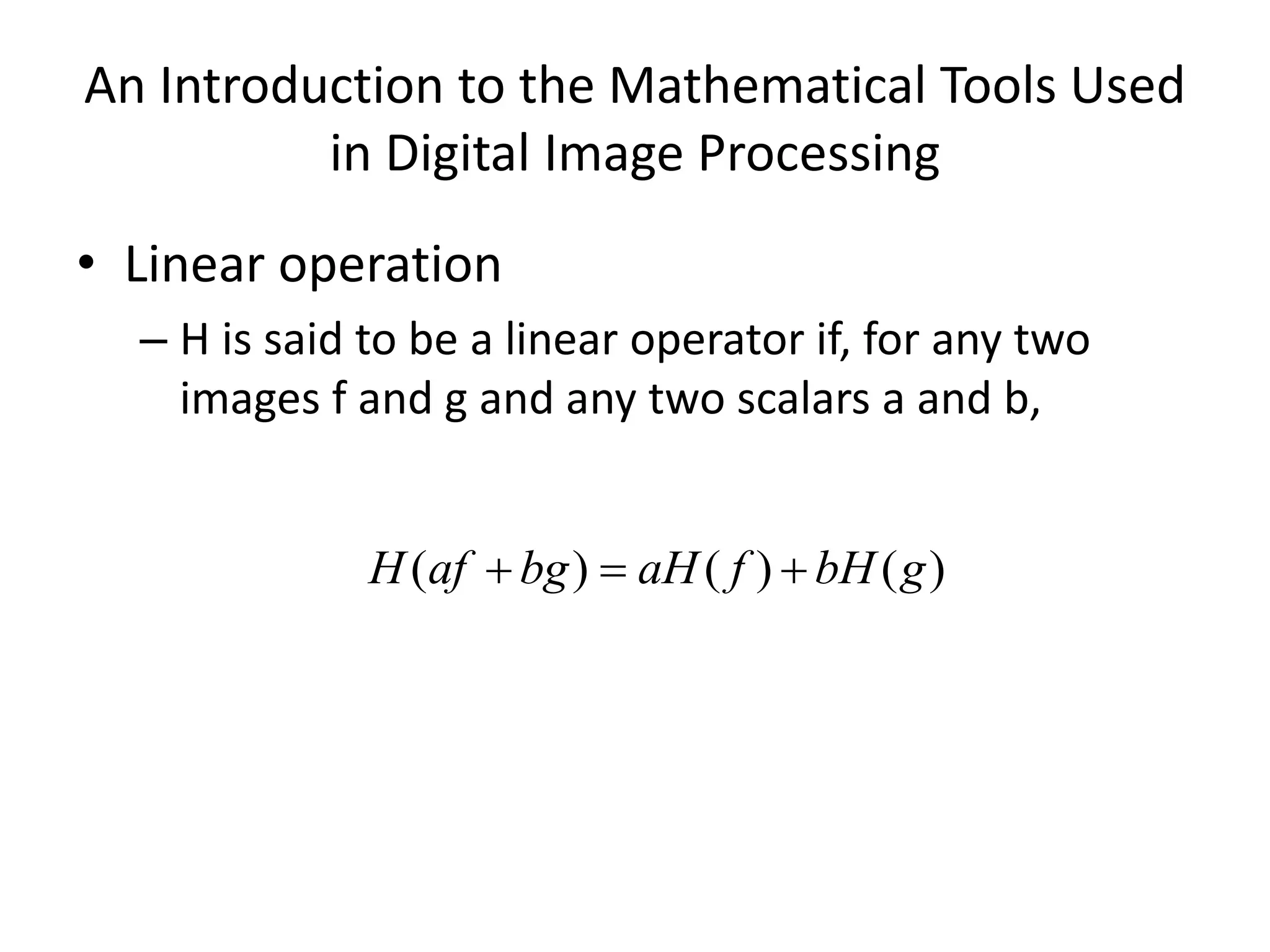
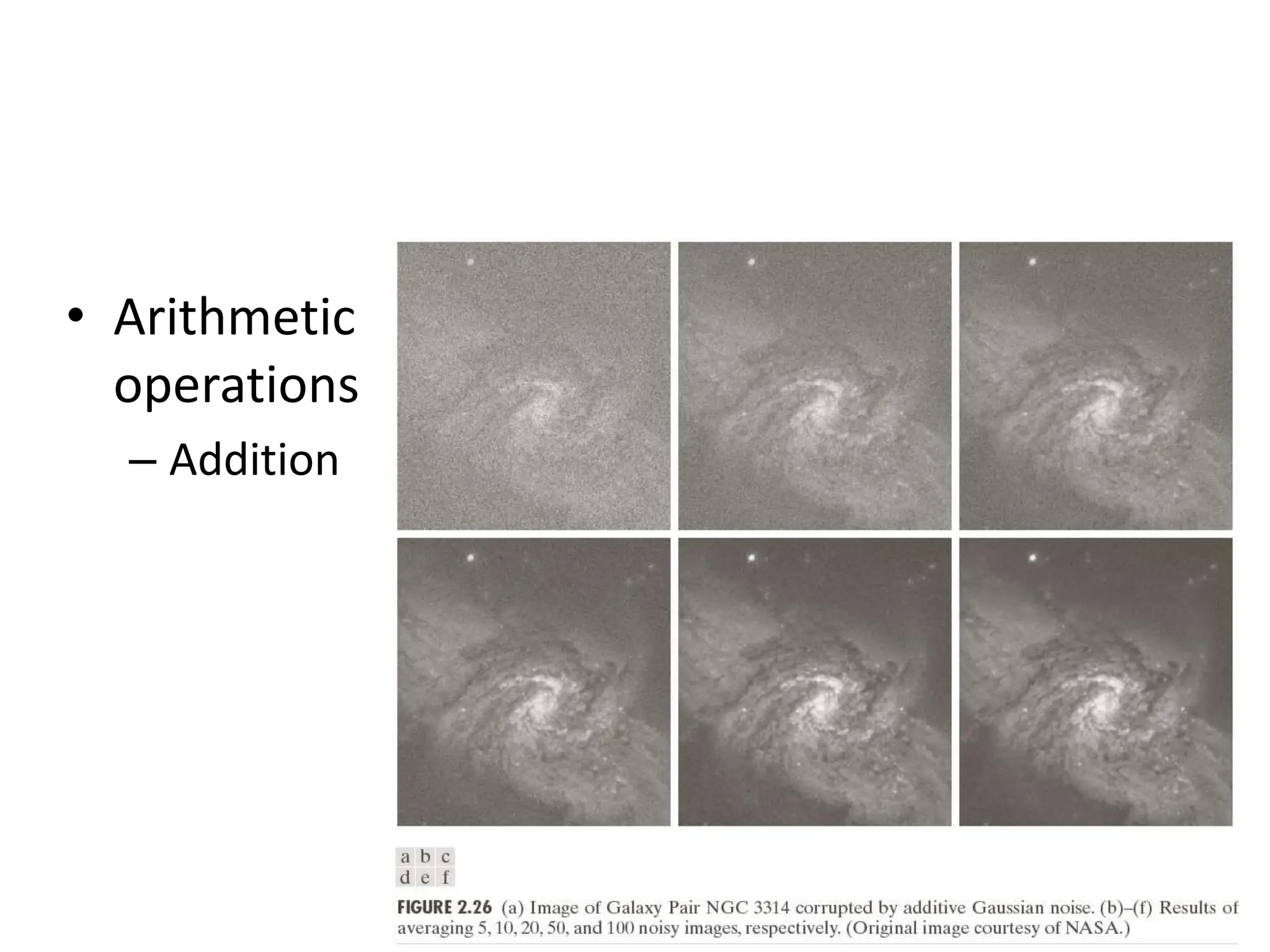
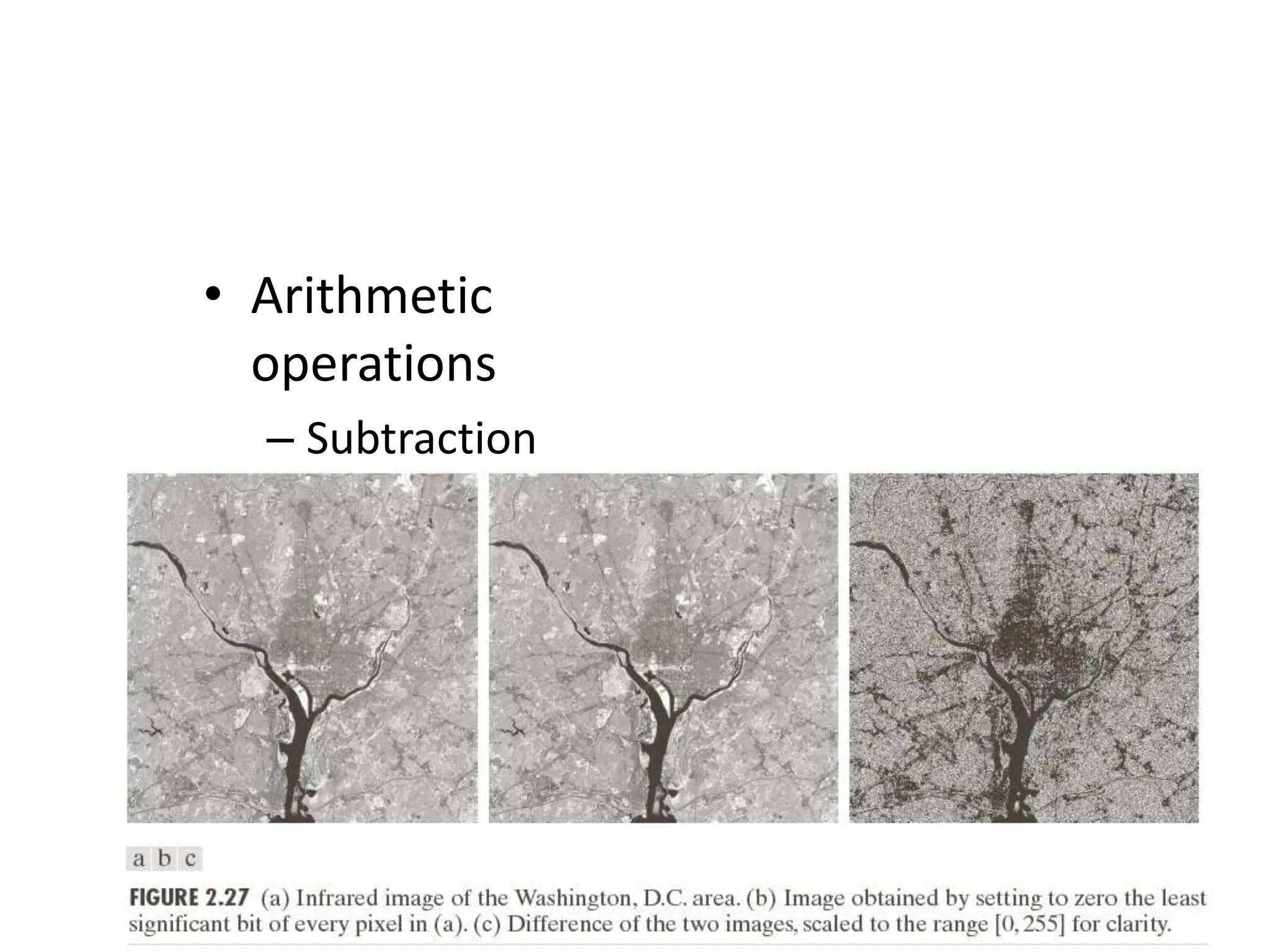
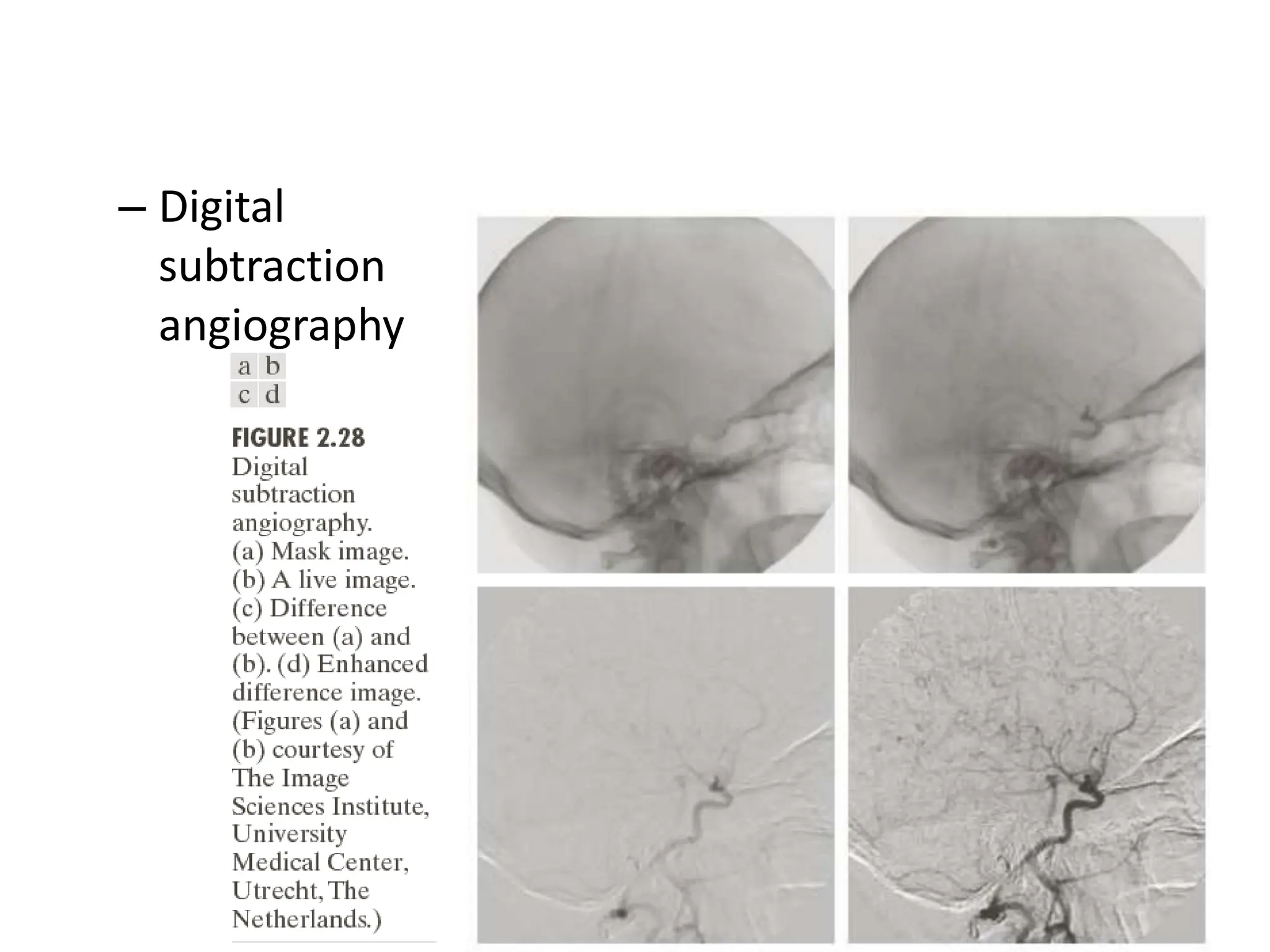
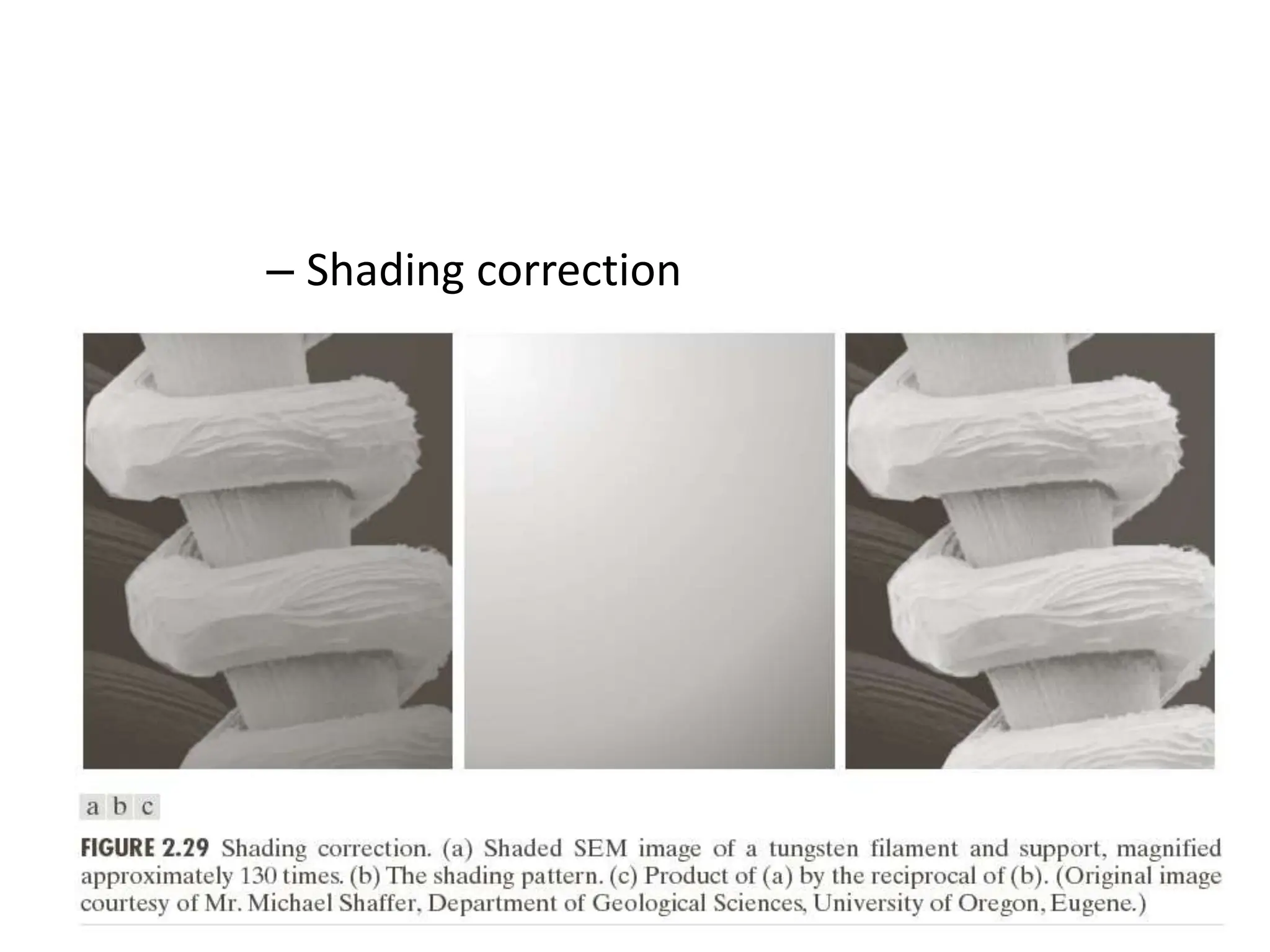
