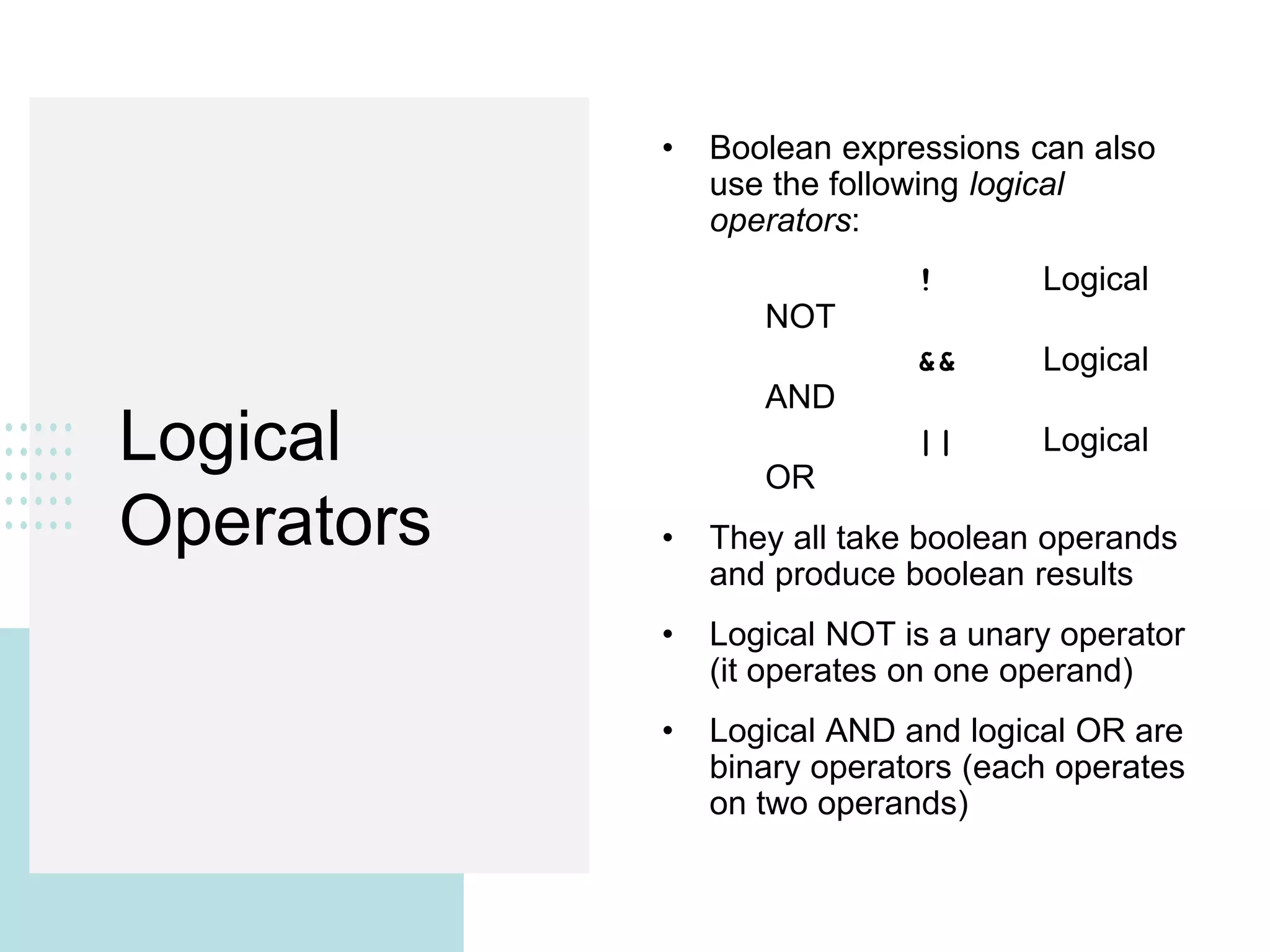
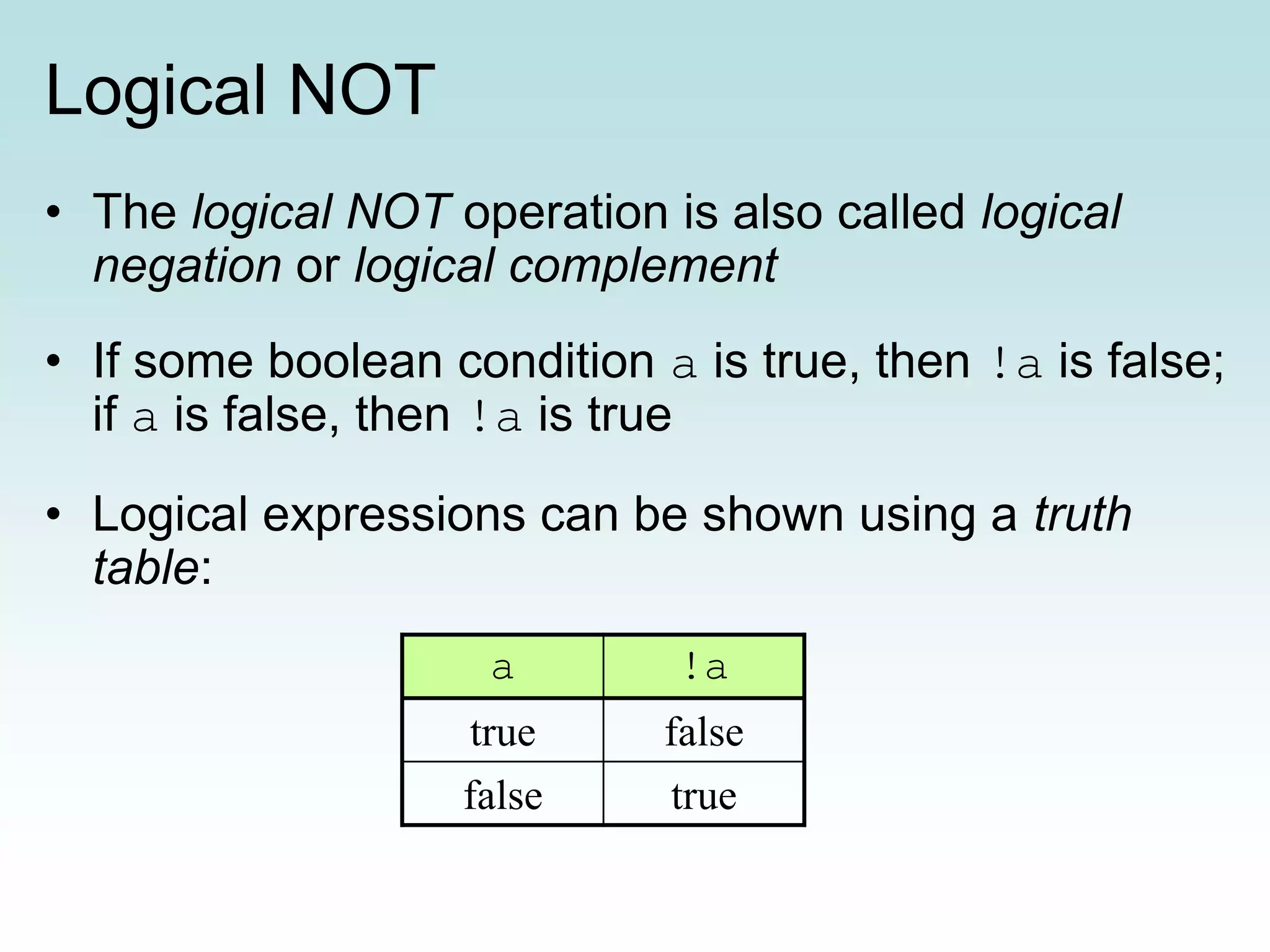
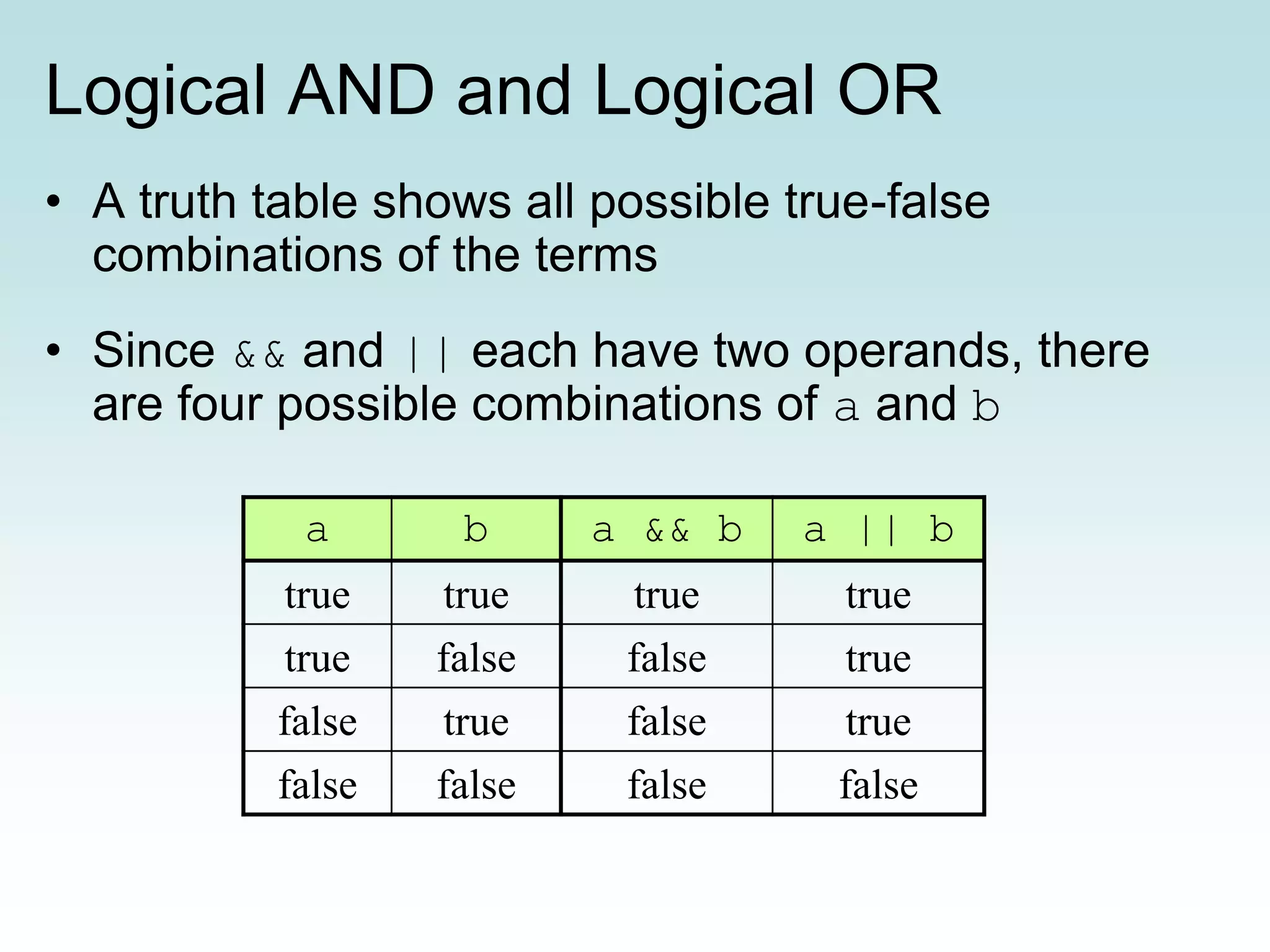
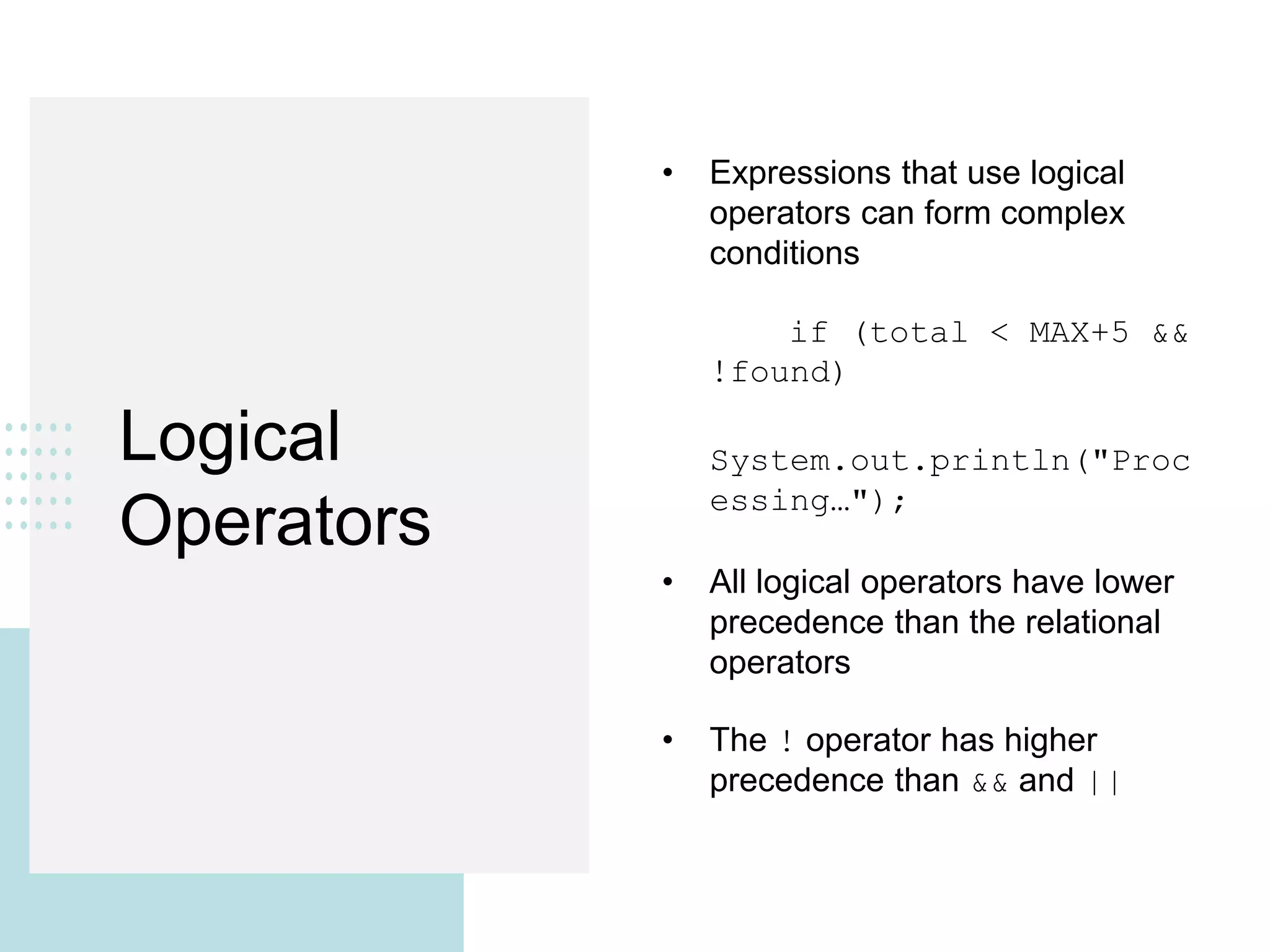
