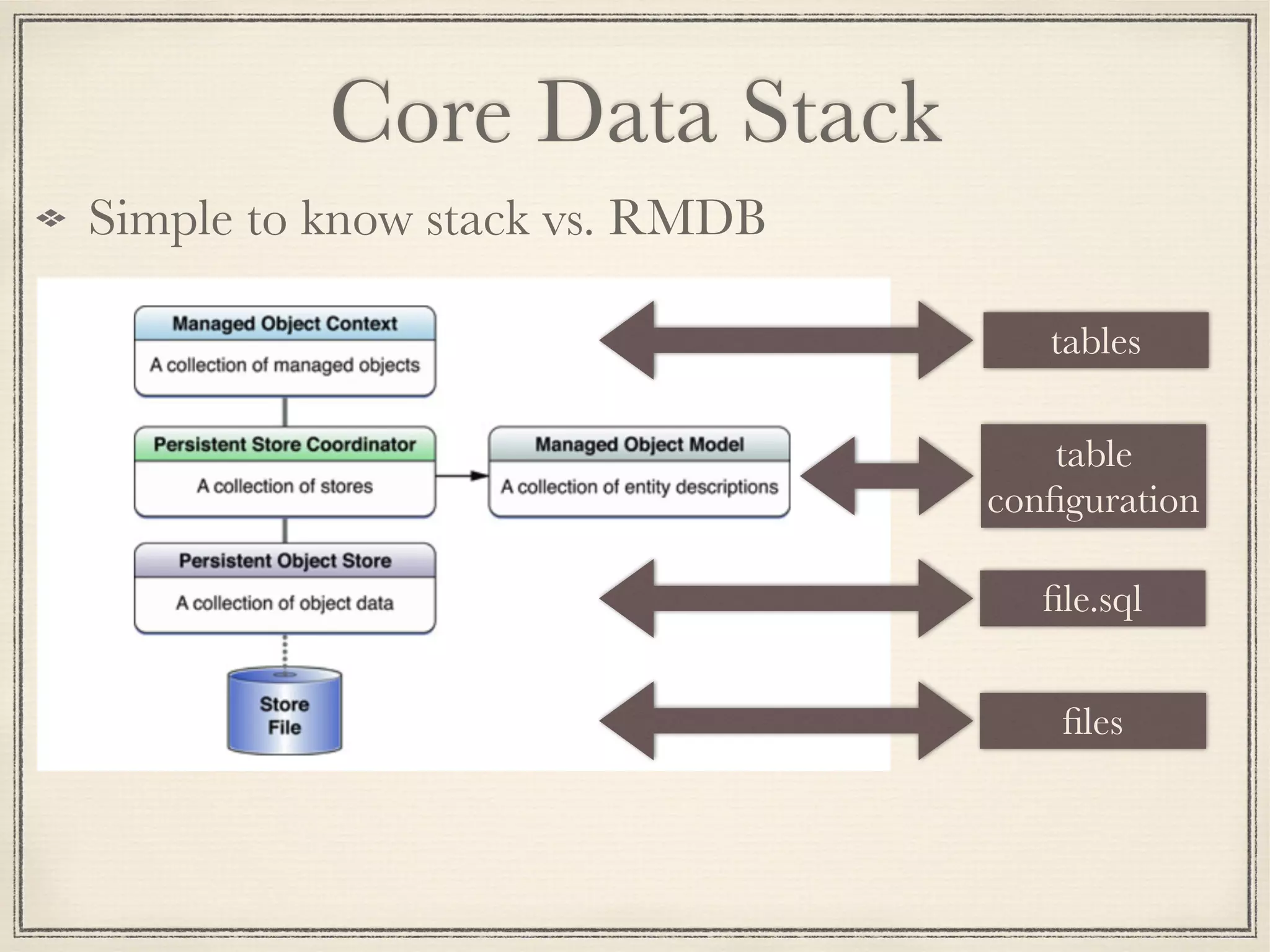
