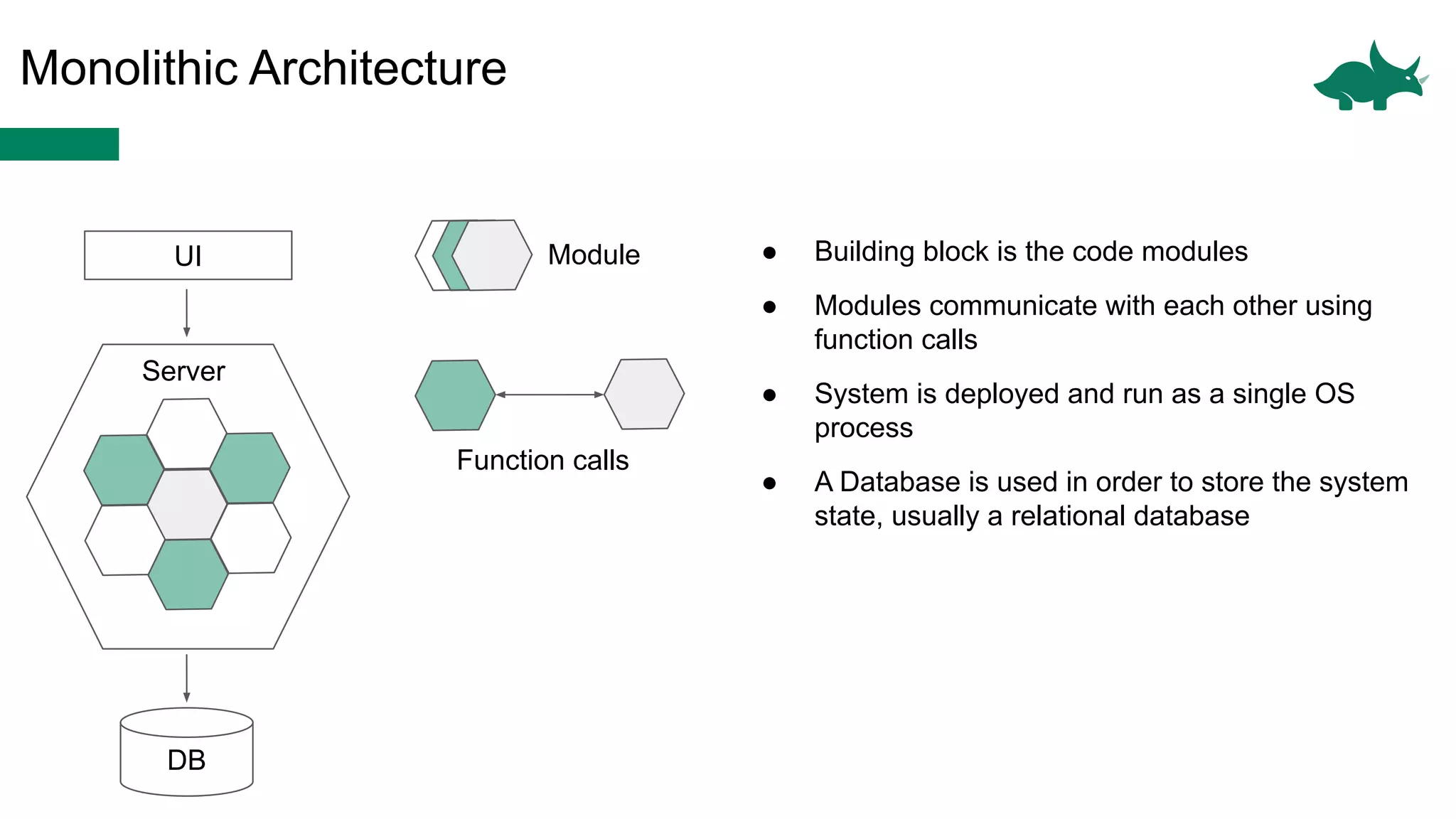
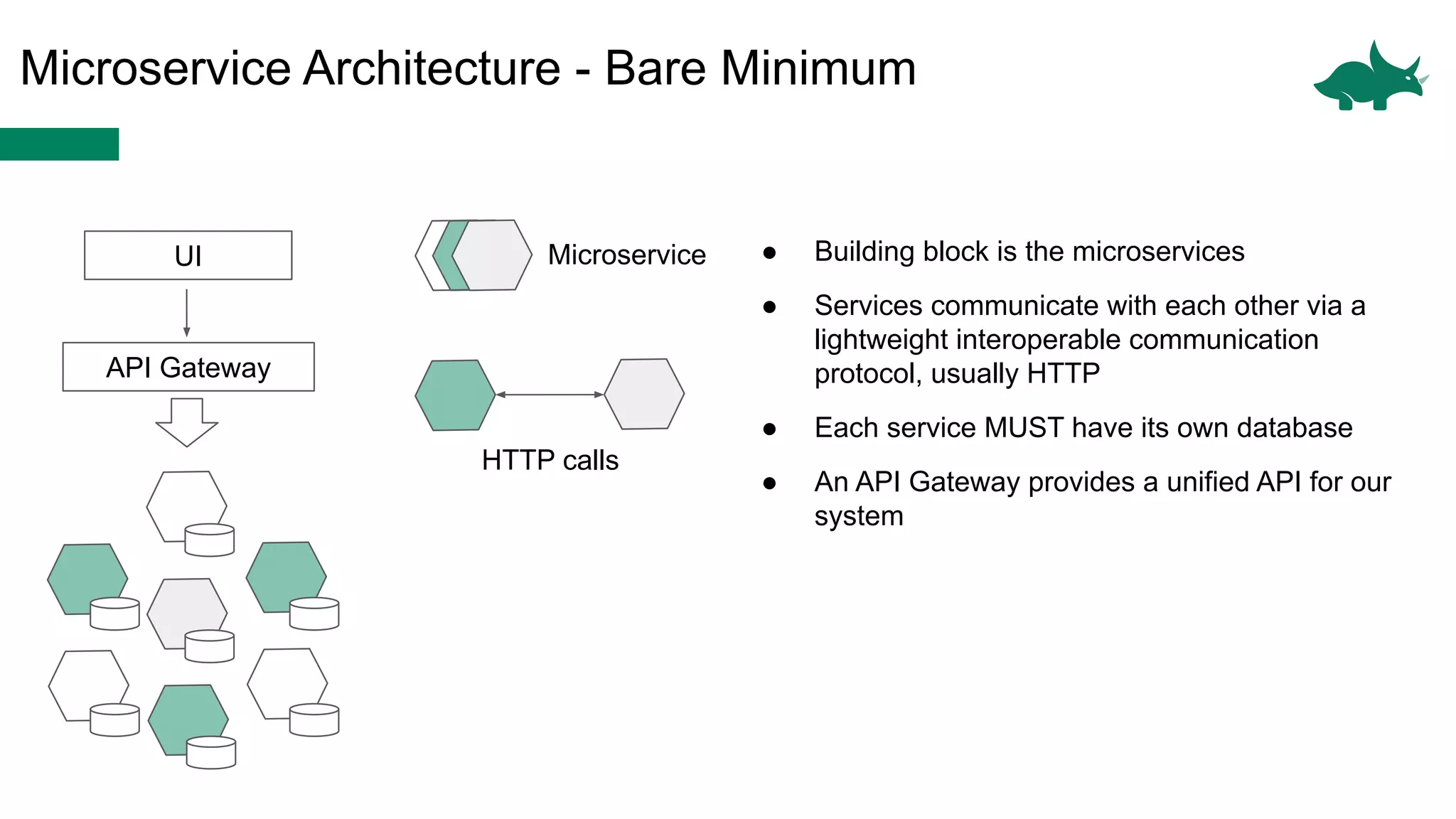
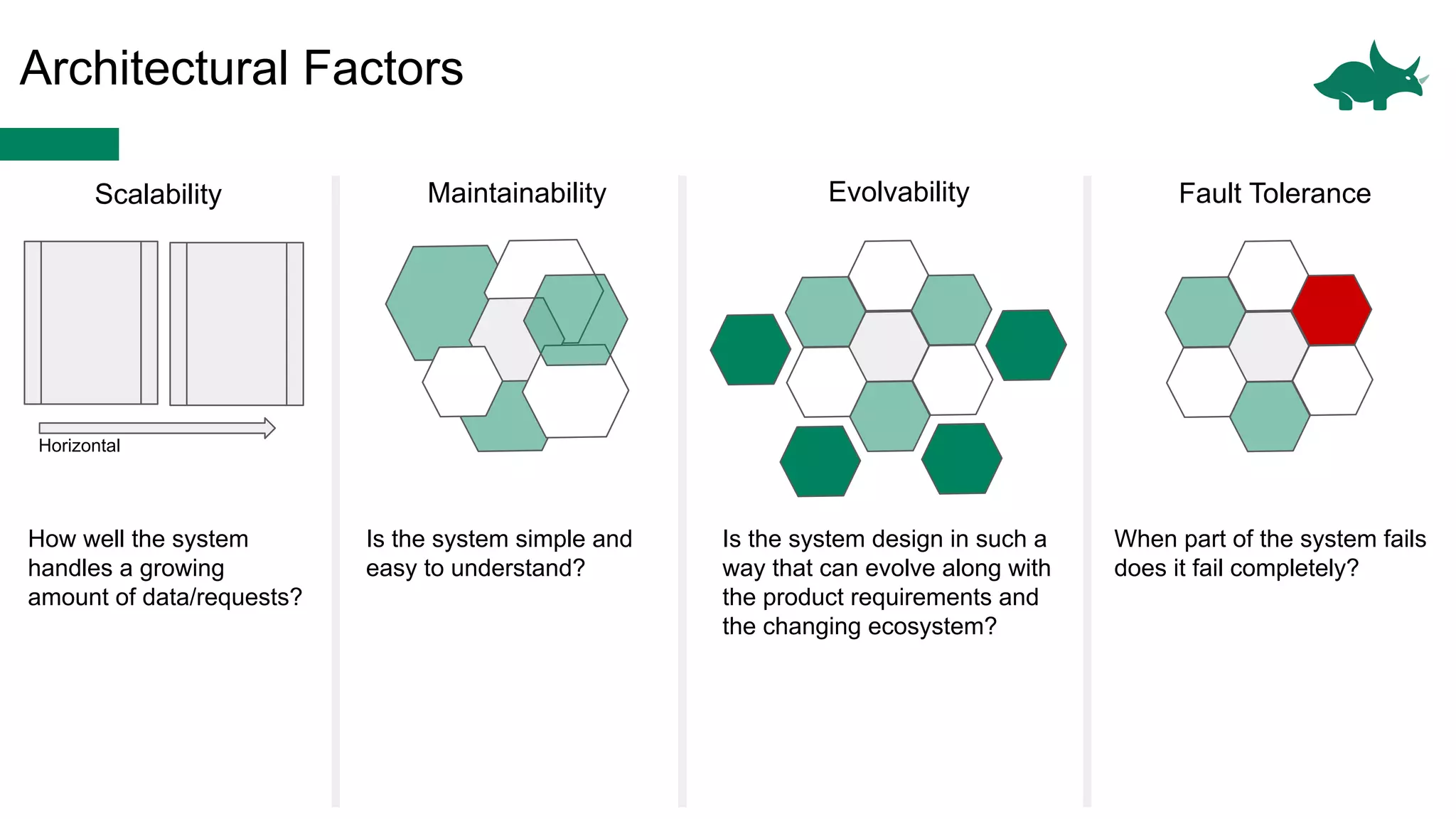
