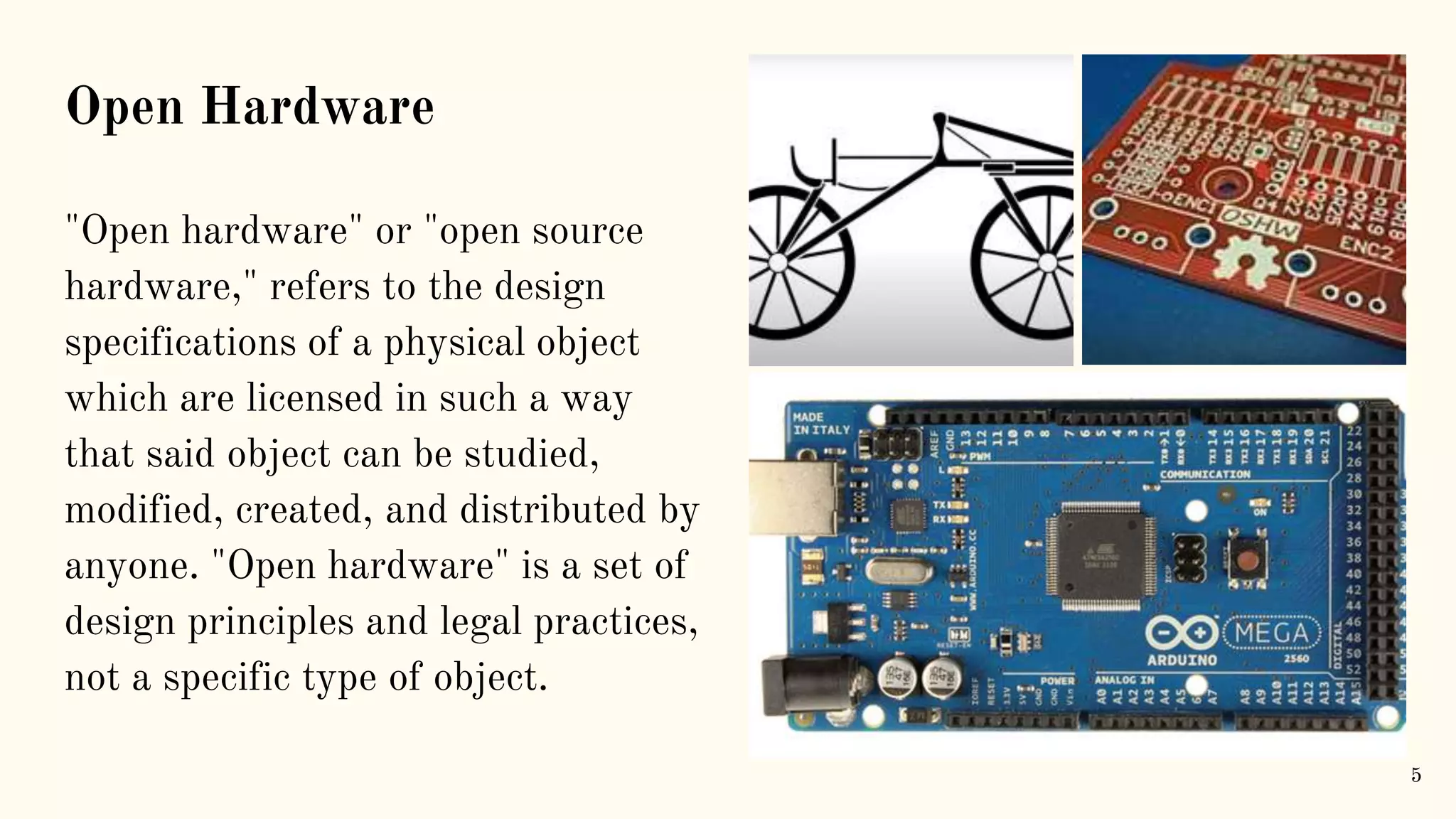
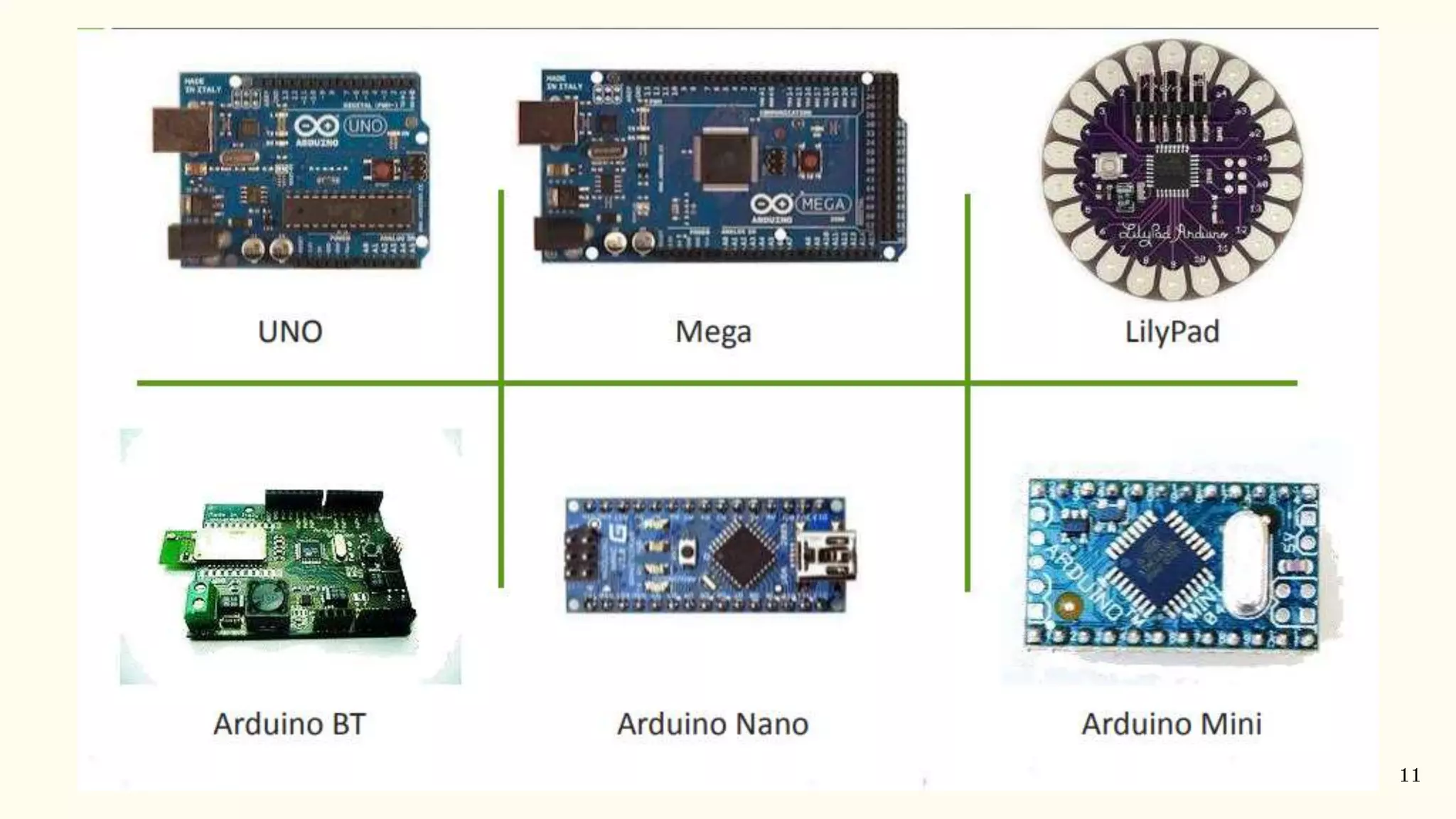
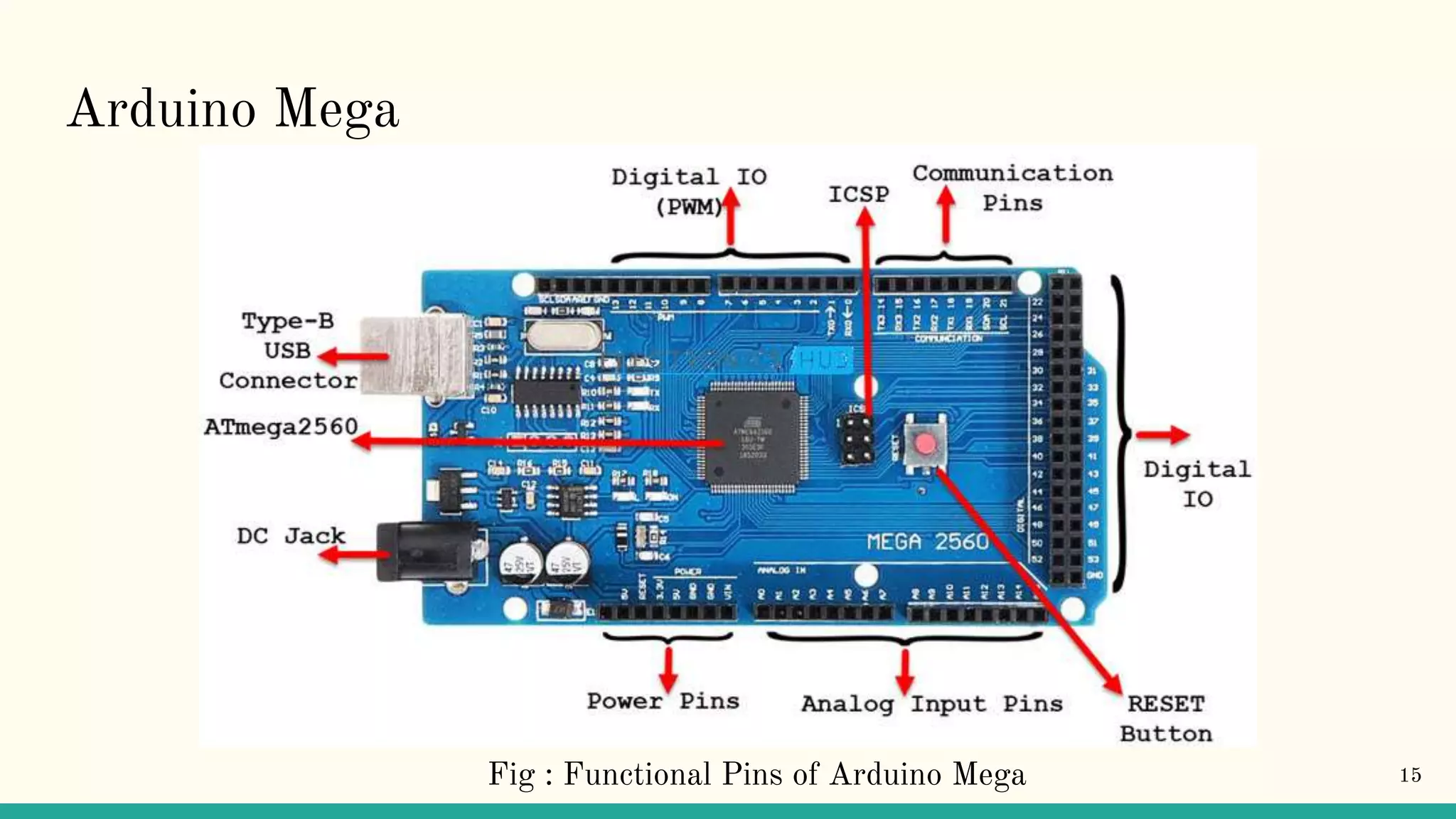
Arduino is an open-source electronics platform that can be used to read inputs like sensors or buttons and turn them into outputs like activating motors or publishing data online. It uses easy to use hardware and software that allows coding to be accessible and transferable using languages like C++. Common Arduino boards include the Arduino Mega, which has 54 digital input/output pins and uses an ATmega2560 microcontroller. To use an Arduino board, the Arduino IDE software must be installed to write and upload code to the board. Programming involves using data types, operators, control flow statements like if/else and loops, and defining a setup and loop structure.














![Statement and Operators Statement represents a command, it ends with ; Ex: int x; x=13; Operators are symbols that used to indicate a specific function: - Math operators: [+,-,*,/,%,^] - Logic operators: [==, !=, &&, ||] - Comparison operators: [==, >, <, !=, <=, >=] Syntax: ; Semicolon, {} curly braces, //single line comment, /*Multi-line comments*/ 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoarduino-221104115657-faa9a08d/75/Introduction-to-Arduino-19-2048.jpg)