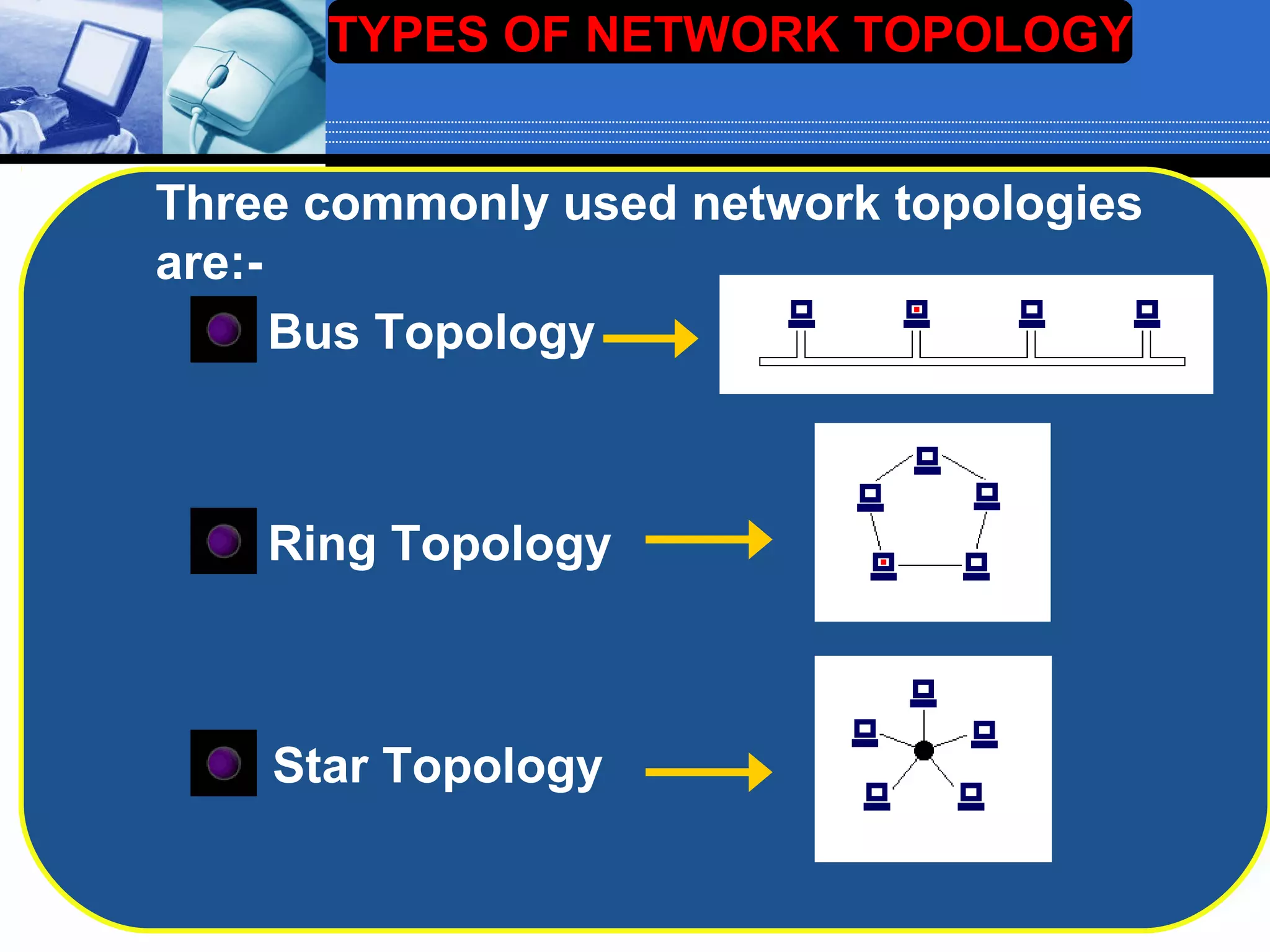
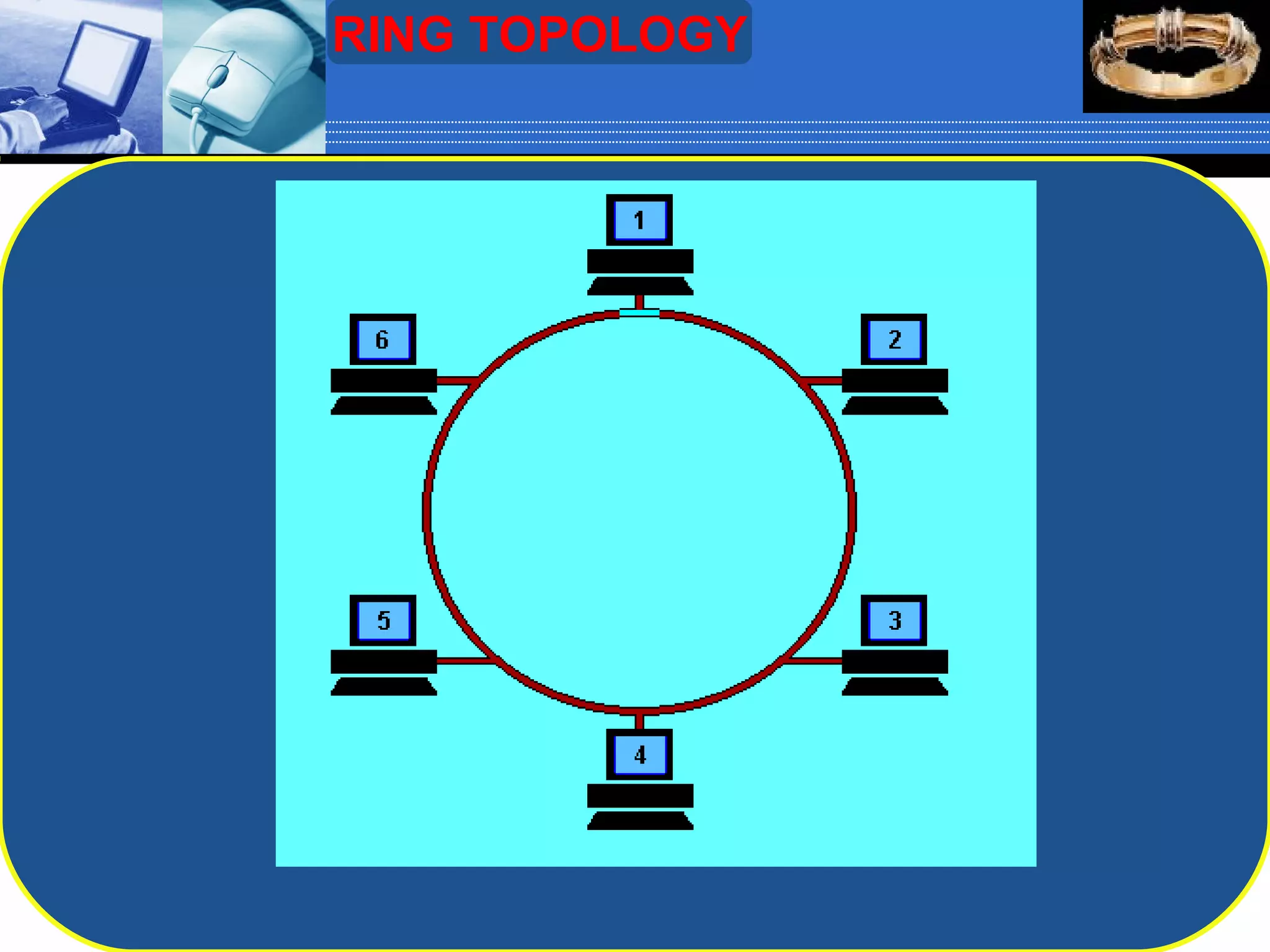
