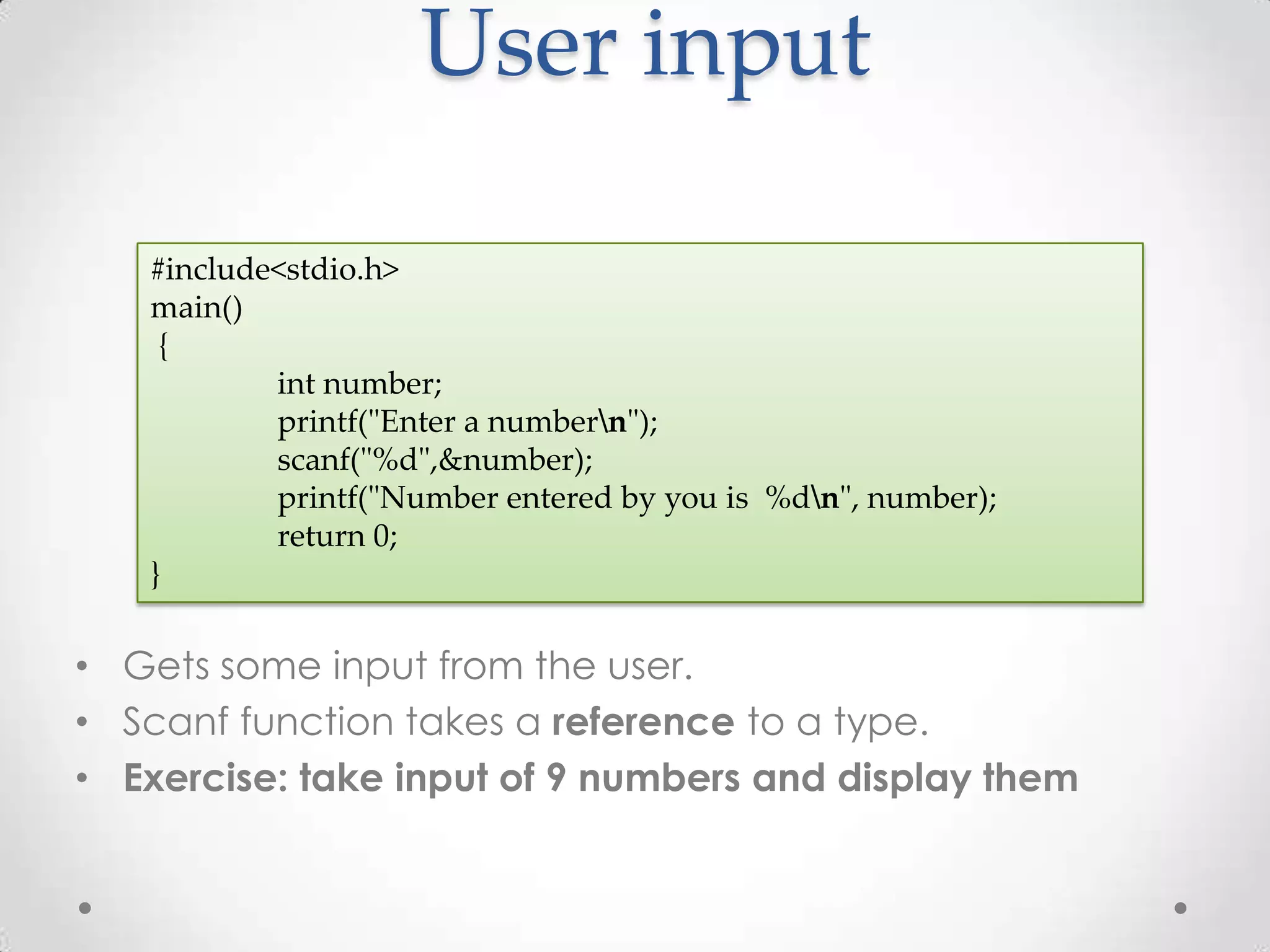
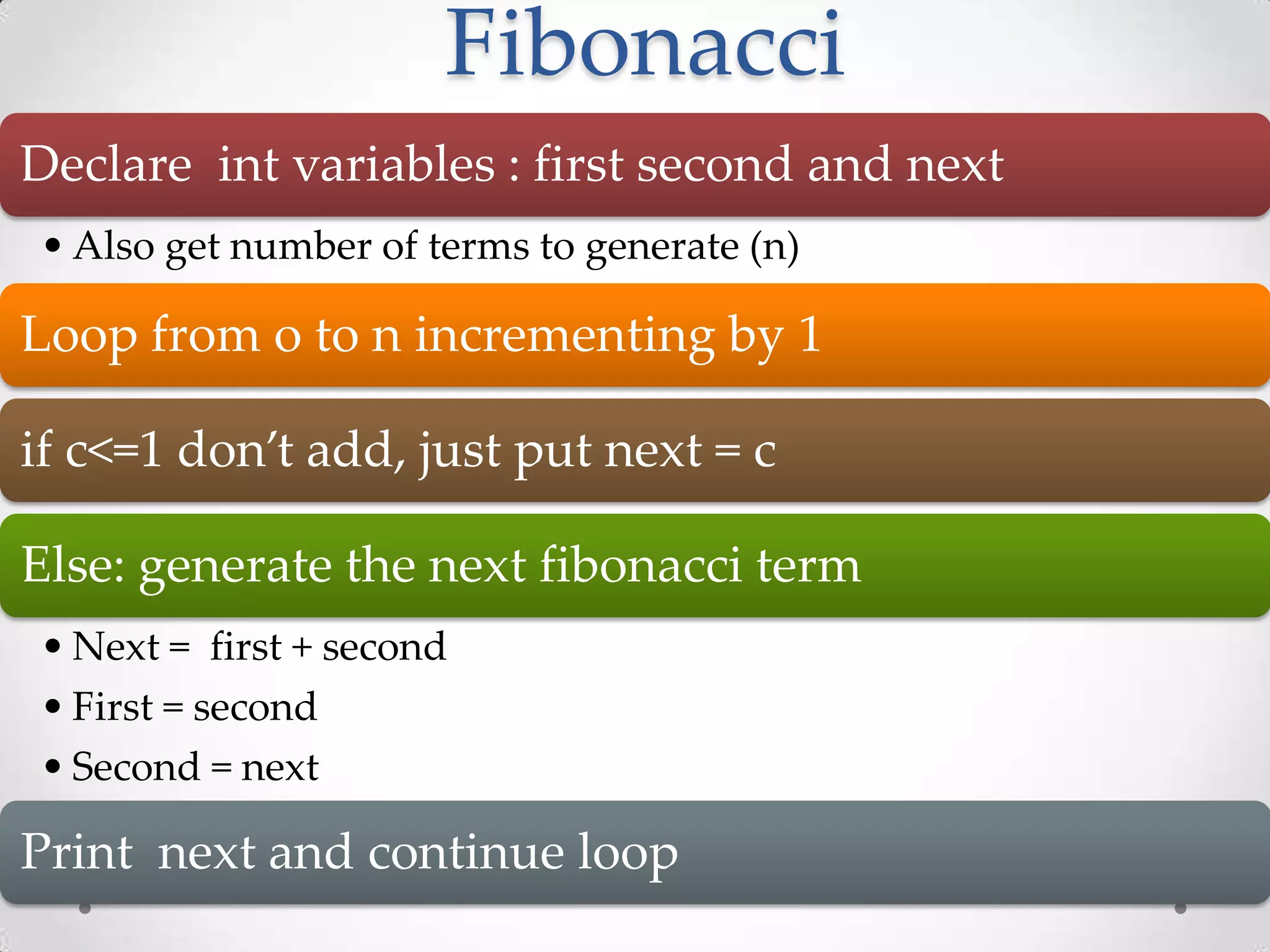
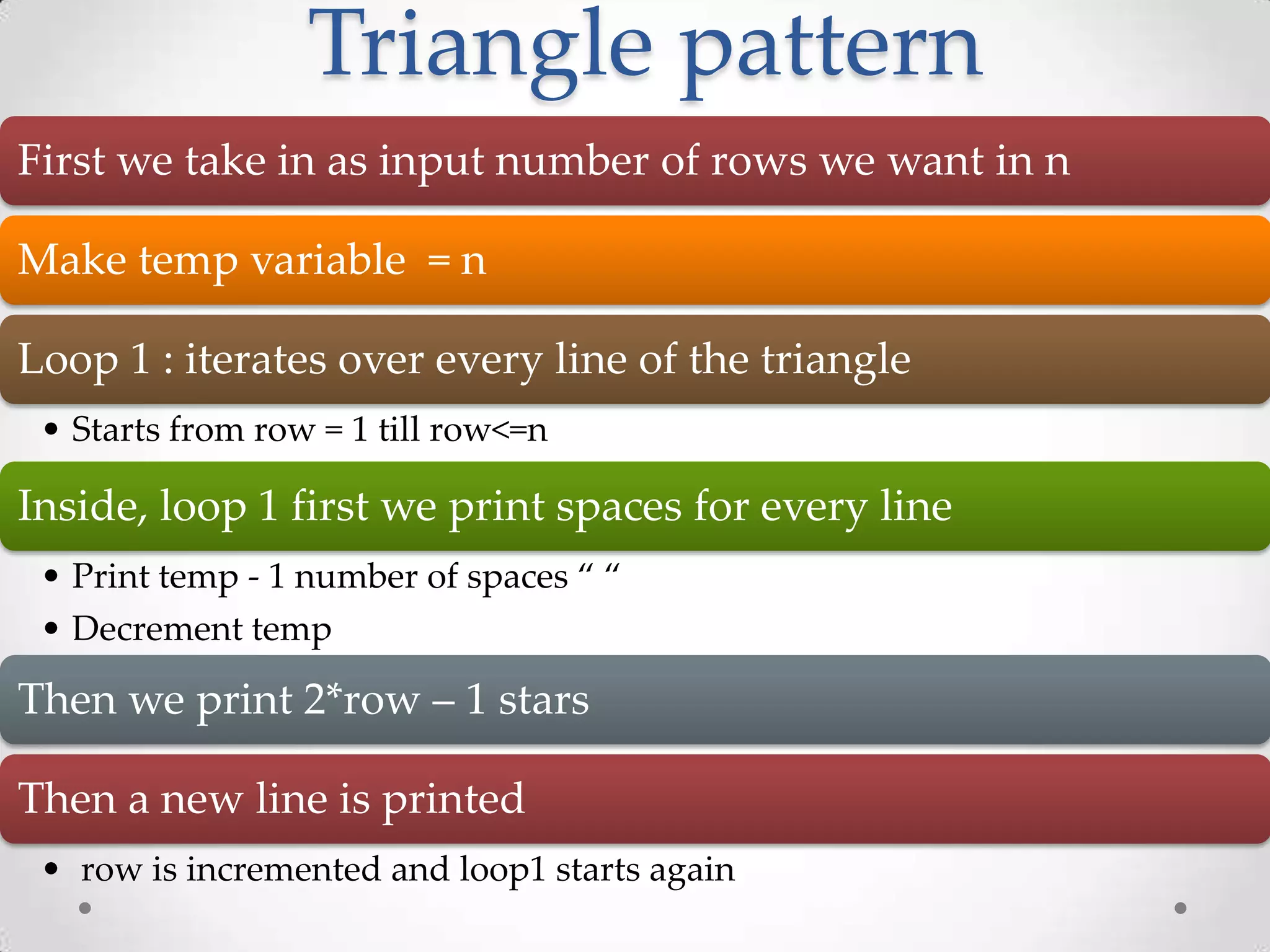
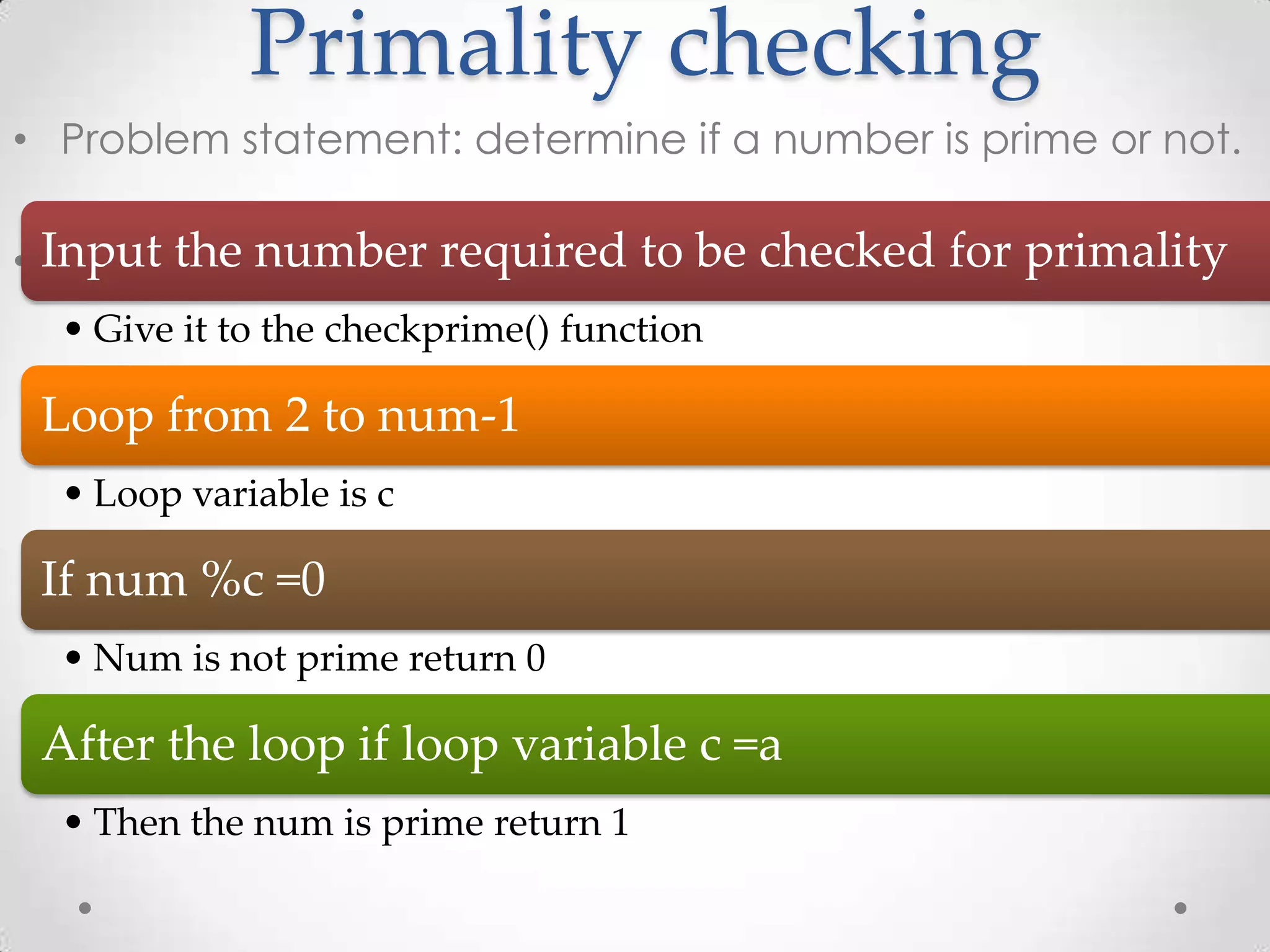
The document is a comprehensive guide on programming in C, covering various topics such as basic input/output, control structures, data types, functions, arrays, structures, and advanced concepts like recursion and prime checking. Each section includes example code snippets and explanations for typical tasks like reading user input, performing arithmetic operations, and manipulating arrays and strings. It serves as a valuable resource for learning and understanding C programming through practical examples.


![Command line arguments • Command #include<stdio.h> line main(int argc, char *argv[]) parameters { are passed to int c; the program printf("Number arguments passed: %dn", argc); from cmd command for ( c = 0 ; c < argc ; c++) printf("%d. argument passed is %sn", c+1, argv[c]); prompt return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-4-2048.jpg)

![Array I/O Declare an integer array • size of array has to be a constant Input how many elements the user requires in the array as (n) • The user input should not be greater than the array size declared Run a for loop from 0 to n and scanf it into &array[c] Run another for loop and print the complete array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-6-2048.jpg)
