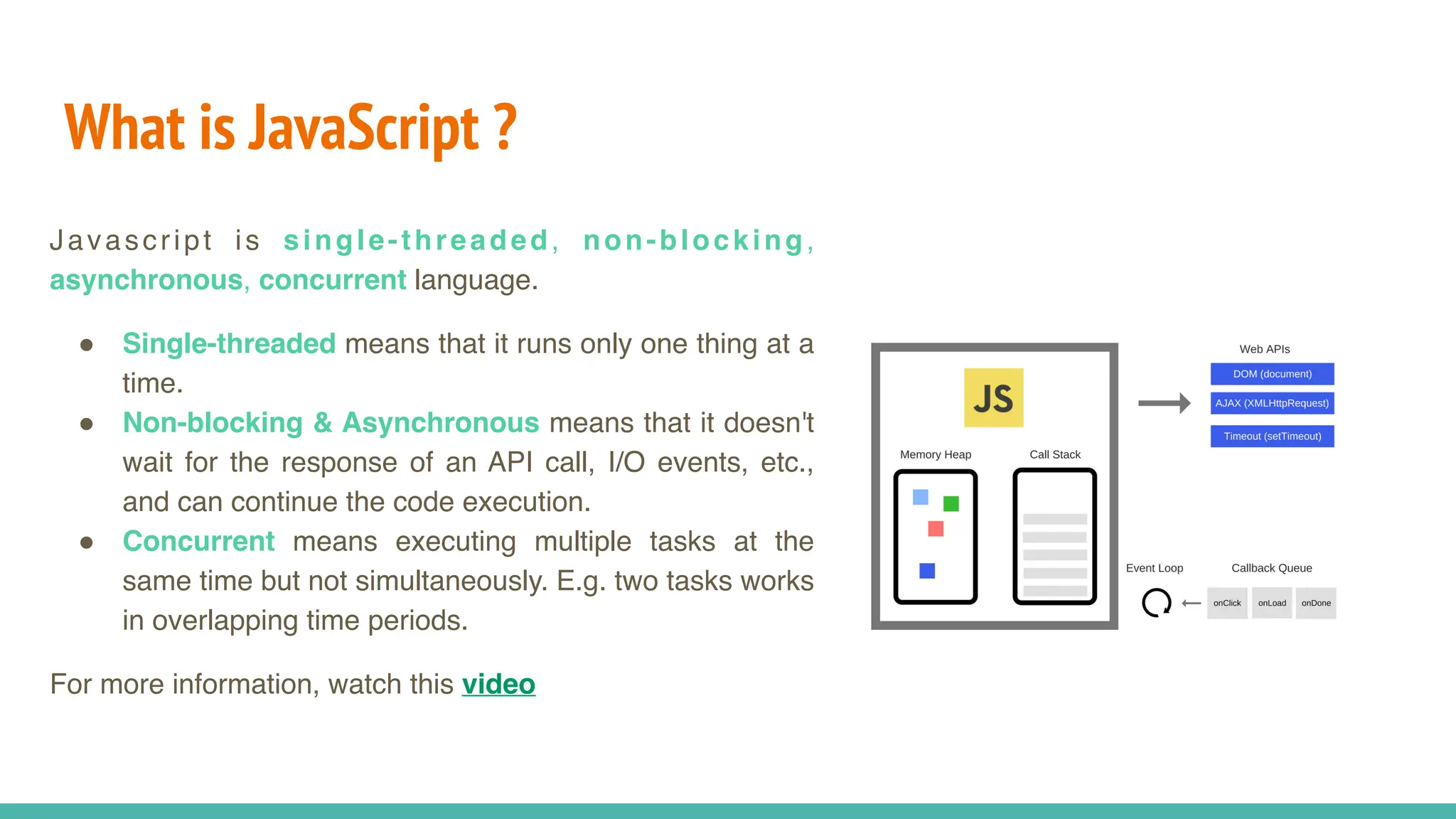
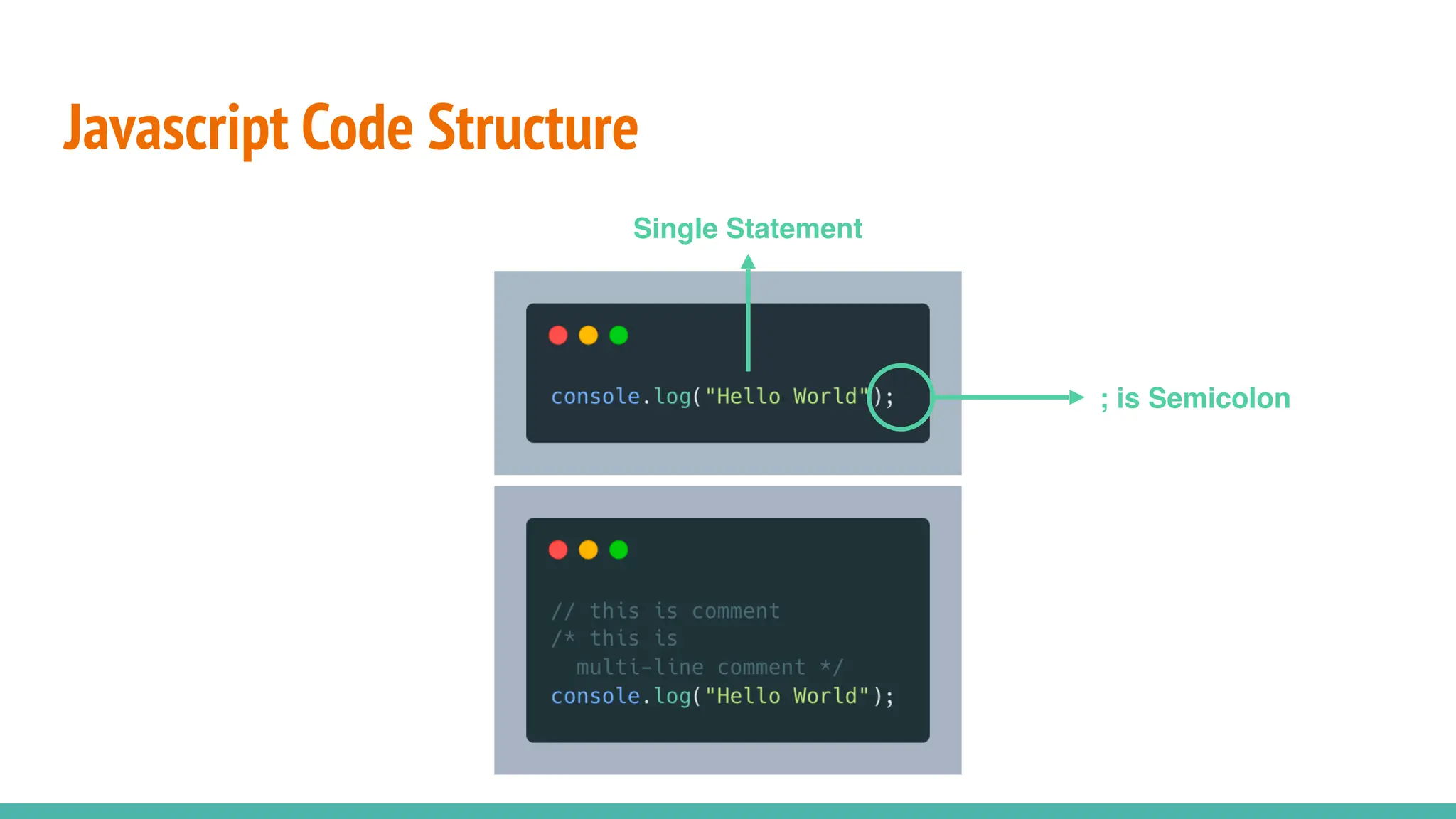
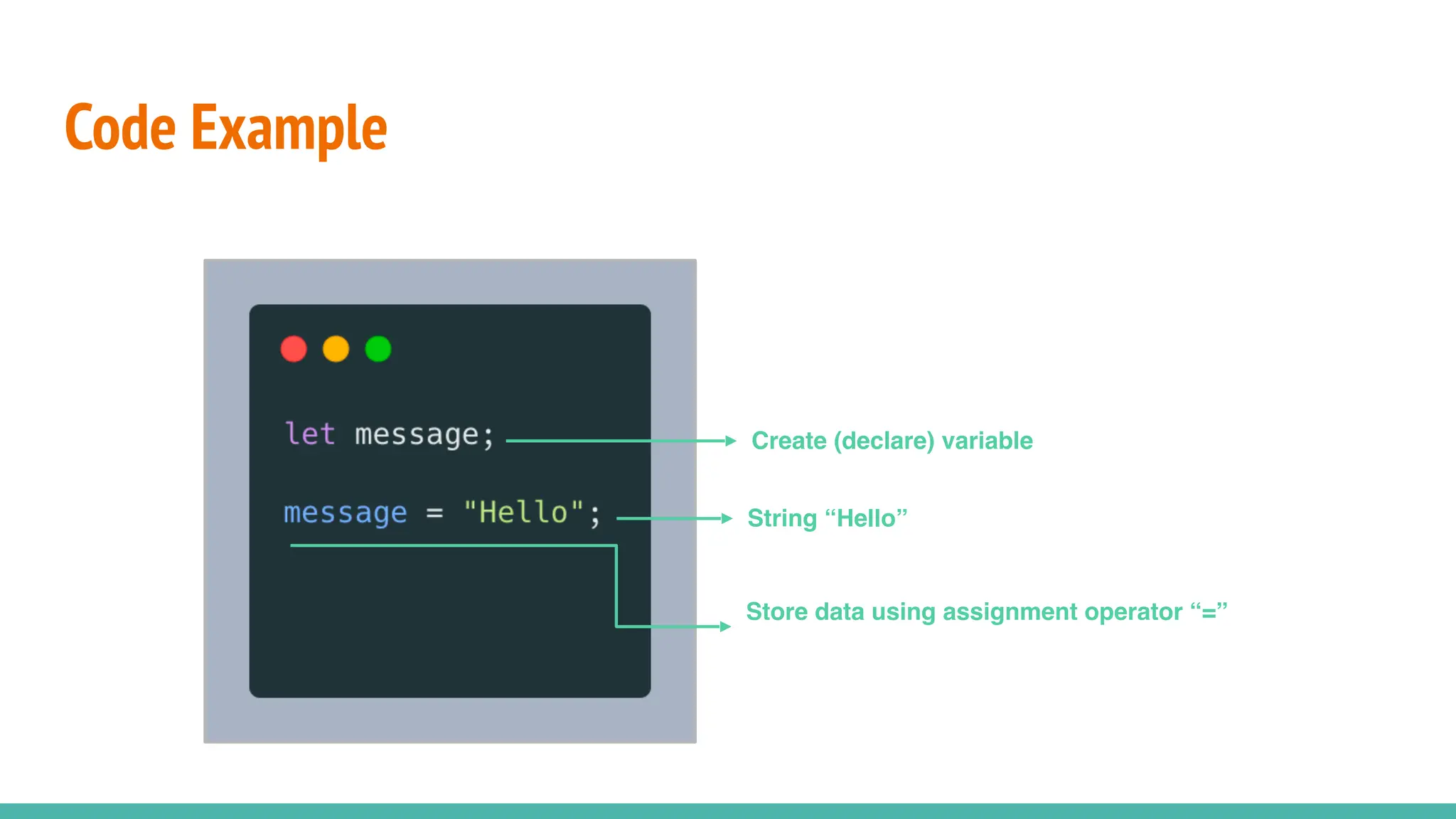
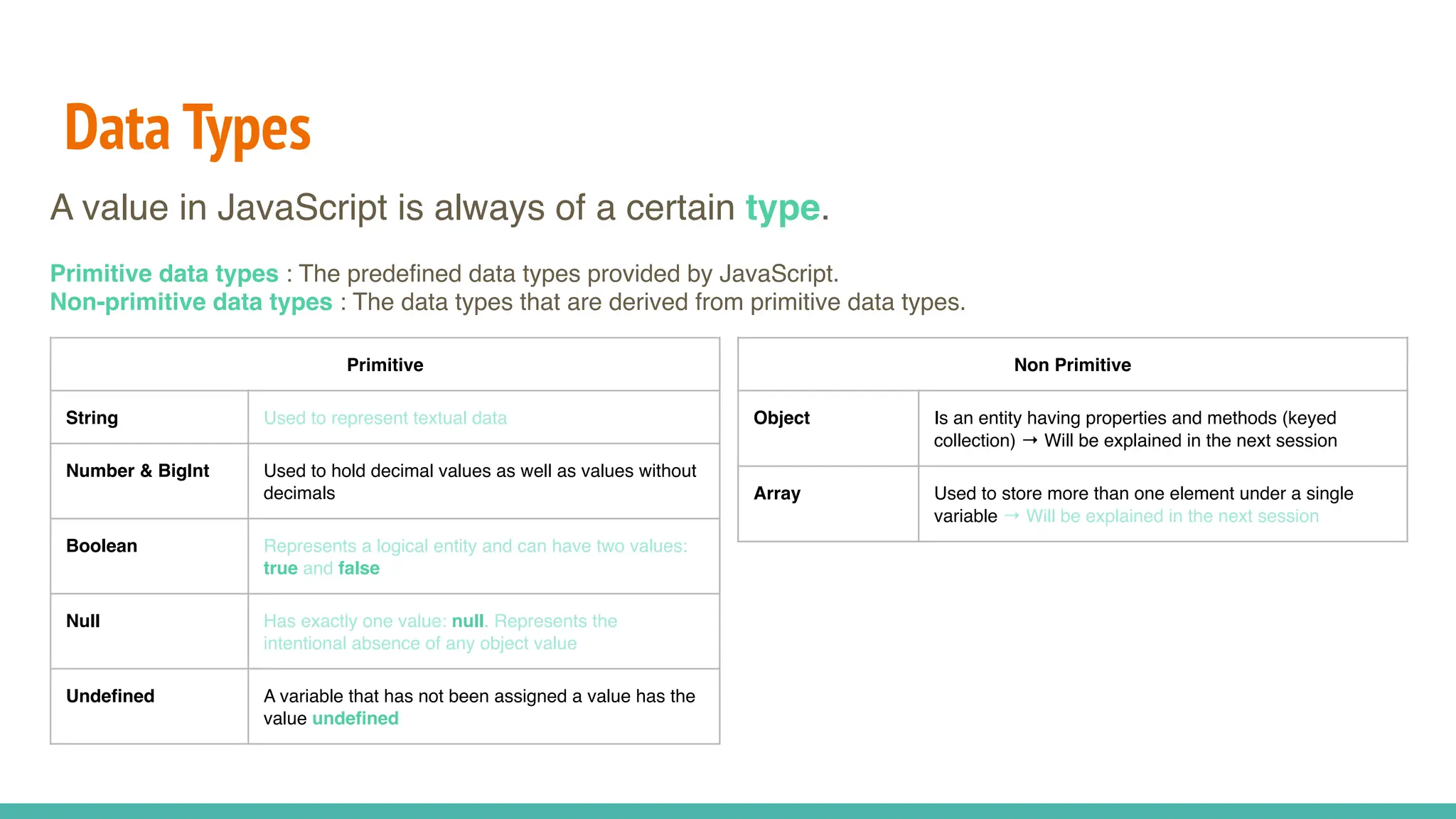
