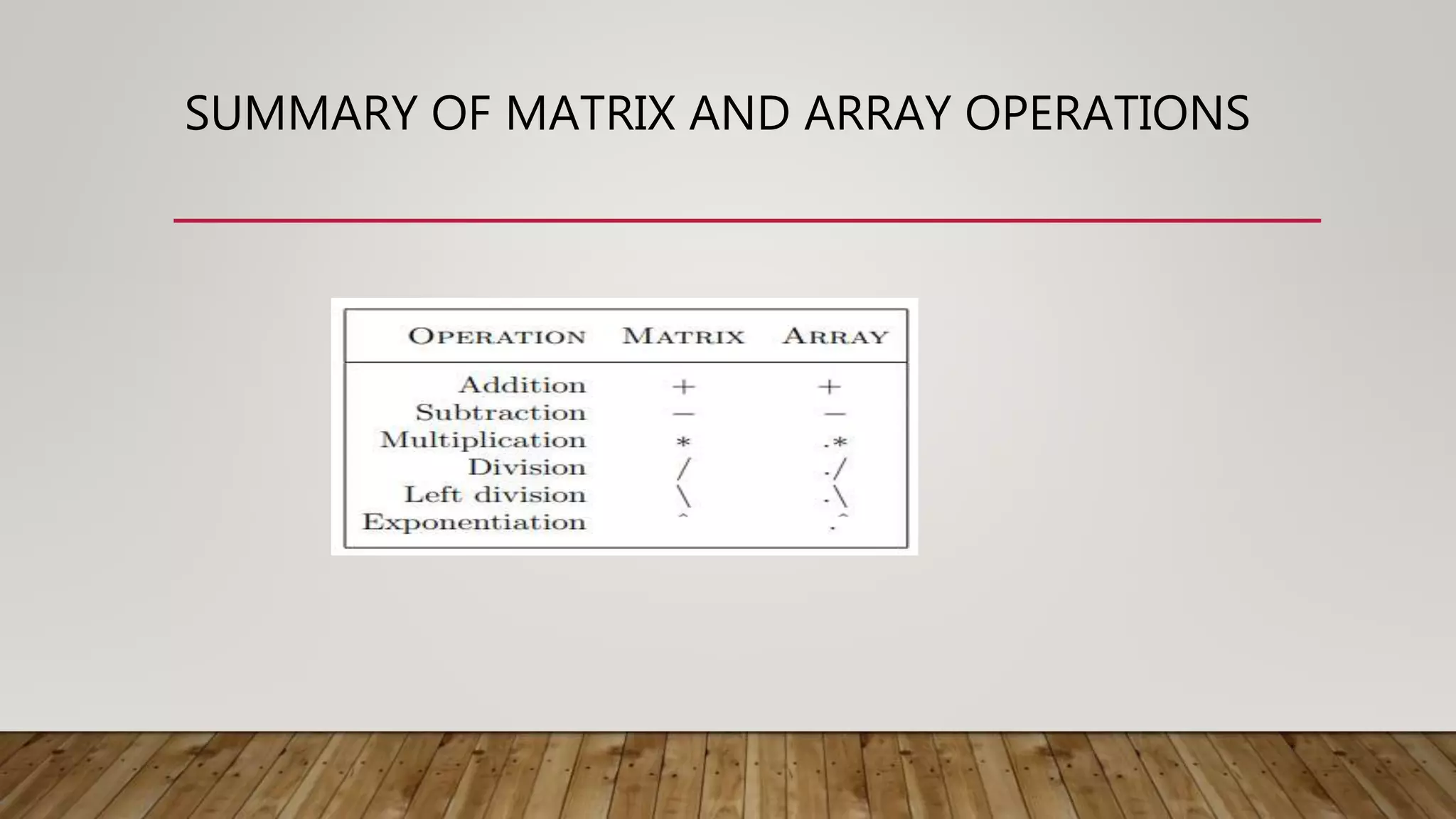
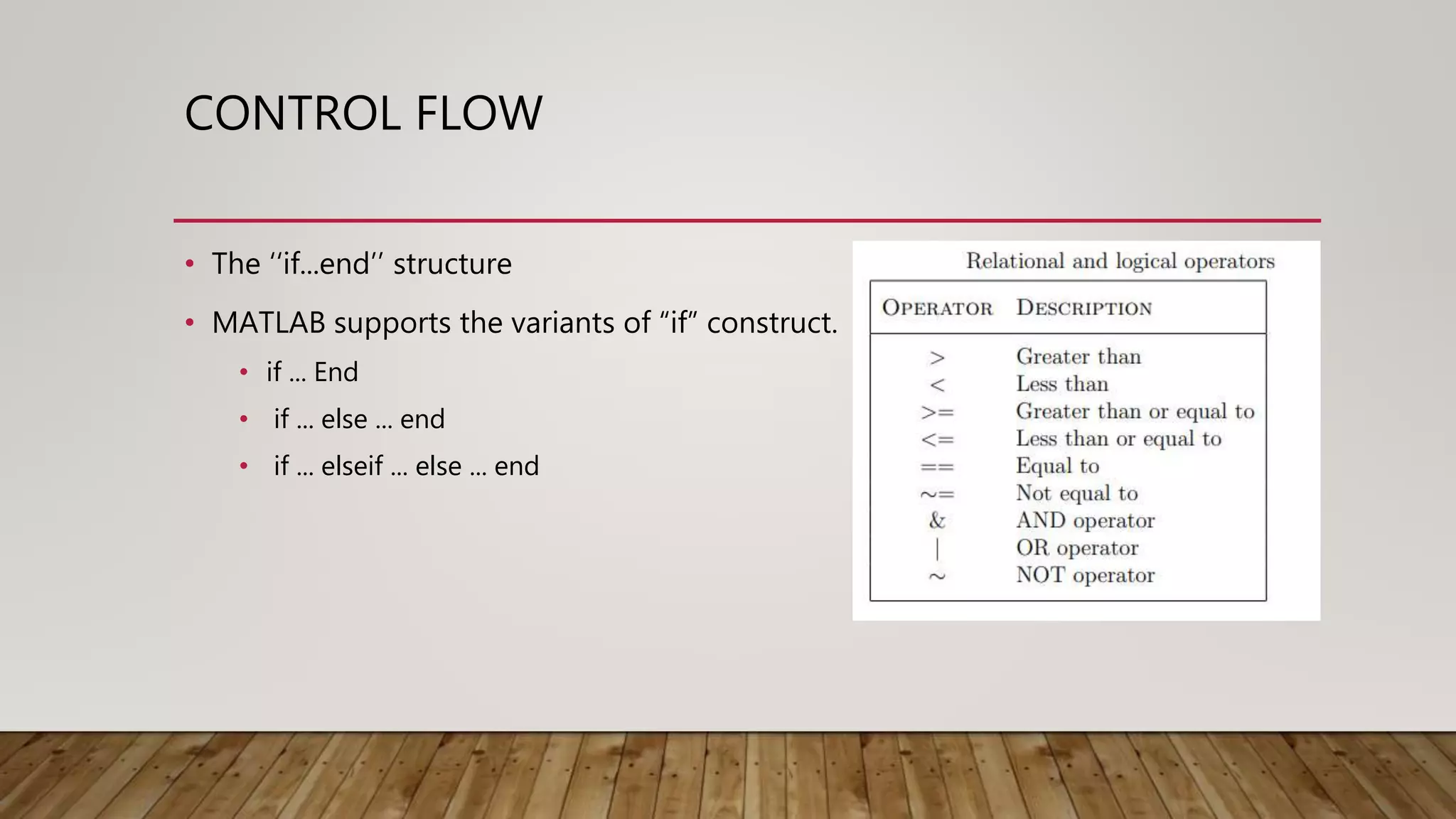
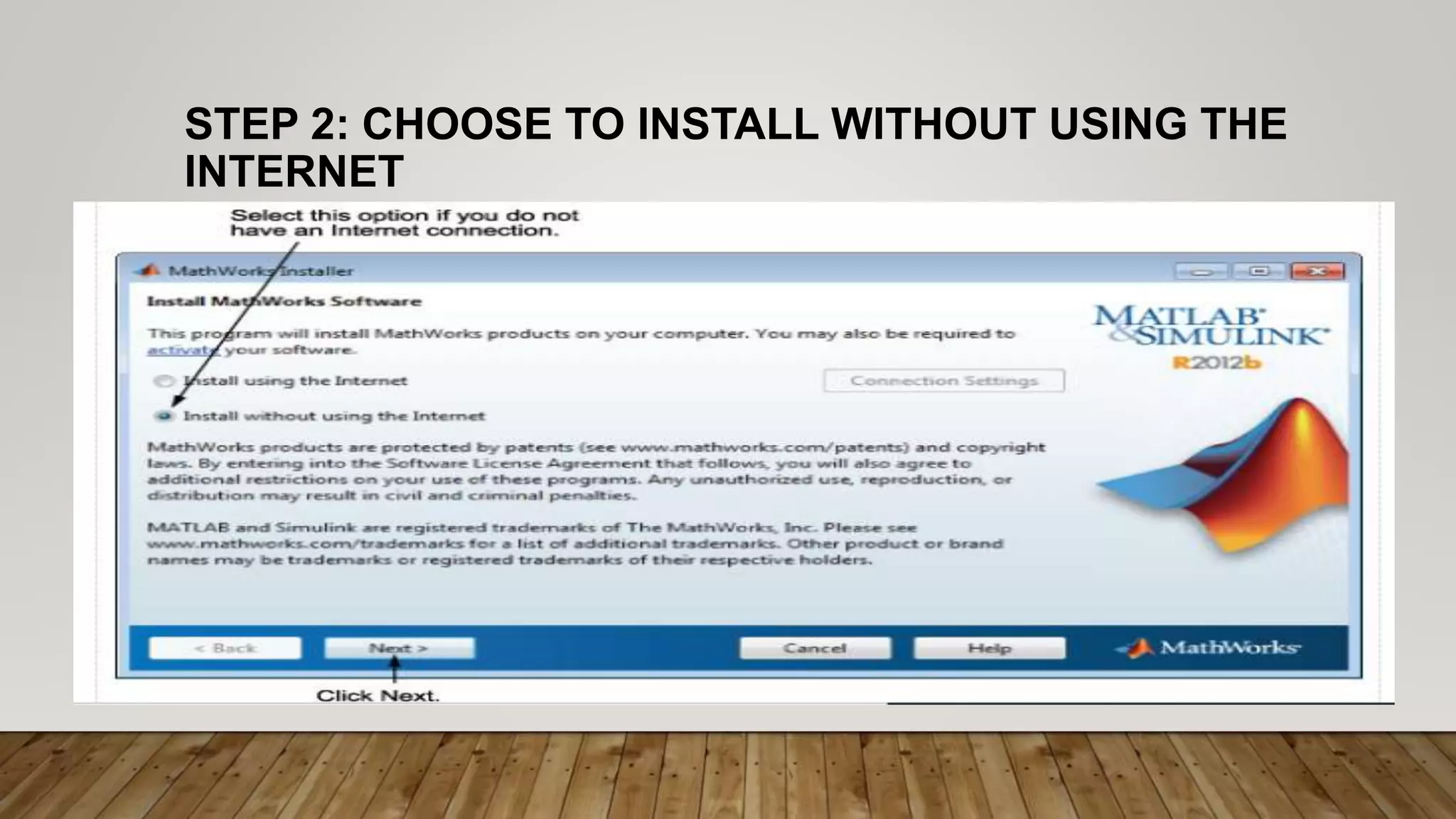