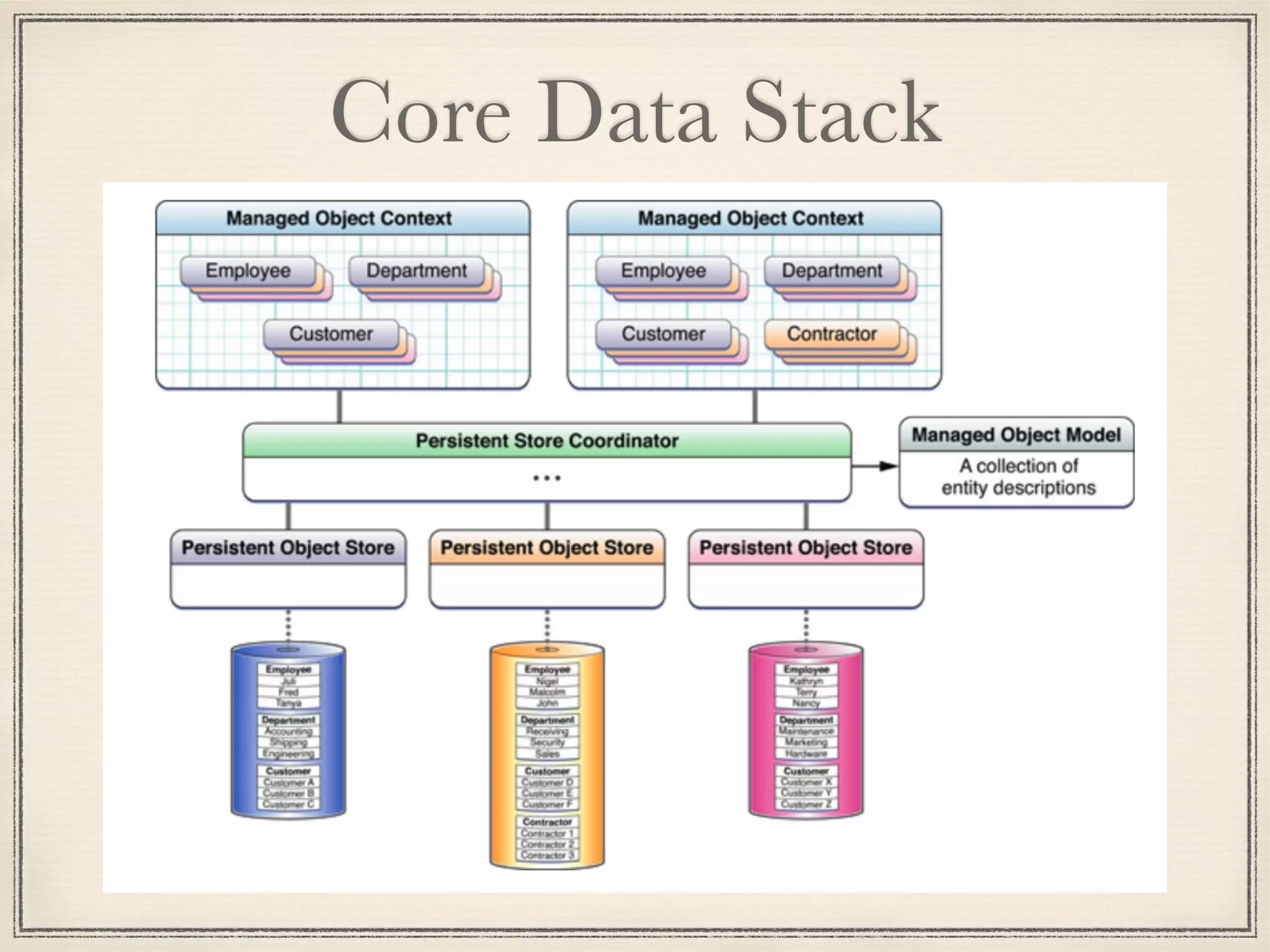
