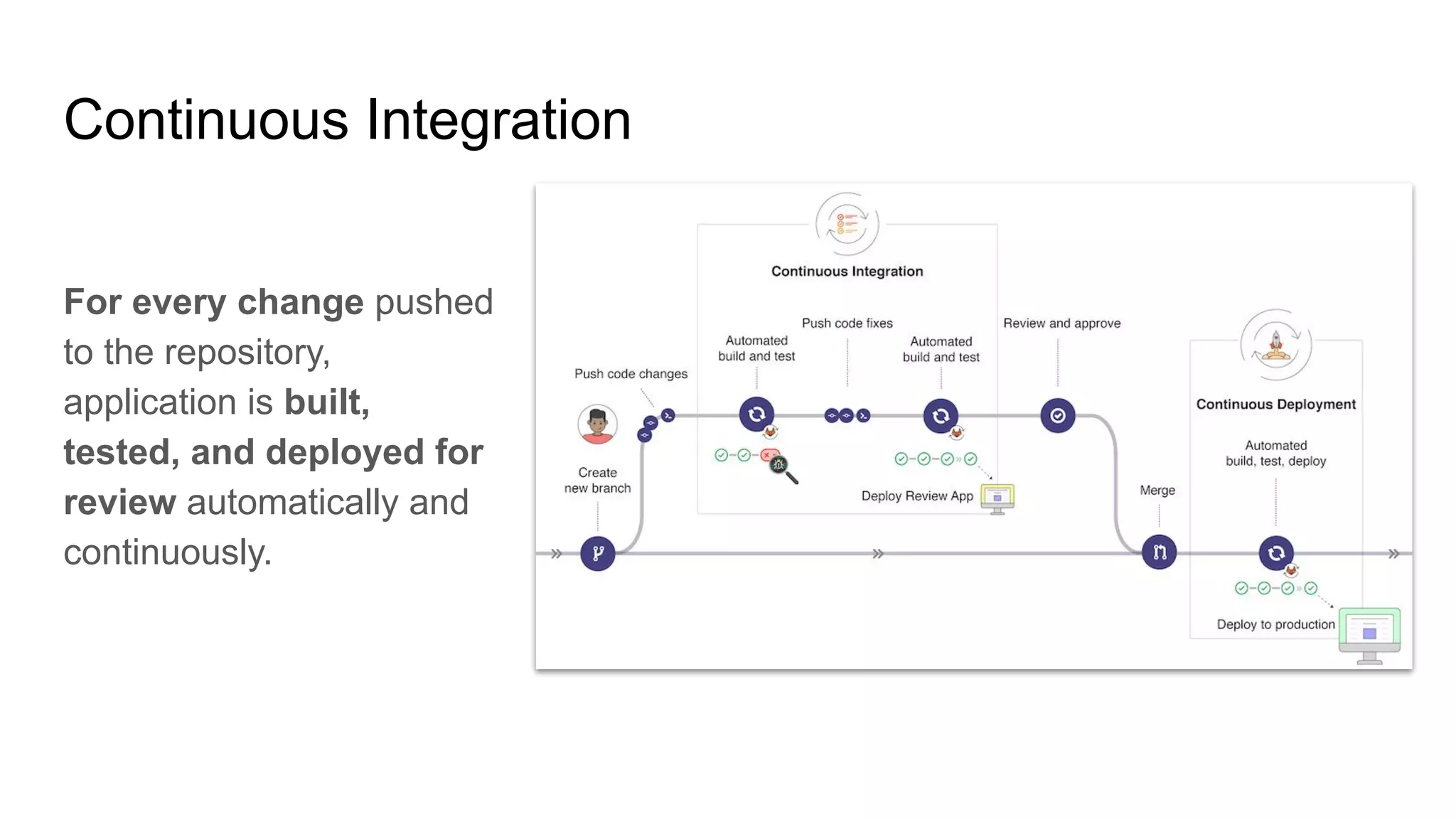
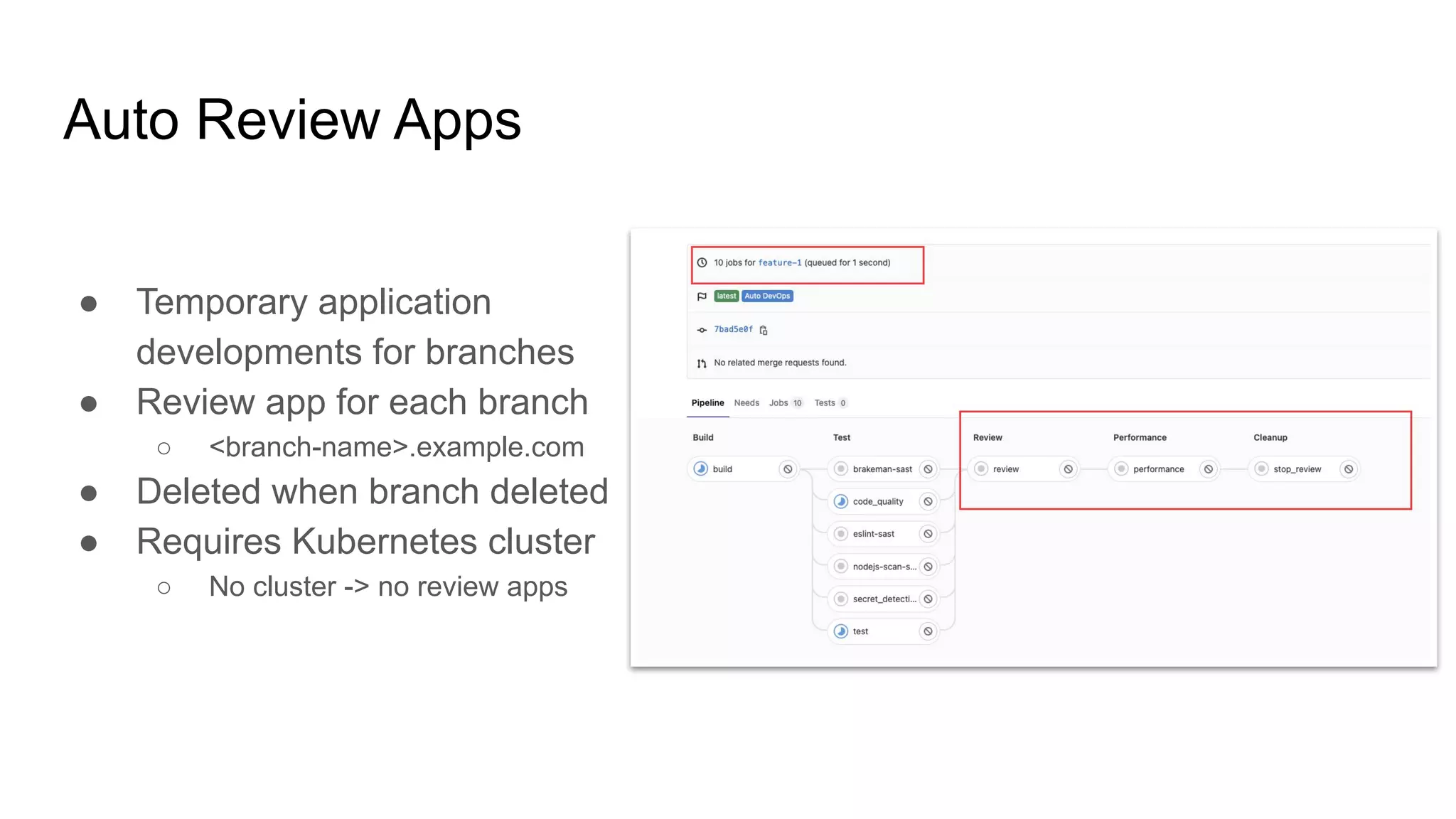
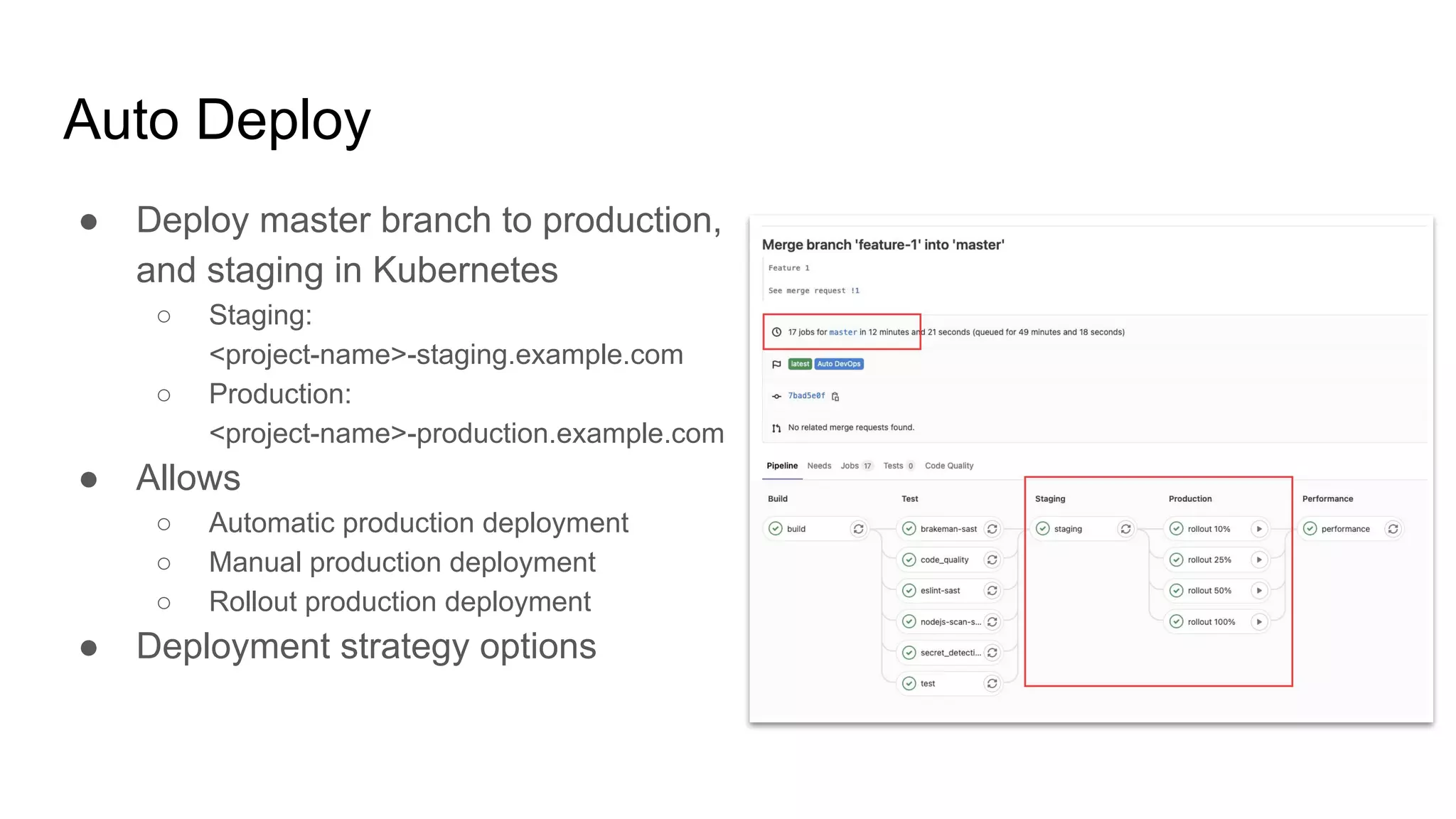
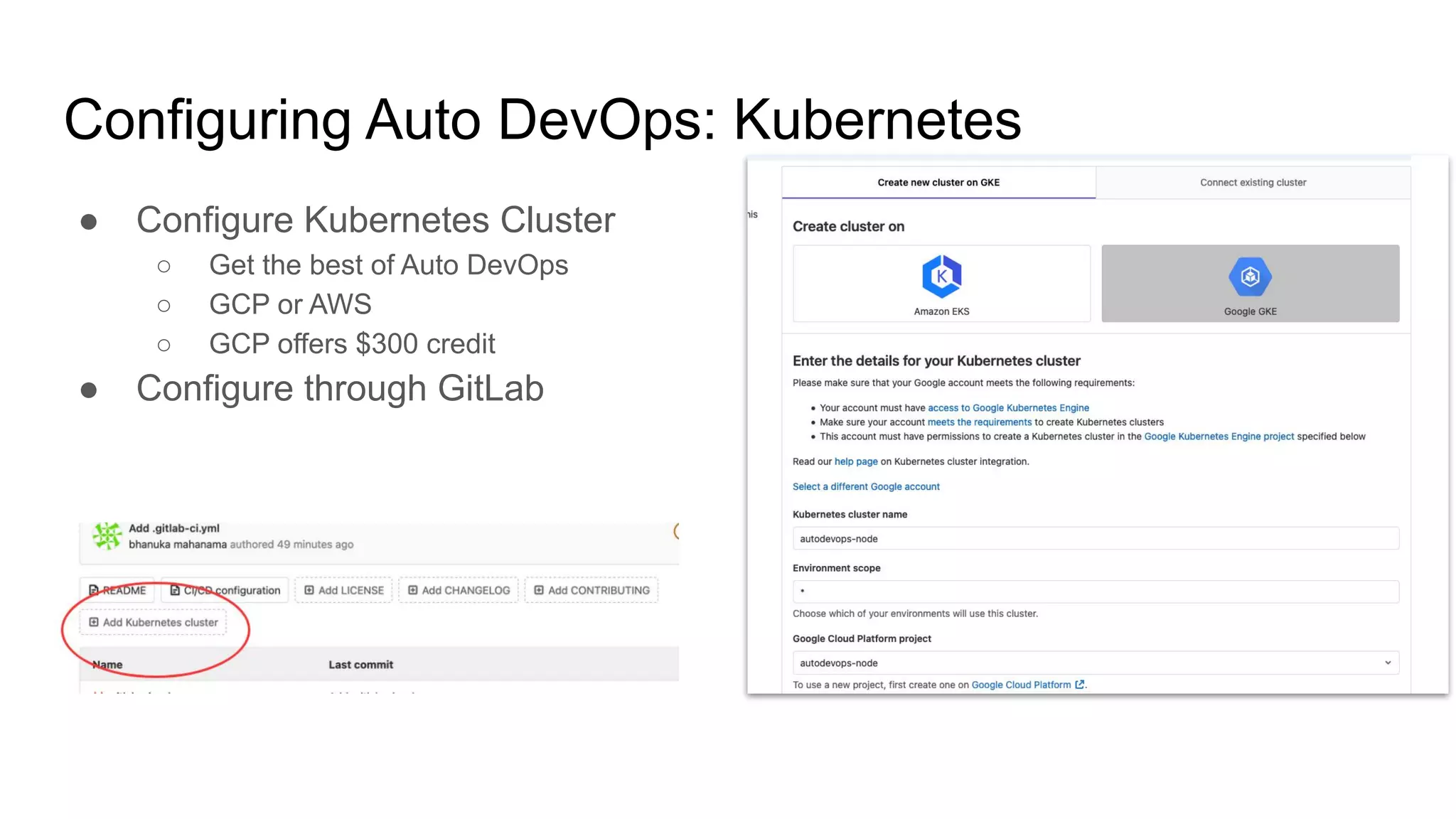
