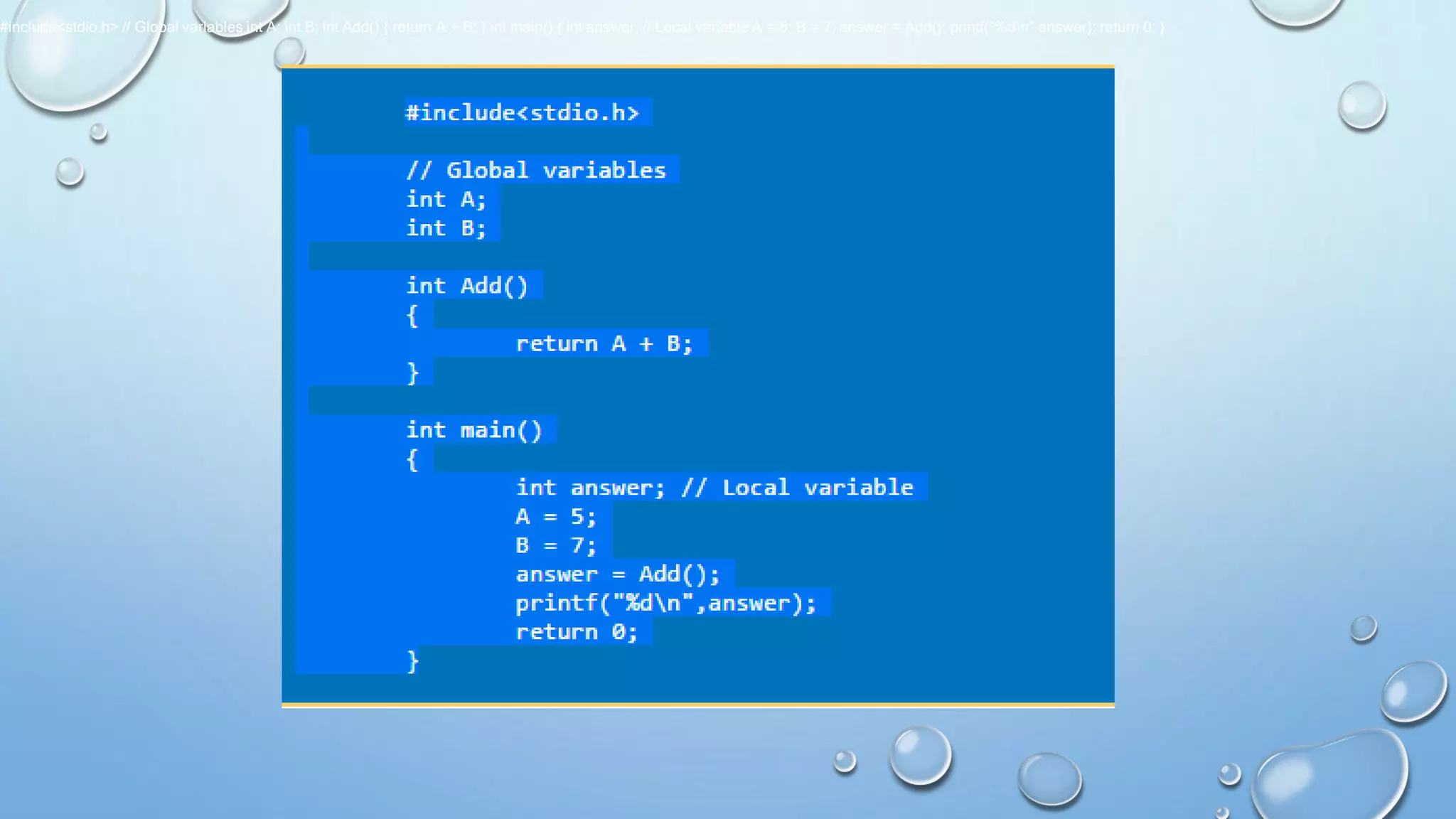
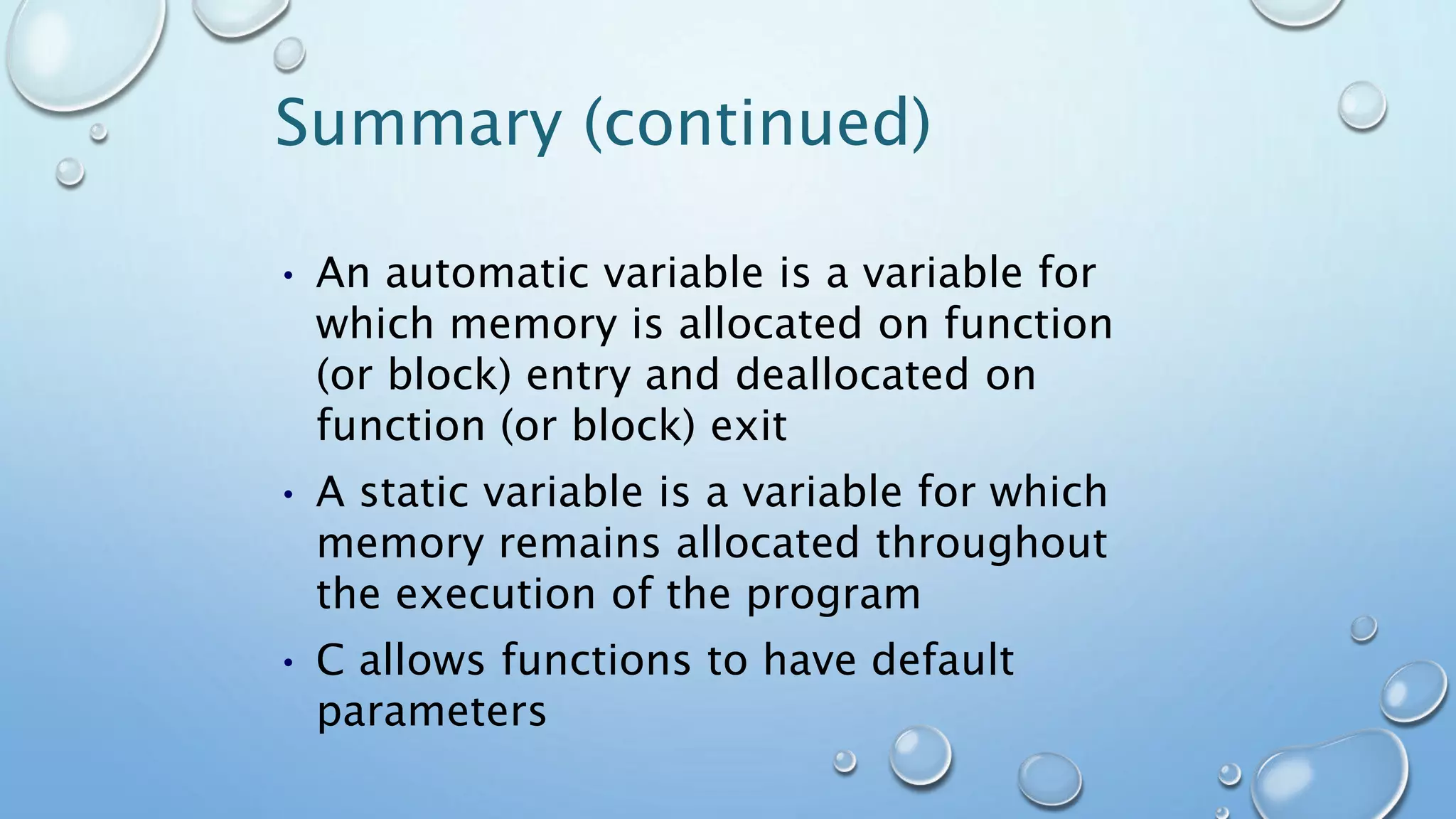
The document discusses global and local variables in C programming. It states that global variables can be accessed within any function, while local variables declared inside a function can only be used within that function. It provides an example program that declares integer variables A and B globally and assigns them values within main(), then calls a function Add() that returns the sum of A and B using the global variables. The document also covers passing arrays to functions, noting the syntax requires specifying the array name without size in the function prototype and definition.









![#include <stdio.h> float average(float a[]); int main(){ float avg, c[]={23.4, 55, 22.6, 3, 40.5, 18}; avg=average(c); /* Only name of array is passed as argument. */ printf("Average age=%.2f",avg); return 0; } float average(float a[ ]) { int i; float avg, sum=0.0; for(i=0;i<6;++i){ sum+=a[i]; } avg =(sum/6); return avg; } Output Average age=27.08 C program to pass an array containing age of person to a function. This function should find average age and display the average age in main function.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-161201182158/75/Global-variables-sorting-static-variables-function-and-arrays-15-2048.jpg)

![#include void Function(int c[2][2]); int main(){ int c[2][2],i,j; printf("Enter 4 numbers:n"); for(i=0;i<2;++i) for(j=0;j<2;++j){ scanf("%d",&c[i][j]); } Function(c); /* passing multi-dimensional array to function */ return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-161201182158/75/Global-variables-sorting-static-variables-function-and-arrays-17-2048.jpg)
![void Function(int c[2][2]){ /* Instead to above line, void Function(int c[][2]){ is also valid */ int i,j; printf("Displaying:n"); for(i=0;i<2;++i) for(j=0;j<2;++j) printf("%dn",c[i][j]); } Output Enter 4 numbers: 2 3 4 5 Displaying: 2 3 4 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-161201182158/75/Global-variables-sorting-static-variables-function-and-arrays-18-2048.jpg)
