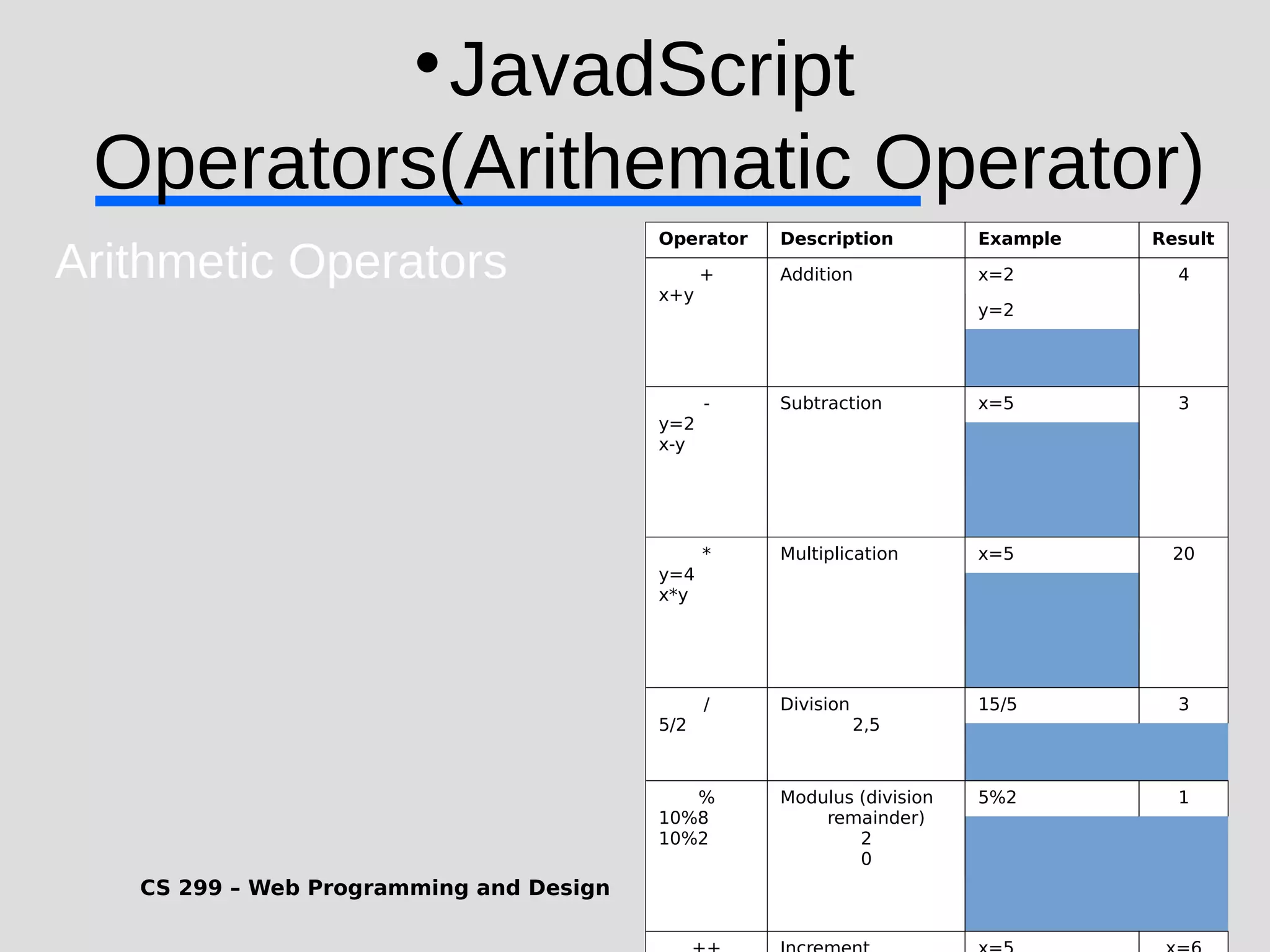
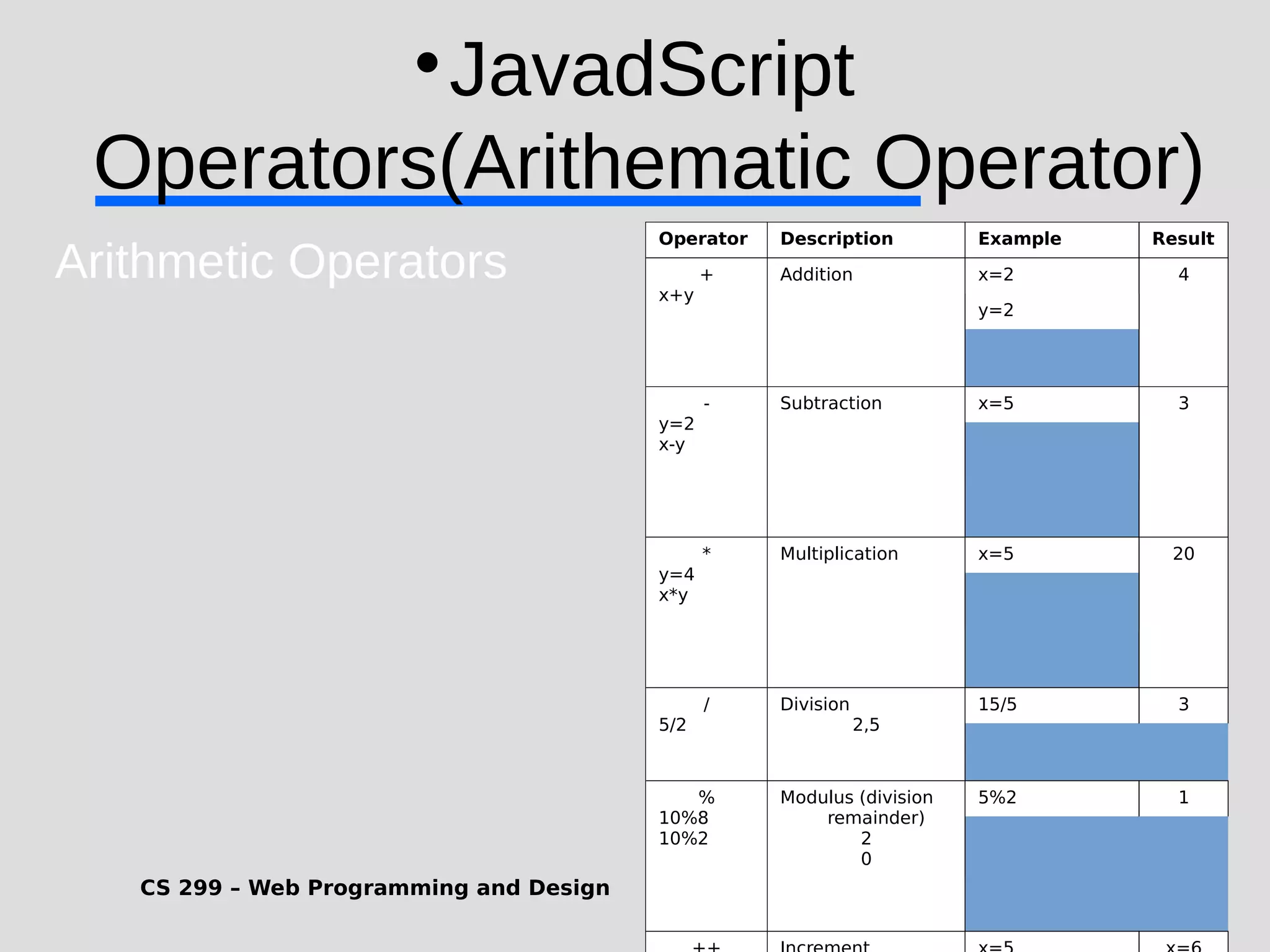
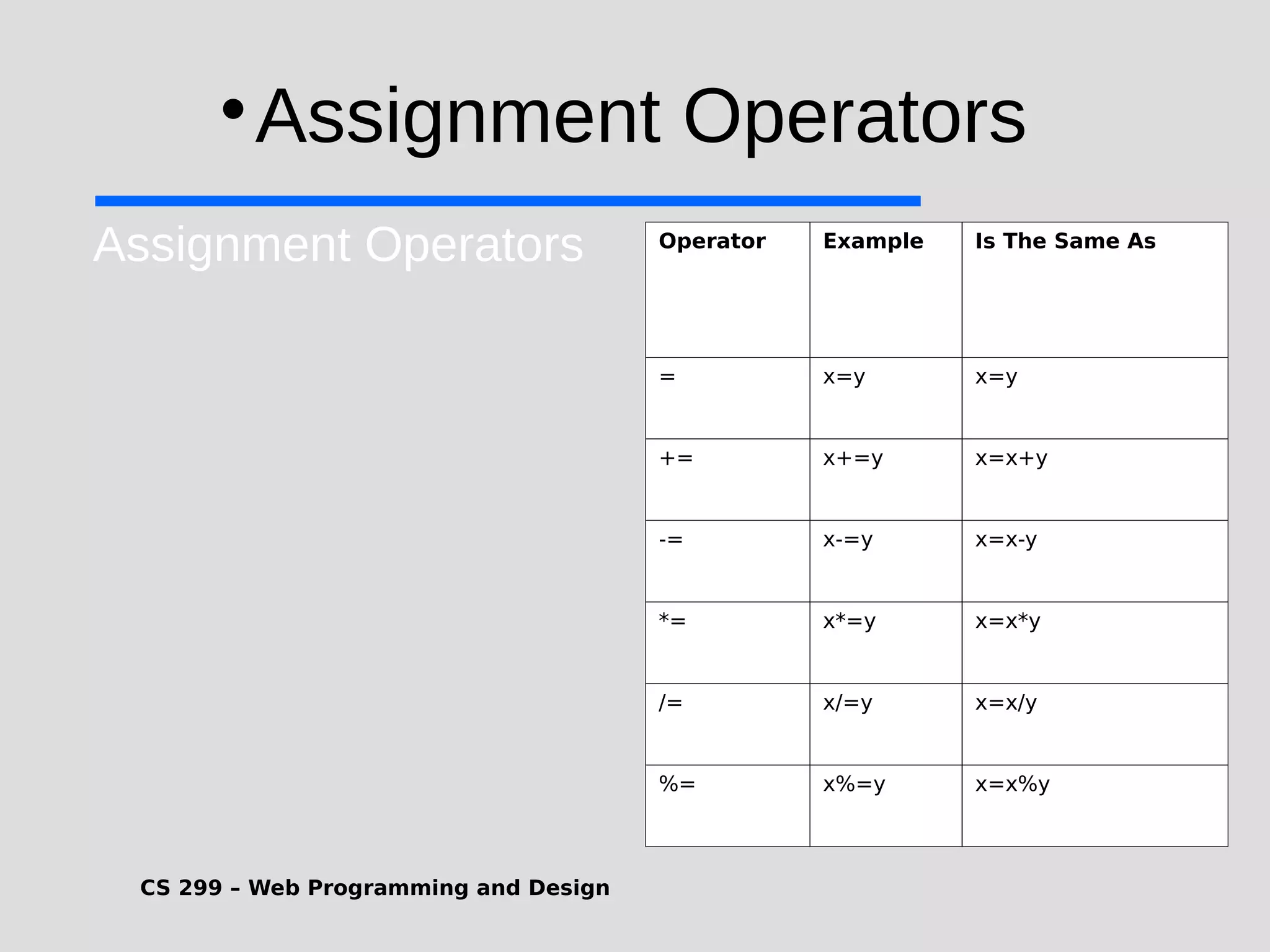