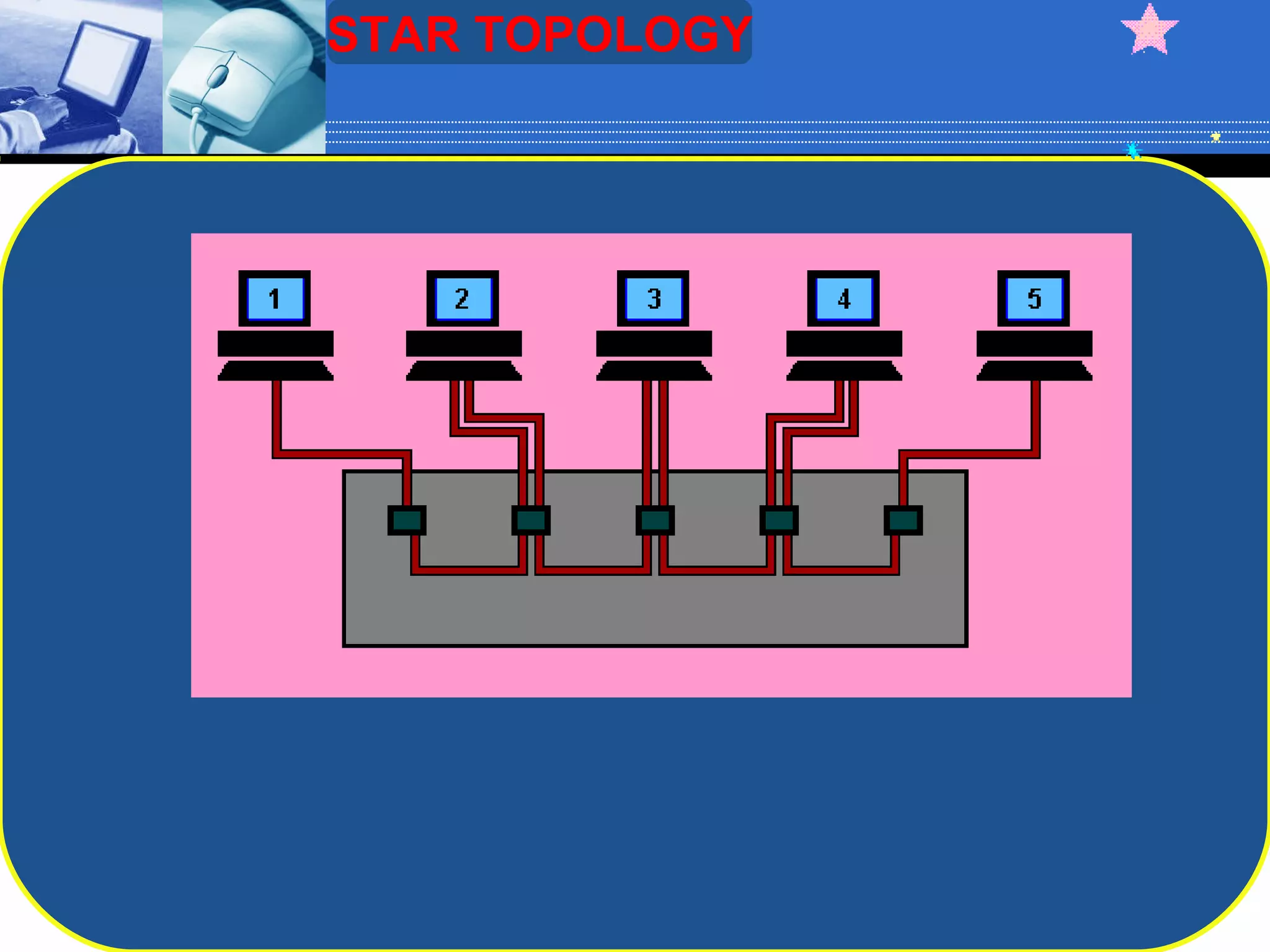
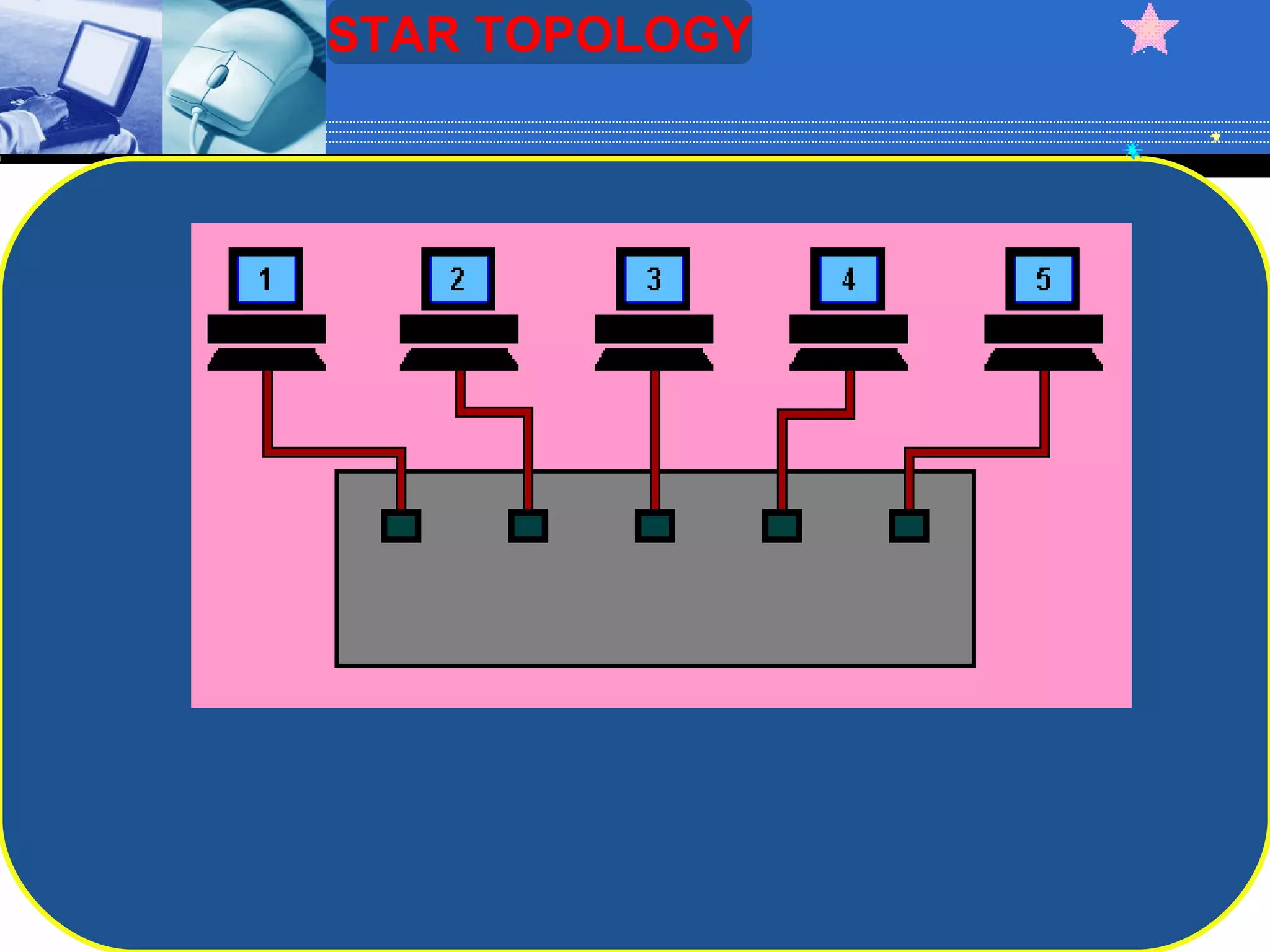
