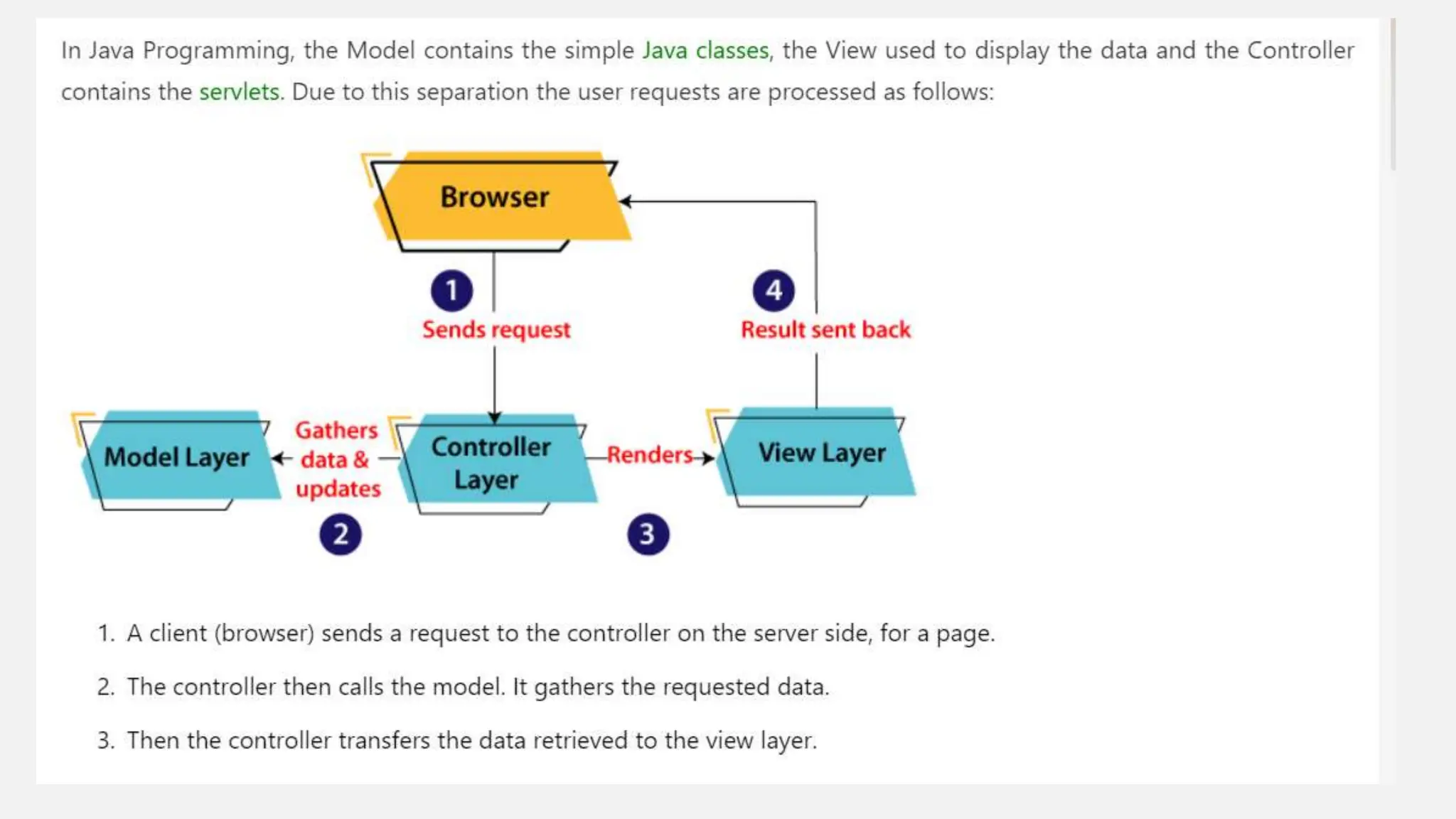
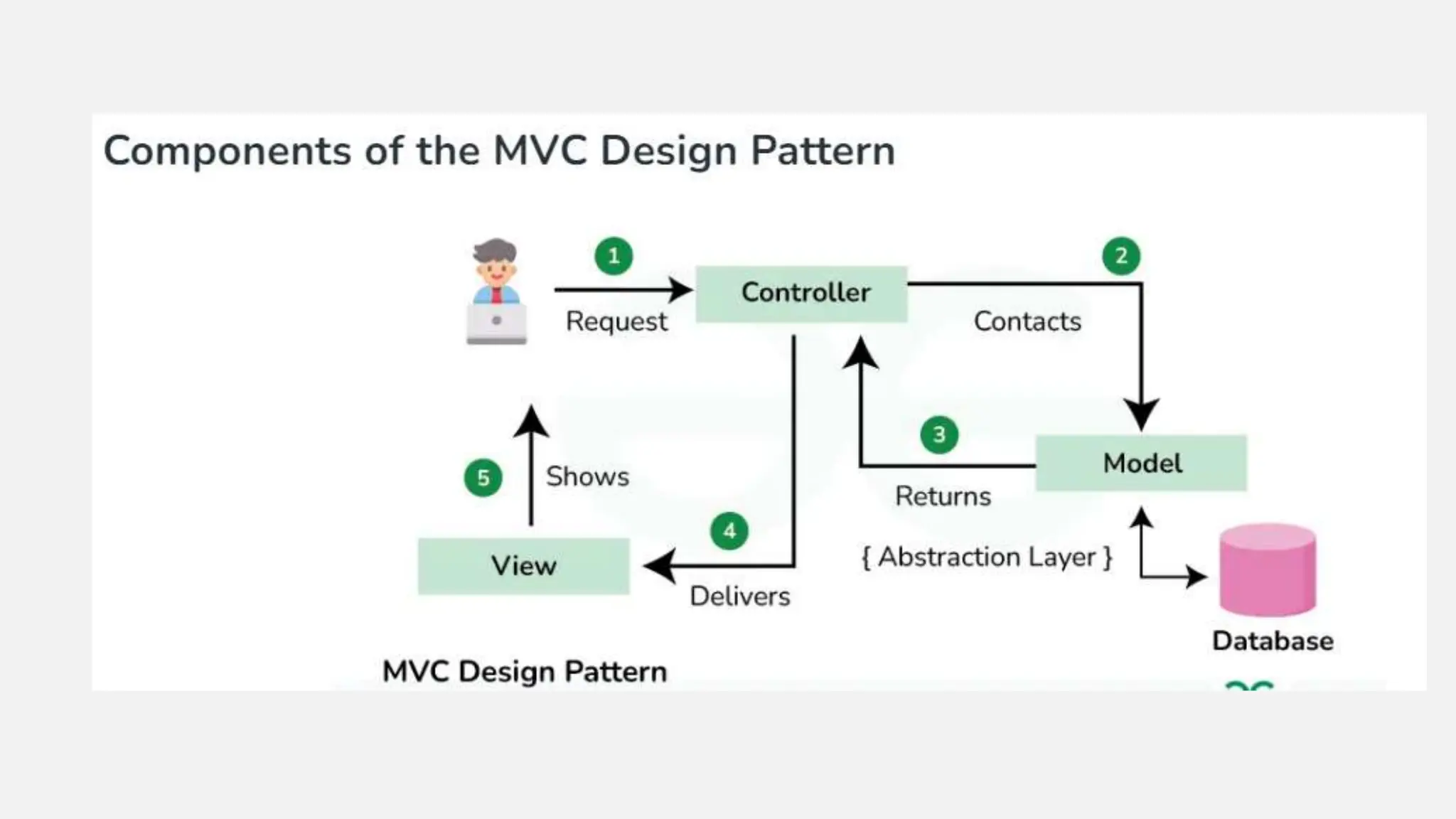
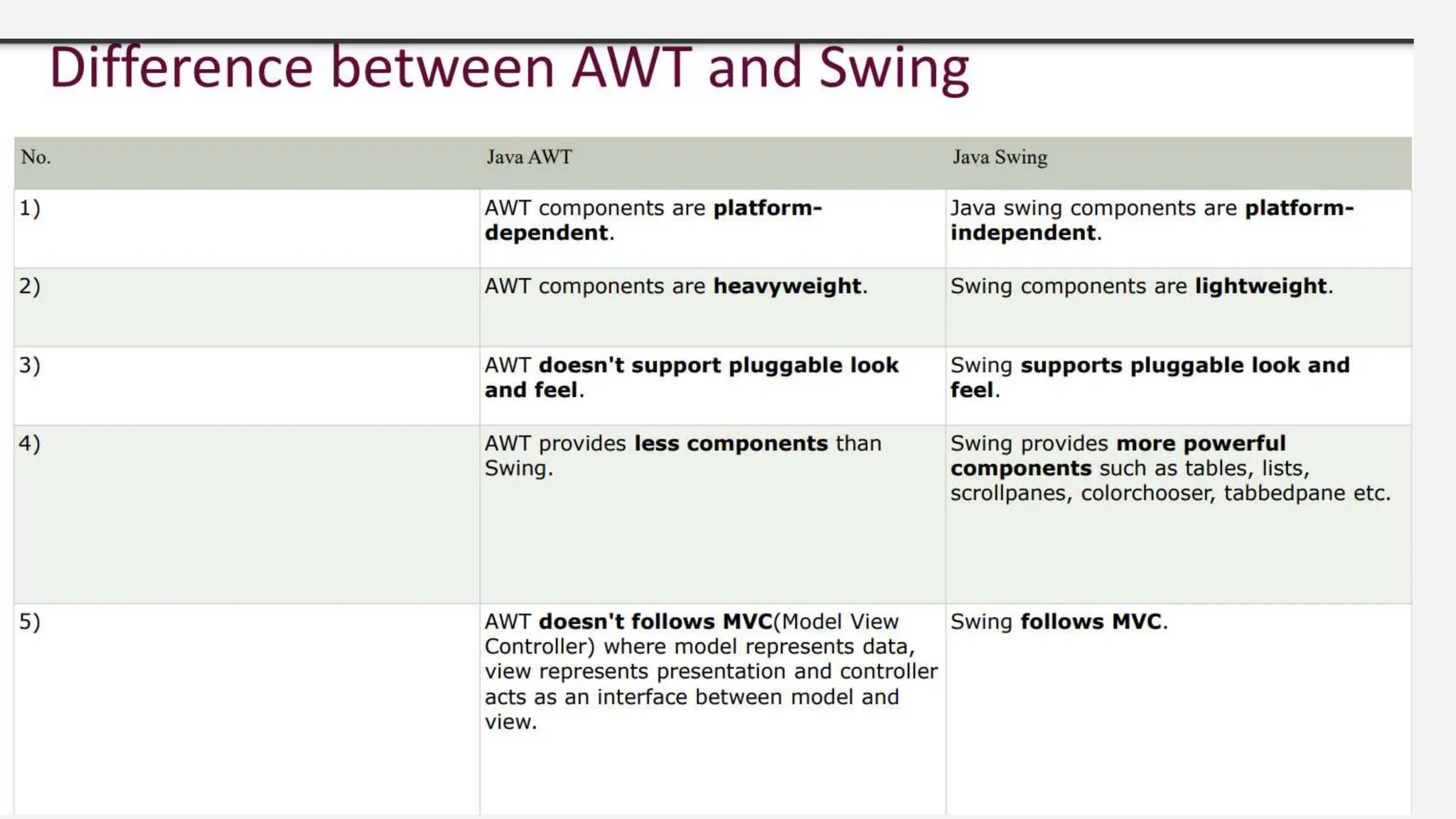
Java Swing is a powerful GUI toolkit for developing desktop applications with platform independence and a rich set of customizable components. It employs a Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture to enhance scalability and maintainability, allowing for efficient event handling and flexible layout management. Swing also supports customizable themes through a pluggable look and feel, making it versatile for developers across different operating systems.