![#include<stdio.h> main() { int array[100], n, c; printf("Enter the number of elements in arrayn"); scanf("%d", &n); printf("Enter %d elementsn", n); for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ ) scanf("%d", &array[c]); printf("Array elements entered bu you are:n"); for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ ) printf("array[%d] = %dn", c, array[c]); return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-7-2048.jpg)


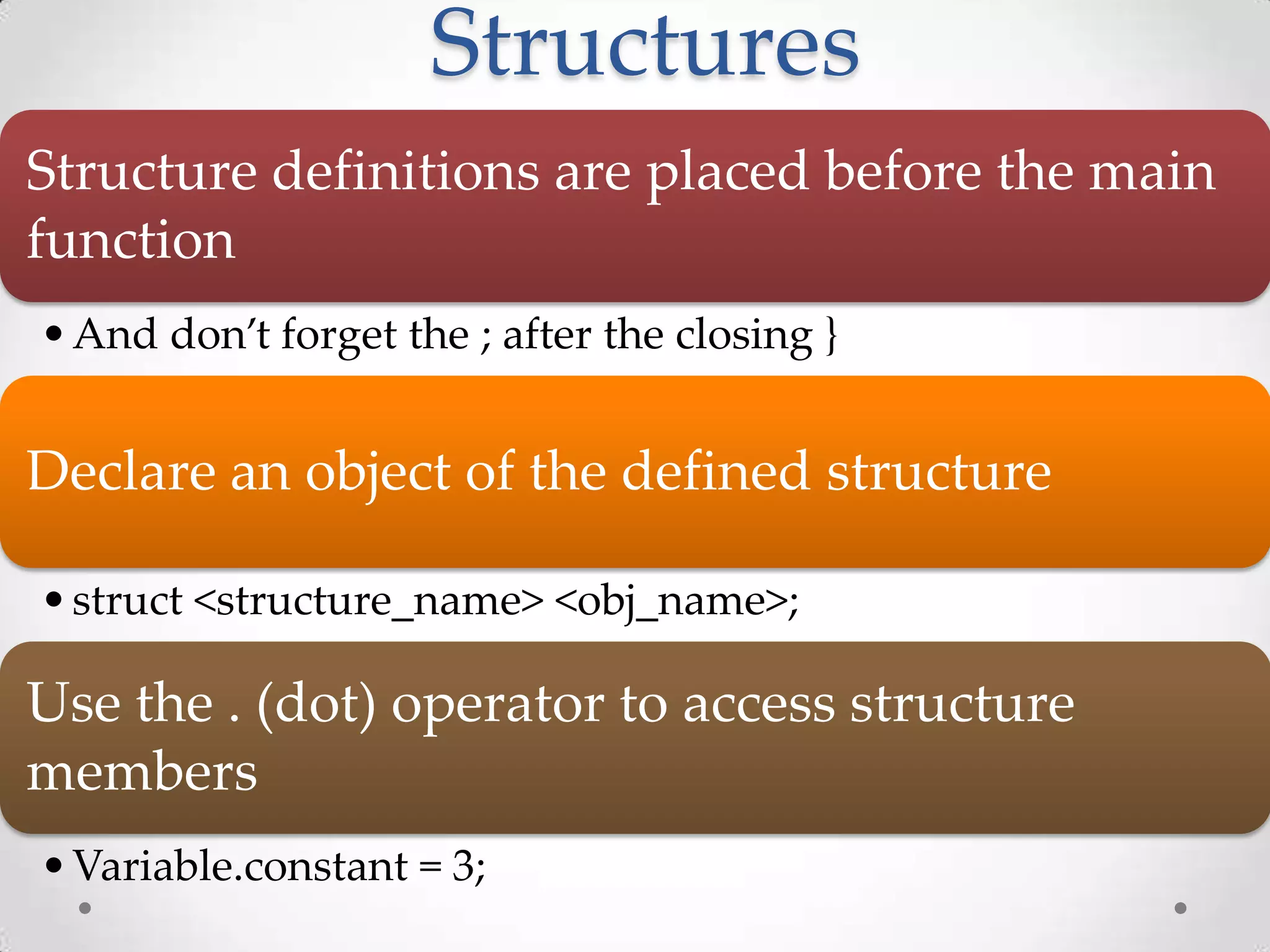
![#include<stdio.h> struct programming { float constant; char *pointer; }; main() { struct programming variable; char string[] = "Programming in Software Development."; variable.constant = 1.23; variable.pointer = string; printf("%fn", variable.constant); printf("%sn", variable.pointer); return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-11-2048.jpg)

































![Arrays – max and min Declare the array,max,size,c and location=1 Take the num of elements from the user First a loop must input all aray elements from the user • The loop goes from 0 till array size Initalize a variable called maximum to array[0] Loop from 1 till array size to find maximum element • Check with a condition each time whether the array is greater than maximum • Store the array variable in maximum and increment the value of the size of the array each time After the loop ends, maximum will hold the maximum element](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-48-2048.jpg)
![#include<stdio.h> main() { int array[100], maximum, size, c, location = 1; printf("Enter the number of elements in arrayn"); scanf("%d",&size); printf("Enter %d integersn", size); for ( c = 0 ; c < size ; c++ ) scanf("%d", &array[c]); maximum = array[0]; for ( c = 1 ; c < size ; c++ ) { if ( array[c] > maximum ) { maximum = array[c]; location = c+1; } } printf("Maximum element is present at location number %d and it's value is %d.n", location, maximum); return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-49-2048.jpg)
![Binary search Declare as variables first,last,middle ,n,search and array • Scan array from user and sort it! Scan variable to be searched and store it in search variable Initialize the index variables first,last and middle • Middle = (first + last)/2 start a while loop until first <= last Check if search is on right side or left side of middle (x > a[mid] or x<a[mid]) • If x > a[mid] then min = mid+1 • If x<a[mid] then max = mid -1 • If x = a[mid] then we have found element and we stop loop Then update mid itself and continue loop If loop completes and first>last, then we have not found element](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-50-2048.jpg)
![#include<stdio.h> main() { int c, first, last, middle, n, search, array[100]; printf("Enter number of elementsn"); scanf("%d",&n); printf("Enter %d integersn", n); for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ ) scanf("%d",&array[c]); printf("Enter value to findn"); scanf("%d",&search); first = 0; last = n - 1; middle = (first+last)/2;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-51-2048.jpg)
![while( first <= last ) { if ( array[middle] < search ) first = middle + 1; else if ( array[middle] == search ) { printf("%d found at location %d.n", search, middle+1); break; } else last = middle - 1; middle = (first + last)/2; } if ( first > last ) printf("Not found! %d is not present in the list.n", search); return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-52-2048.jpg)
