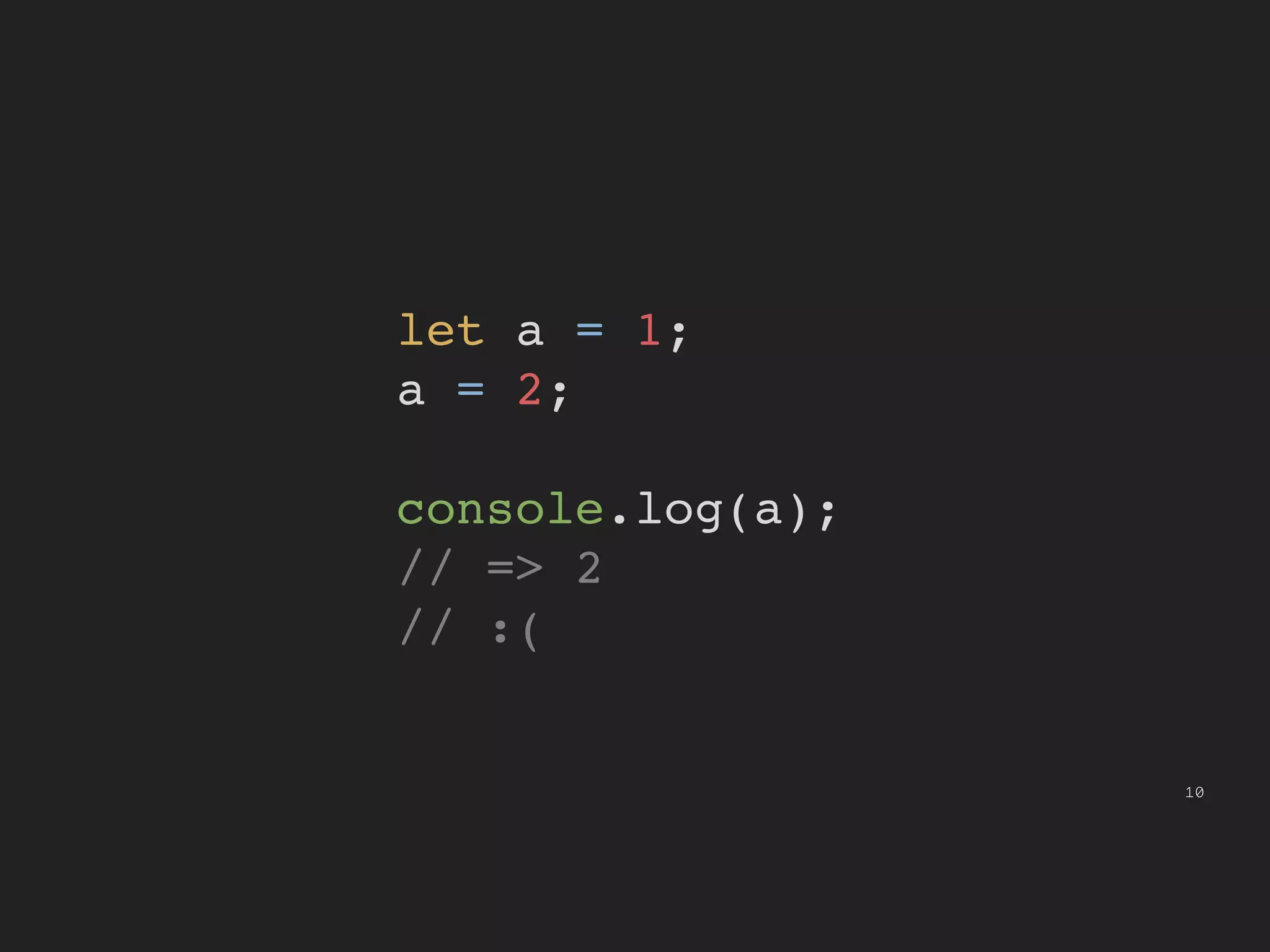
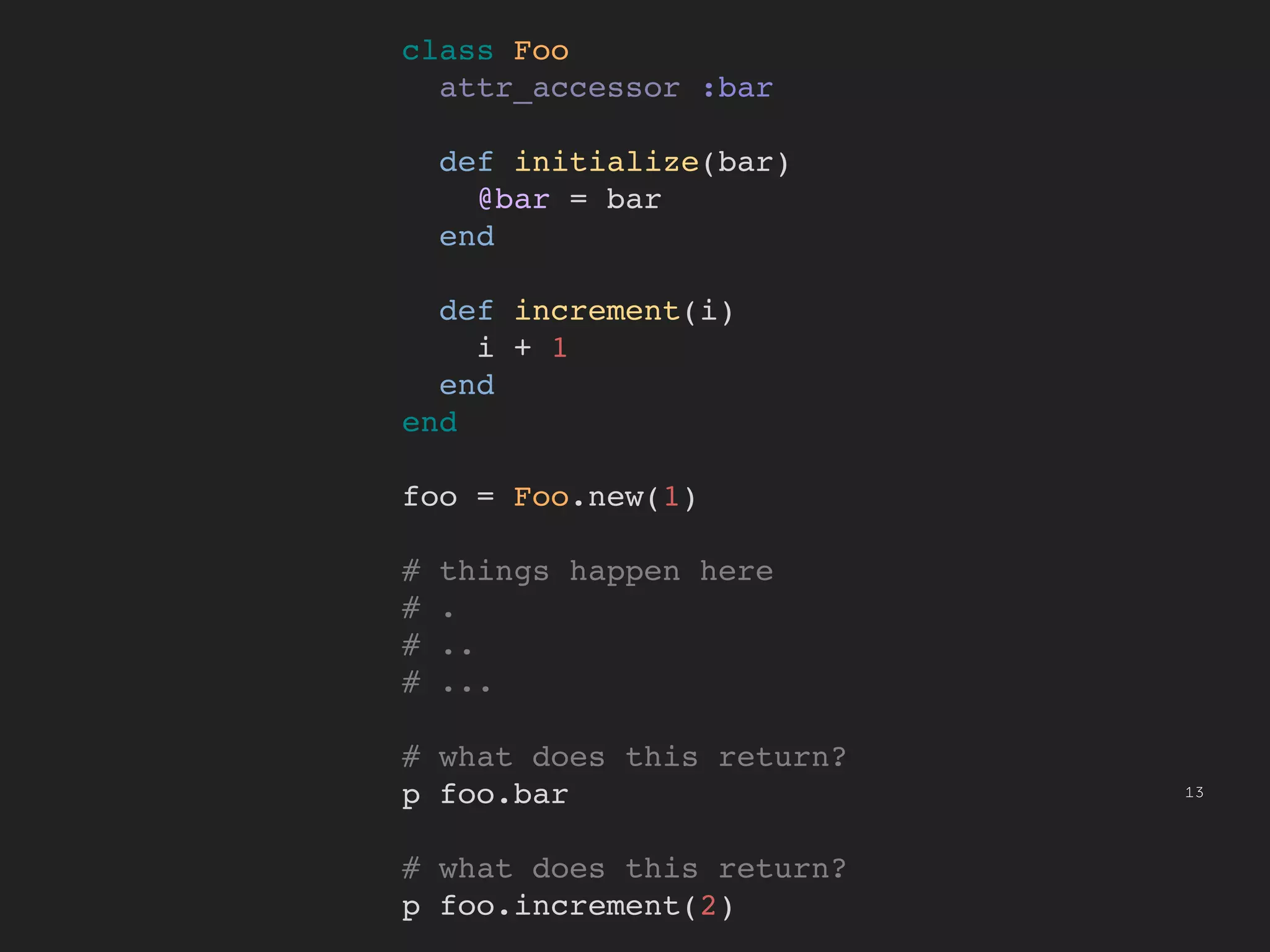
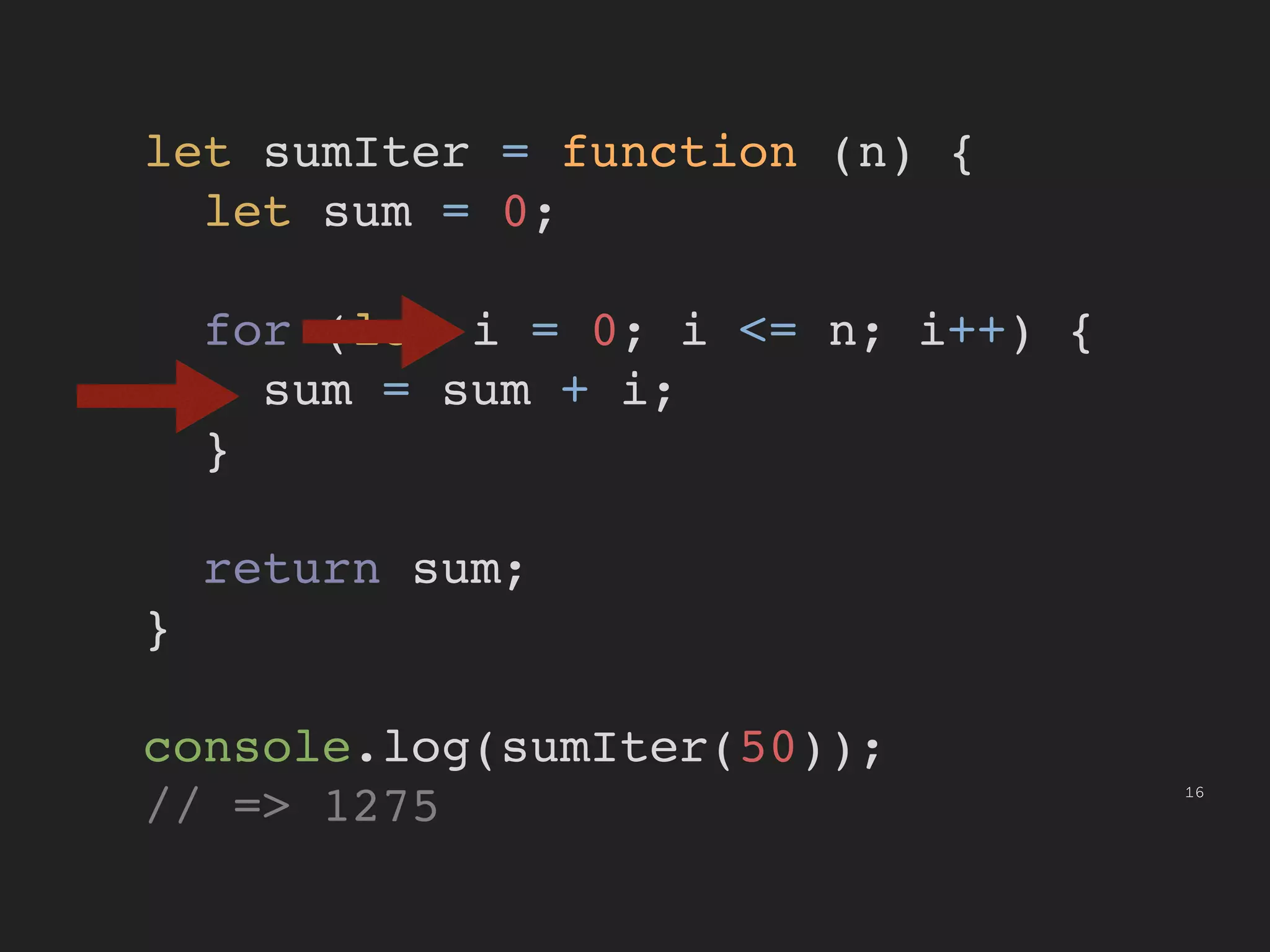
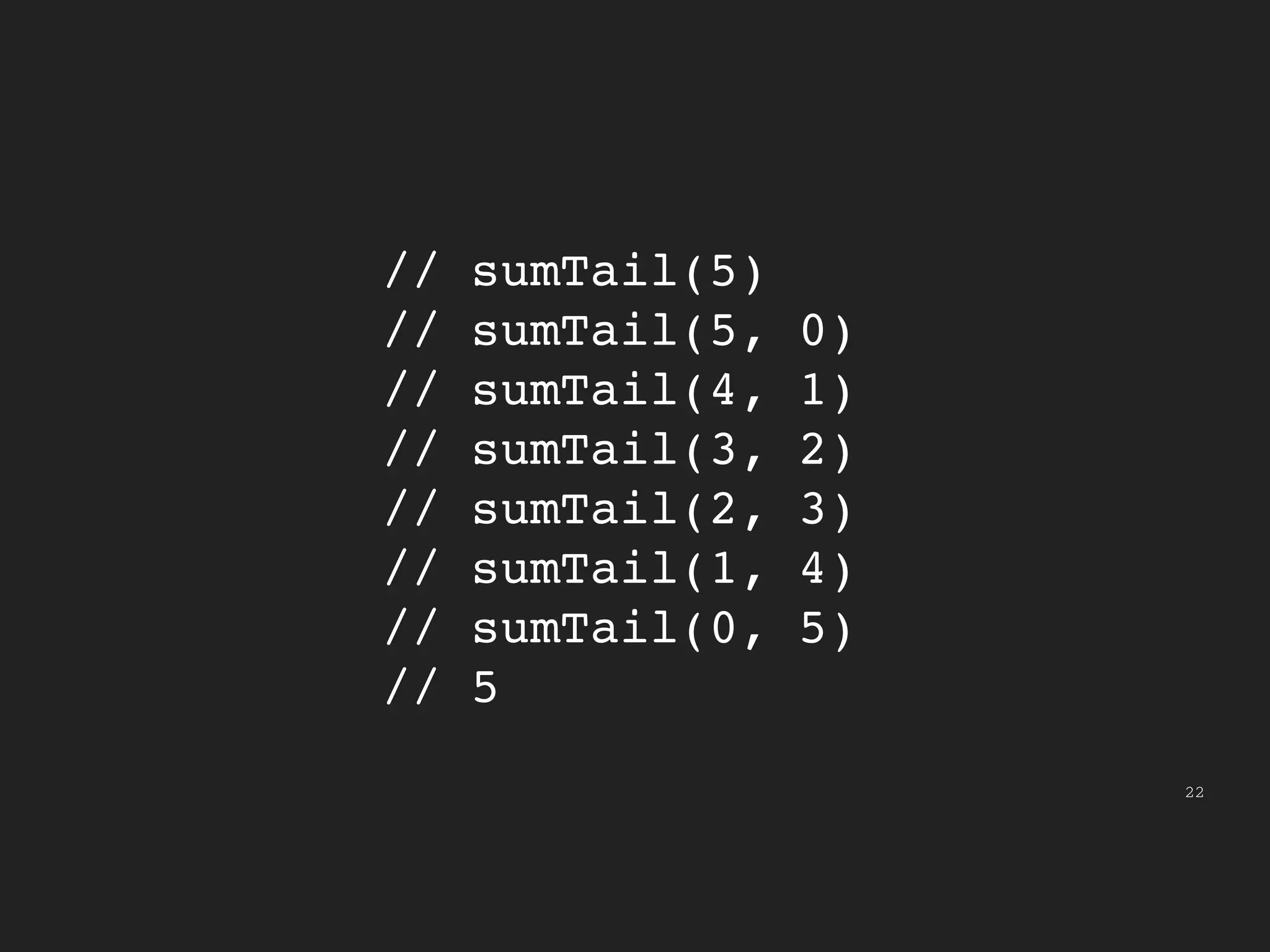
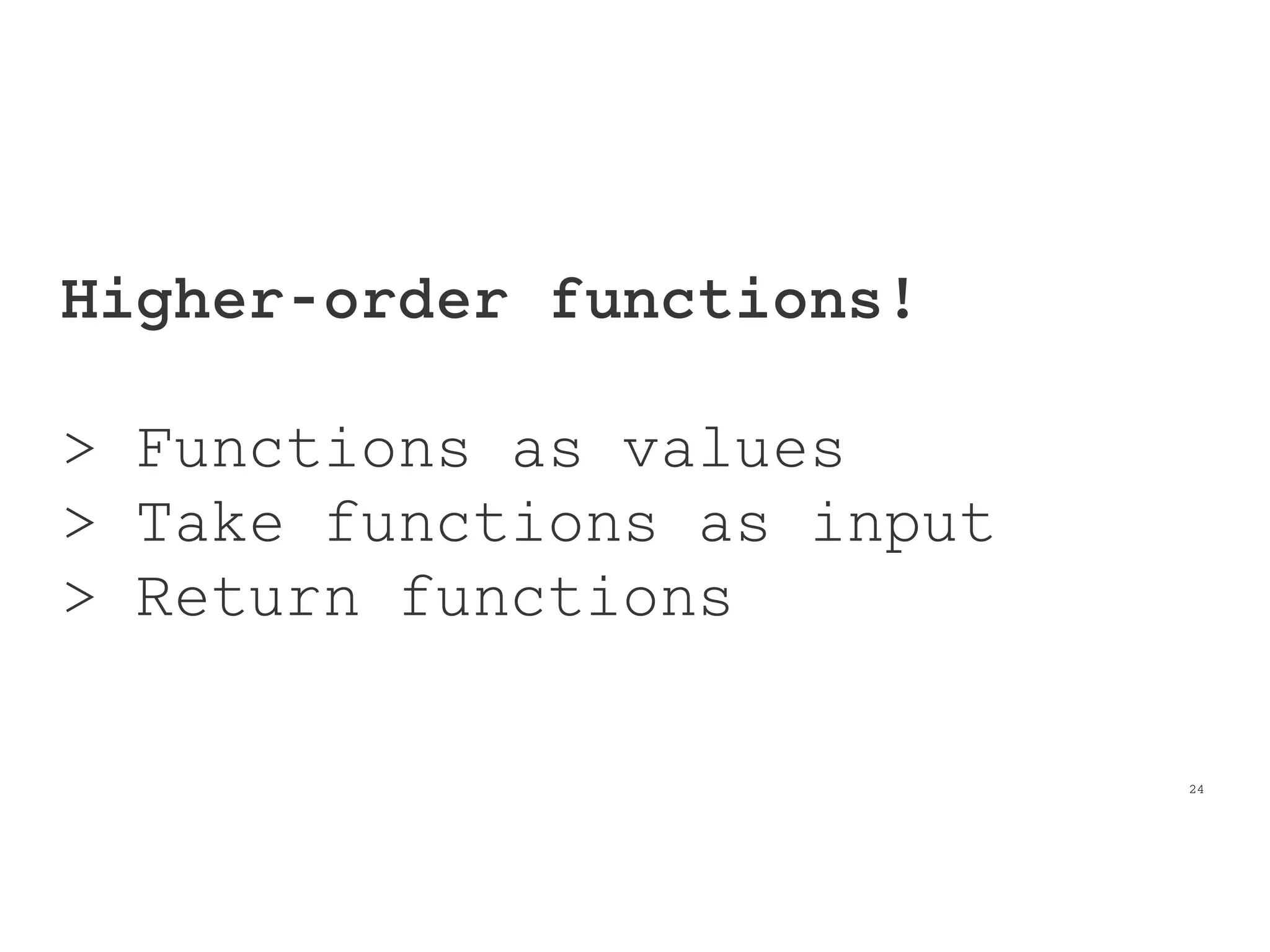
This document provides an introduction to functional programming concepts in JavaScript. It discusses implementing reduce, map, and filter functions without mutation or state by using recursion and higher-order functions. Reduce is implemented using tail recursion to sum the elements of a collection. Map and filter are then implemented using only the reduce