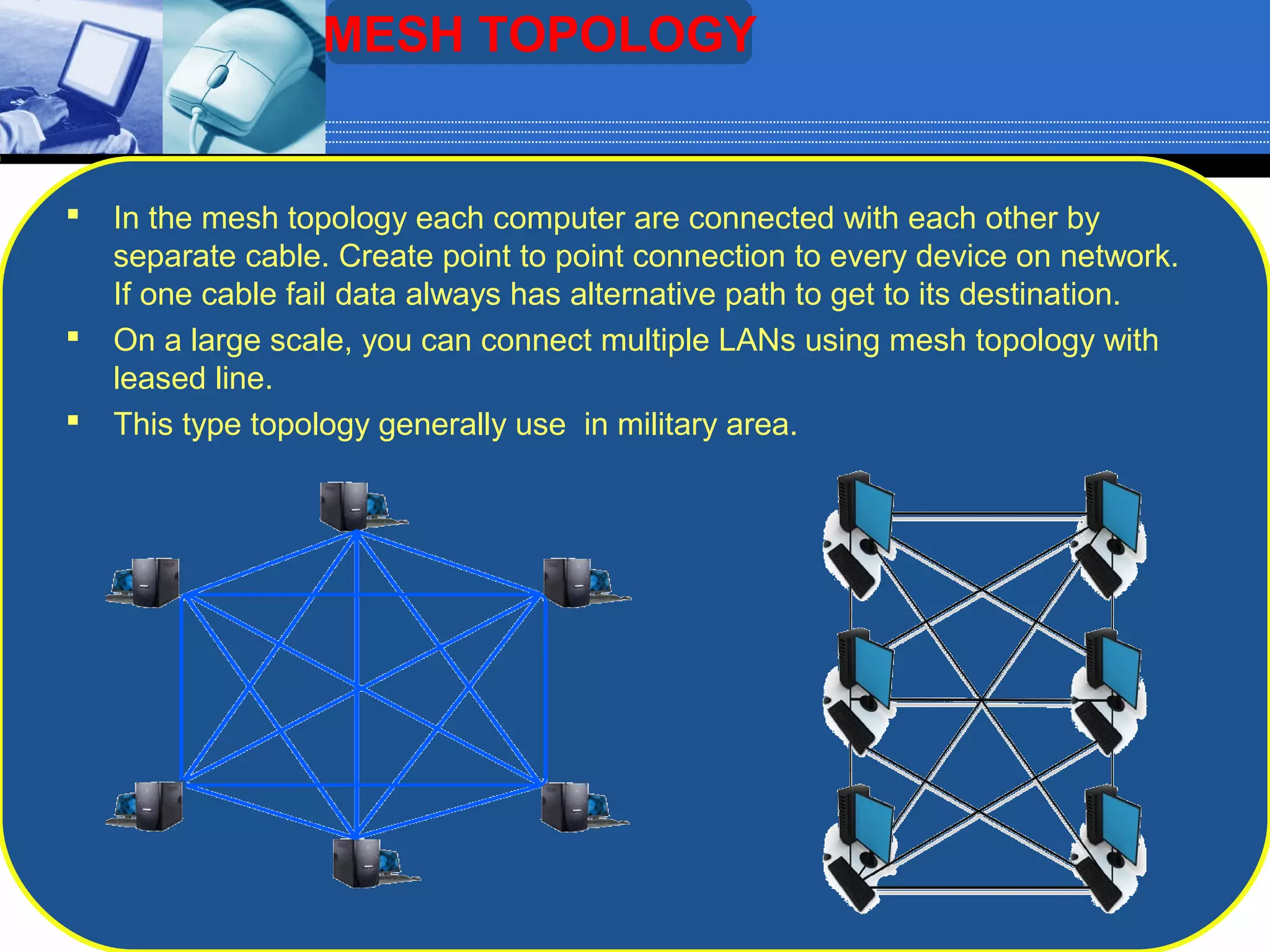
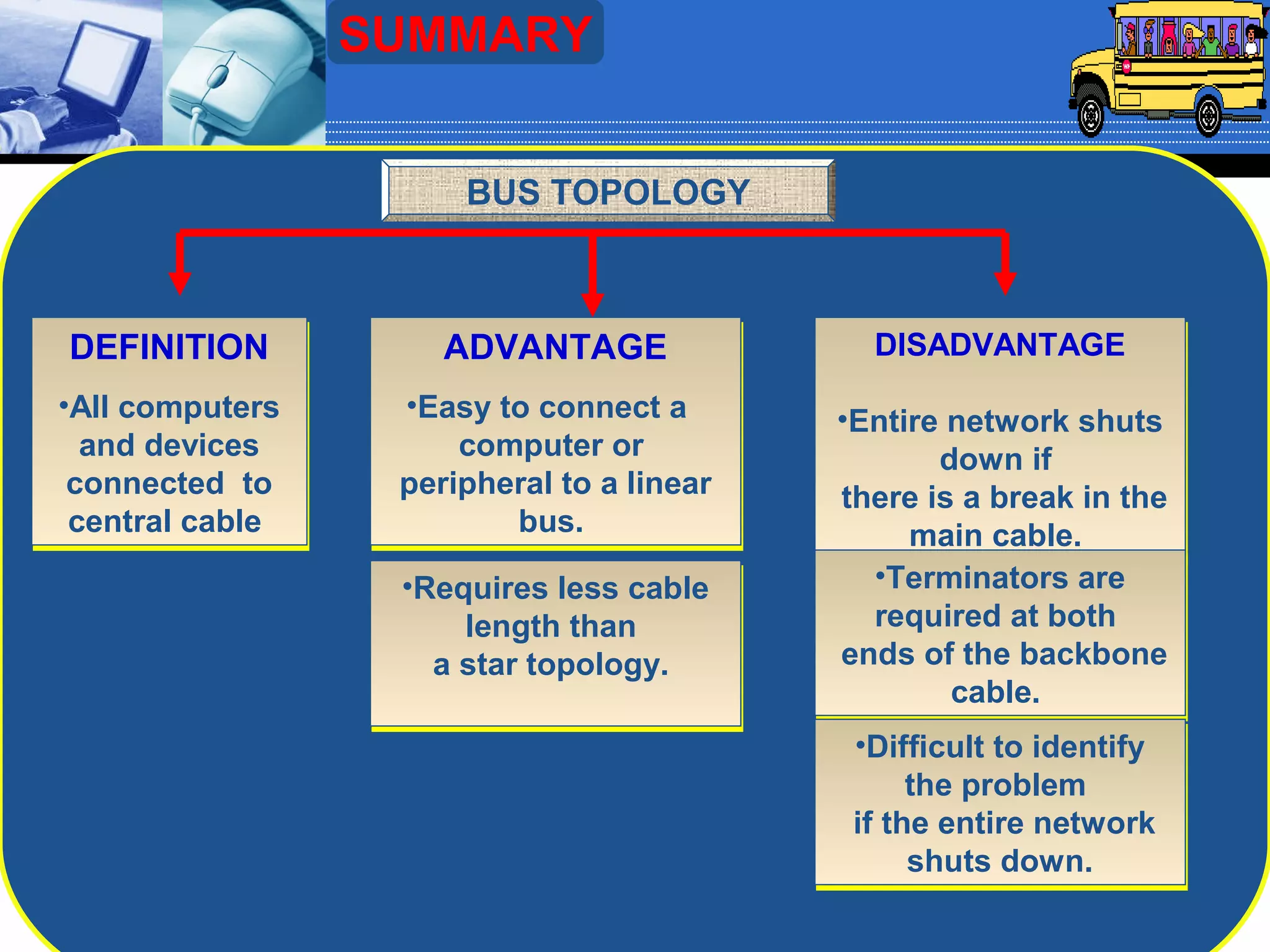
