Want to command automation, analytics, and AI with elegance? It starts with Python mastery—the go-to skill in today’s tech stack! Whether you're a beginner or exploring DSA for working professionals, Python unlocks the power to think logically and build efficiently. With the best online professional certificates and hands-on projects, TutorT Academy ensures you don’t just learn Python—you live it. From syntax to scalability, master it all and future-proof your career!




![For example - For example - my_list = [i for i in range(1, 10)] a = lambda x, y : x*y print(a(7, 19)) What is List Comprehension? Give an Example. What is a lambda function? List comprehension is a syntax construction to ease the creation of a list based on an existing iterable. A lambda function is an anonymous function. This function can have any number of parameters but can have just one statement. Question Question 8 9 Curated by Curated by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-6-2048.jpg)












![os.remove() os.unlink() Lst[ Initial : End : IndexJump ] How to delete a file using Python? What is slicing in Python? We can delete a file using Python by following approaches: Python Slicing is a string operation for extracting a part of the string, or some part of a list. With this operator, one can specify where to start the slicing, where to end, and specify the step. List slicing returns a new list from the existing list. Question Question 39 40 Curated by Curated by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-23-2048.jpg)






![>>> thelist=['a','b'] >>> for i,j in enumerate(thelist): ... print i,j ... 0 a 1 b High readability reduces cost of program maintenance open source support third party packages modularity code reverse. What is the improvement in the enumerate() function of Python? In Python, enumerate() function is an improvement over regular iteration. The enumerate() function returns an iterator that gives (0, item[0]). Question 54 uses and benefits of python Question 55 Curated by Curated by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-32-2048.jpg)
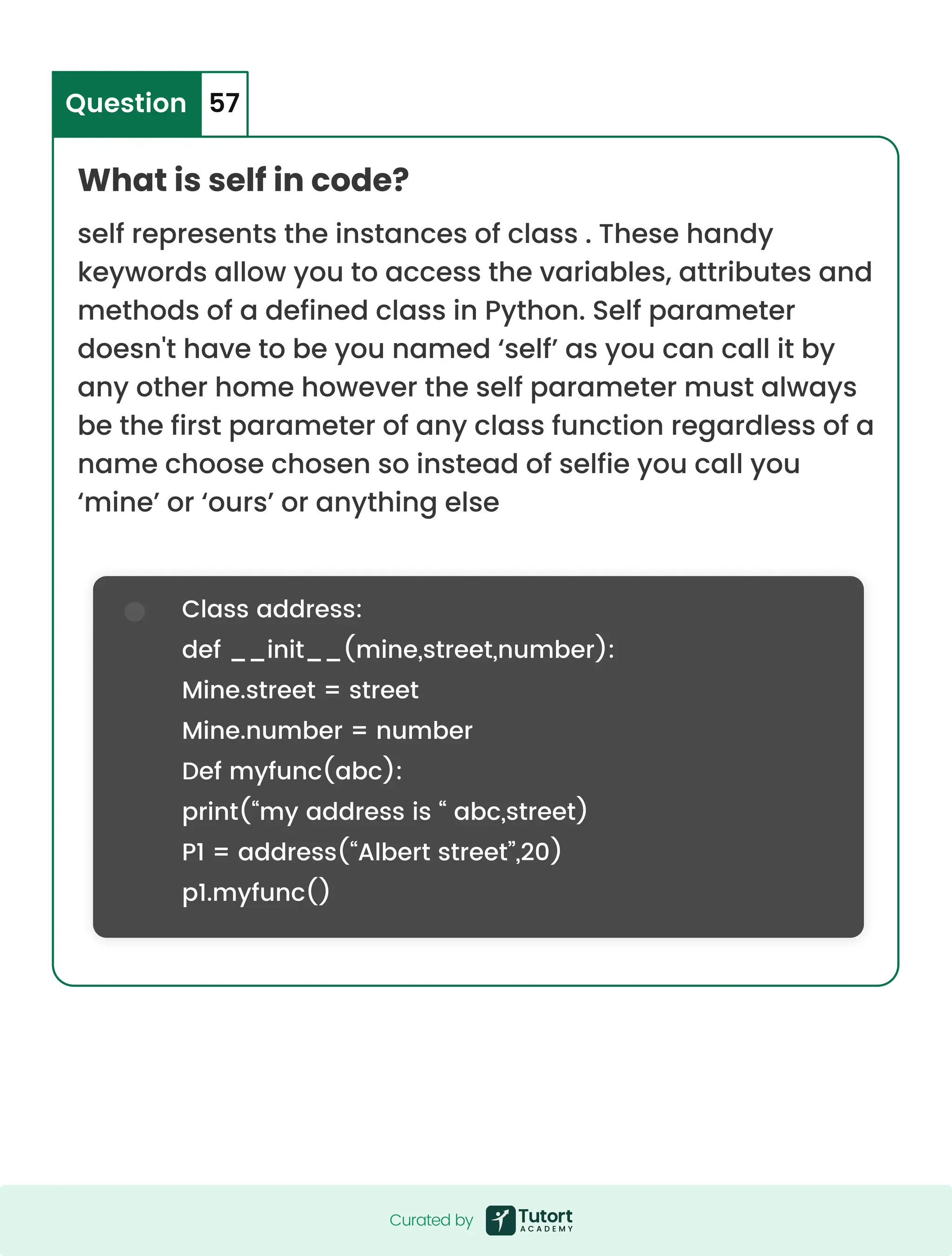
![What is comprehension in Python? It provide us with the short and a concise way to construct a new sequences [such as a list set dictionary etc] using sequences which have been already defined Python supports four types of a comprehension Question 58 A. List comprehension- it provide an elegant way to create a new list.The following is the basic structure of a list comprehension output list= [ output_execution for var in input_list if (var satisfy this condition)] Note - list comprehension may or may not contain and if condition list comprehension can contain multiple for nested list conference comprehension list comprehension set comprehension dictionary comprehension generator comprehension Curated by Curated by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-35-2048.jpg)
