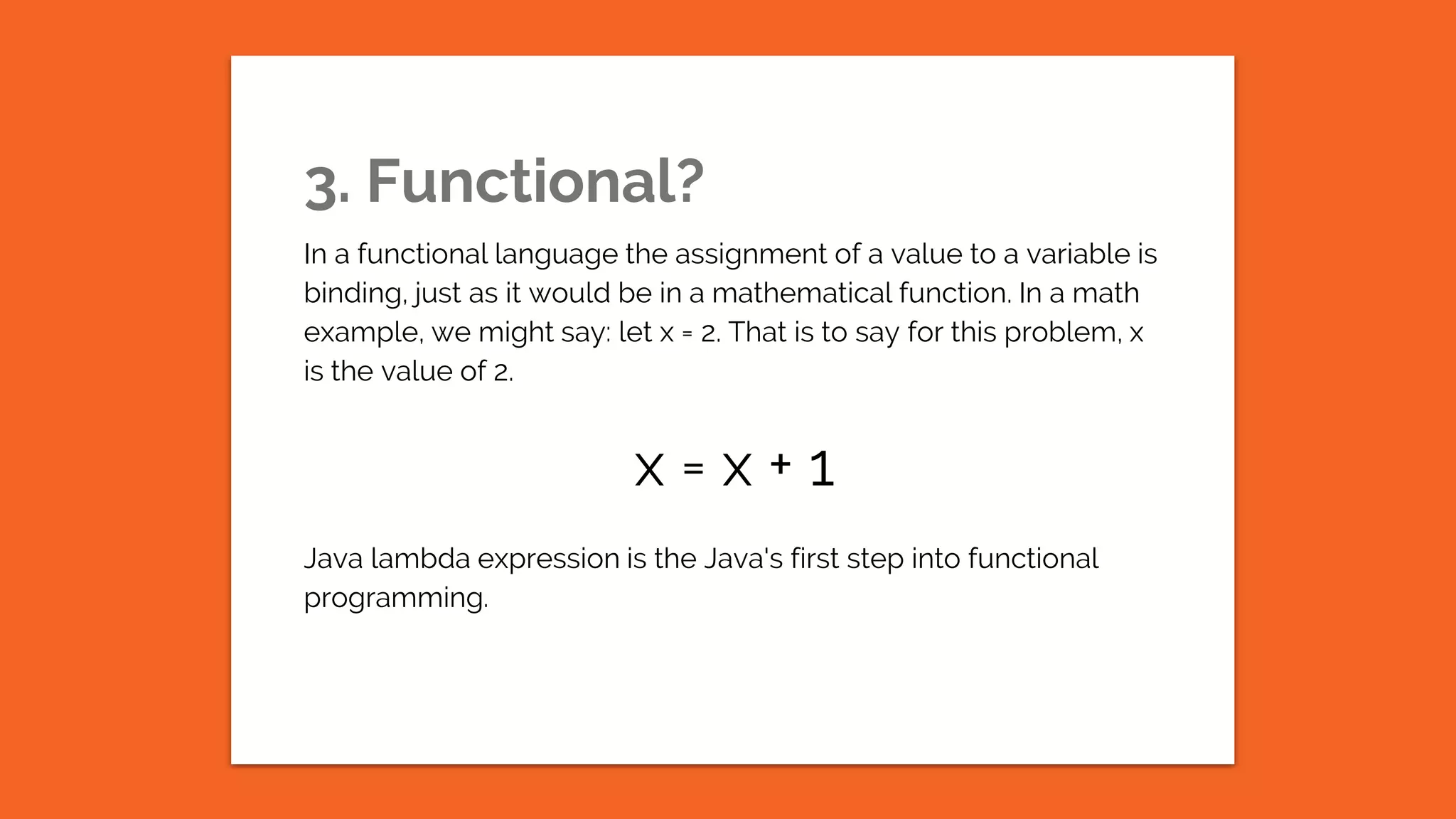
This document provides an overview of the Erlang programming language. It discusses that Erlang is a general purpose, concurrent, functional programming language developed at Ericsson for building distributed, fault-tolerant systems. It notes some of Erlang's key uses in telecommunications, banking, messaging, and e-commerce where high-availability is required. The document also summarizes that Erlang uses processes instead of threads to enable concurrency, and that it relies on recursion rather than loops for iteration due to its functional nature.









![Hello World!! % hello world program -module(hello_world). -export([hello/0]). hello() -> io:fwrite("Hello, world!n"). 1> c(hello_world). 2> hello_world:hello(). Hello, world! ok](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cslijbqrq4hl8akhughw-signature-a92a8a7b5521333e6b396479f88abdd79383bf86f8b6175abb3822b9ecf50879-poli-180930185319/75/Introduction-to-Erlang-Programming-Language-11-2048.jpg)

![Simple Example -module(recursive). -export([fac/1]). fac(N) when N == 0 -> 1; fac(N) when N > 0 -> N*fac(N-1). fac(0) -> 1; fac(N) when N > 0 -> N*fac(N-1).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cslijbqrq4hl8akhughw-signature-a92a8a7b5521333e6b396479f88abdd79383bf86f8b6175abb3822b9ecf50879-poli-180930185319/75/Introduction-to-Erlang-Programming-Language-13-2048.jpg)

