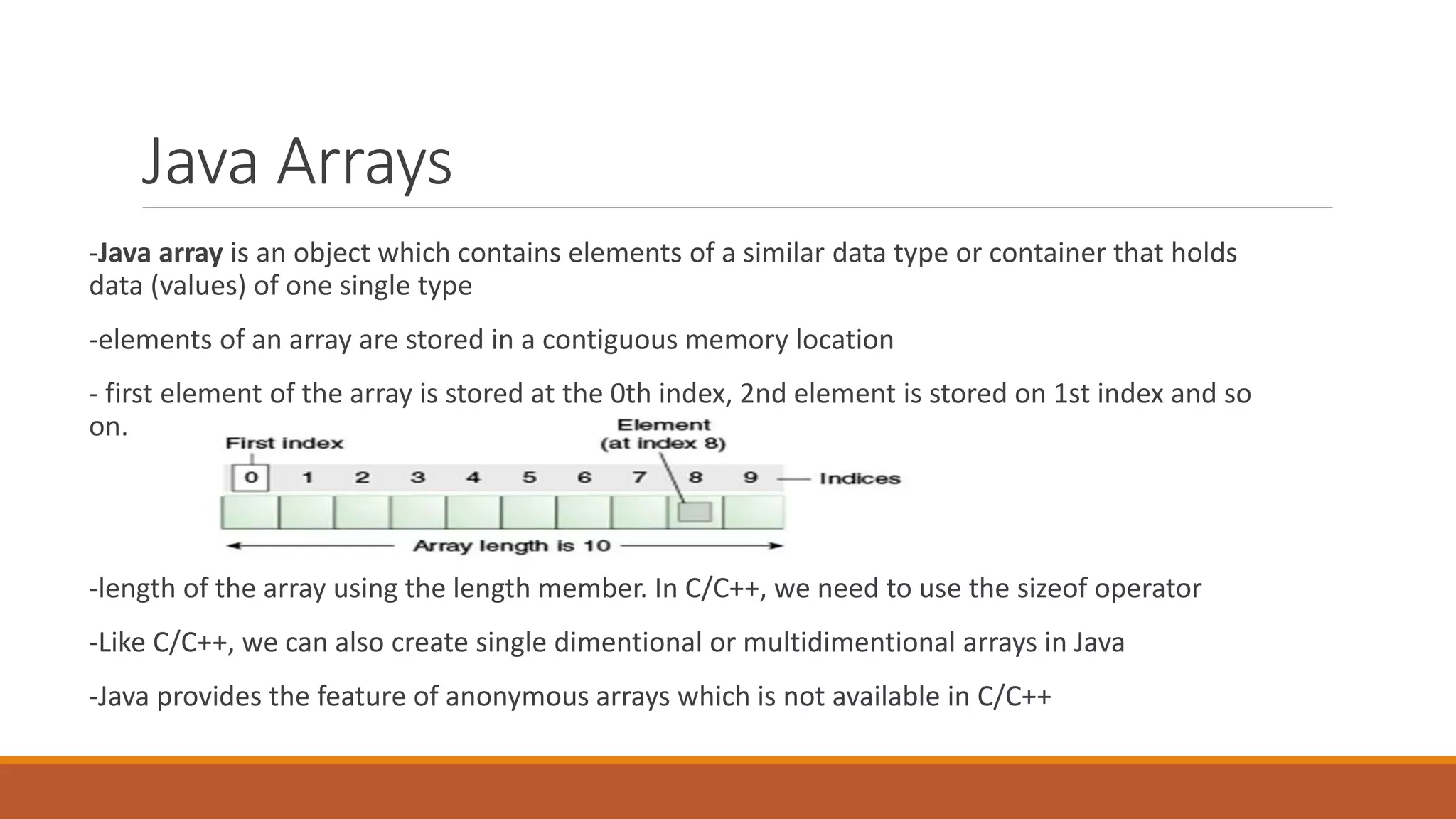
Java arrays allow storing multiple elements of the same type in contiguous memory locations. Arrays can have one or more dimensions. Some key points about Java arrays include: - Elements are accessed via an integer index from 0 to length-1. - Arrays have a fixed size set at creation time. - Common operations include initialization, traversal, passing to methods, and returning from methods. - Exceptions like ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException may occur if invalid indexes are used.