![#without using list comprehension Input_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 7,7] Output_list=[ ] #look for constructing output for var in input_list: If var % 2 ==0: Output_list.append(var) print(“Output list using for loop, output_list) # Constructing output list using for loop output list is equal to[] for war in range(1, 10): output_list.append(var ** 2): print(“Output list using for loops: “,output_list ) 1. example one suppose we want to create an output list which contains only the even number which are present in the input list let's see how to do this using for loops and list comprehension and decide which method suits better Output = output list using for loop : [2 4 4 6] output = output list using for loop : [1 4 9 16 25 36 49 64 81] 2. Suppose we want to create an output list which contains squares of all the numbers from 1 to 9 let's see how to do this using for loops and list comprehension Curated by Curated by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-36-2048.jpg)
![B. Dictionary comprehension Extending the idea of list comprehensions, we can also create a dictionary using dictionary comprehensions. The basic structure of a dictionary comprehension looks like below. Example #1: Suppose we want to create an output dictionary which contains only the odd numbers that are present in the input list as keys and their cubes as values. Let’s see how to do this using for loops and dictionary comprehension. output = output list using for comprehension: [1 4 9 16 25 36 49 64 81] #using list comprehension list_using_comprehension=[ var * 2 for var in range(1,10)] print(“Output list using for loops: “, list_using_comprehension ) output_dict = {key:value for (key, value) in iterable if (key, value satisfy this condition)} Curated by Curated by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-37-2048.jpg)
![Example #2: Given two lists containing the names of states and their corresponding capitals, construct a dictionary which maps the states with their respective capitals. Let’s see how to do this using for loops and dictionary comprehension. Output: Output Dictionary using for loop: {1: 1, 3: 27, 5: 125, 7: 343} Output: Output Dictionary using dictionary comprehensions: {1: 1, 3: 27, 5: 125, 7: 343} input_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] output_dict = {} # Using loop for constructing output dictionary for var in input_list: if var % 2 != 0: output_dict[var] = var**3 print("Output Dictionary using for loop:", output_dict ) # Using Dictionary comprehensions # for constructing output dictionary input_list = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] dict_using_comp = {var:var ** 3 for var in input_list if var % 2 != 0} print("Output Dictionary using dictionary comprehensions:", dict_using_comp) Curated by Curated by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-38-2048.jpg)
