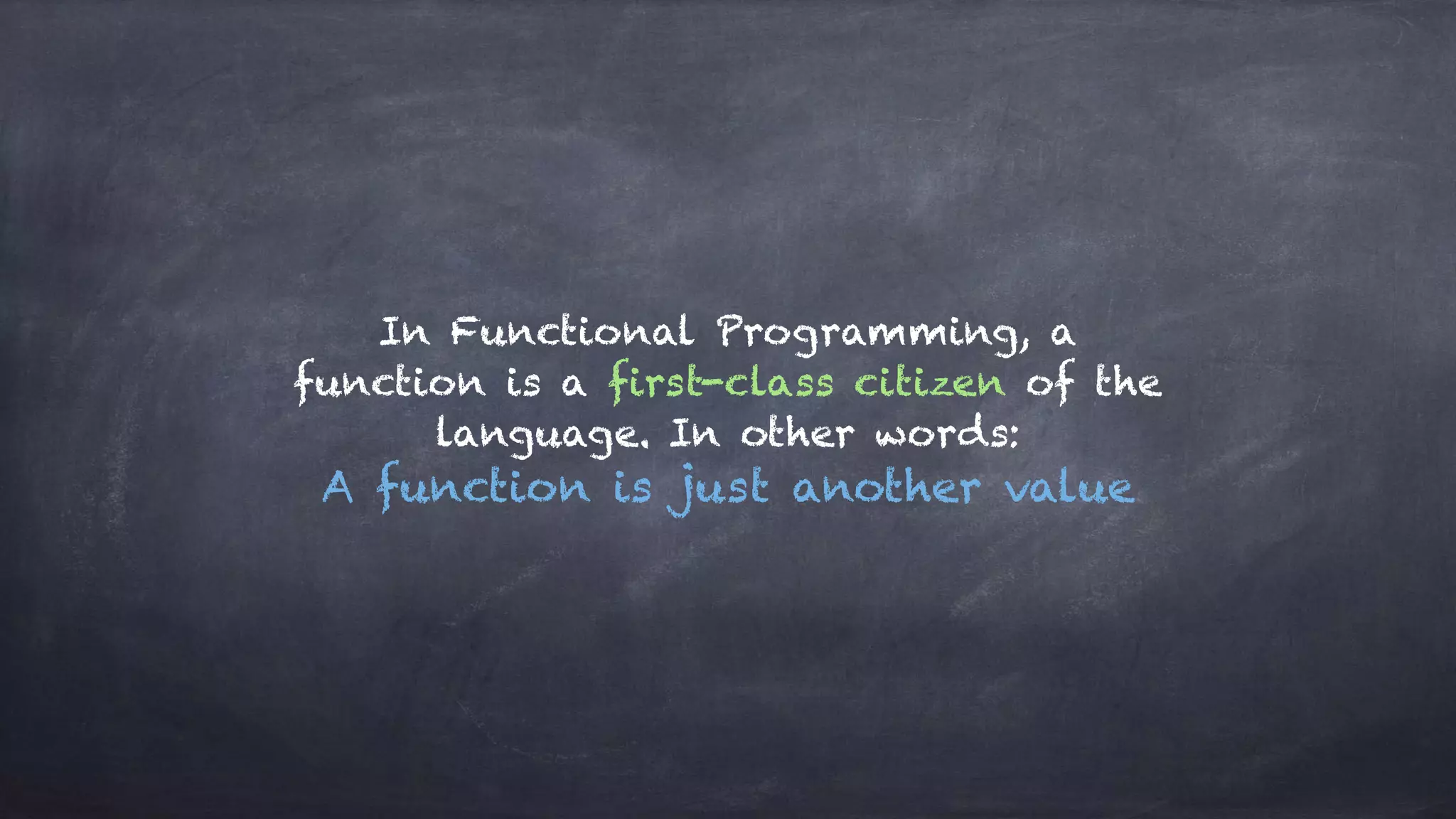
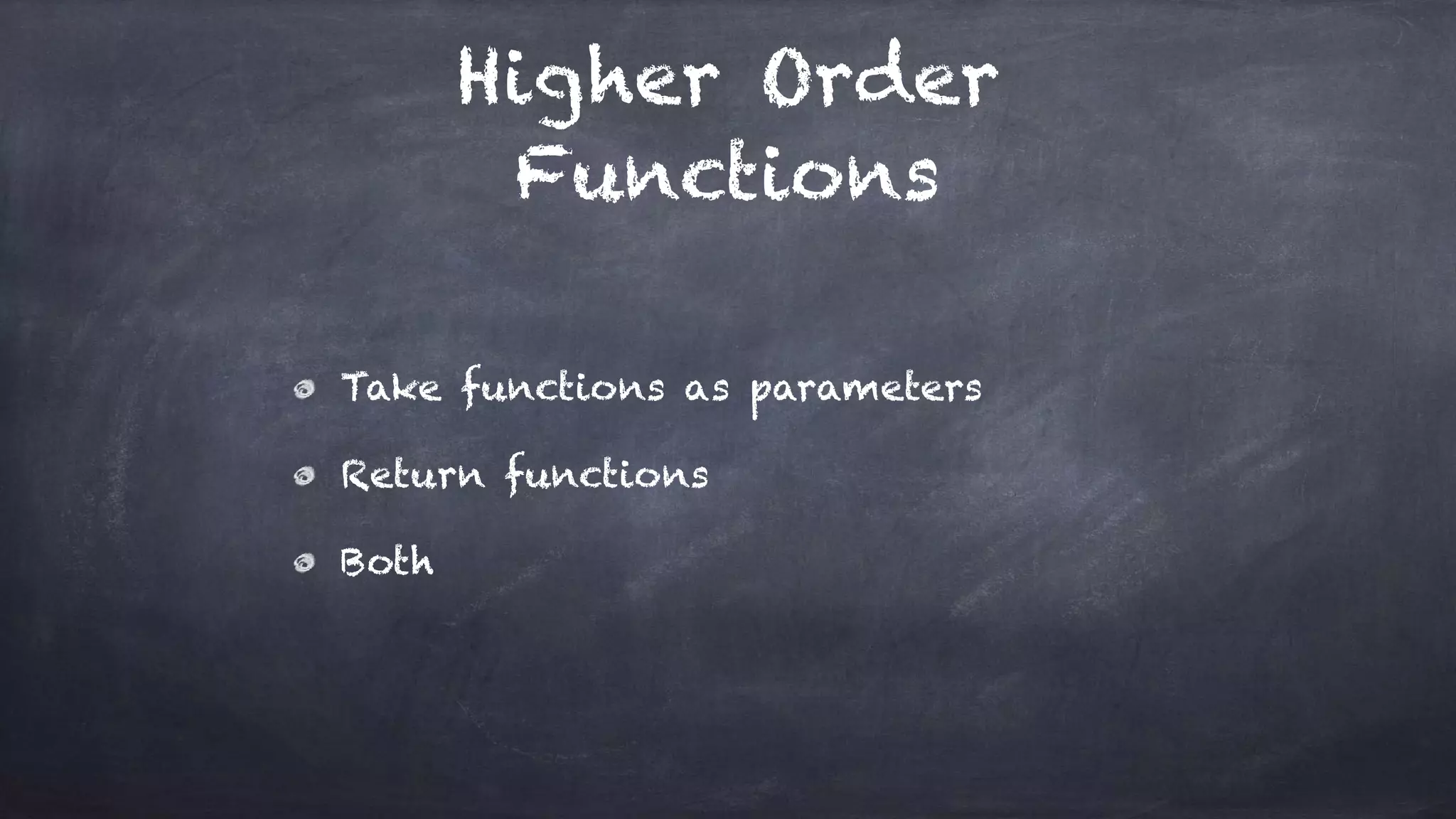
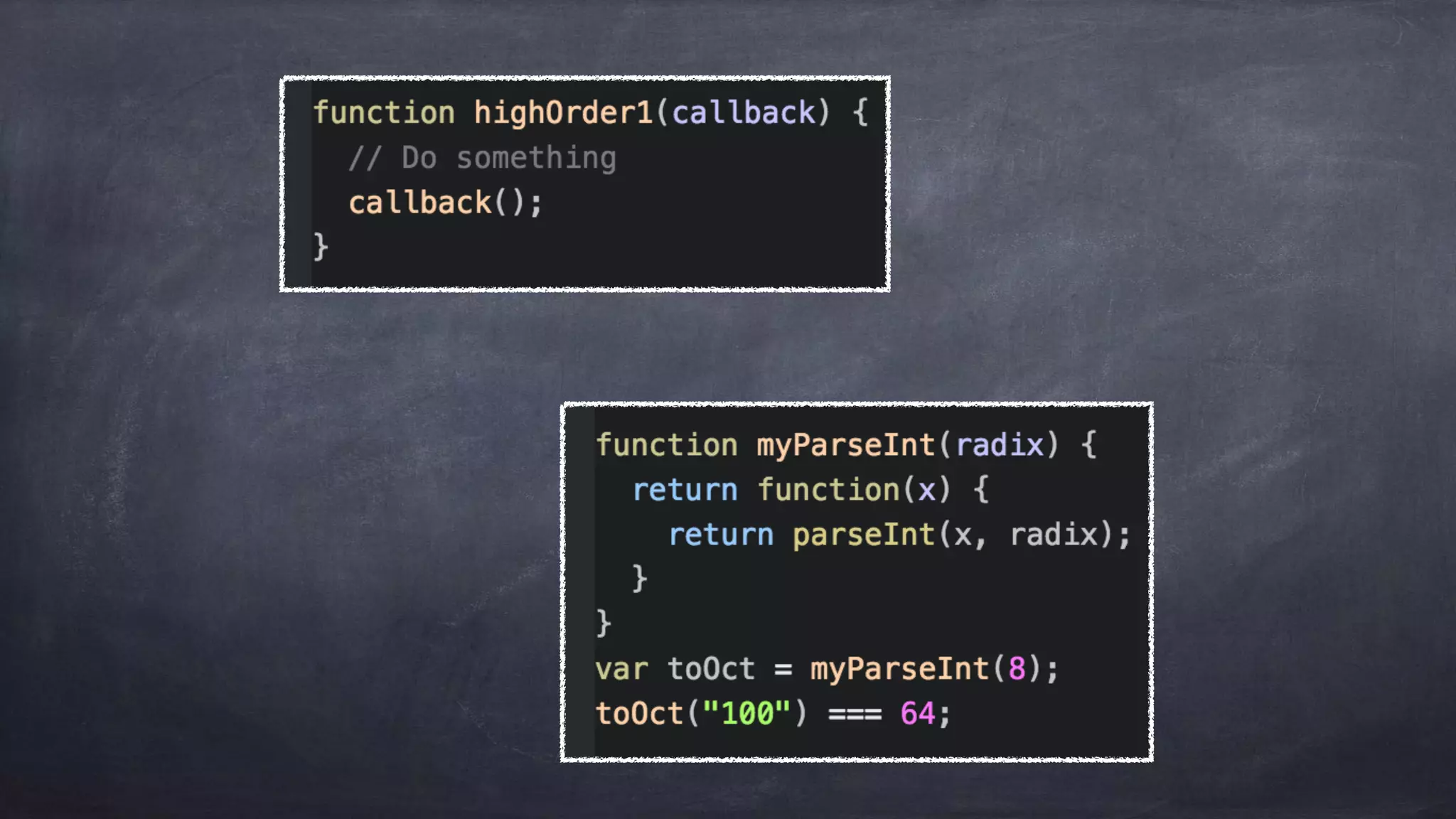
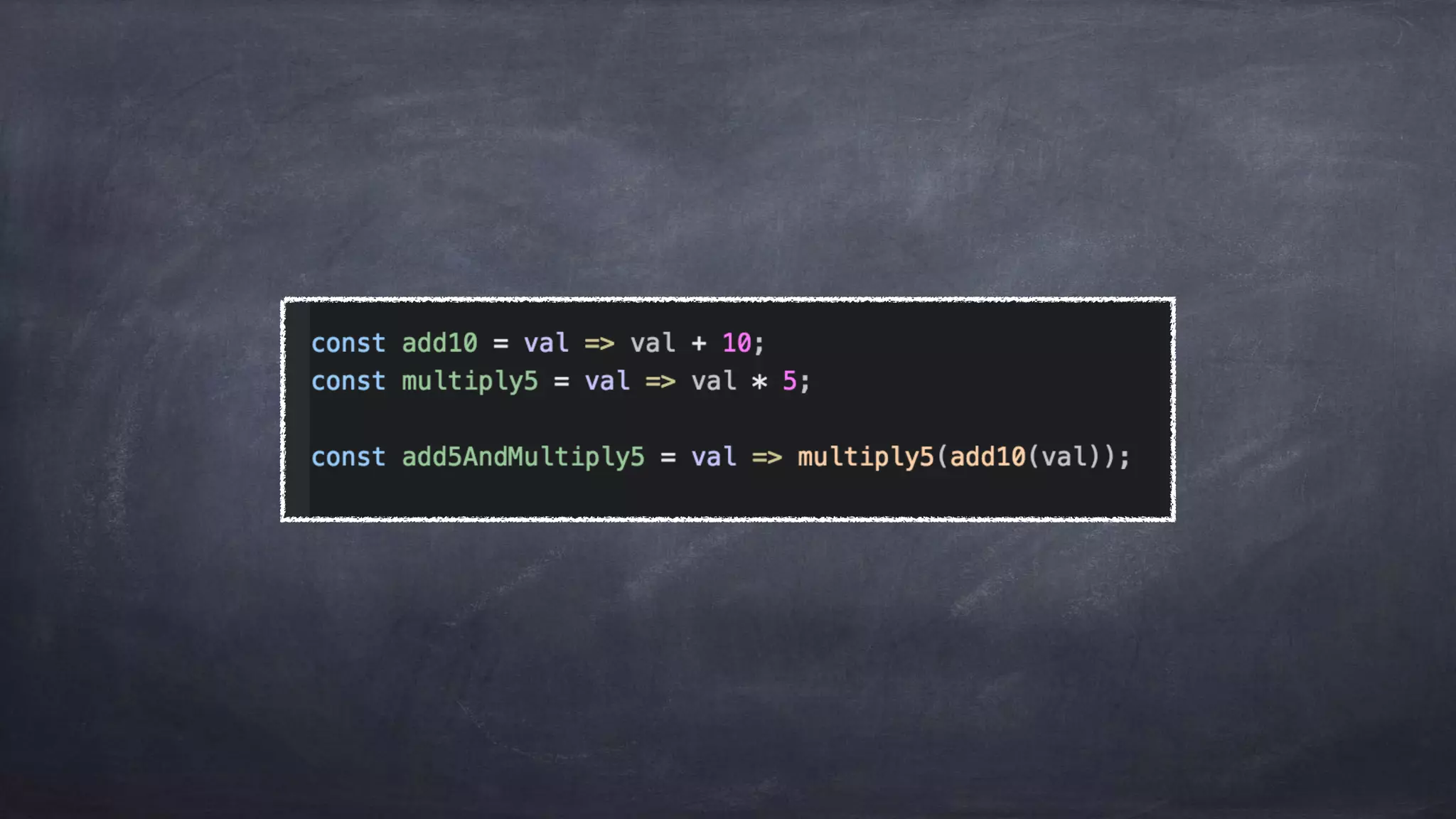
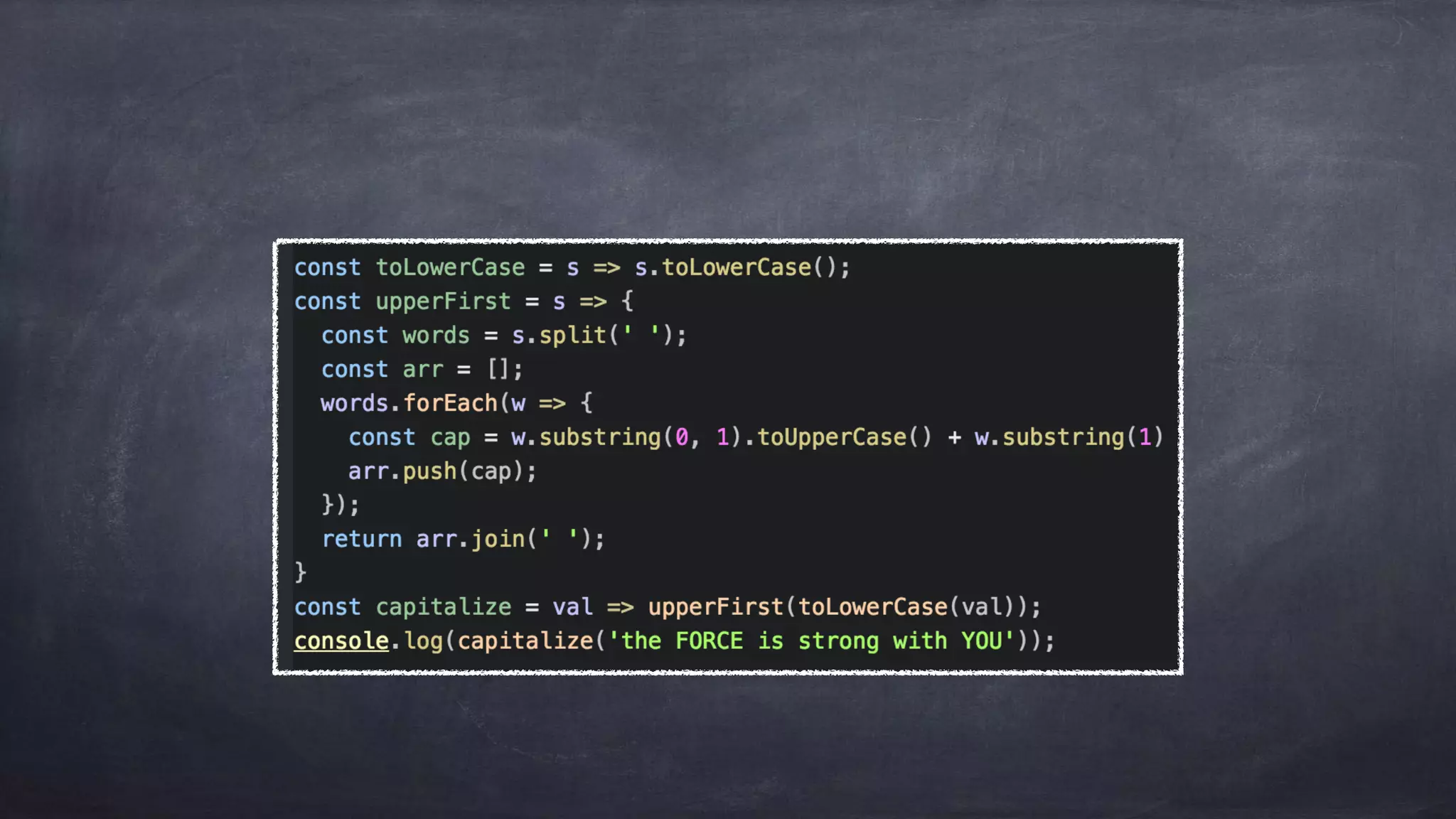
