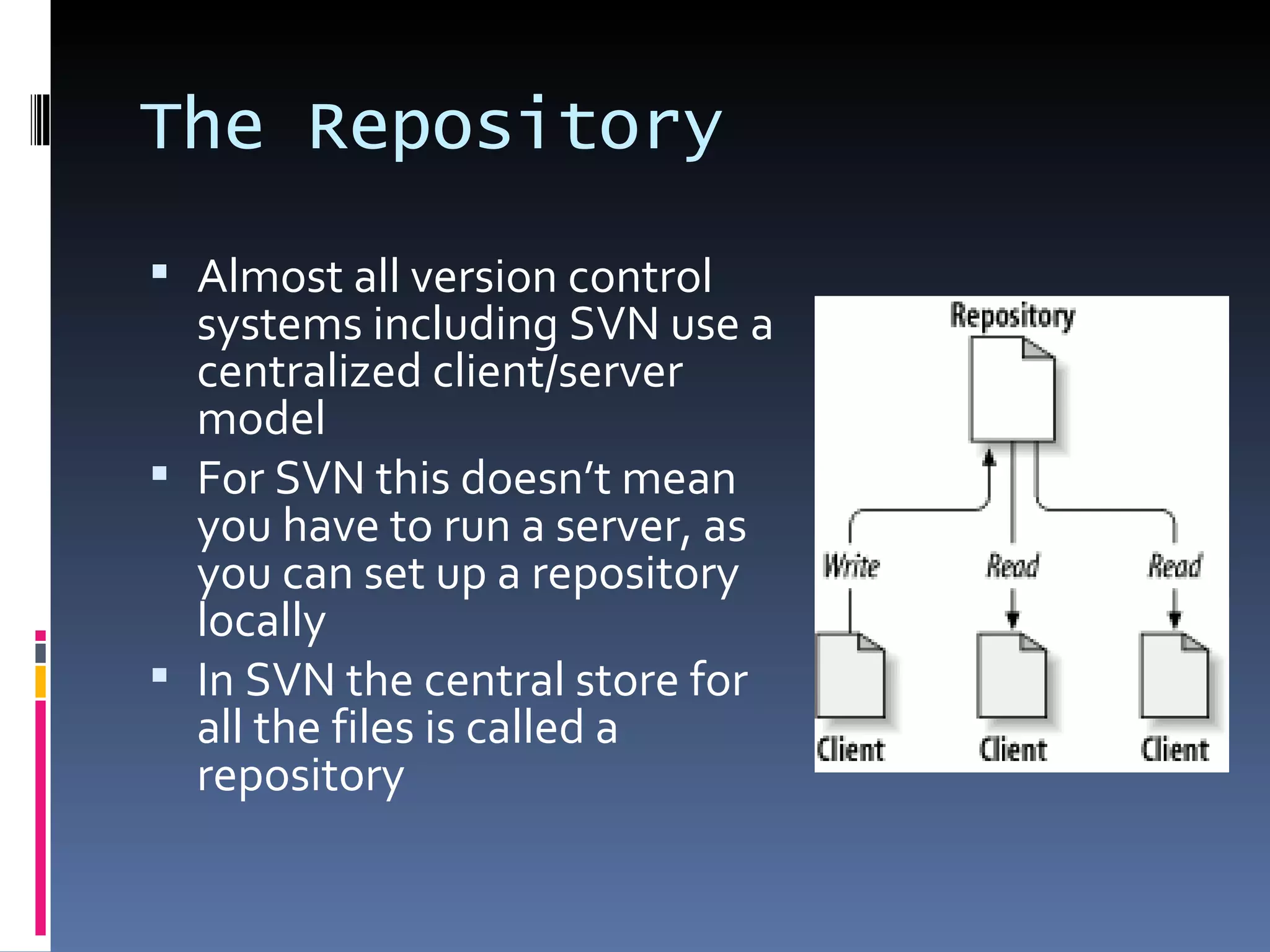
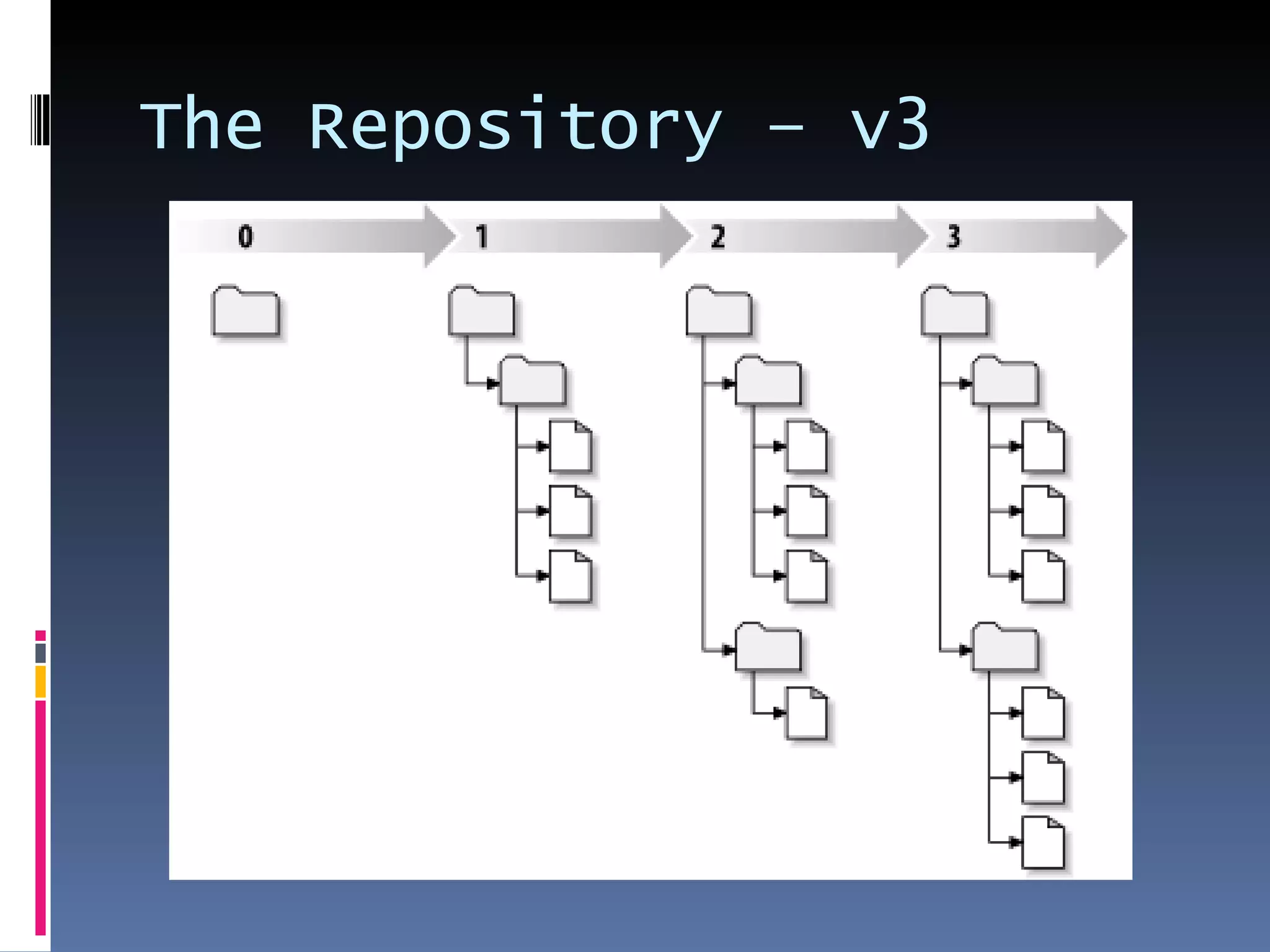