![Reverse an array d Declare the variables n,c,d,temp and 2 arrays with same size • Take the number of elements from the user (n) • Take the array elements from the user We start a single loop that goes forward through one array and backward through the other • C = n+1 to 0 decrementing by 1 used for array a • D = 0 to n-1 incrementing by 1used for array b b[d] = a[c] copies a in reverse to b We can copy b to a again so our original array a is reversed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-53-2048.jpg)
![#include<stdio.h> main() { int n, c, d, temp, a[100], b[100]; printf("Enter the number of elements in arrayn"); scanf("%d",&n); printf("Enter the array elementsn"); for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ ) scanf("%d",&a[c]); for ( c = n - 1, d = 0 ; c >= 0 ; c--, d++ ) b[d] = a[c]; for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ ) a[c] = b[c]; printf("Reverse array isn"); for( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ ) printf("%dn", a[c]); return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-54-2048.jpg)
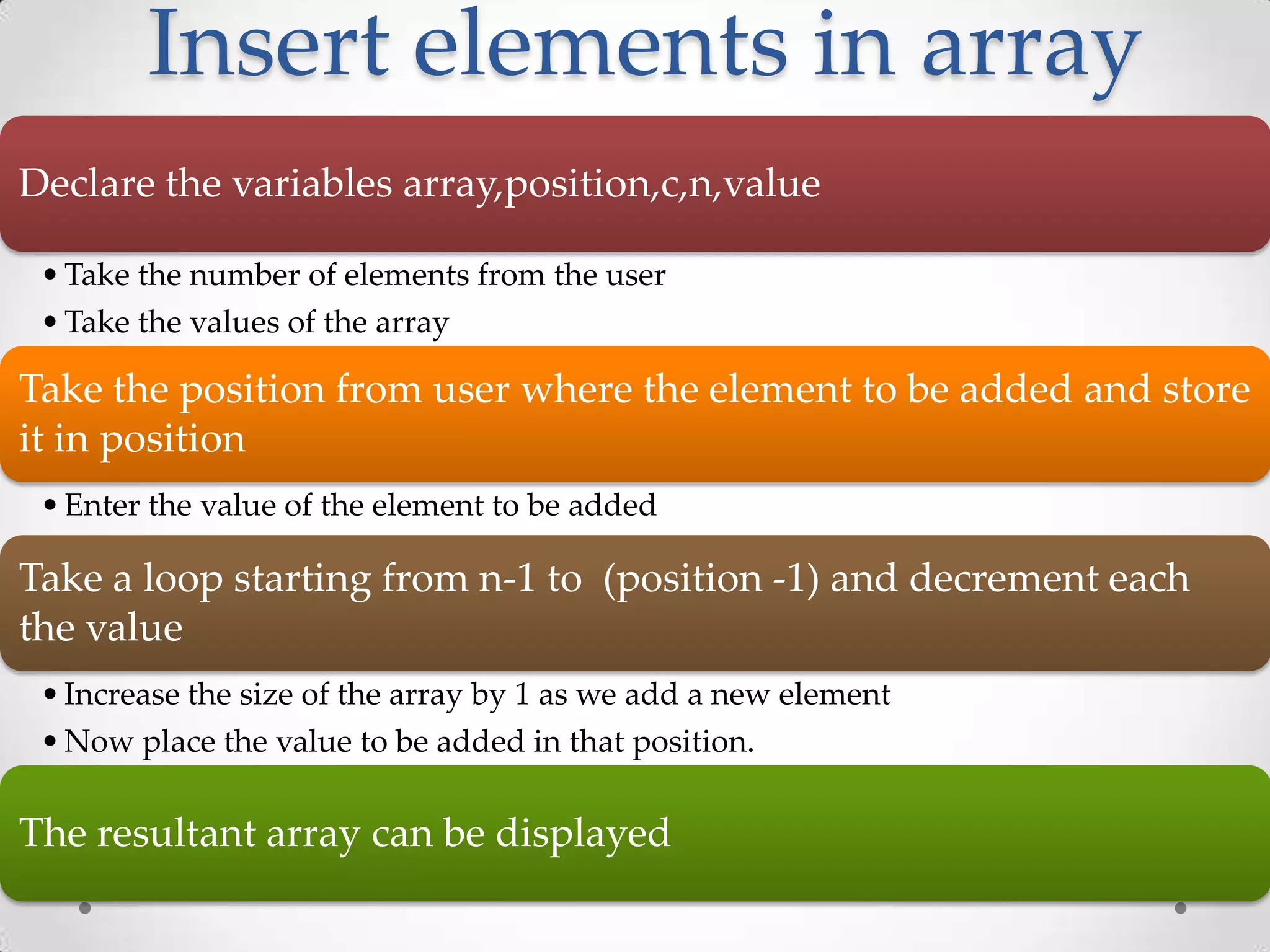
![#include<stdio.h> main() { int array[100], position, c, n, value; printf("Enter number of elements in arrayn"); scanf("%d", &n); printf("Enter %d elementsn", n); for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ ) scanf("%d", &array[c]); printf("Enter the location where you wish to insert an elementn"); scanf("%d", &position); printf("Enter the value to insertn"); scanf("%d", &value);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-56-2048.jpg)