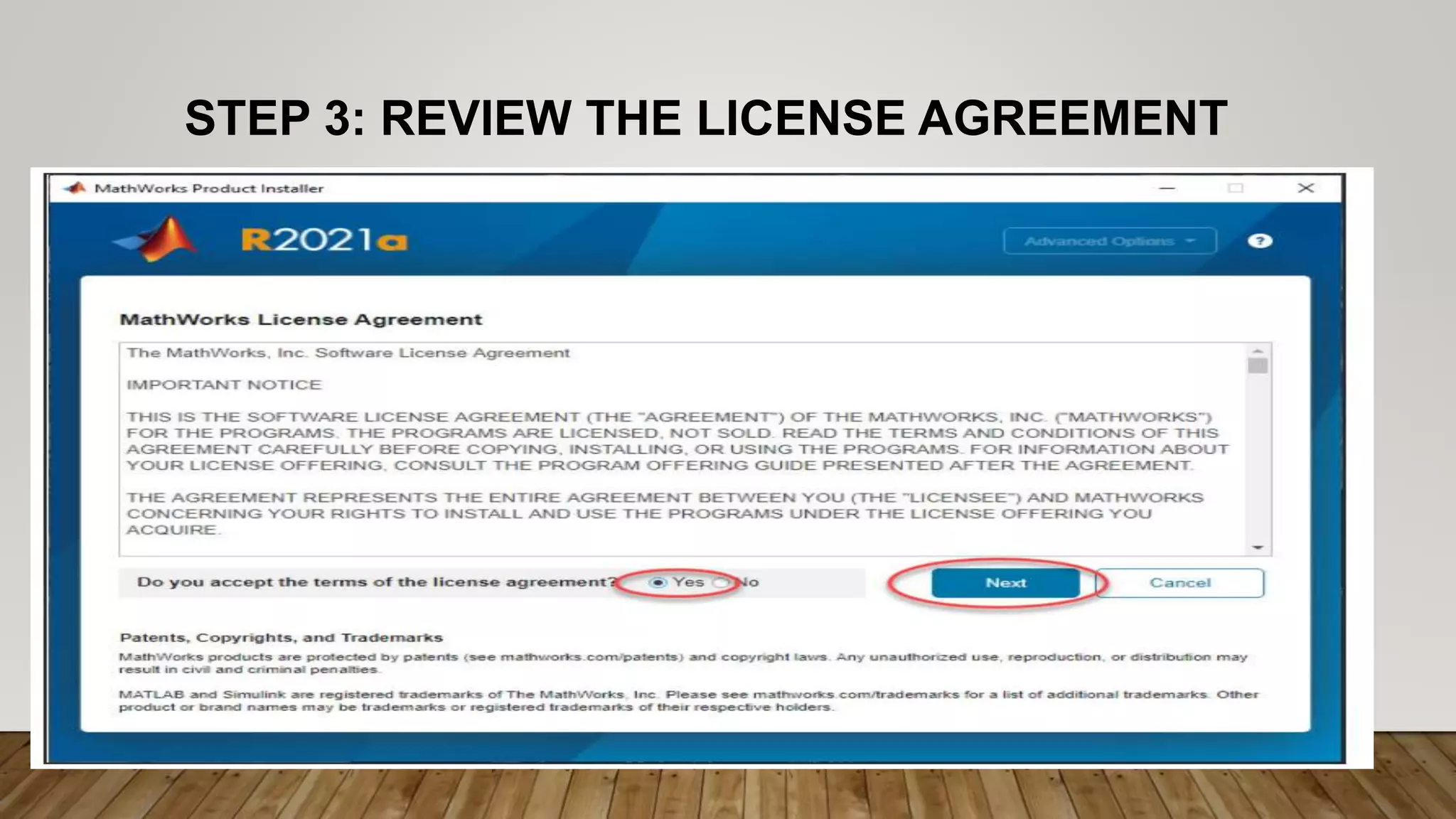
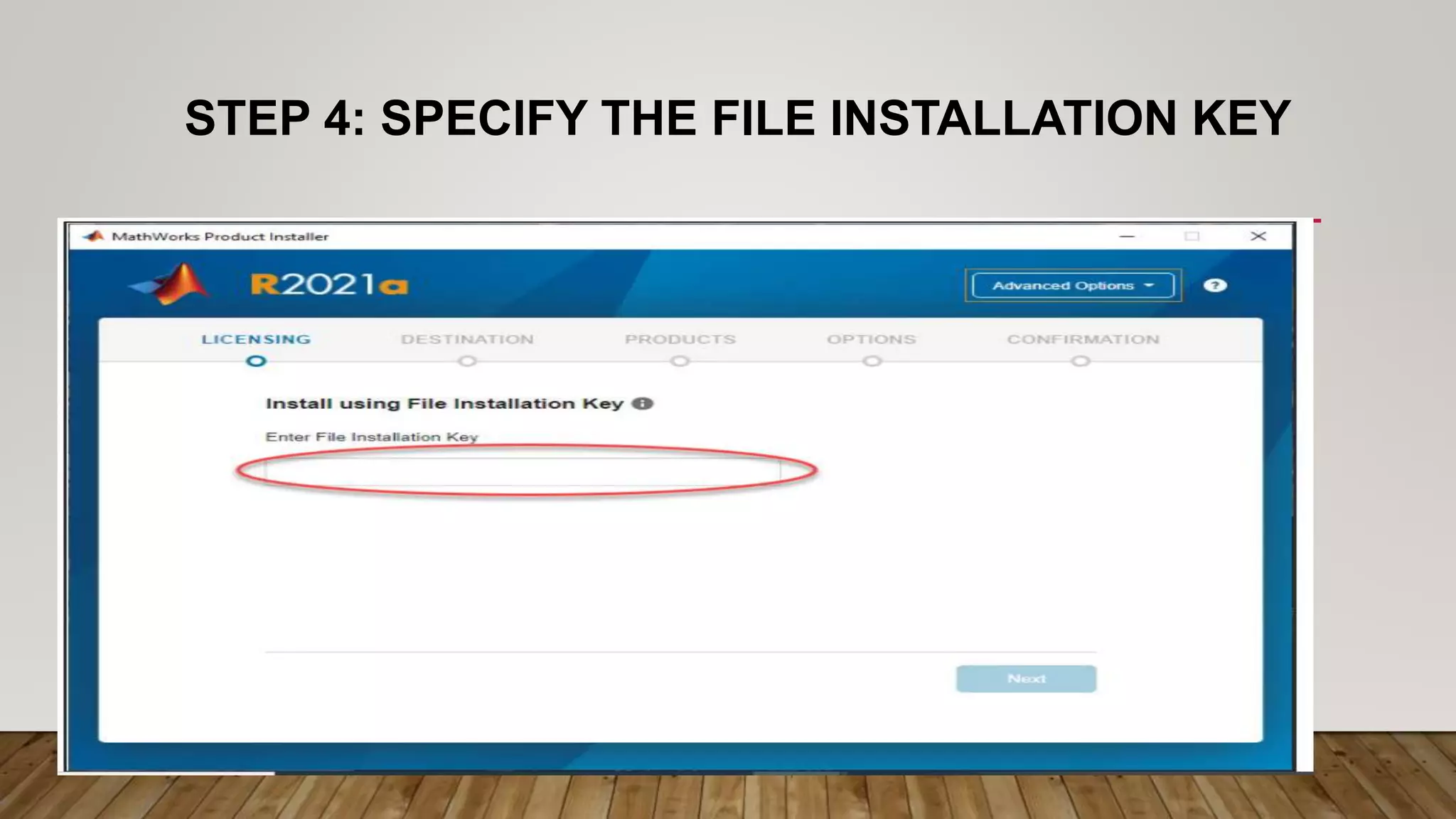
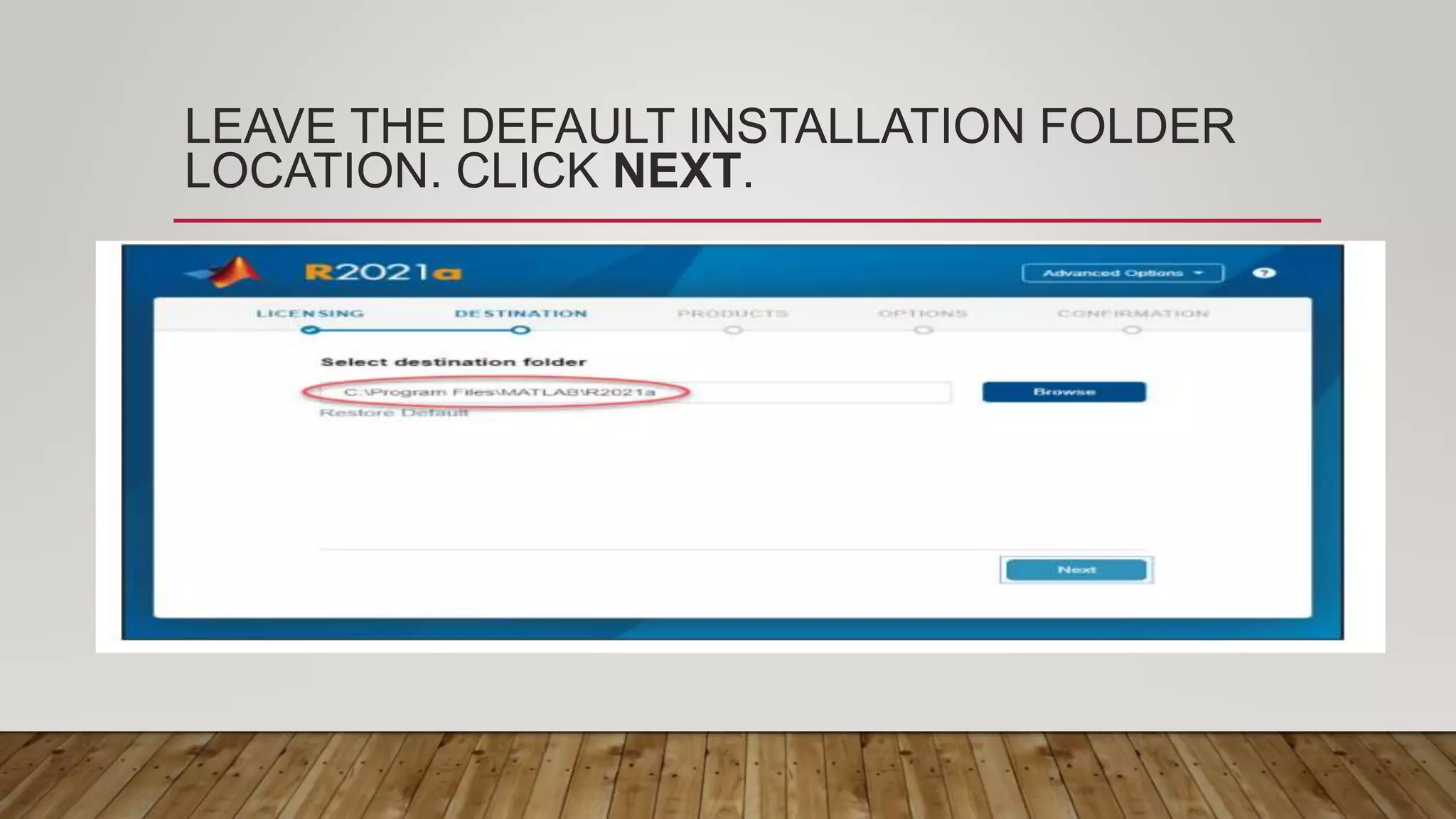
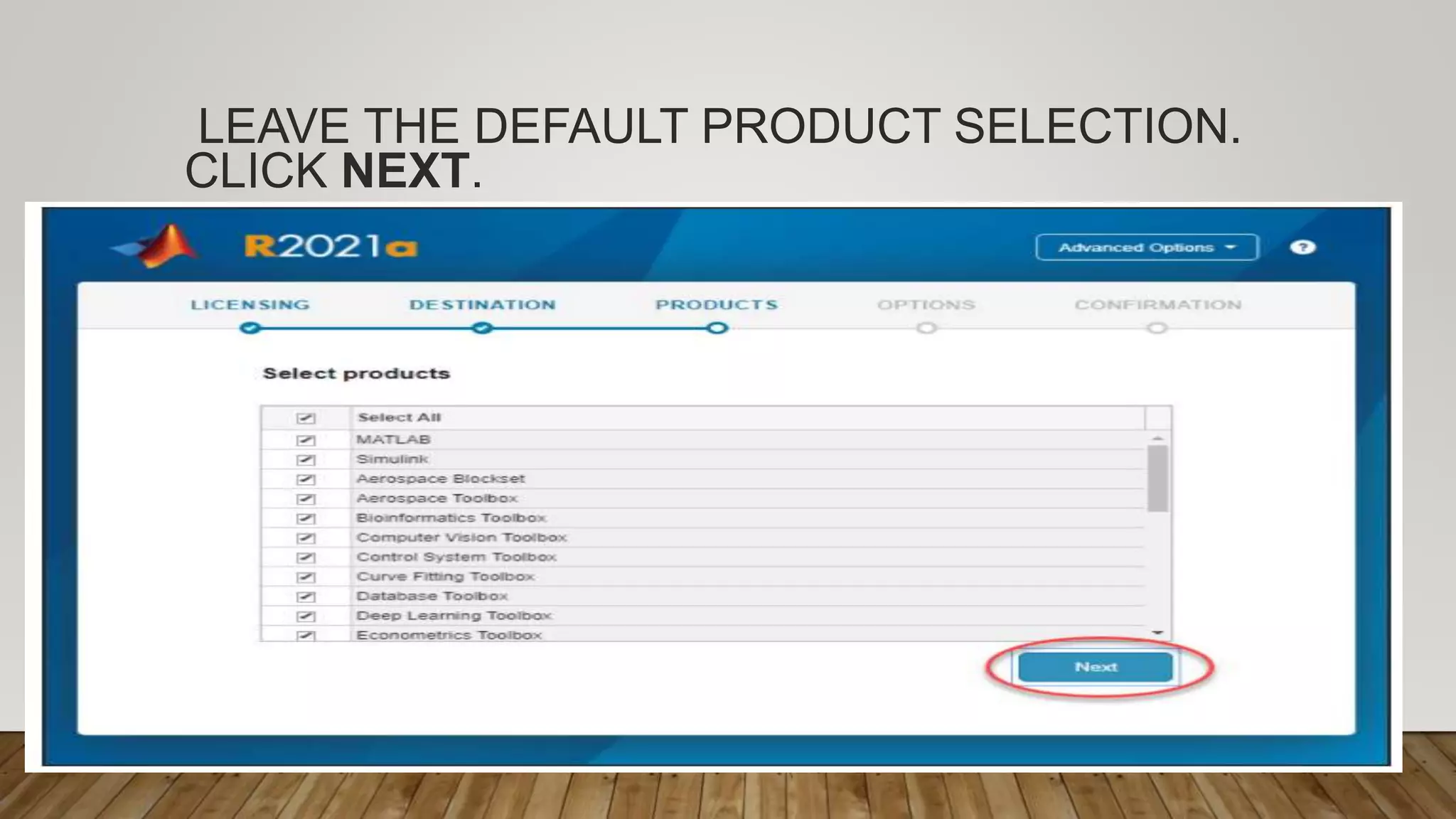
