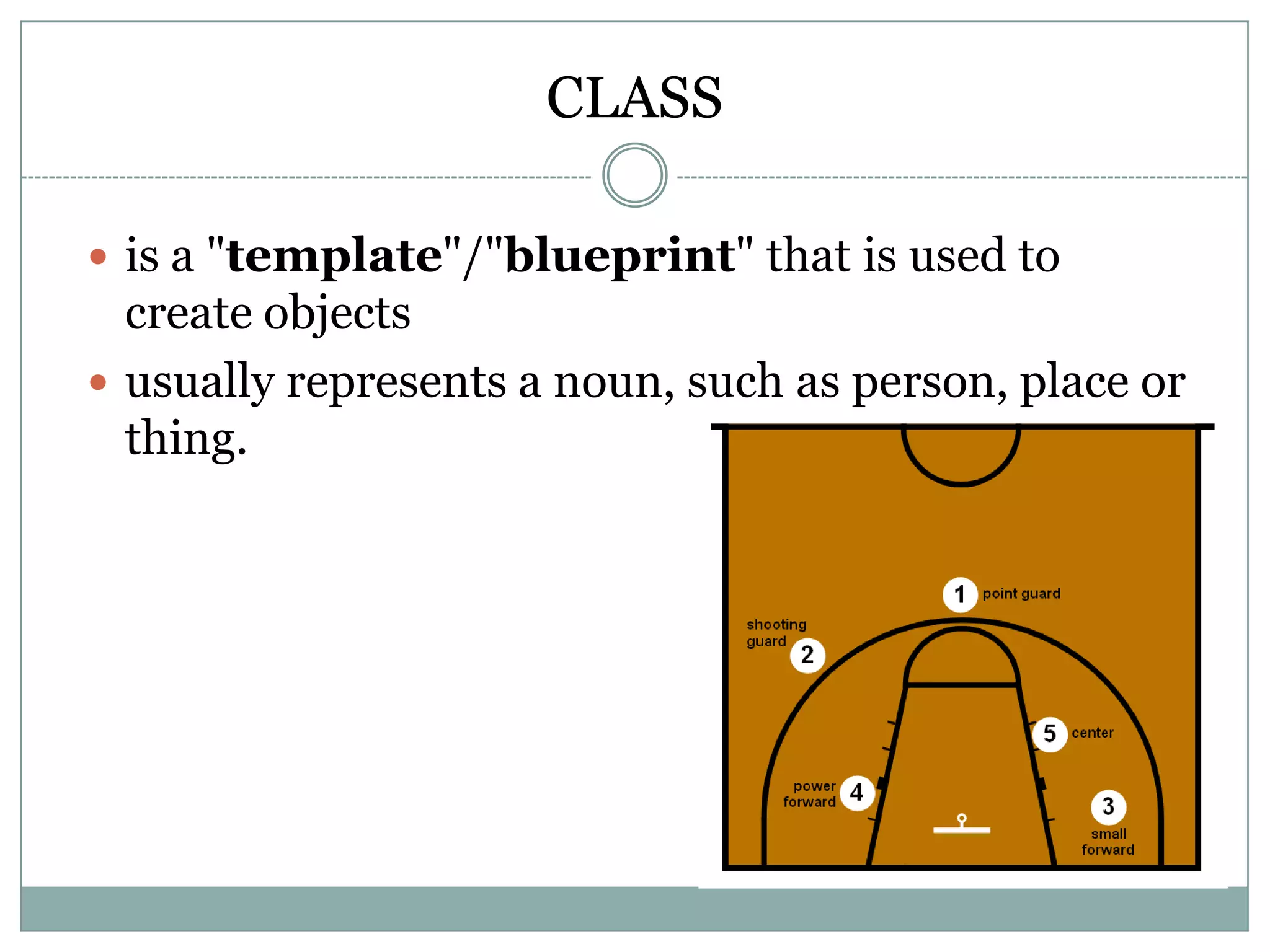
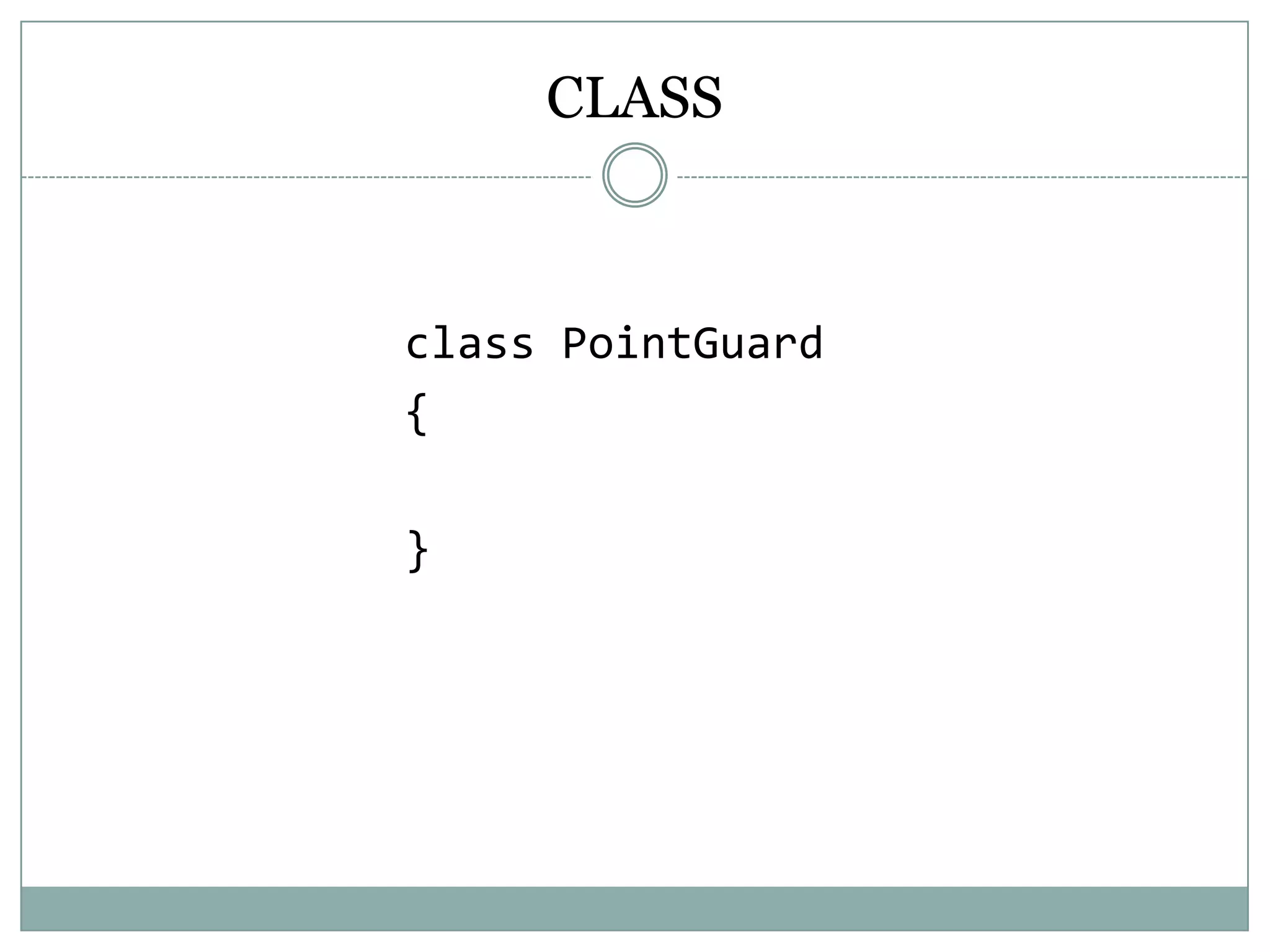
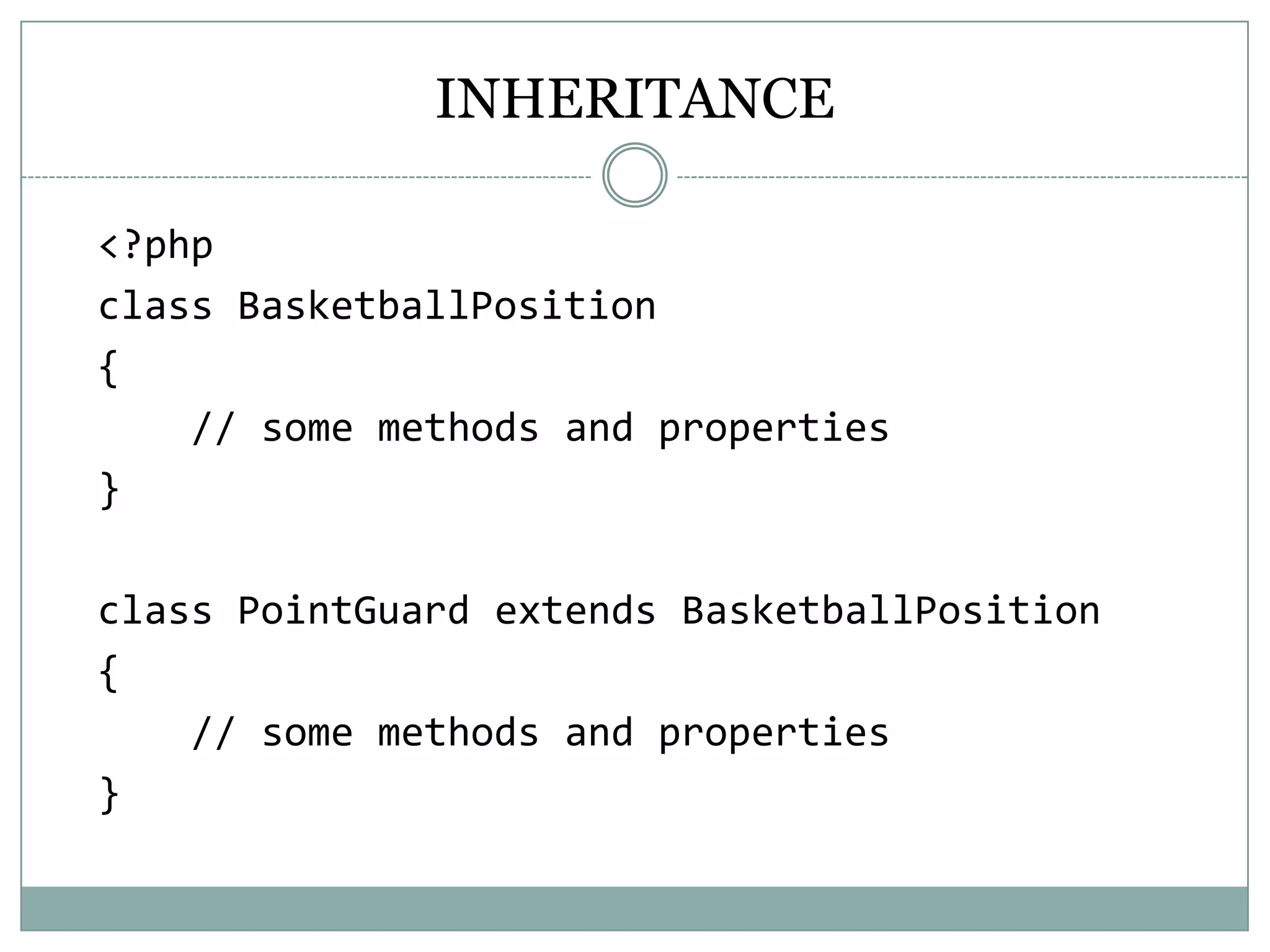
