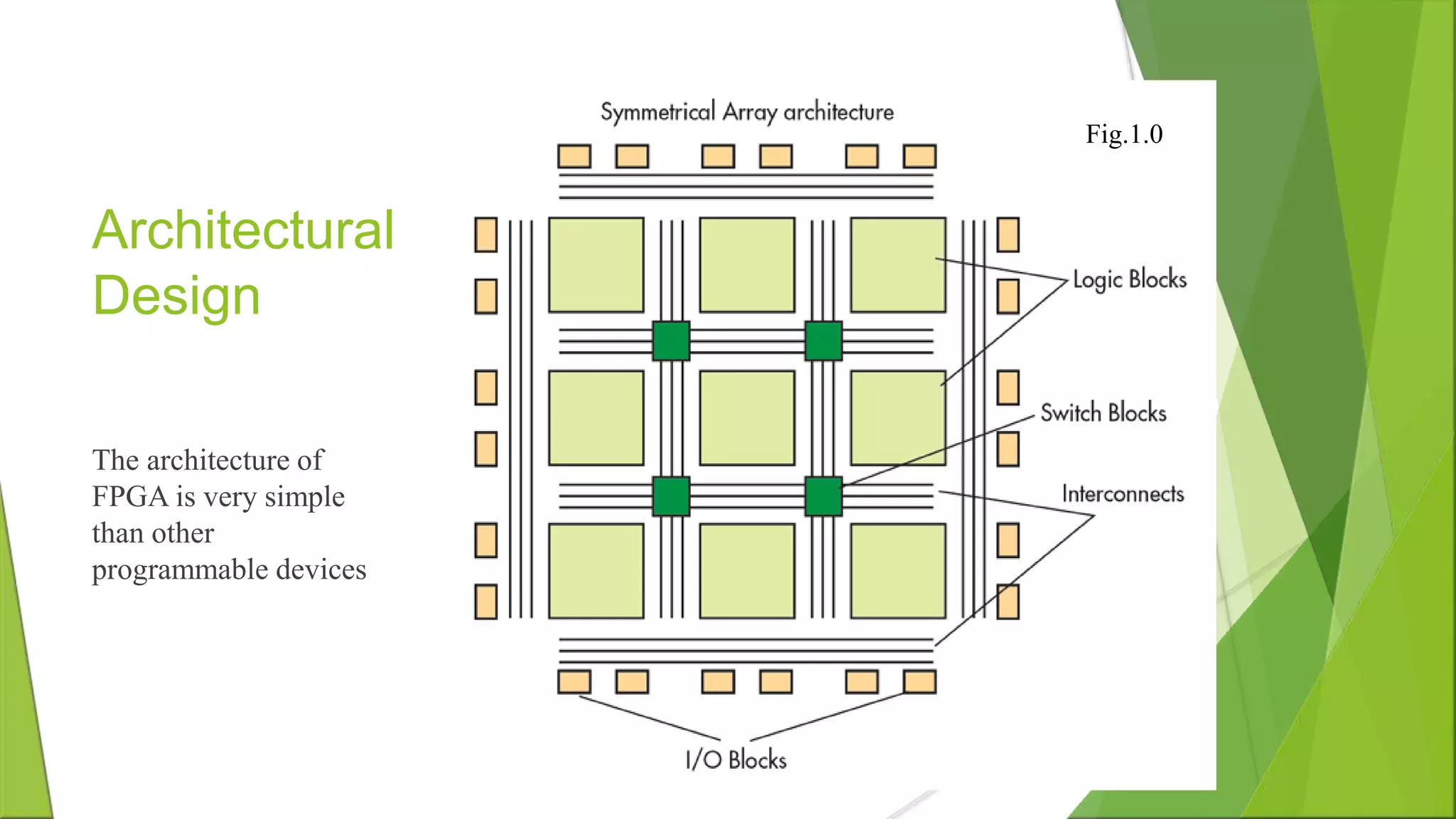
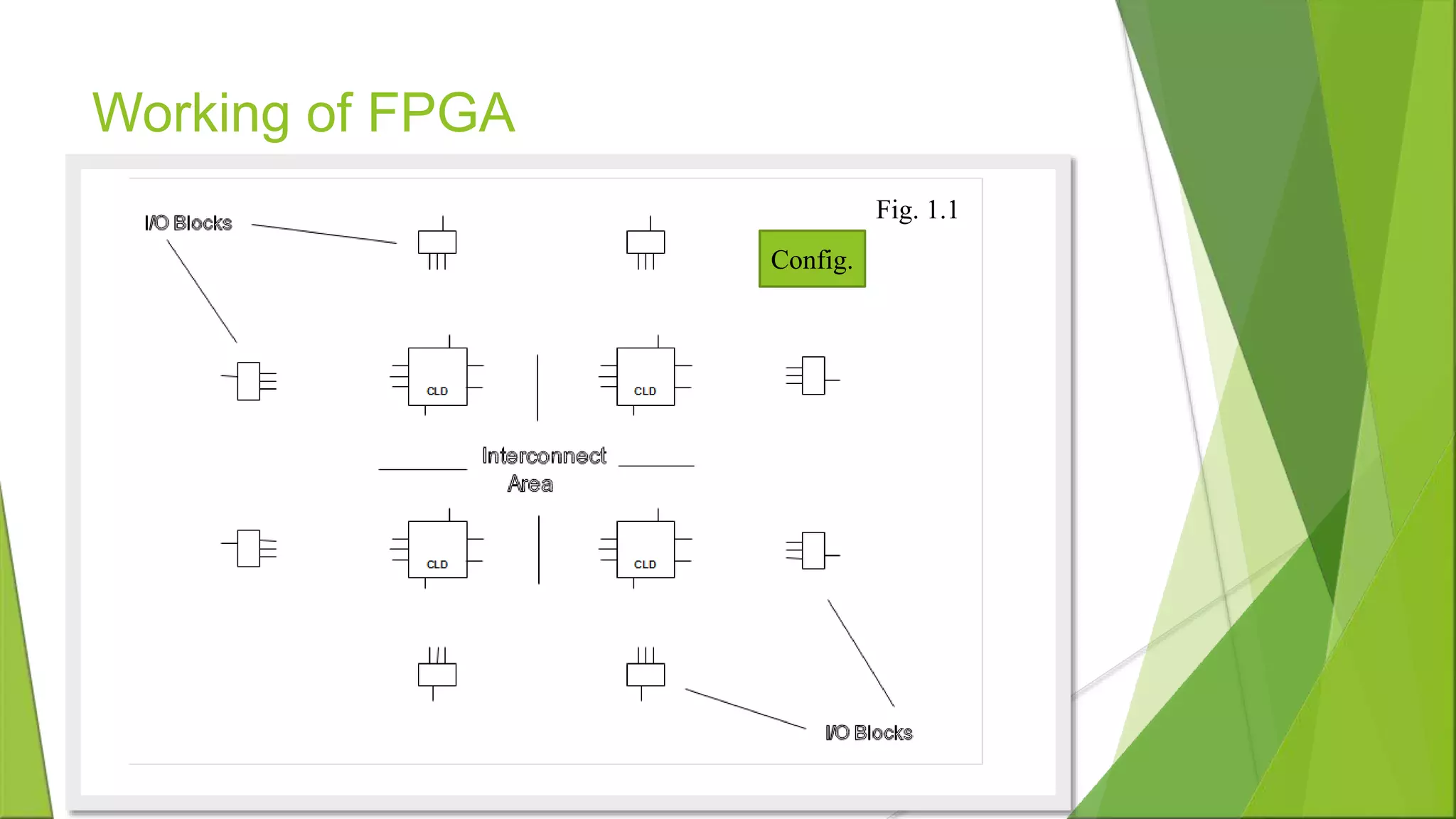
The document discusses Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs), highlighting their programmability, cost-effectiveness, and versatility in applications such as automation and communication. It outlines the architecture, operational mechanisms, and programming methods for FPGAs, along with their advantages and disadvantages compared to other devices like microprocessors and ASICs. Key points include their fast reconfiguration capability and long-term maintainability, despite lower speeds than ASICs.