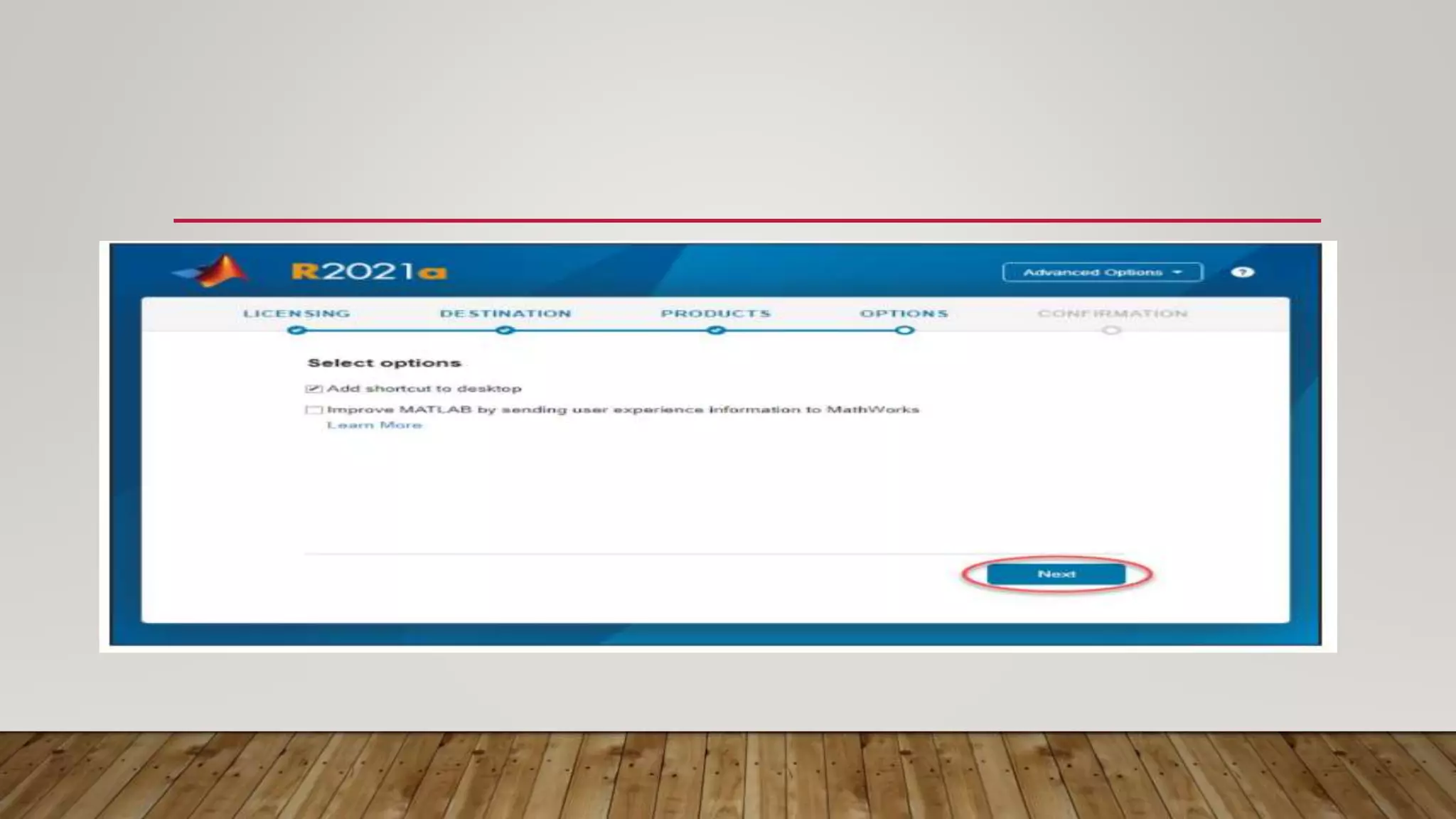
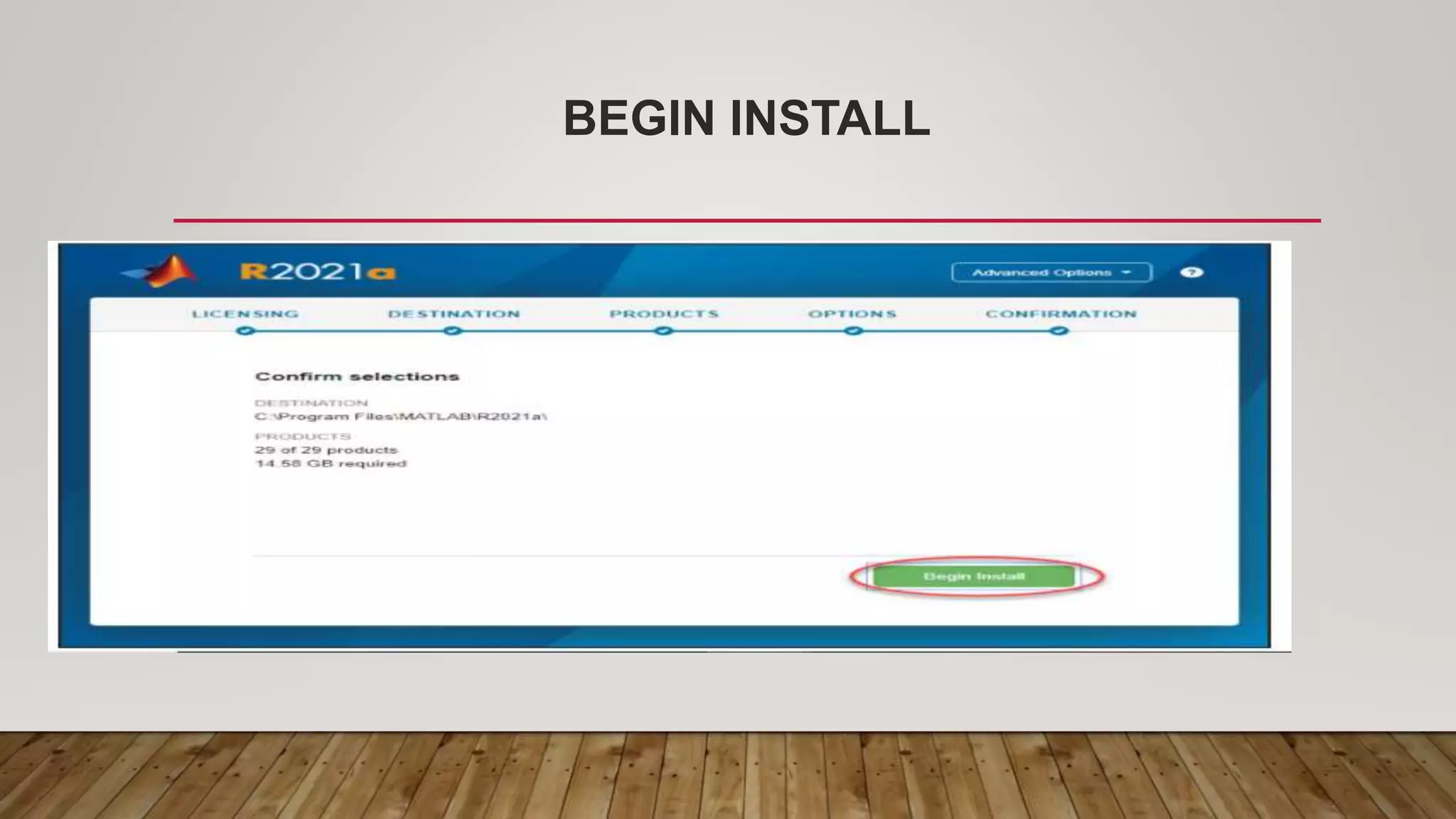
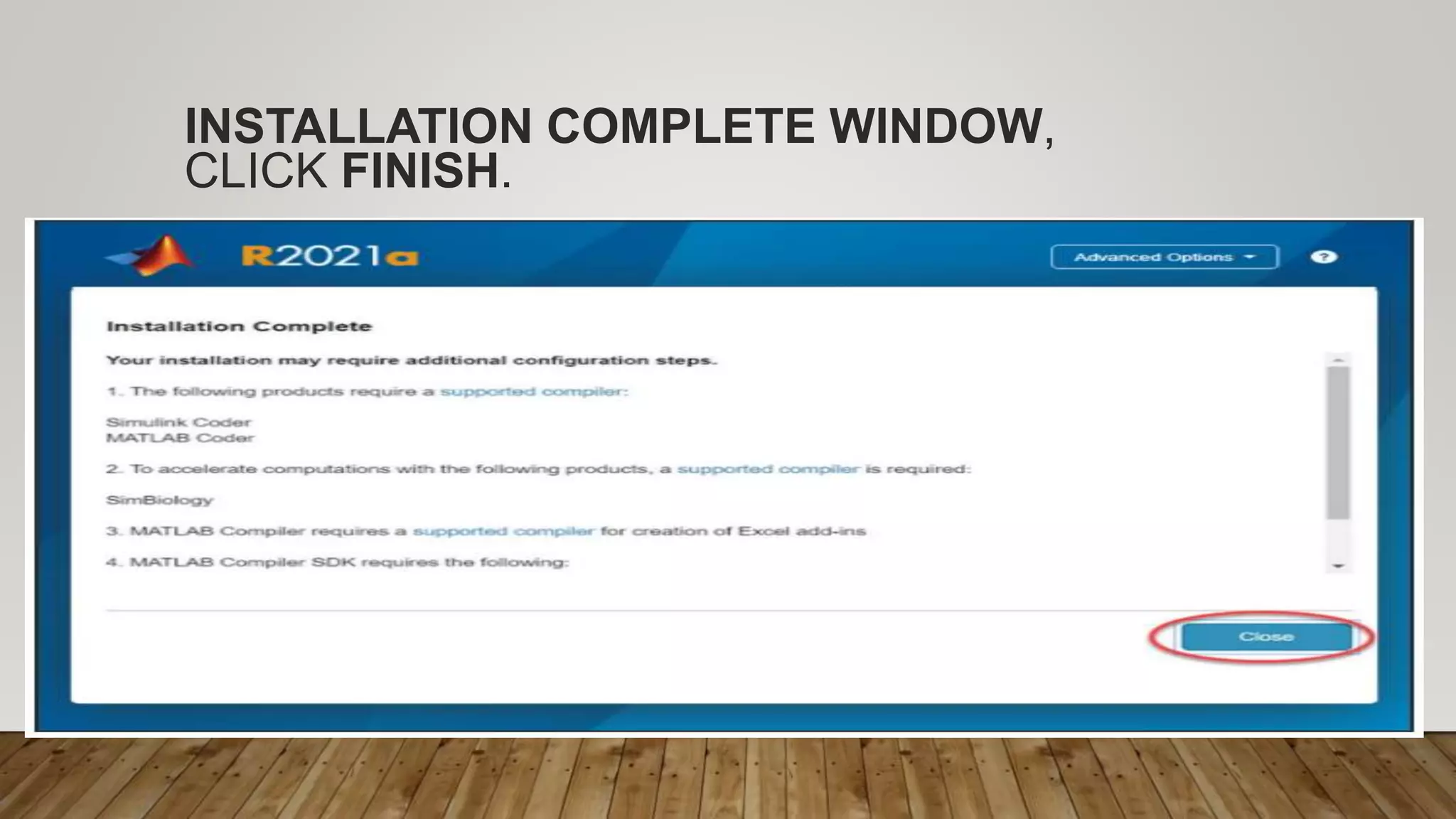