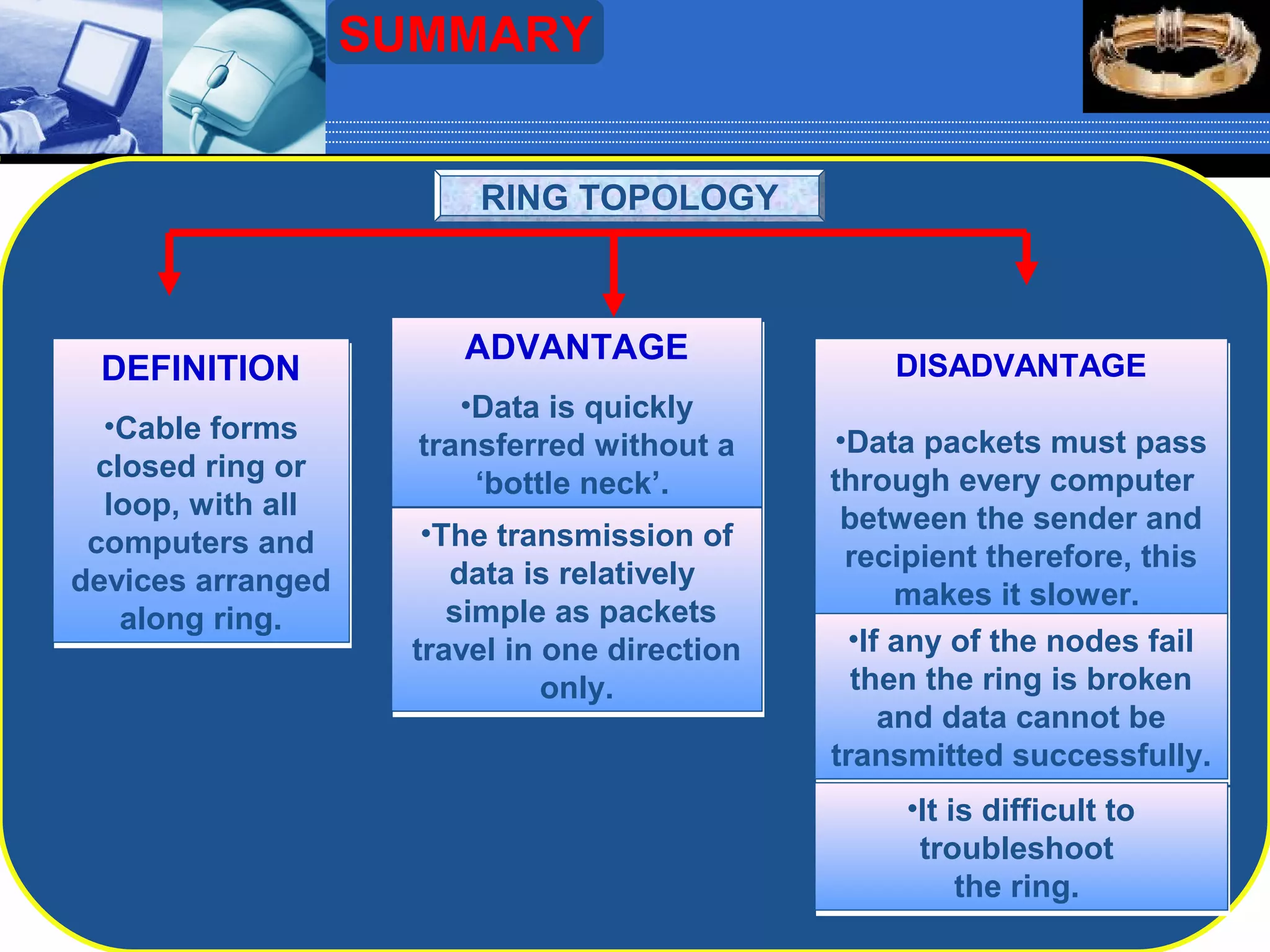
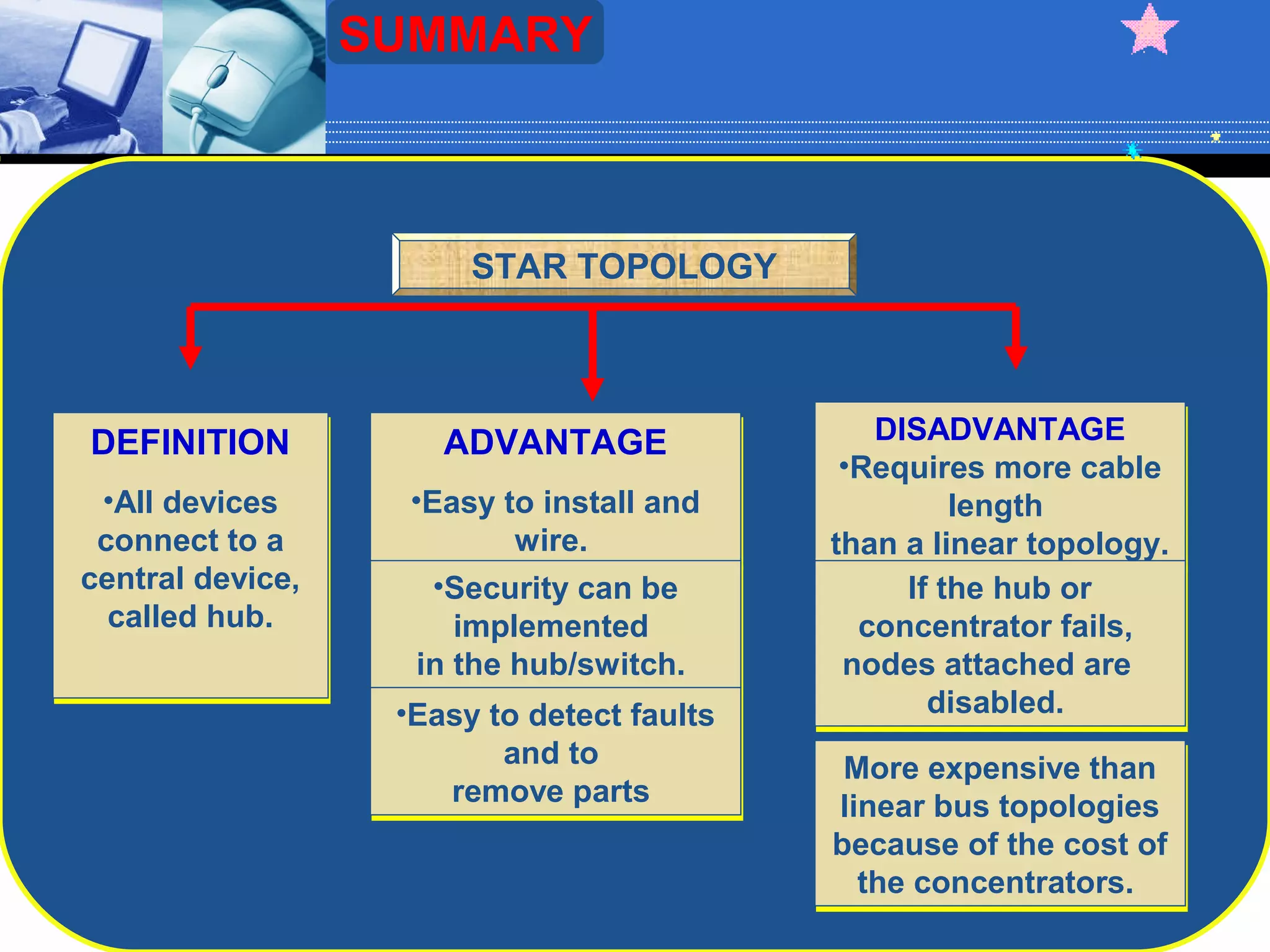