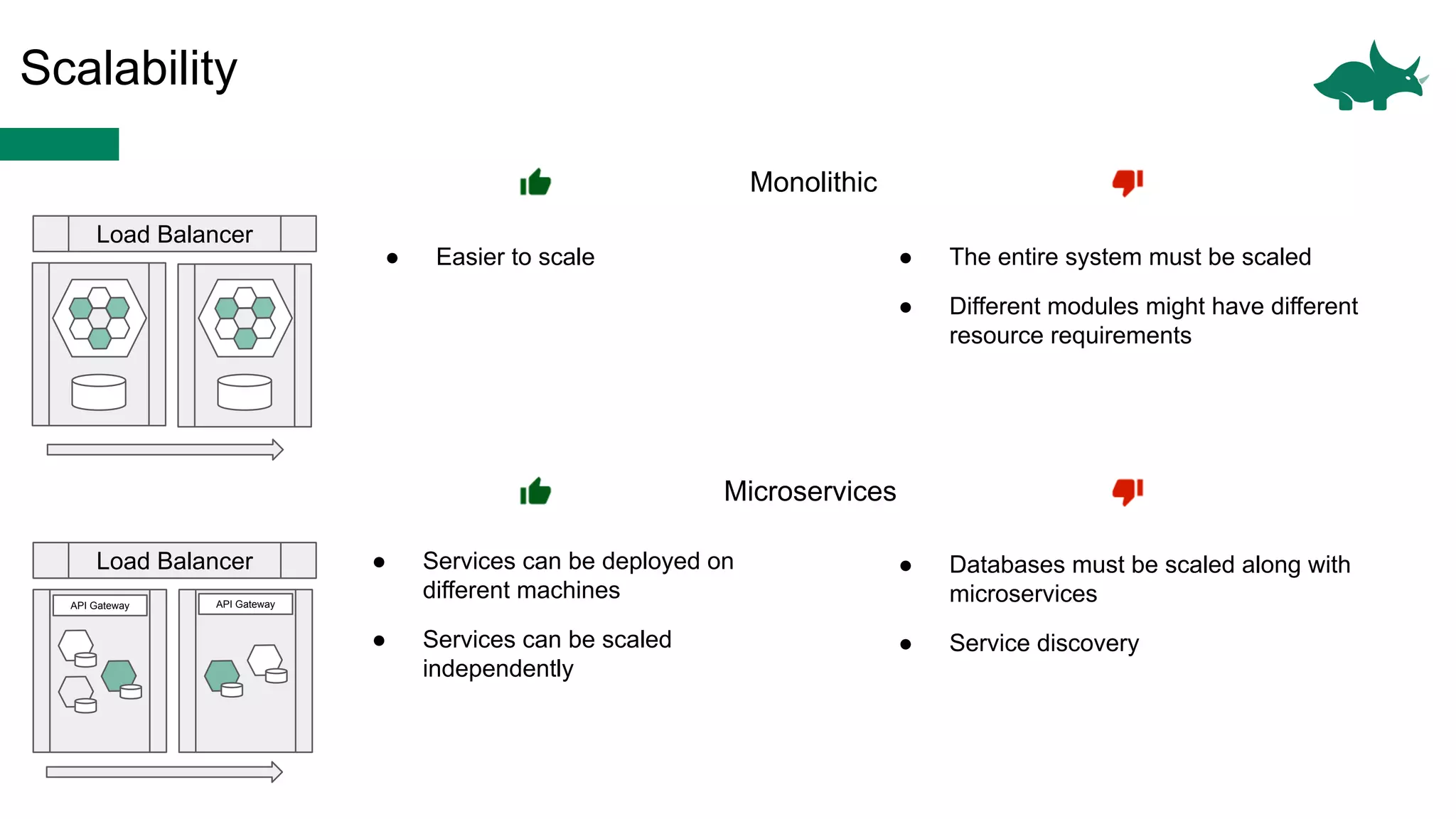
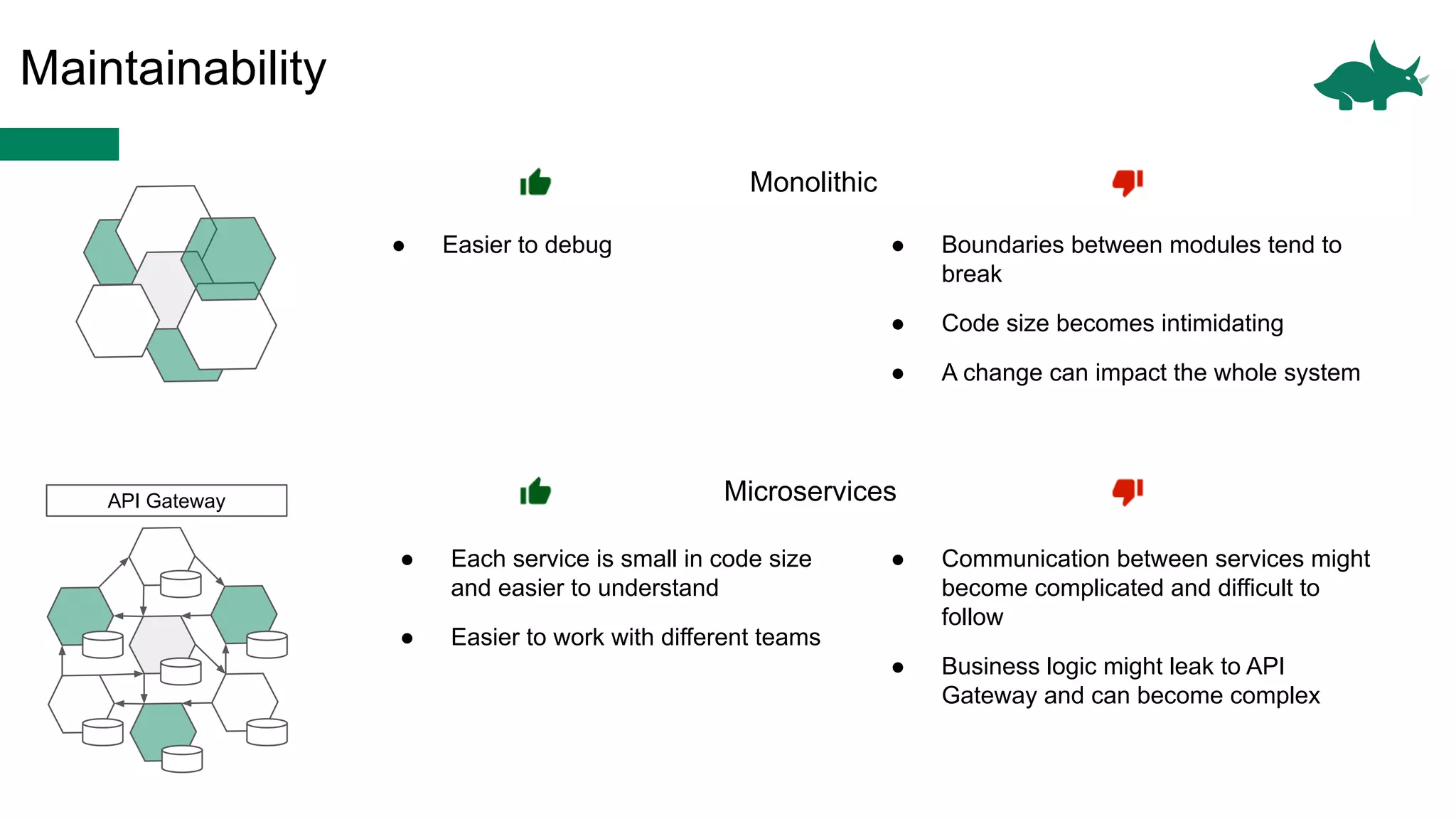
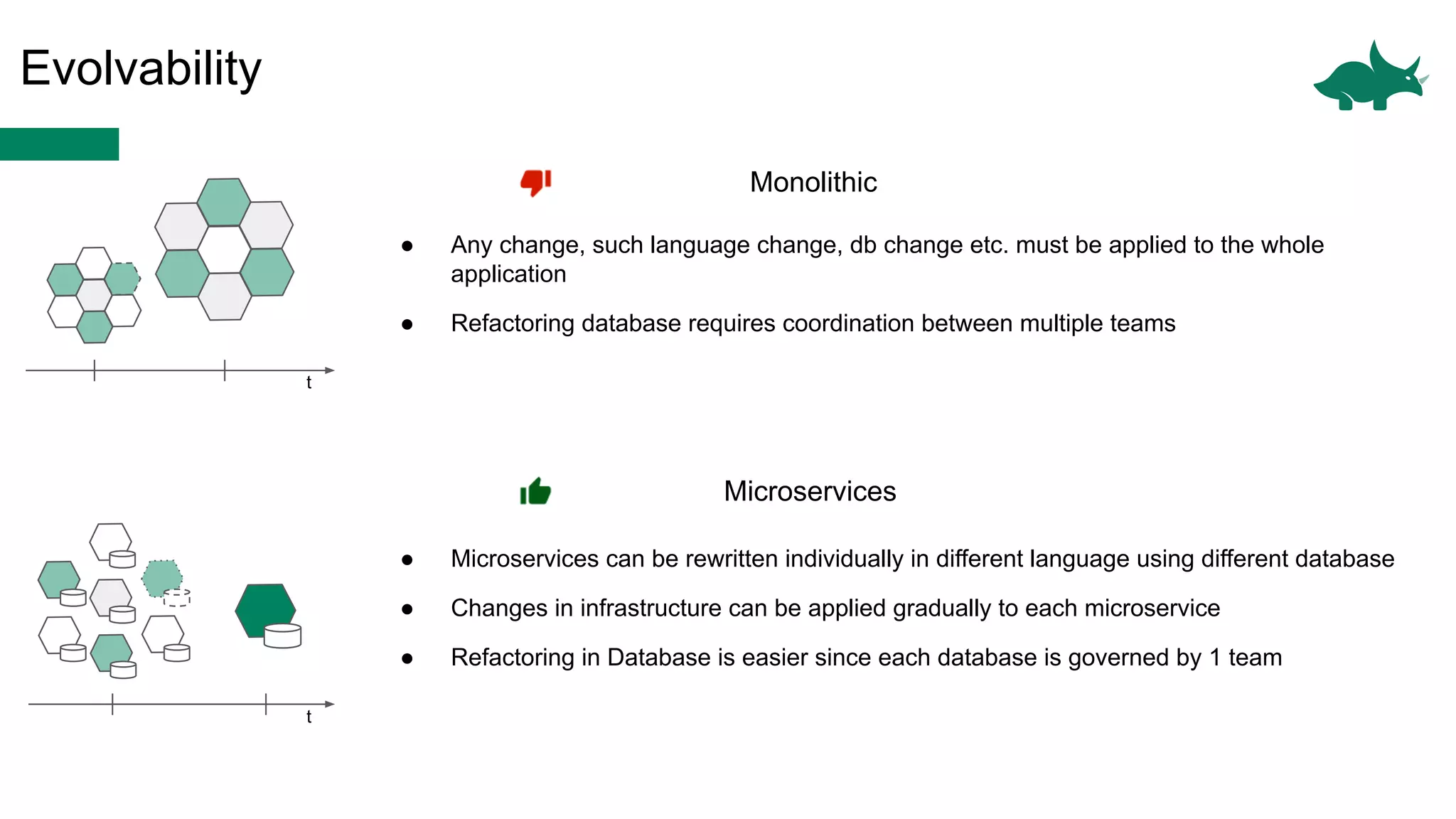
