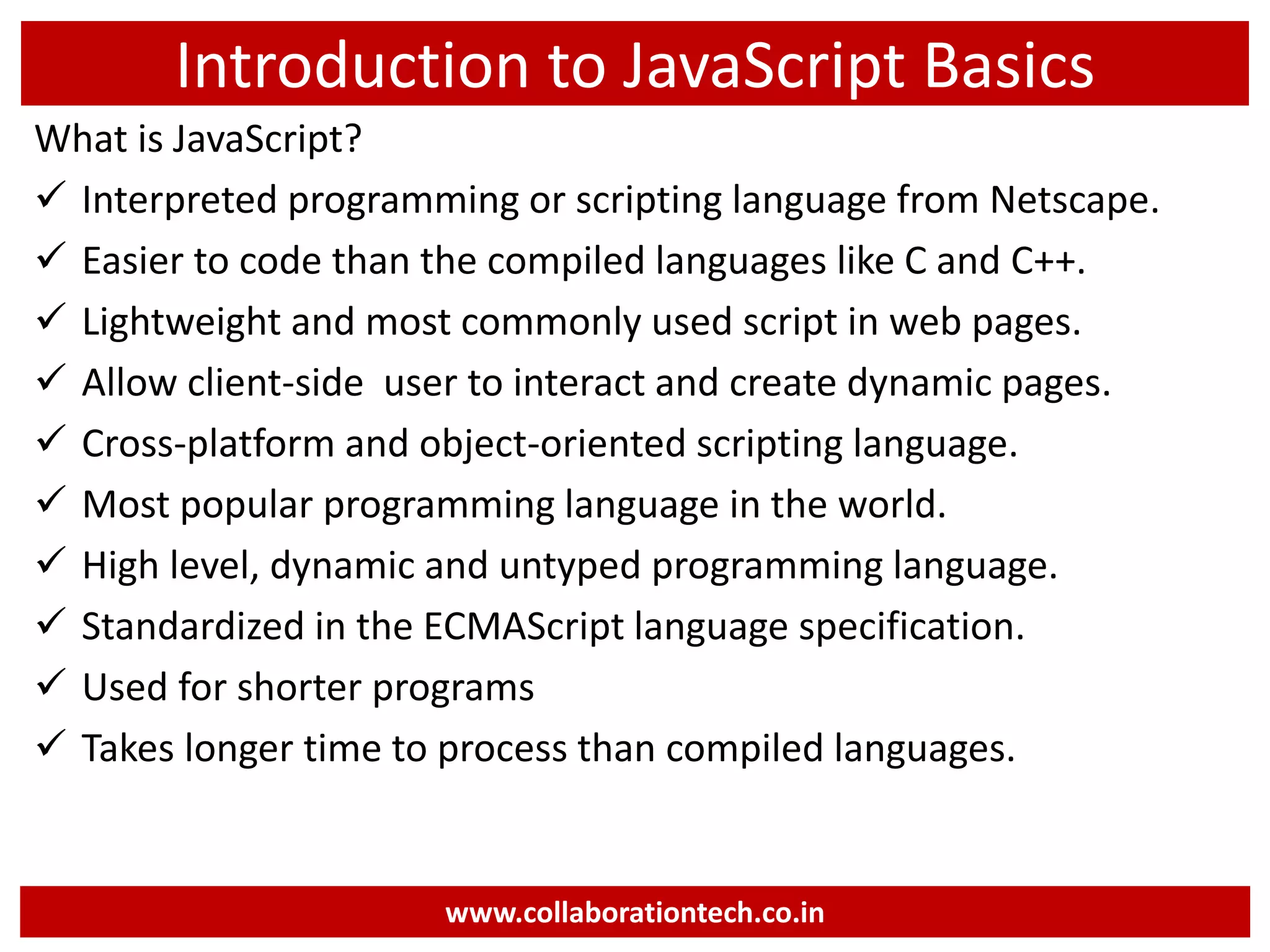
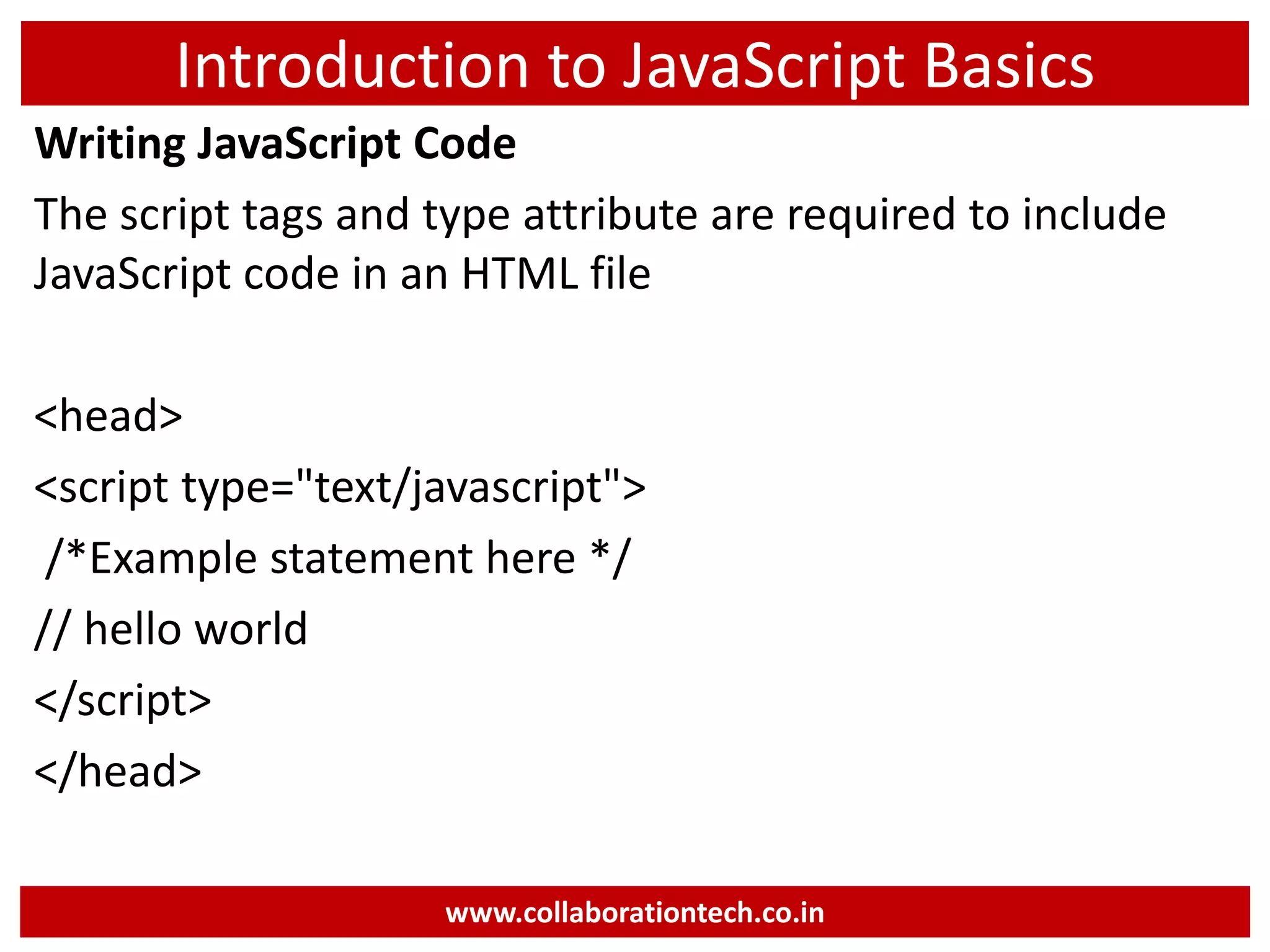
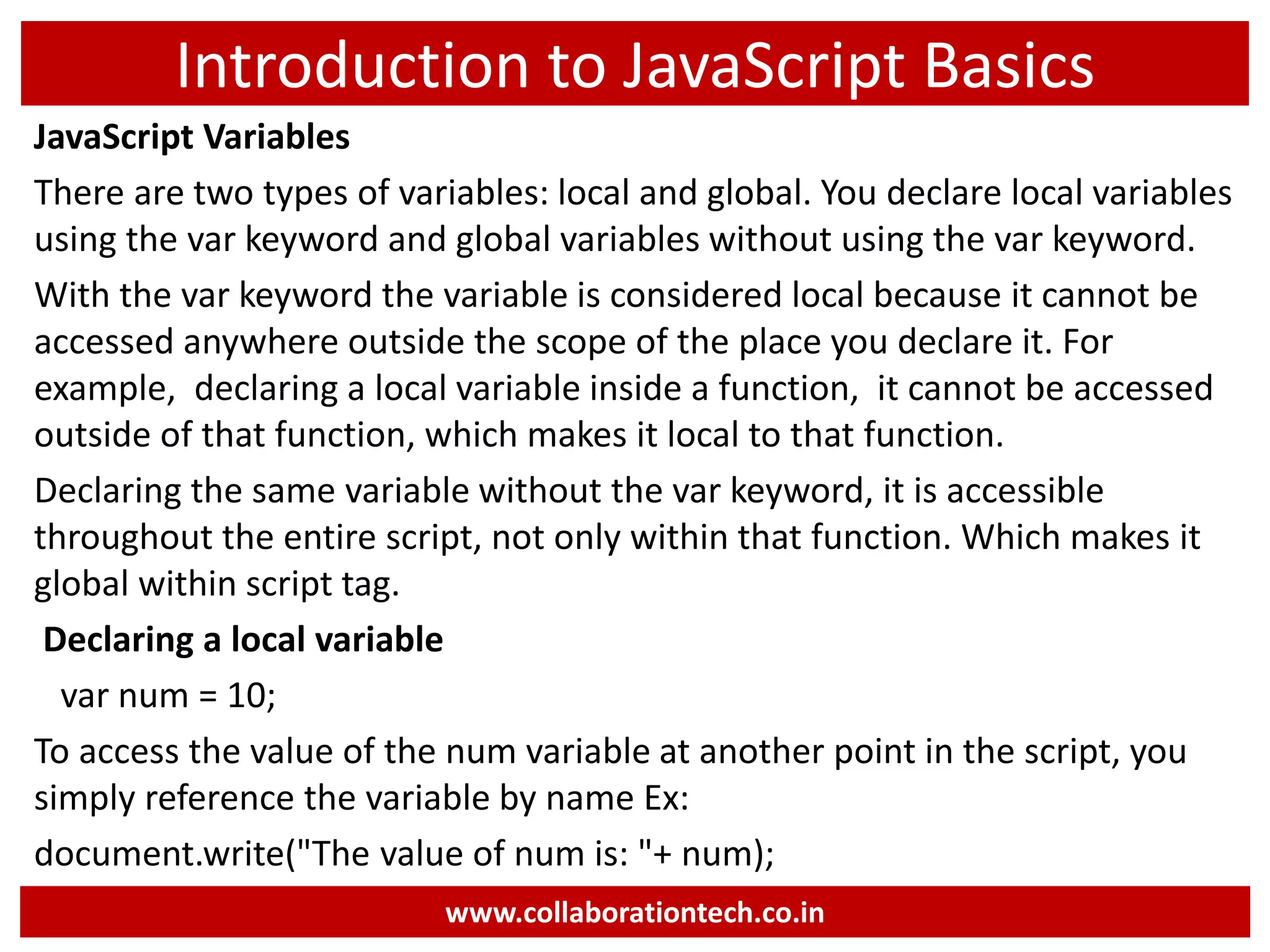
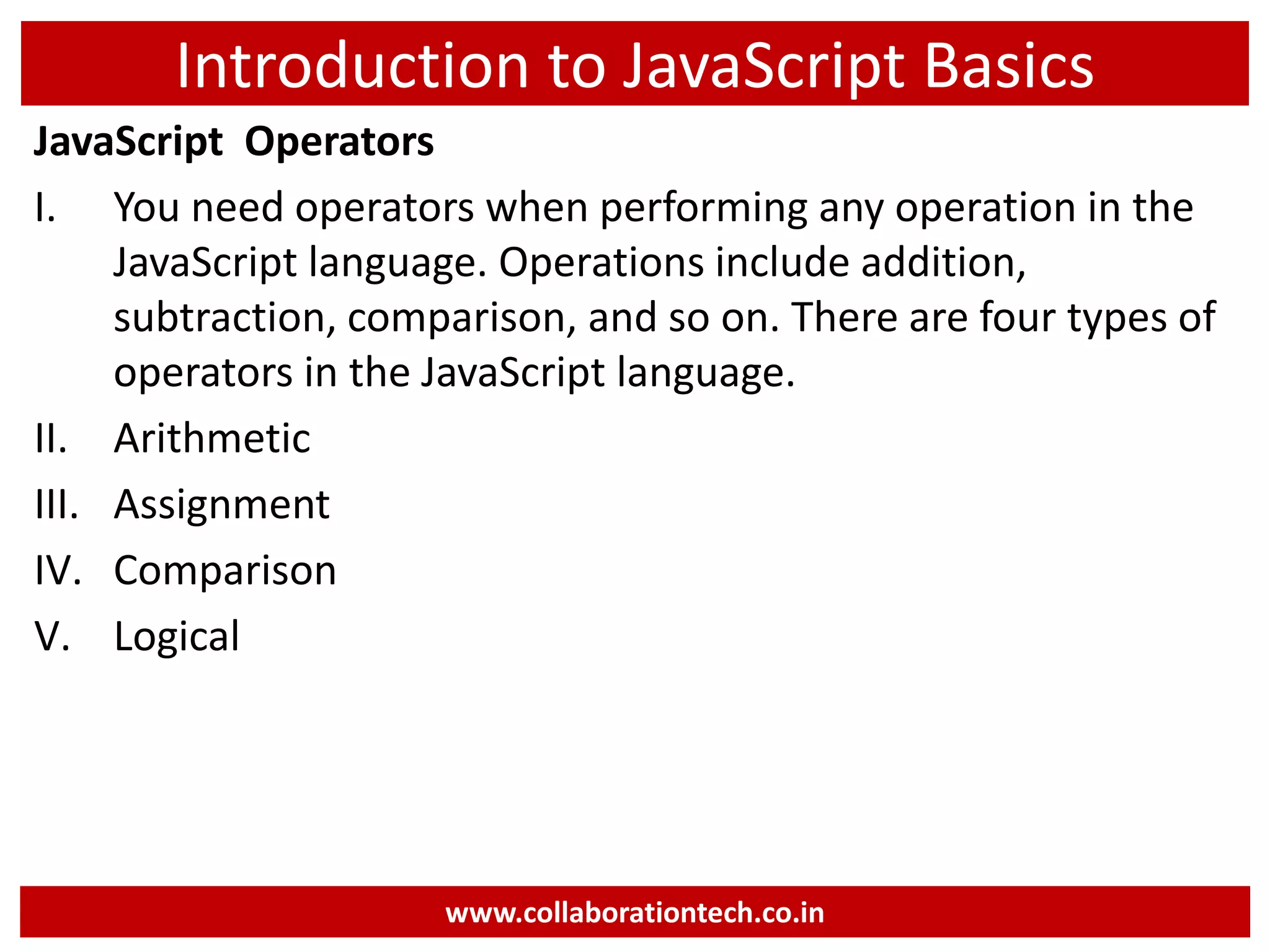
This document provides an introduction to JavaScript programming basics. It discusses what JavaScript is, where it is used, frameworks, writing code, using external files, variables, operators, arrays, control structures, and using JavaScript in HTML. The presentation was given by Ramananda M.S. Rao from Collaboration Technologies in Bengaluru, India.





![Introduction to JavaScript Basics Storing similar values in an array var colors = new Array("orange", "blue", "red", "brown"); document.write("Orange: "+ colors[0]); document.write("Blue: "+ colors[1]); document.write("Red: "+ colors[2]); document.write("Brown: "+ colors[3]); It is also possible to assign a value to a position in an array or update an item's value in an array, just as you accessed an item in an array Assigning values to specific positions in an array var colors = new Array(); colors[0] = "orange"; colors[1] = "blue"; colors[2] = "red"; colors[3] = "brown"; document.write("Blue: "+ colors[1]); // Update blue to purple colors[1] = "purple"; document.write("Purple: "+ colors[1]); www.collaborationtech.co.in](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascript-intro-170124104759/75/Introduction-to-JavaScript-Programming-12-2048.jpg)