Embed presentation
Downloaded 39 times

![import java.util.Scanner; class GetInput { public static void main(String args[]) { int a; Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Enter an integer"); a = in.nextInt(); System.out.println("You entered integer "+a); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handlinginputsviascannerclass-141113091449-conversion-gate02/75/Handling-inputs-via-scanner-class-3-2048.jpg)
![import java.util.Scanner; class GetInput { public static void main(String args[]) { float b; Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Enter a float"); b = in.nextFloat(); System.out.println("You entered float "+b); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handlinginputsviascannerclass-141113091449-conversion-gate02/75/Handling-inputs-via-scanner-class-4-2048.jpg)
![import java.util.Scanner; class GetInput { public static void main(String args[]) { String s; Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Enter a string"); s = in.nextLine(); System.out.println("You entered string"+s); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handlinginputsviascannerclass-141113091449-conversion-gate02/75/Handling-inputs-via-scanner-class-5-2048.jpg)
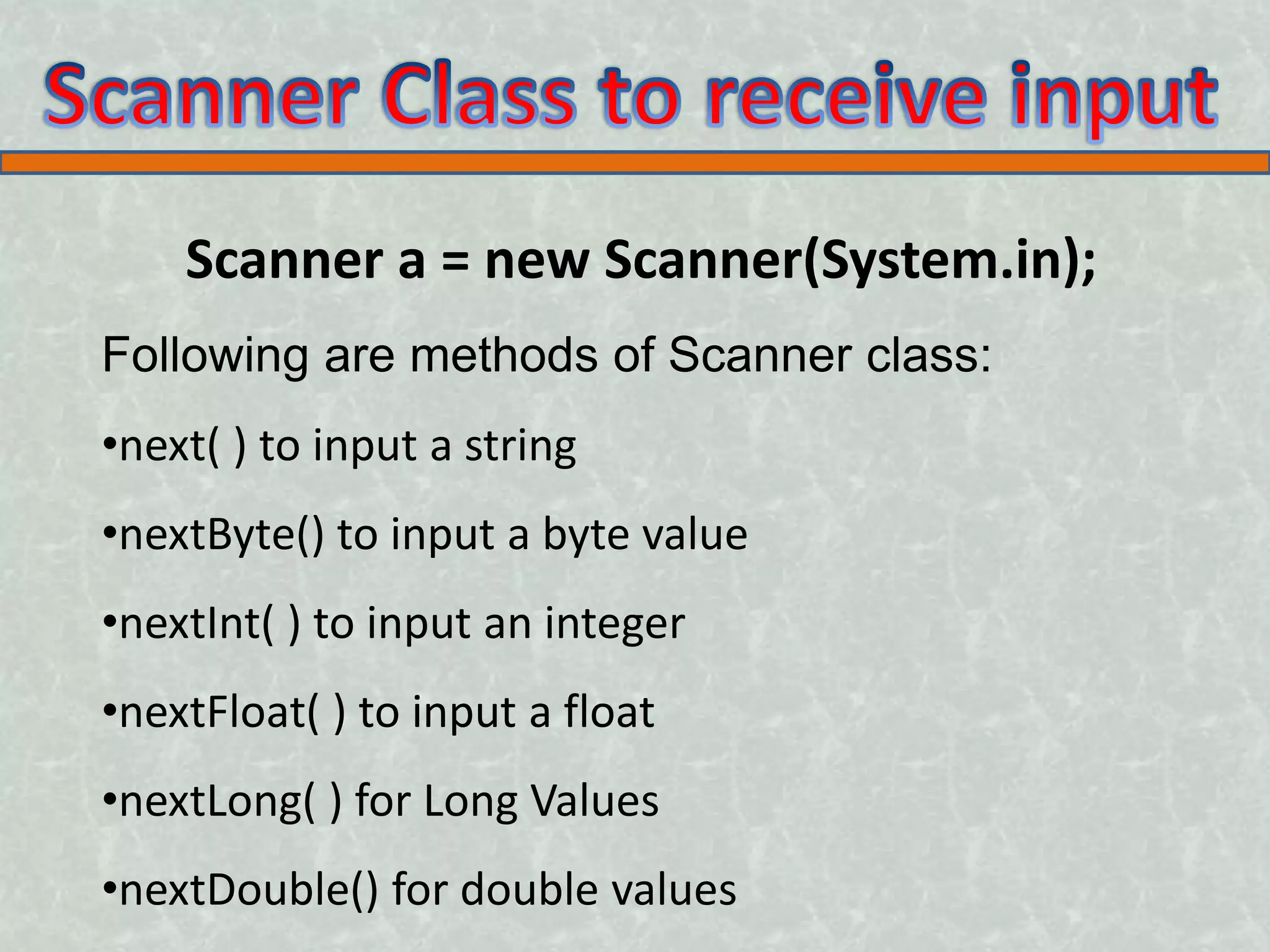
The Scanner class in Java allows user input through methods like nextInt(), nextFloat(), and nextLine(). It is located in the java.util package. A Scanner object is created, passing System.in, and then various next methods are used to input integers, floats, strings and other data from the user.


![import java.util.Scanner; class GetInput { public static void main(String args[]) { int a; Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Enter an integer"); a = in.nextInt(); System.out.println("You entered integer "+a); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handlinginputsviascannerclass-141113091449-conversion-gate02/75/Handling-inputs-via-scanner-class-3-2048.jpg)
![import java.util.Scanner; class GetInput { public static void main(String args[]) { float b; Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Enter a float"); b = in.nextFloat(); System.out.println("You entered float "+b); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handlinginputsviascannerclass-141113091449-conversion-gate02/75/Handling-inputs-via-scanner-class-4-2048.jpg)
![import java.util.Scanner; class GetInput { public static void main(String args[]) { String s; Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Enter a string"); s = in.nextLine(); System.out.println("You entered string"+s); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handlinginputsviascannerclass-141113091449-conversion-gate02/75/Handling-inputs-via-scanner-class-5-2048.jpg)