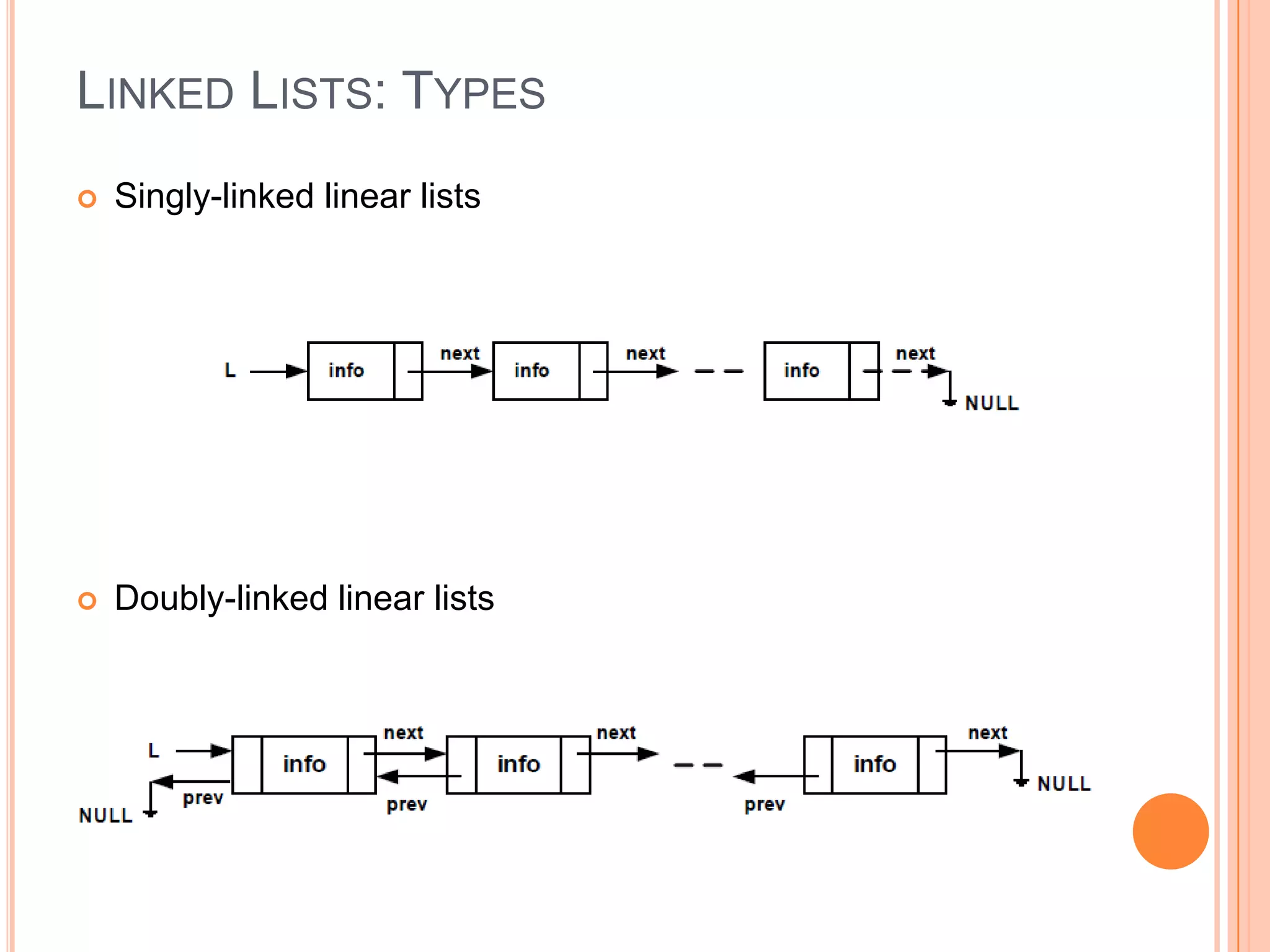
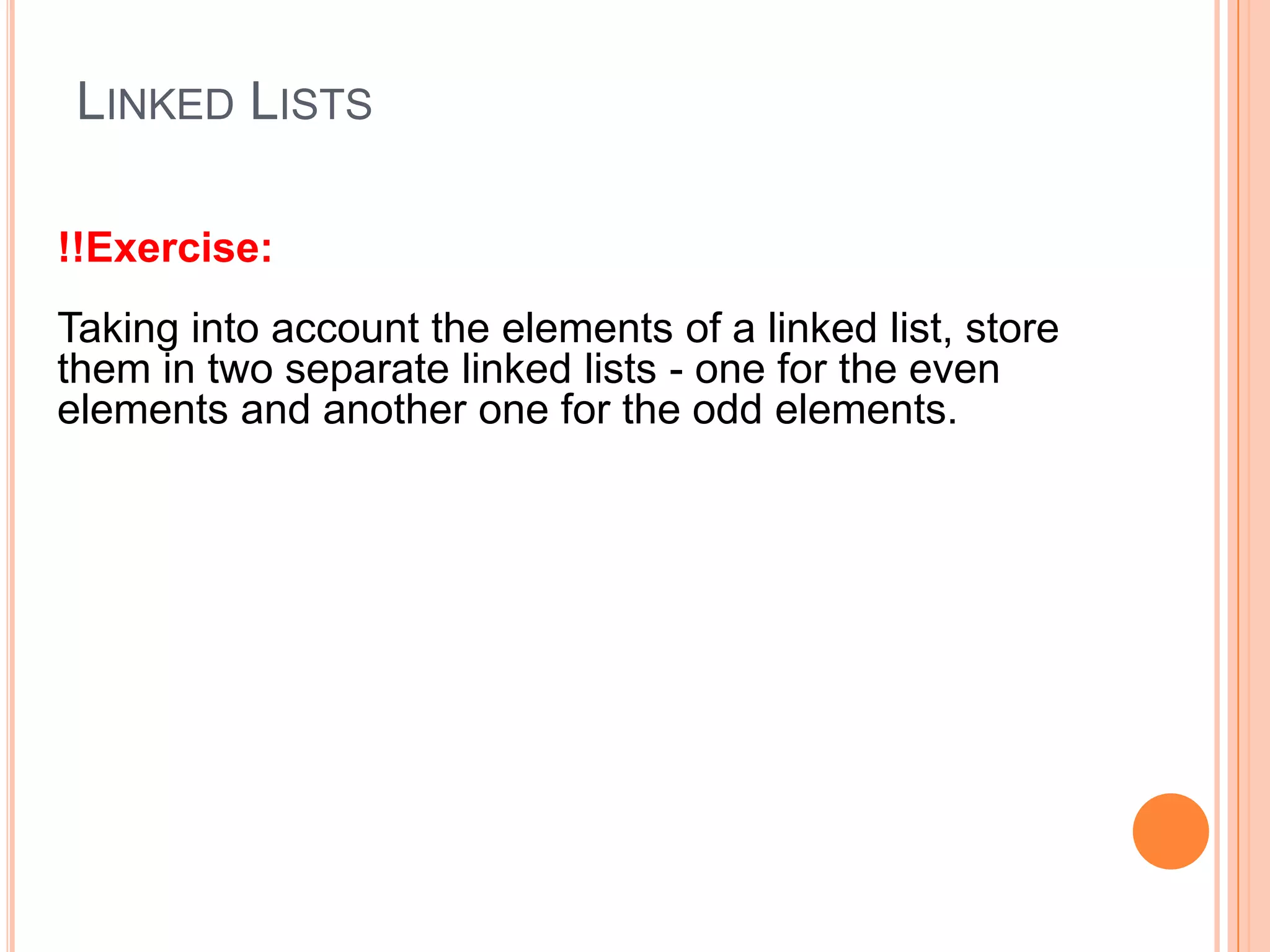
This document discusses linked lists and their implementation and operations. It covers: - The basics of linked lists and how they are implemented differently than dynamic arrays. Linked lists have nodes that point to the next element, while arrays reallocate size as needed. - Common linked list operations like add, remove, get, and update elements, which work differently based on implementation. - Types of linked lists including singly and doubly linked linear and circular lists. - An exercise to separate the elements of a linked list into two lists based on even and odd elements. - Homework to create a task list application using a linked list to store and remove tasks by priority.