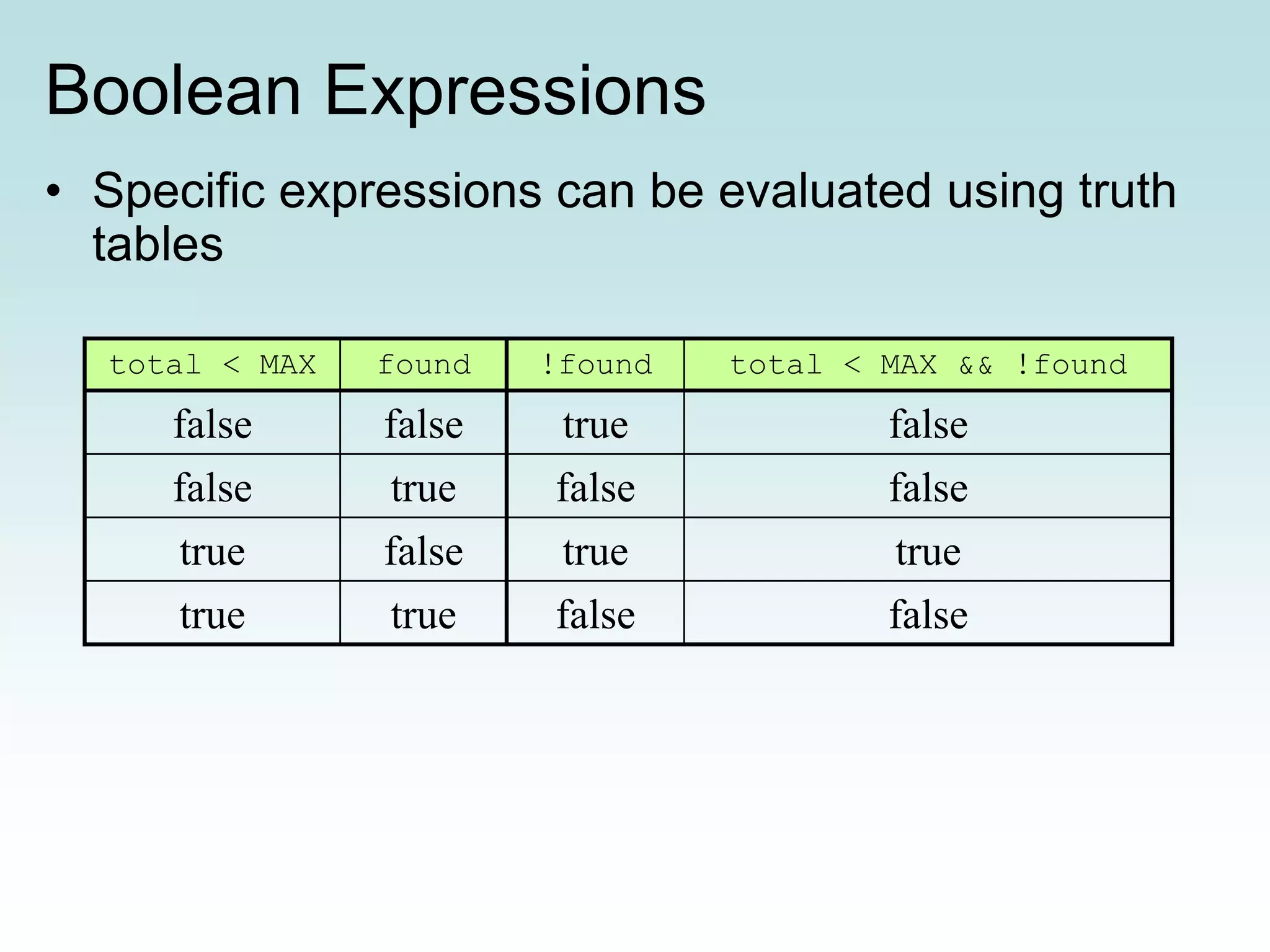
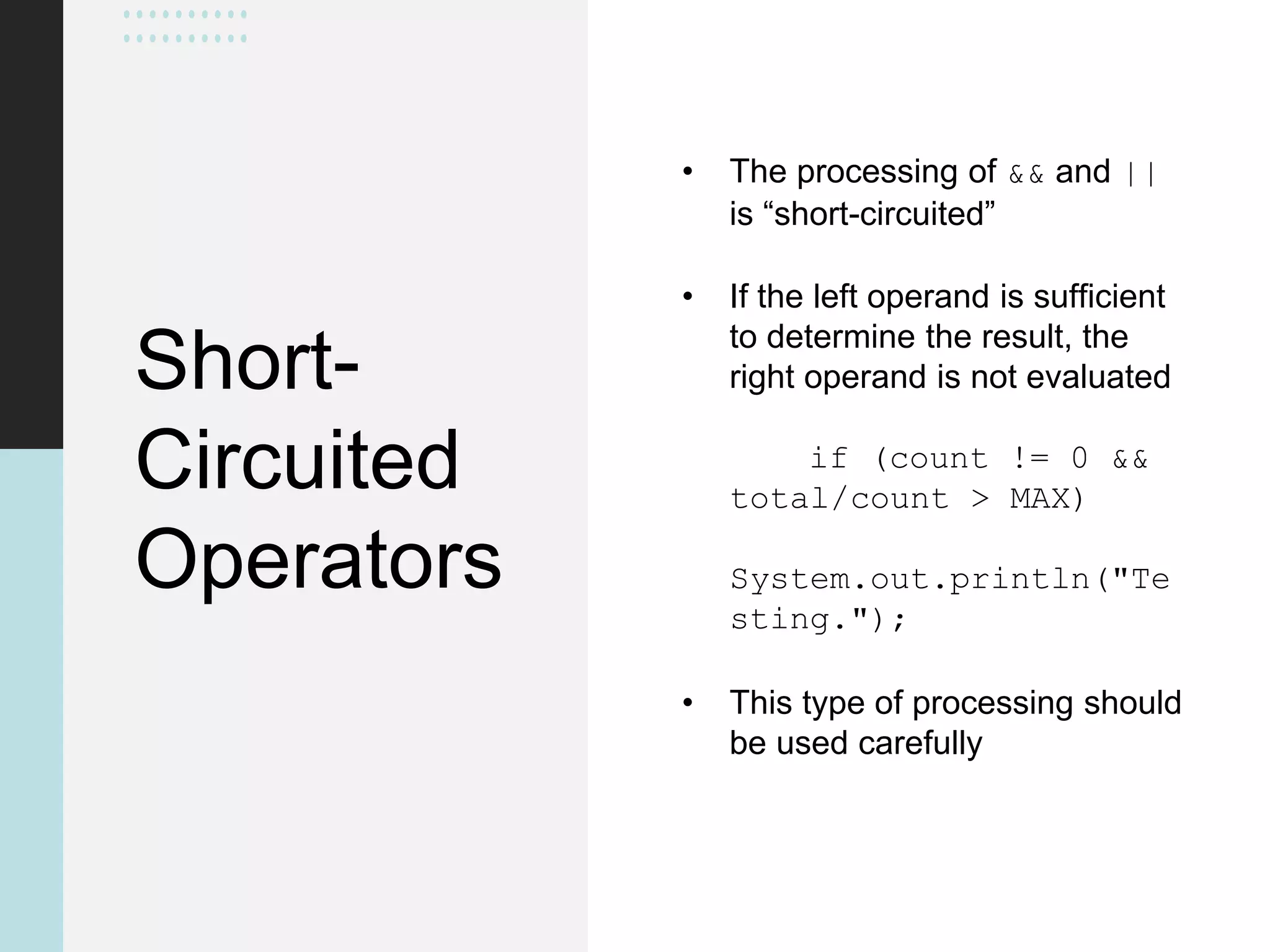
This document discusses conditionals and loops in Java programming. It covers boolean expressions that evaluate to true or false, which are used in conditional statements like if and while statements to control program flow. Logical operators like && and || can be used to build complex conditions. If statements allow executing code conditionally, while loops repeat code execution. Collections like ArrayList are also introduced to store and iterate over multiple values. In summary, conditionals and loops allow controlling program flow, boolean expressions are used in conditions, and logical operators help build complex conditional logic.






