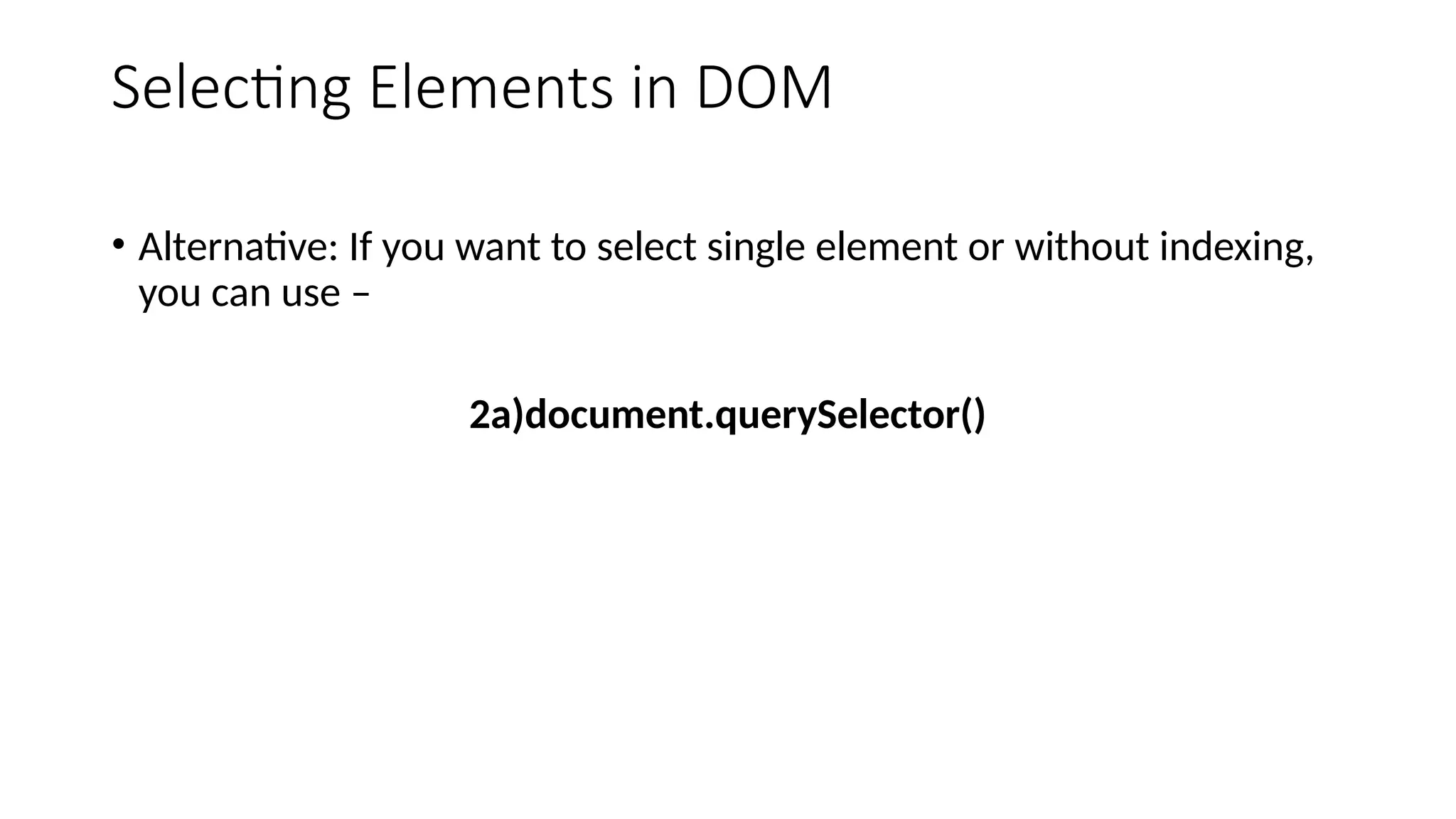
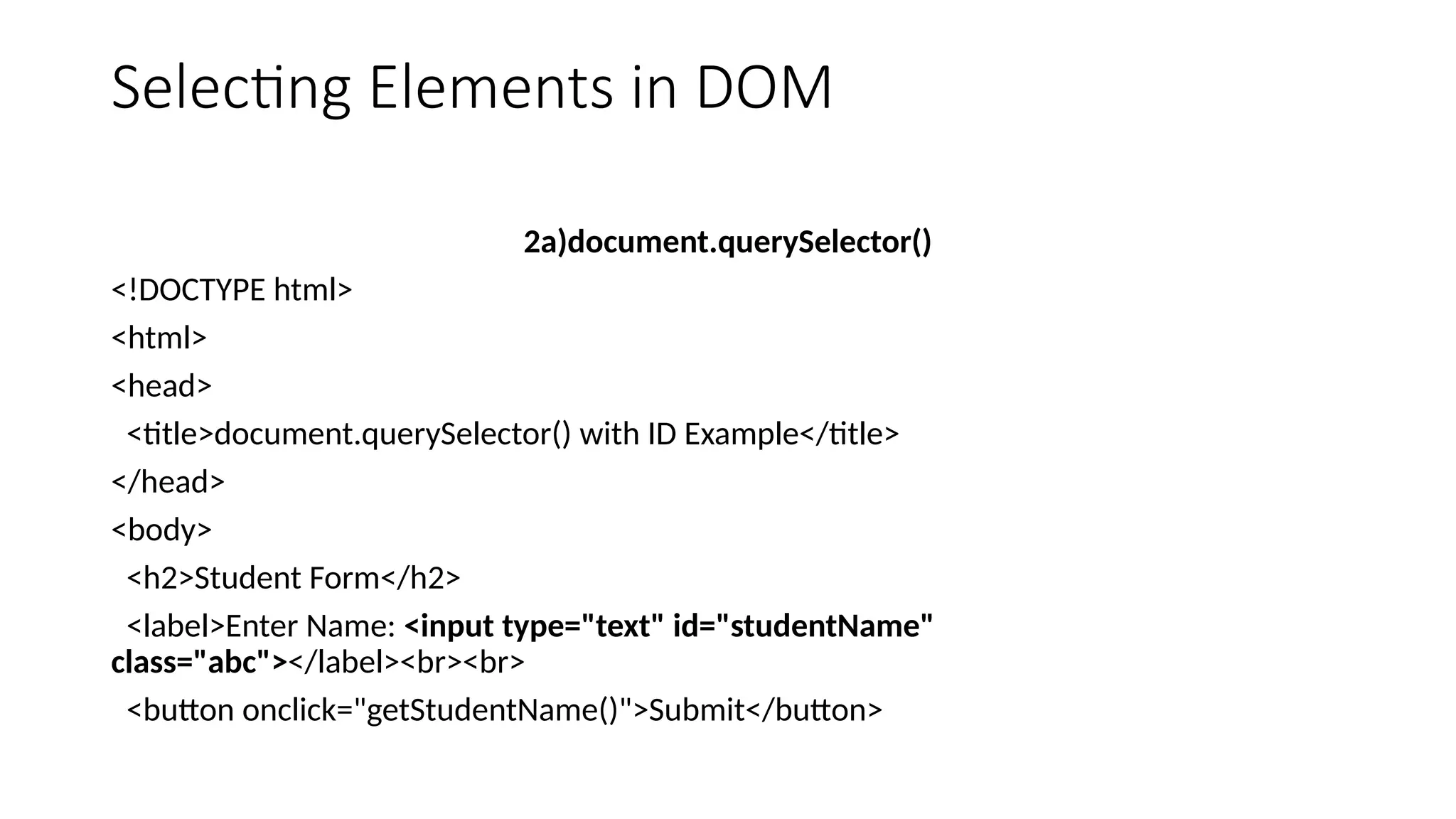
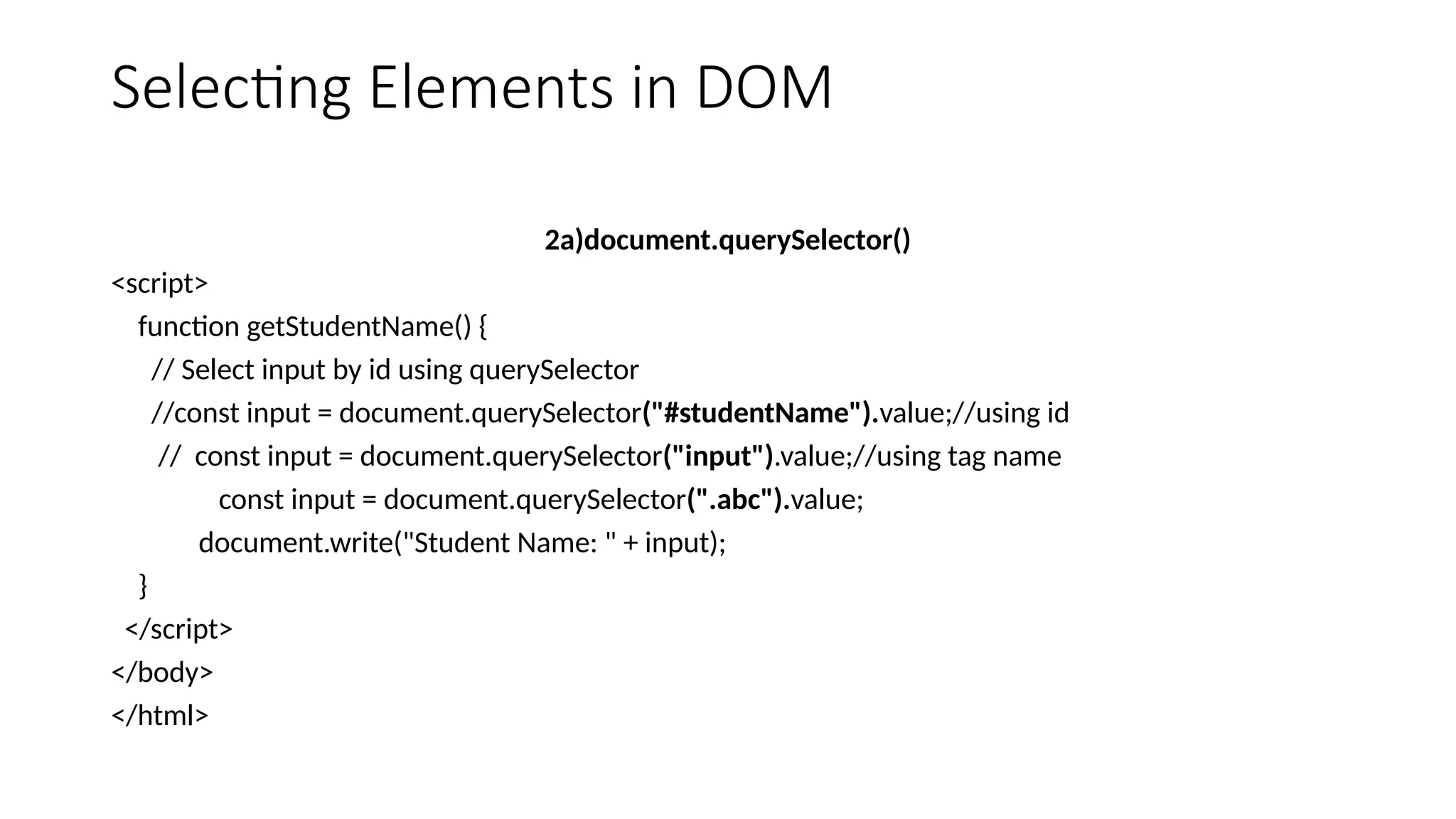
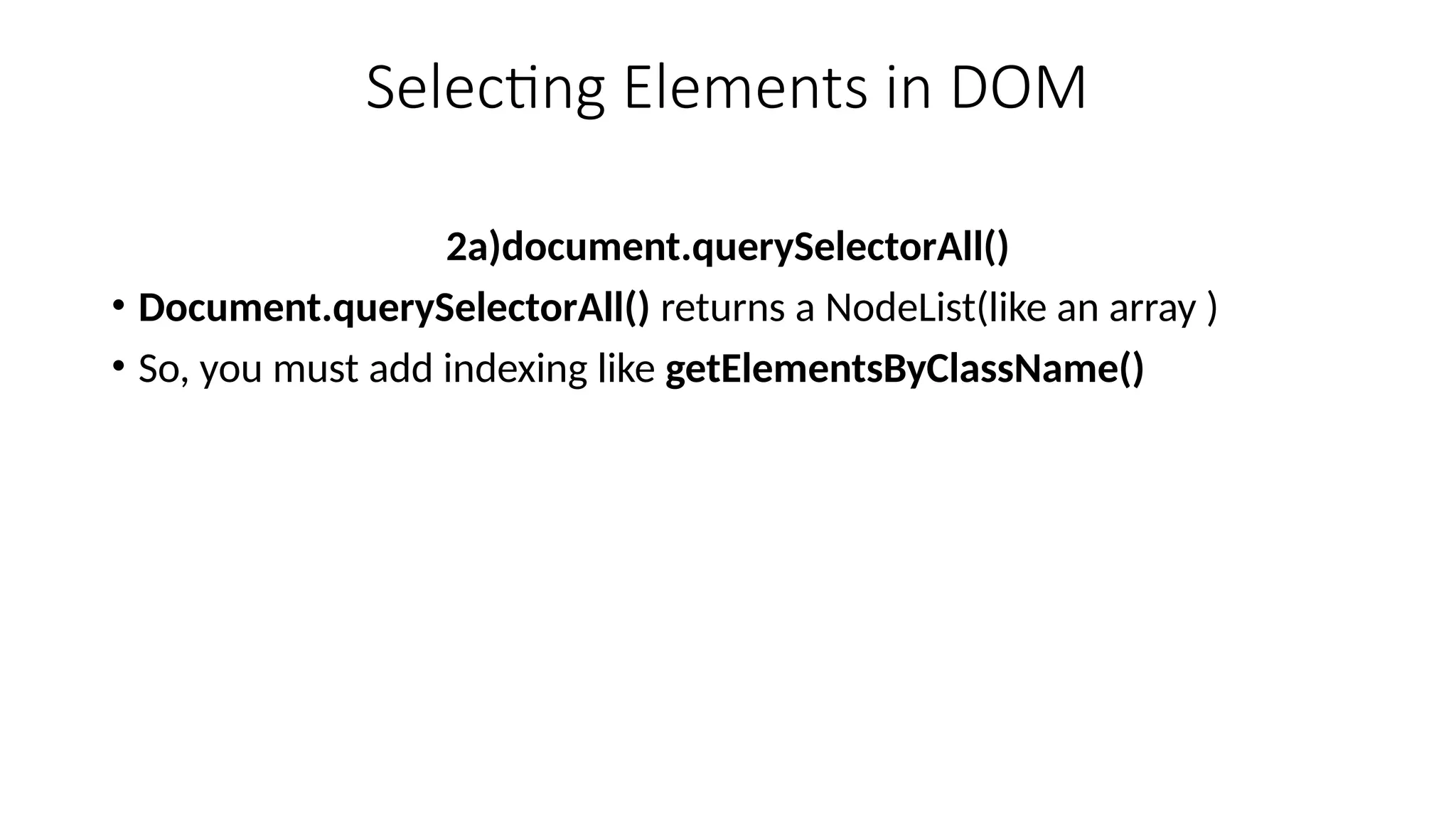
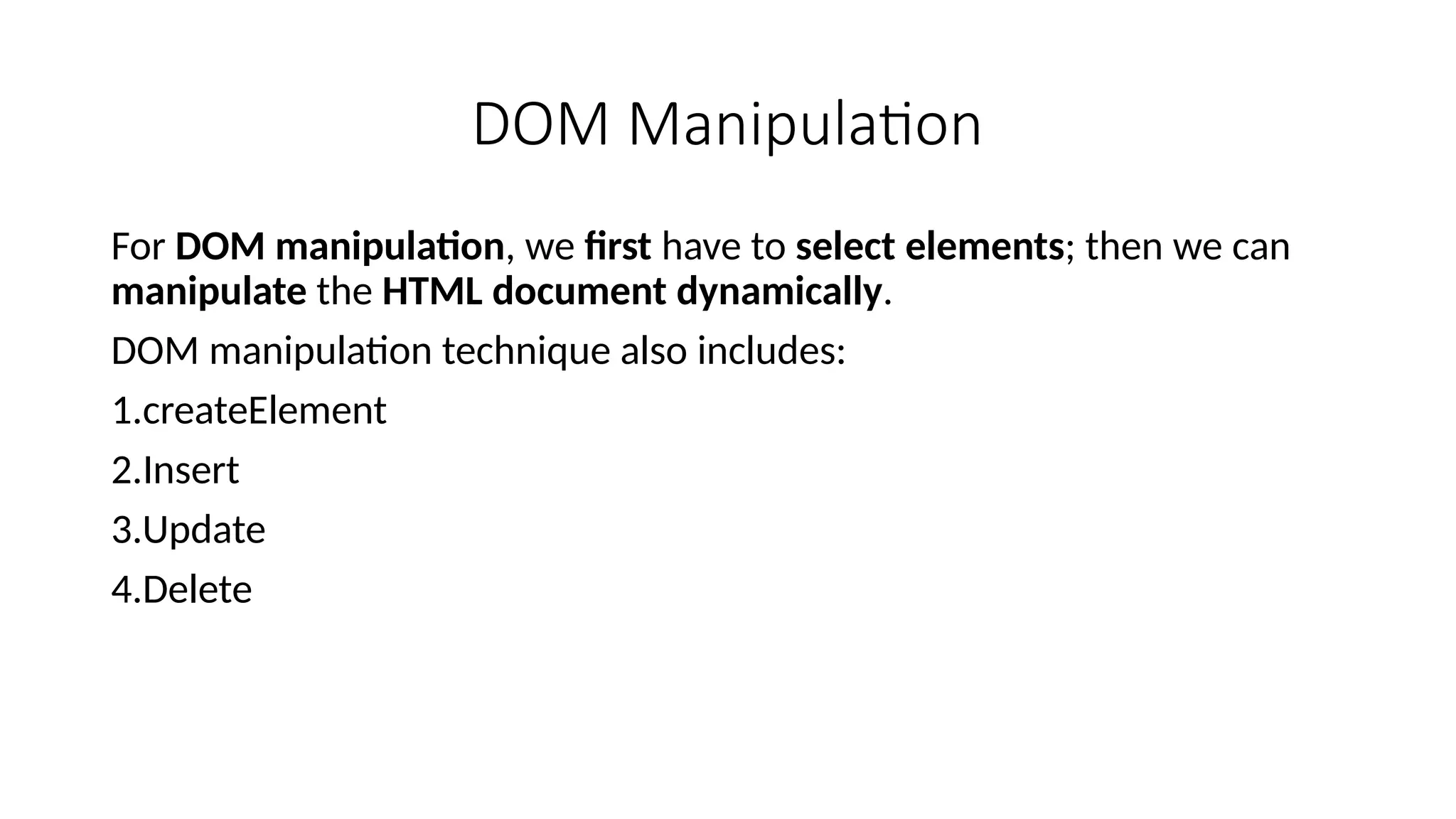
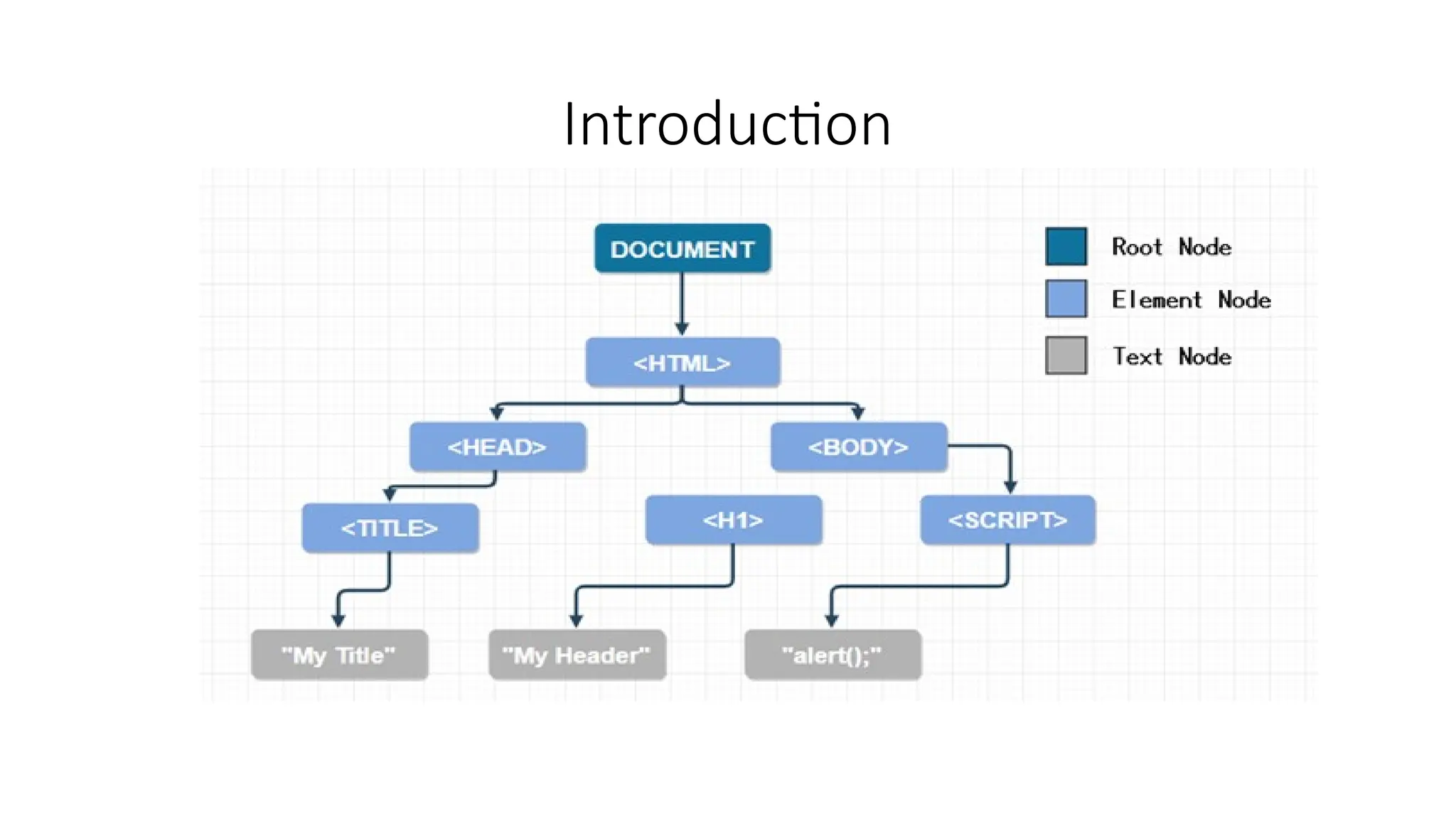
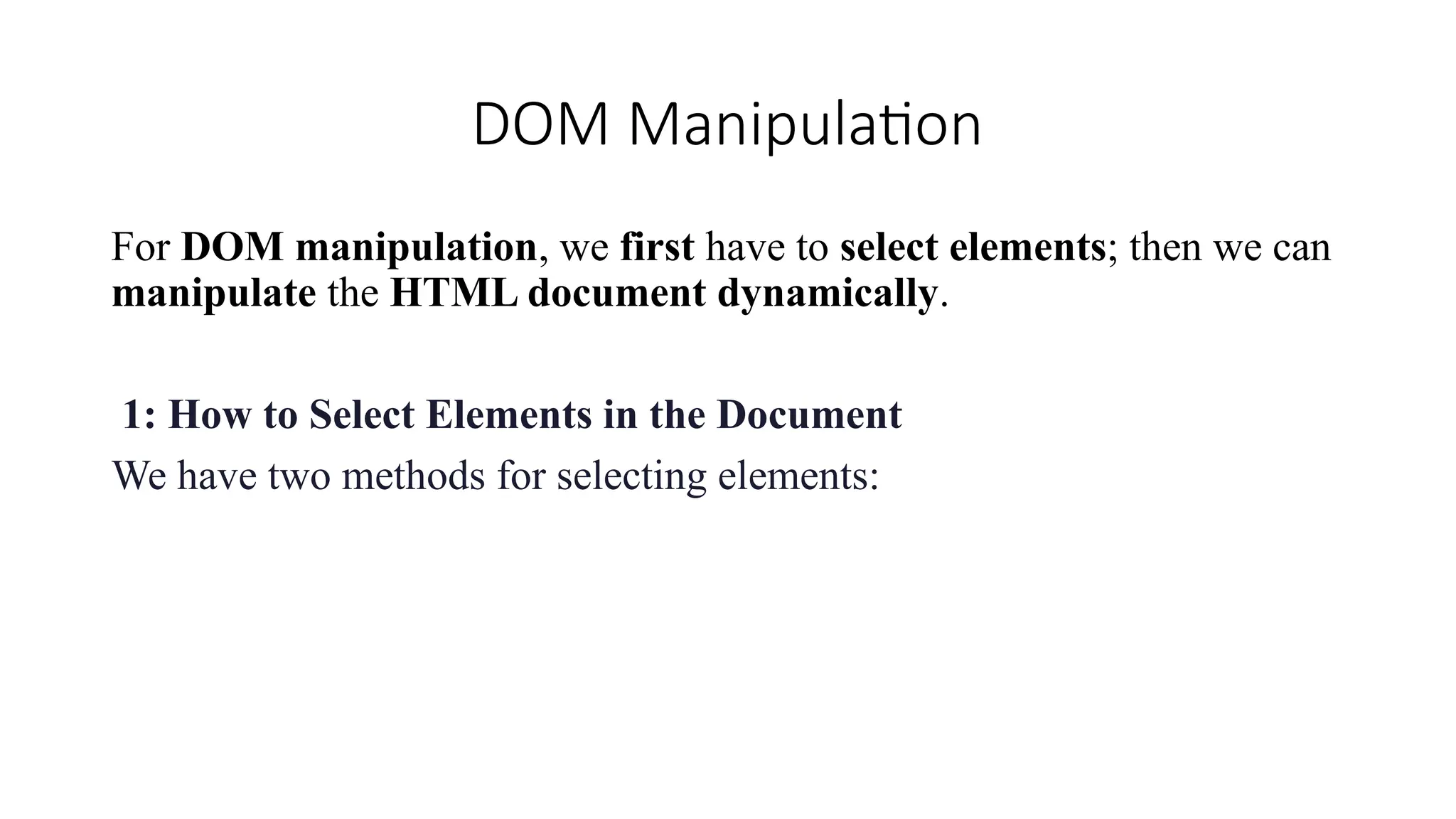