![Output Output Dictionary using for loop: {'Gujarat': 'Gandhinagar', 'Maharashtra': 'Mumbai', 'Rajasthan': 'Jaipur'} Output: Output Dictionary using dictionary comprehensions: {'Rajasthan': 'Jaipur', 'Maharashtra': 'Mumbai', 'Gujarat': 'Gandhinagar'} state = ['Gujarat', 'Maharashtra', 'Rajasthan'] capital = ['Gandhinagar', 'Mumbai', 'Jaipur'] output_dict = {} # Using loop for constructing output dictionary for (key, value) in zip(state, capital): output_dict[key] = value print("Output Dictionary using for loop:", output_dict) # Using Dictionary comprehensions # for constructing output dictionary state = ['Gujarat', 'Maharashtra', 'Rajasthan'] capital = ['Gandhinagar', 'Mumbai', 'Jaipur'] dict_using_comp = {key:value for (key, value) in zip(state, capital)} print("Output Dictionary using dictionary comprehensions:", dict_using_comp) Curated by Curated by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-39-2048.jpg)
![C. set comprehension: Set comprehensions are pretty similar to list comprehensions. The only difference between them is that set comprehensions use curly brackets { }. Let’s look at the following example to understand set comprehensions. Example #1 : Suppose we want to create an output set which contains only the even numbers that are present in the input list. Note that set will discard all the duplicate values. Let’s see how we can do this using for loops and set comprehension. Output: Output Set using for loop: {2, 4, 6} input_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7] output_set = set() # Using loop for constructing output set for var in input_list: if var % 2 == 0: output_set.add(var) print("Output Set using for loop:", output_set) Curated by Curated by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-40-2048.jpg)
![D. generator comprehension Generator Comprehensions are very similar to list comprehensions. One difference between them is that generator comprehensions use circular brackets whereas list comprehensions use square brackets. The major difference between them is that generators don’t allocate memory for the whole list. Instead, they generate each value one by one which is why they are memory efficient. Let’s look at the following example to understand generator comprehension: Output: Output Set using set comprehensions: {2, 4, 6} # Using Set comprehensions # for constructing output set input_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7] set_using_comp = {var for var in input_list if var % 2 == 0} print("Output Set using set comprehensions:",set_using_comp) Curated by Curated by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-41-2048.jpg)
![Output: Output values using generator comprehensions: 2 4 4 6 input_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 7, 7] output_gen = (var for var in input_list if var % 2 == 0) print("Output values using generator comprehensions:", end = ' ') for var in output_gen: print(var, end = ' ') Curated by Curated by Courses Offered by Tutort Data Science and
Artificial Intelligence Program Data Analytics and
Business Analytics Program Learn more Learn more Full Stack Specialisation
In Software Development Learn more Data Structures and Algorithms
with System Design Learn more](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-42-2048.jpg)


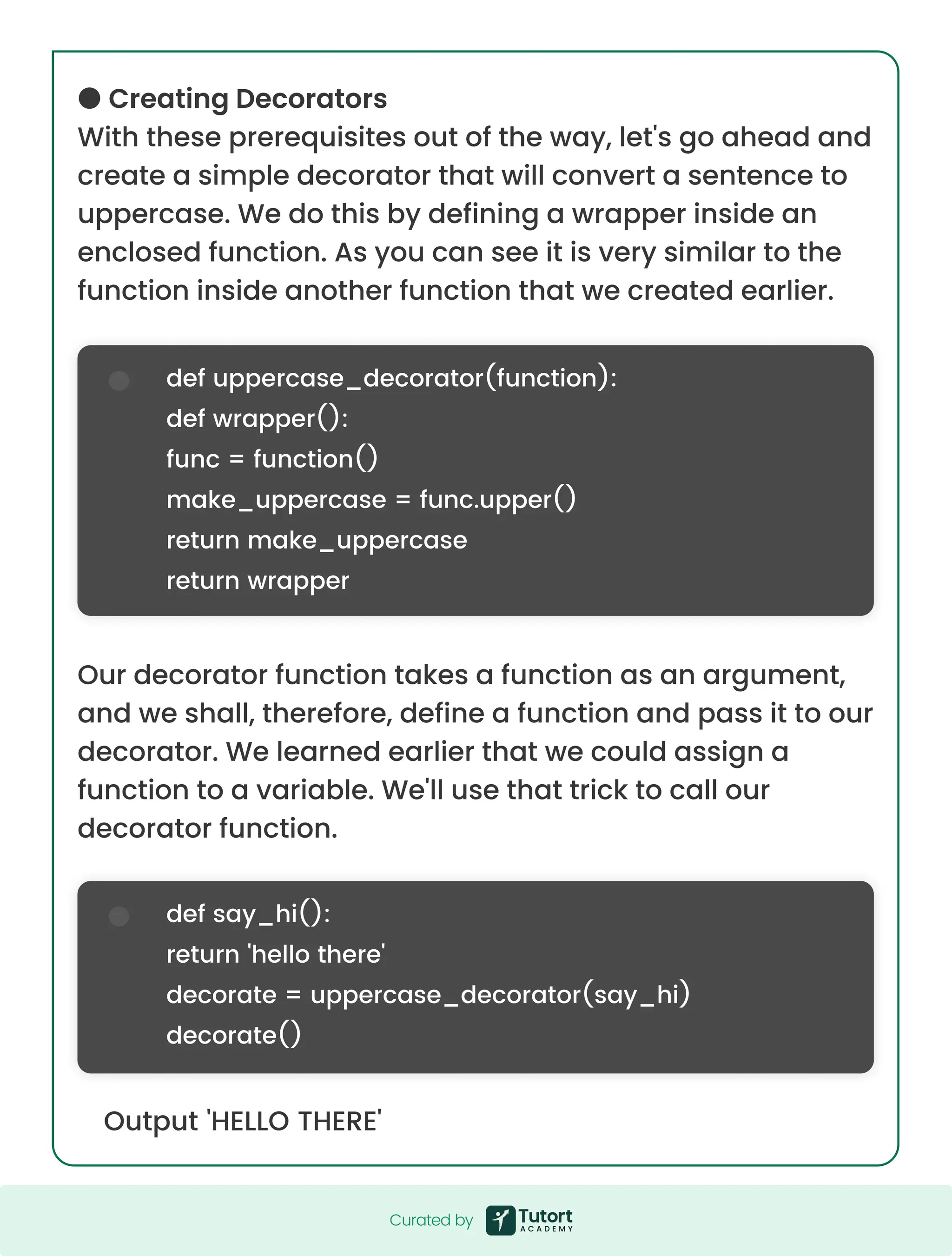
