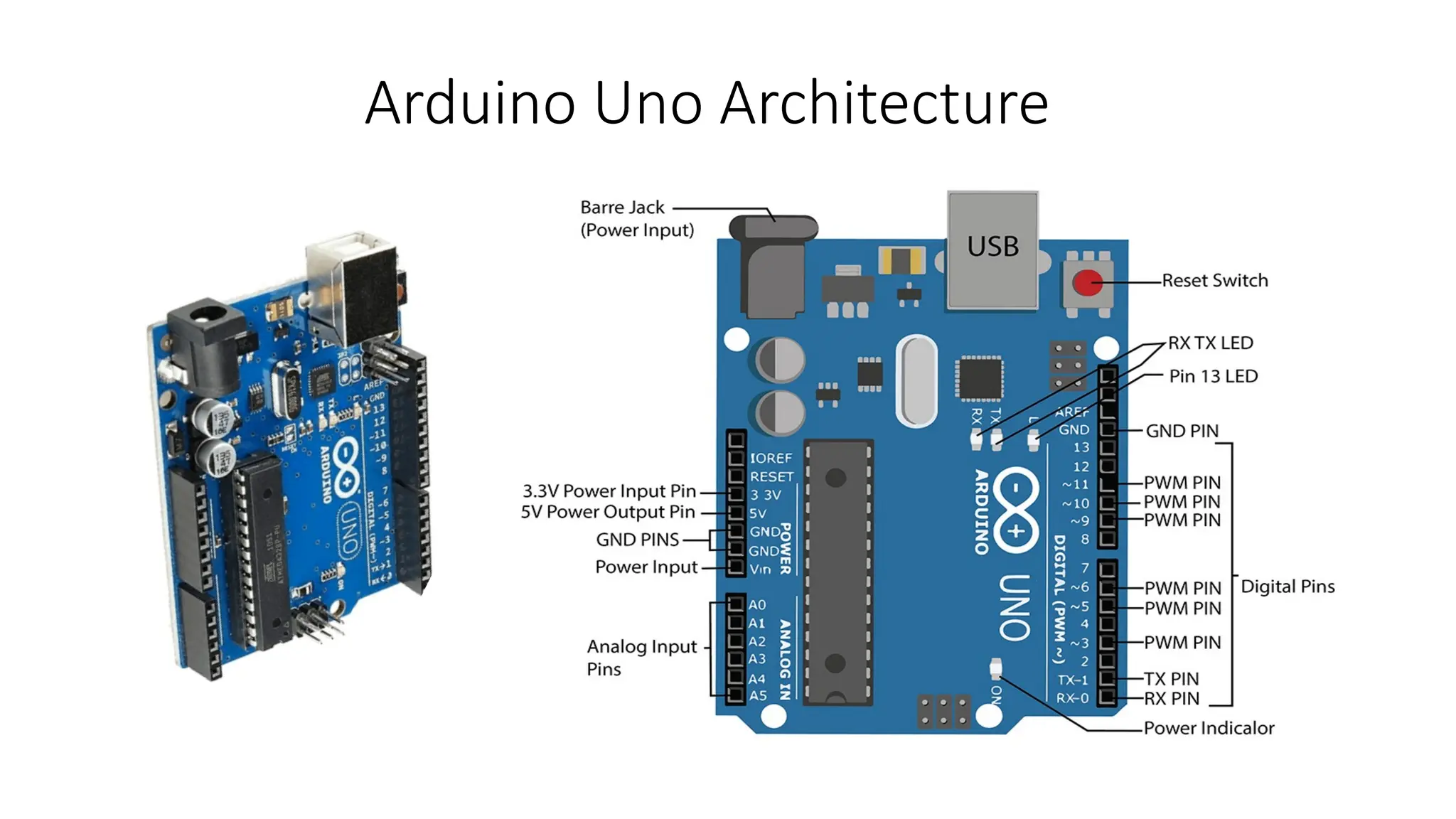
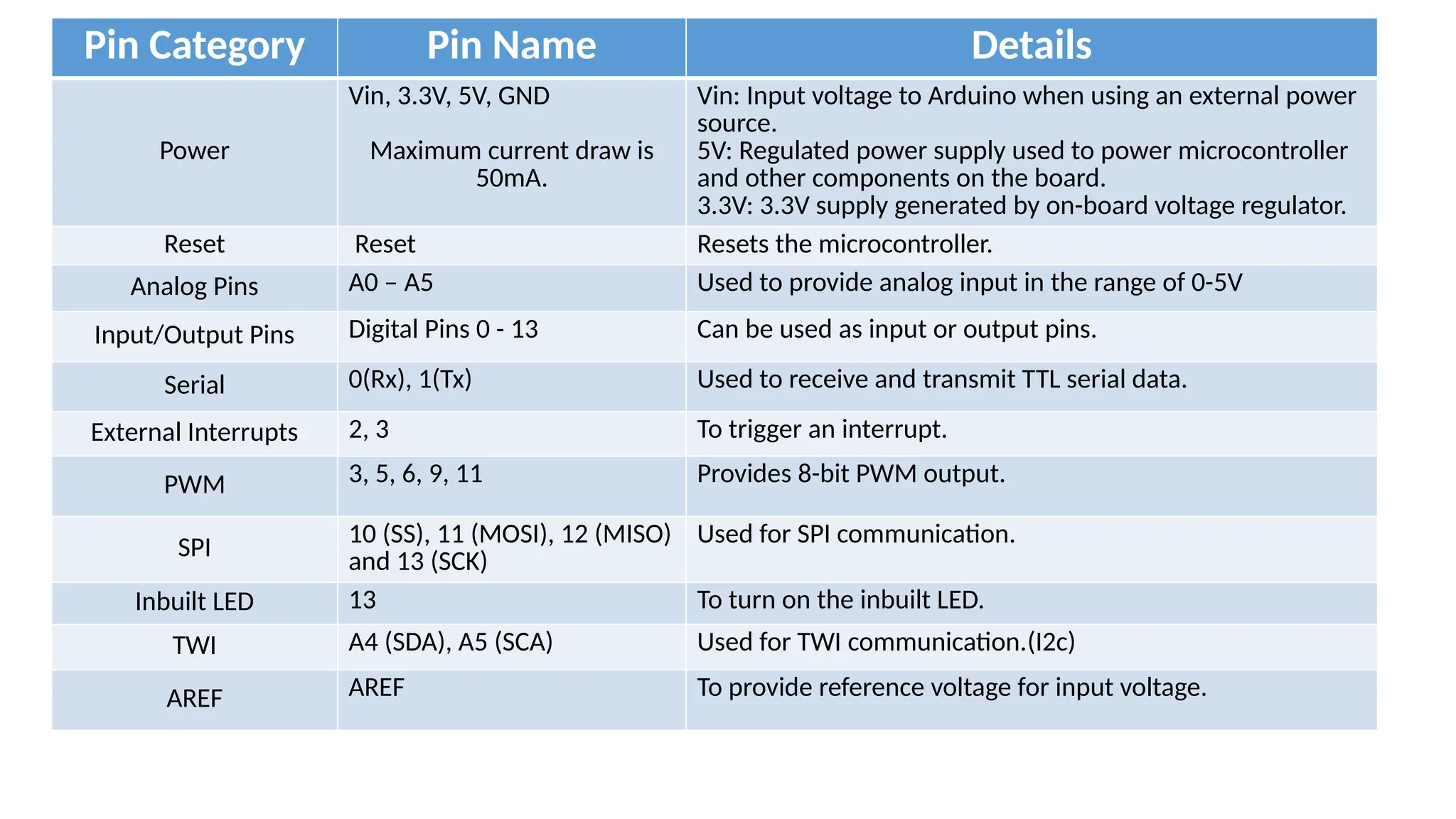
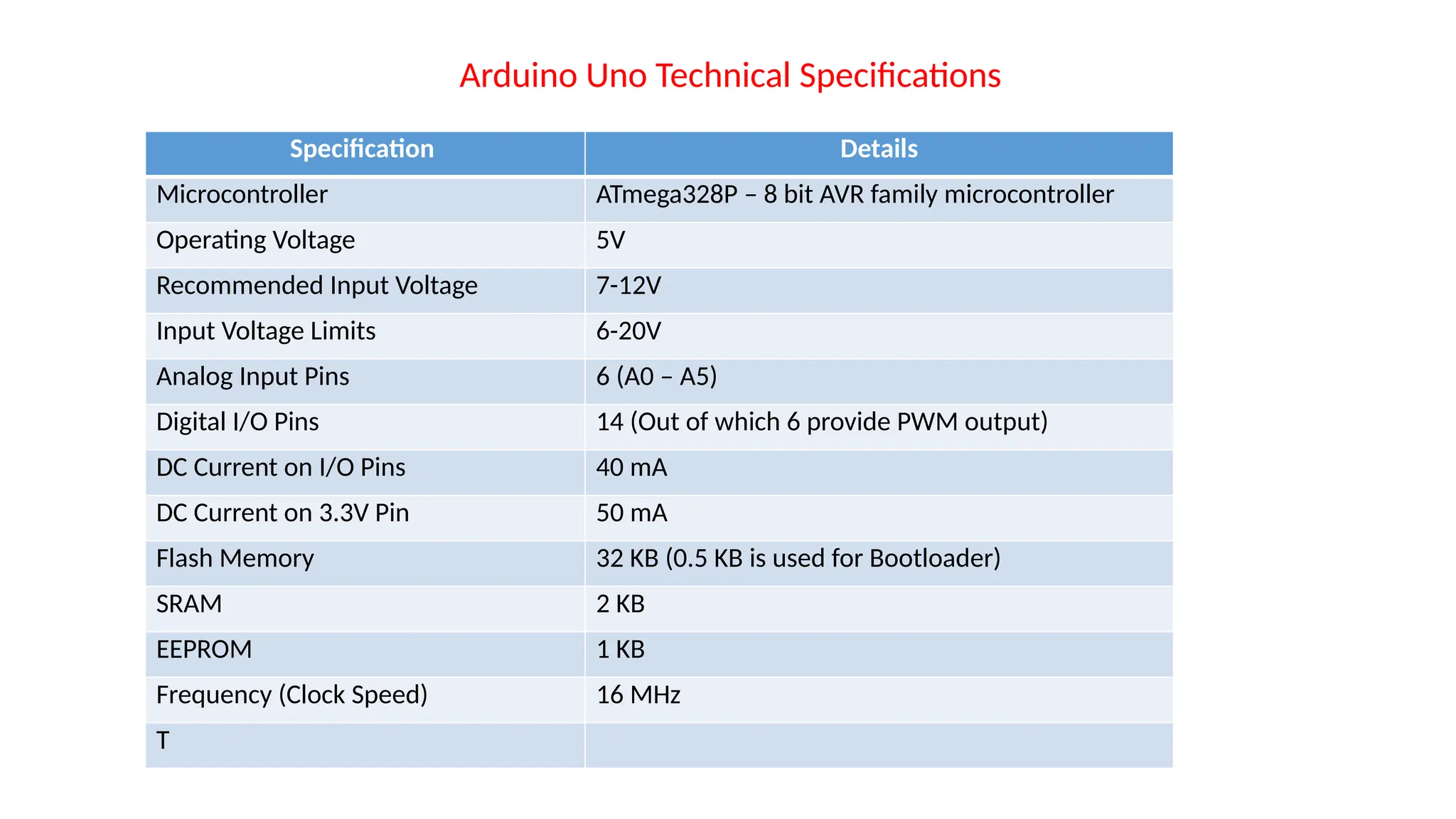