function, demonstrating how these common functional operations can be built up from a core reduce operation. The document encourages further exploration of functional programming with additional resources.





















![27 File.open("/tmp/setec_astronomy", "w") do |f| # do stuff with f end [1, 2, 3].map do |i| i + 1 end # => [2, 3, 4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtofunctional-150522033653-lva1-app6892/75/Functional-Programming-An-Introduction-27-2048.jpg)
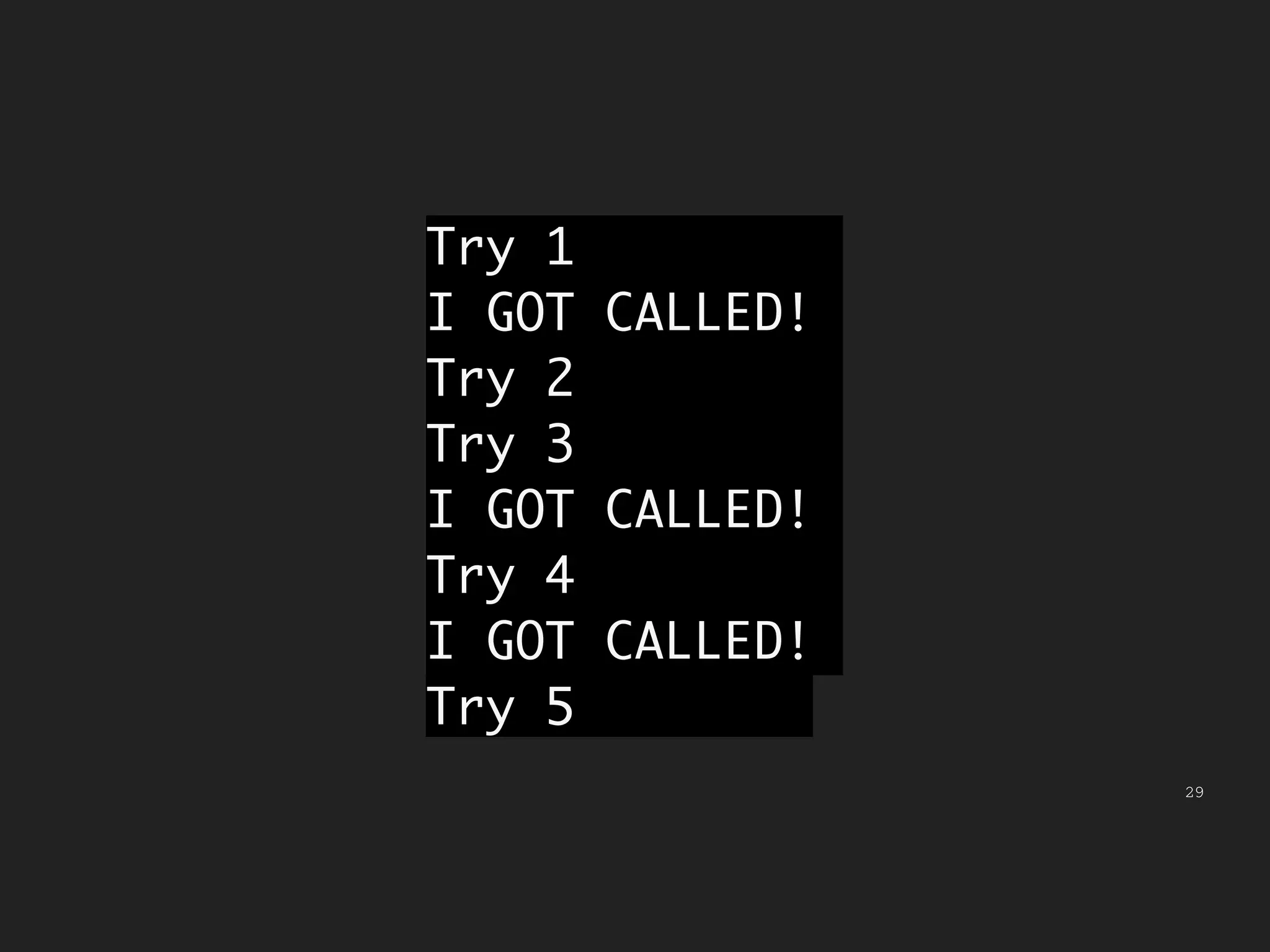