The Document Object Model is the data representation of objects that include the structure and content of a document on the web. A web Page is a document that can be either displayed in browser or as HTML Source. In both cases, it is the same document but the DOM representation allows it to be manipulated/changed/updated. So, When a web page is loaded, the browser creates a DOM of the page automatically.




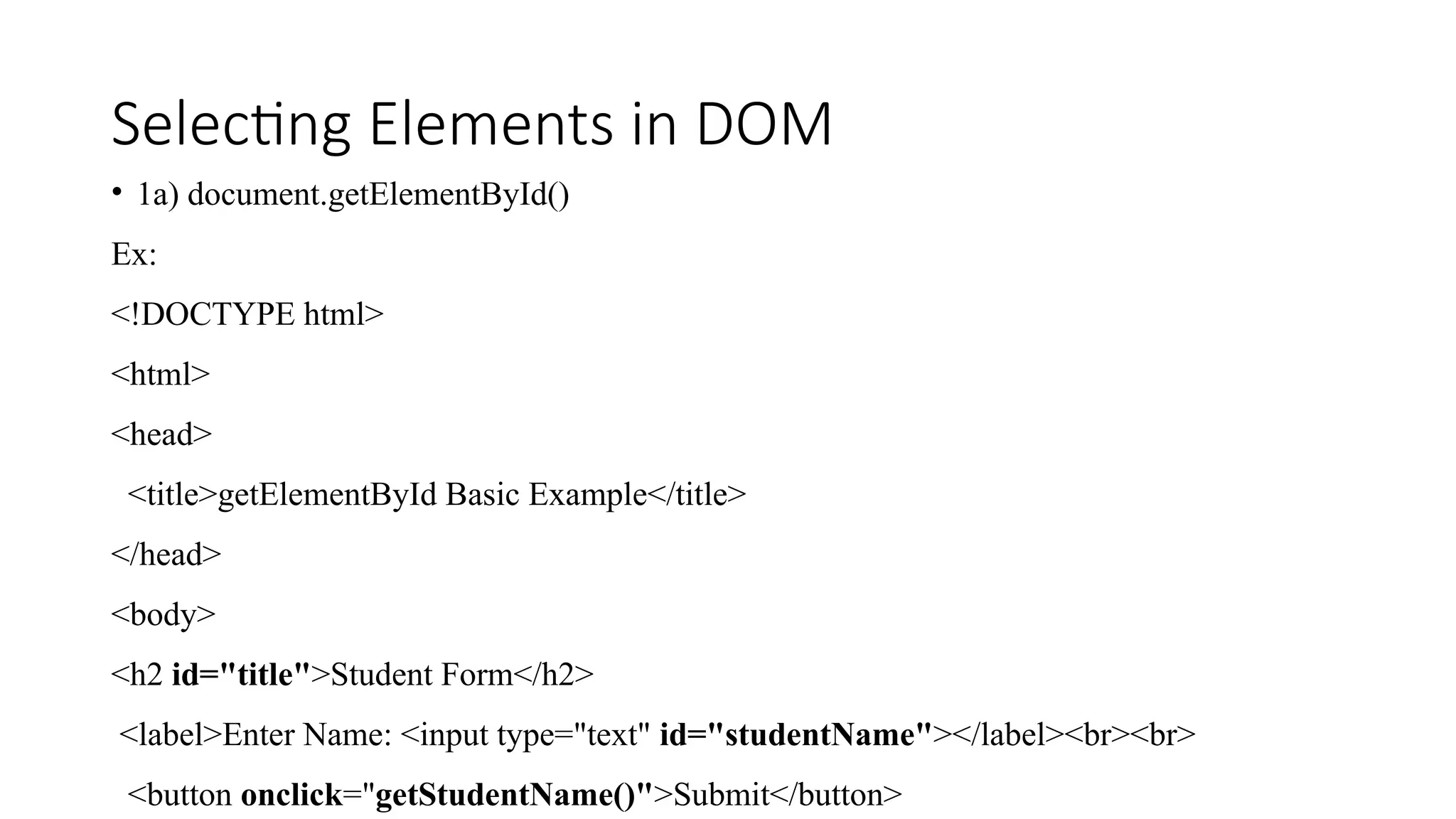
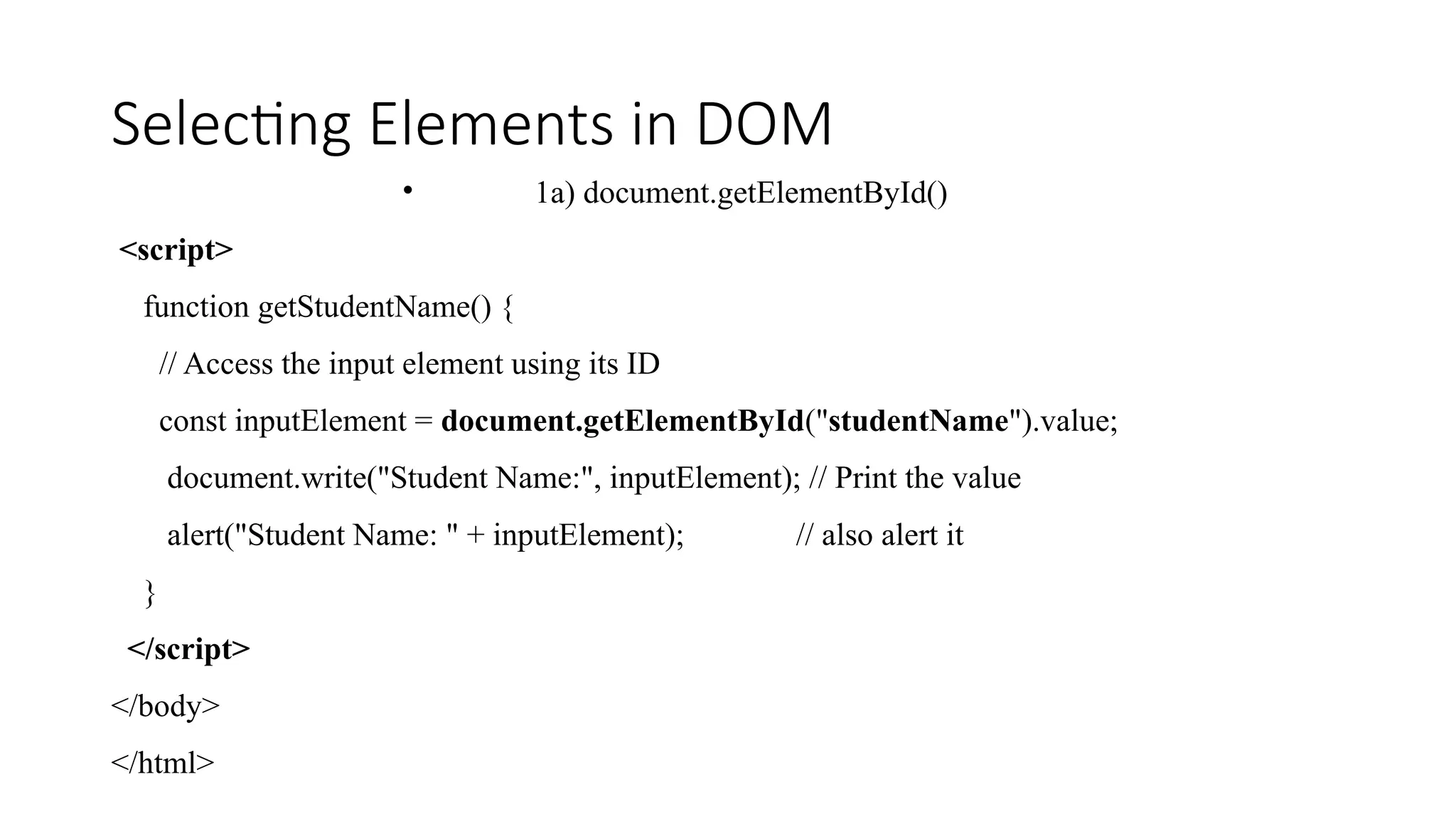
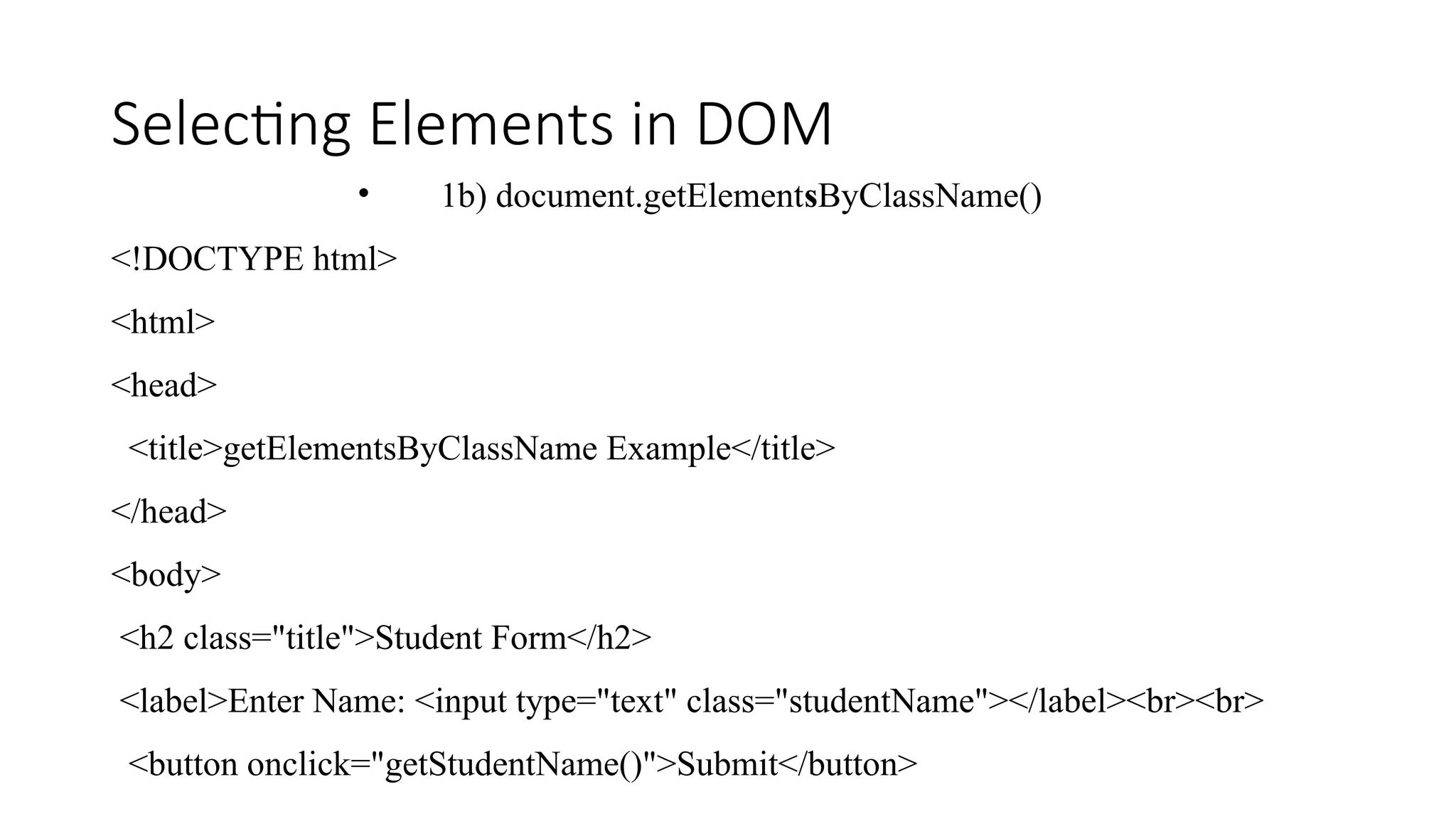
![Selecting Elements in DOM • 1b) document.getElementsByClassName() <script> function getStudentName() { // Step 1: Select the input field by class name const inputElement = document.getElementsByClassName("studentName")[0]; // Step 2: Get the value from the input field const name = inputElement.value; // Step 3: Write to the document (will clear existing page) document.write("Student Name: " + name); } </script> </body> </html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dom-250522142548-f8d2d0f9/75/DOM-document-Object-Model-in-java-Script-pptx-12-2048.jpg)
![Selecting Elements in DOM • 1b) document.getElementsByClassName() • getElementsByClassName() returns a collection (array-like), so we access the first element with [0] . You must access specific item using [index] like [0]. • .value is not a property of a collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dom-250522142548-f8d2d0f9/75/DOM-document-Object-Model-in-java-Script-pptx-13-2048.jpg)

![Selecting Elements in DOM • 1c) document.getElementsByTagName() • <script> function getStudentName() { // Step 1: Access all input elements using tag name const inputs = document.getElementsByTagName("input"); // Step 2: Get the value of the first input field const studentName = inputs[0].value; // Step 3: Display the value using document.write document.write("Student Name: " + studentName); } </script> </body> </html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dom-250522142548-f8d2d0f9/75/DOM-document-Object-Model-in-java-Script-pptx-15-2048.jpg)