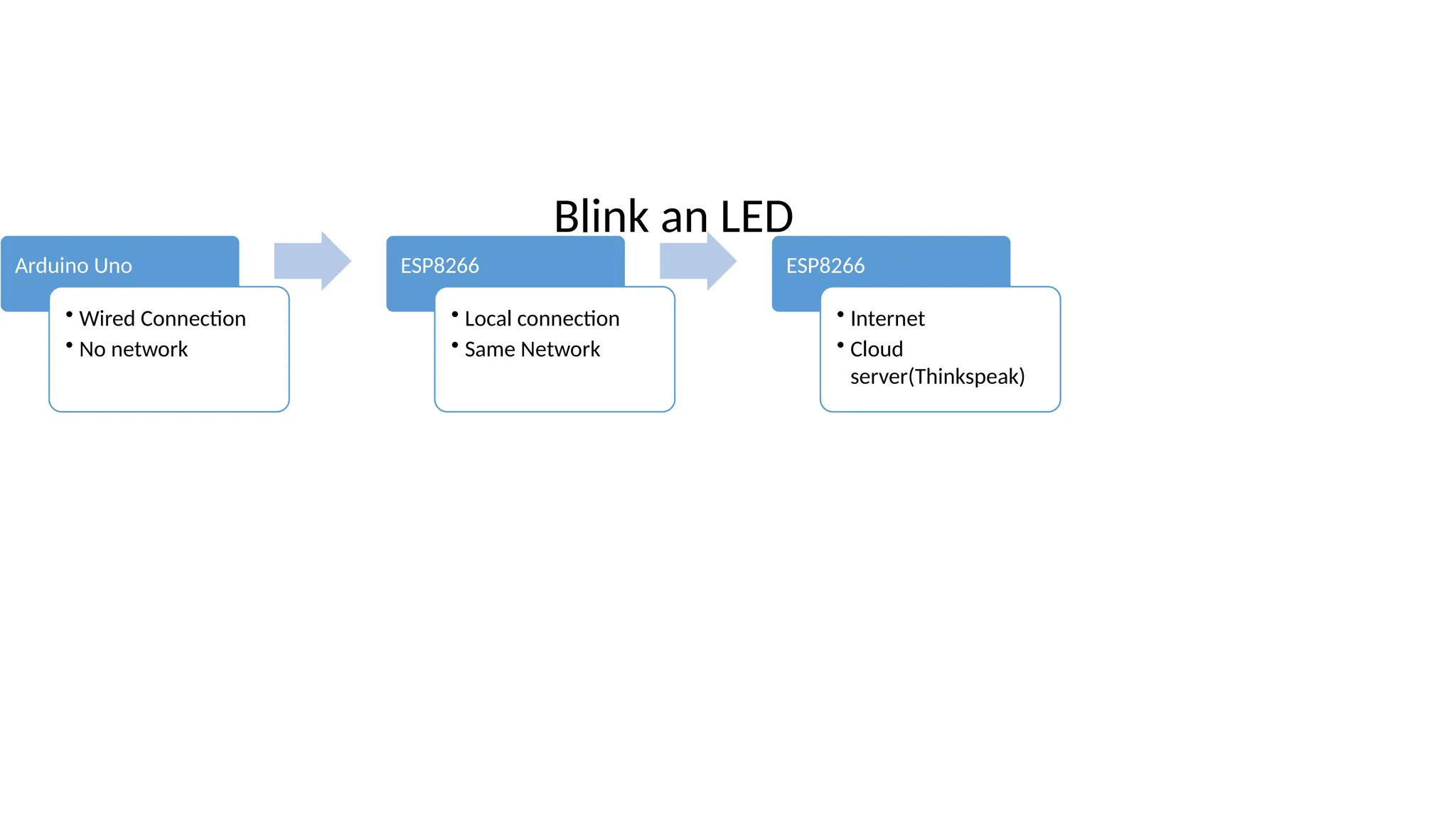
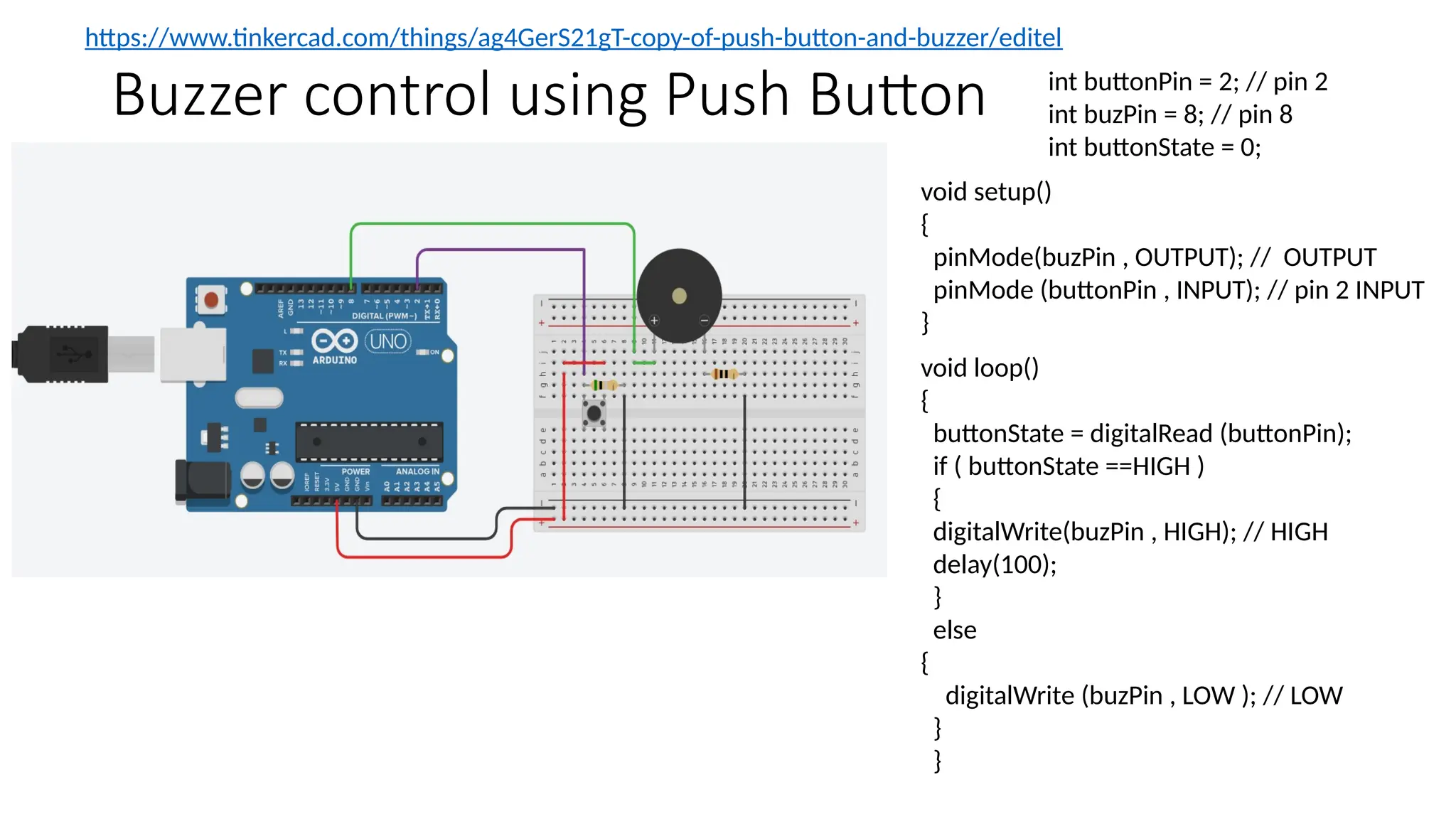
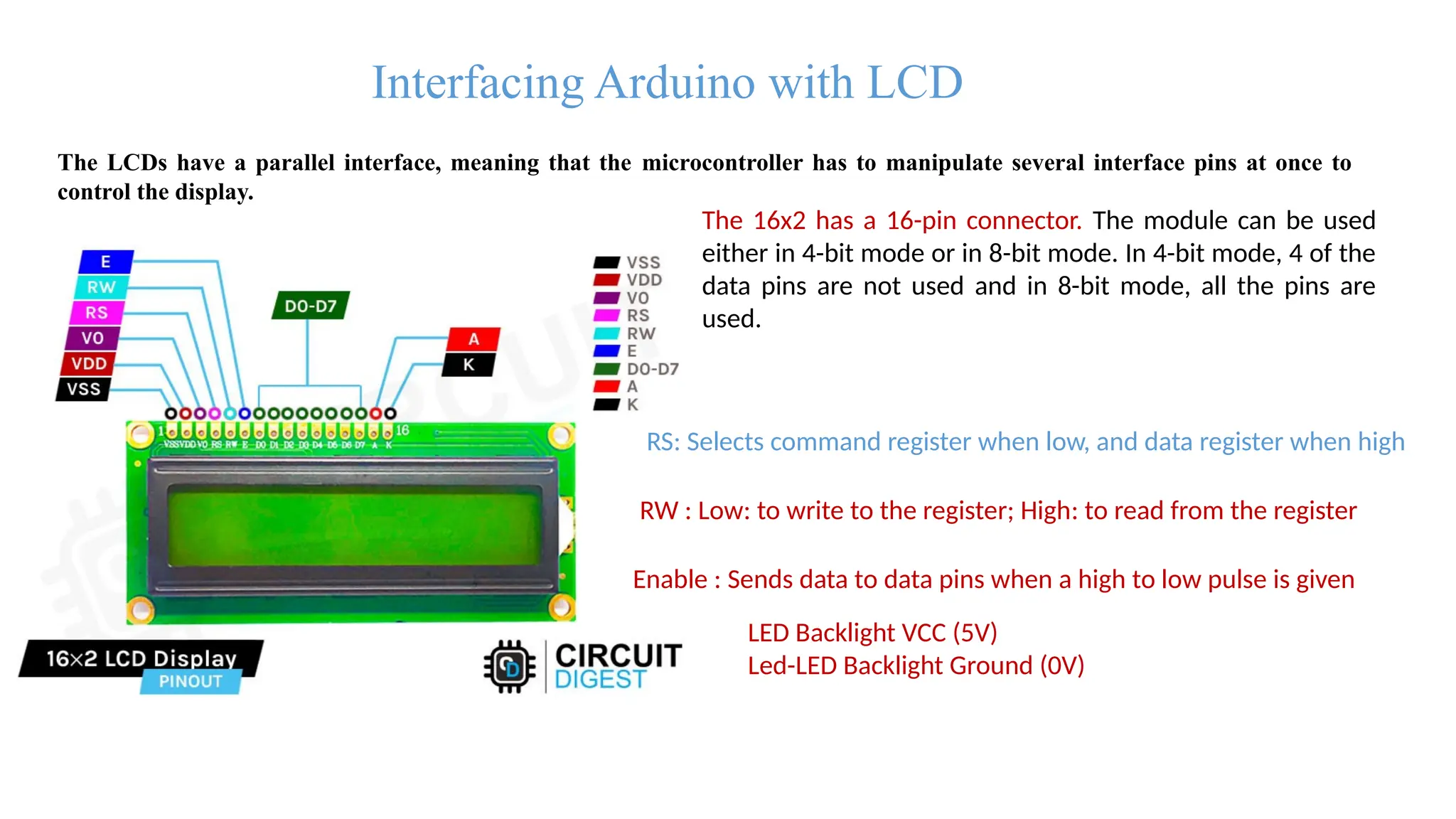
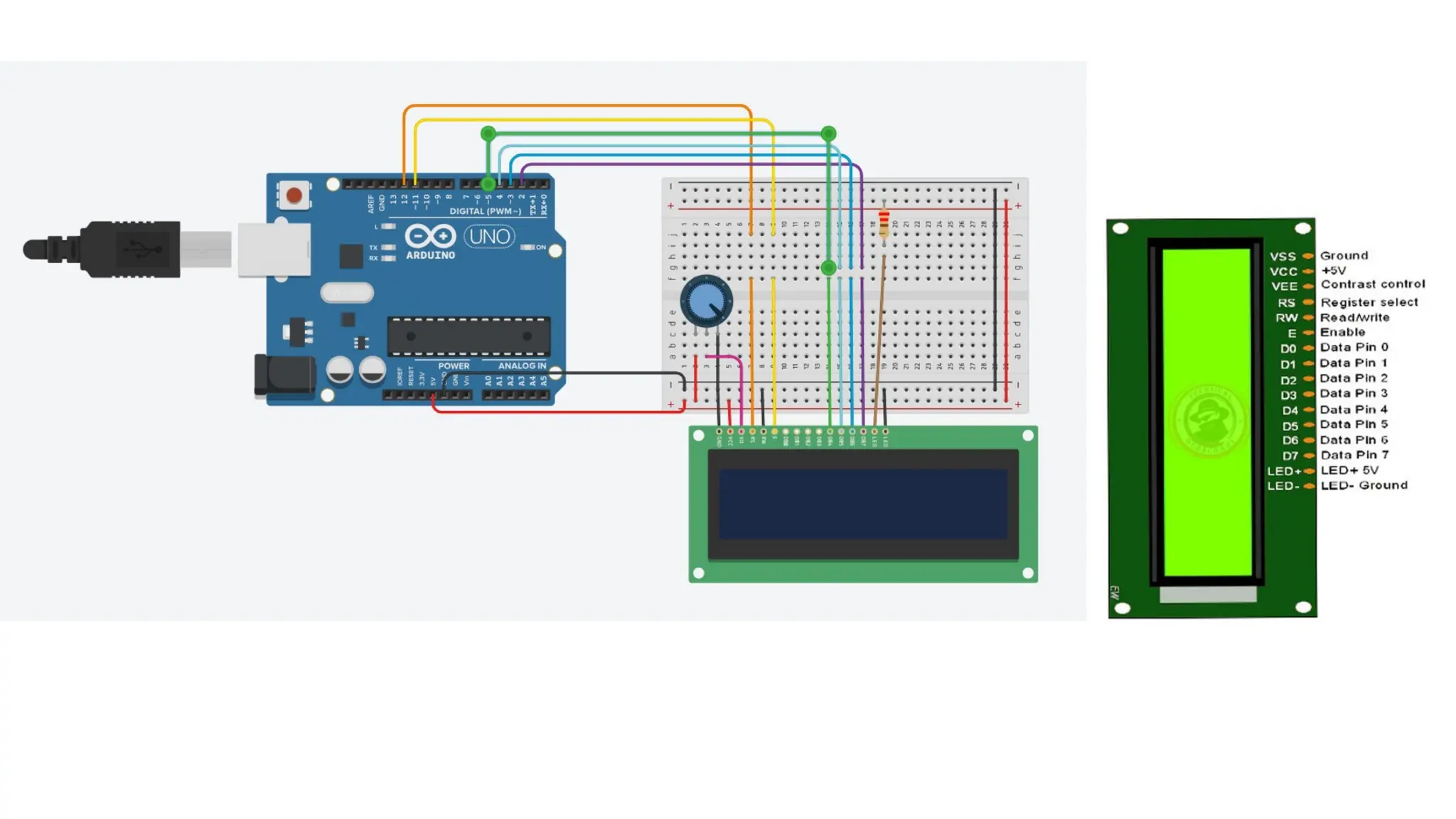