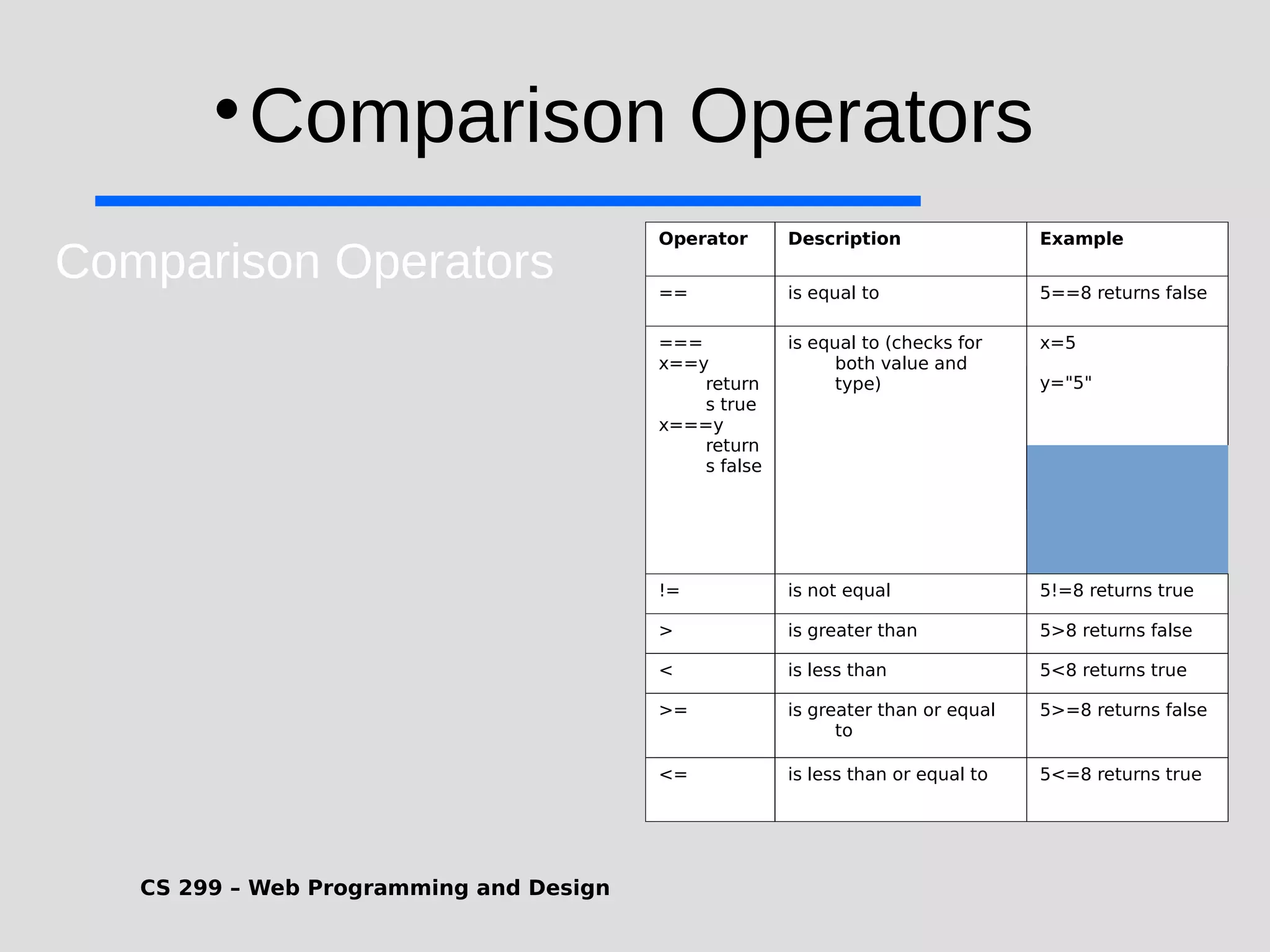
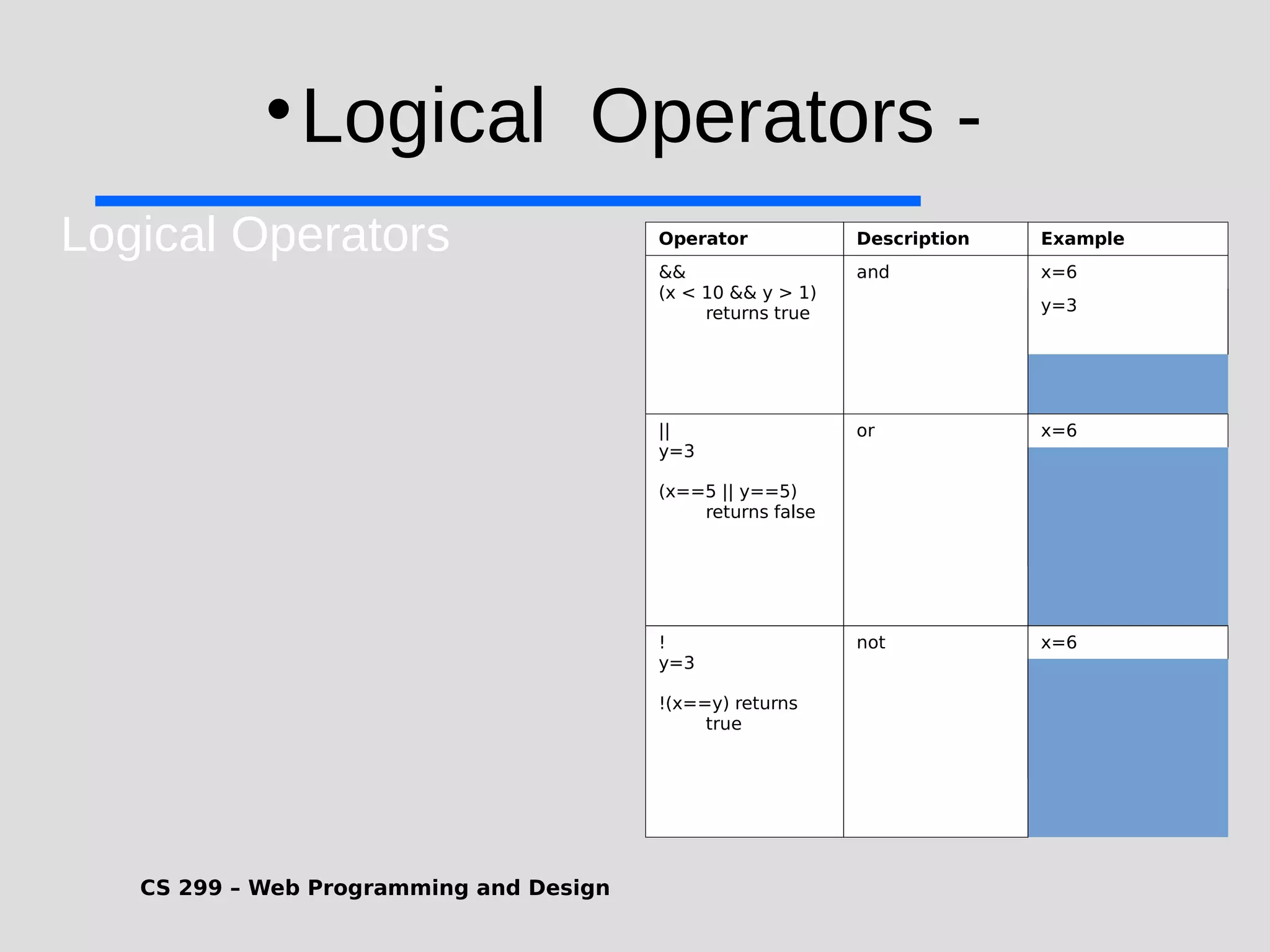
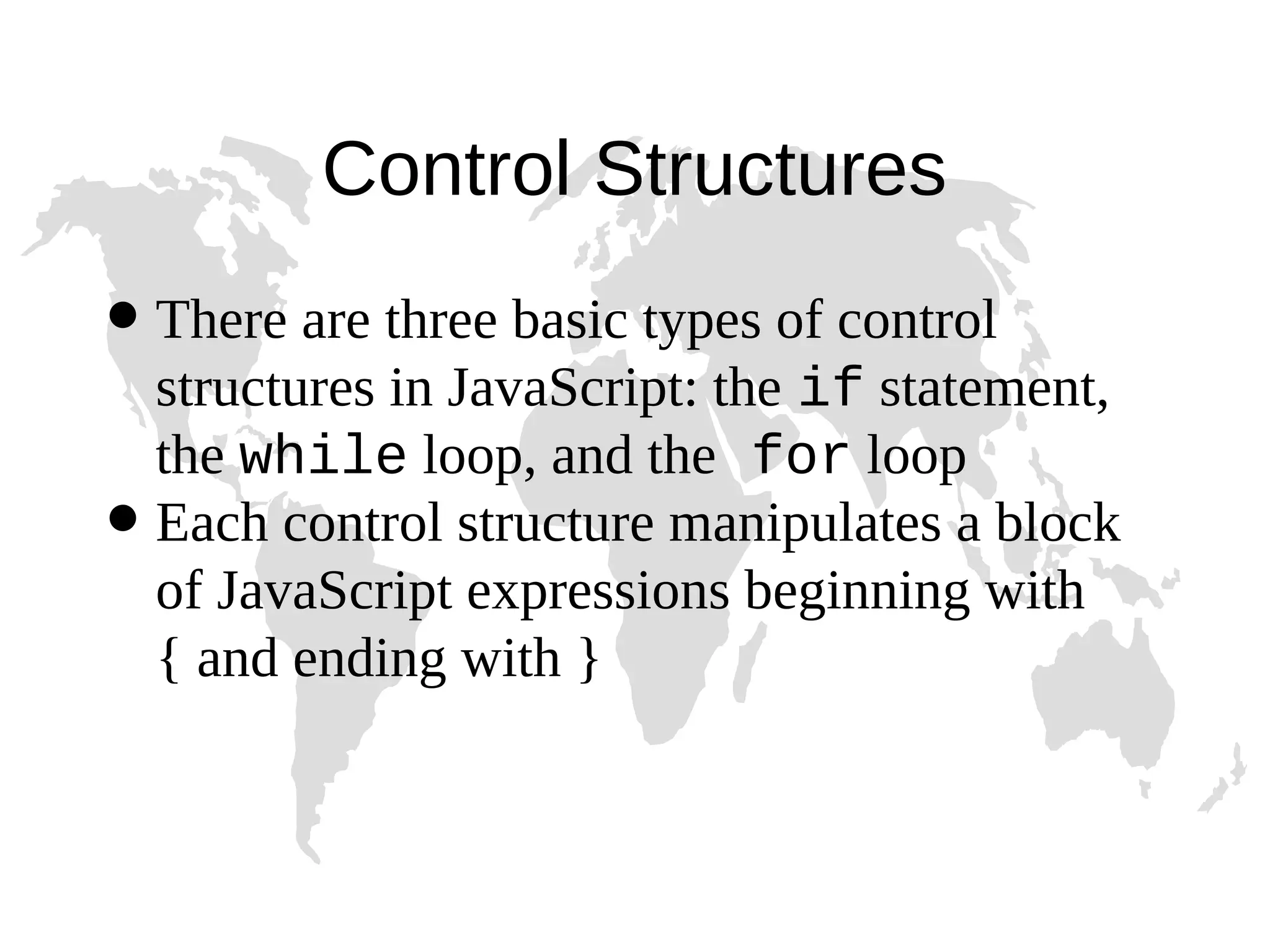
