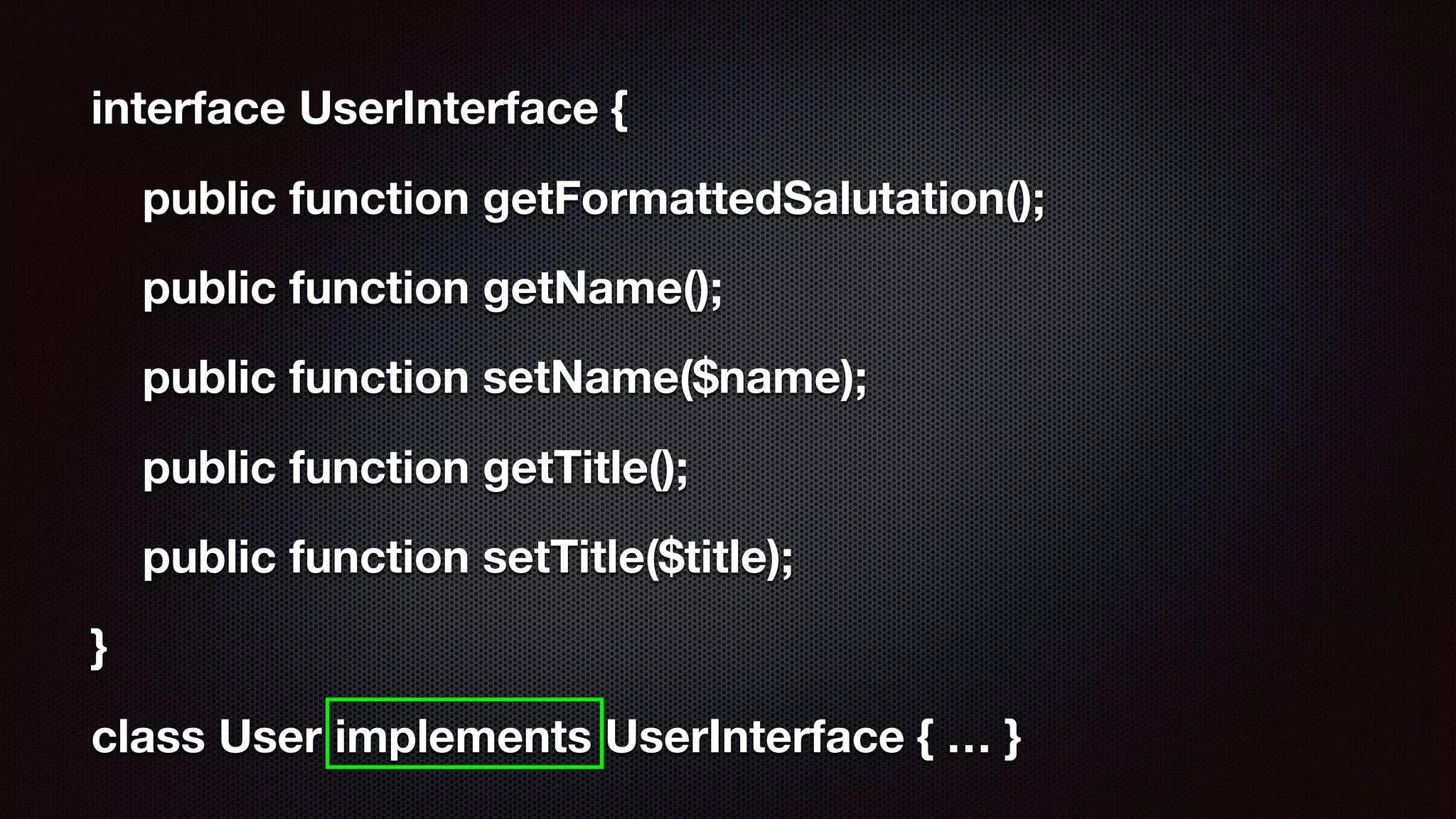
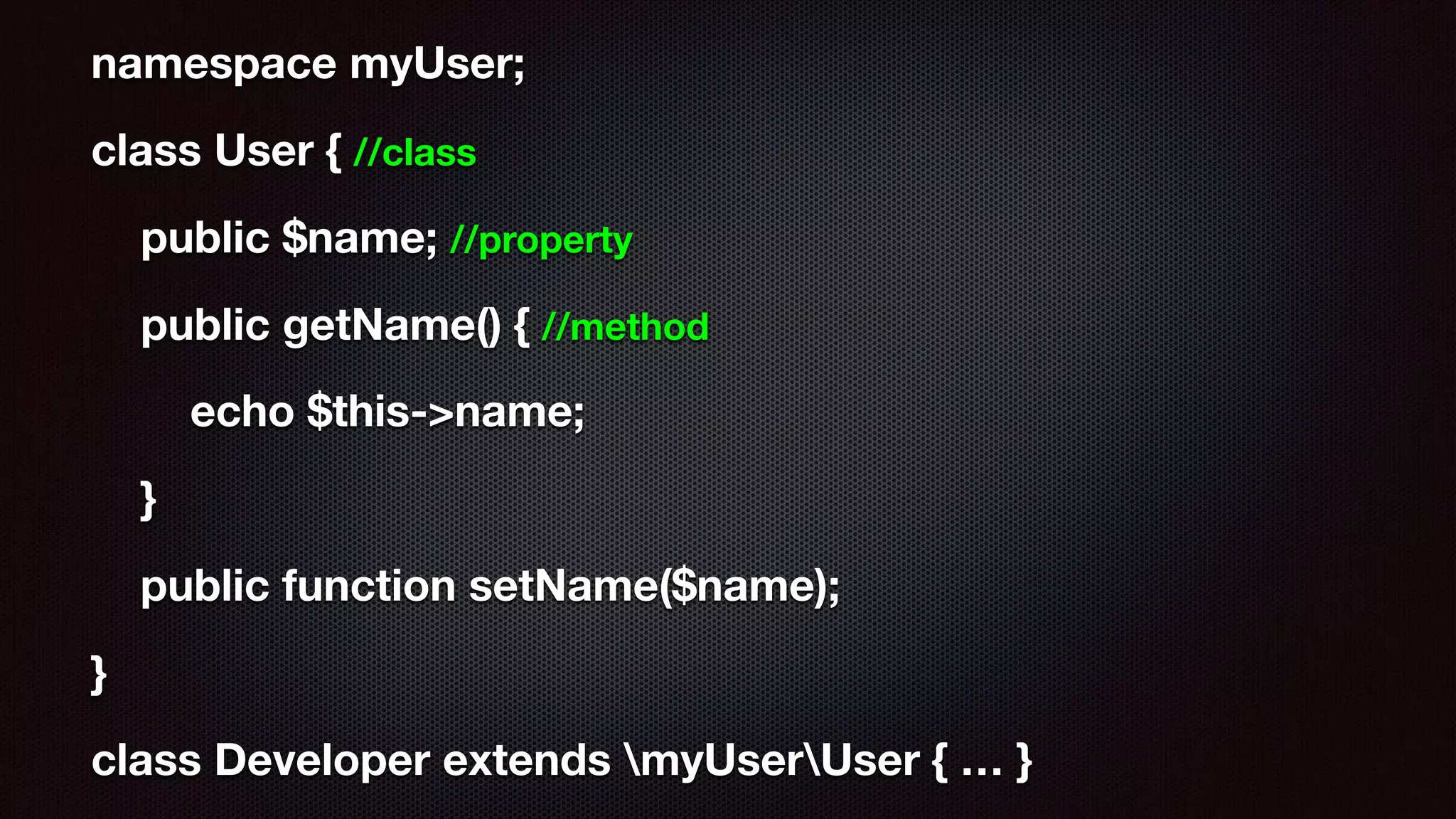
Alena Holligan presented on demystifying object-oriented programming in PHP. She discussed key OOP concepts like classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, interfaces, abstract classes and traits. The presentation covered terminology, creating classes and objects, encapsulation, inheritance and polymorphism through subclasses and interfaces. Later sections discussed namespaces, type declarations, magic methods, magic constants and static methods. The goal was to explain core OOP concepts in PHP through examples and challenges for attendees.






