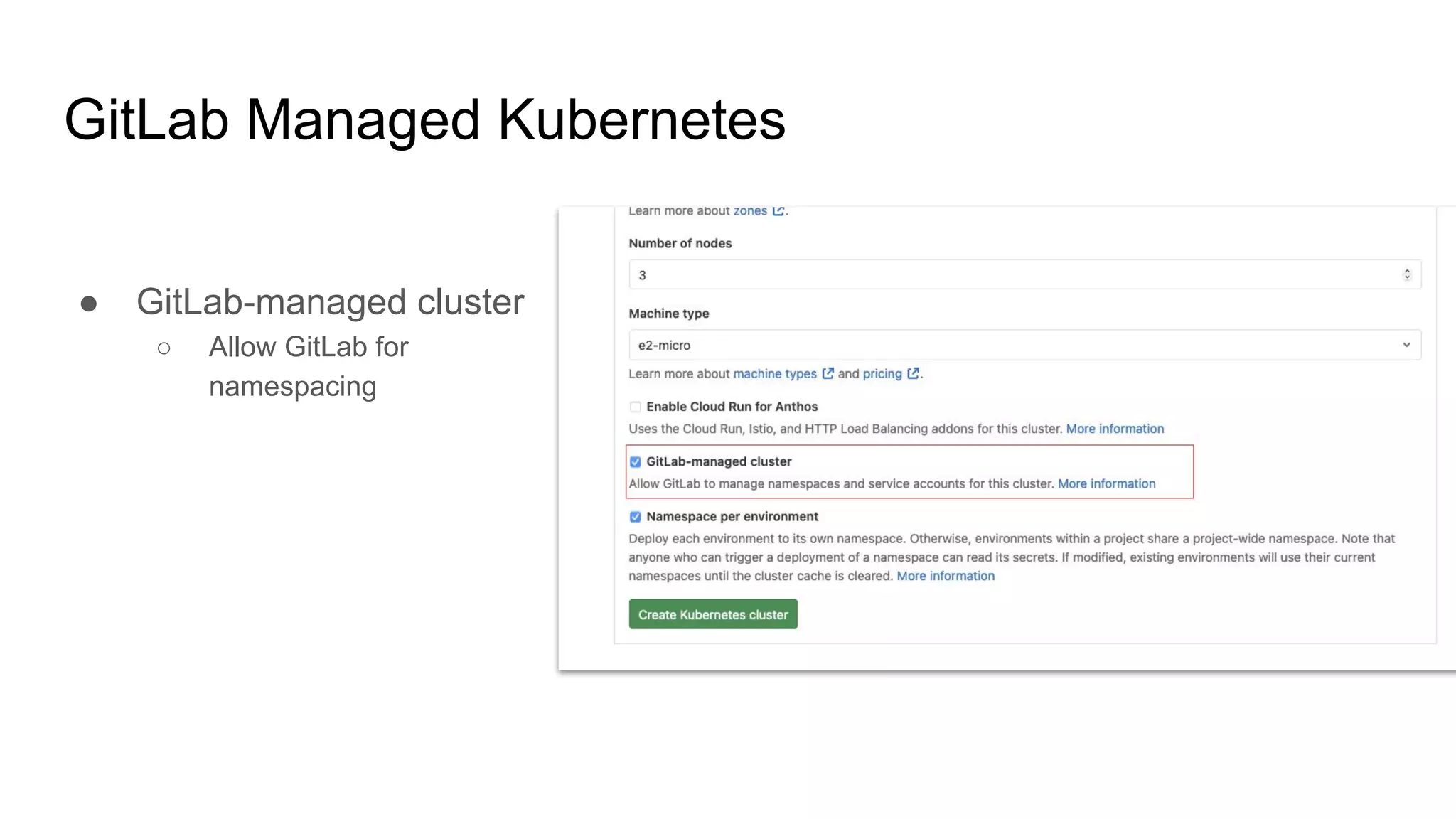
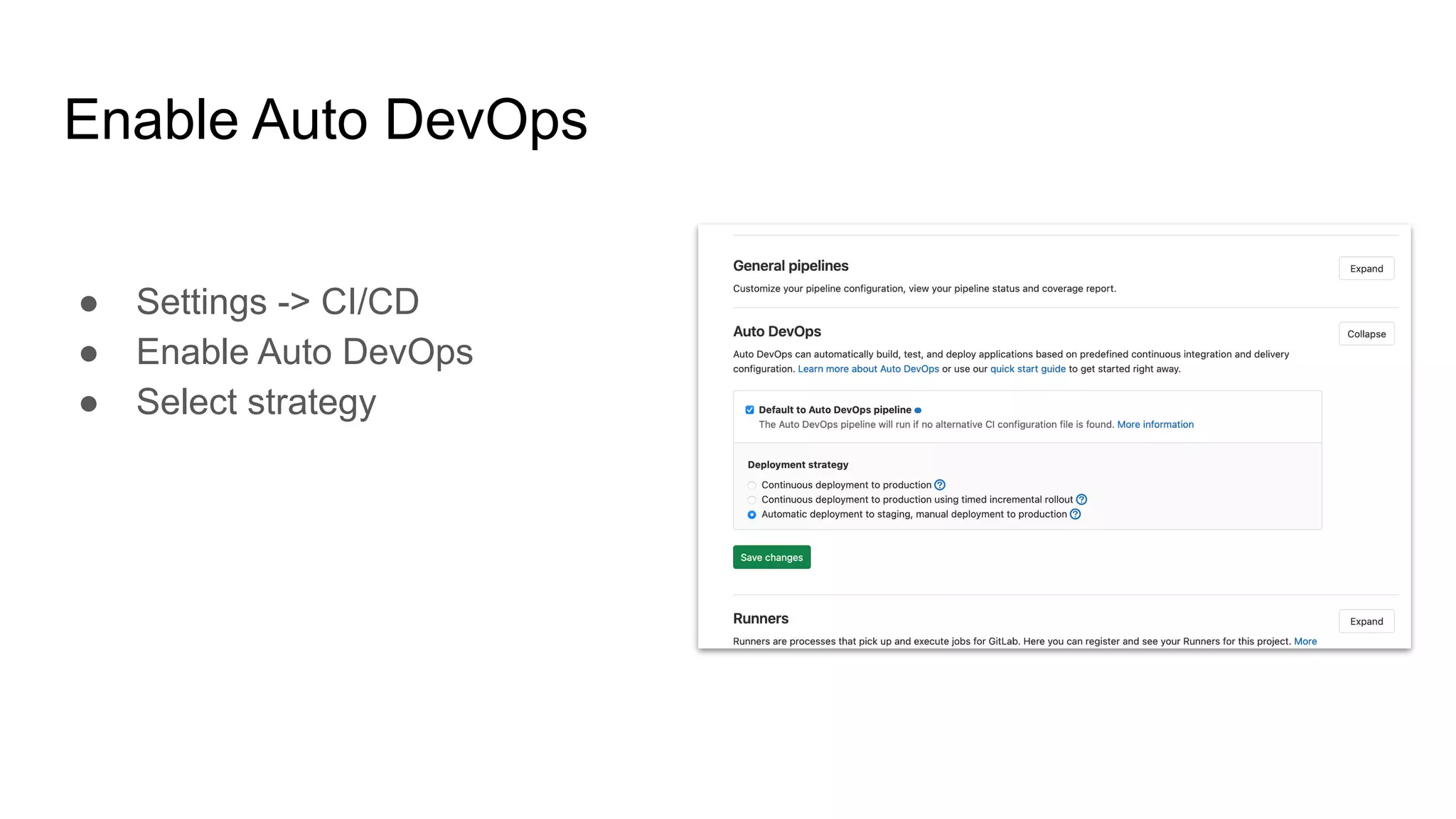
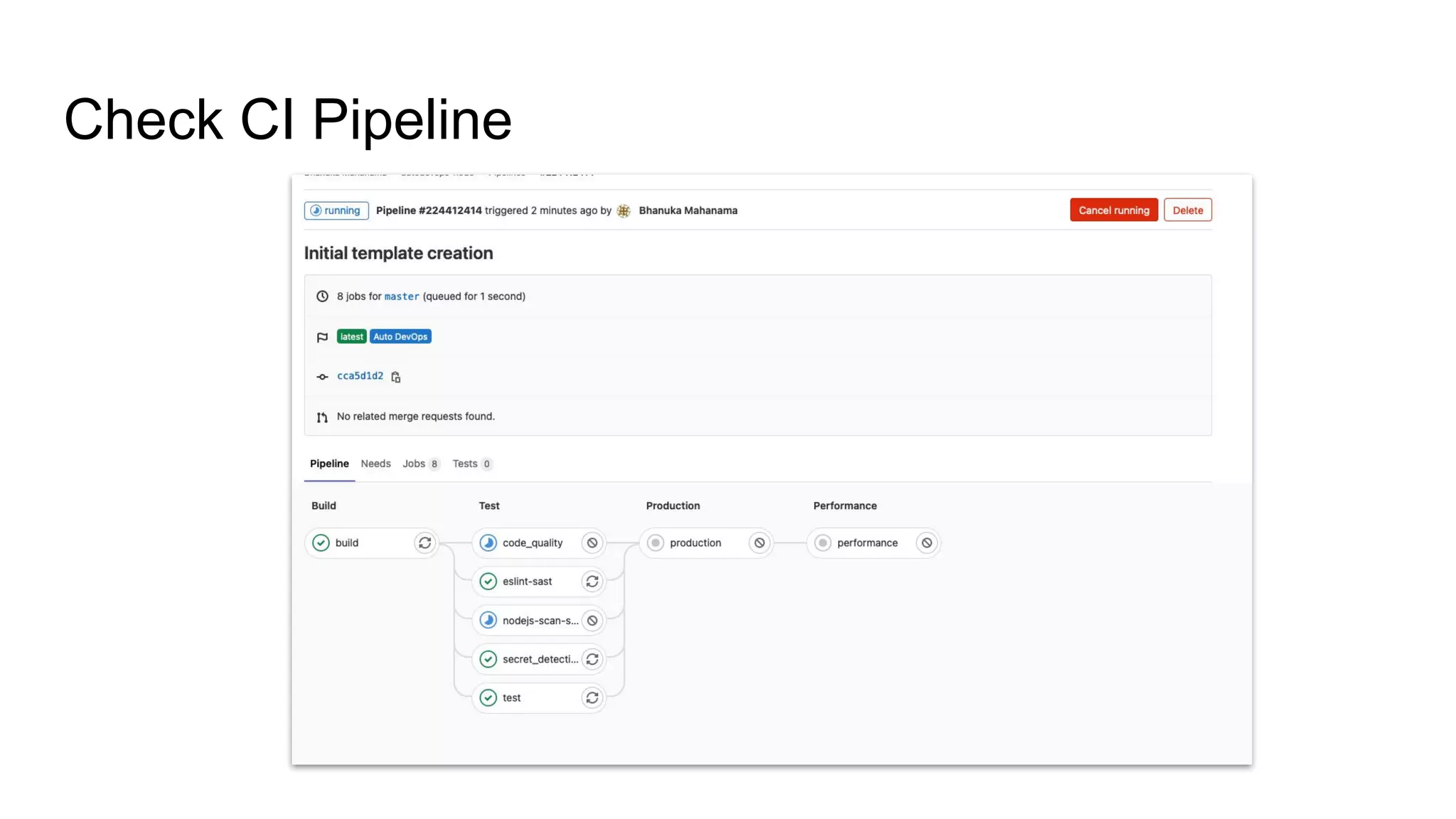
This document discusses continuous integration (CI) pipelines in GitLab, including standard GitLab CI and Auto DevOps. Standard GitLab CI requires configuring pipelines, jobs, clusters, and environments manually, while Auto DevOps automatically generates CI/CD pipelines based on a project's code and requires minimal configuration. Auto DevOps provides features like automatic building, testing, code quality checks, security testing, and deployment. It utilizes Docker, Kubernetes, Helm, and GitLab runners to containerize applications and deploy them. The document demonstrates how to enable and configure Auto DevOps on GitLab, including setting up a Kubernetes cluster to deploy apps to production and staging environments.