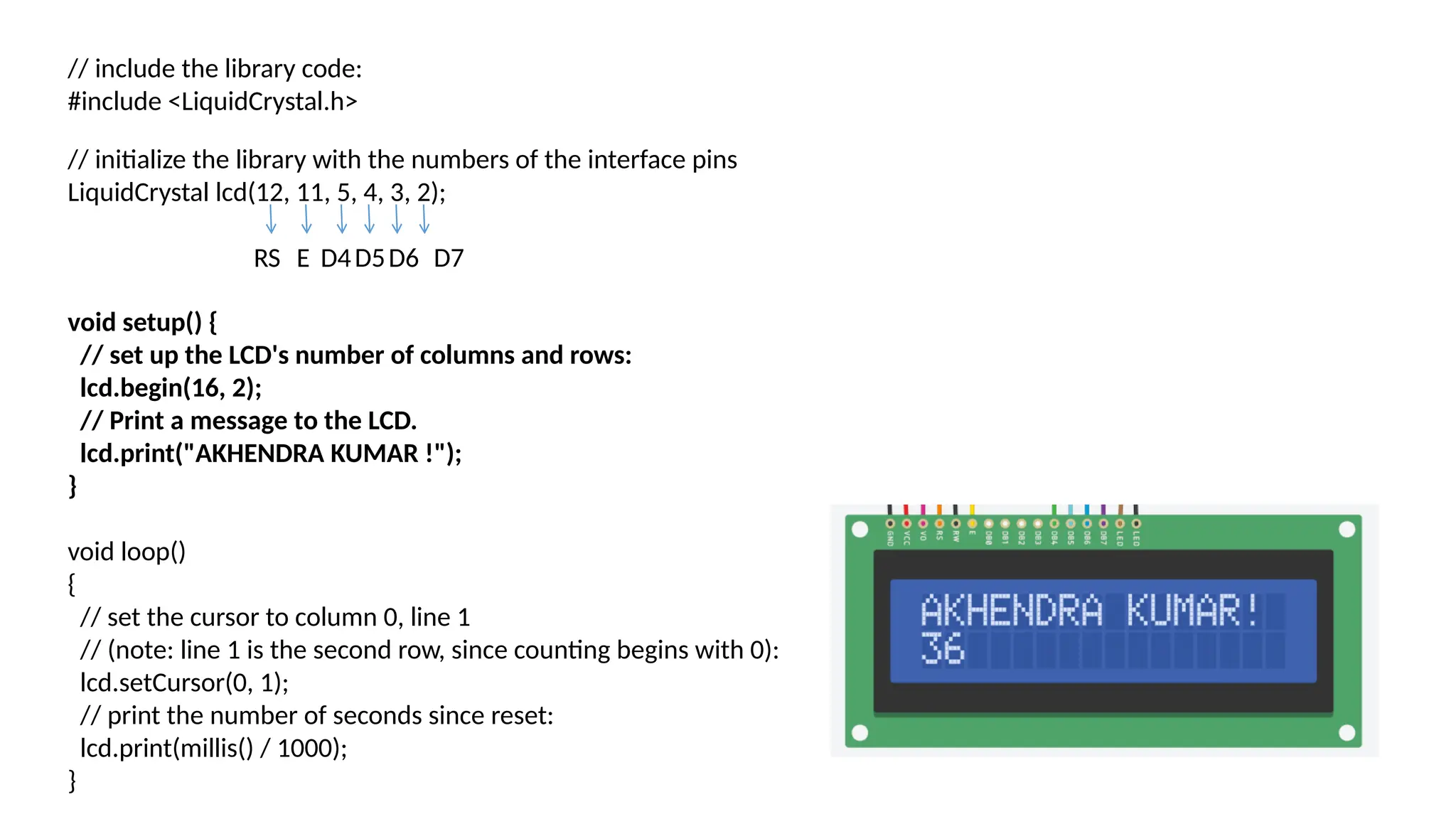
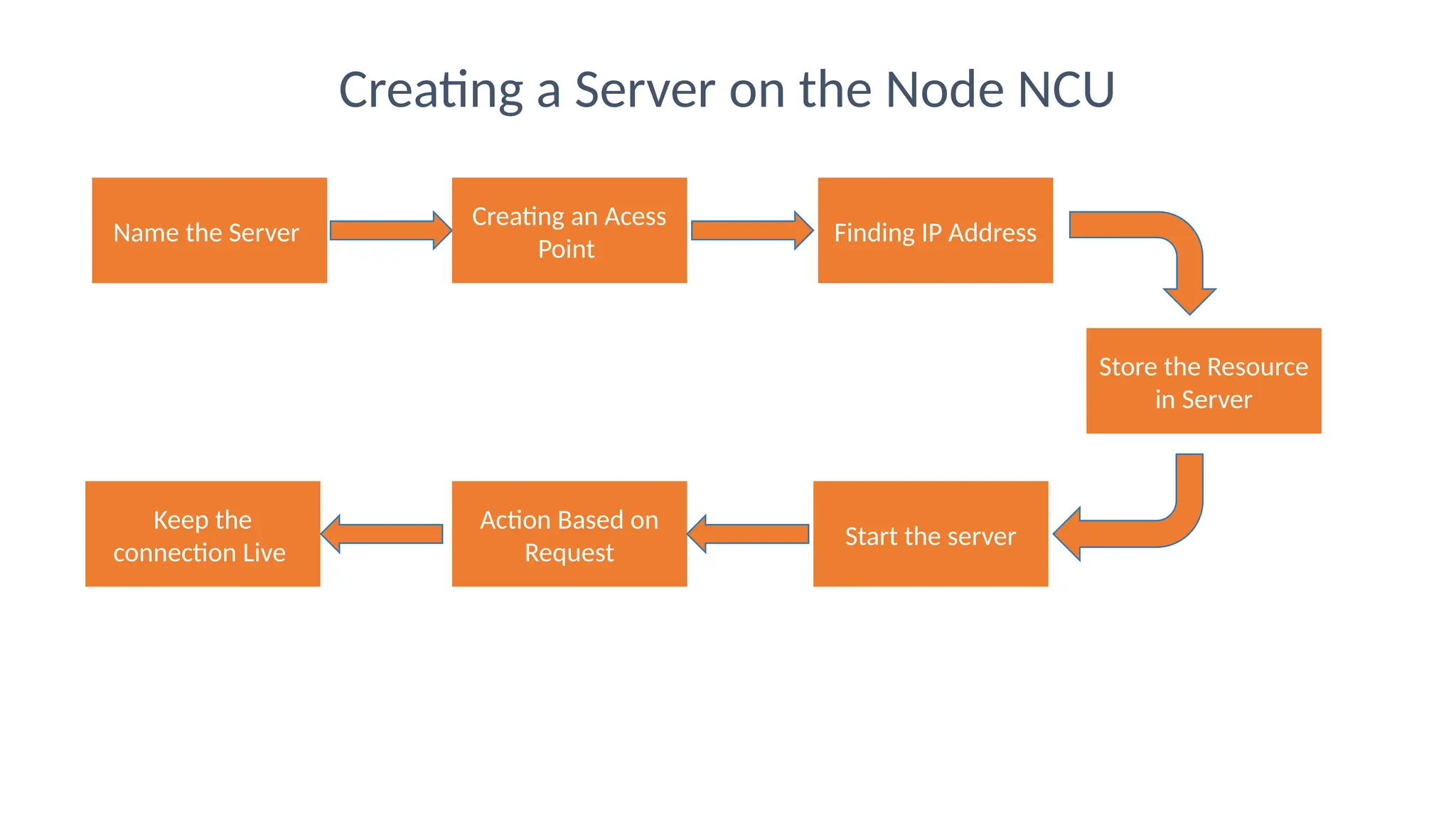
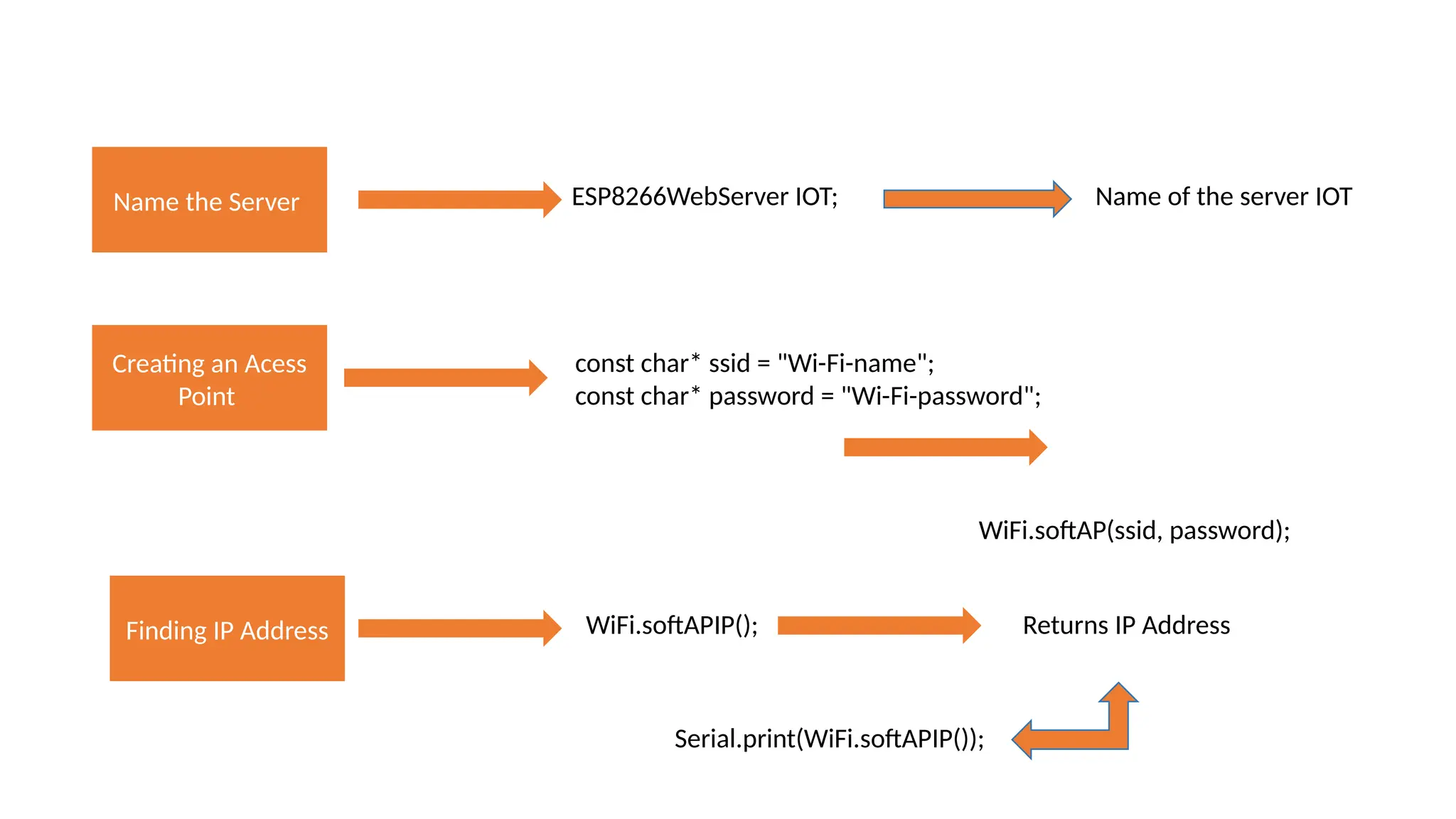