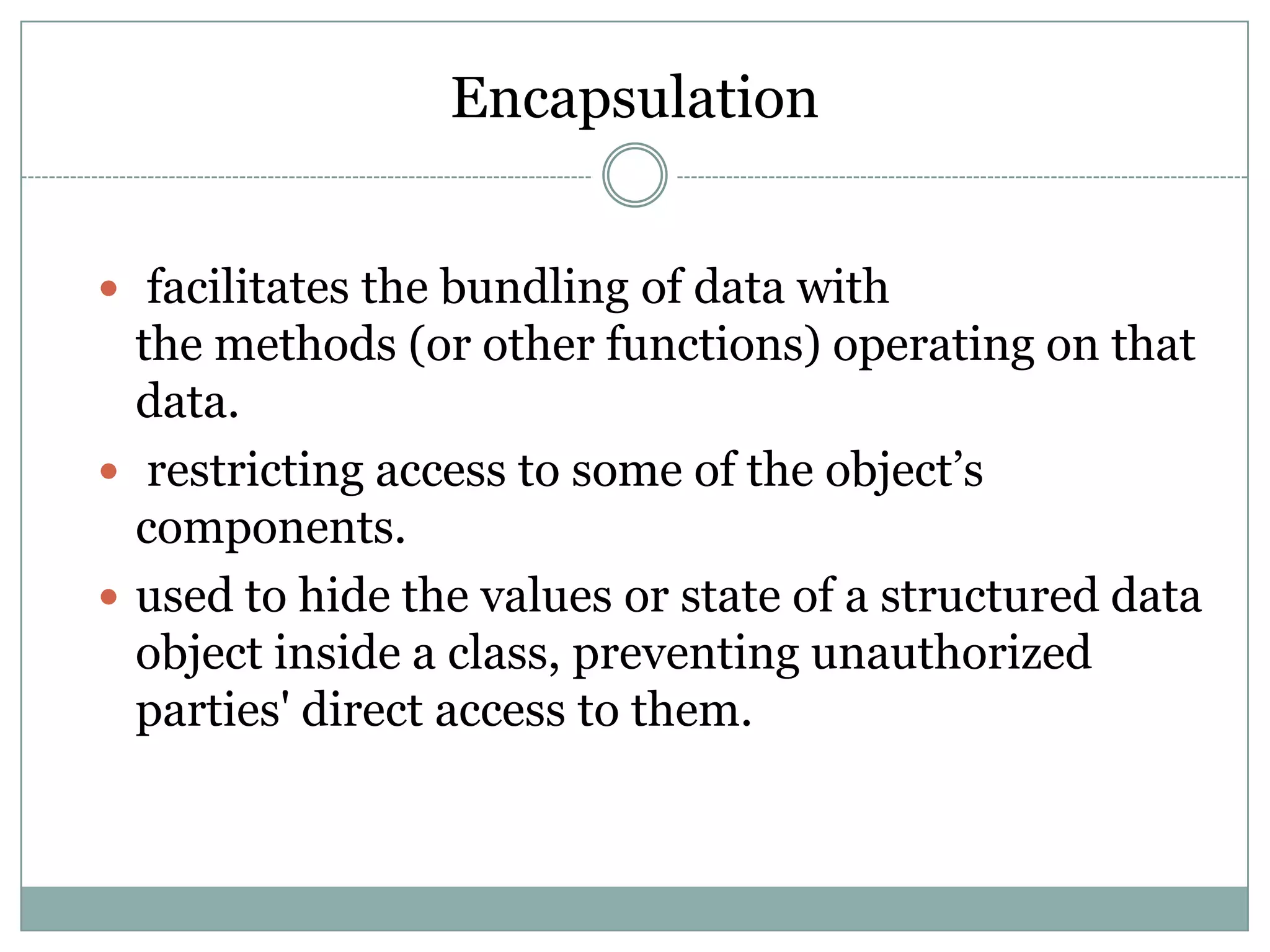
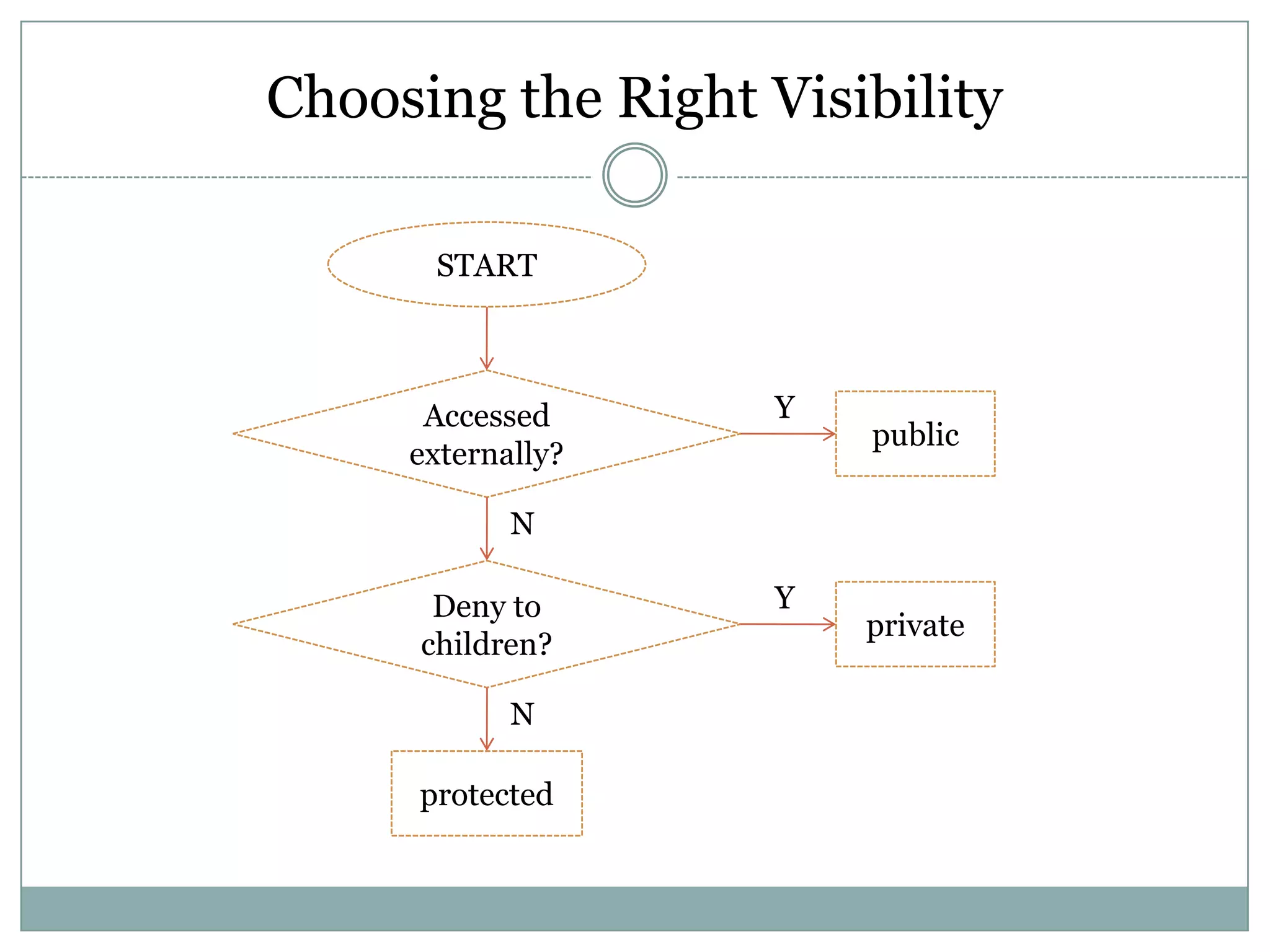