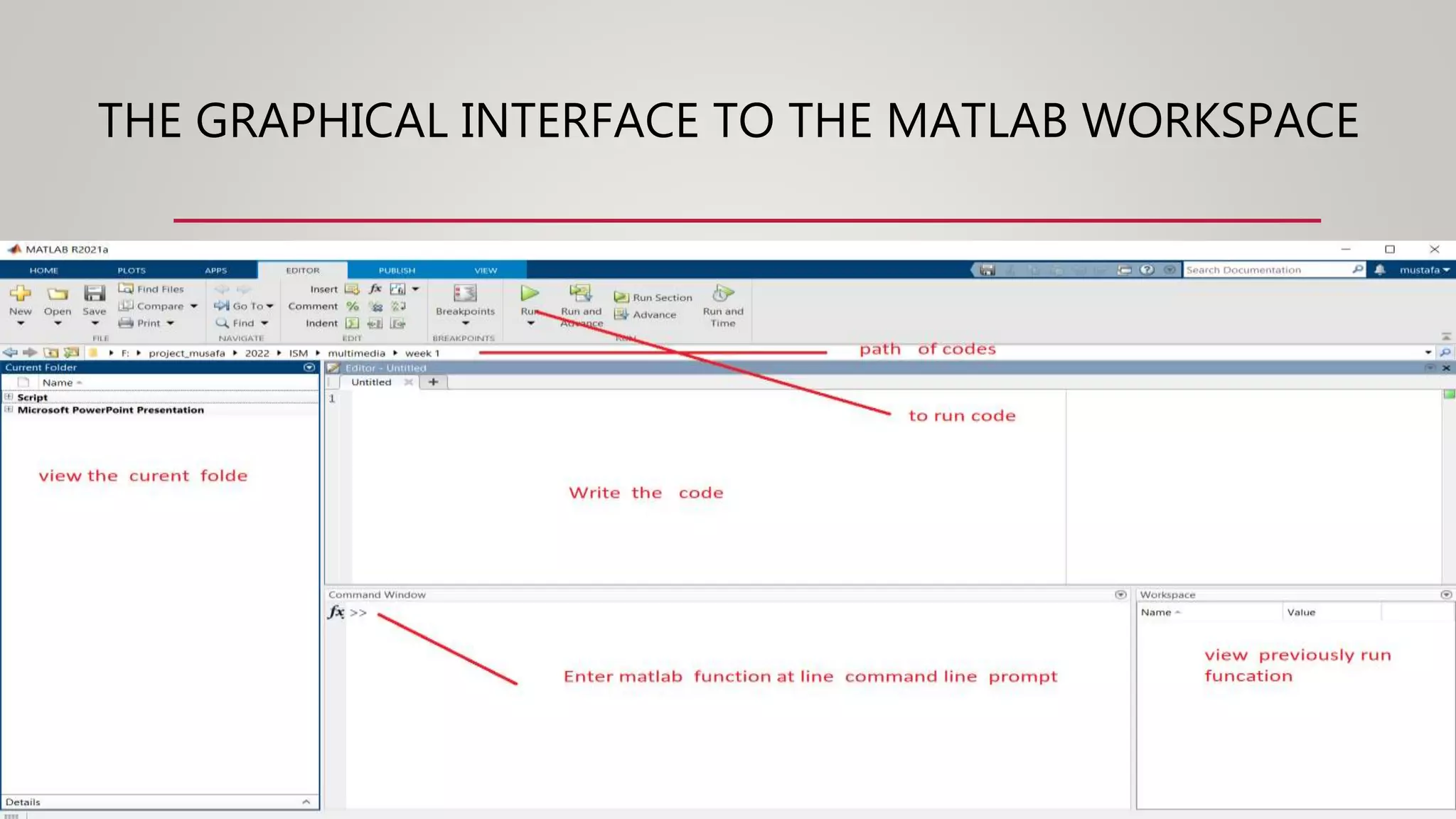
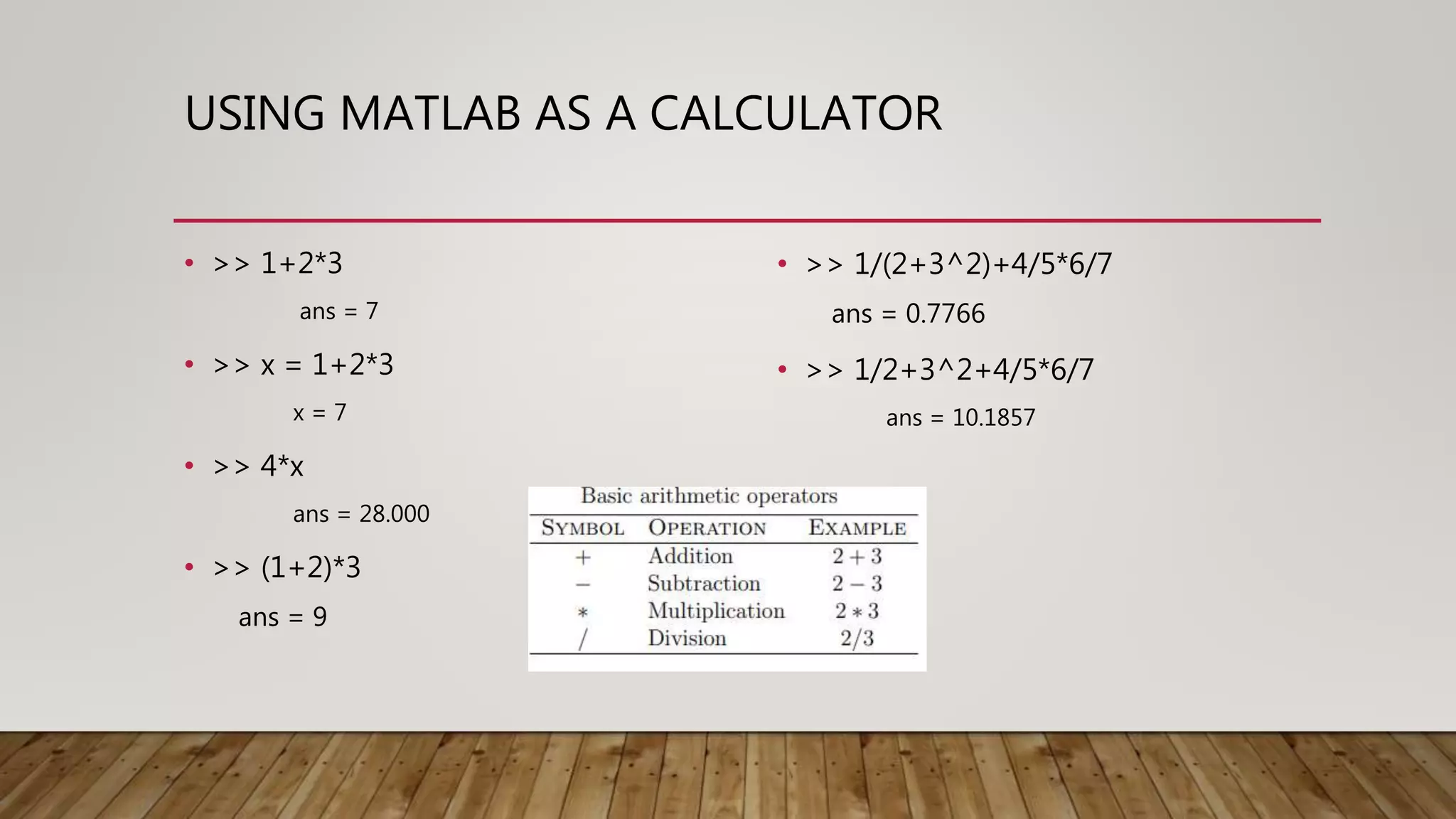
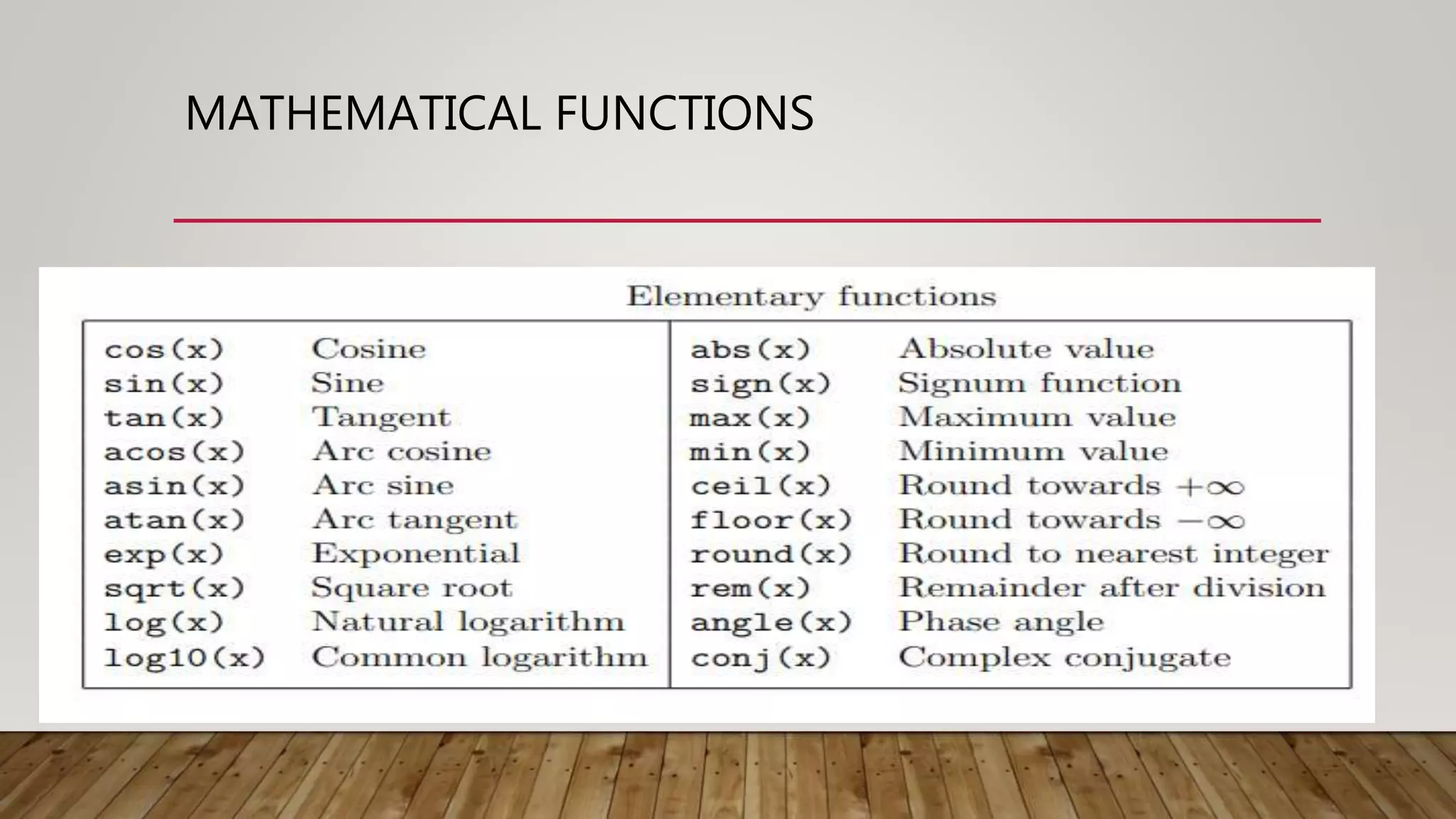
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to MATLAB, detailing the installation process for MATLAB R2021a and basic functionalities including using it as a calculator, managing the workspace, and generating vectors and matrices. It covers fundamental programming concepts such as creating script files, control flow with 'if' and 'for' statements, and array operations. Additionally, it references external resources for further study on MATLAB applications.