![28 // take a function as an argument let callMeMaybe = function (f) { if (Math.random() < 0.5) { return f(); } else { return undefined; } } for (var i of [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) { console.log(`Try ${i}`); callMeMaybe(function () { console.log("I GOT CALLED!"); }); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtofunctional-150522033653-lva1-app6892/75/Functional-Programming-An-Introduction-28-2048.jpg)


![32 let coll = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; let result = reduce(coll, 0, function (i, sum) { return sum + i; }); console.log(result); // => 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtofunctional-150522033653-lva1-app6892/75/Functional-Programming-An-Introduction-32-2048.jpg)
![33 let reduce = function (coll, acc, fn) { if (coll.length === 0) { return acc; } let head = coll[0]; let rest = coll.slice(1, coll.length); let newAcc = fn(head, acc); return reduce(rest, newAcc, fn); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtofunctional-150522033653-lva1-app6892/75/Functional-Programming-An-Introduction-33-2048.jpg)

![35 let coll = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; let result = map(coll, function (i) { return i + 1; }); console.log(result); // => [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtofunctional-150522033653-lva1-app6892/75/Functional-Programming-An-Introduction-35-2048.jpg)
![36 let map = function (coll, fn) { return reduce(coll, [], function (i, acc) { return acc.concat(fn(i)); }); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtofunctional-150522033653-lva1-app6892/75/Functional-Programming-An-Introduction-36-2048.jpg)

![38 let coll = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; let result = filter(coll, function (i) { return i < 4; }); console.log(result); // => [1, 2, 3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtofunctional-150522033653-lva1-app6892/75/Functional-Programming-An-Introduction-38-2048.jpg)
![39 let filter = function (coll, fn) { return reduce(coll, [], function (i, acc) { if (fn(i)) { return acc.concat(i); } else { return acc; } }); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtofunctional-150522033653-lva1-app6892/75/Functional-Programming-An-Introduction-39-2048.jpg)