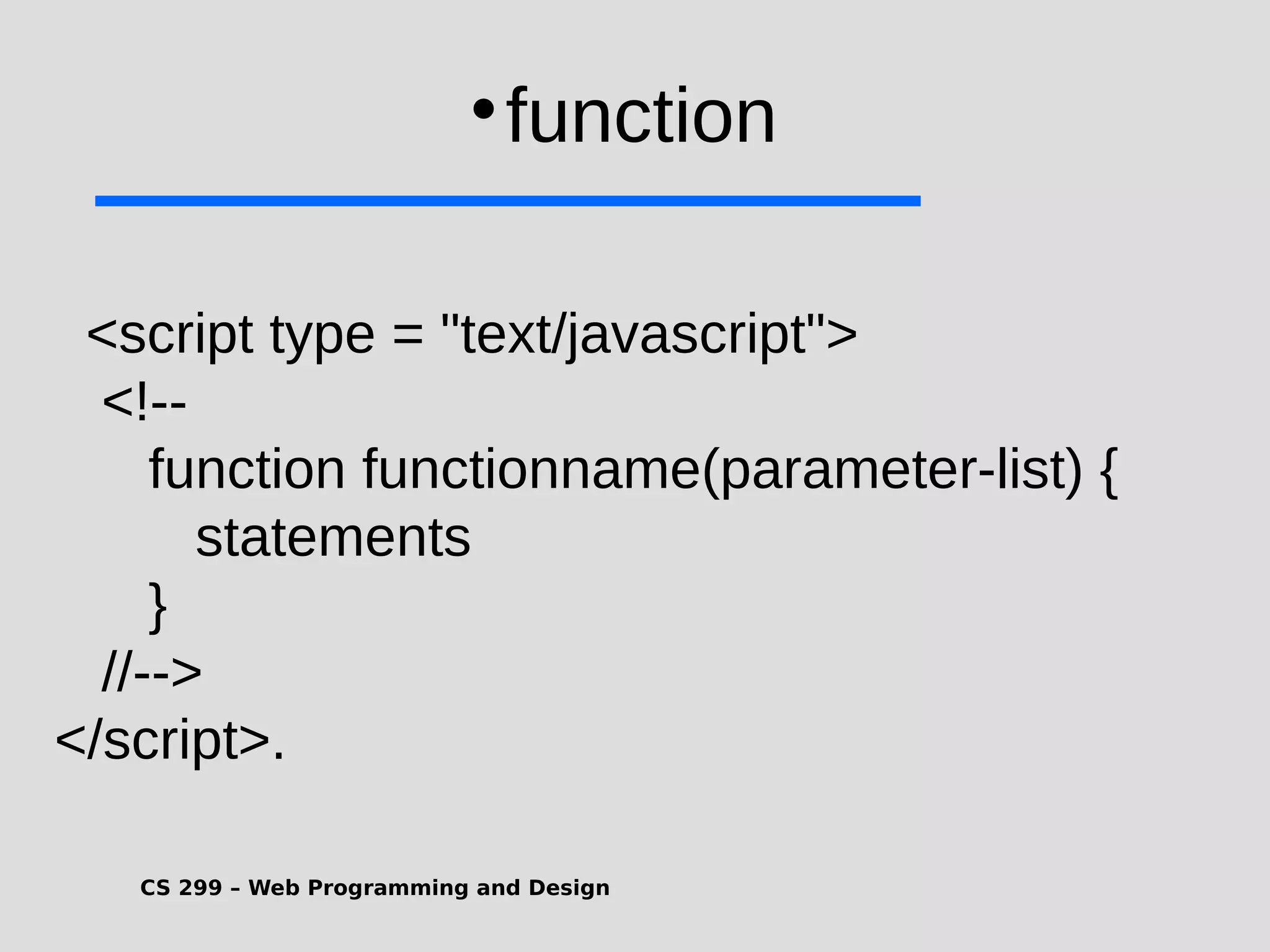
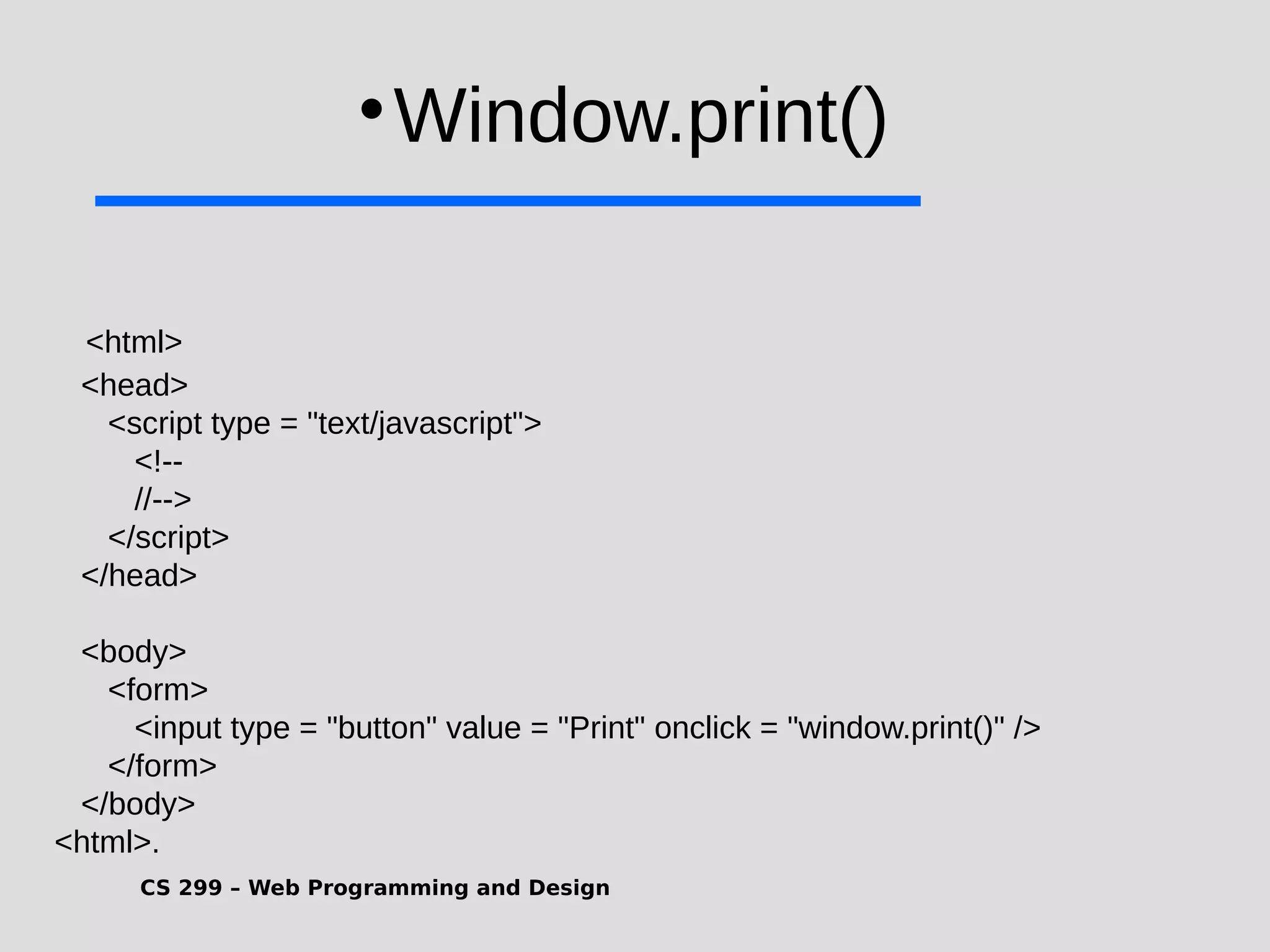
1) JavaScript is a scripting language that adds interactivity to HTML pages and allows dynamic updating of content. It is embedded directly in HTML and is run in web browsers. 2) JavaScript can put dynamic text on HTML pages, react to user events like clicks, modify HTML elements, validate form data, detect the user's browser, and create cookies. 3) JavaScript code is typically included in <script> tags in HTML pages and can be placed in the <head> or <body> sections or linked externally. Common statements include comments, variables, operators, conditional statements, and loops. Functions are used to encapsulate repeatable code.