![for ( c = n - 1 ; c >= position - 1 ; c-- ) array[c+1] = array[c]; array[position-1] = value; printf("Resultant array isn"); for( c = 0 ; c <= n ; c++ ) printf("%dn", array[c]); return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-57-2048.jpg)
![#include<stdio.h> main() { int array[100], position, c, n; printf("Enter number of elements in arrayn"); scanf("%d", &n); printf("Enter %d elementsn", n); for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ ) scanf("%d", &array[c]); printf("Enter the location where you wish to delete elementn"); scanf("%d", &position);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-58-2048.jpg)
![if ( position >= n+1 ) printf("Deletion not possible.n"); else { for ( c = position - 1 ; c < n - 1 ; c++ ) array[c] = array[c+1]; printf("Resultant array isn"); for( c = 0 ; c < n - 1 ; c++ ) printf("%dn", array[c]); } return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-59-2048.jpg)
![Matrix Addition Declare all matrixes and matrix sizes, first, second and sum • Matrix are 2D arrays and are declared as first[10][10] A nested for loop from 0 to m and 0 to n is used to input matrix 1 and 2 • m and n are the sizes of the matrix A nested for loop is used for matrix addition • Loop 1 variable is c, goes from 0 to m • Loop 2 variable is d, goes from 0 to n sum[c][d] = first[c][d] + second[c][d] • Print the sum matrix](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-60-2048.jpg)
