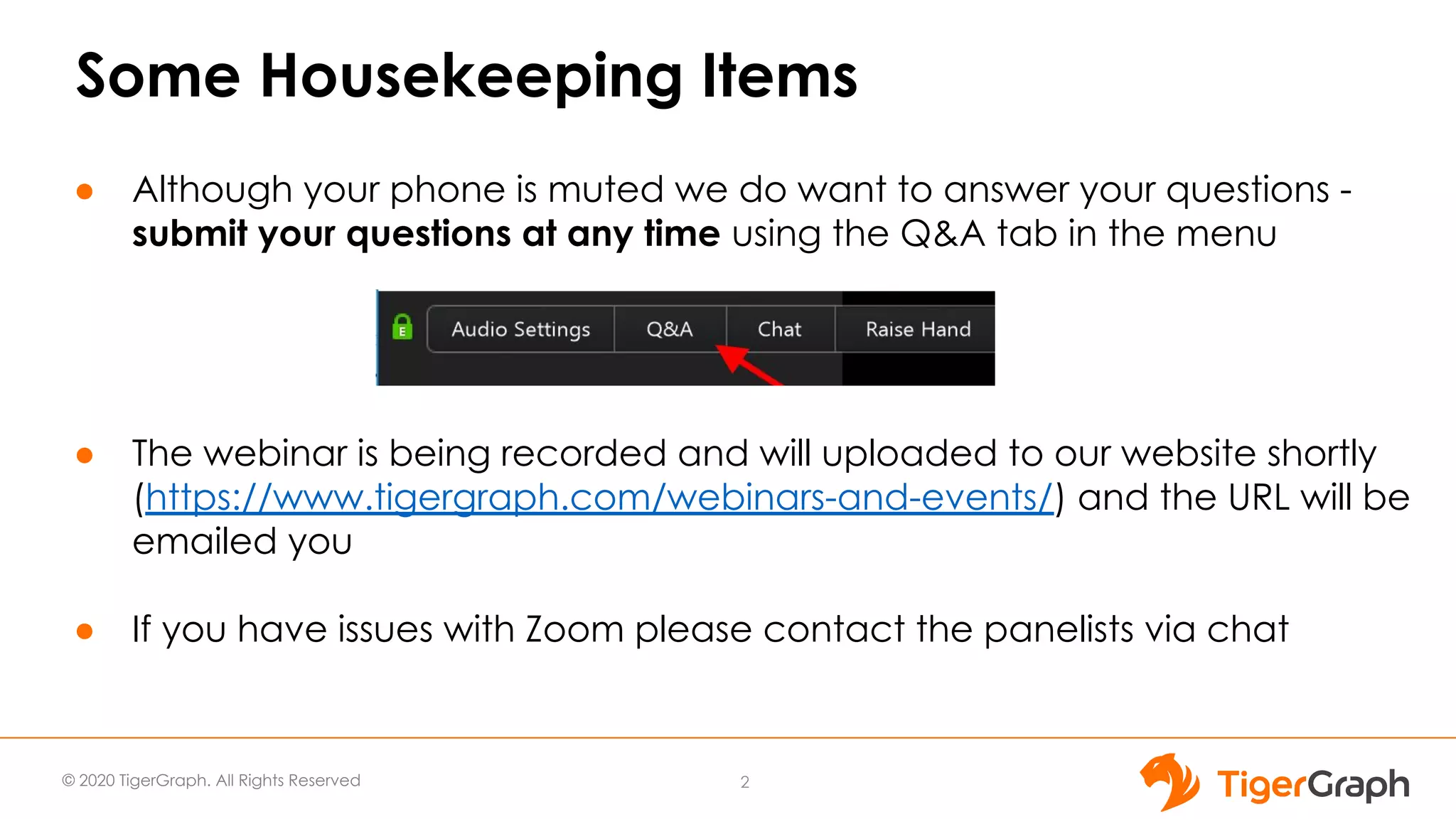
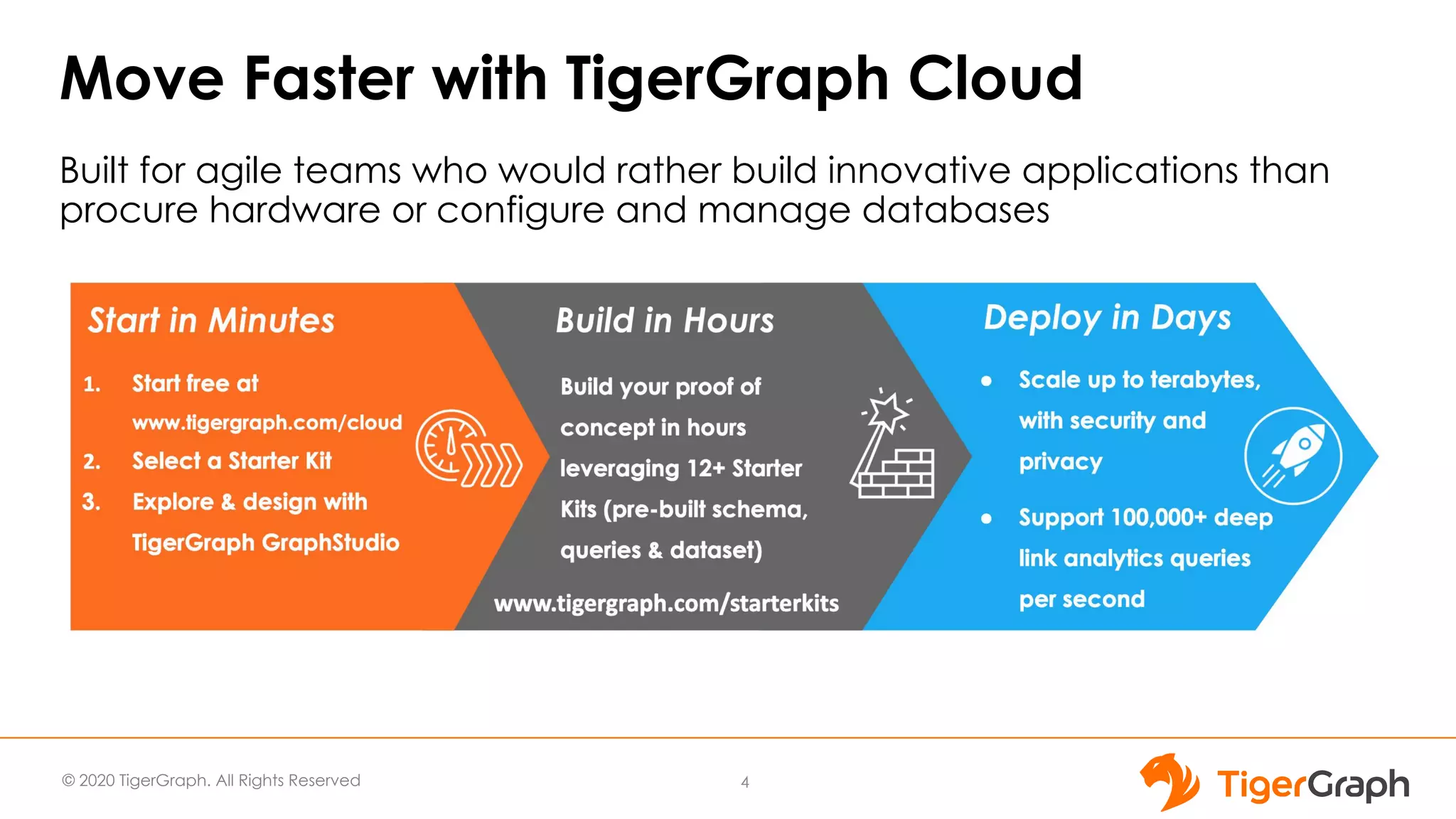
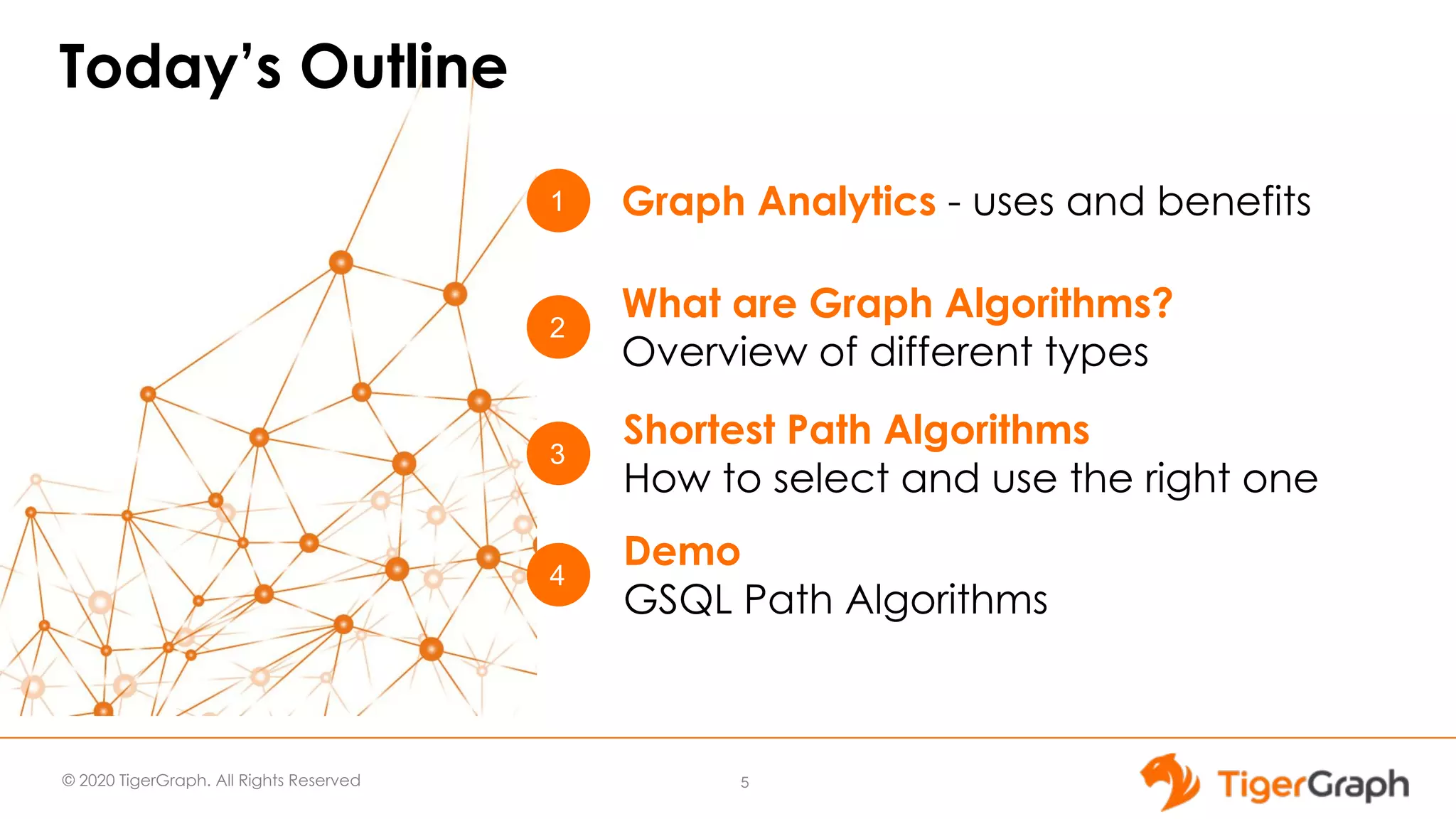
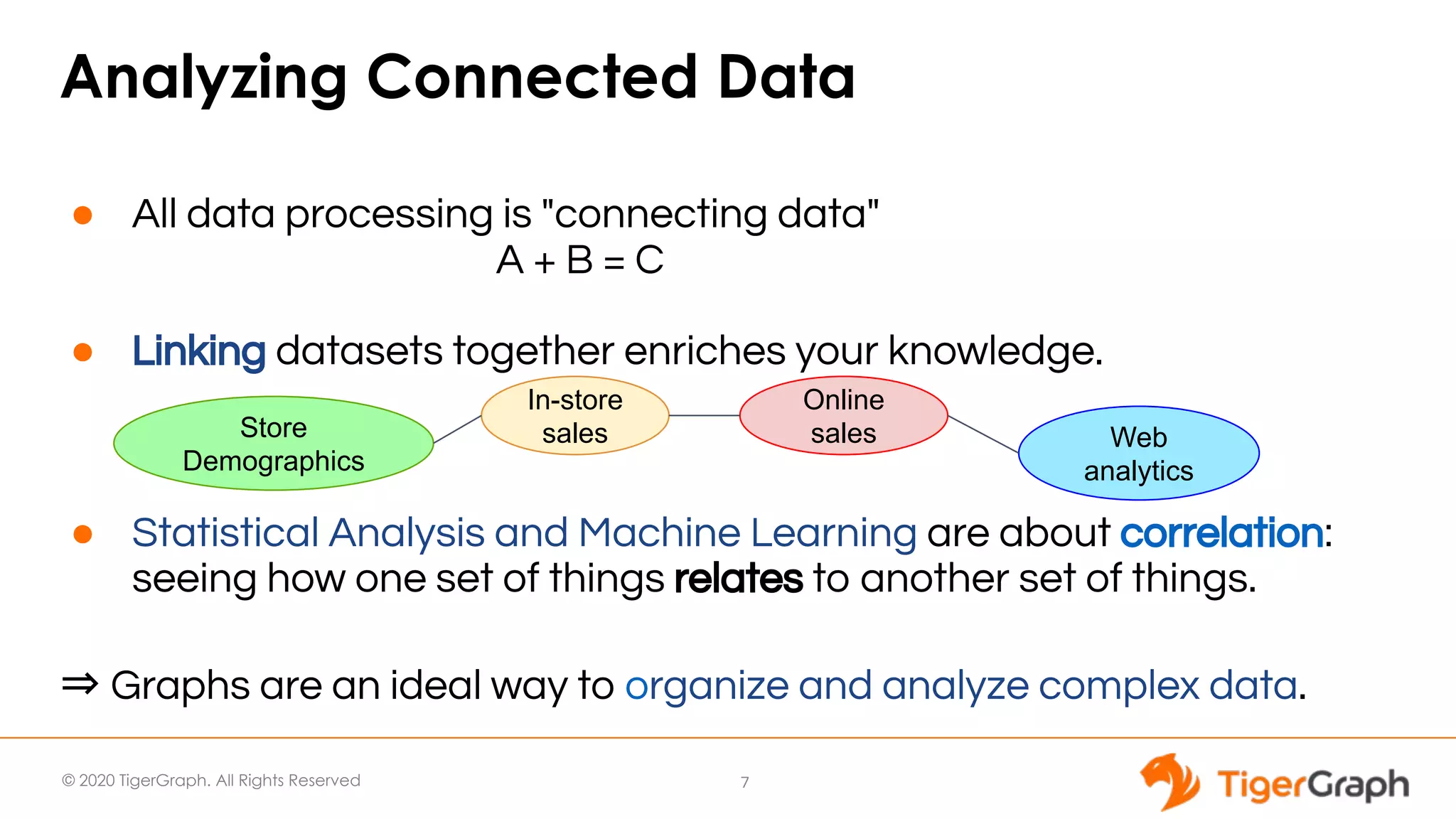