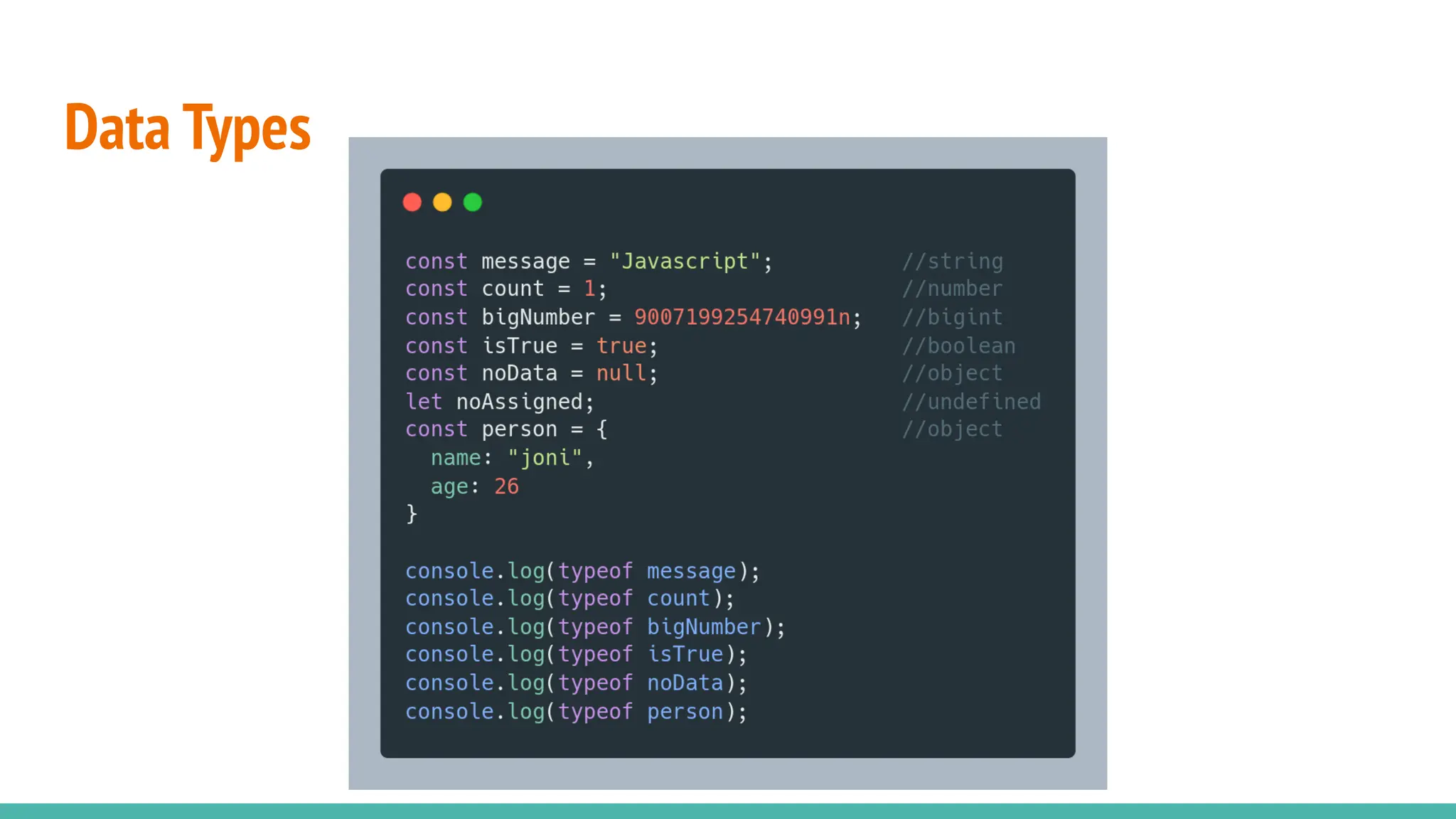
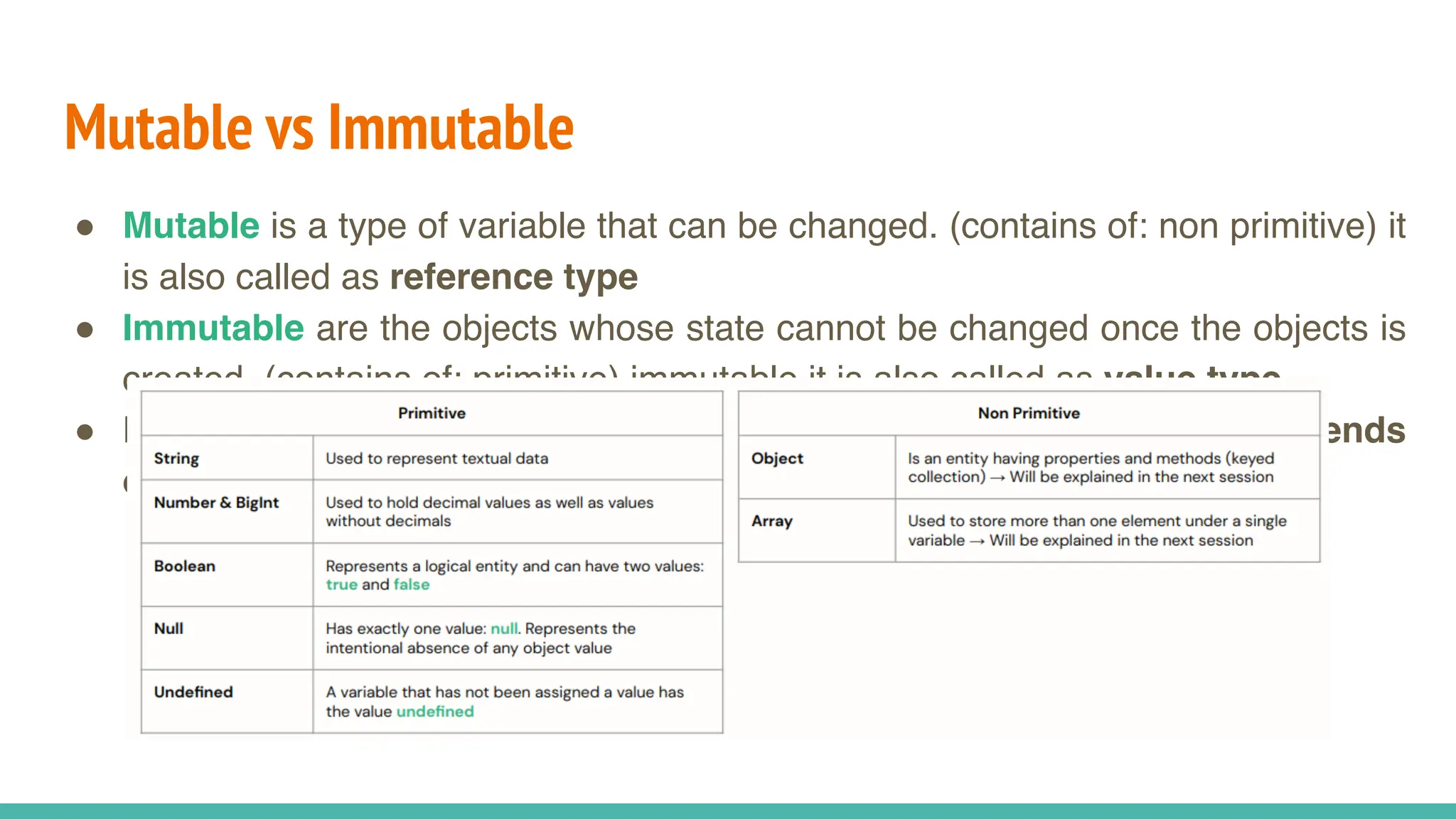
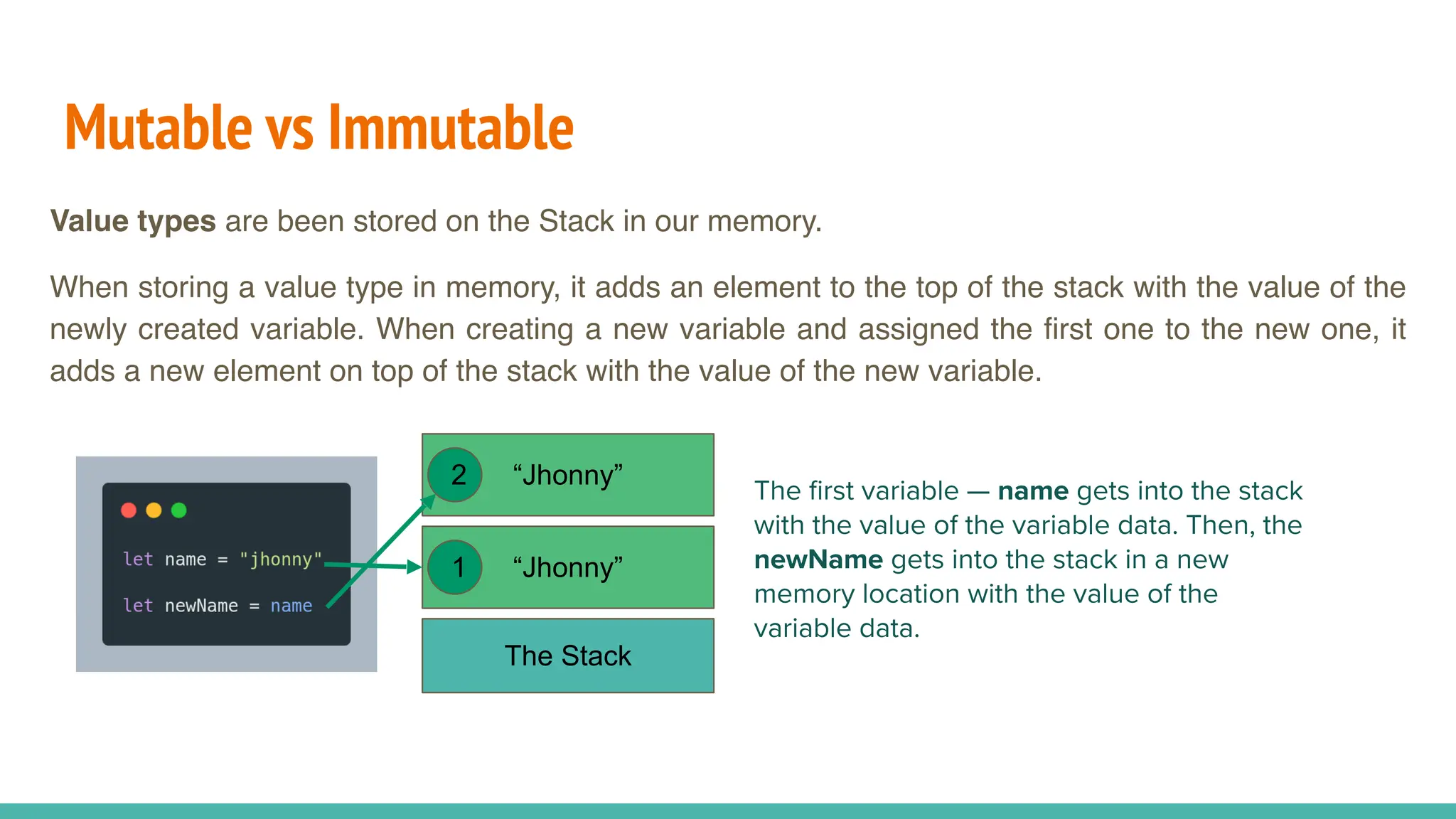
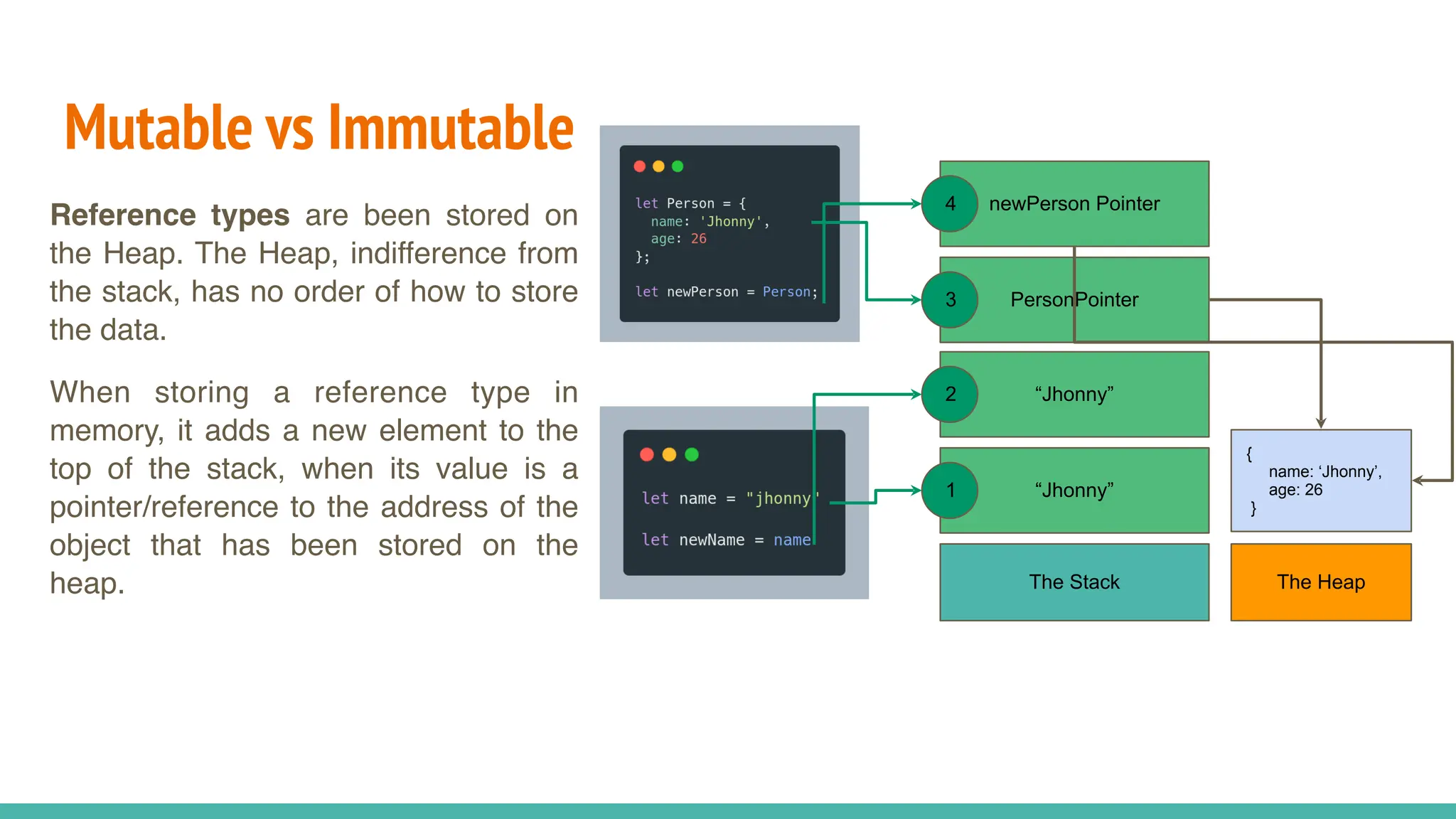