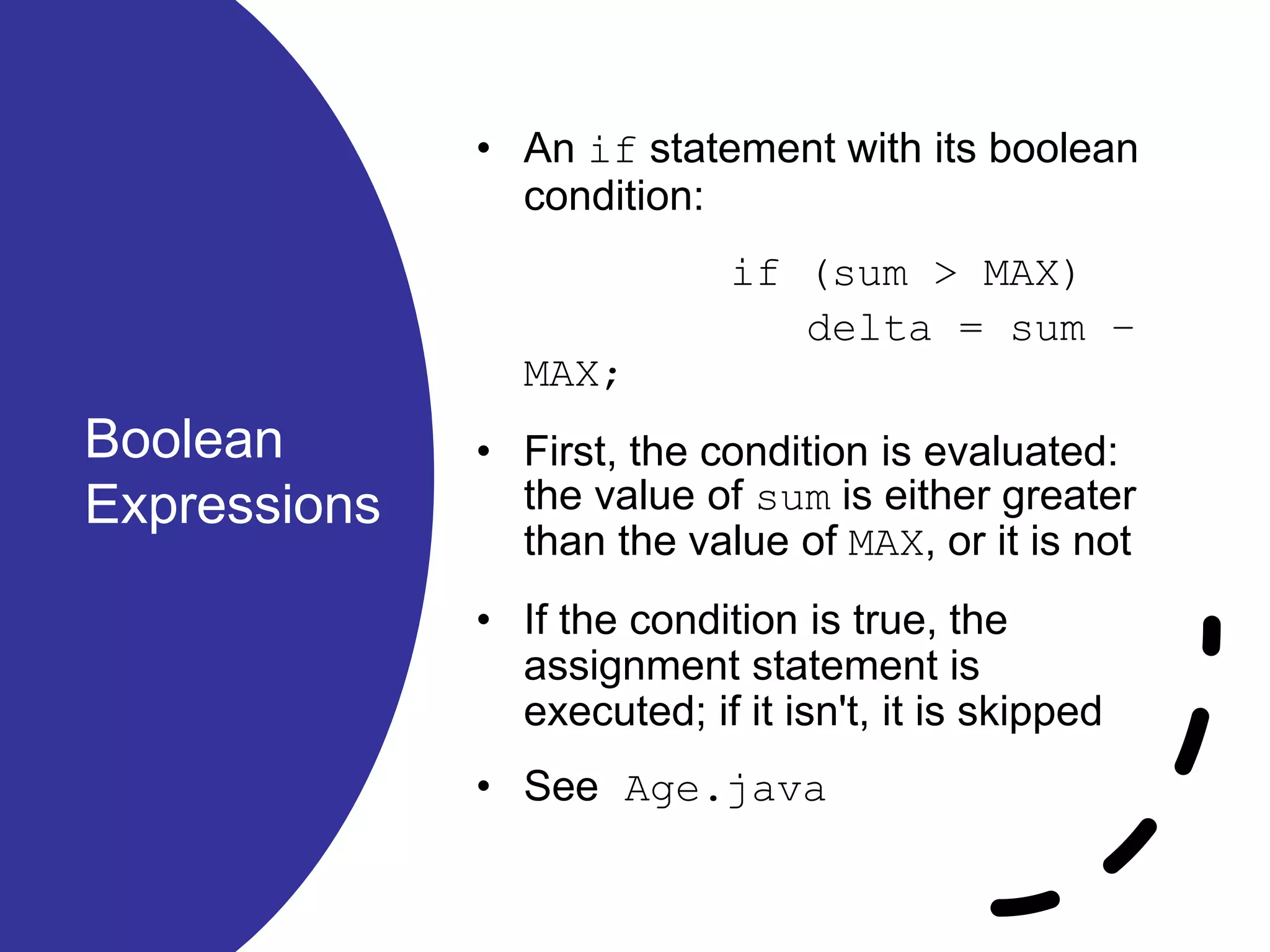
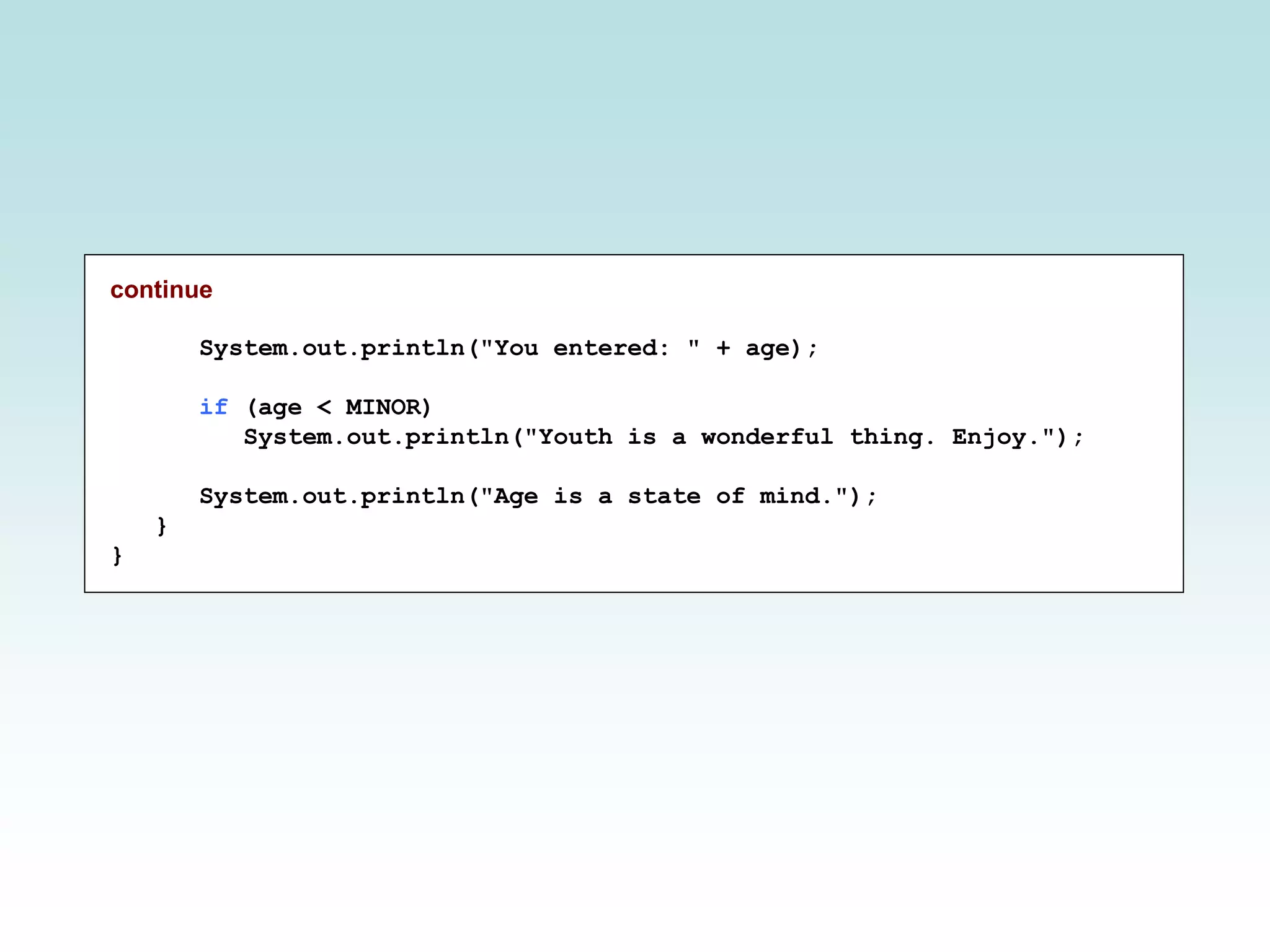
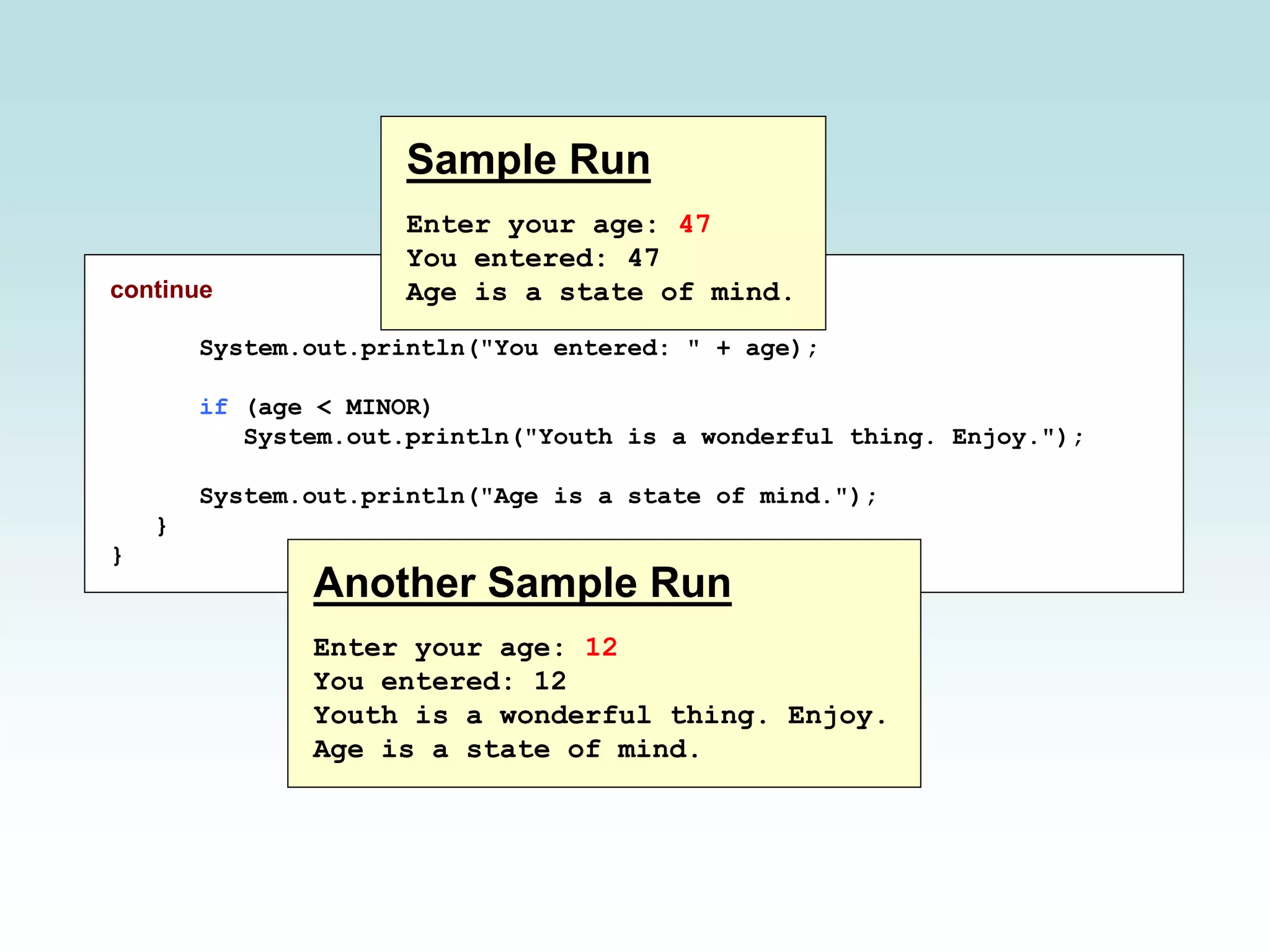
![//******************************************************************** // Age.java Author: Lewis/Loftus // // Demonstrates the use of an if statement. //******************************************************************** import java.util.Scanner; public class Age { //----------------------------------------------------------------- // Reads the user's age and prints comments accordingly. //----------------------------------------------------------------- public static void main(String[] args) { final int MINOR = 21; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter your age: "); int age = scan.nextInt(); continue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap05-part2-200316131626/75/Java-Chapter-05-Conditions-Loops-part-2-10-2048.jpg)