![#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> main() { int m, n, c, d, first[10][10], second[10][10], sum[10][10]; printf("Enter the number of rows and columns of matrix "); scanf("%d%d",&m,&n); printf("Enter the elements of first matrixn"); for ( c = 0 ; c < m ; c++ ) for ( d = 0 ; d < n ; d++ ) scanf("%d",&first[c][d]); printf("Enter the elements of second matrixn");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-61-2048.jpg)
![for ( c = 0 ; c < m ; c++ ) for ( d = 0 ; d < n ; d++ ) sum[c][d] = first[c][d]+ second[c][d]; printf("Sum of entered matrices:-n"); for ( c = 0 ; c < m ; c++ ) { for ( d = 0 ; d < n ; d++ ) printf("%dt",sum[c][d]); printf("n"); } getch(); return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-62-2048.jpg)
![Matrix Transpose Declare 2 matrixes and sizes • A nested for loop from 0 to m and 0 to n is used to input matrix • m and n are the sizes of the matrix A nested for loop is used to transpose • Loop 1 variable is c, goes from 0 to m • Loop 2 variable is d, goes from 0 to n Transpose[c][d] = matrix[d][c] Print the transposed matrix](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-63-2048.jpg)
![#include<stdio.h> main() { int m, n, c, d, matrix[10][10], transpose[10][10]; printf("Enter the number of rows and columns of matrix "); scanf("%d%d",&m,&n); printf("Enter the elements of matrix n"); for( c = 0 ; c < m ; c++ ) { for( d = 0 ; d < n ; d++ ) { scanf("%d",&matrix[c][d]); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-64-2048.jpg)
