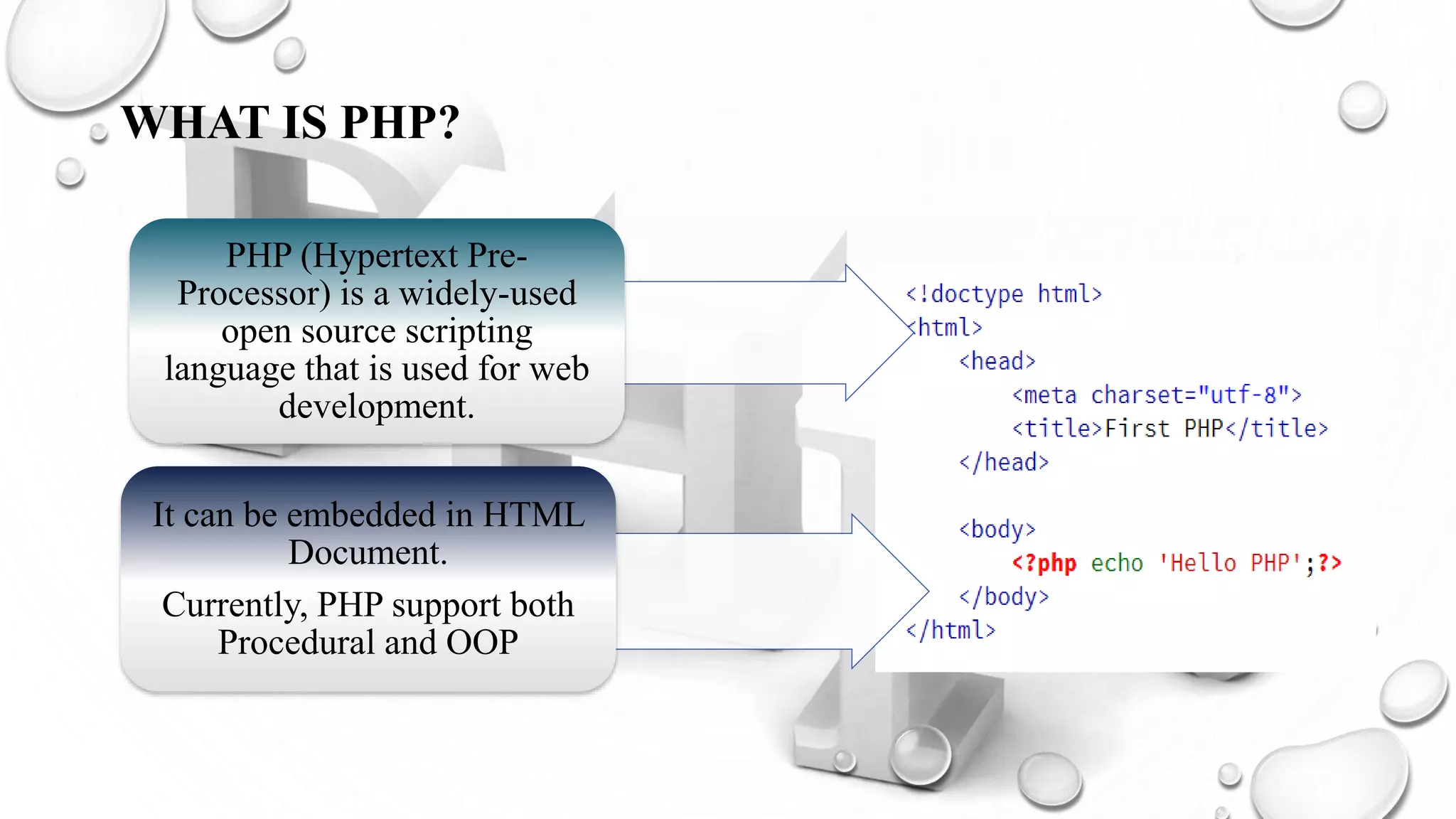
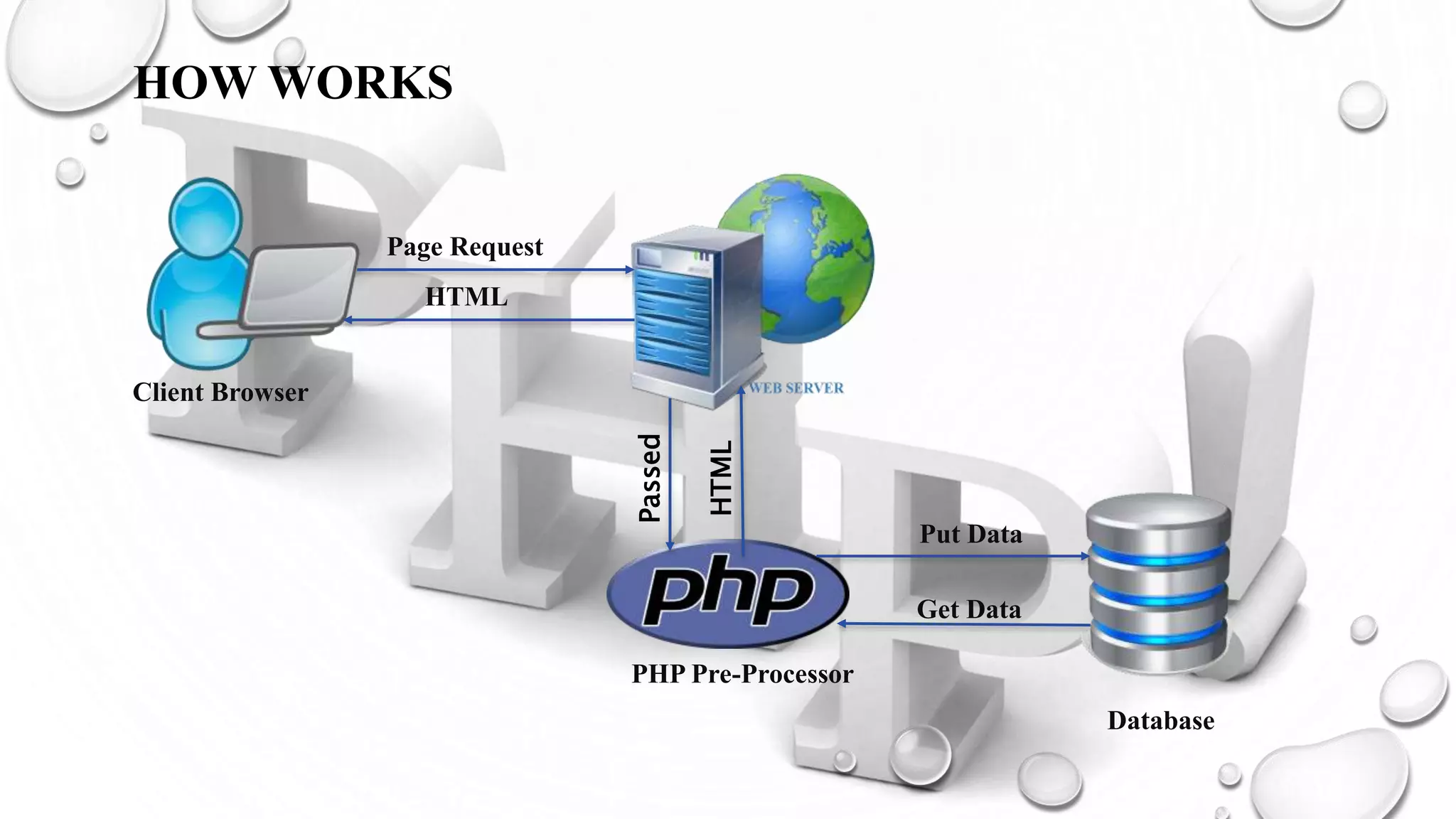