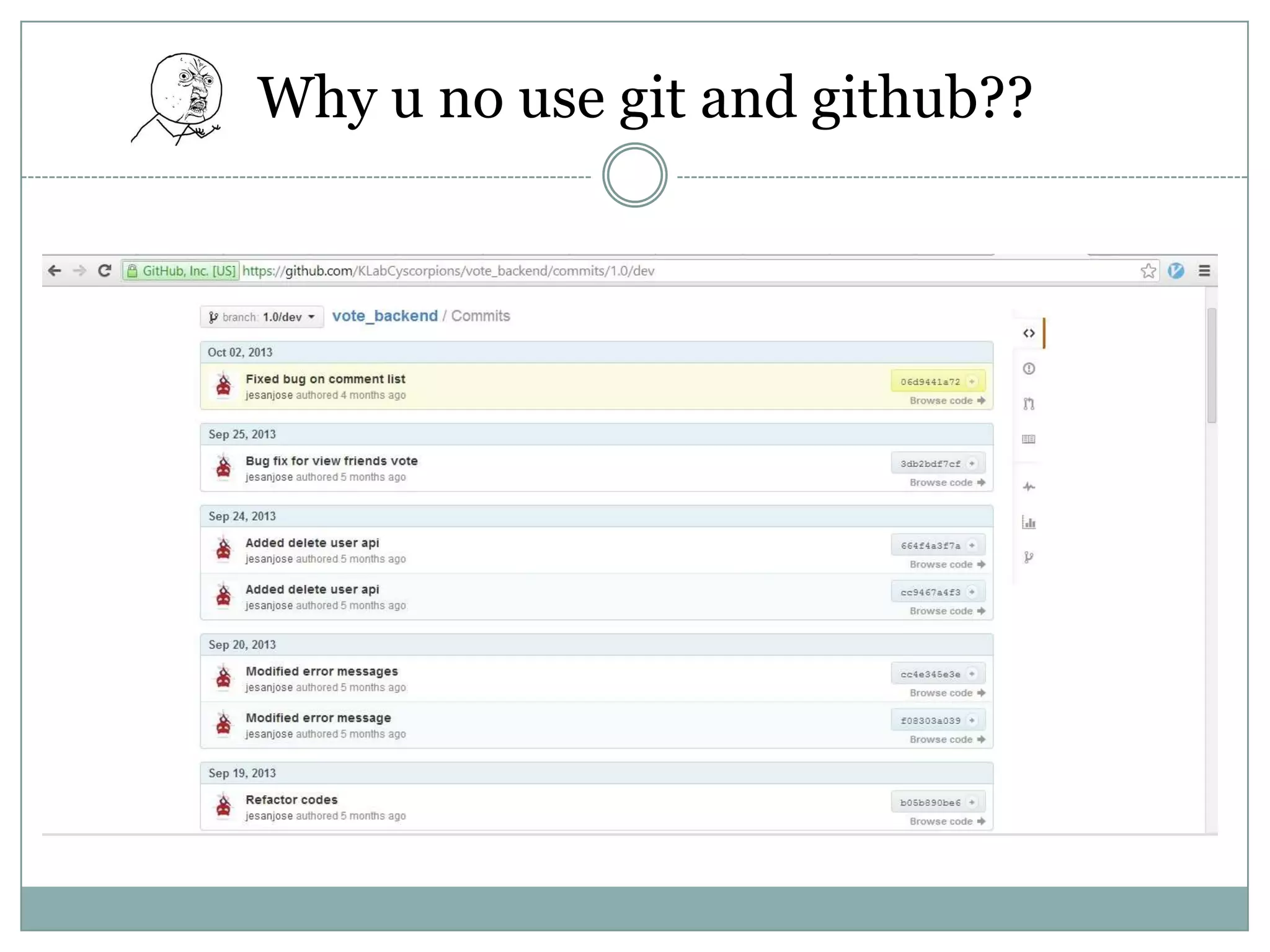
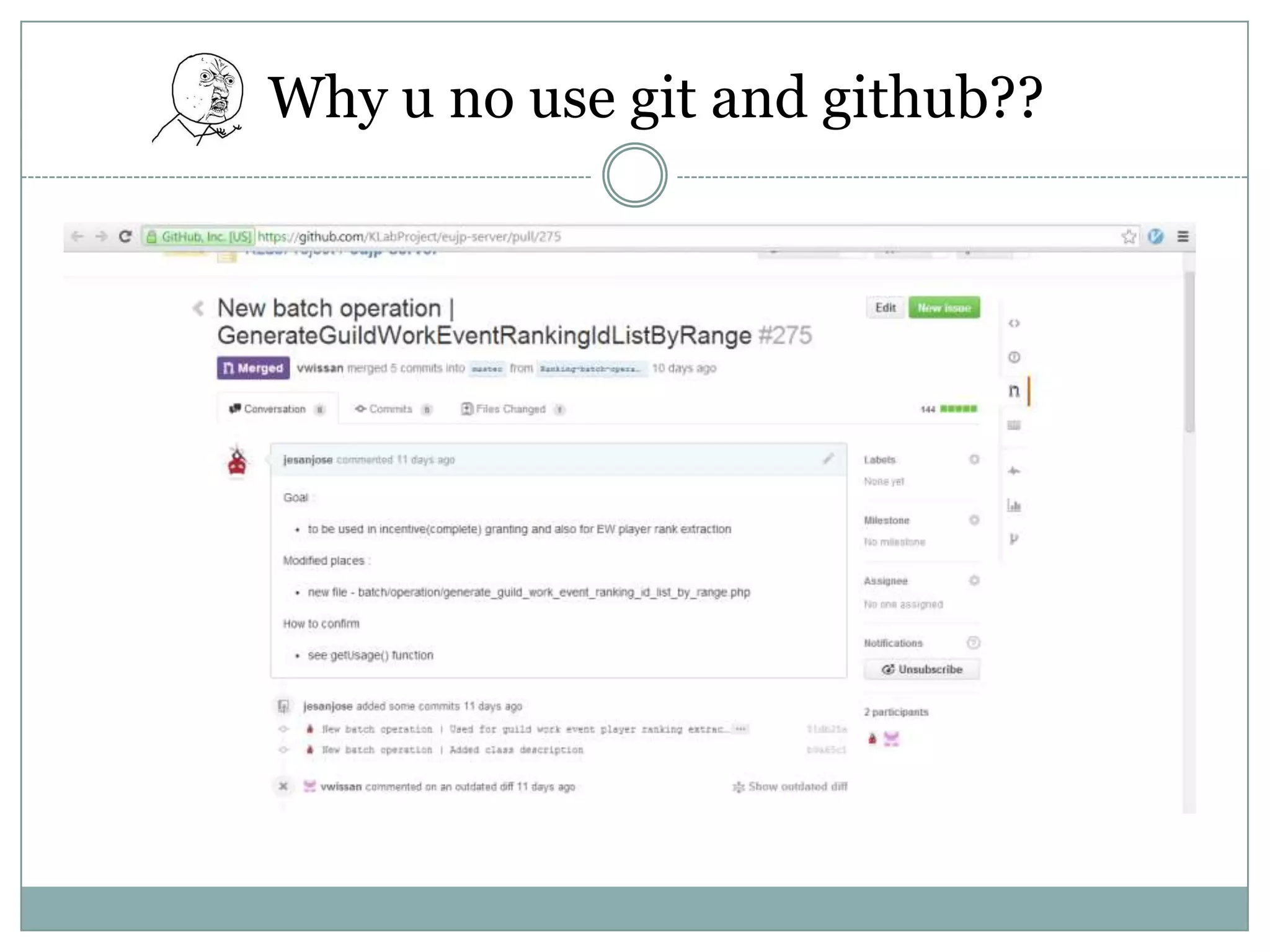
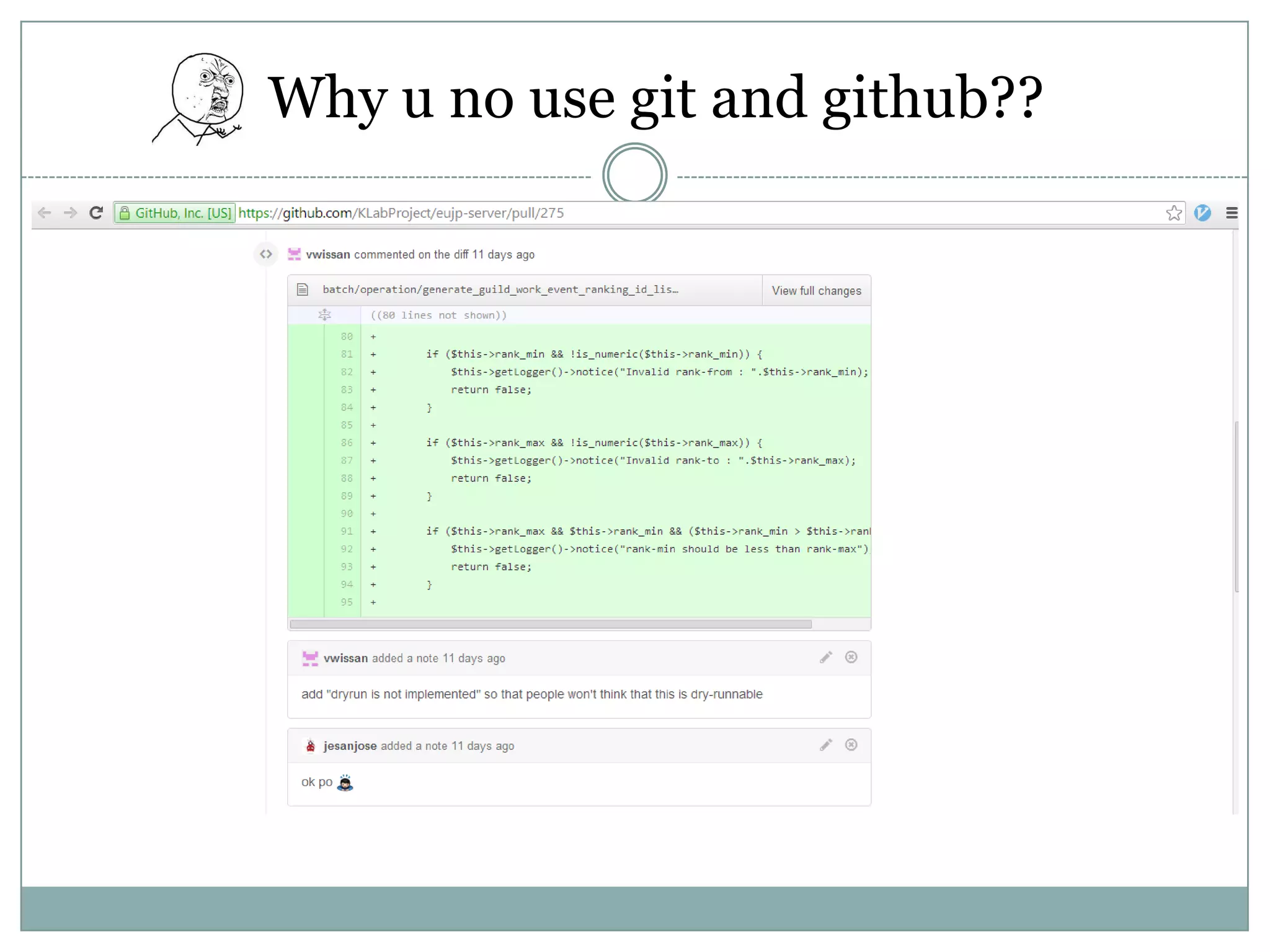
PHP is an open-source scripting language that is commonly used for web development. It stands for Hypertext Preprocessor. PHP is free, platform independent, has great documentation and a large active community. It is also easy to learn with a simple syntax and many tutorials available. PHP supports object-oriented programming which treats functions and data as objects. Key concepts of OOP in PHP include classes, objects, inheritance, encapsulation and class properties/methods. Git and GitHub can be used for version control and collaboration on PHP projects.