![for( c = 0 ; c < m ; c++ ) { for( d = 0 ; d < n ; d++ ) { transpose[d][c] = matrix[c][d]; } } printf("Transpose of entered matrix :-n"); for( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ ) { for( d = 0 ; d < m ; d++ ) { printf("%dt",transpose[c][d]); } printf("n"); } return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-65-2048.jpg)
![Matrix multiplication Declare all matrixes and matrix sizes, first, second and mul •Input sizes and the two input matrixes Check sizes of matrix for conformity •m,n are sizes of matrix 1 •p,q are sizes of matrix 2 •Then if n == p only multiplication can take place 3 nested for loops are used •Loop1 c from 0 to m •Loop2 d from o to n •Loop3 k from 0 to p In loop3 sum = sum+first[c][k]*second[k][d] After loop3 ends, in loop2 •mul[c][d] = sum •Sum = 0 After all loops terminate, mul can be printed as resultant matrix](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-66-2048.jpg)
![#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> main() { int m, n, p, q, c, d, k, sum = 0; int first[10][10], second[10][10], mul[10][10]; printf("Enter the number of rows and columns of first matrixn"); scanf("%d%d",&m,&n); printf("Enter the elements of first matrixn"); for ( c = 0 ; c < m ; c++ ) for ( d = 0 ; d < n ; d++ ) scanf("%d",&first[c][d]); printf("Enter the number of rows and columns of second matrixn"); scanf("%d%d",&p,&q);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-67-2048.jpg)
![if ( n != p ) printf("Matrices with entered orders can't be multiplied with each other.n"); else { printf("Enter the elements of second matrixn"); for ( c = 0 ; c < p ; c++ ) for ( d = 0 ; d < q ; d++ ) scanf("%d",&second[c][d]); for ( c = 0 ; c < m ; c++ ) { for ( d = 0 ; d < n ; d++ ) { for ( k = 0 ; k < p ; k++ ) { sum = sum + first[c][k]*second[k][d]; } mul[c][d] = sum; sum = 0; } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-68-2048.jpg)