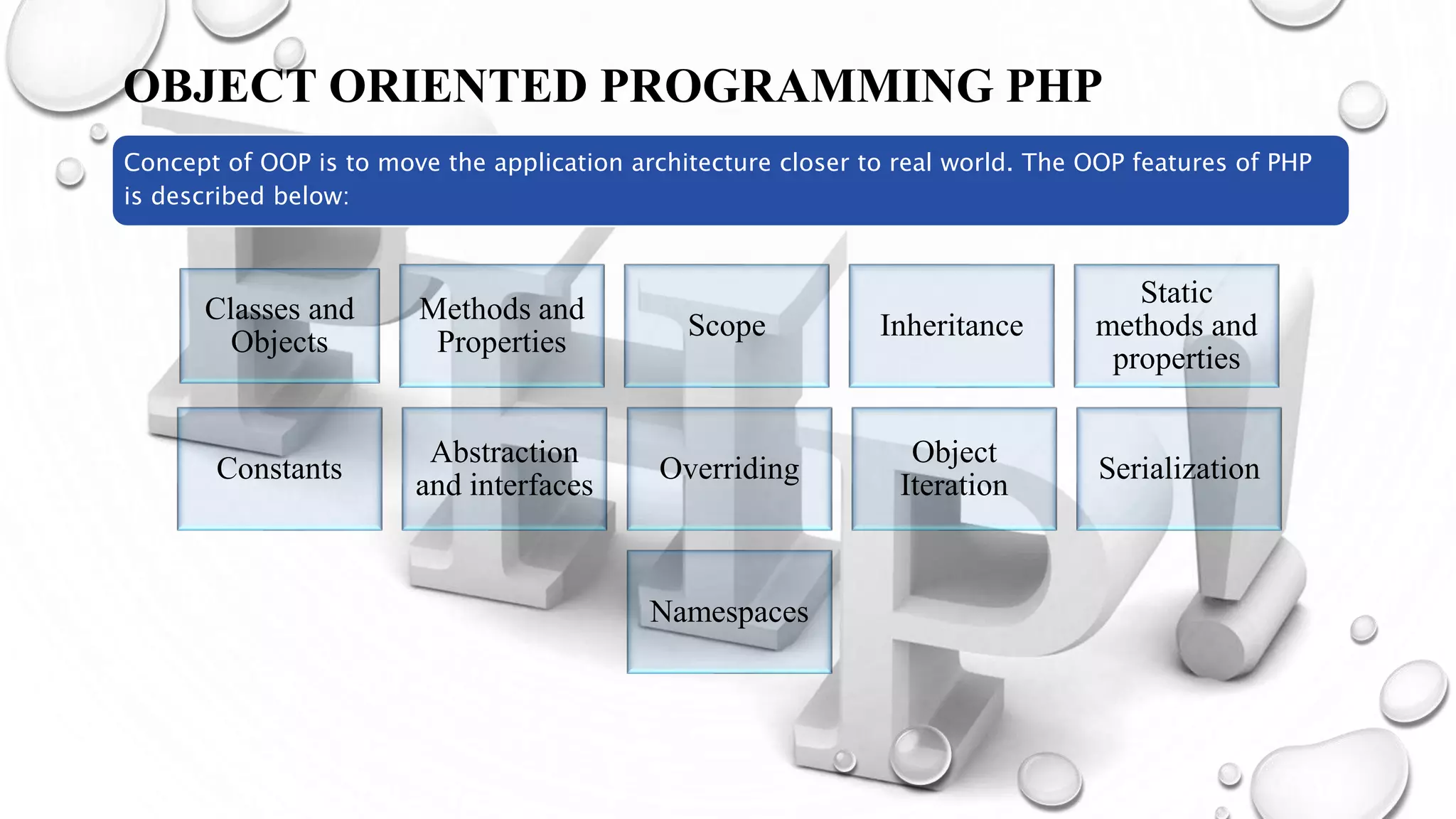
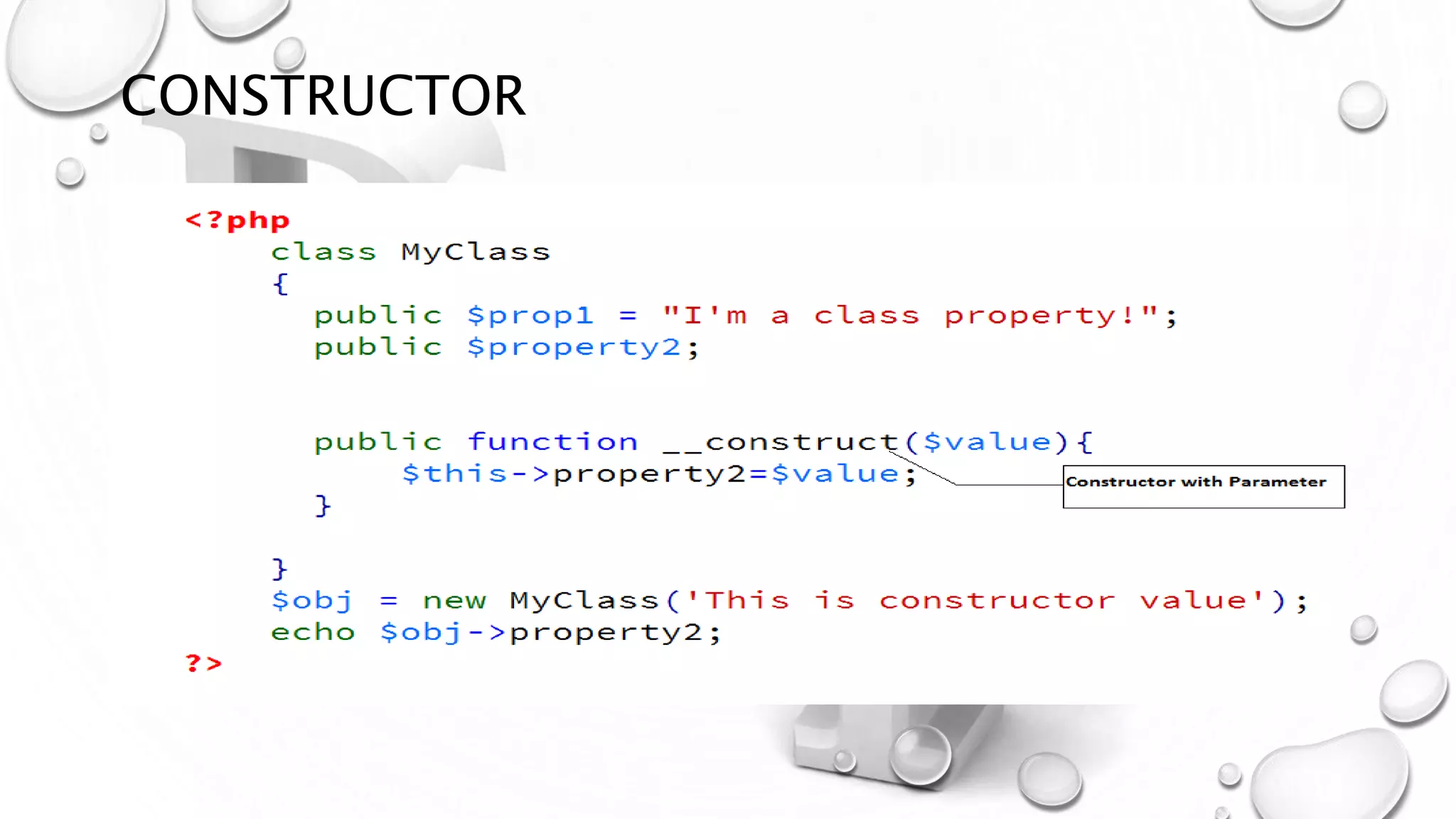
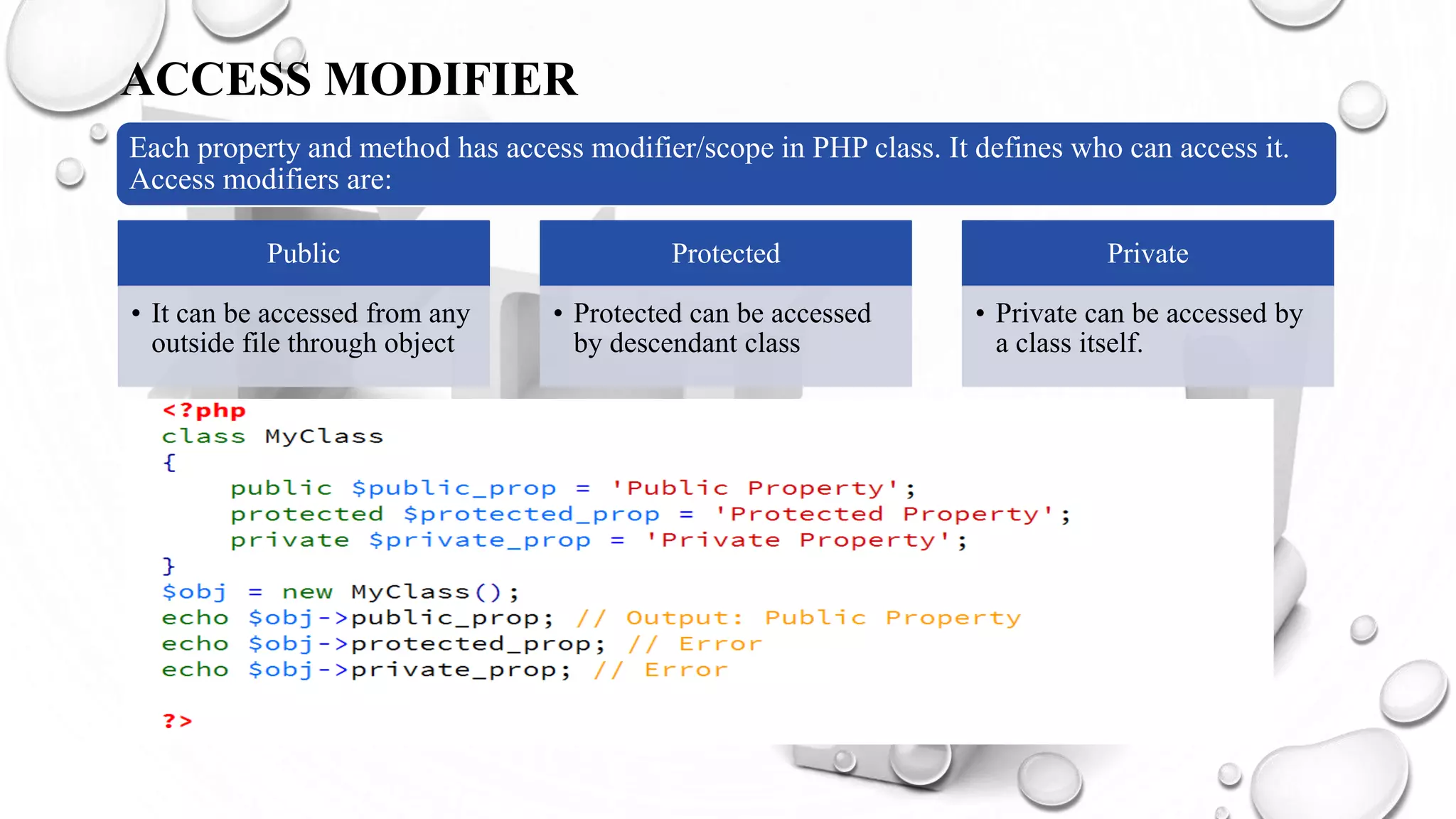