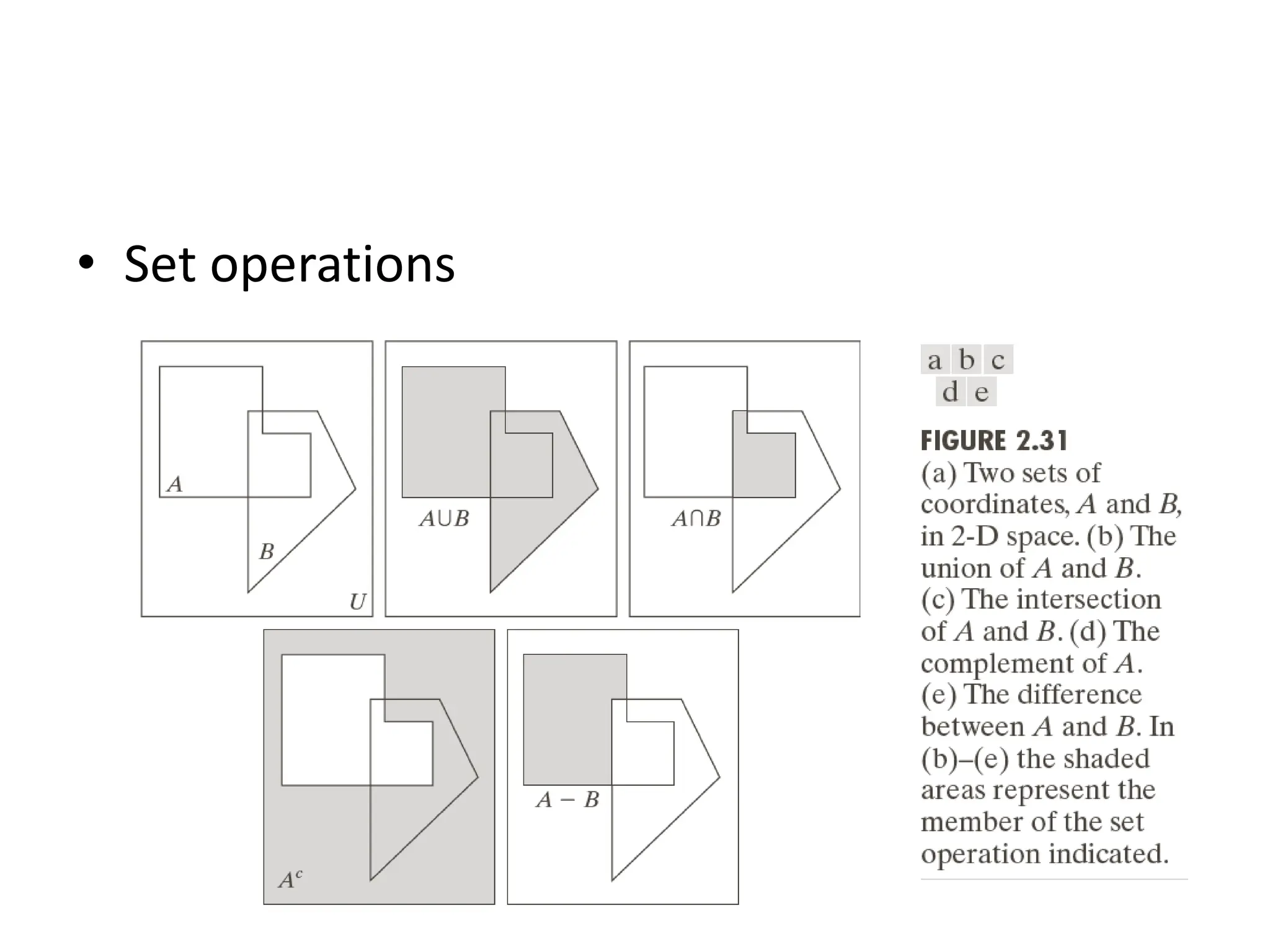
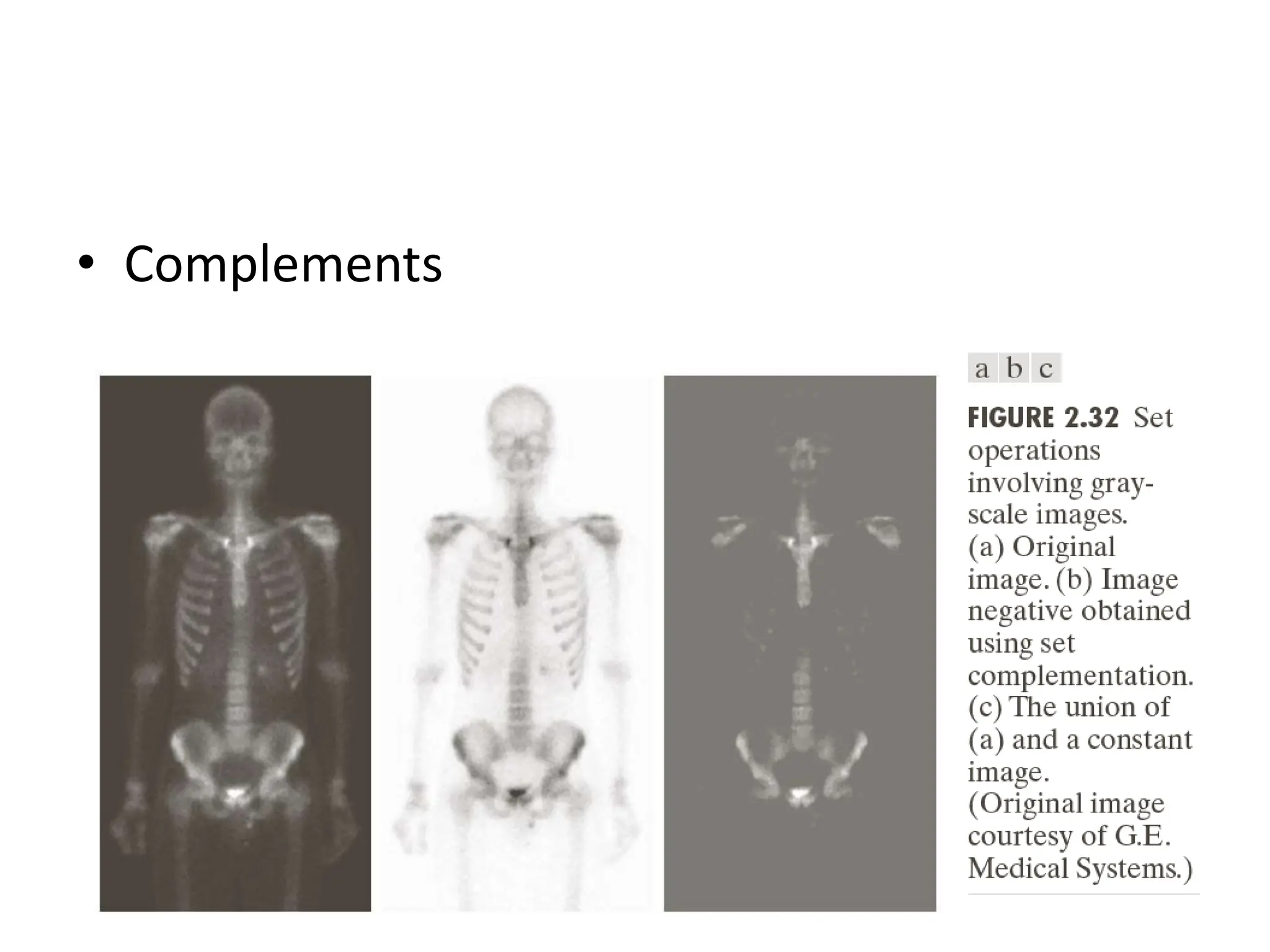
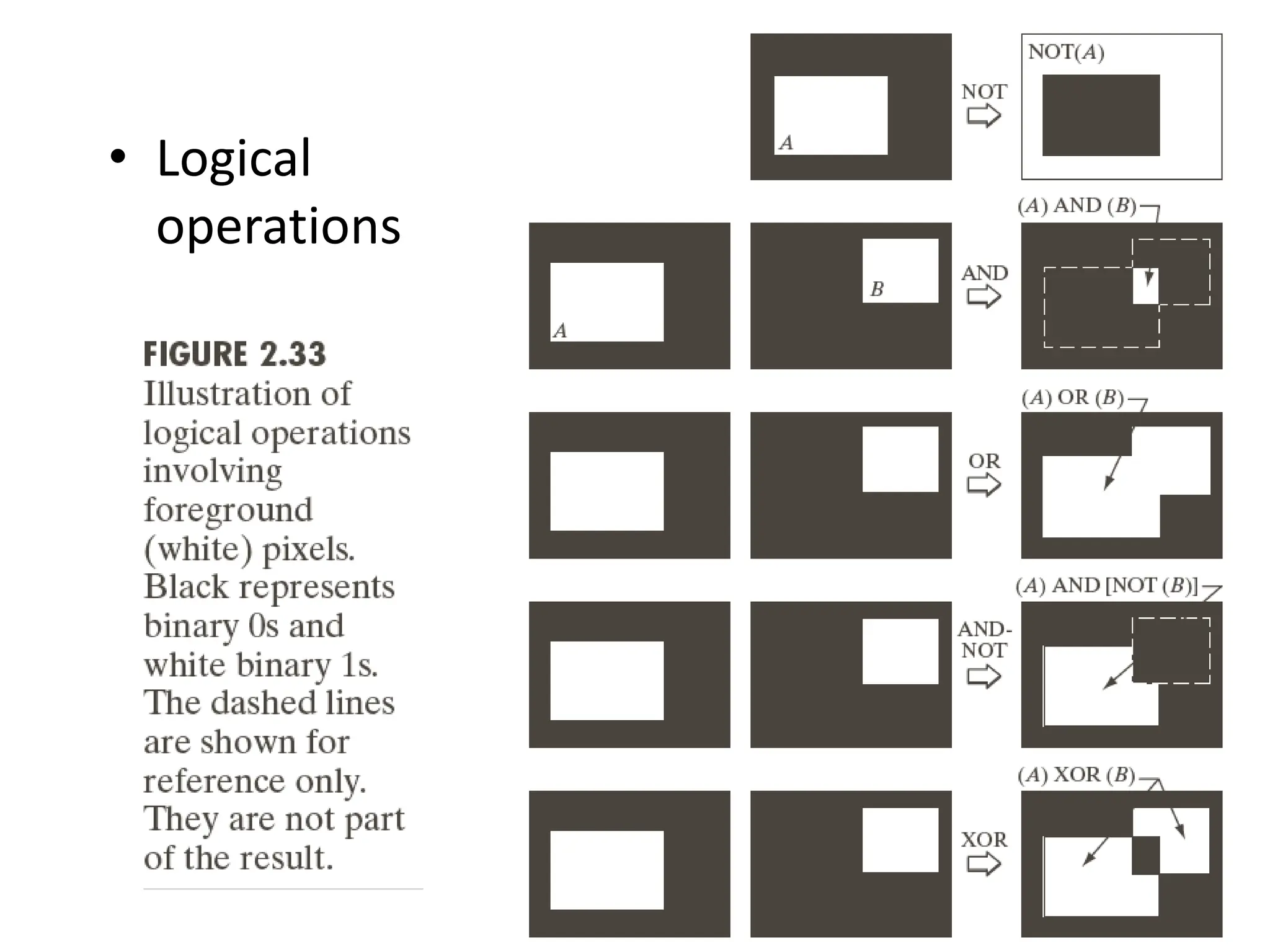
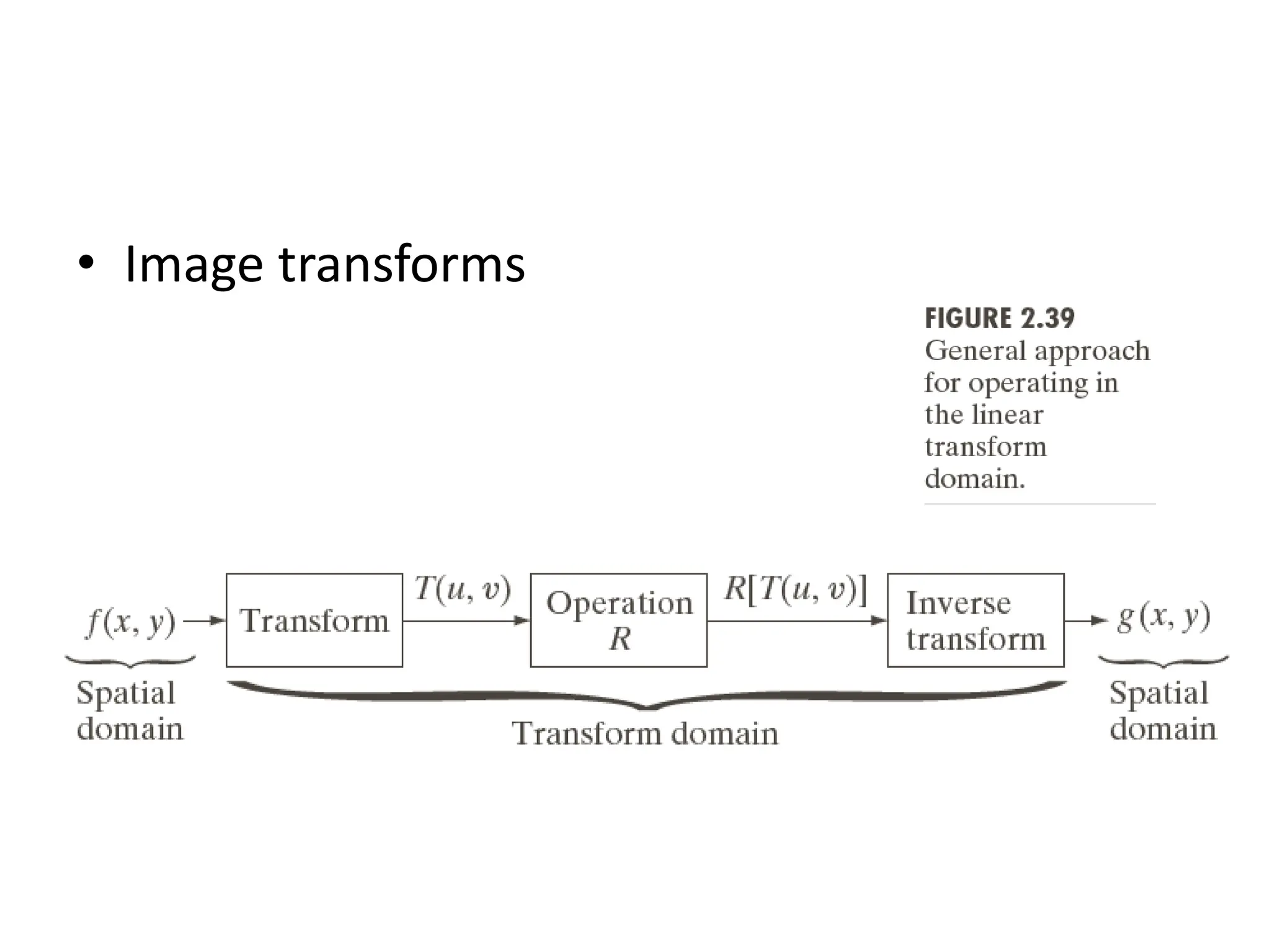
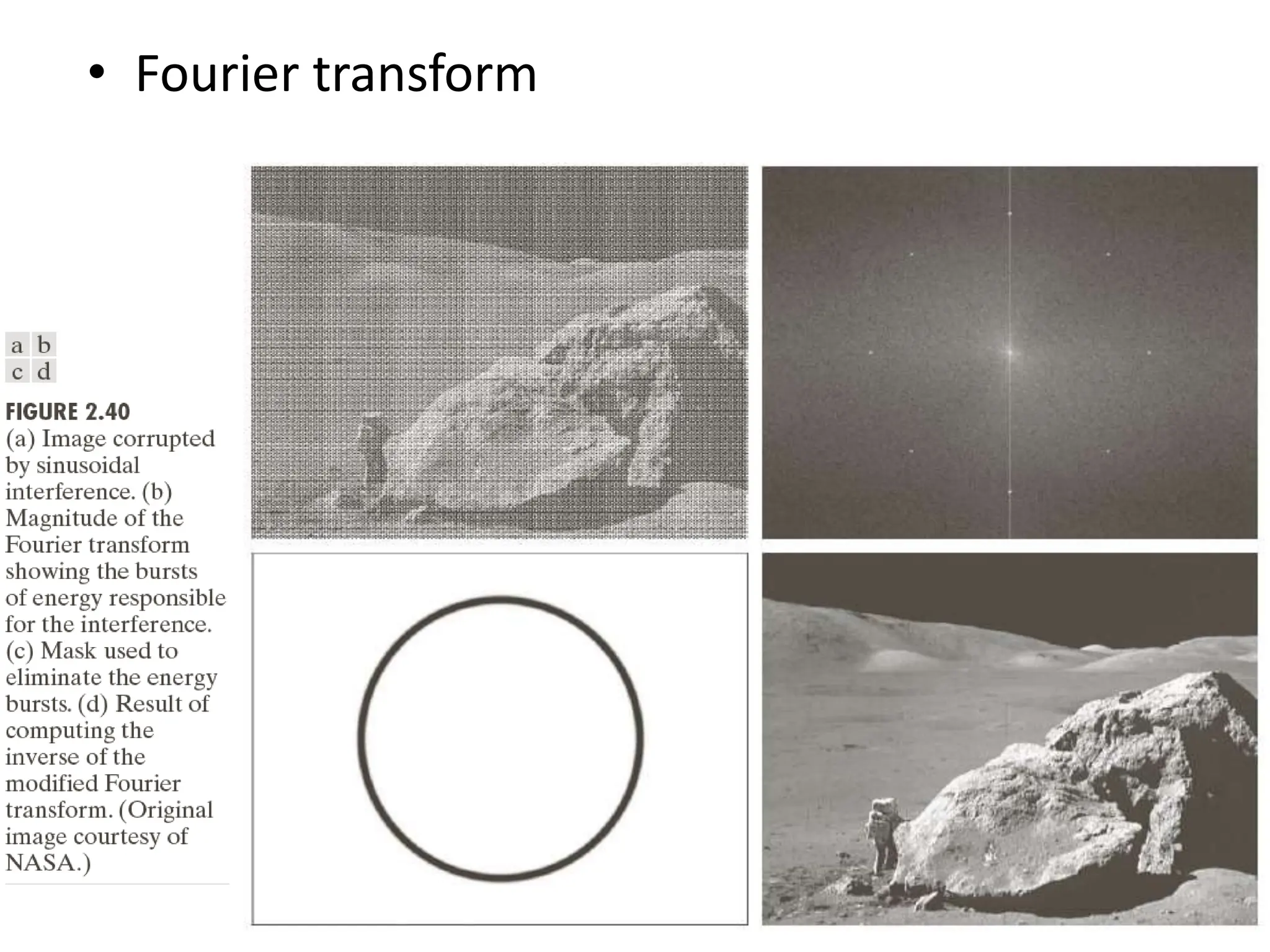