![#include<stdio.h> main() { char array[100]; printf("Enter a stringn"); scanf("%s",&array); printf("You entered the string %sn",array); return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-70-2048.jpg)
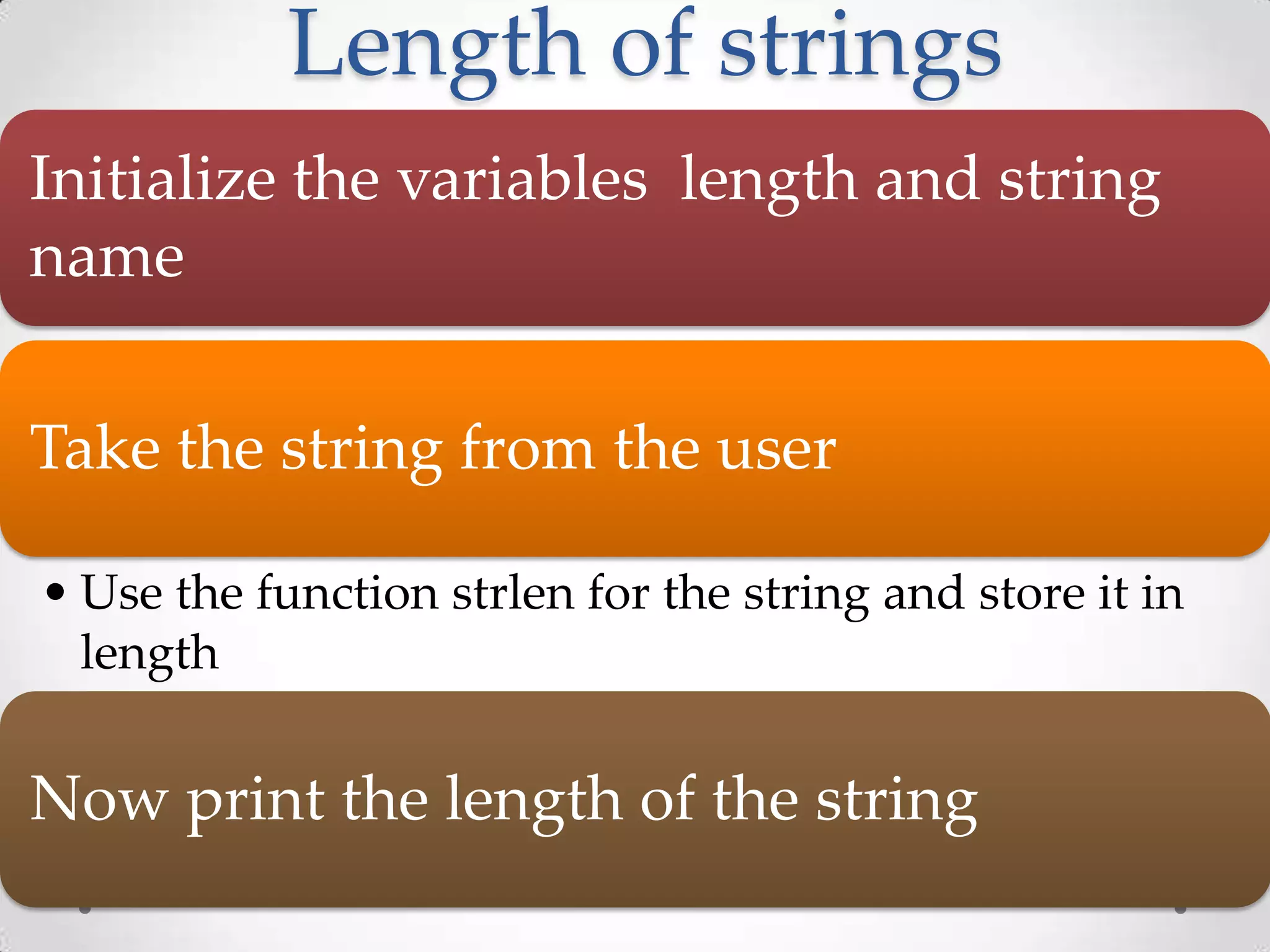
![#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> main() { char a[100]; int length; printf("Enter a string to calculate it's lengthn"); gets(a); length = strlen(a); printf("Length of entered string is = %dn",length); return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-72-2048.jpg)



![#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> main() { char a[100], b[100]; printf("Enter the string to check if it is a palindromen"); gets(a); strcpy(b,a); strrev(b); if( strcmp(a,b) == 0 ) printf("Entered string is a palindrome.n"); else printf("Entered string is not a pailndrome.n"); return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-76-2048.jpg)

![include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<stdlib.h> main() { char ch, fname[25]; FILE *fp; printf("Enter the name of file you wish to see "); gets(fname); fp = fopen(fname,"r"); printf("The contents of %s file are :- nn",fname); while( ( ch = fgetc(fp) ) != EOF) printf("%c",ch); getch(); fclose(fp); return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wiap-c002-120720015915-phpapp01/75/Introduction-to-Basic-C-programming-02-78-2048.jpg)