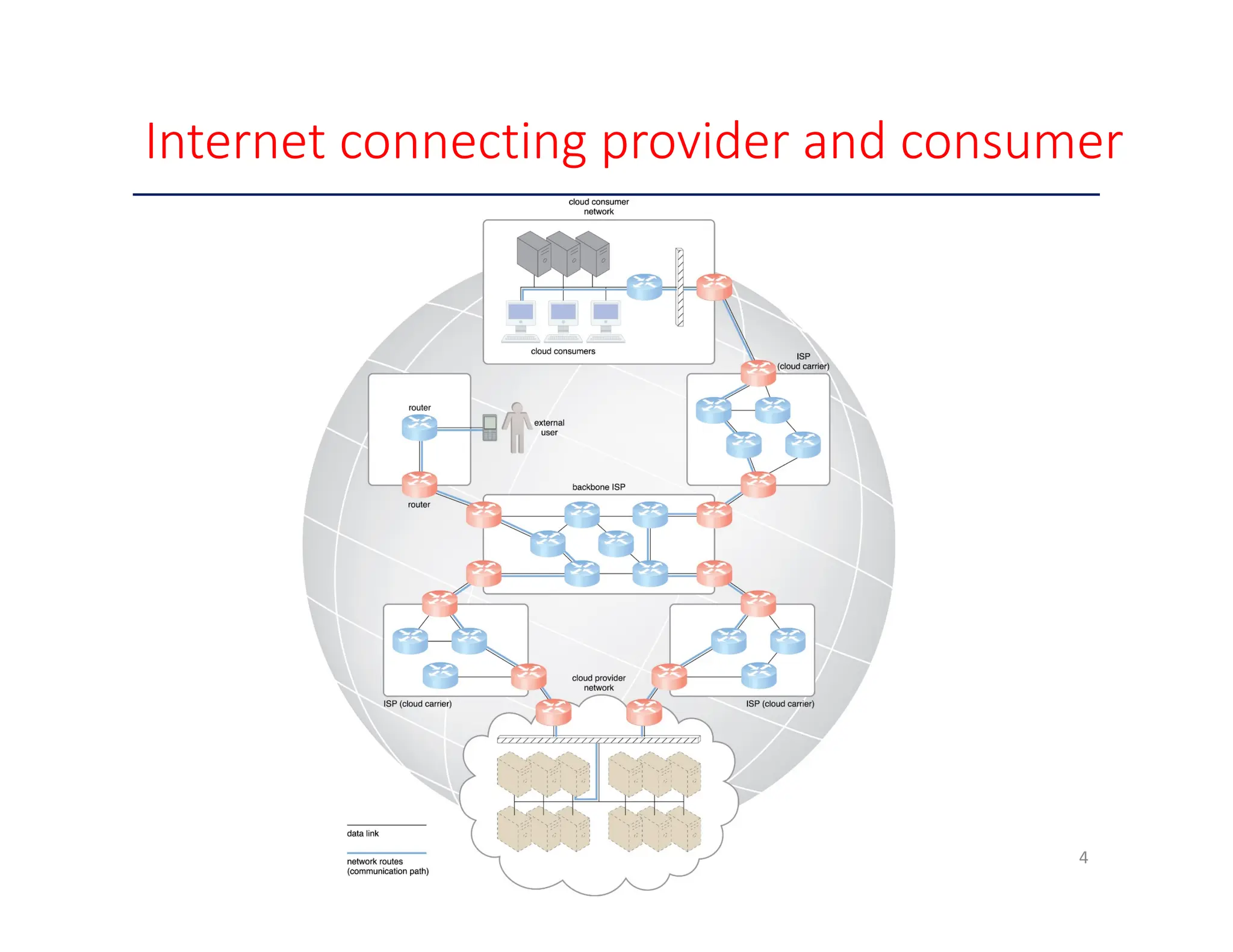
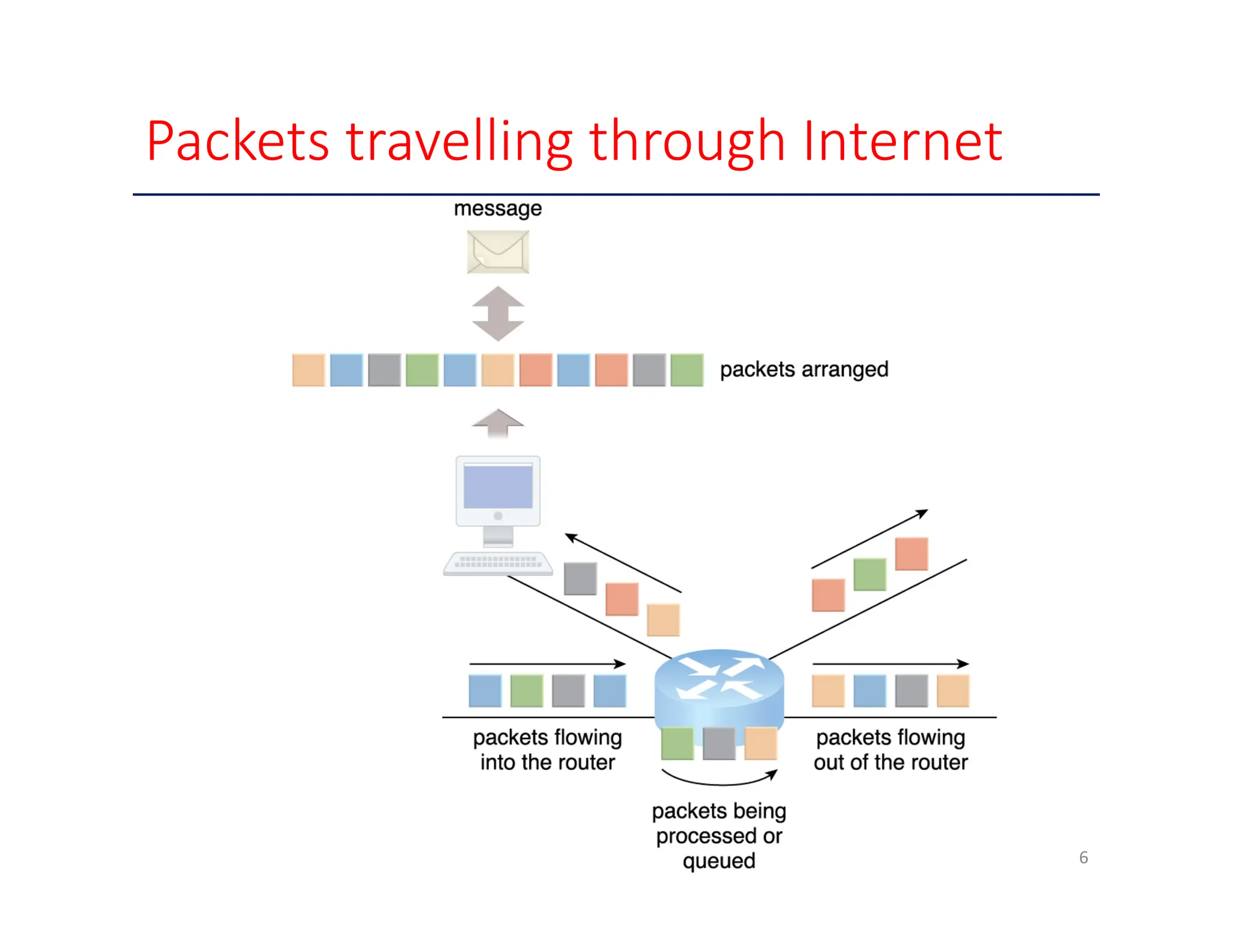
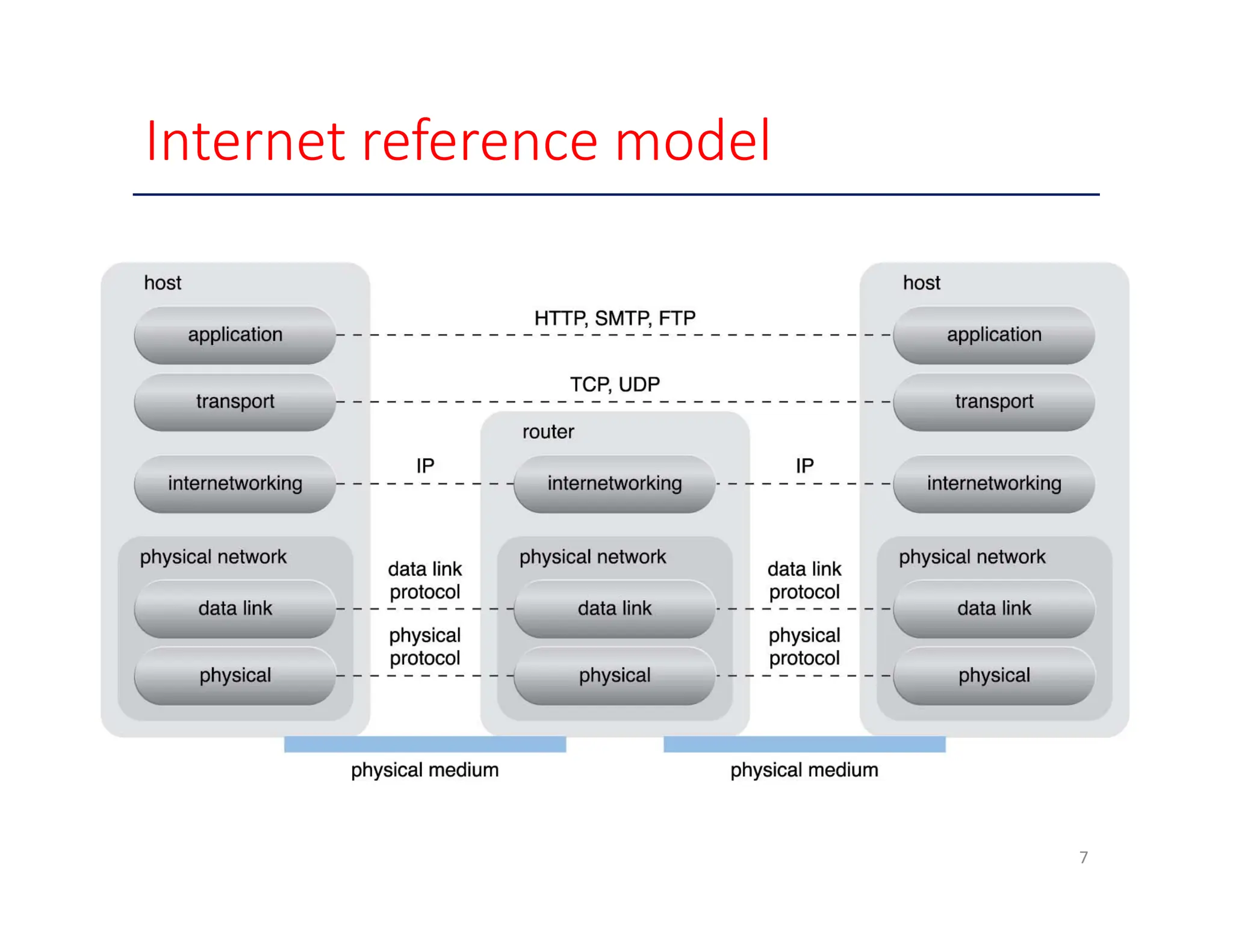