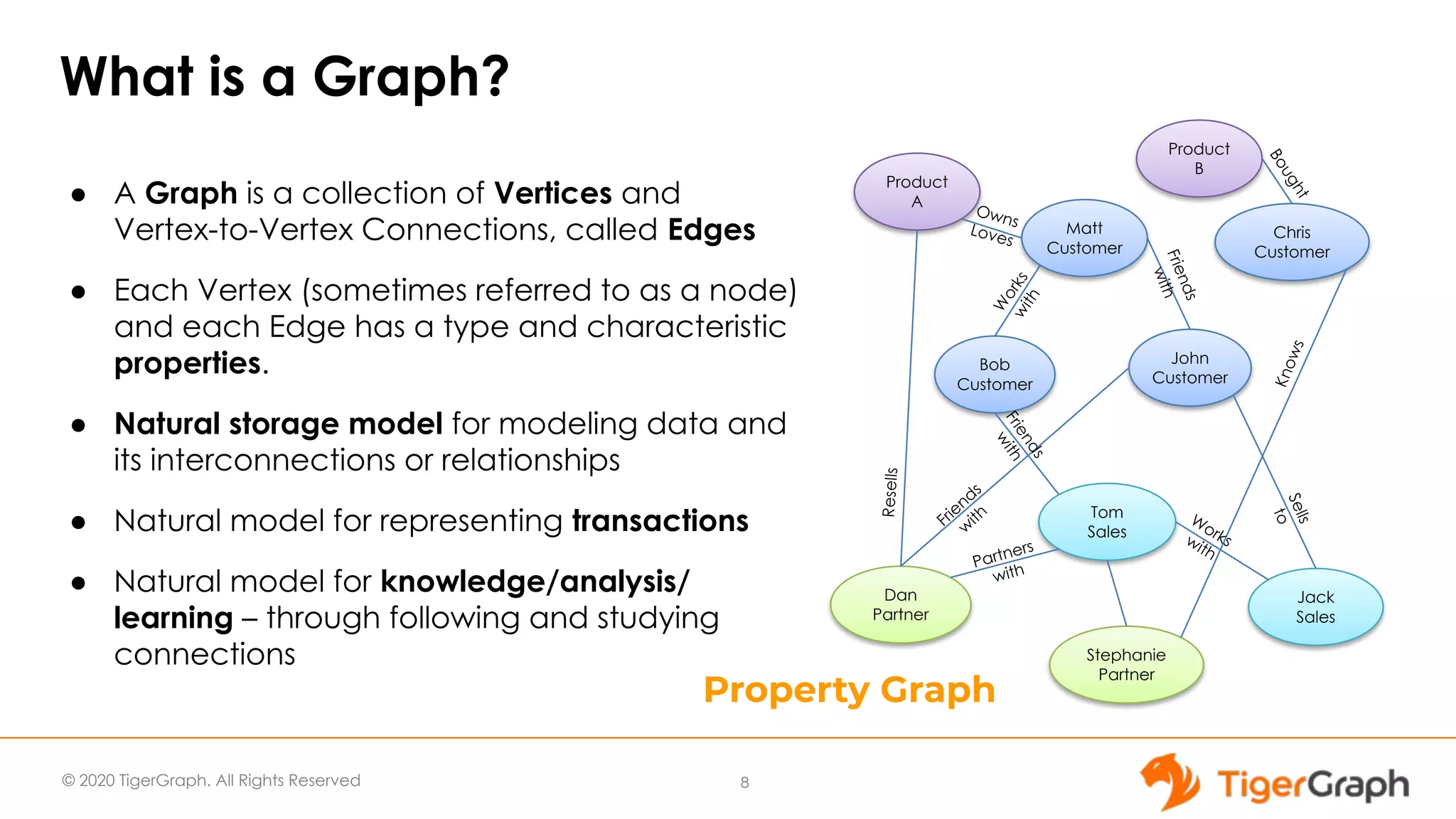
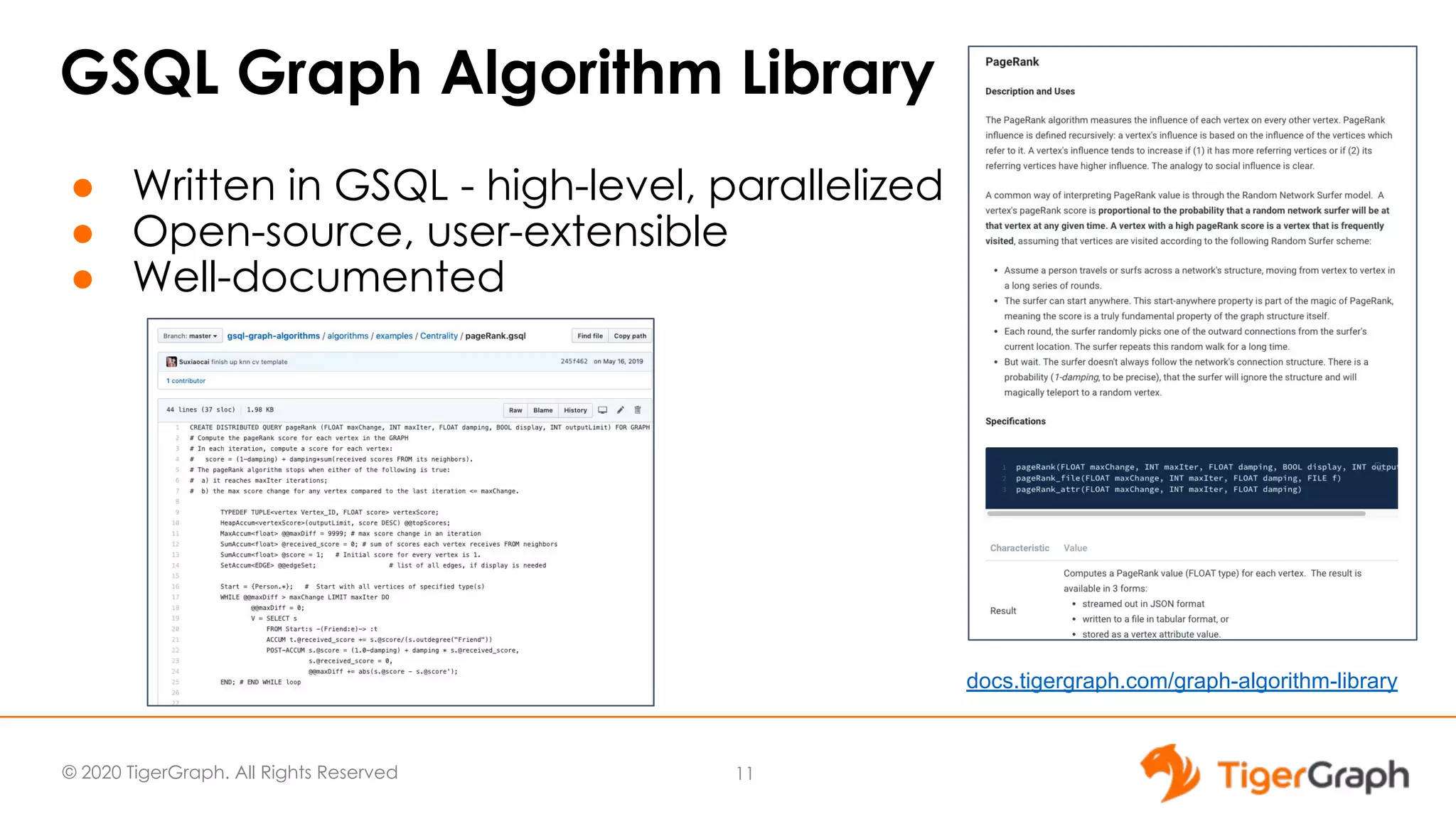
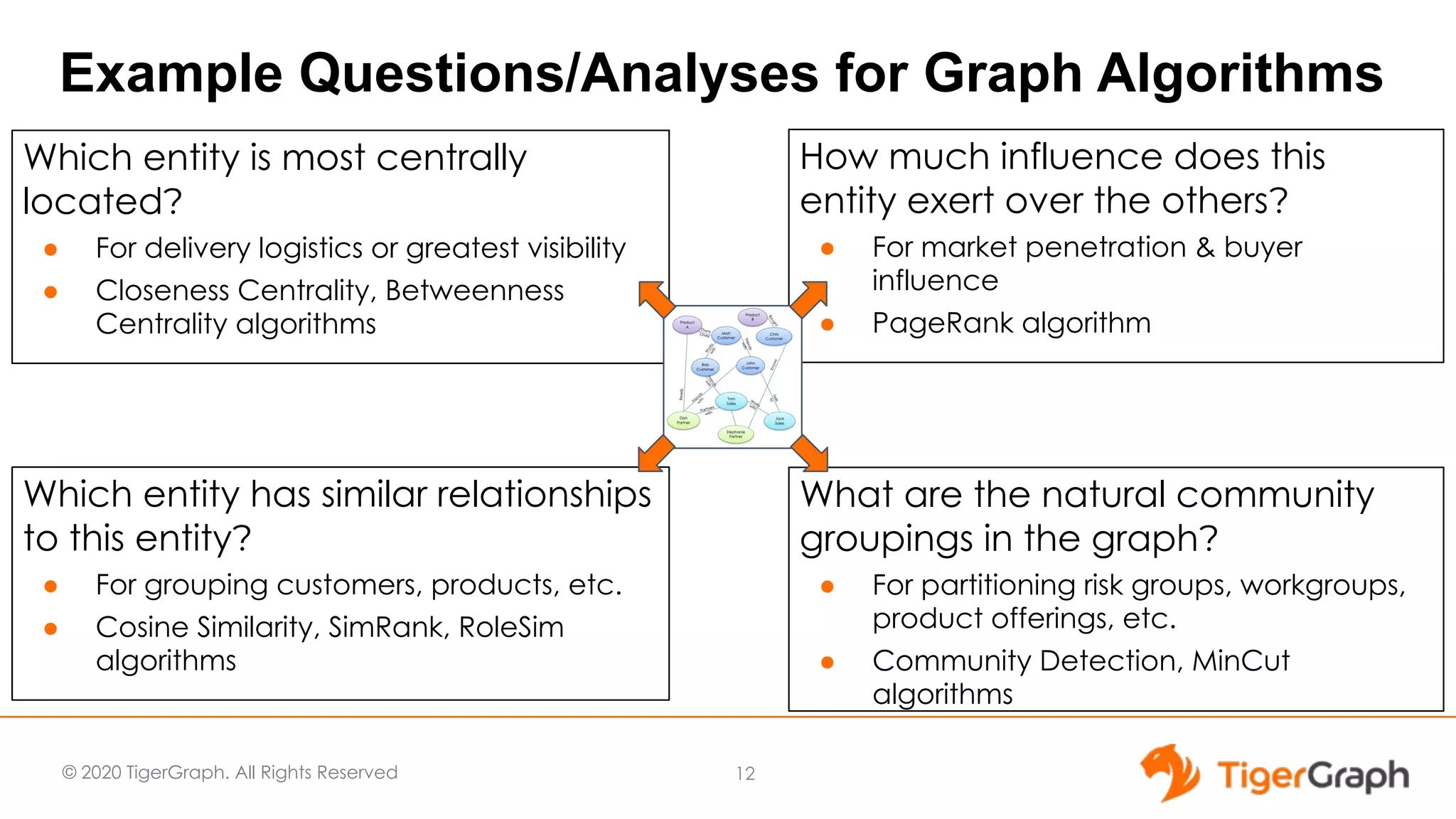
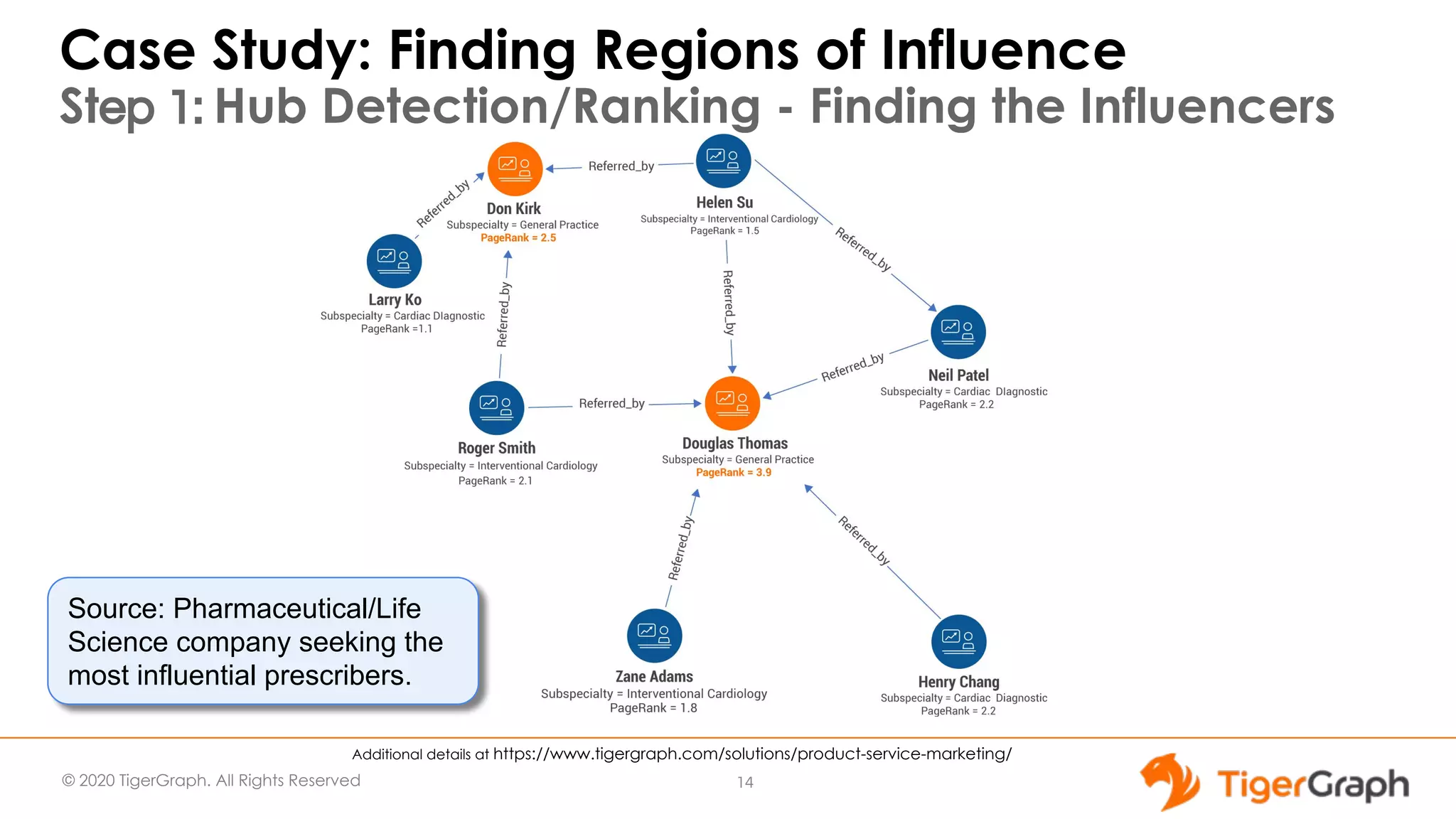