![Using a child class $developer = new Developer();
$developer->setName(”Jane Smith”);
$developer->setTitle(“Ms”); echo $developer->getFormatedSalutation();
echo "<br />”; $developer->skills = array("JavasScript", "HTML", "CSS");
$developer->skills[] = “PHP"; echo $developer->getSkillsString();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/demystifyingoop-161018200226/75/Demystifying-Object-Oriented-Programming-ZendCon-2016-23-2048.jpg)





![Creating Traits trait Toolkit {
public $tools = array();
public function setTools($task) {
switch ($task) {
case “eat":
$this->tools[] =
array("Spoon", "Fork", "Knife");
exit;
...
}
}
public function showTools() {
return implode(", ",$this->skills);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/demystifyingoop-161018200226/75/Demystifying-Object-Oriented-Programming-ZendCon-2016-30-2048.jpg)







![Type Declarations class Conference {
public $title;
private $attendees = array();
public function addAttendee(User $person) {
$this->attendees[] = $person;
}
public function getAttendees(): array {
foreach($this->attendees as $person) {
$attendee_list[] = $person;
}
return $attendee_list;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/demystifyingoop-161018200226/75/Demystifying-Object-Oriented-Programming-ZendCon-2016-39-2048.jpg)





![Adding a Static Methods class User {
public $encouragements = array(
“You are beautiful!”,
“You have this!”,
public static function encourage()
{
$int = rand(count($this->encouragements));
return $this->encouragements[$int];
}
...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/demystifyingoop-161018200226/75/Demystifying-Object-Oriented-Programming-ZendCon-2016-45-2048.jpg)