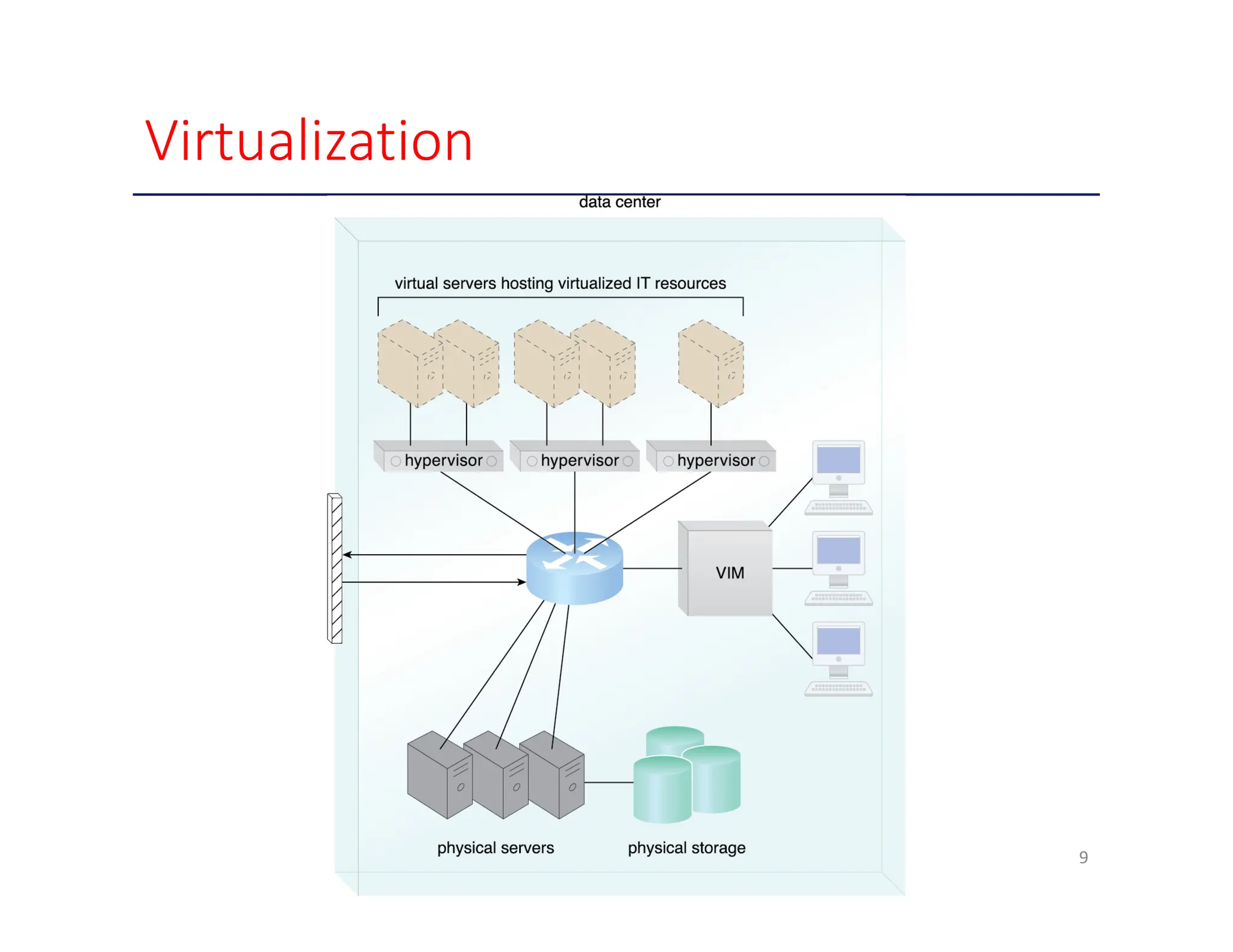
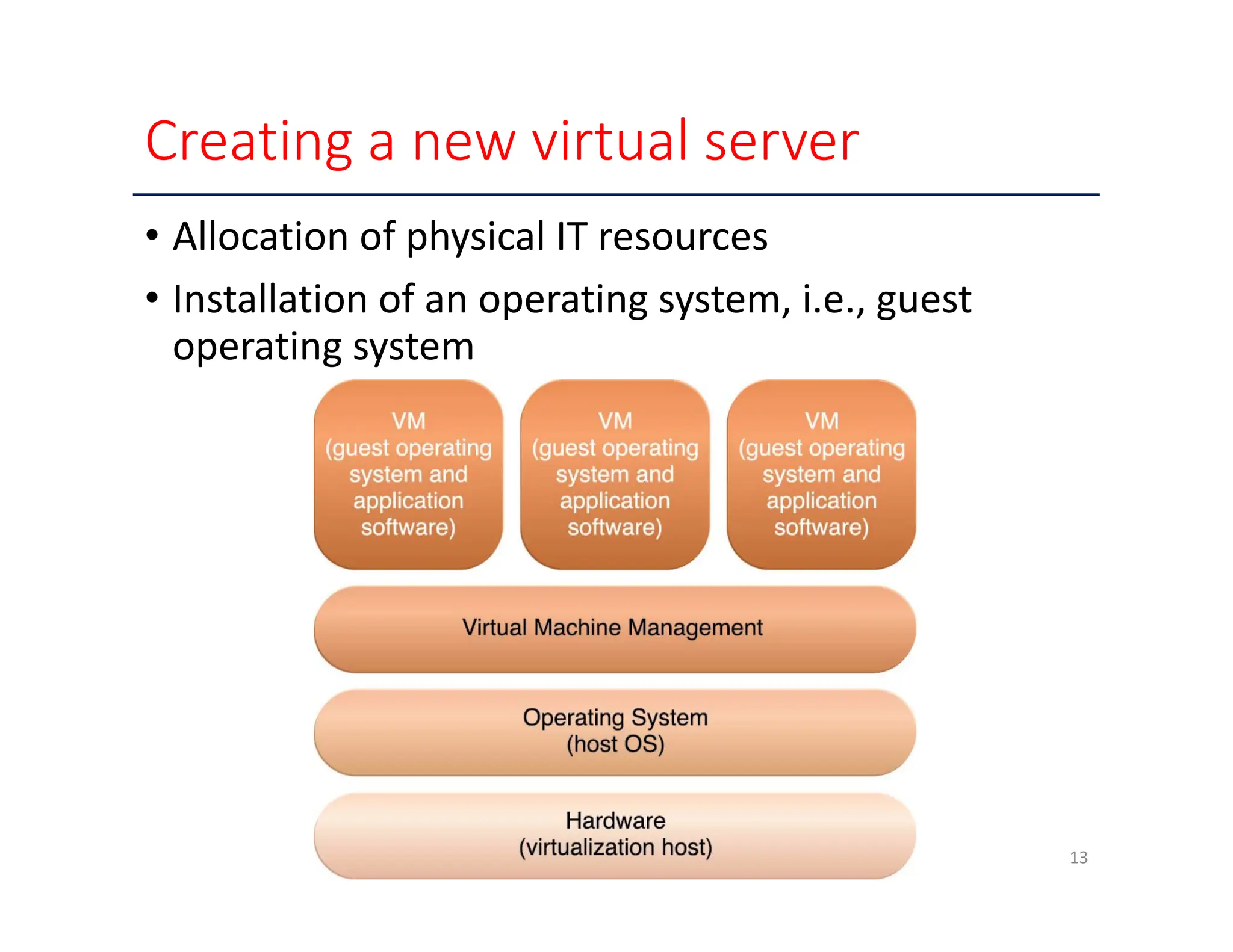
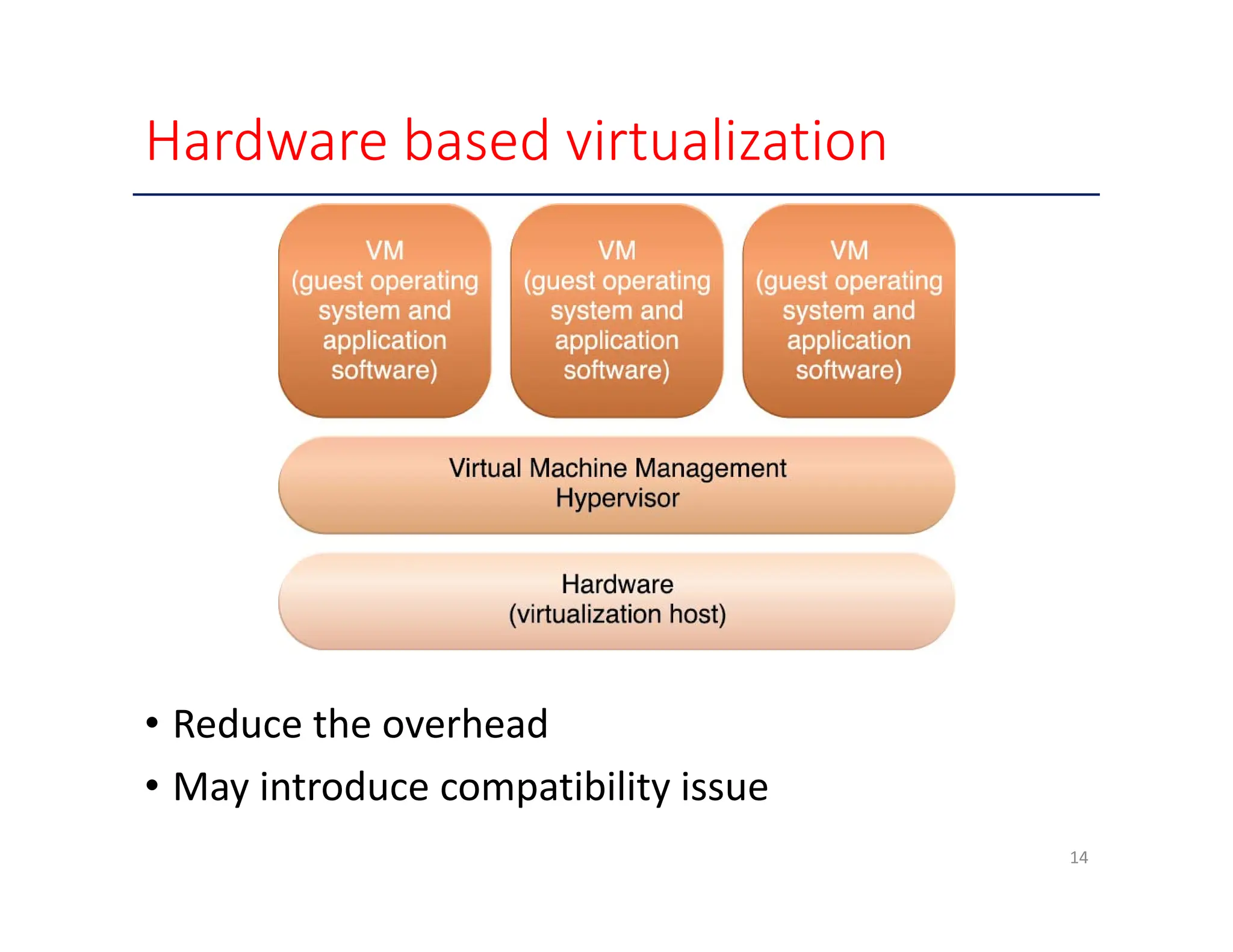