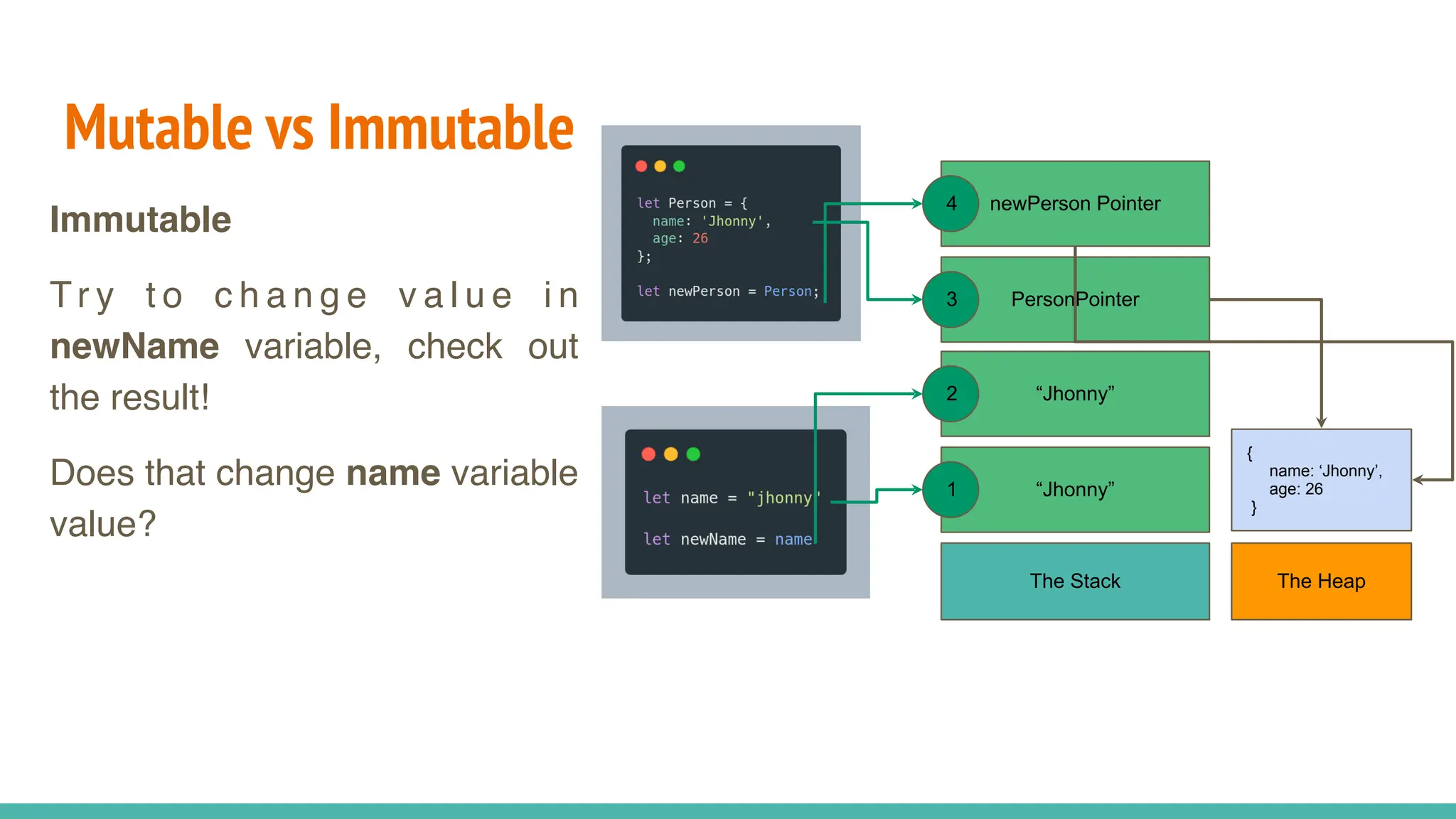
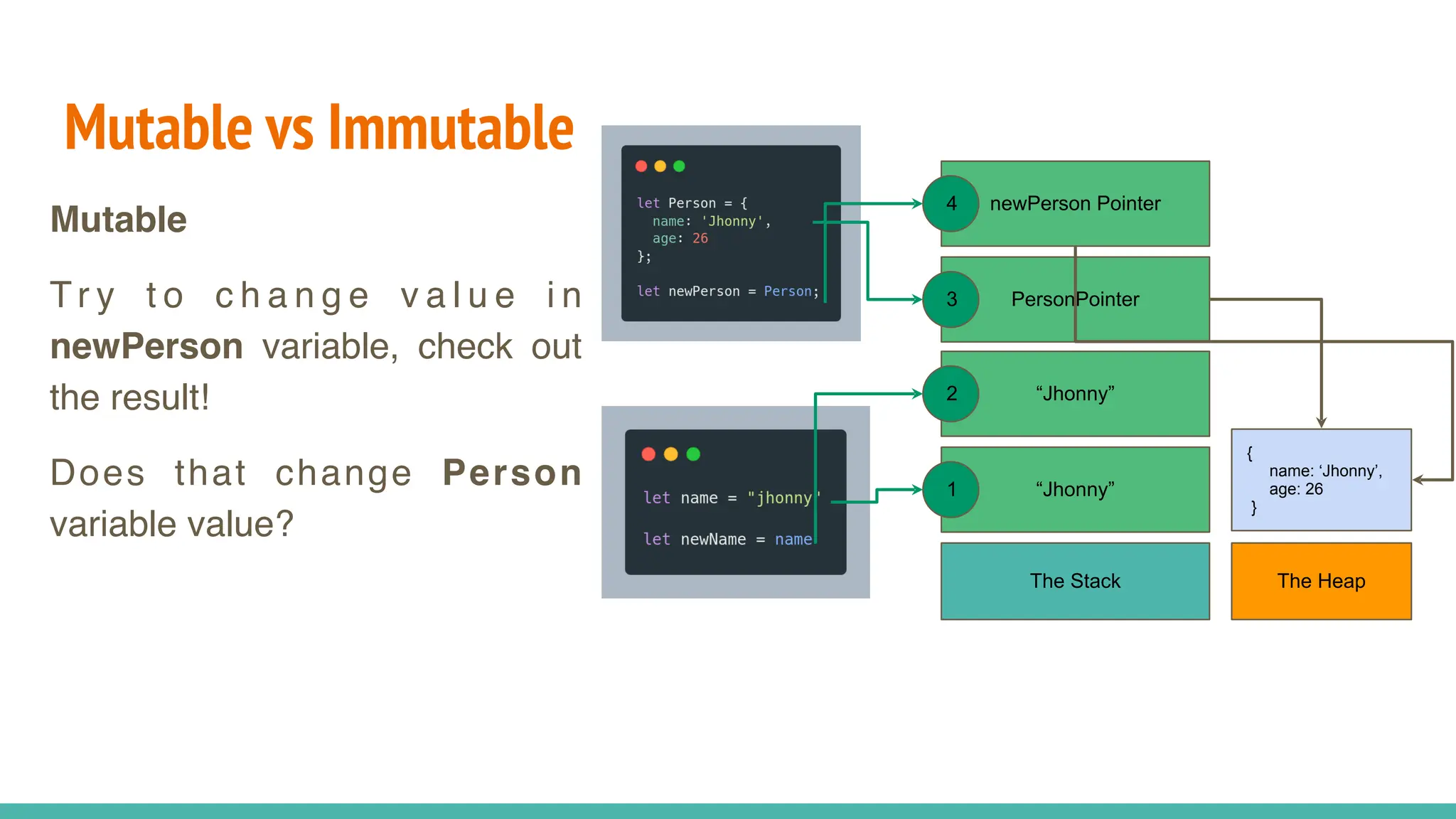
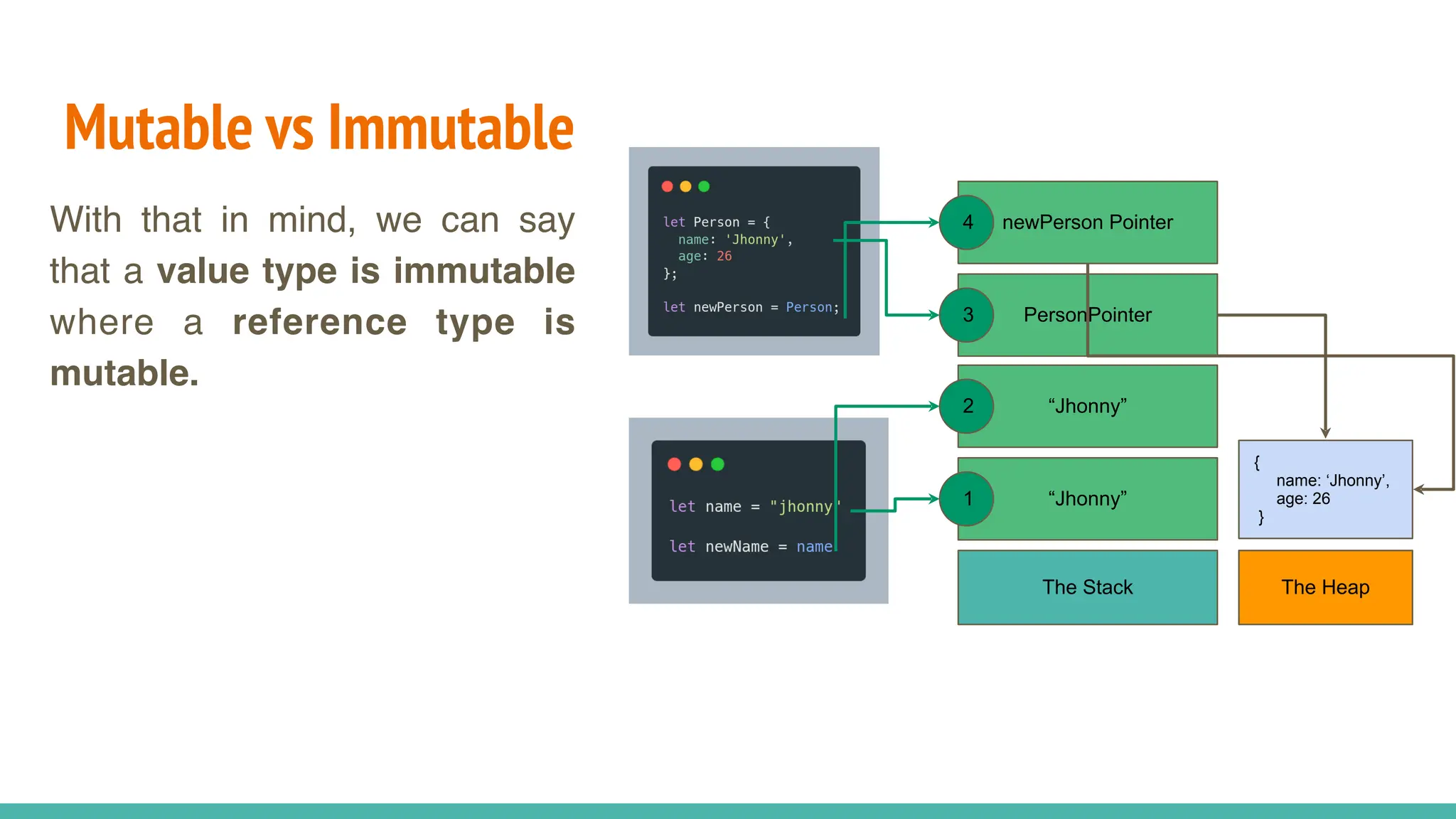
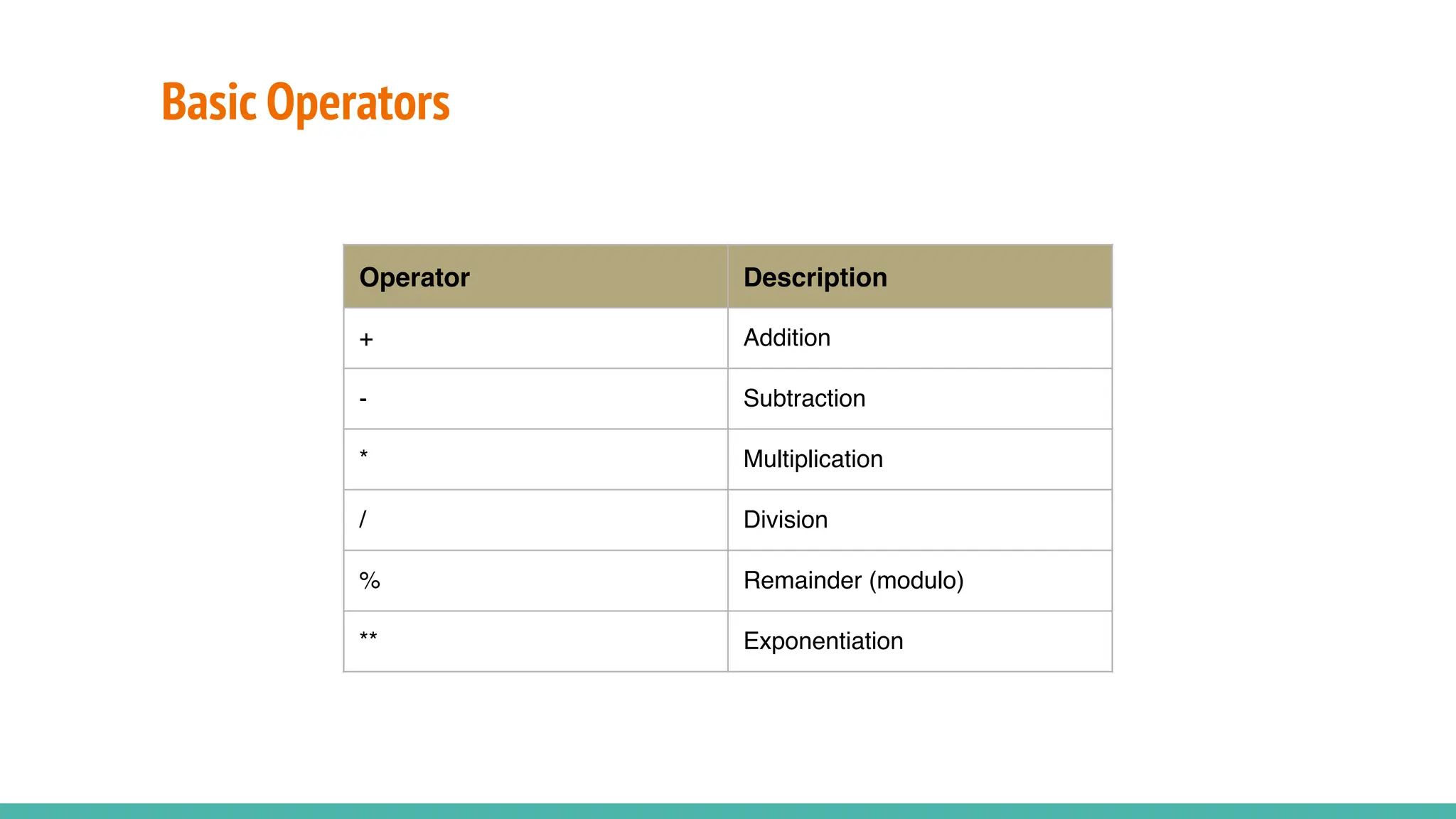