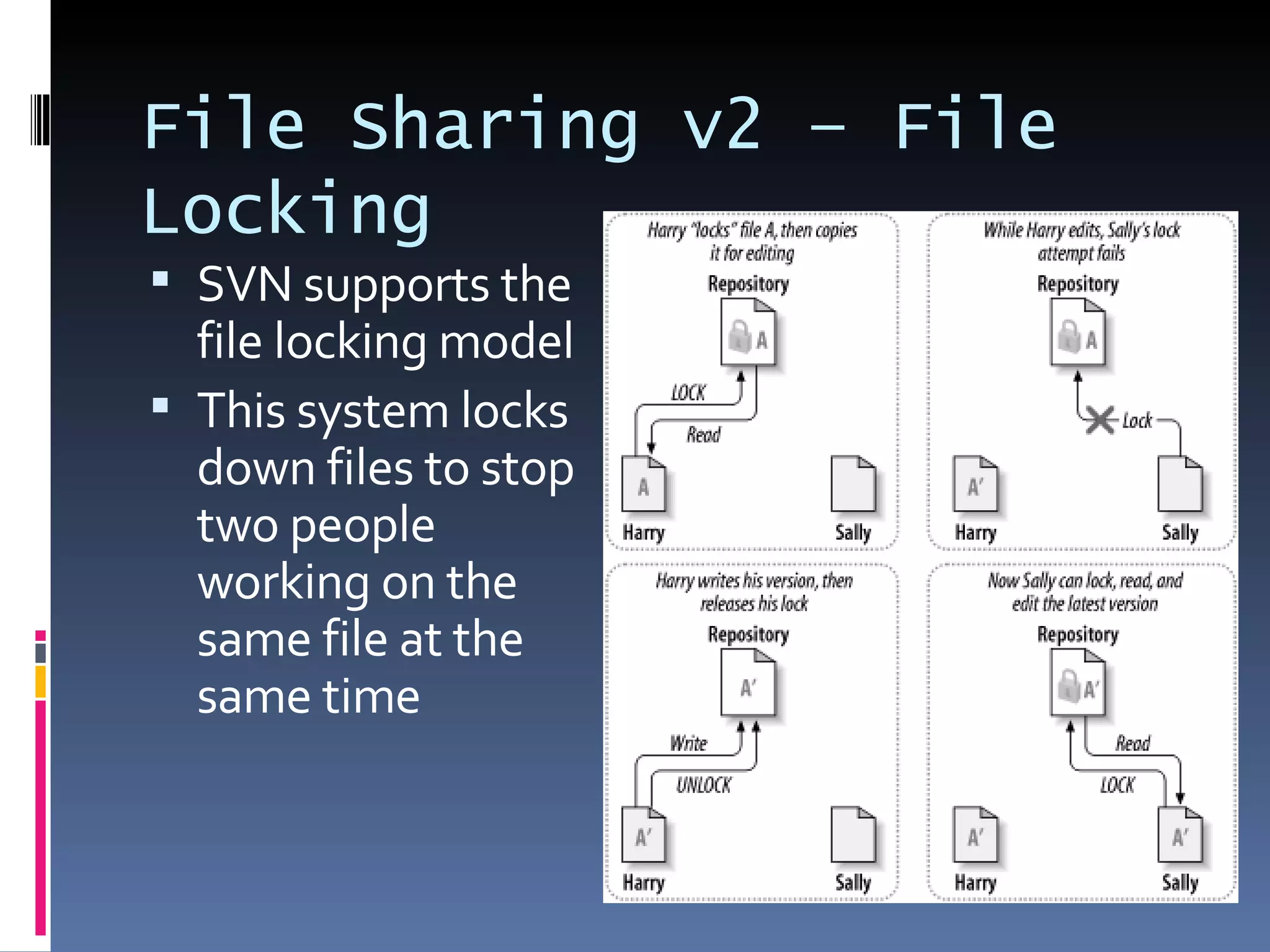
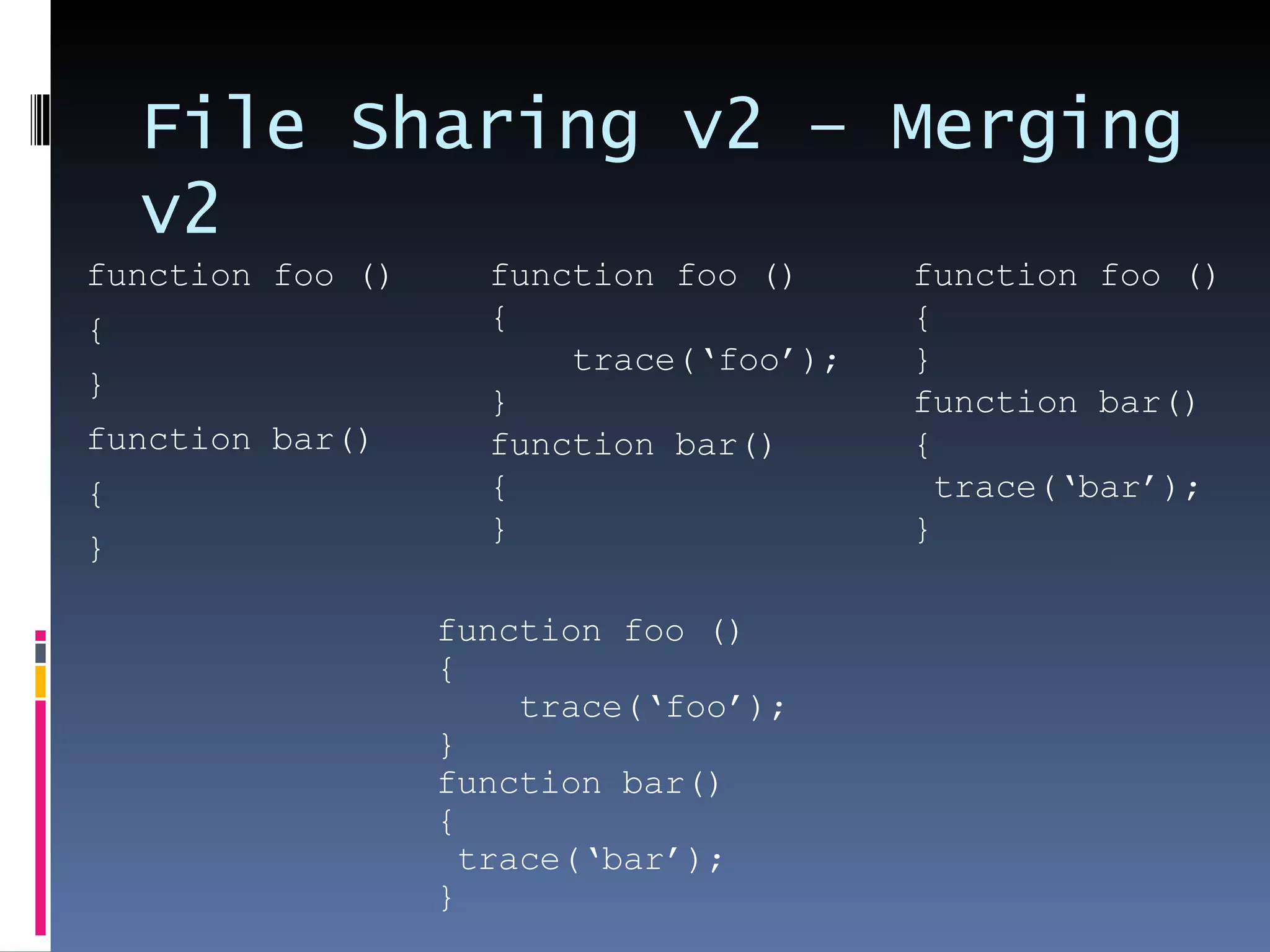
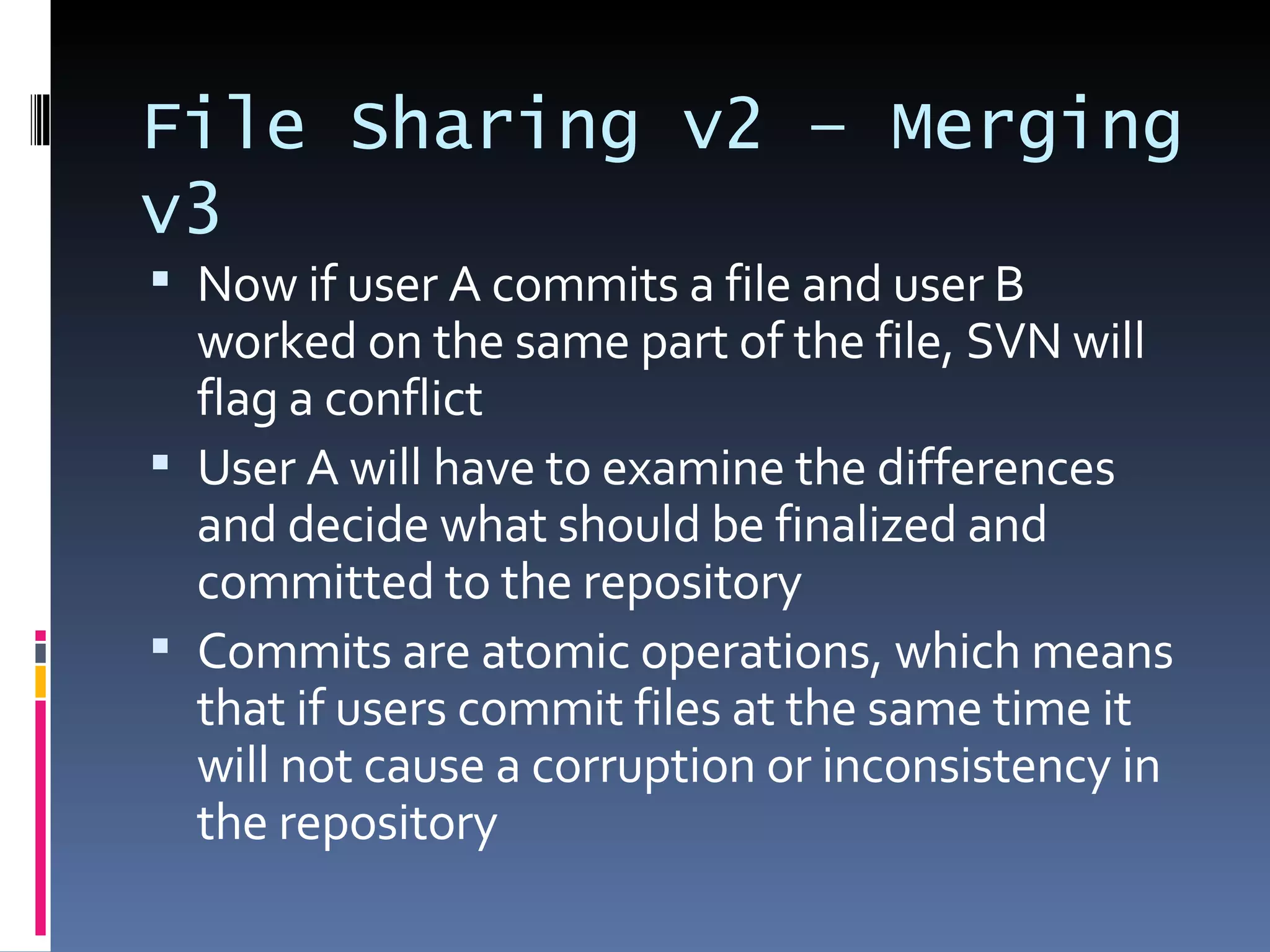