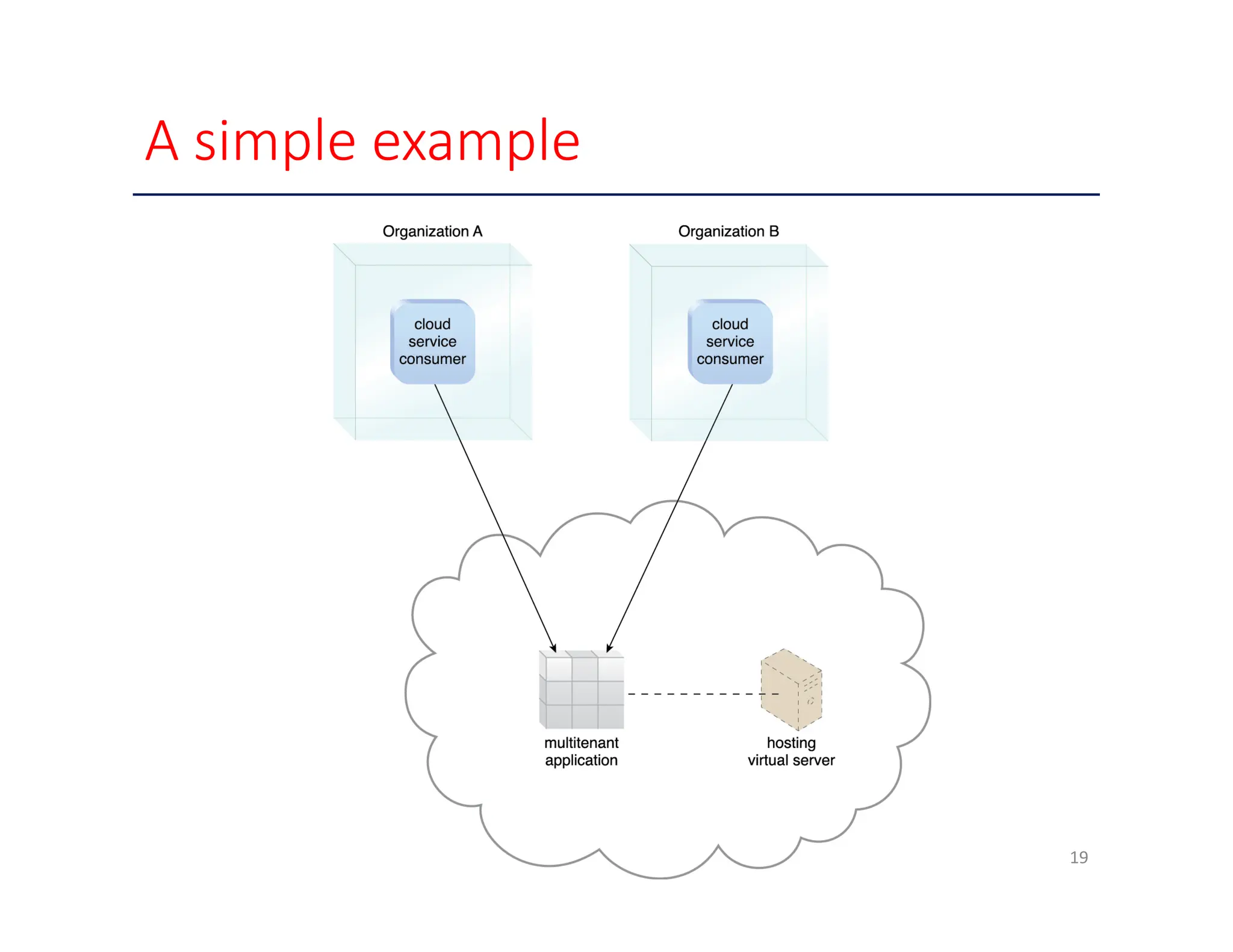
The document outlines various enabling technologies for cloud computing, including broadband networks, data center technology, virtualization, web technologies, and multitenant technology. It highlights the importance of network connectivity for cloud services, describes the architecture of data centers, and explains virtualization processes. Additionally, it discusses web technologies and multitenant capabilities that allow simultaneous access while maintaining data security among different users.