This document provides an overview of how to write a basic "Hello World" program in Java. It outlines the steps needed, including setting up a development environment with a text editor and the Java Development Kit, creating a Java file with the class and main method, writing the "Hello World" print statement, compiling and running the program. The summary provides a high-level view of the key activities and process for writing a simple first Java program.




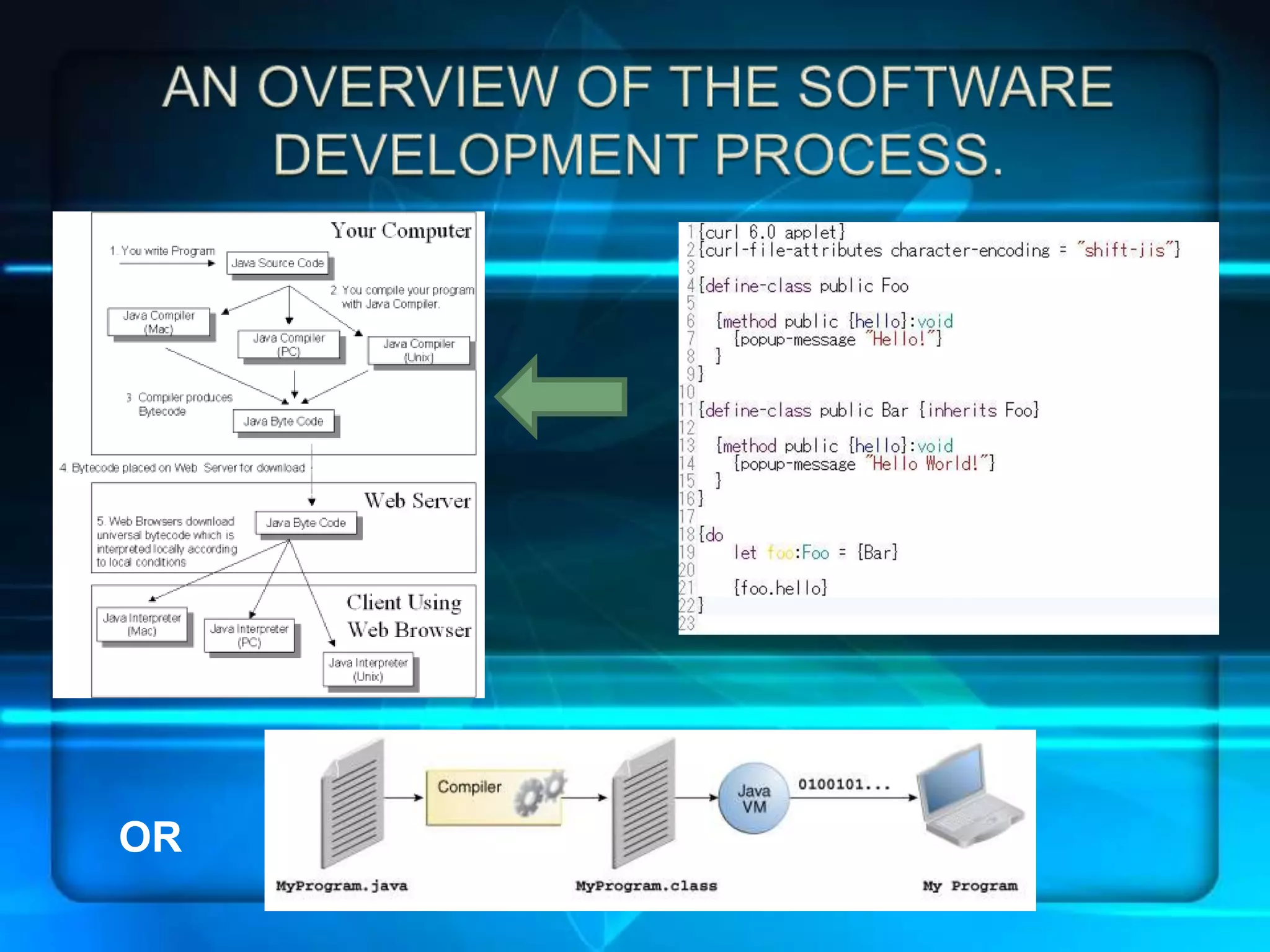




![HOW TO WRITE YOUR FIRST PROGRAM IN JAVA InordertostartwritingprogramsinJava,setupyour workenvironment.ManyprogrammersuseIntegrated DevelopmentEnvironments(IDEs)suchasEclipseand NetbeansfortheirJavaprogramming,butonecanwrite aJavaprogramandcompileitwithoutbloatedIDEs. Any sort of Notepad-like program will suffice for programming in Java.Hardcore programmers sometimes prefer to use text editors that are within the terminal such as vim and emacs. A very good text editor that can be installed on both a Windows machine and on a linux-based machine (Mac, Ubuntu, etc.) is Sublime Text, which is what we will be using in this tutorial. Make sure that you have the Java Software Development KIT installed. You will need this for compiling your program. We will first create a program that prints "Hello World." In your text editor, create a new file and save it as "HelloWorld.java". HelloWorld is your class name and you will need your class name to be the same name as your file. Declare your class and your main method. The main method public static void main(String[] args) is the method that will be executed when the programming is running. Write the line of code that will print out "Hello World." Put it all together Save your file and open up command prompt or terminal to compile the program Run the program. Congratulations, you have made your first Java program!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaprogrammingmandm-9neumannjgmnhs-150209081240-conversion-gate02/75/Java-Programming-M-M-17-2048.jpg)