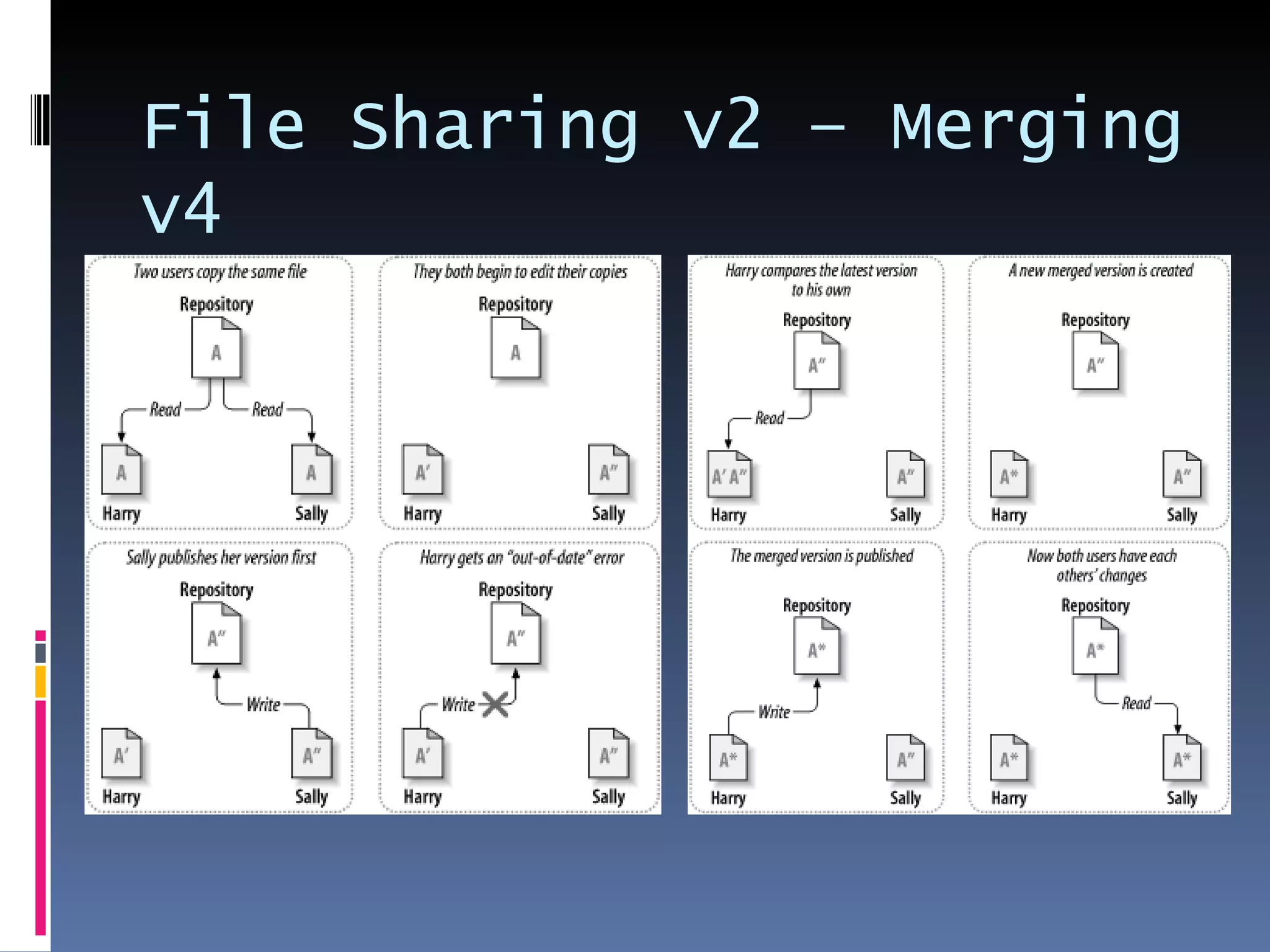
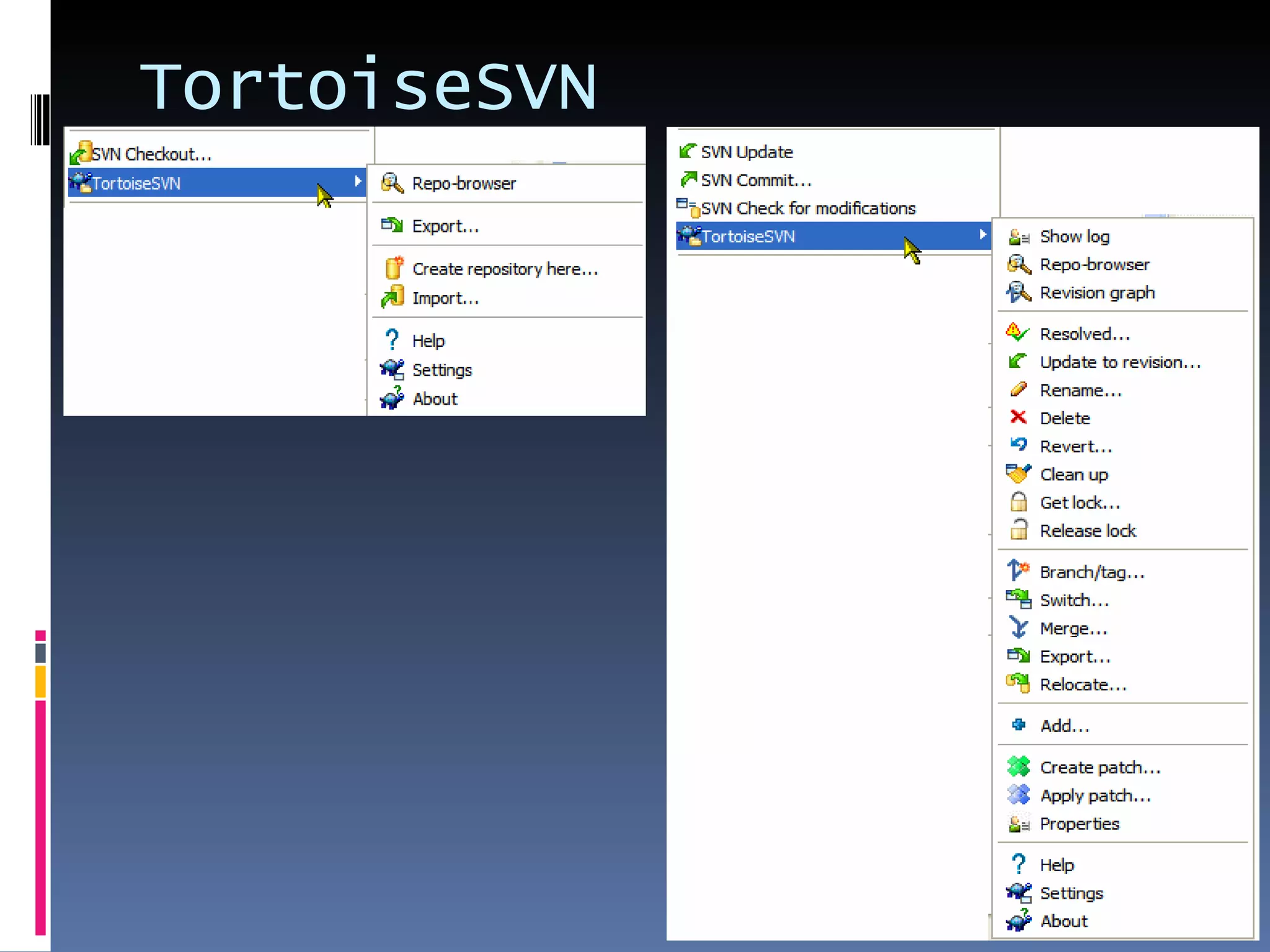