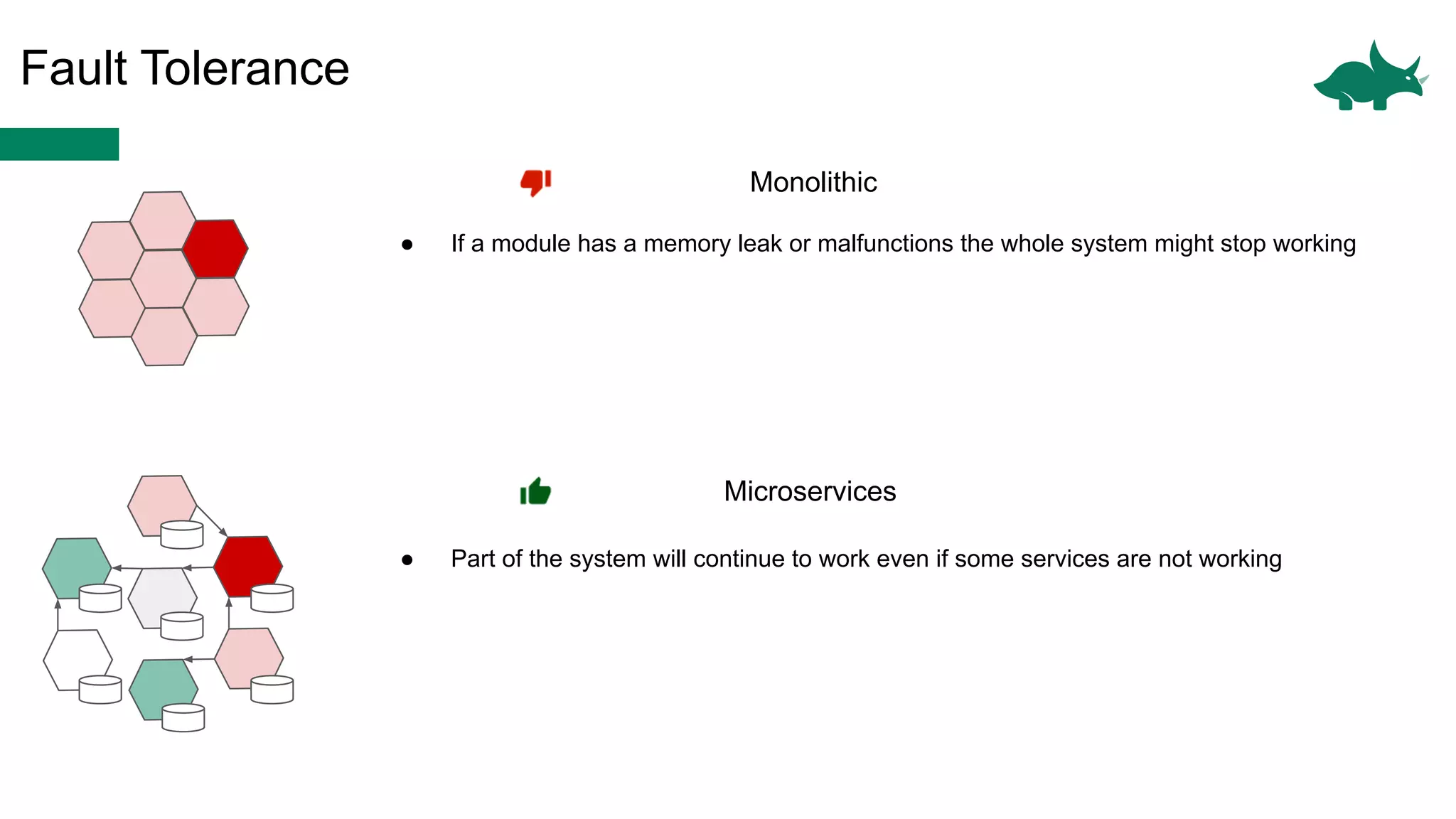
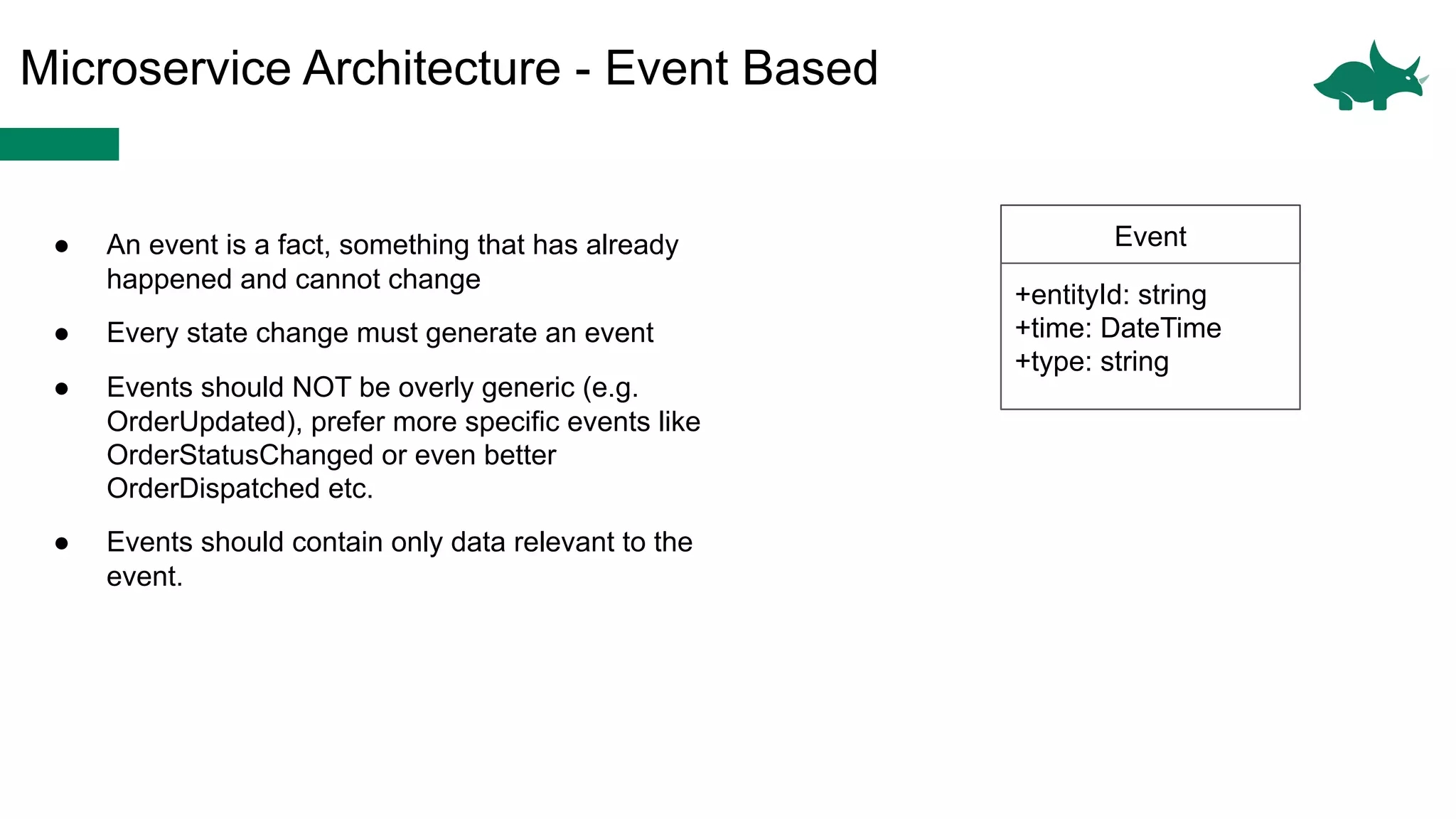
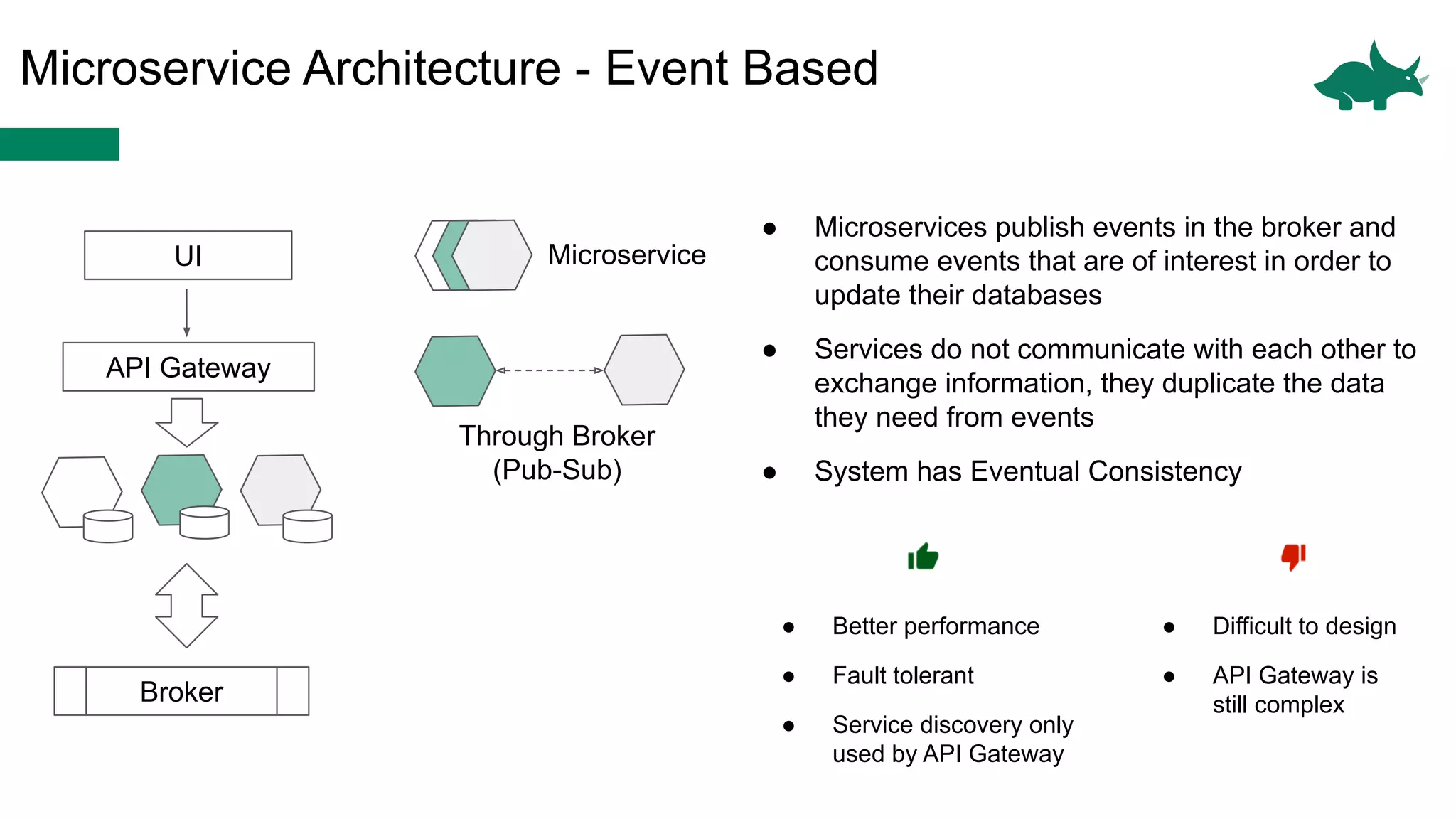