![(cont.,) Syntax to declare an array-Single dimension dataType[] arr; (or) dataType []arr; (or) dataType arr[]; Instantiation of an Array in Java arrayRefVar=new datatype[size]; -creating an object-creating instance of the class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-arrayoperators-210825071157/75/Java-Programming-4-2048.jpg)
![Example //Java Program to illustrate how to declare, instantiate, initialize //and traverse the Java array. class Testarray{ public static void main(String args[]){ int a[]=new int[5];//declaration and instantiation a[0]=10;//initialization a[1]=20; a[2]=30; a[3]=40; a[4]=50; //traversing array for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)//length is the property of array System.out.println(a[i]); }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-arrayoperators-210825071157/75/Java-Programming-5-2048.jpg)
![(Cont.,) int a[]={33,3,4,5};//declaration, instantiation and initialization class Testarray1{ public static void main(String args[]){ int a[]={33,3,4,5};//declaration, instantiation and initialization //printing array for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)//length is the property of array System.out.println(a[i]); }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-arrayoperators-210825071157/75/Java-Programming-6-2048.jpg)
![for each loop The Java for-each loop prints the array elements one by one. It holds an array element in a variable, then executes the body of the loop. for(data_type variable:array){ //body of the loop } //Java Program to print the array elements using for-each loop class Testarray1{ public static void main(String args[]){ int arr[]={33,3,4,5}; //printing array using for-each loop for(int i:arr) System.out.println(i); }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-arrayoperators-210825071157/75/Java-Programming-7-2048.jpg)
![Passing Array to a Method class Testarray2{ //creating a method which receives an array as a parameter static void min(int arr[]) { int min=arr[0]; for(int i=1;i<arr.length;i++) if(min>arr[i]) min=arr[i]; System.out.println(min); } public static void main(String args[]) { int a[]={33,3,4,5};//declaring and initializing an array min(a);//passing array to method } } Guess the output?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-arrayoperators-210825071157/75/Java-Programming-8-2048.jpg)
![Anonymous Array in Java public class TestAnonymousArray{ //creating a method which receives an array as a parameter static void printArray(int arr[]) { for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) System.out.println(arr[i]); } public static void main(String args[]){ printArray(new int[]{10,22,44,66});//passing anonymous array to method }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-arrayoperators-210825071157/75/Java-Programming-9-2048.jpg)
![Returning Array from the Method //Java Program to return an array from the method class TestReturnArray{ //creating method which returns an array static int[] get(){ return new int[]{10,30,50,90,60}; } public static void main(String args[]){ //calling method which returns an array int arr[]=get(); //printing the values of an array for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) System.out.println(arr[i]); }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-arrayoperators-210825071157/75/Java-Programming-10-2048.jpg)
![ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException Java Virtual Machine (JVM) throws an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if length of the array in negative, equal to the array size or greater than the array size while traversing the array. //Java Program to demonstrate the case of //ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException in a Java Array. public class TestArrayException{ public static void main(String args[]){ int arr[]={50,60,70,80}; for(int i=0;i<=arr.length;i++){ System.out.println(arr[i]); } }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-arrayoperators-210825071157/75/Java-Programming-11-2048.jpg)

![Multidimensional Array Syntax to Declare dataType [][]arrayRefVar; (or) dataType arrayRefVar[][]; (or) dataType []arrayRefVar[]; Example to instantiate int[][] arr=new int[3][3];//3 row and 3 column Example to initialize arr[0][0]=1; arr[0][1]=2; arr[0][2]=3; arr[1][0]=4; arr[1][1]=5; arr[1][2]=6; arr[2][0]=7; arr[2][1]=8; arr[2][2]=9;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-arrayoperators-210825071157/75/Java-Programming-13-2048.jpg)
![Example //Java Program to illustrate the use of multidimensional array class Testarray3{ public static void main(String args[]){ //declaring and initializing 2D array int arr[][]={{1,2,3},{2,4,5},{4,4,5}}; //printing 2D array for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ for(int j=0;j<3;j++){ System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" "); } System.out.println(); } }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-arrayoperators-210825071157/75/Java-Programming-14-2048.jpg)
![Jagged Array creating odd number of columns in a 2D array, it is known as a jagged array. In other words, it is an array of arrays with different number of columns. class TestJaggedArray{ public static void main(String[] args){ //declaring a 2D array with odd columns int arr[][] = new int[3][]; arr[0] = new int[3]; arr[1] = new int[4]; arr[2] = new int[2]; //initializing a jagged array int count = 0; for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++) for(int j=0; j<arr[i].length; j++) arr[i][j] = count++; //printing the data of a jagged array for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){ for (int j=0; j<arr[i].length; j++){ System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" "); } System.out.println();//new line}}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-arrayoperators-210825071157/75/Java-Programming-15-2048.jpg)