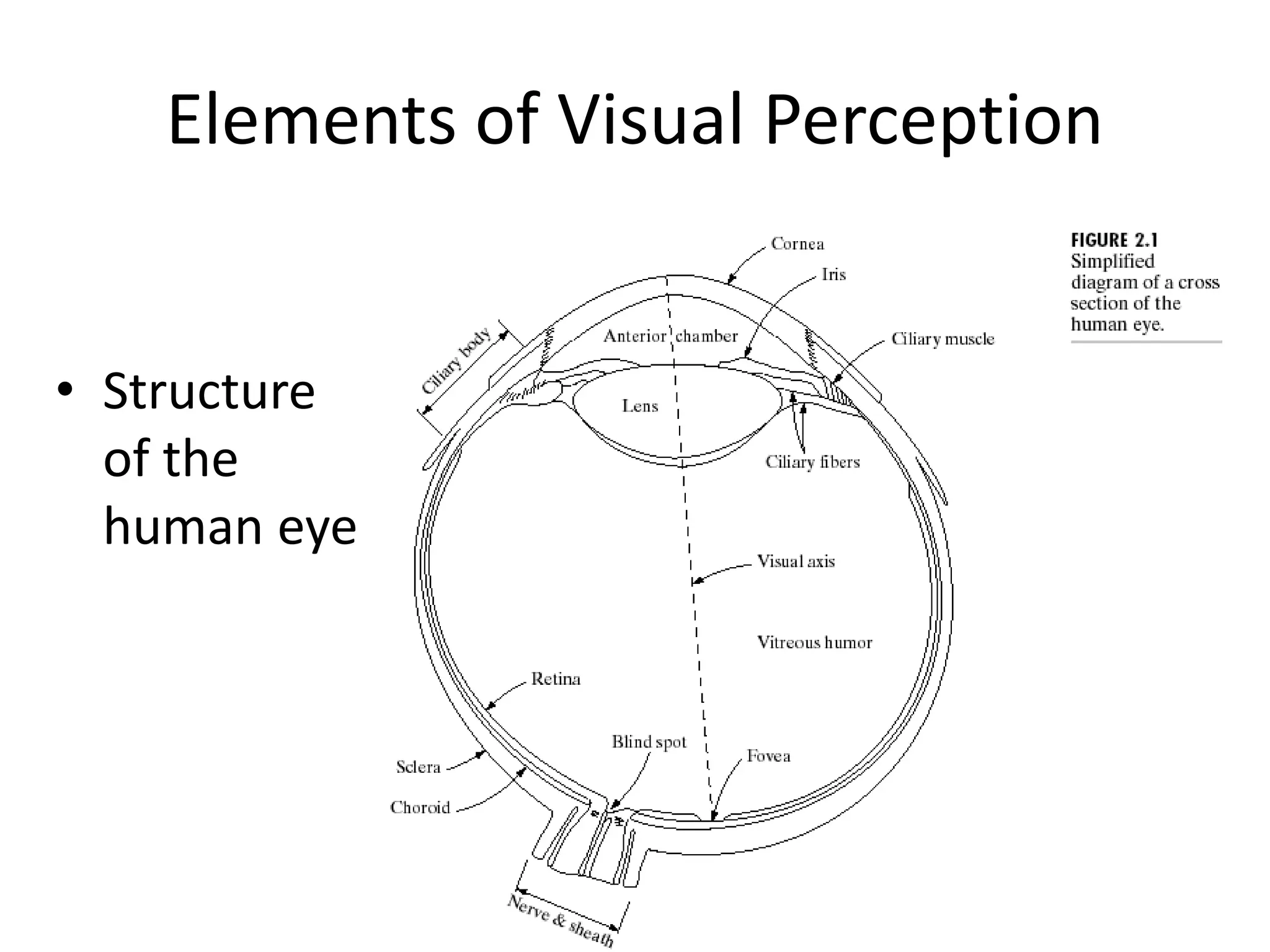
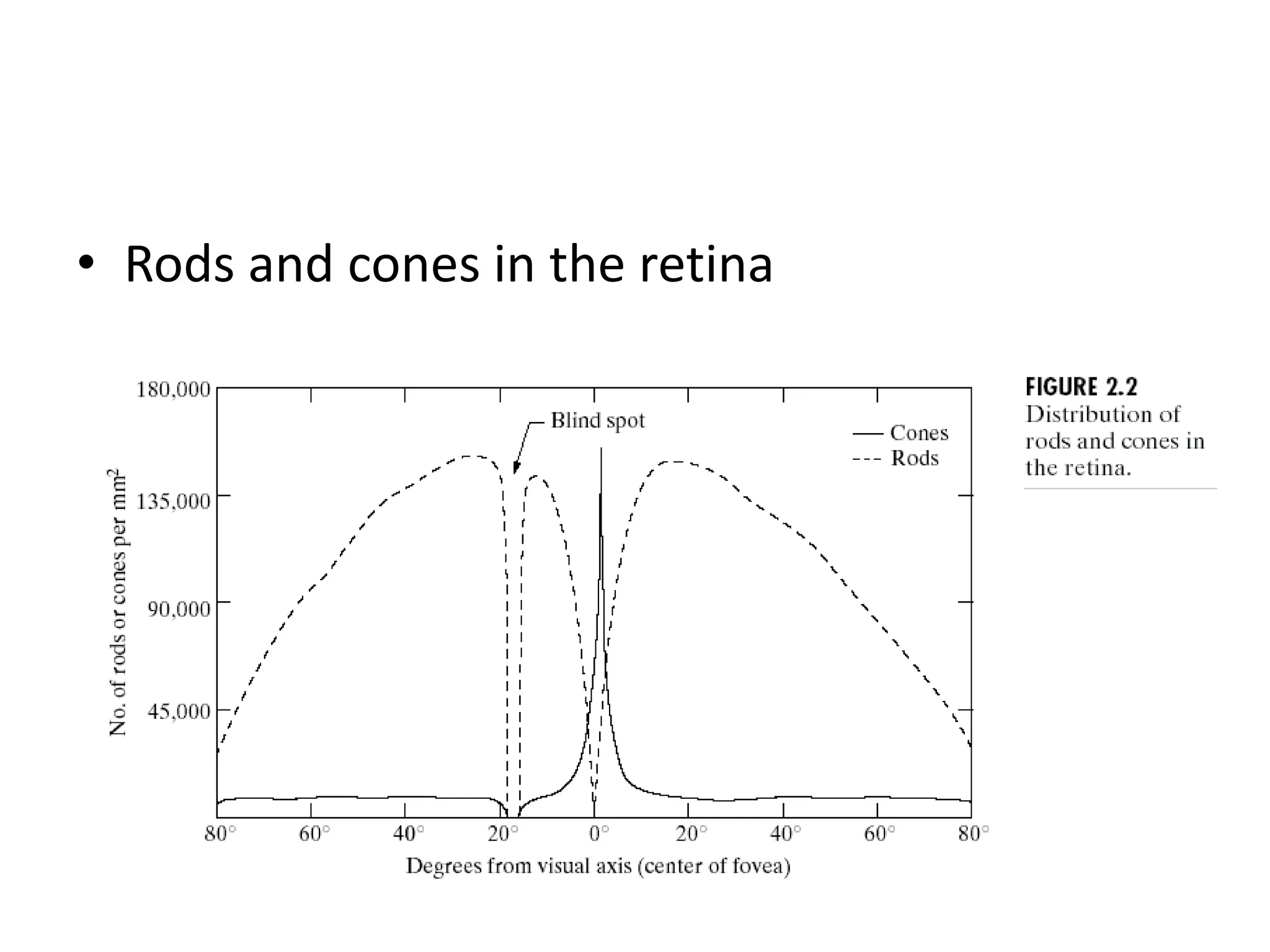
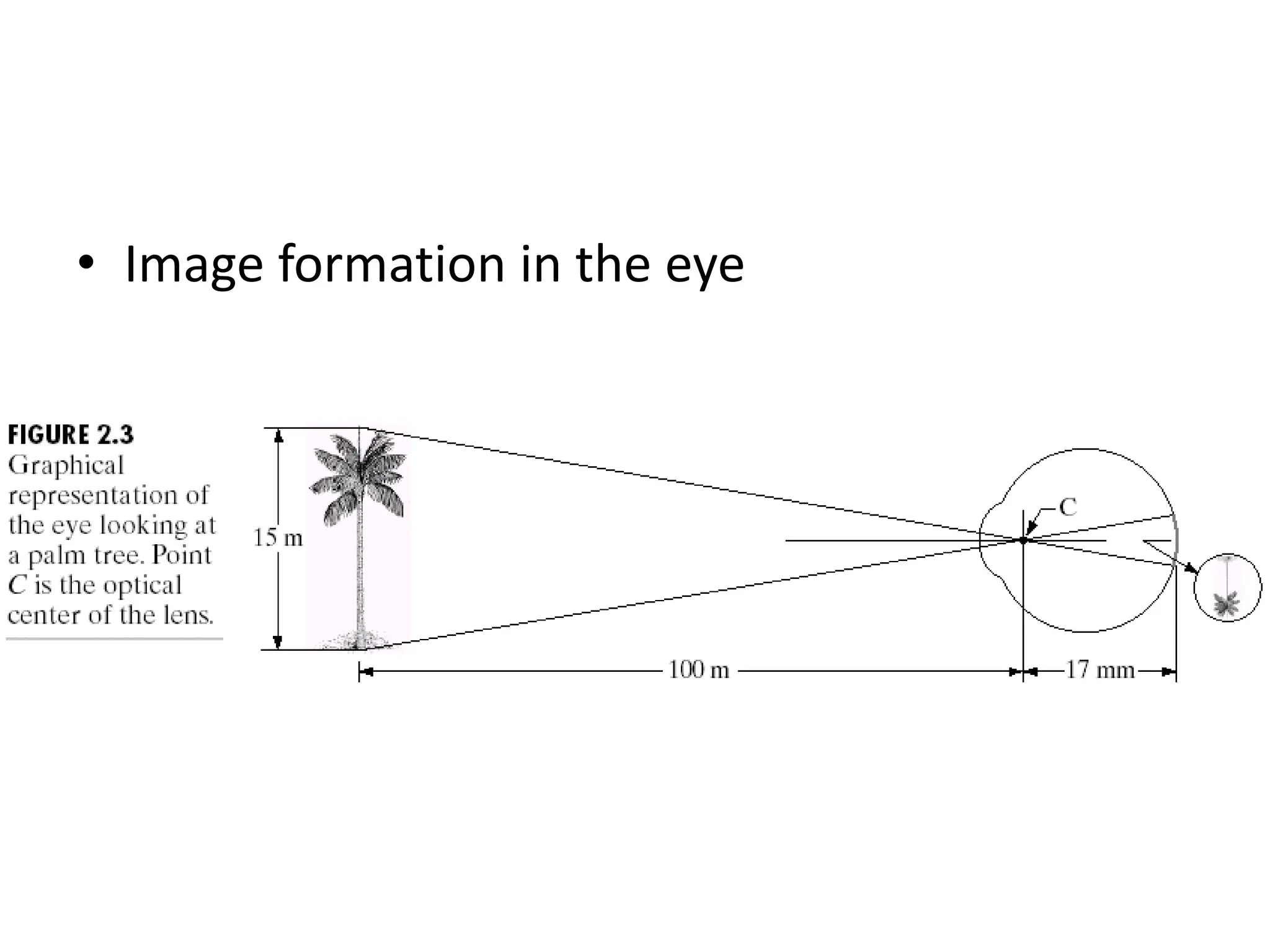
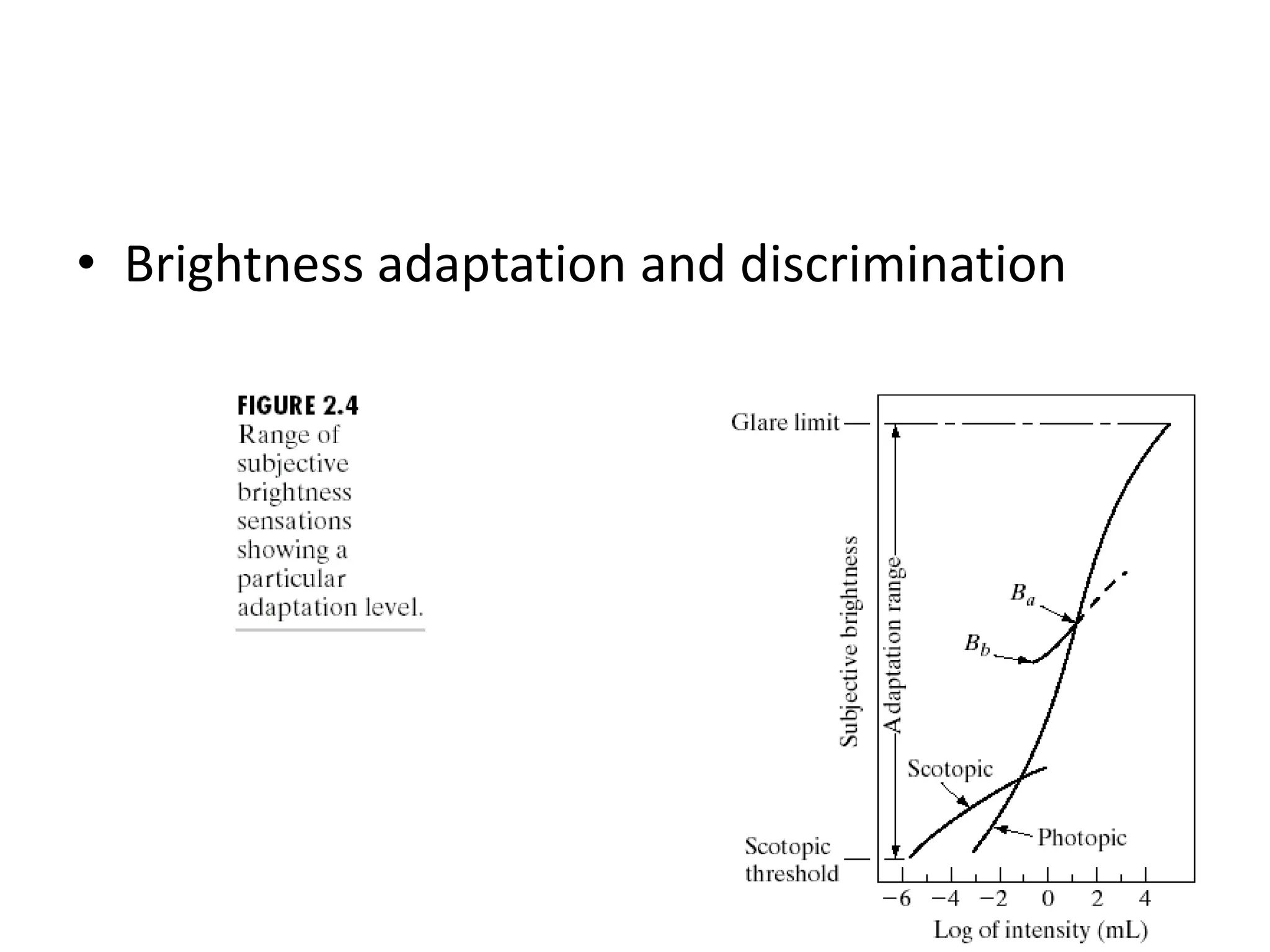
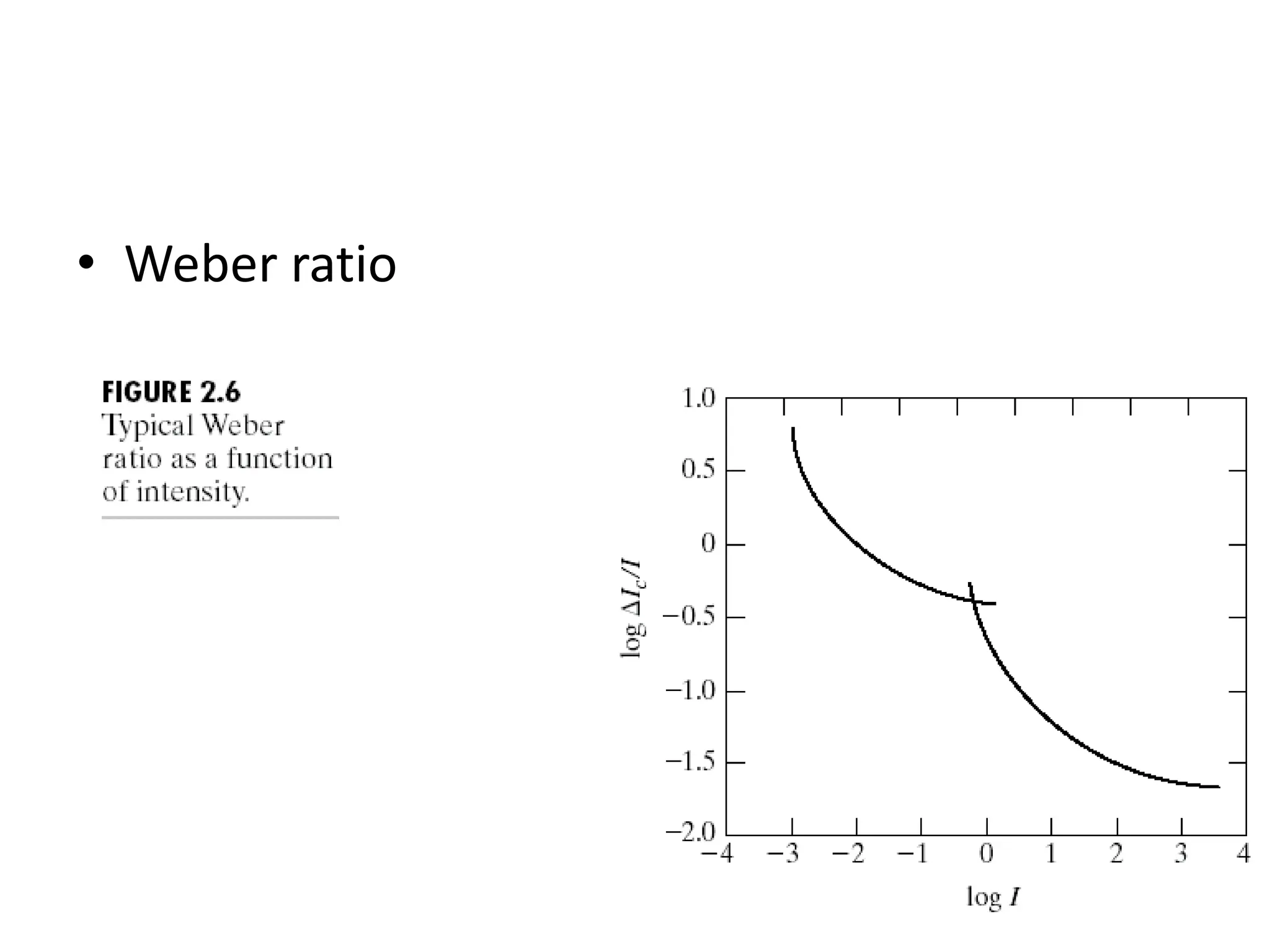