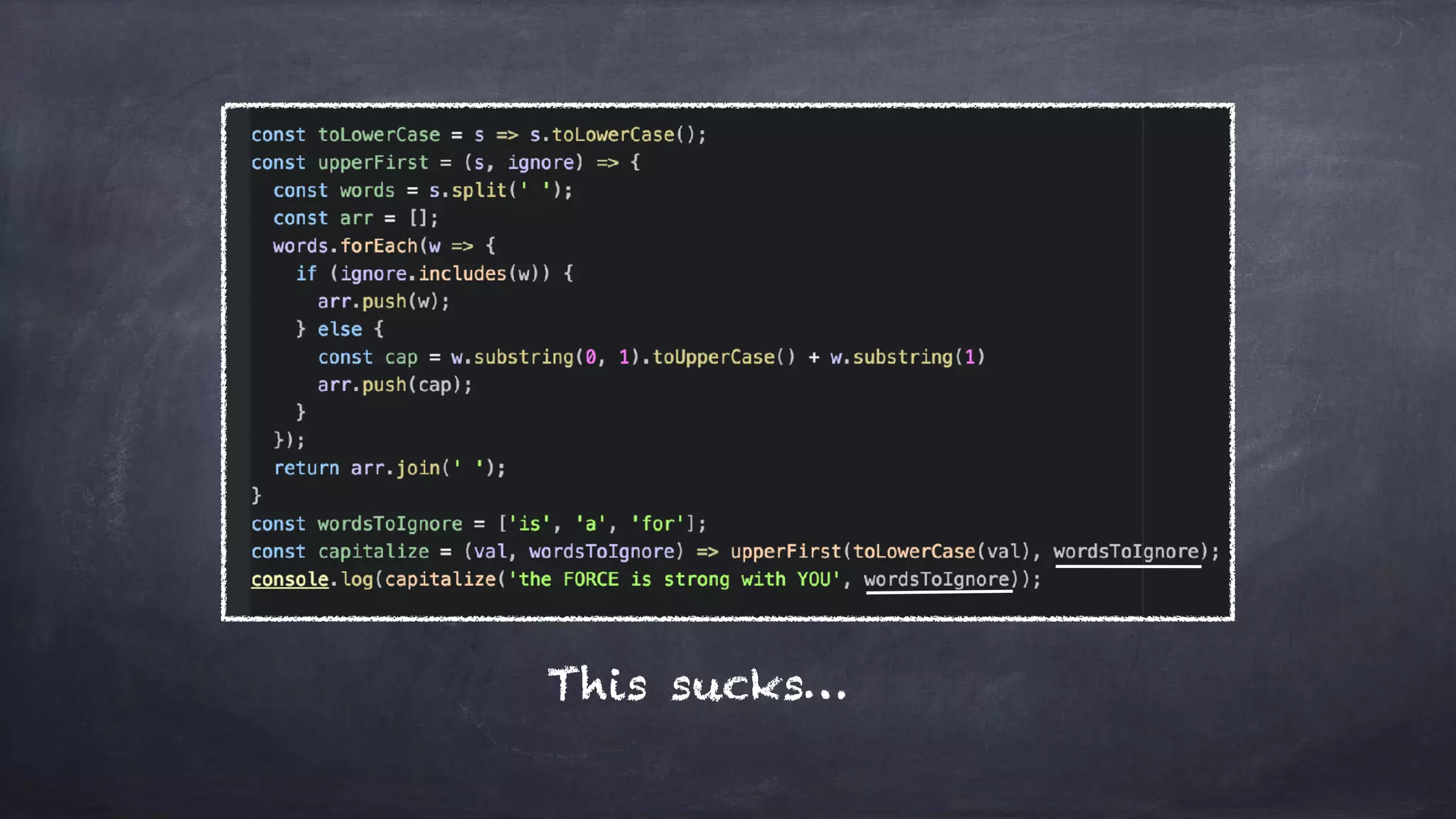
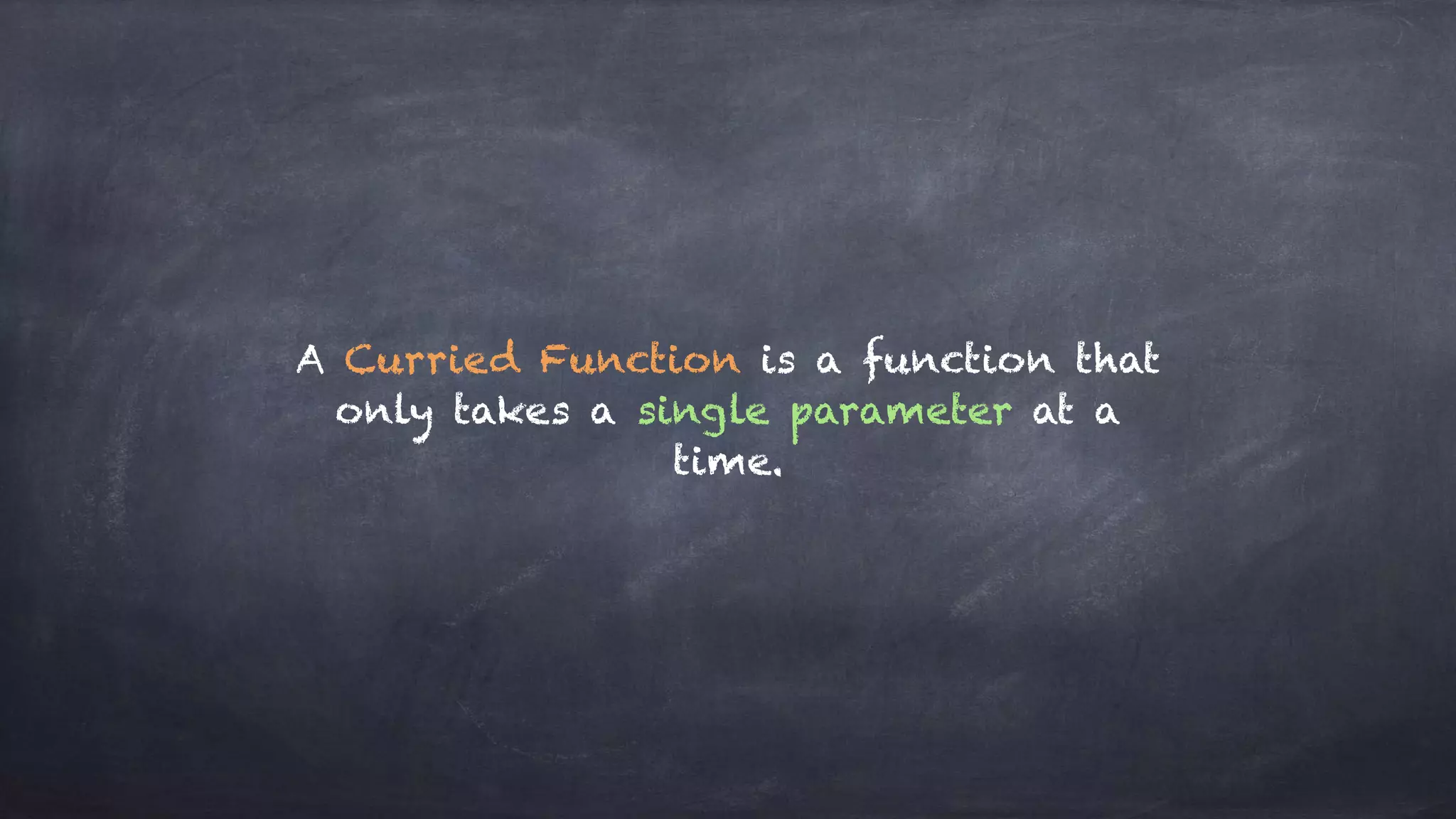
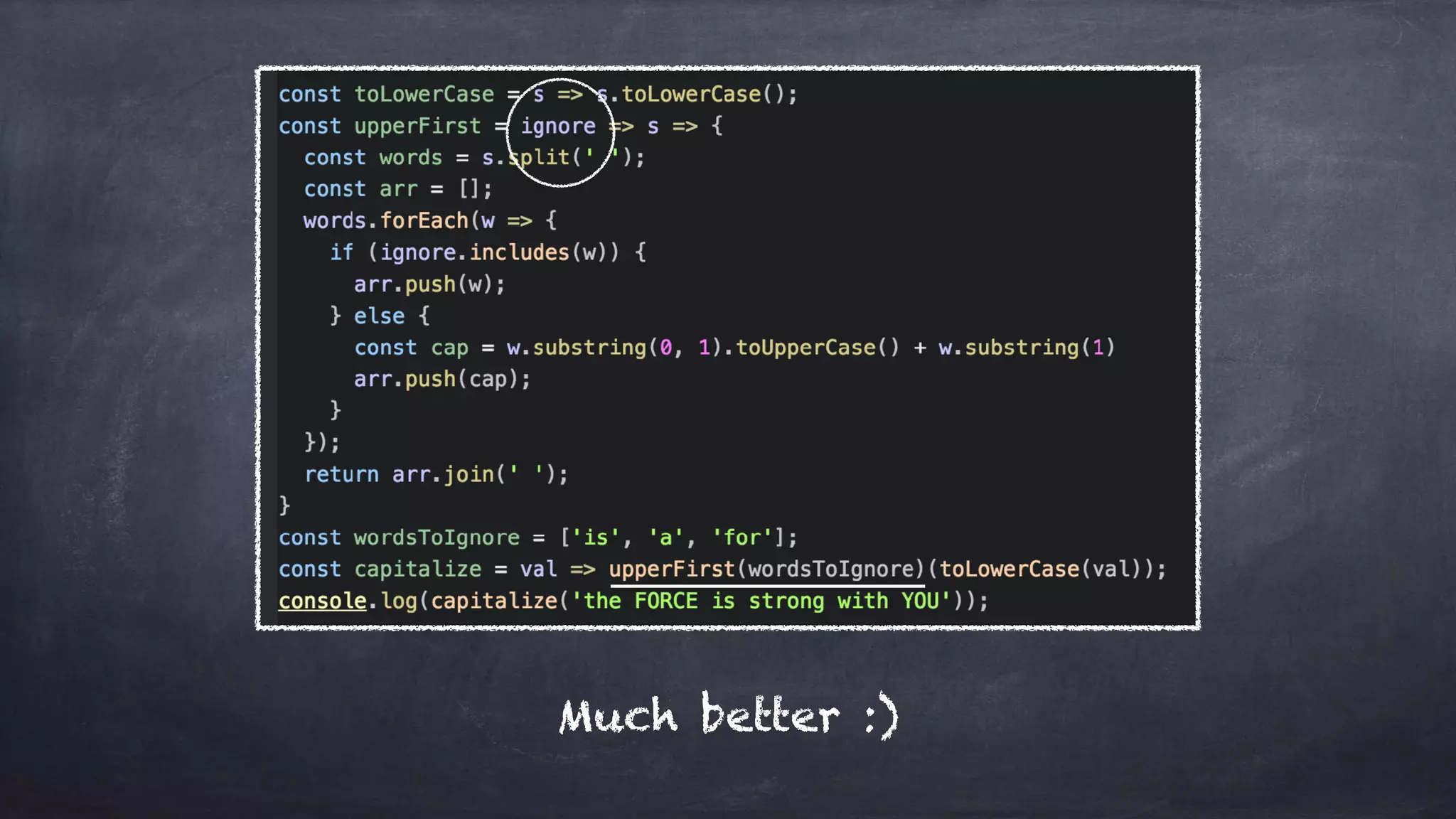
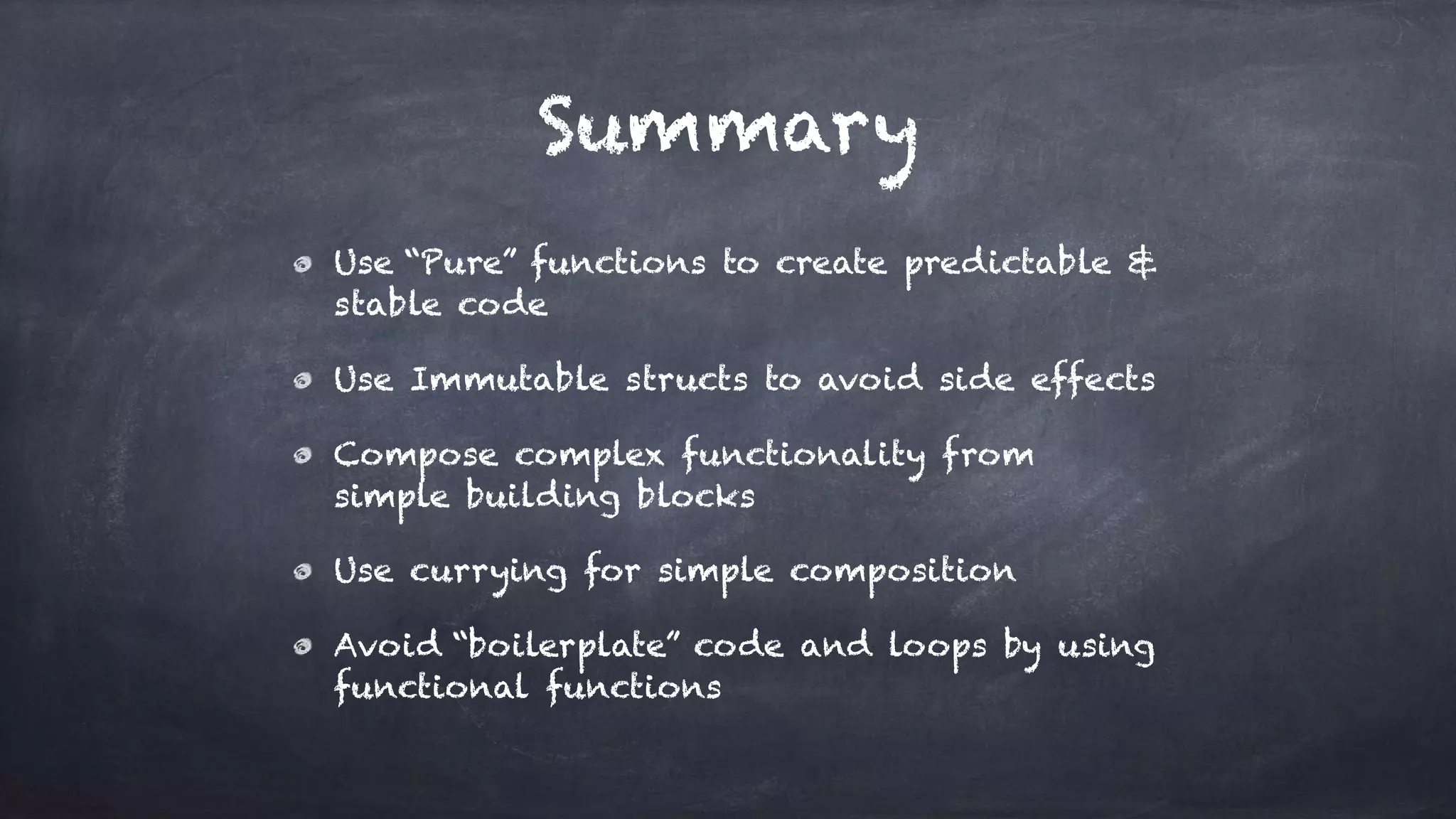