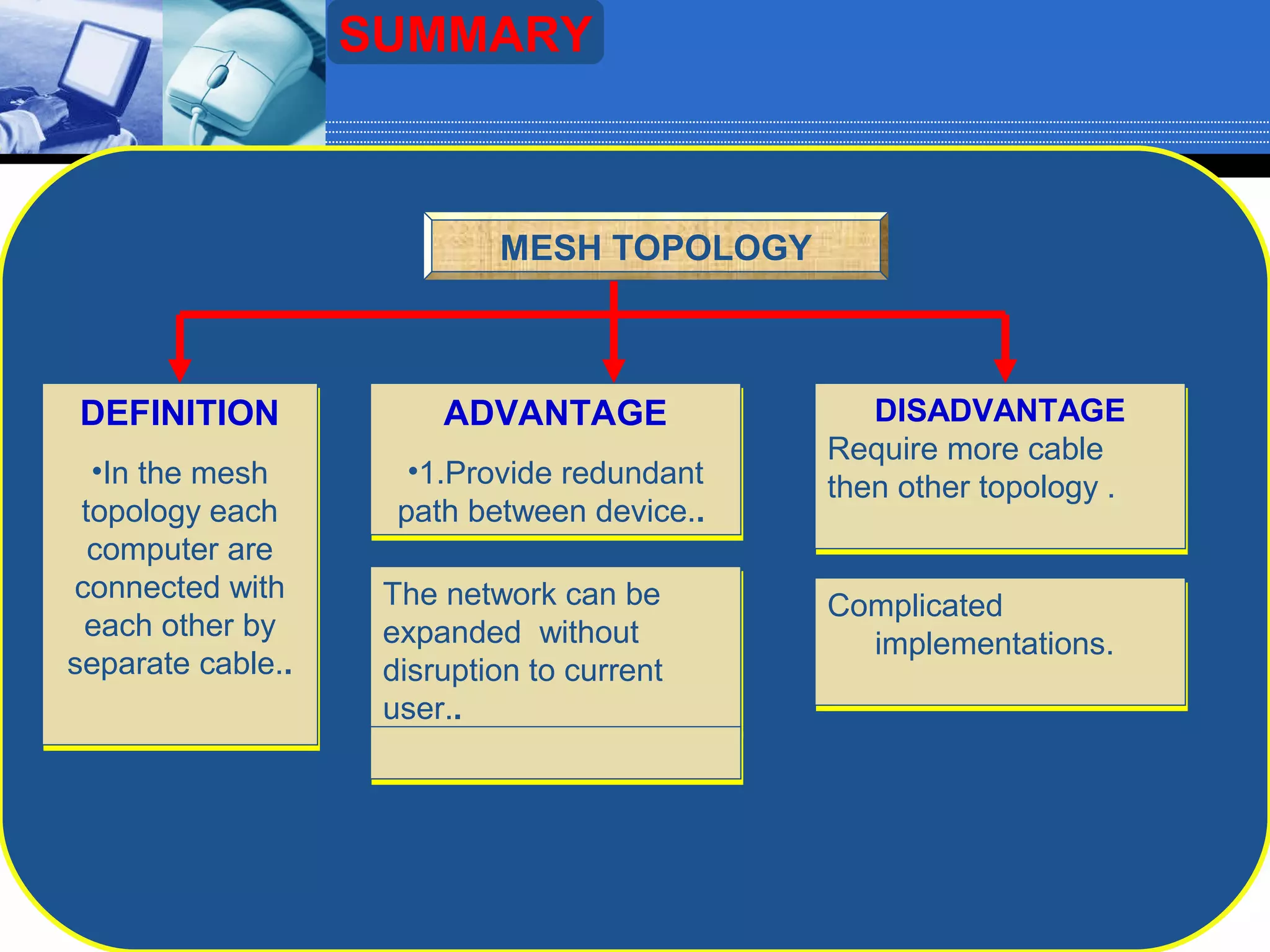
The document discusses different types of computer network topologies. It defines network topology as the physical configuration of cables, computers, and other devices on a network. The key network topologies covered are bus, ring, star, and mesh. Advantages and disadvantages of each topology are summarized.