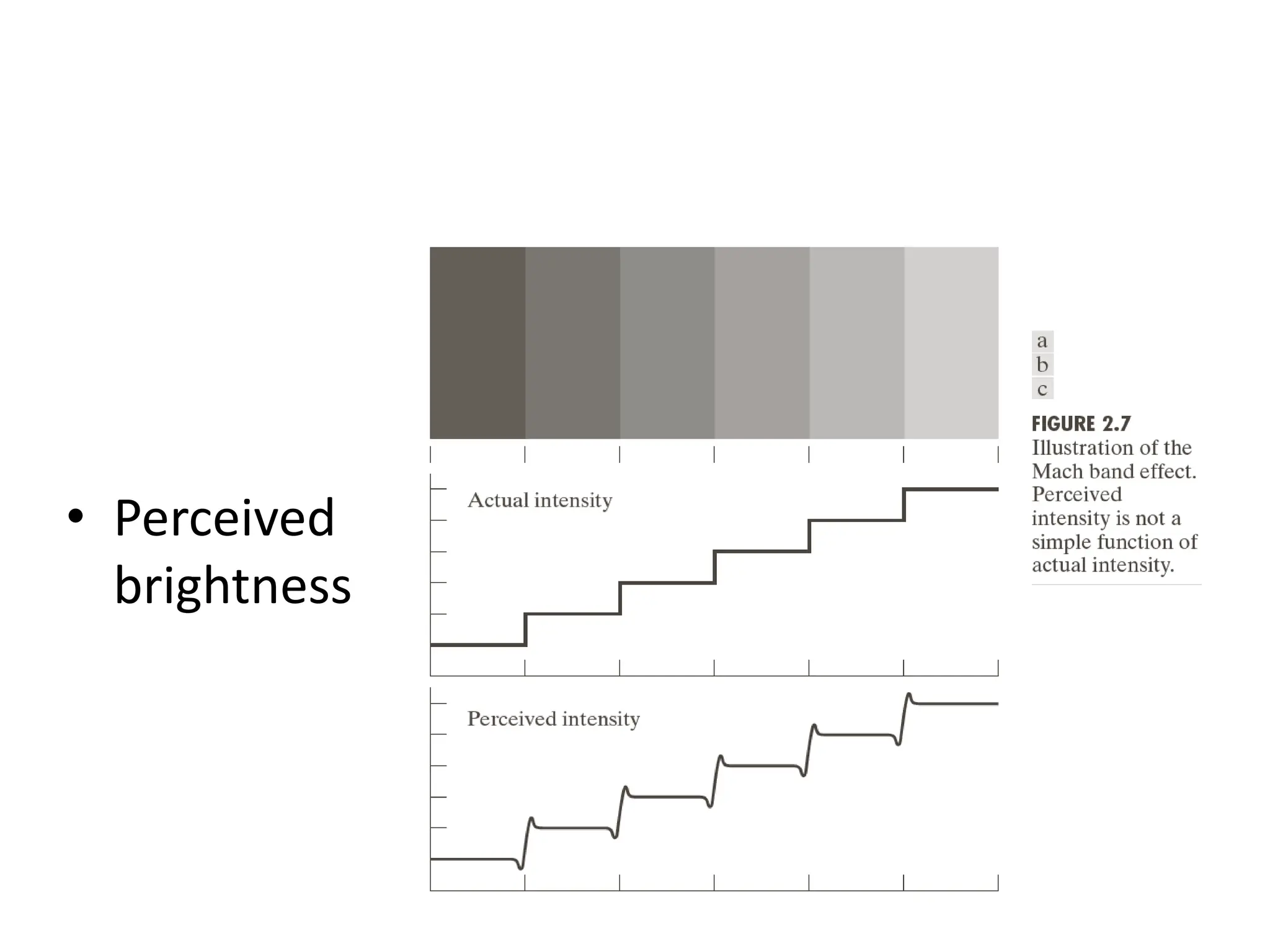
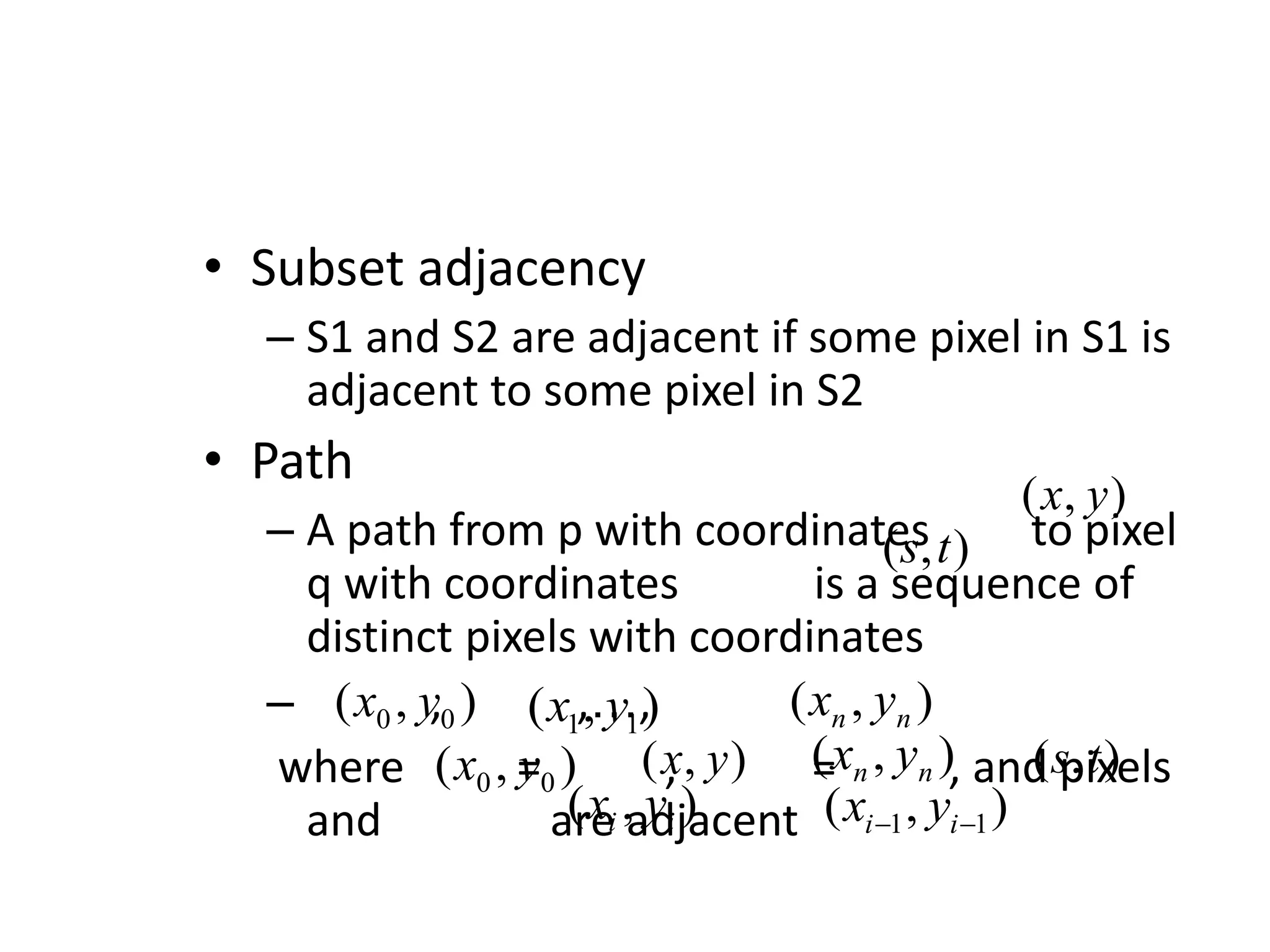
The document discusses key concepts in digital image processing including: 1) Elements of visual perception such as the structure of the eye, rods and cones, and brightness discrimination. 2) How digital images are formed including image sensing, sampling, quantization, and the relationship between pixels in an image such as neighborhoods and adjacency. 3) Common operations and transformations that can be performed on digital images including arithmetic, set, logical, and affine transformations as well as image transforms like the Fourier transform.











![• Distance measures – Euclidean distance – City-block distance – Chessboard distance 2 1 2 2 ] ) ( ) [( ) , ( t y s x q p De | ) ( | | ) ( | ) , ( 4 t y s x q p D |) ) ( | |, ) ( max(| ) , ( 8 t y s x q p D ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap2-240311152425-76b07b67/75/digital-image-processing-chapter-two-fundamentals-39-2048.jpg)