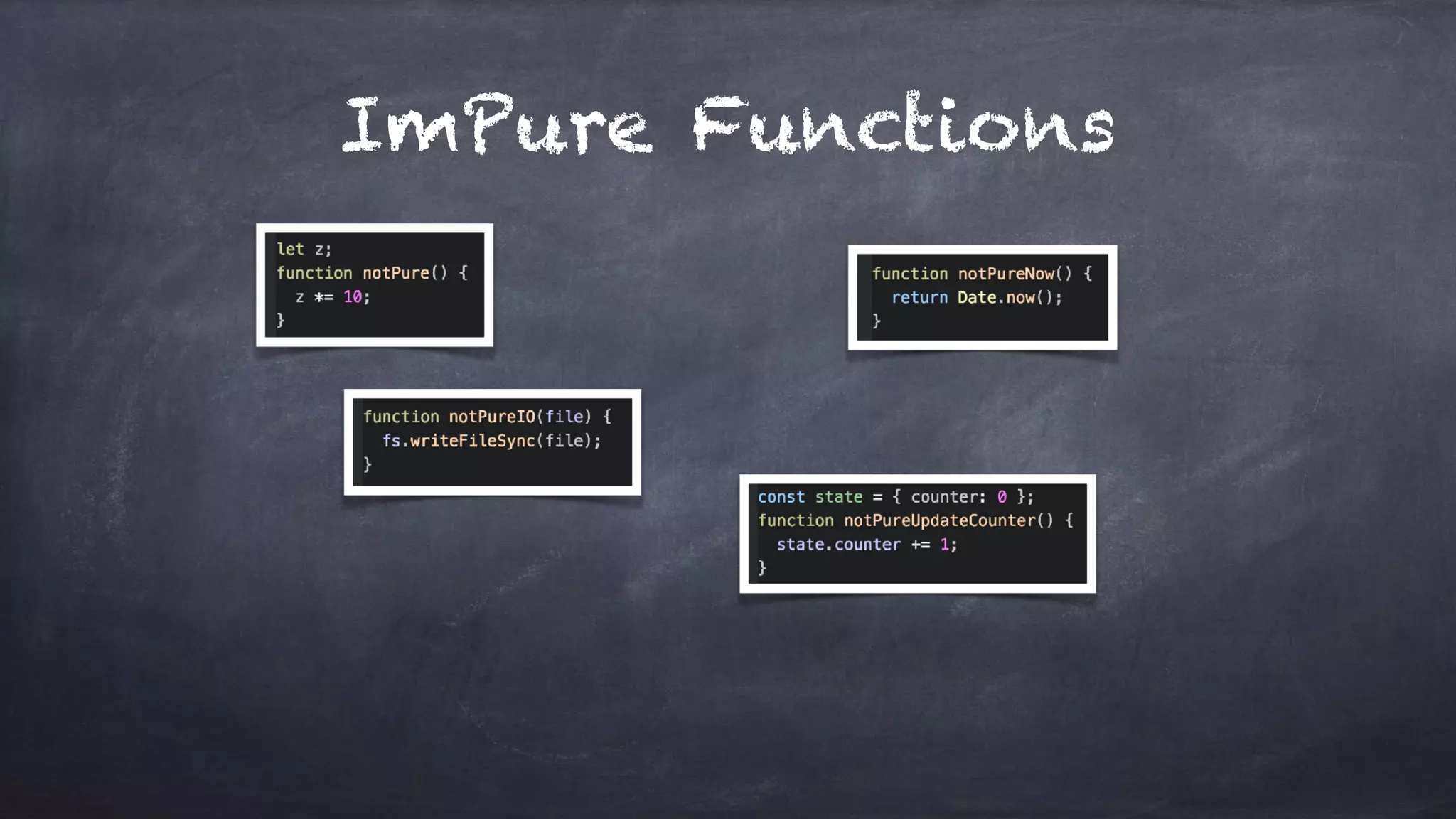
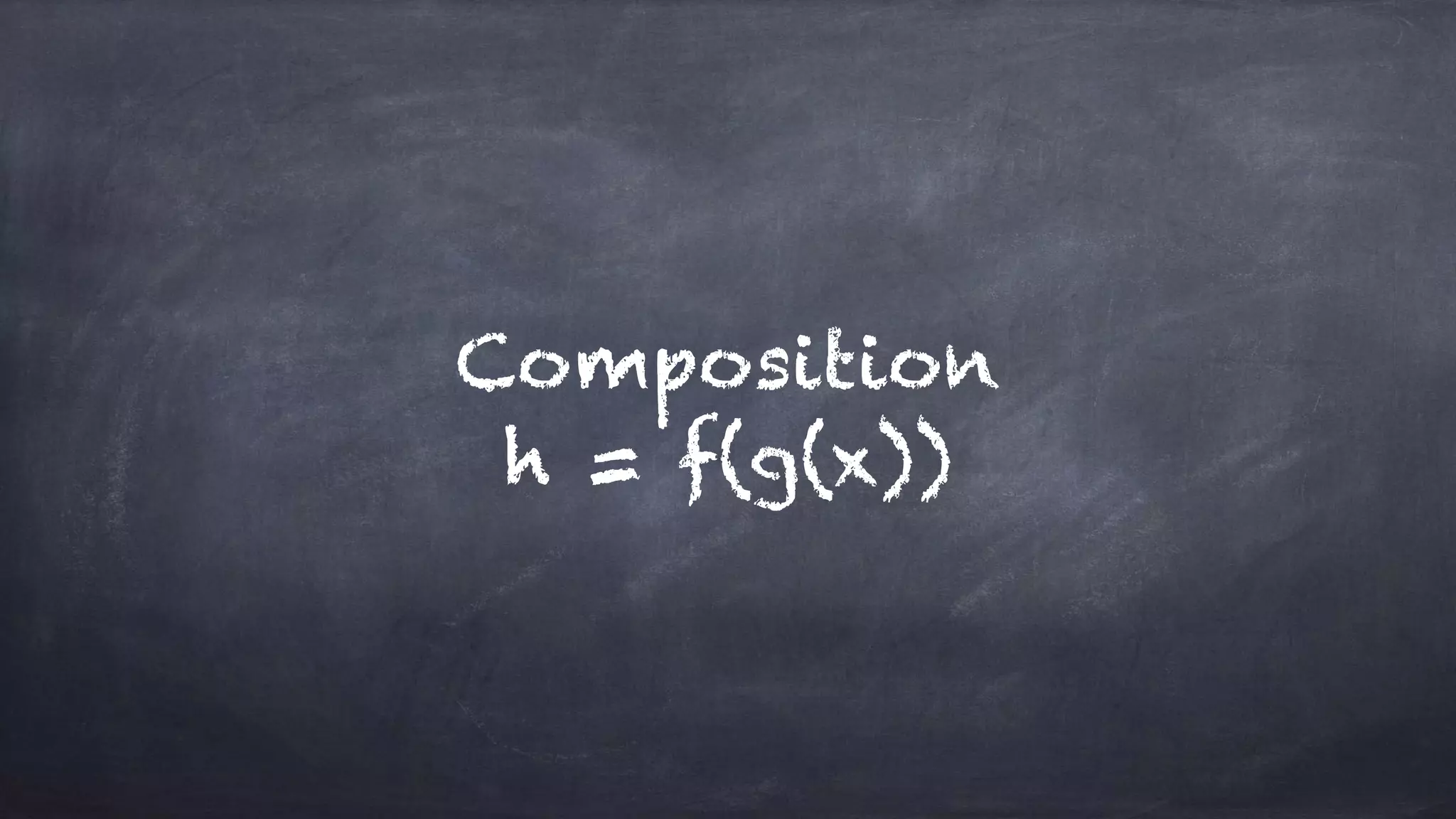The document discusses the limitations of object-oriented programming (OOP) and advocates for a shift to functional programming (FP) due to its mathematical approach, which enhances testability, maintainability, and concurrency handling. It highlights key FP principles such as purity, immutability, and higher-order functions, alongside demonstrating immutable patterns in languages like JavaScript. The document concludes by recommending the use of pure functions, immutable structures, and function composition to create stable and predictable code.














![Simple Immutable tweaks arr.push(val) —> [].concat(arr, val) obj[‘key’] = val —> Object.assign({key: val}, obj) ImmutableObj = Object.freeze(obj)
** Object assign is limited to shallow cloning and may produce strange outcomes.
see:
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/ JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Object/create](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtofunctionalprogramming2-170301075633/75/Intro-to-functional-programming-18-2048.jpg)