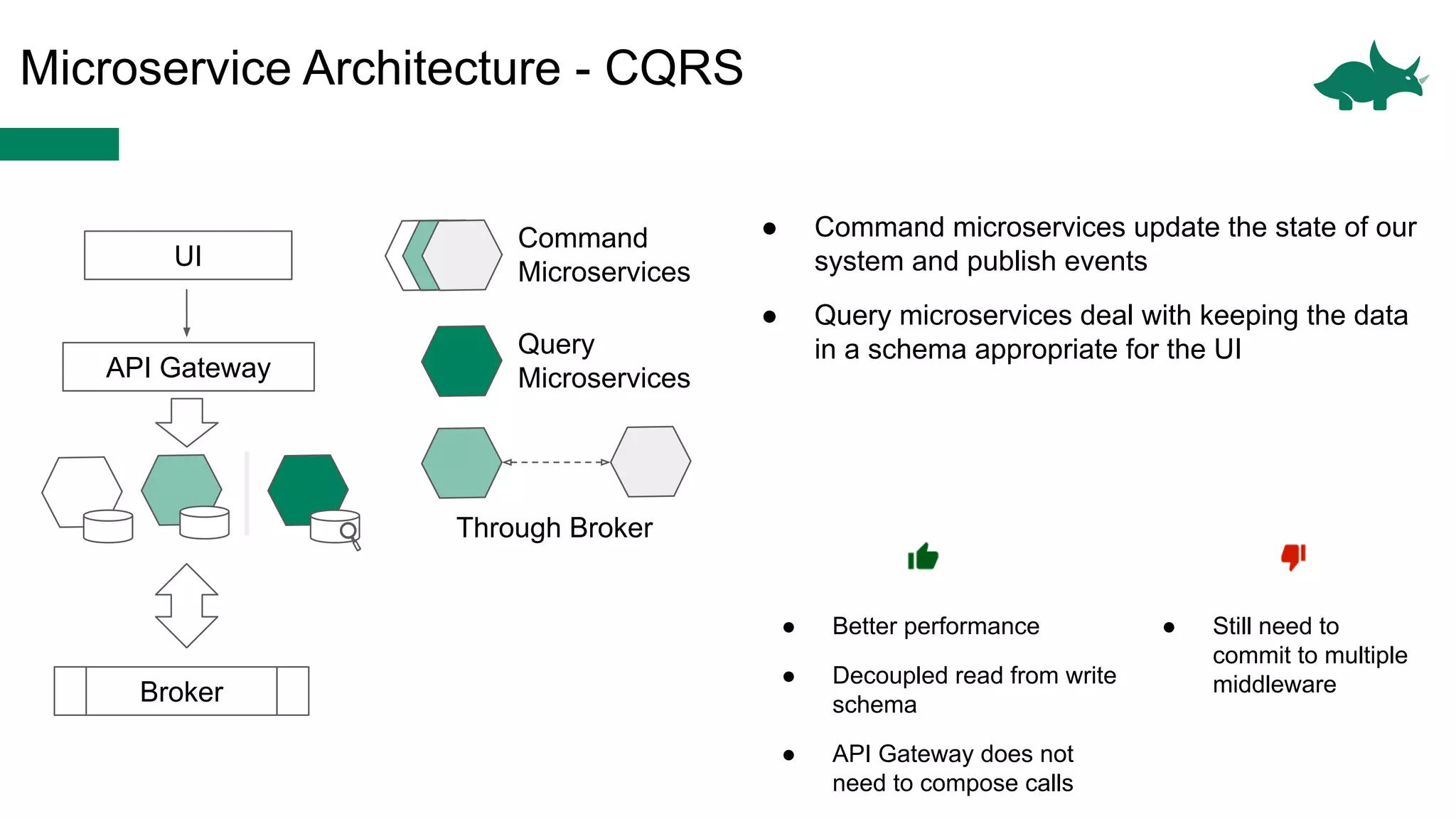
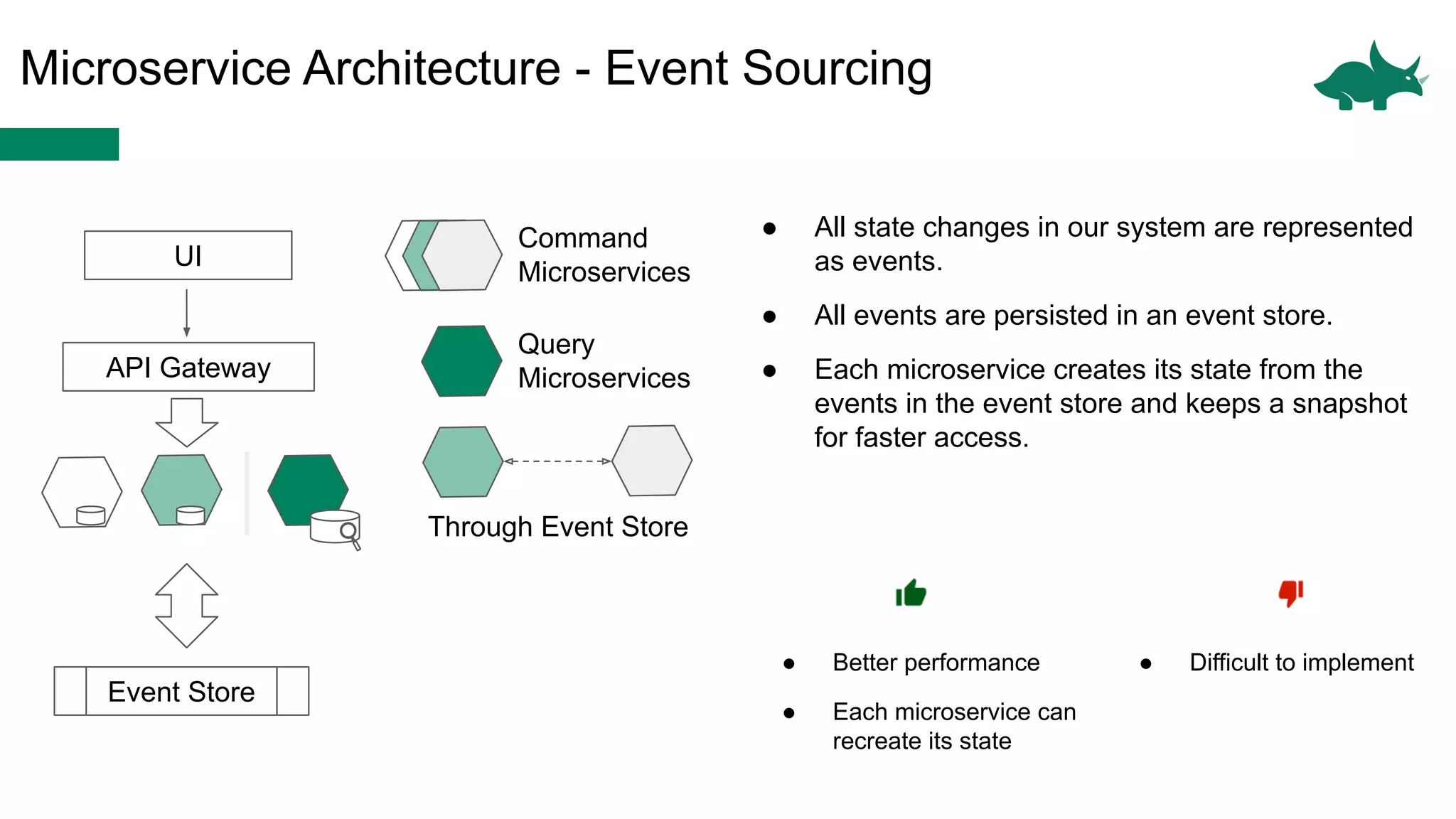
The document discusses the differences between monolithic and microservices architectures, focusing on their advantages and disadvantages. It emphasizes the benefits of event-based microservices, including improved scalability, maintainability, and fault tolerance through mechanisms like event sourcing and command-query responsibility segregation (CQRS). Key architectural factors such as scalability, maintainability, and evolvability are outlined, alongside considerations for system design and communication between services.