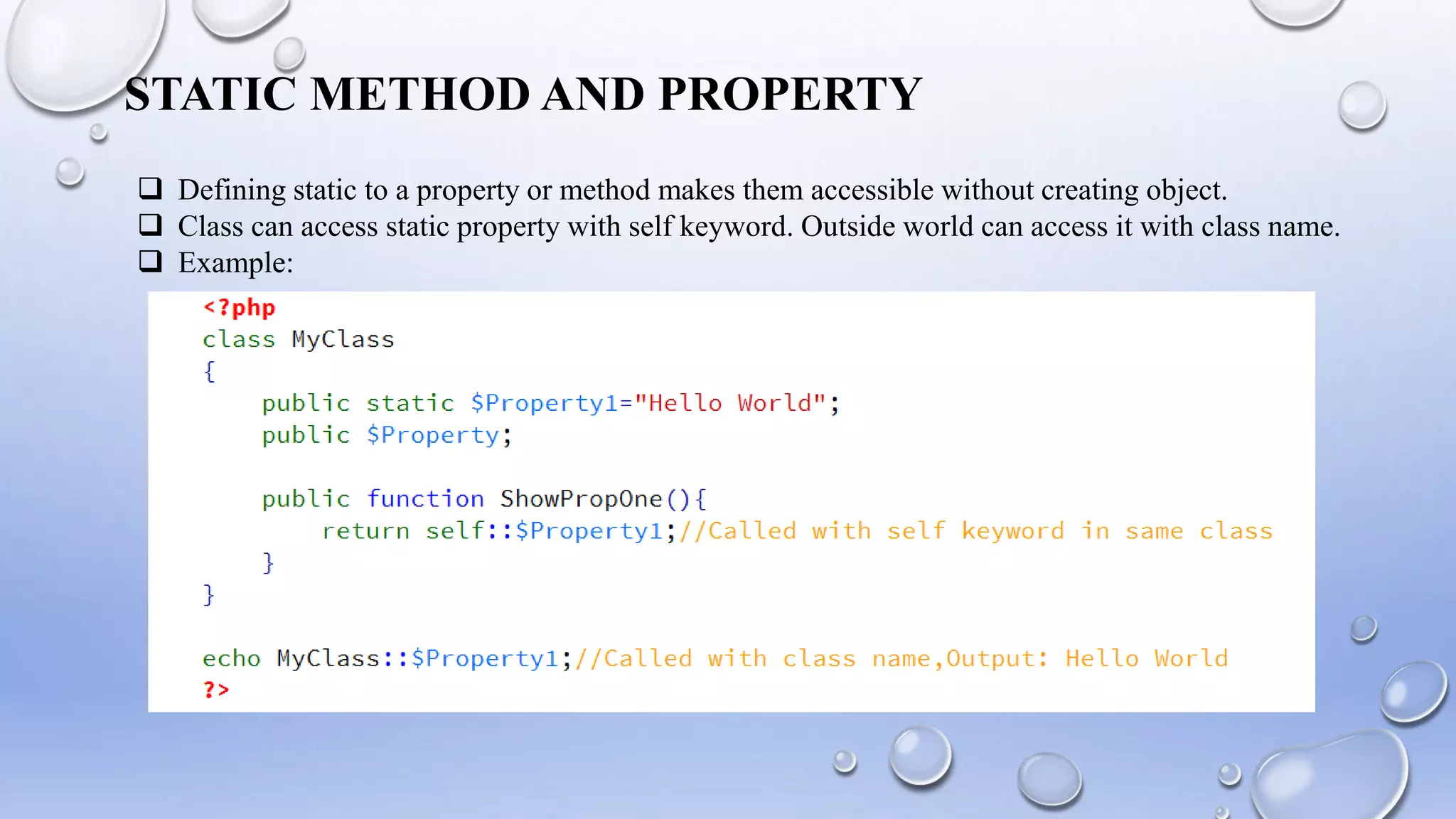
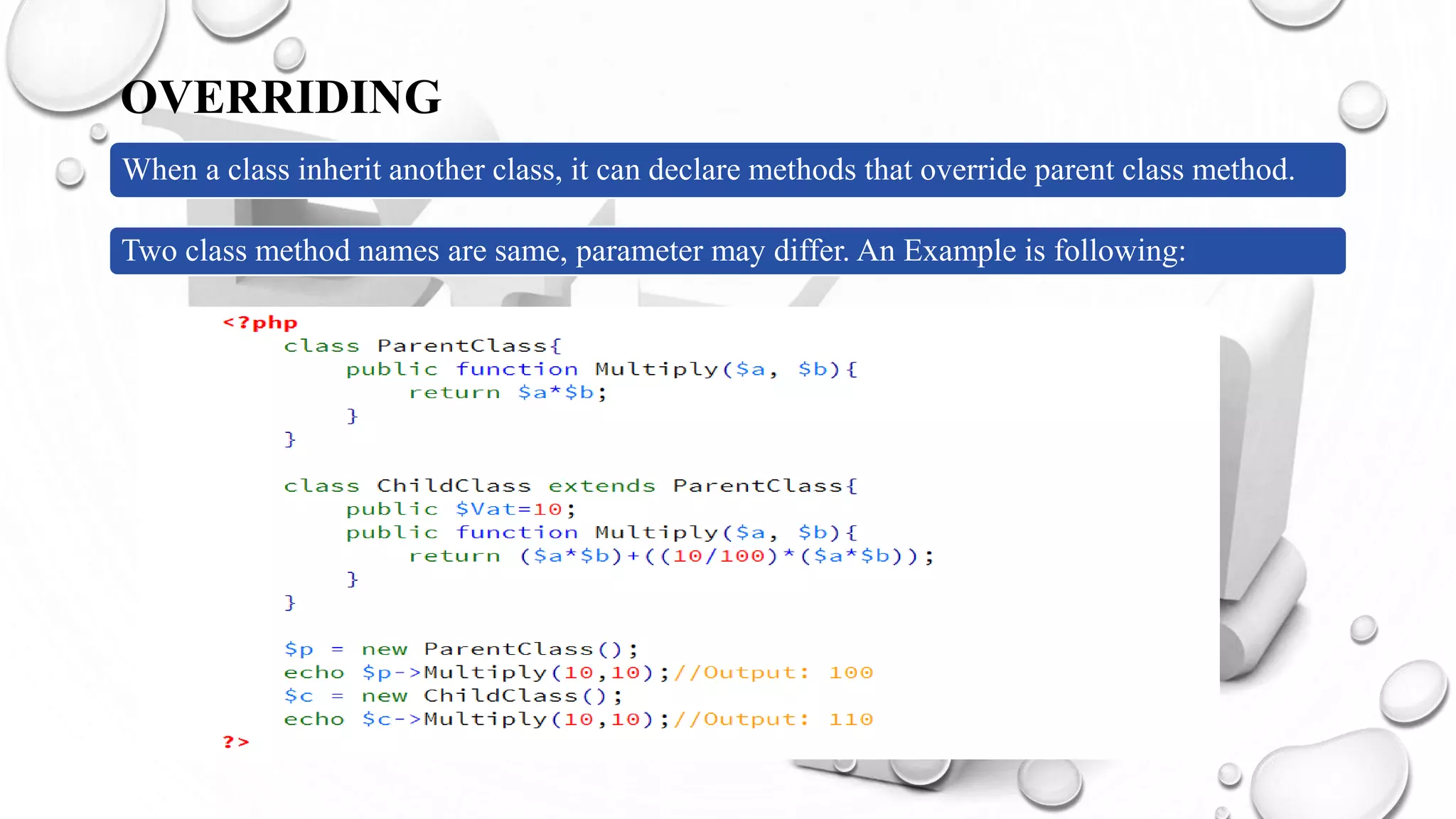
