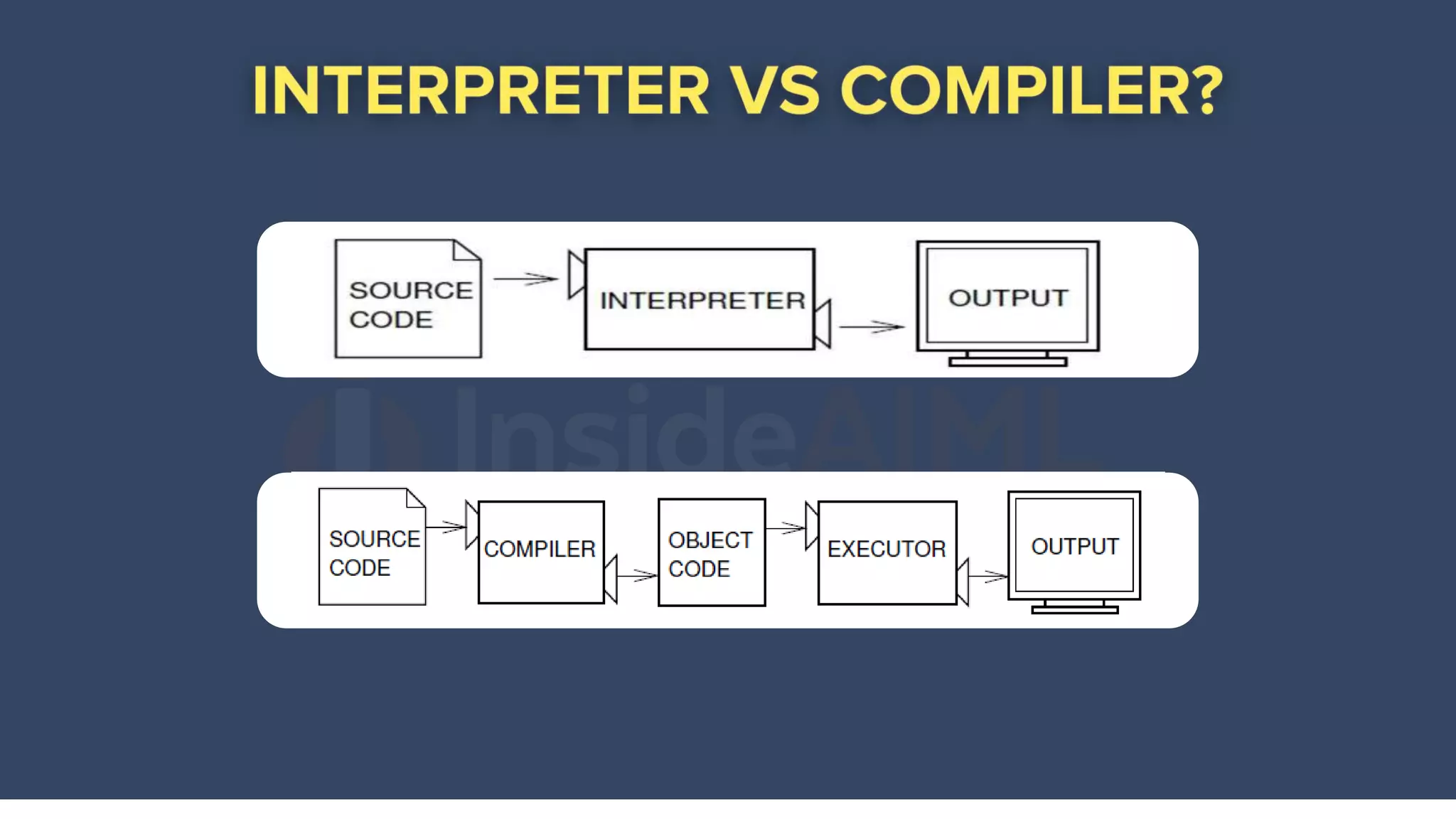
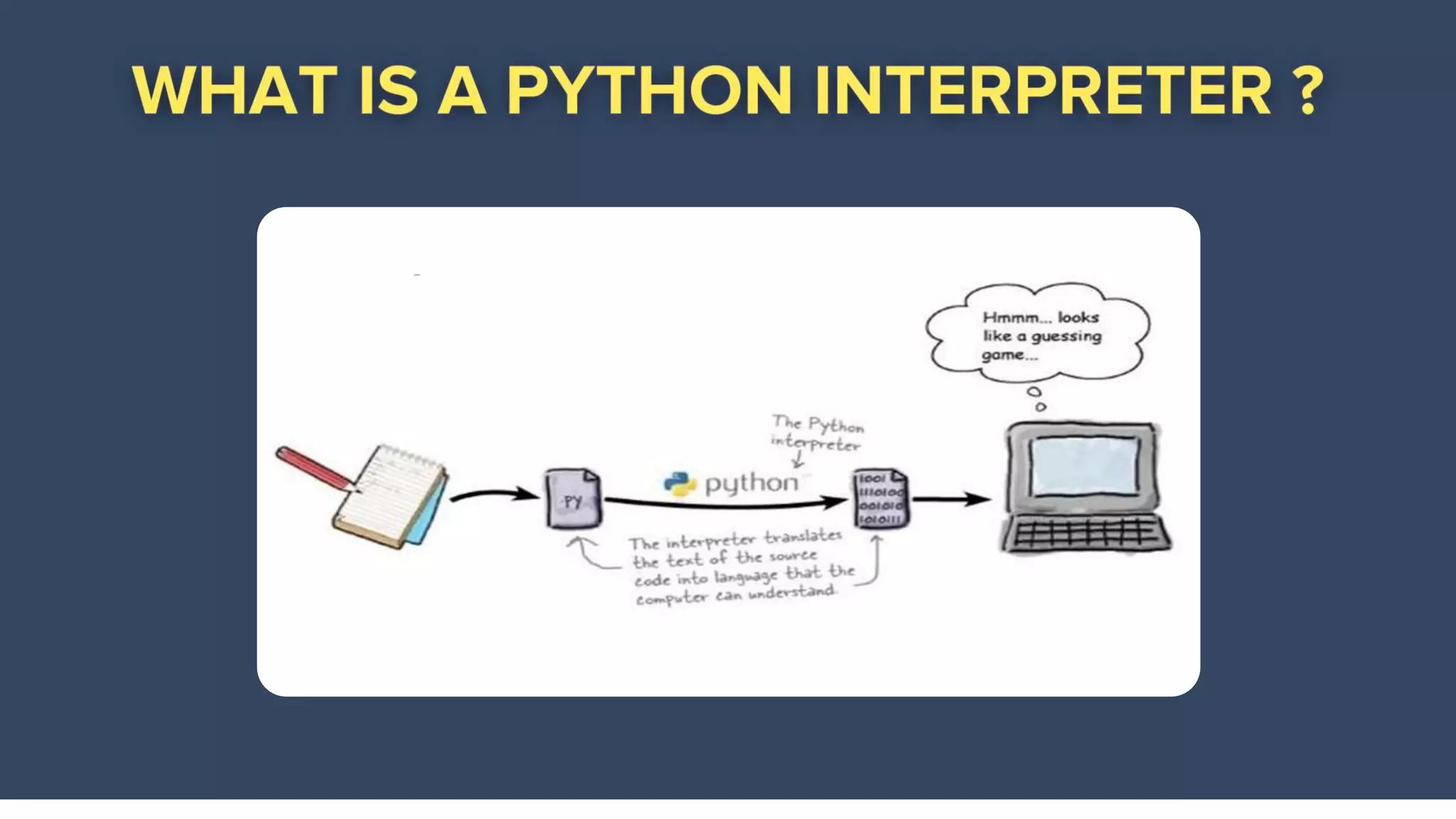
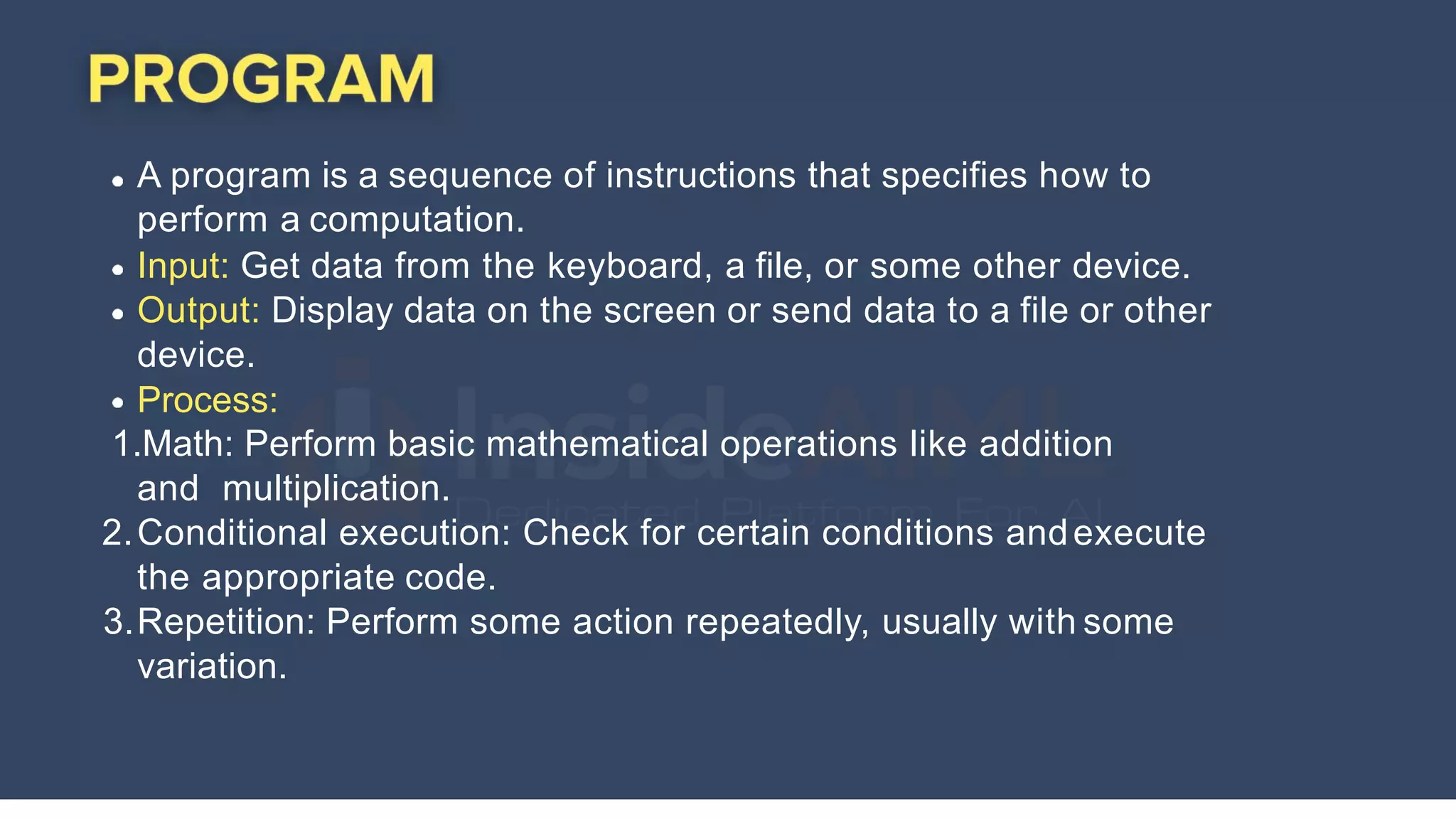
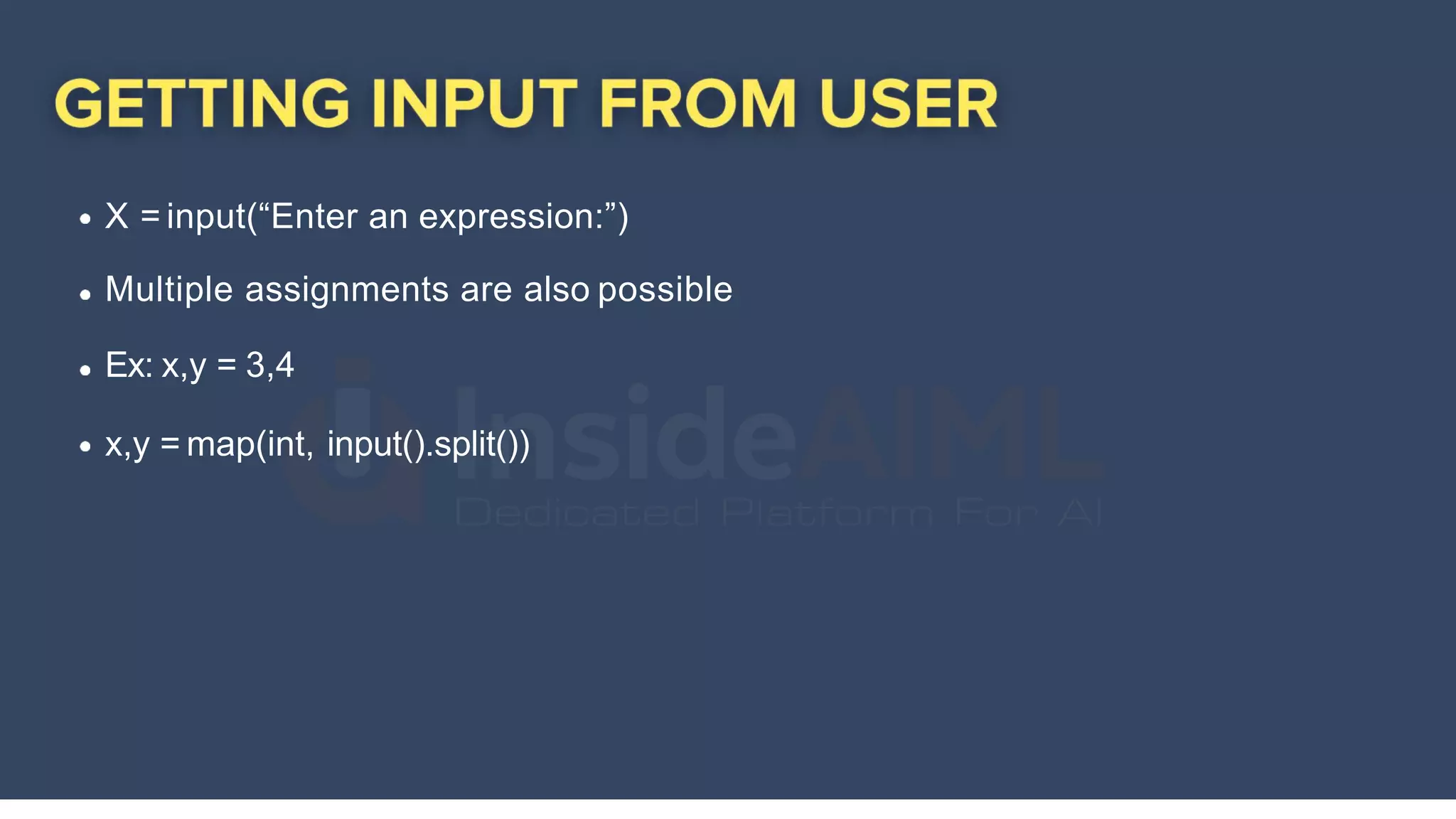
The document provides an overview of Python programming, highlighting its versatility in various domains such as web development, data science, and scripting. It covers fundamental concepts including data types, variables, functions, and control flow, along with syntax for creating and using these elements. Additionally, it mentions the ease of learning Python and its extensive standard library that enhances functionality.
































![Indexing is used to extract individual characters from astring Indexing in python starts from 0. S =‘welcome’ S[0] = ‘w’ S[1]=‘e’ ….](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopythonprogramming-210518114757/75/Introduction-to-Python-Programming-37-2048.jpg)
![Slicing is taking subsets from a string. Lower limit is inclusive where as Upper limit isexclusive. S=‘welcome’ S[0:2] ?? S[0:] ?? S[:3] ?? S[:] ??? S[0:4]??](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopythonprogramming-210518114757/75/Introduction-to-Python-Programming-38-2048.jpg)