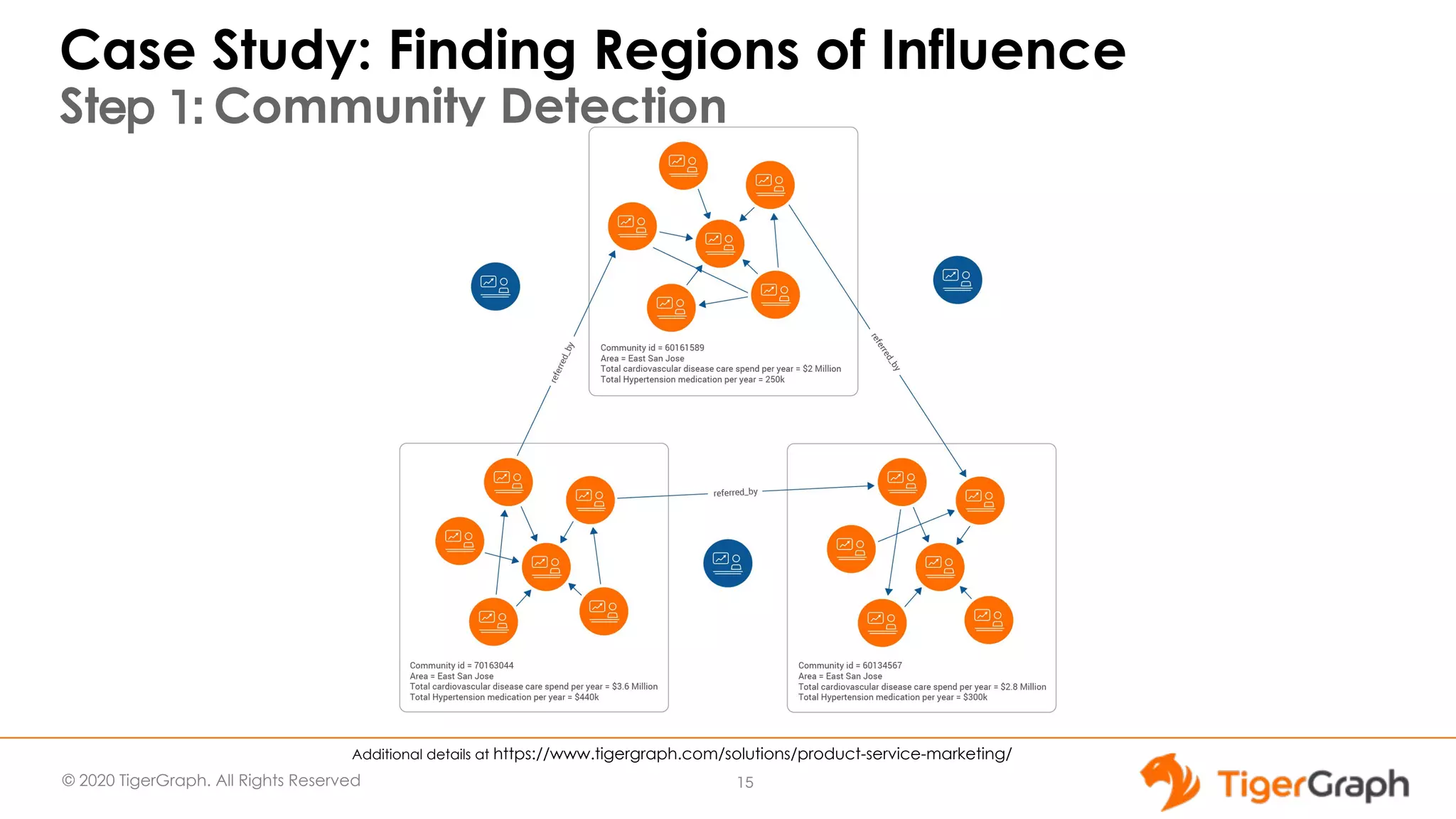
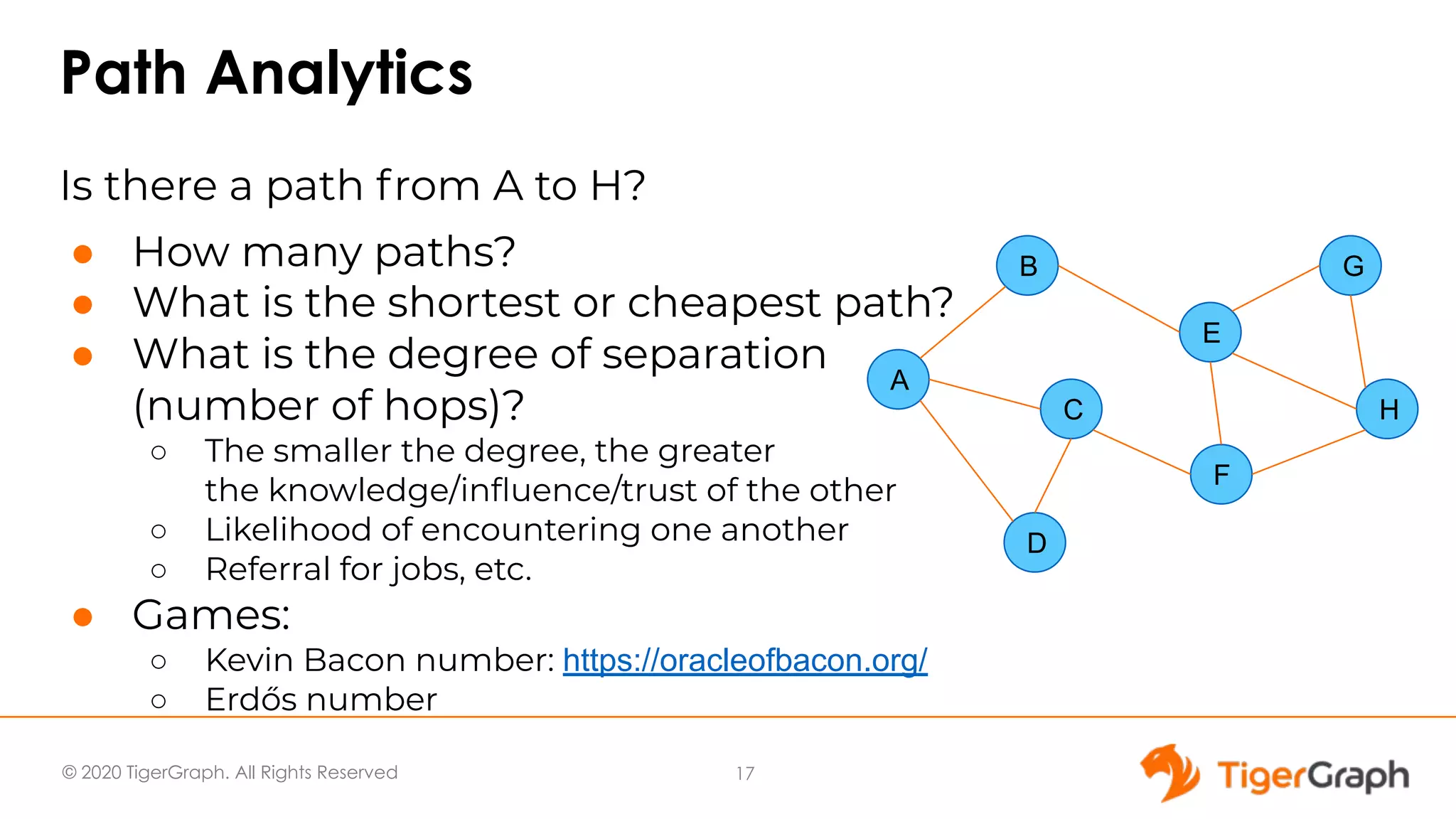
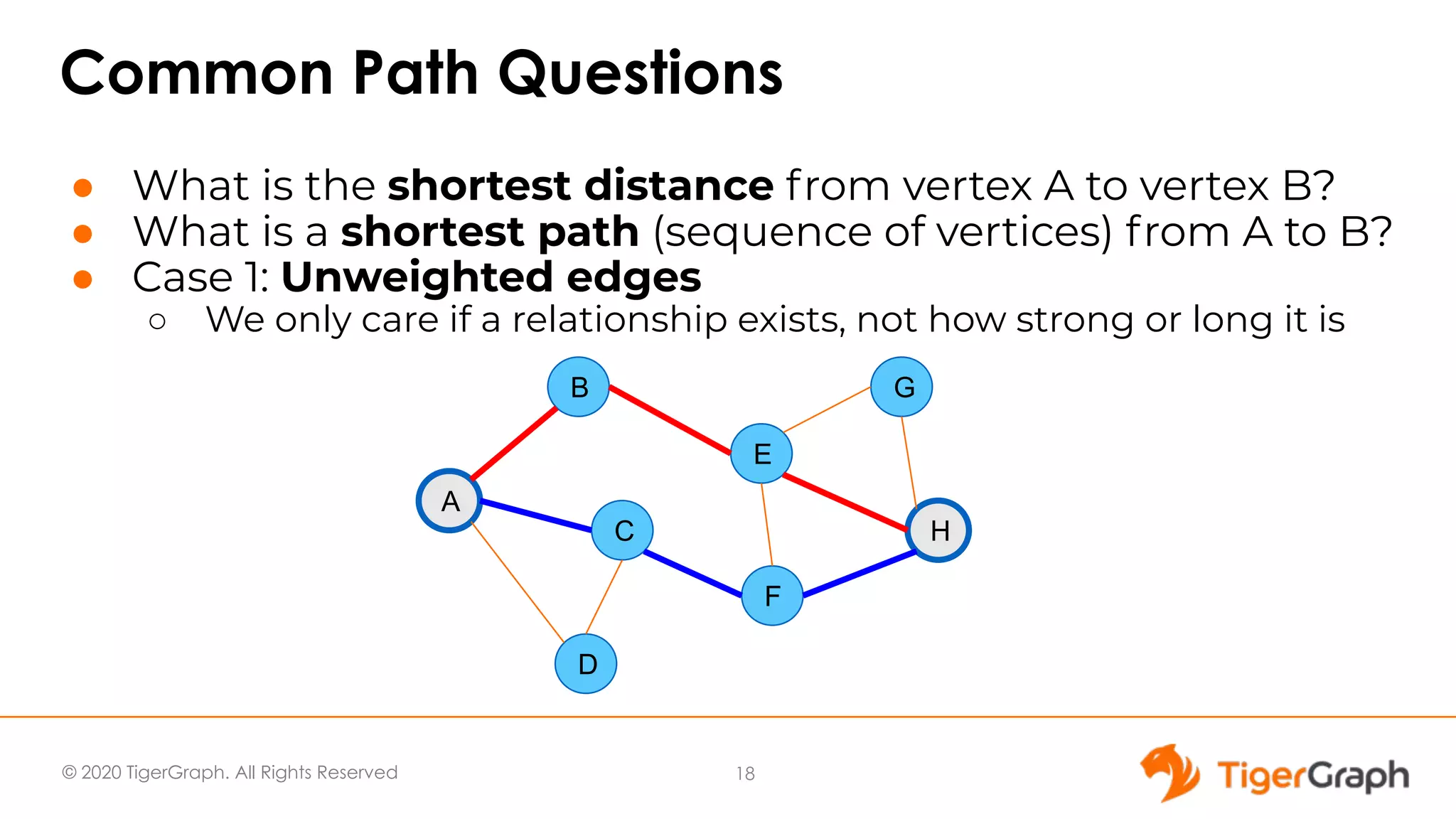