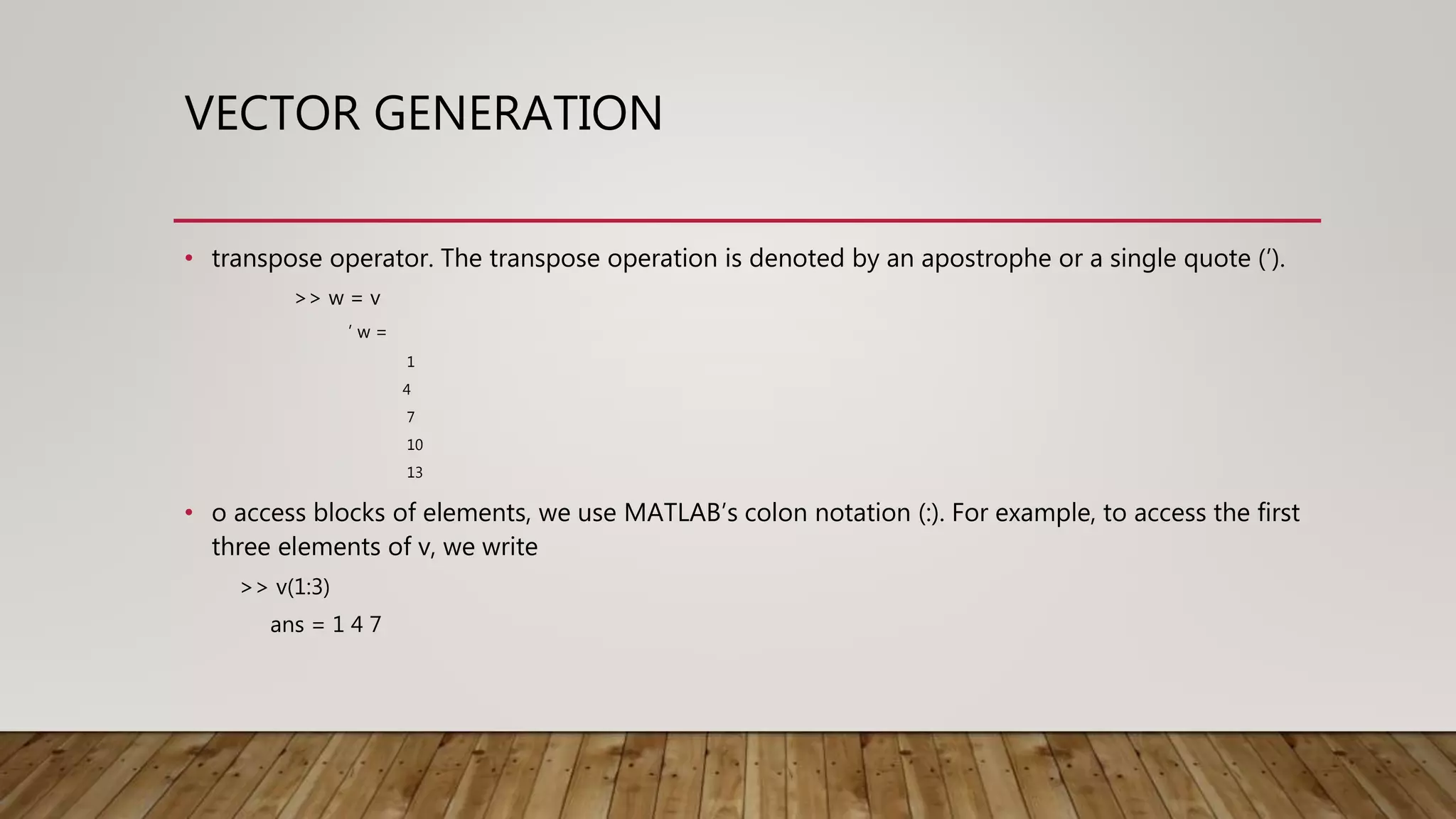
![VECTOR GENERATION • For example, to enter a row vector, v, type >> v = [1 4 7 10 13] v = 1 4 7 10 13 • Column vectors are created in a similar way, however, semicolon (;) must separate the components of a column vector, >> w = [1;4;7;10;13] w = 1 4 7 10 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationshareslide-220311192654/75/Introduction-to-programming-in-MATLAB-16-2048.jpg)
![ENTERING A MATRIX • A matrix is an array of numbers. To type a matrix into MATLAB you must • begin with a square bracket, [ • separate elements in a row with spaces or commas (,) • use a semicolon (;) to separate rows • end the matrix with another square bracket, ]. 20 • We can then view a particular element in a matrix by specifying its location. We write, >> A(2,1) • ans = 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationshareslide-220311192654/75/Introduction-to-programming-in-MATLAB-18-2048.jpg)
![DELETING ROW OR COLUMN • To delete a row or column of a matrix, use the empty vector operator, [ ]. >> A(3,:) = [] A = 1 2 3 4 5 6 DIMENSION • To determine the dimensions of a matrix or vector, use the command size. For example, >> size(A) ans = 3 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationshareslide-220311192654/75/Introduction-to-programming-in-MATLAB-19-2048.jpg)