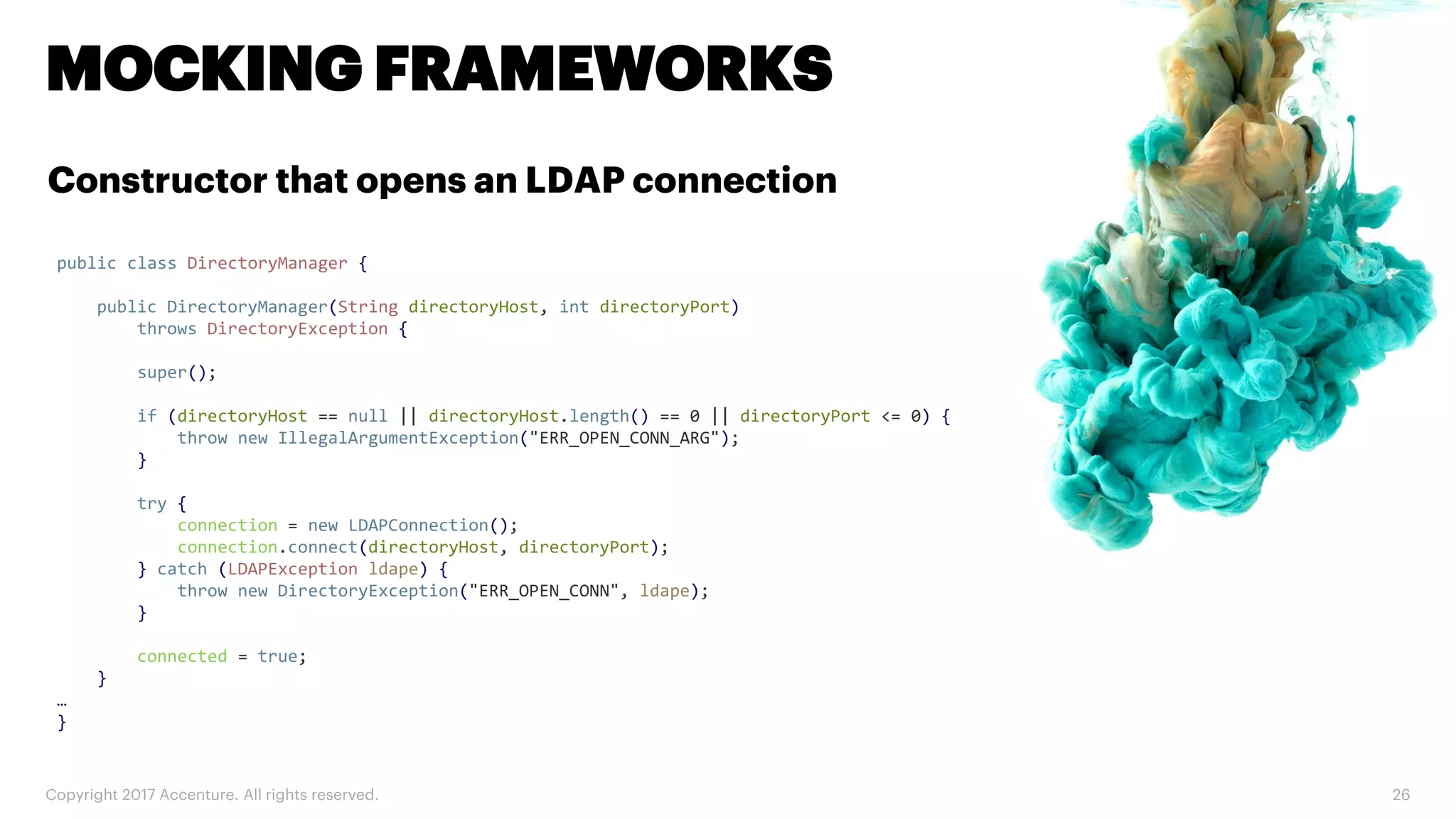
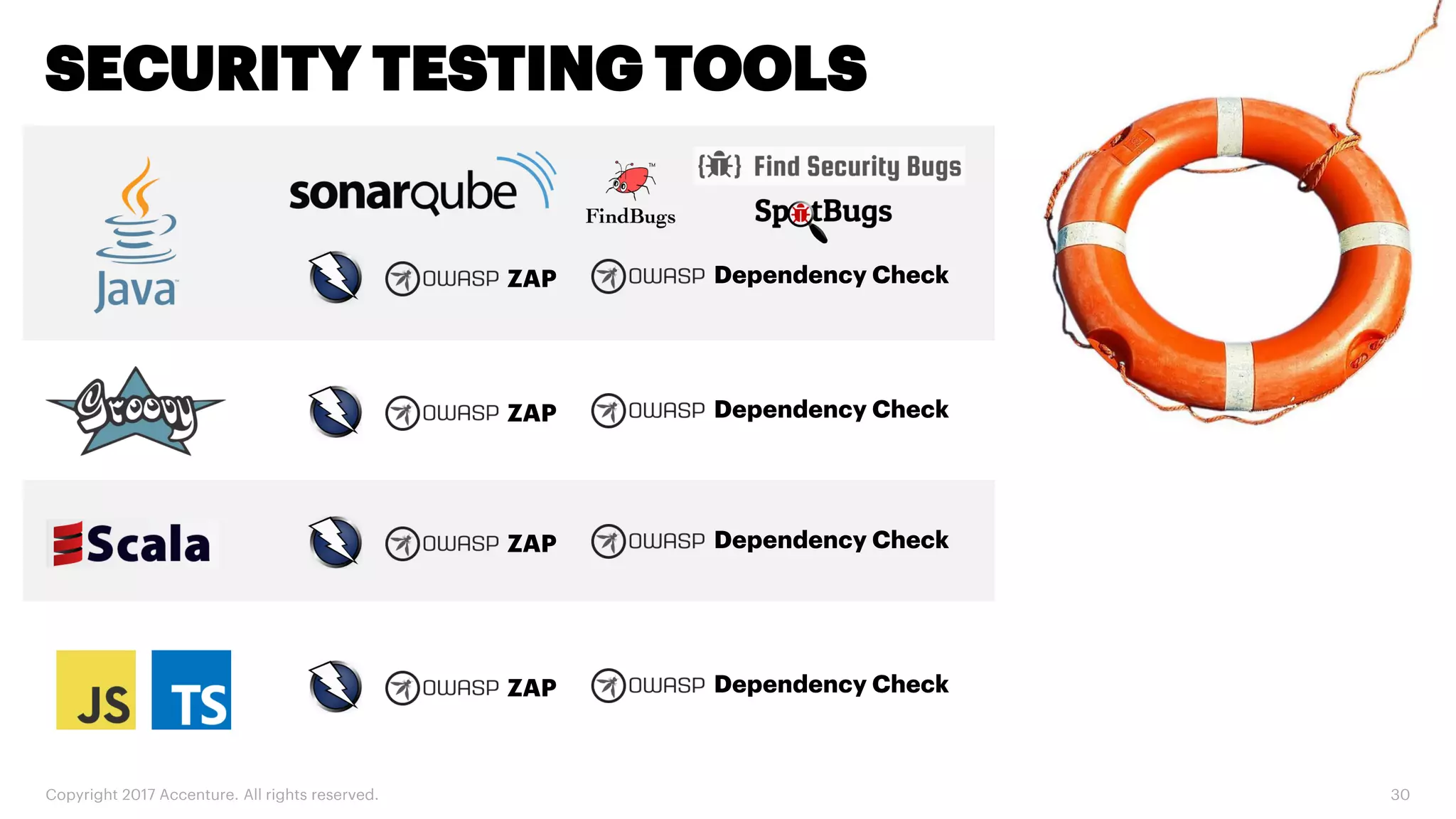
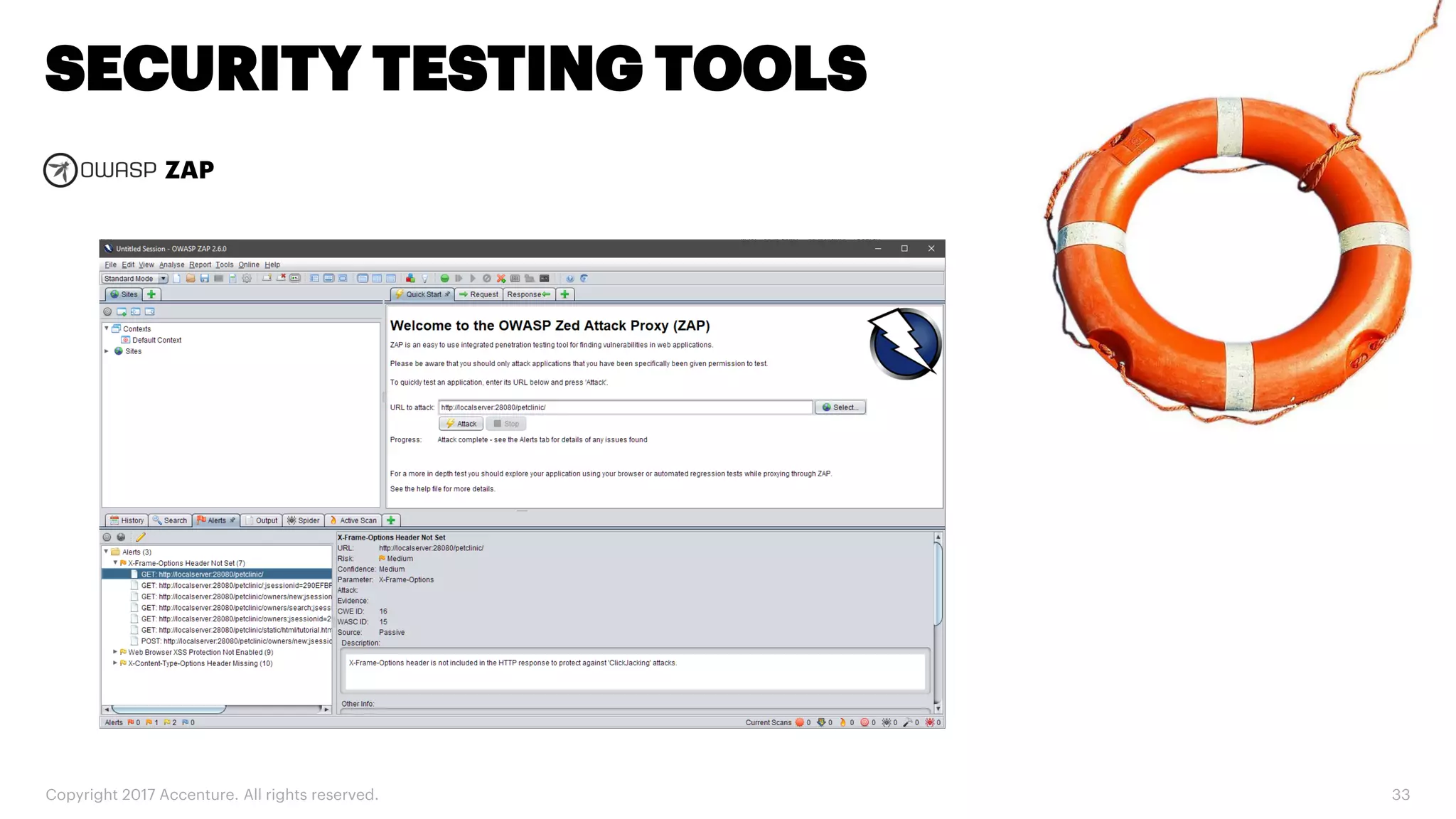
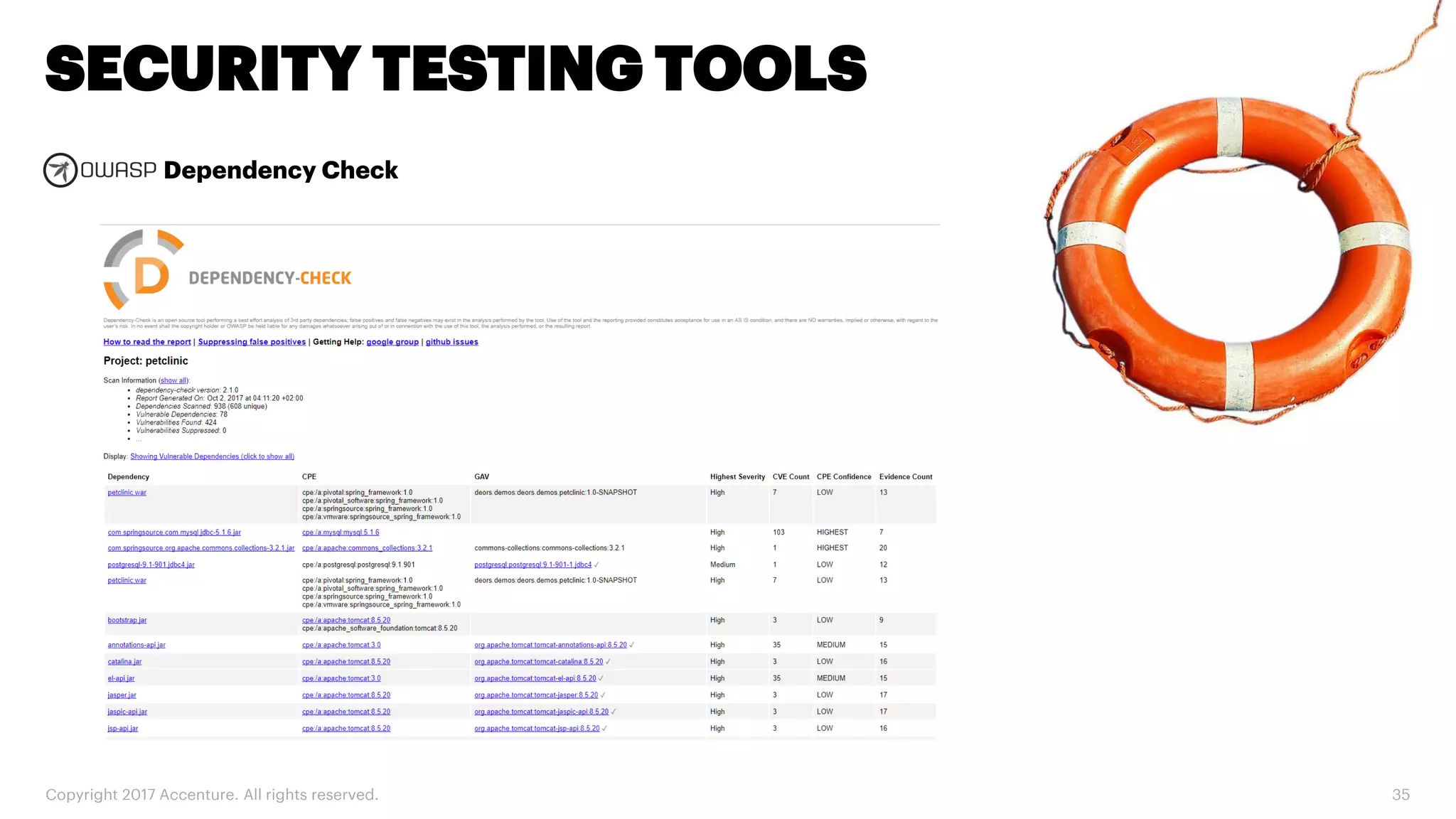
The document discusses various code inspection, testing, and security testing tools that can be used to improve code quality. It recommends profiling code with static analysis tools to check for coding standards and best practices. It also suggests measuring code coverage and using mutation testing to understand which parts of the code are not being tested. Finally, it emphasizes the importance of security testing with tools that can check for vulnerabilities both in code and dependencies. Mocking tools are also recommended to make tests independent of the environment.