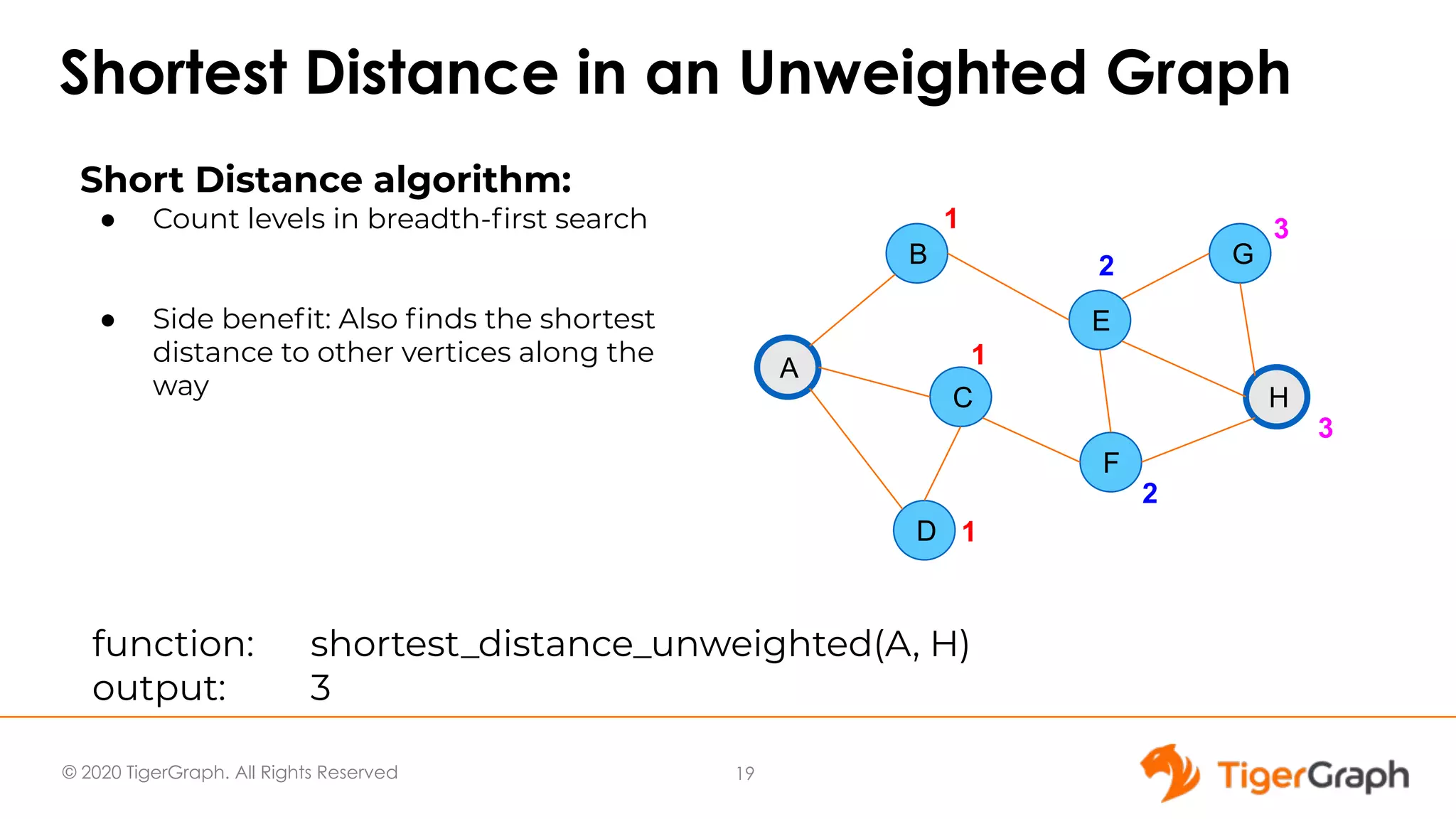
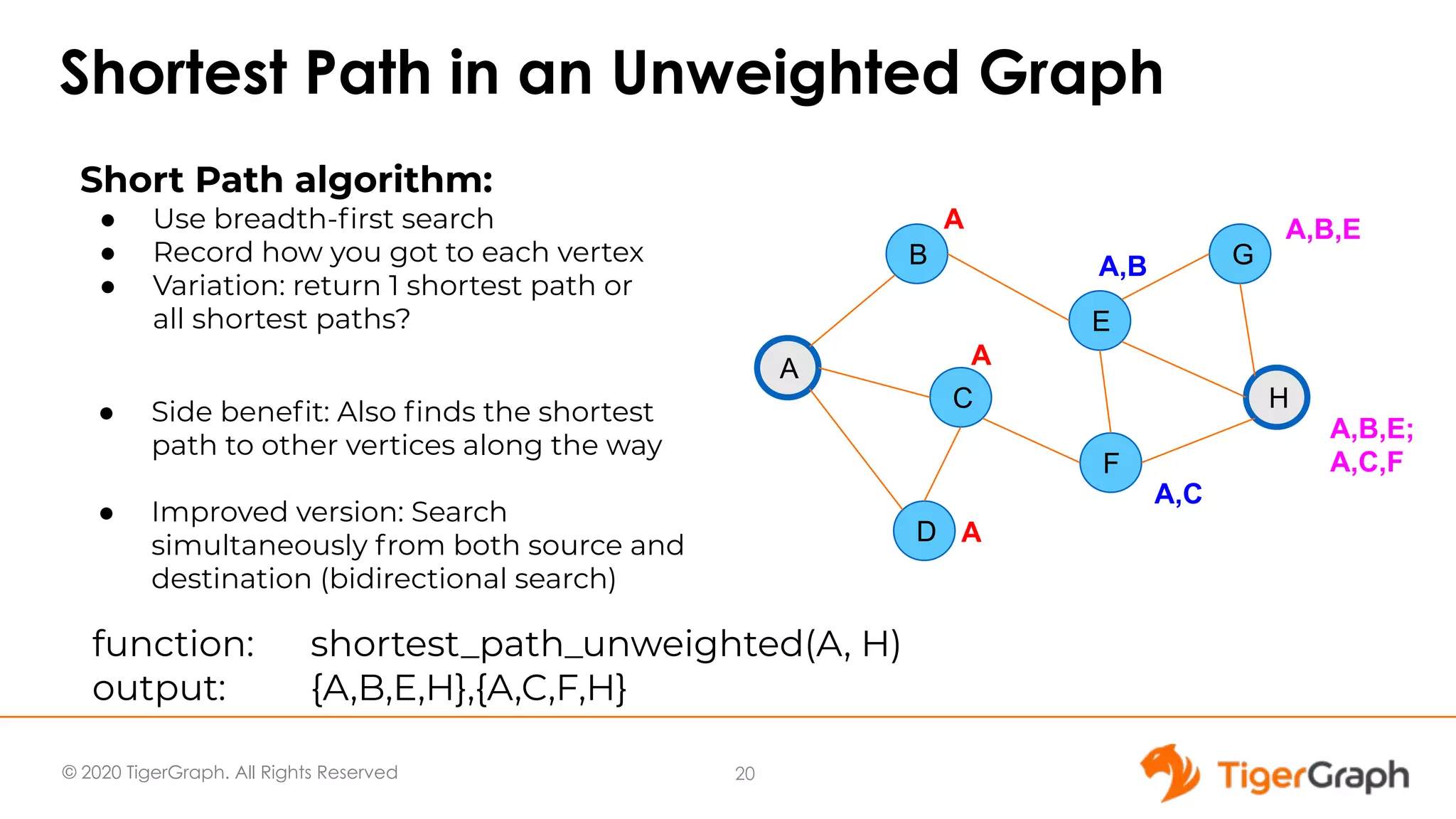
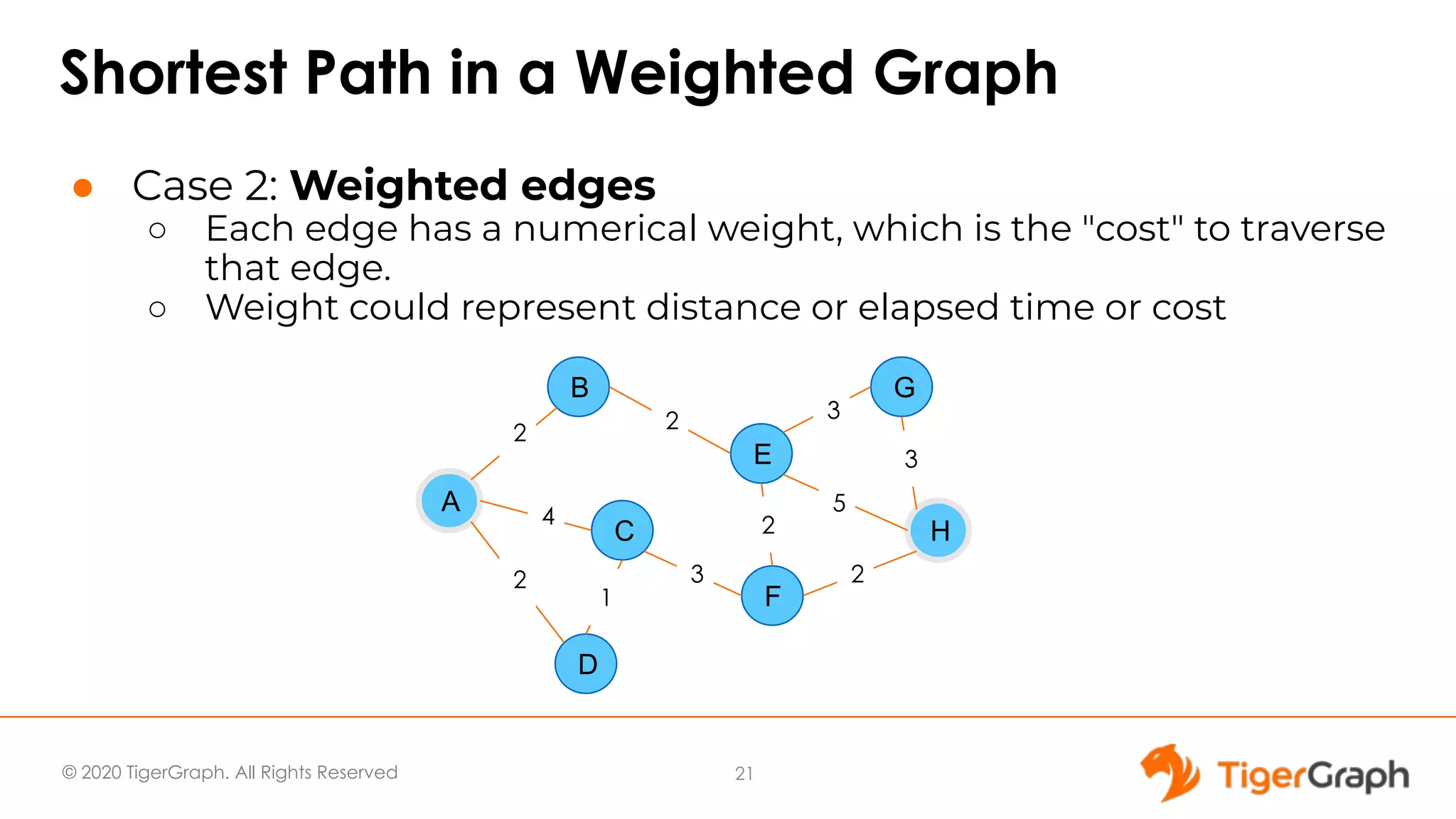
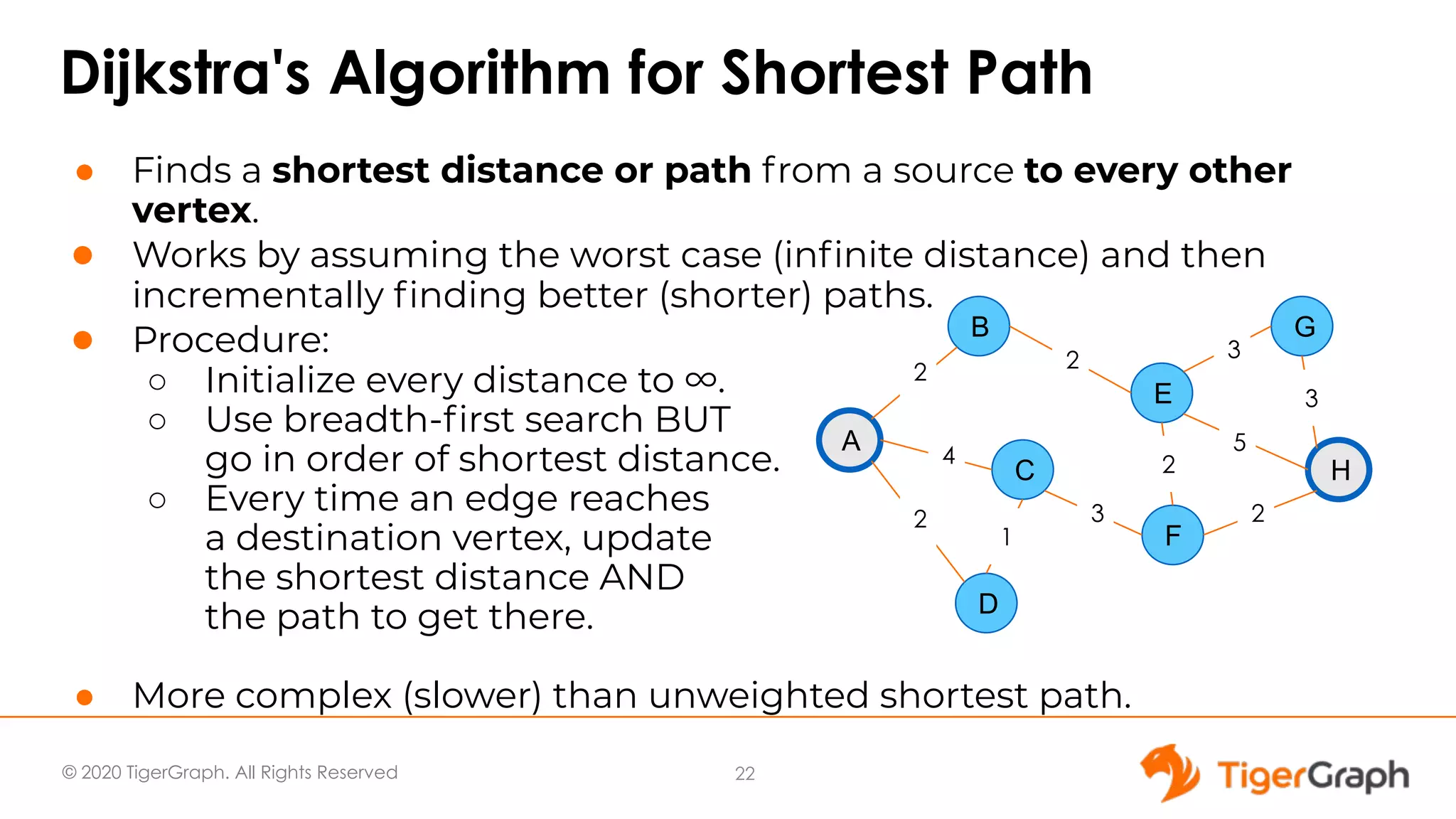