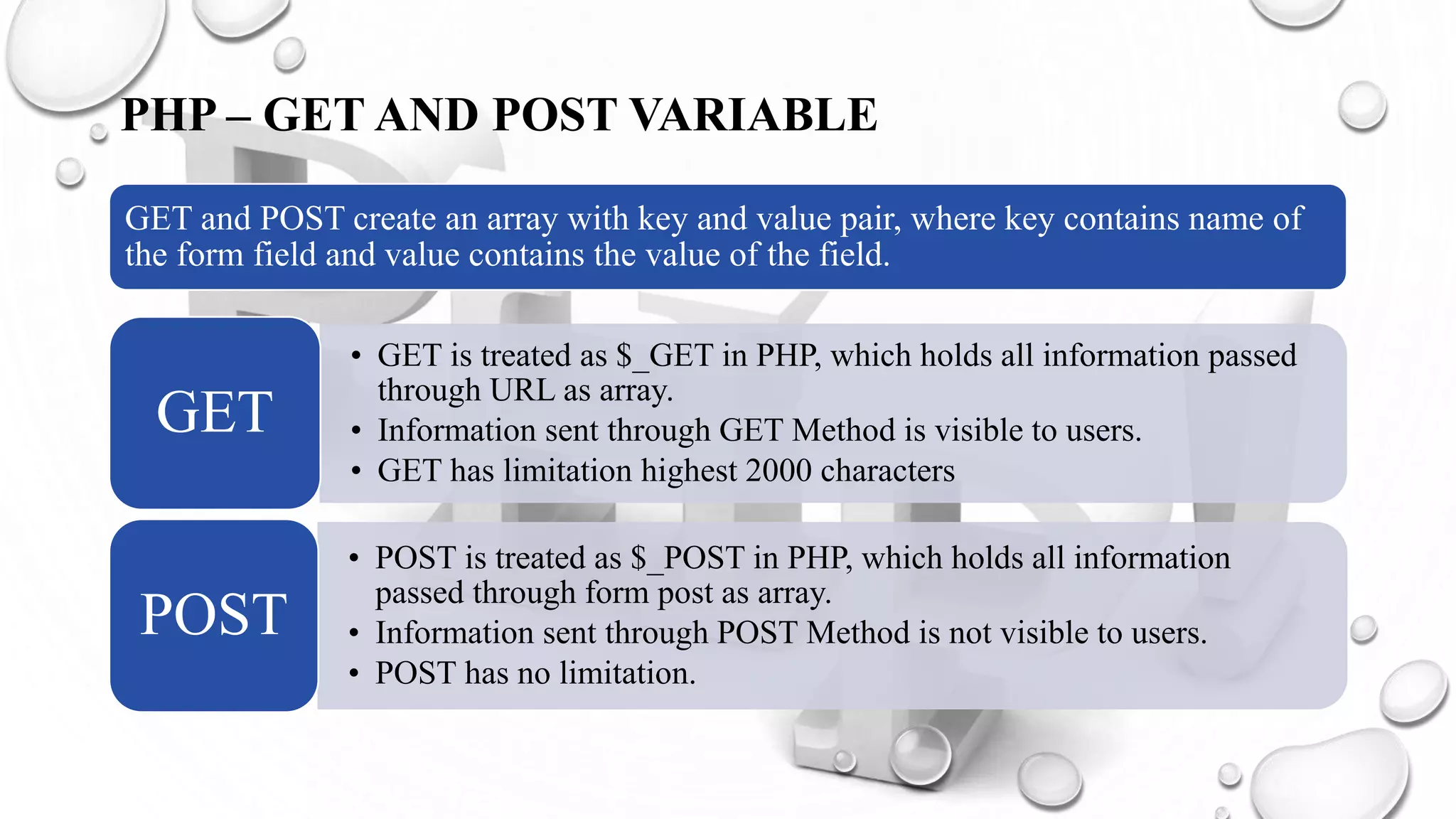
This document introduces PHP and its basic concepts. PHP is an open source scripting language widely used for web development. It allows embedding code into HTML documents. Key topics covered include what PHP is, its history and how it works, its capabilities, why it is used, benefits for students, basic and object-oriented programming in PHP, GET and POST methods, sessions and cookies. Popular PHP frameworks and content management systems built with PHP are also listed.