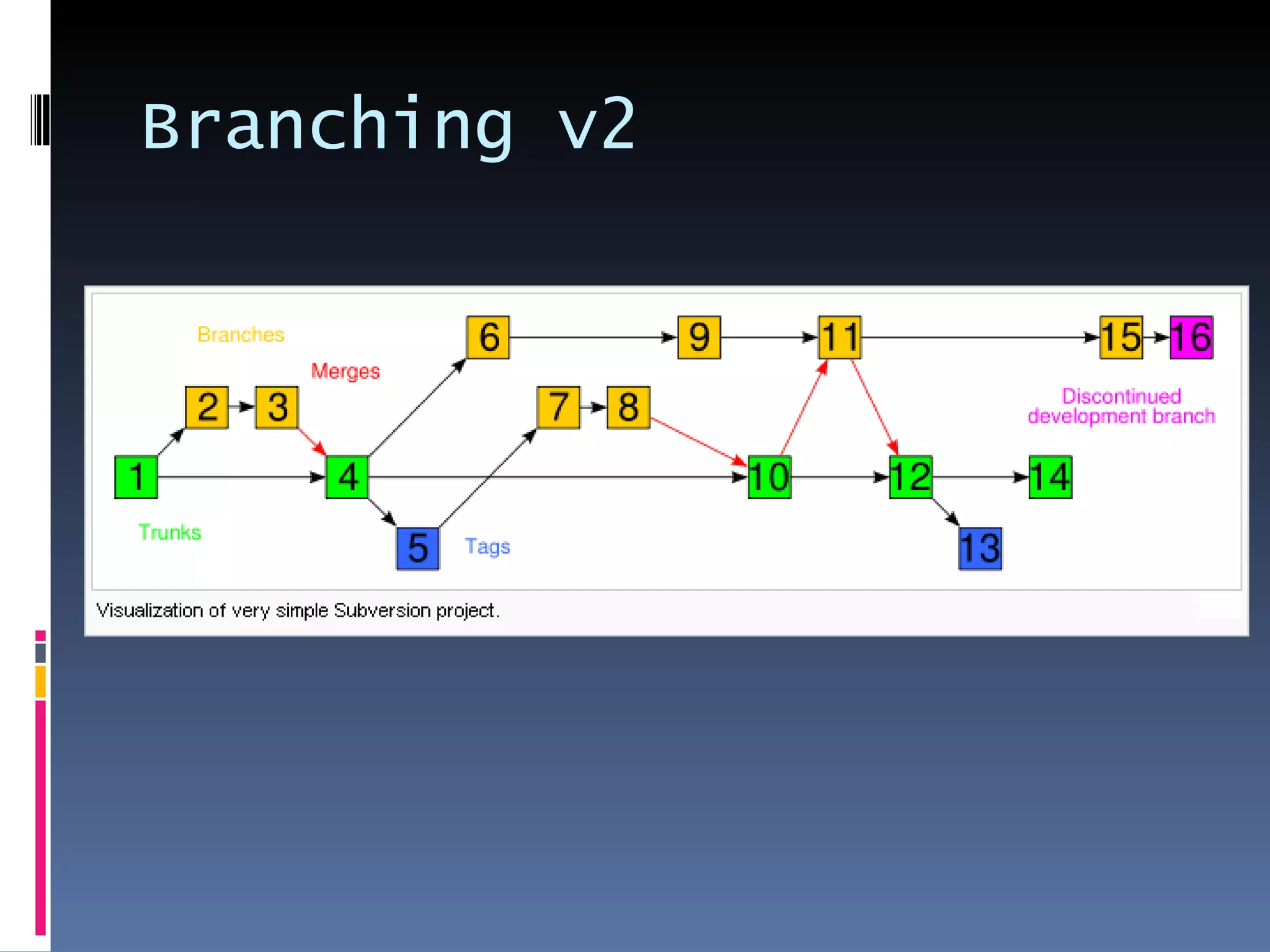
I'm a Flex developer who has been using Subversion (SVN) for version control since 2005. SVN is a centralized version control system where developers can check out files from a central repository, work on them locally, and check in changes. It allows developers to work on the same files simultaneously and merges changes automatically. Popular SVN clients include TortoiseSVN for Windows and Subclipse for Eclipse.