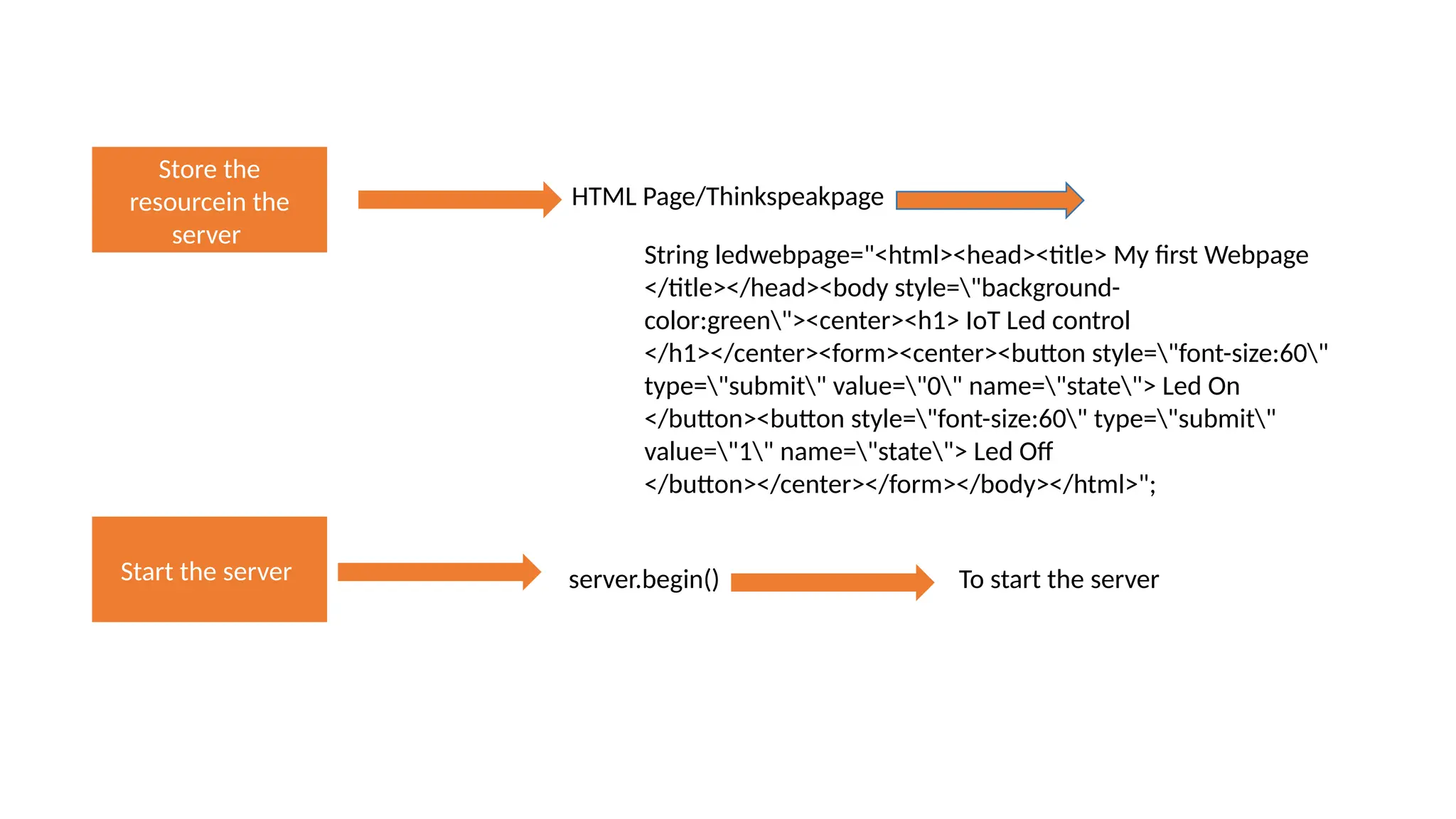
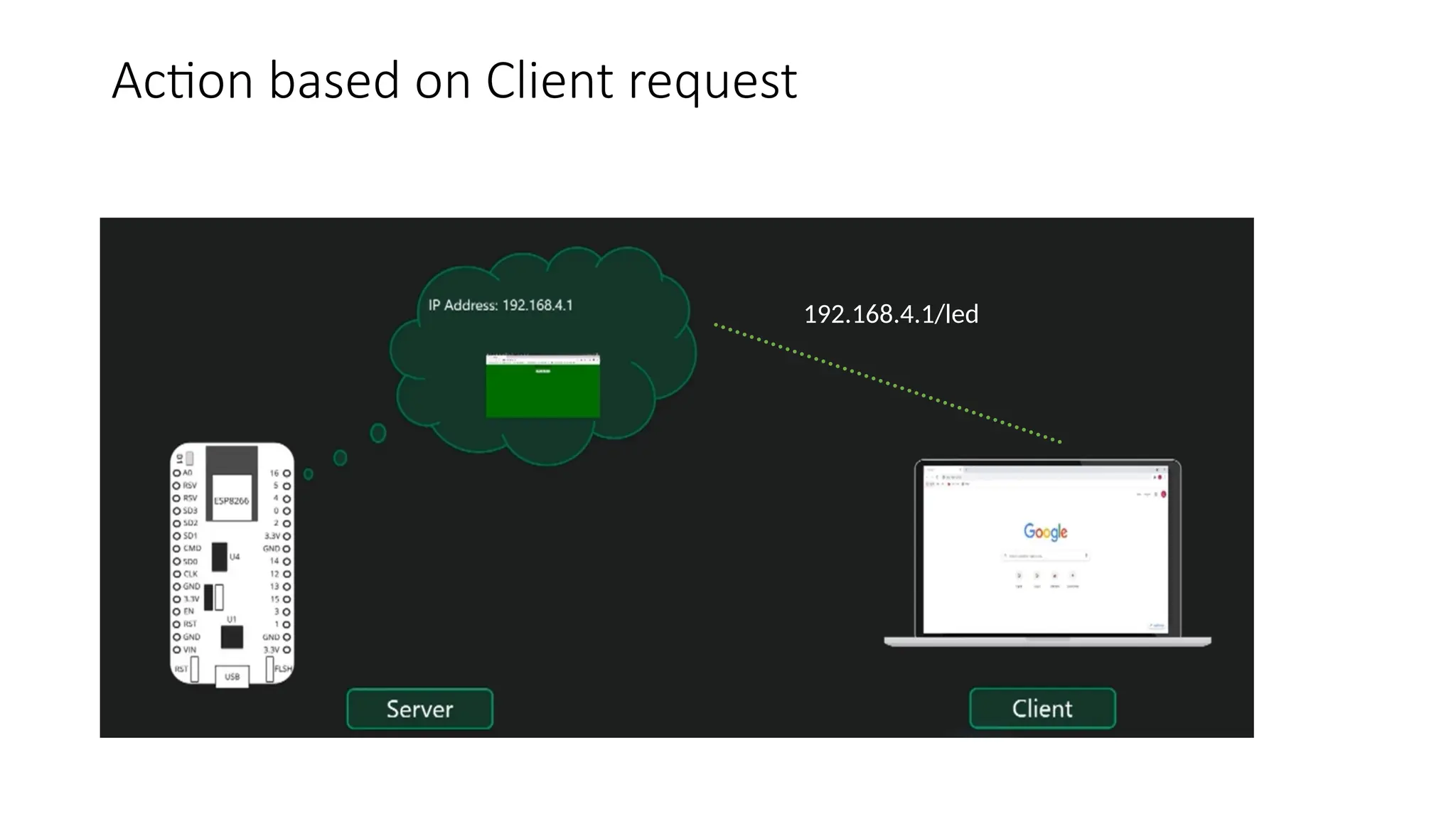
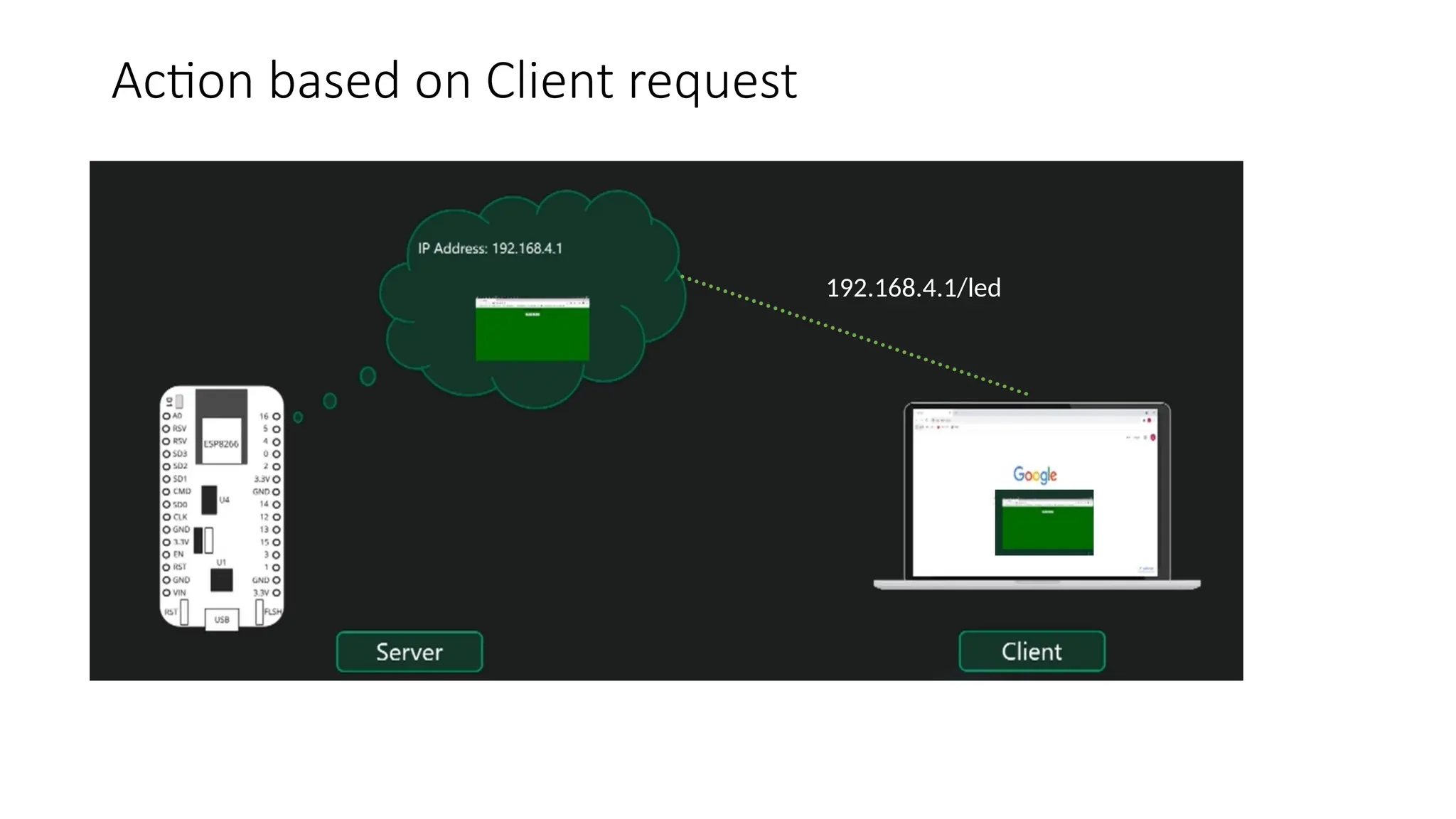