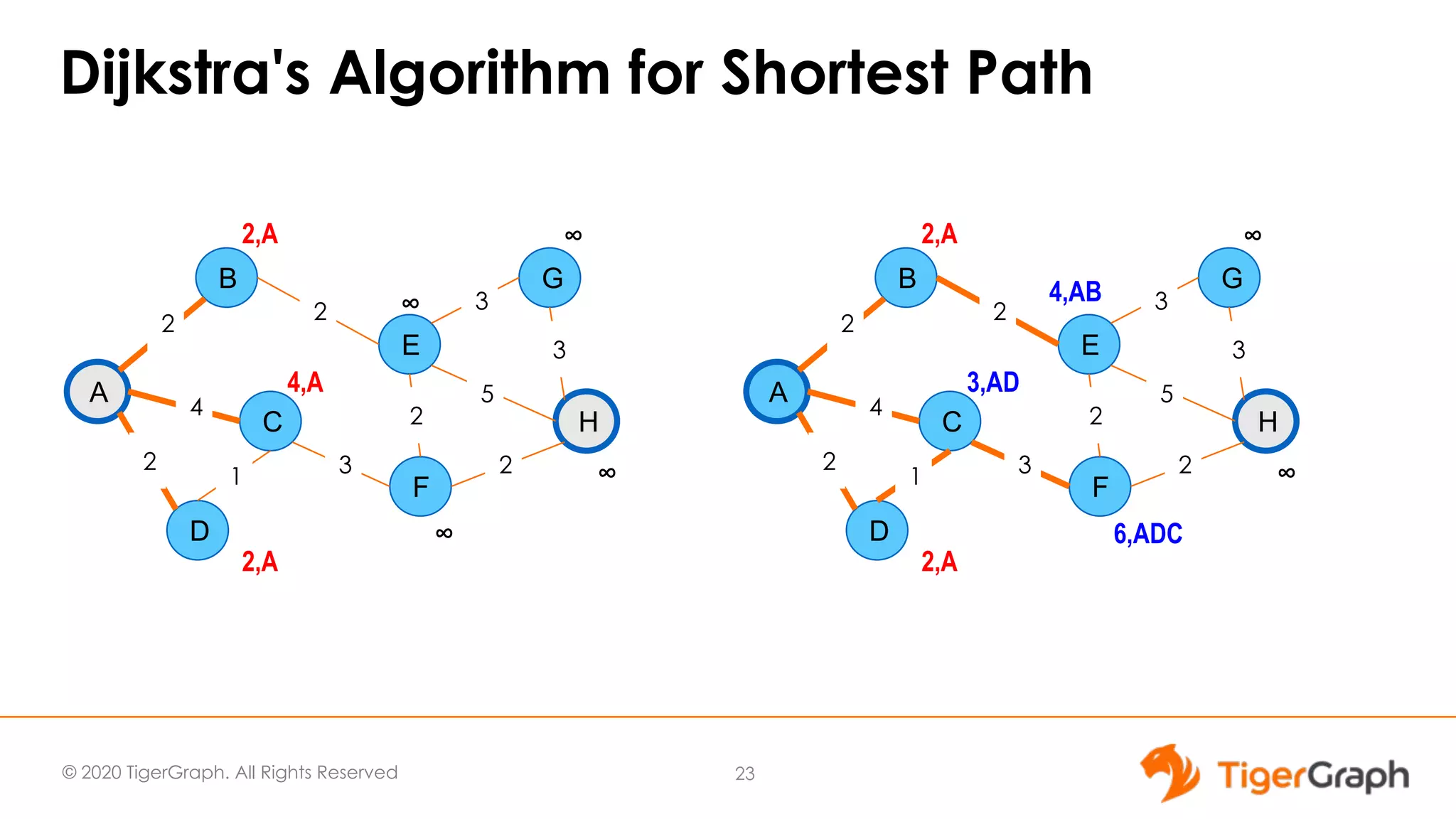
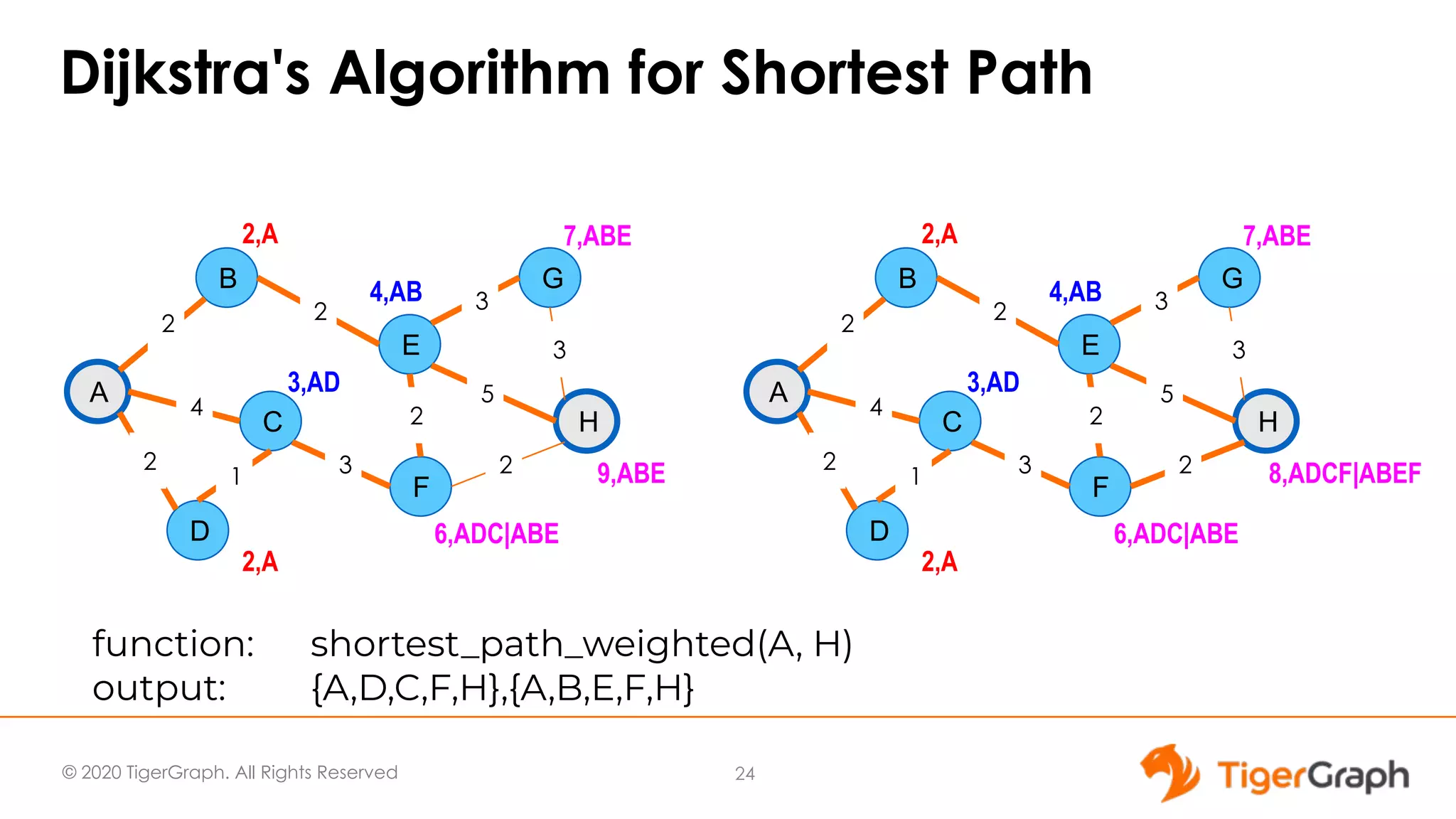
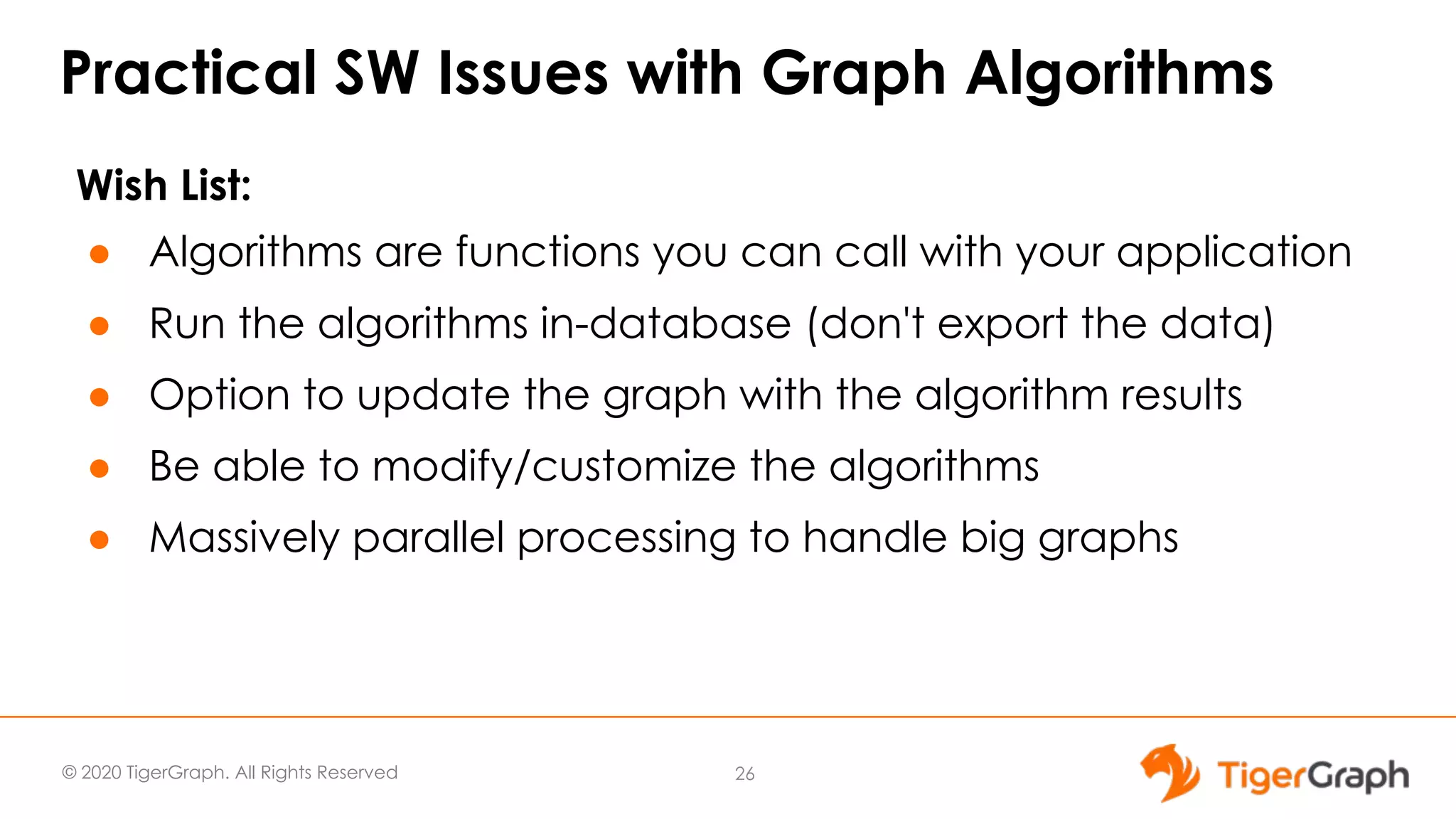
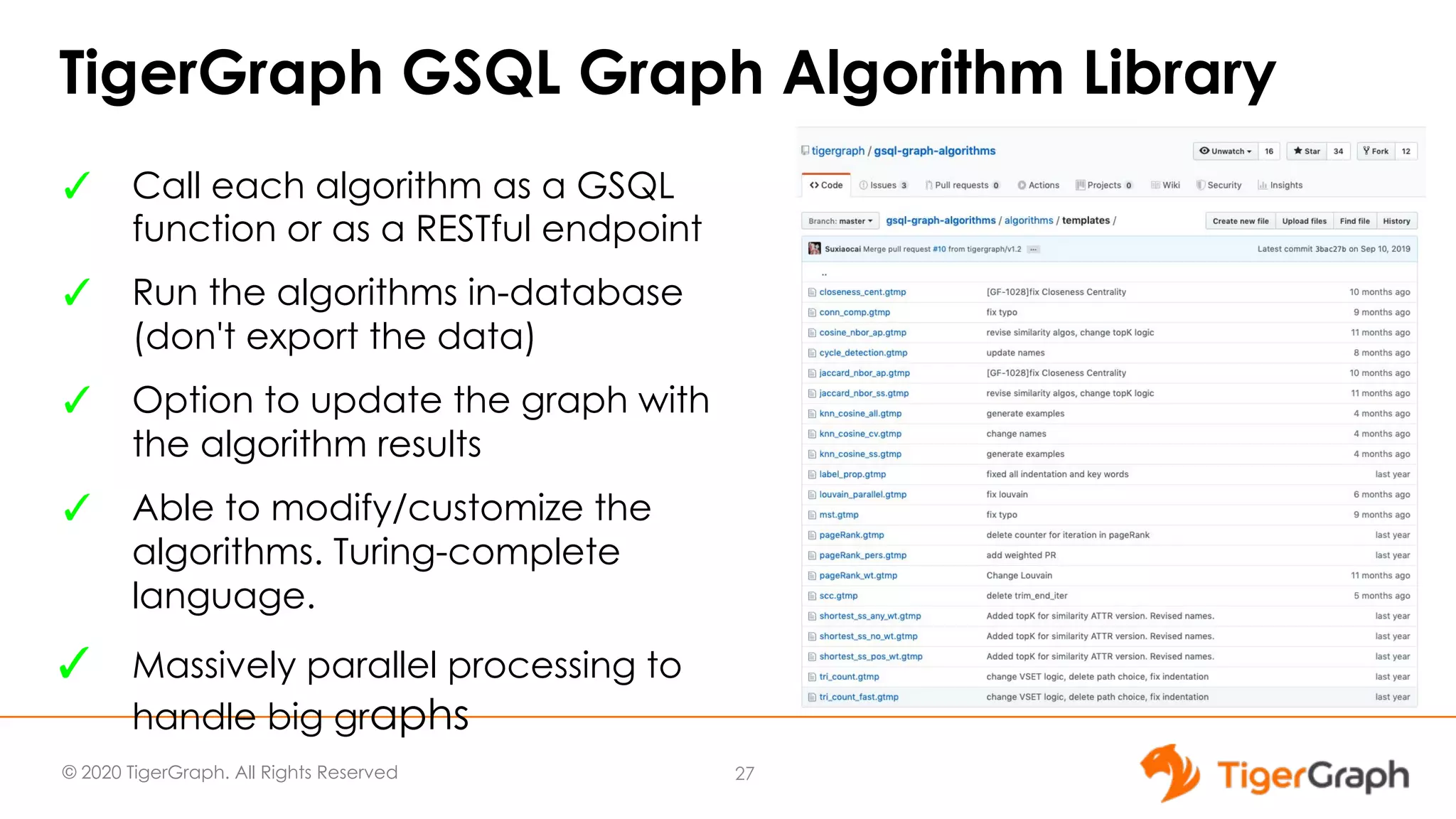
The document presents a webinar focused on graph algorithms for advanced analytics, specifically discussing shortest path algorithms. It highlights the significance of graphs in modeling complex data relationships and introduces the TigerGraph GSQL graph algorithm library as a tool for analyzing connected data. Various algorithm types are detailed, along with practical examples and case studies to illustrate their applications in real-world scenarios.