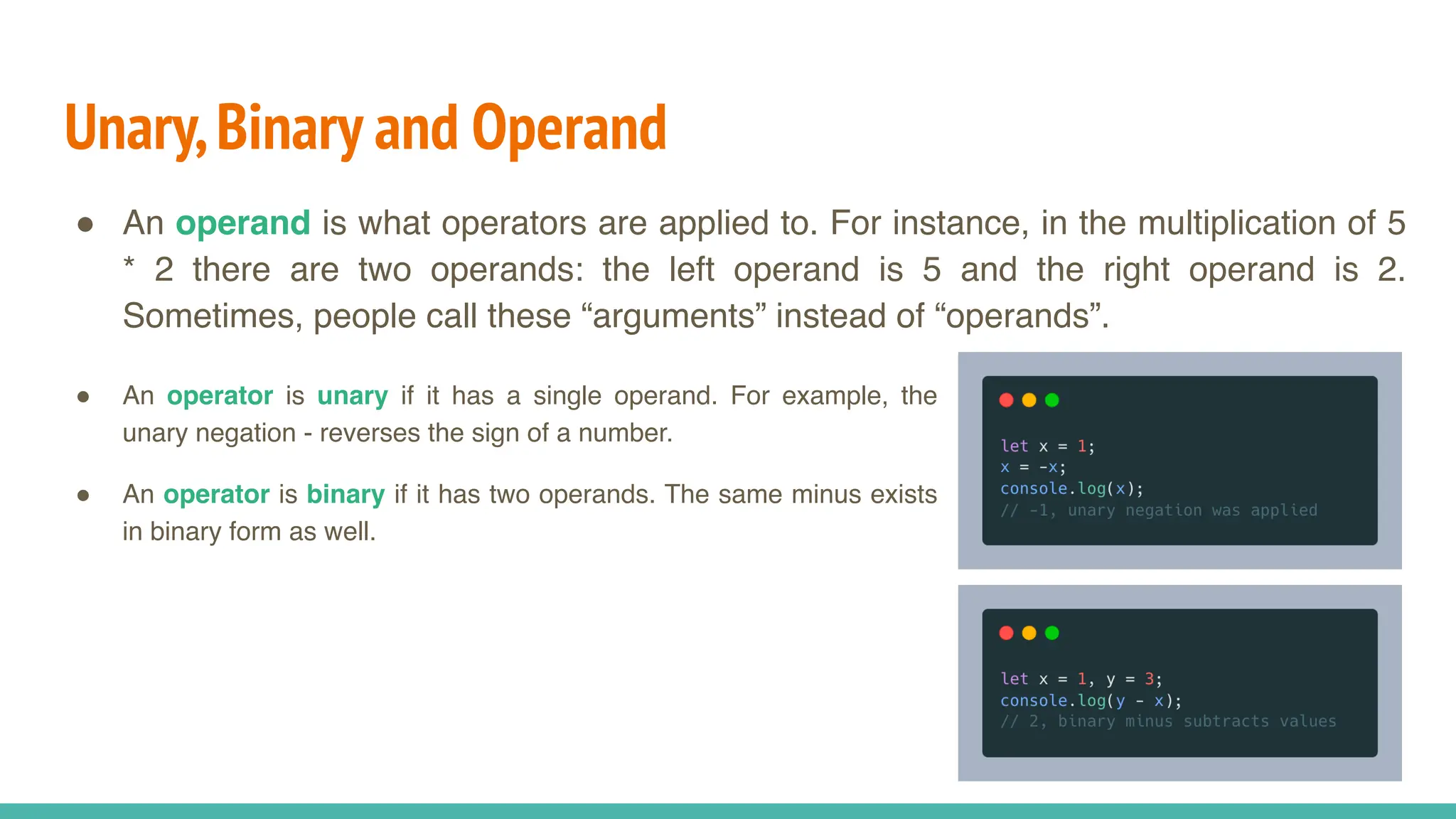
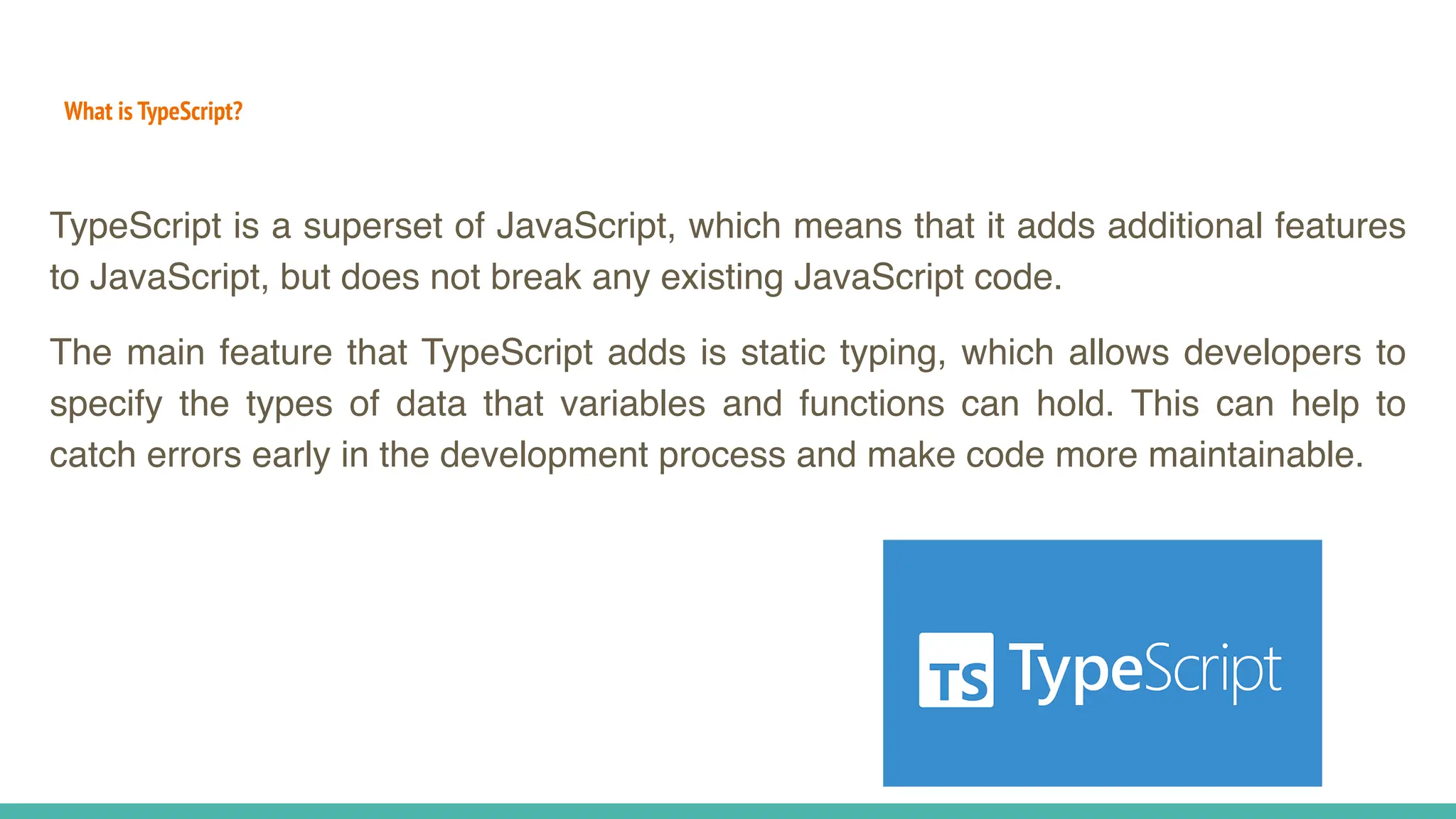
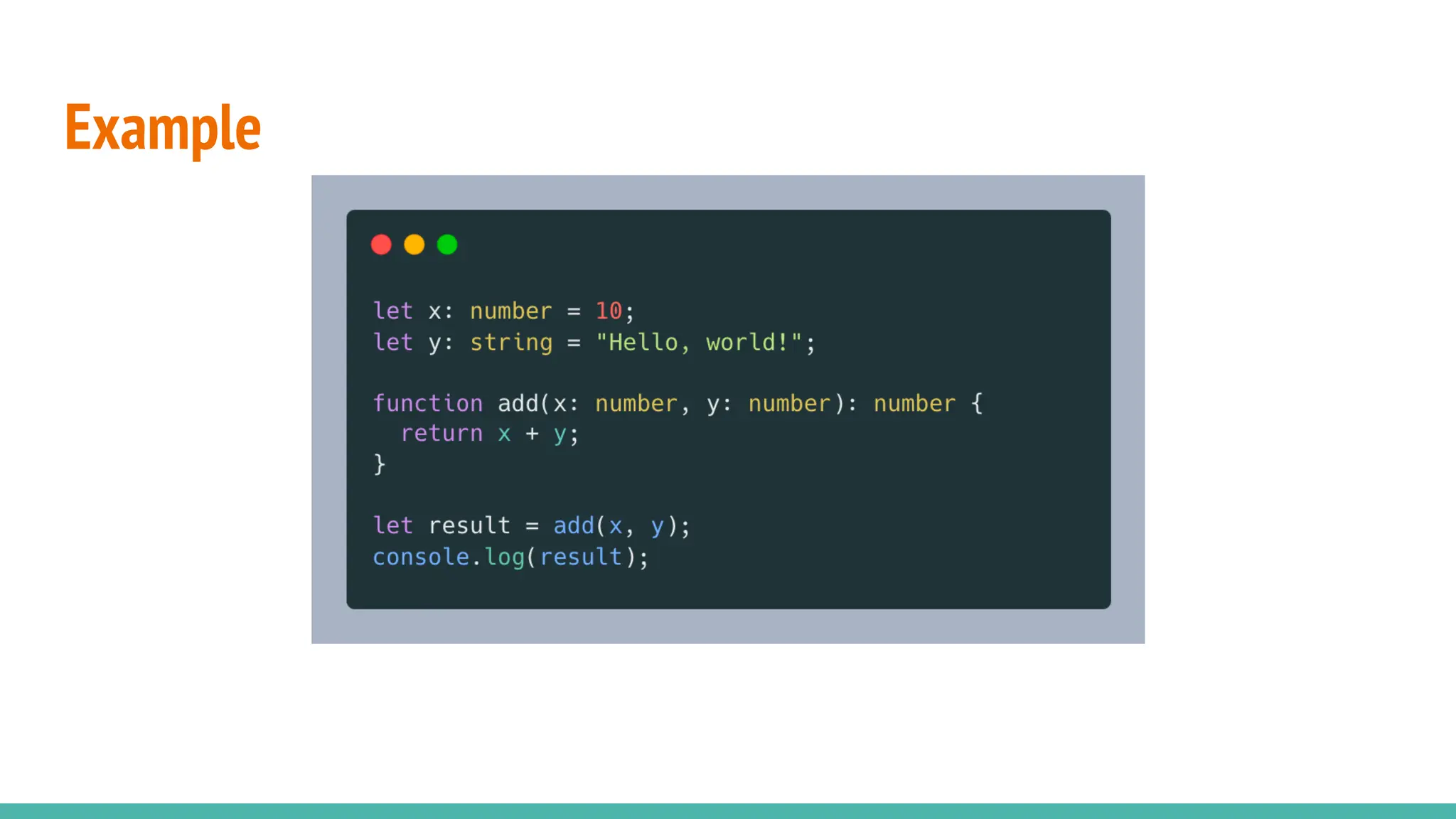
JavaScript is a dynamically typed, interpreted, and loosely typed programming language primarily used for web development. It enables interactive web pages by handling user events, modifying the DOM (Document Object Model), and making asynchronous requests. TypeScript is a statically typed superset of JavaScript, developed by Microsoft. It adds optional static typing and other powerful features to JavaScript, making it more robust and maintainable. Which One Should You Use? If you're working on small projects or quick scripts, JavaScript is fine. If you're building large-scale applications or enterprise projects, TypeScript is better for maintainability and reducing bugs.