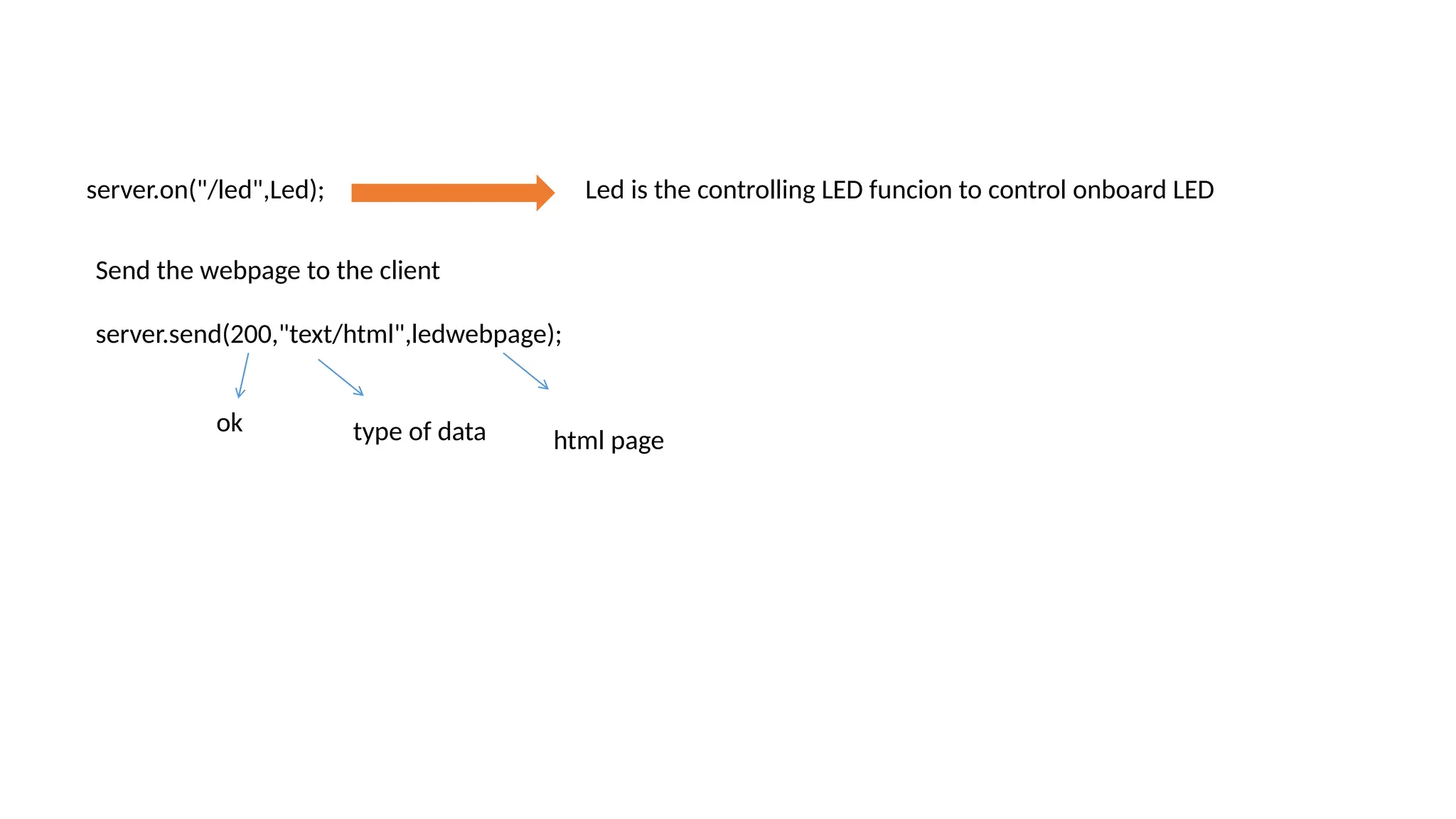
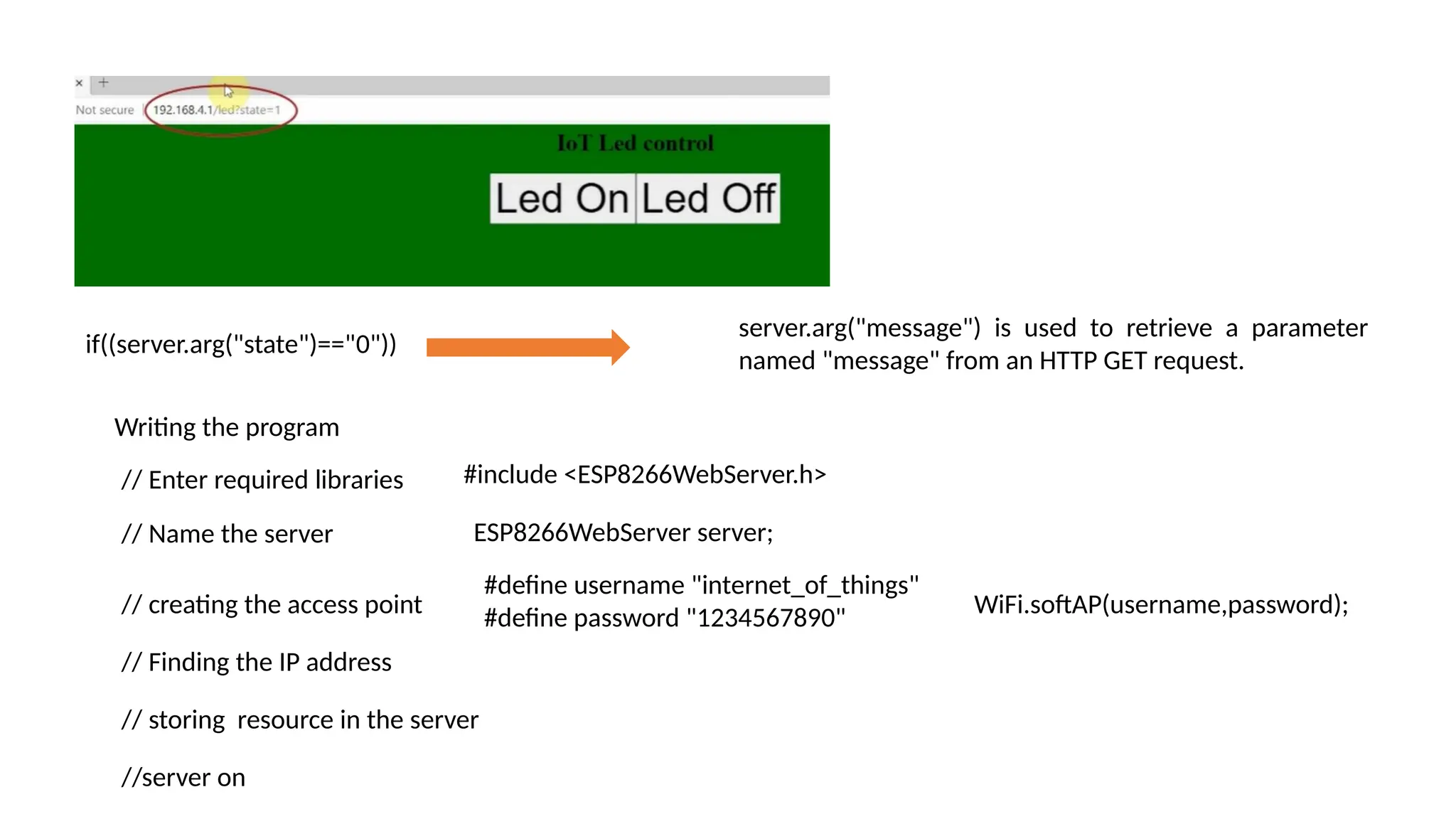
The document provides an overview of the Arduino simulation environment, detailing the architecture of the Arduino Uno, its technical specifications, and programming functions. It explains how to set up the IDE, write software, and interface various components like LEDs, push buttons, buzzers, and LCDs with Arduino. Additionally, it covers basic concepts of embedded programming and includes example code for controlling LEDs and creating a web server using an ESP8266.