![Output 'HELLO THERE' @uppercase_decorator def say_hi(): return 'hello there' say_hi() def split_string(function): def wrapper(): func = function() splitted_string = func.split() return splitted_string return wrapper @split_string @uppercase_decorator def say_hi(): return 'hello there' say_hi() ['HELLO', 'THERE'] We can use multiple decorators to a single function. However, the decorators will be applied in the order that we've called them. Below we'll define another decorator that splits the sentence into a list. We'll then apply the uppercase_decorator and split_string decorator to a single function. However, Python provides a much easier way for us to apply decorators. We simply use the @ symbol before the function we'd like to decorate. Let's show that in practice below. Curated by Curated by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-47-2048.jpg)








![What is the difference between split() and slicing in Python? How can you randomize the items of a list in place in Python? Question Question 68 69 Both split() function and slicing work on a String object. By using split() function, we can get the list of words from a String. E.g. 'a b c '.split() returns [‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’] Slicing is a way of getting substring from a String. It returns another String. E.g. >>> 'a b c'[2:3] returns b This can be easily achieved by using the Shuffle() function from the random library as shown below: Output: [‘Loves’,’He’ ,’To ,’In’, ‘Python’,’Code’] from random import shuffle List = ['He', 'Loves', 'To', 'Code', 'In', 'Python'] shuffle(List) print(List) Curated by Curated by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-58-2048.jpg)


![Similarly, a binary file can be opened by appending ‘b’ with them as follows: To append the content in the files, we can use the append mode (a): For text files, the mode would be ‘at’ For binary files, it would be ‘ab’ To remove duplicate elements from the list we use the set() function. Consider the below example: read-only mode (rb) write-only mode (wb) read–write mode (rwb) demo_list=[5,4,4,6,8,12,12,1,5] unique_list = list(set(demo_list)) output:[1,5,6,8,12] How will you remove duplicate elements from a list? Question 74 Curated by Curated by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-63-2048.jpg)
![How can you generate random numbers in Python? What is slicing in Python? Question Question 77 78 This is achieved with importing the random module,it is the module that is used to generate random numbers. Syntax: Slicing is a process used to select a range of elements from sequence data type like list, string and tuple. Slicing is beneficial and easy to extract out the elements. It requires a : (colon) which separates the start index and end index of the field. All the data sequence types List or tuple allows us to use slicing to get the needed elements. Although we can get elements by specifying an index, we get only a single element whereas using slicing we can get a group or appropriate range of needed elements. Syntax - List_name[start:stop] import random random.random # returns the floating point random number between the range of [0,1]. Curated by Curated by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theultimate80questions-250616053000-fd6f1d18/75/Python-Panache-Code-Like-a-Pro-Not-a-Programmer-65-2048.jpg)