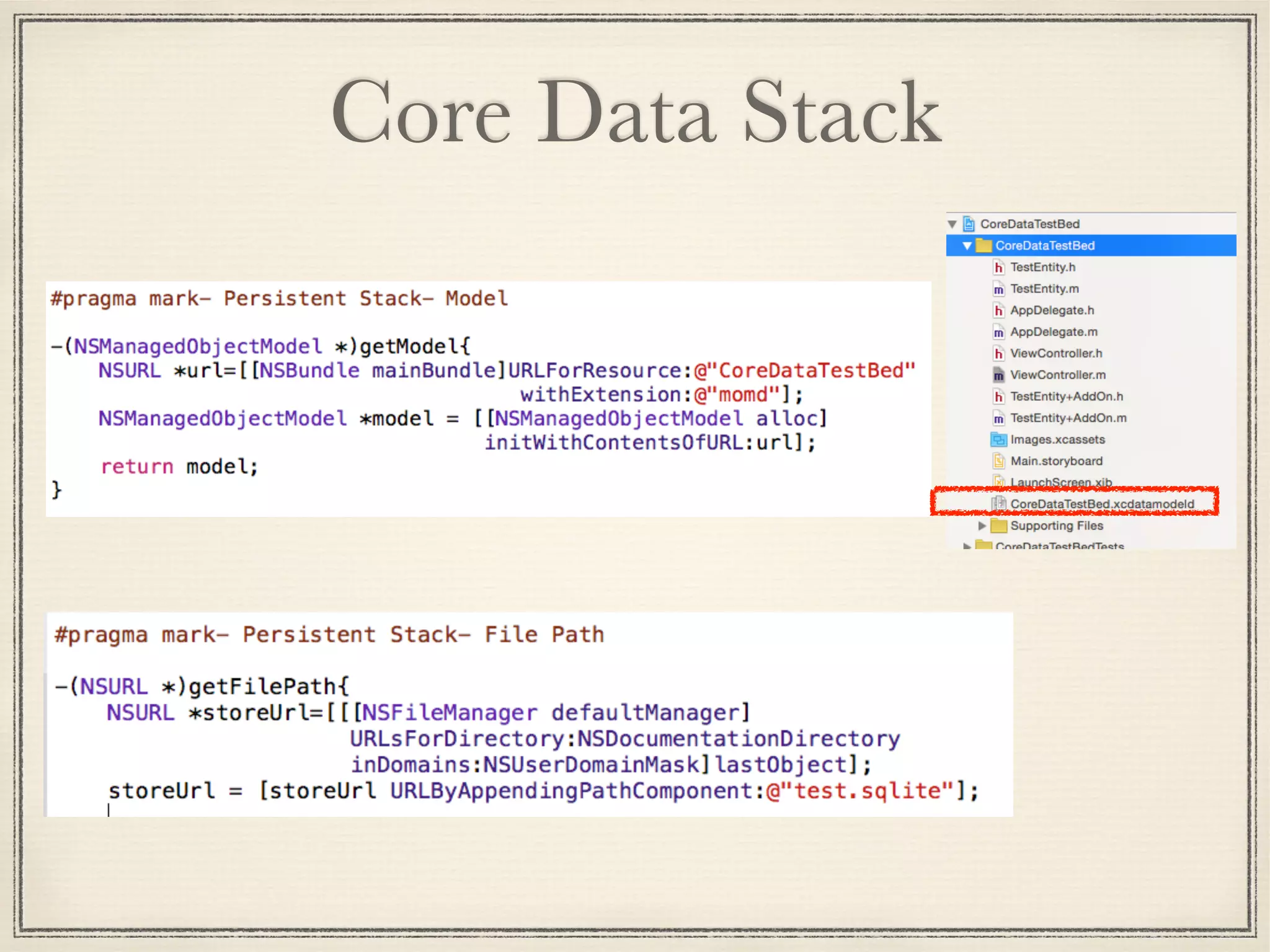
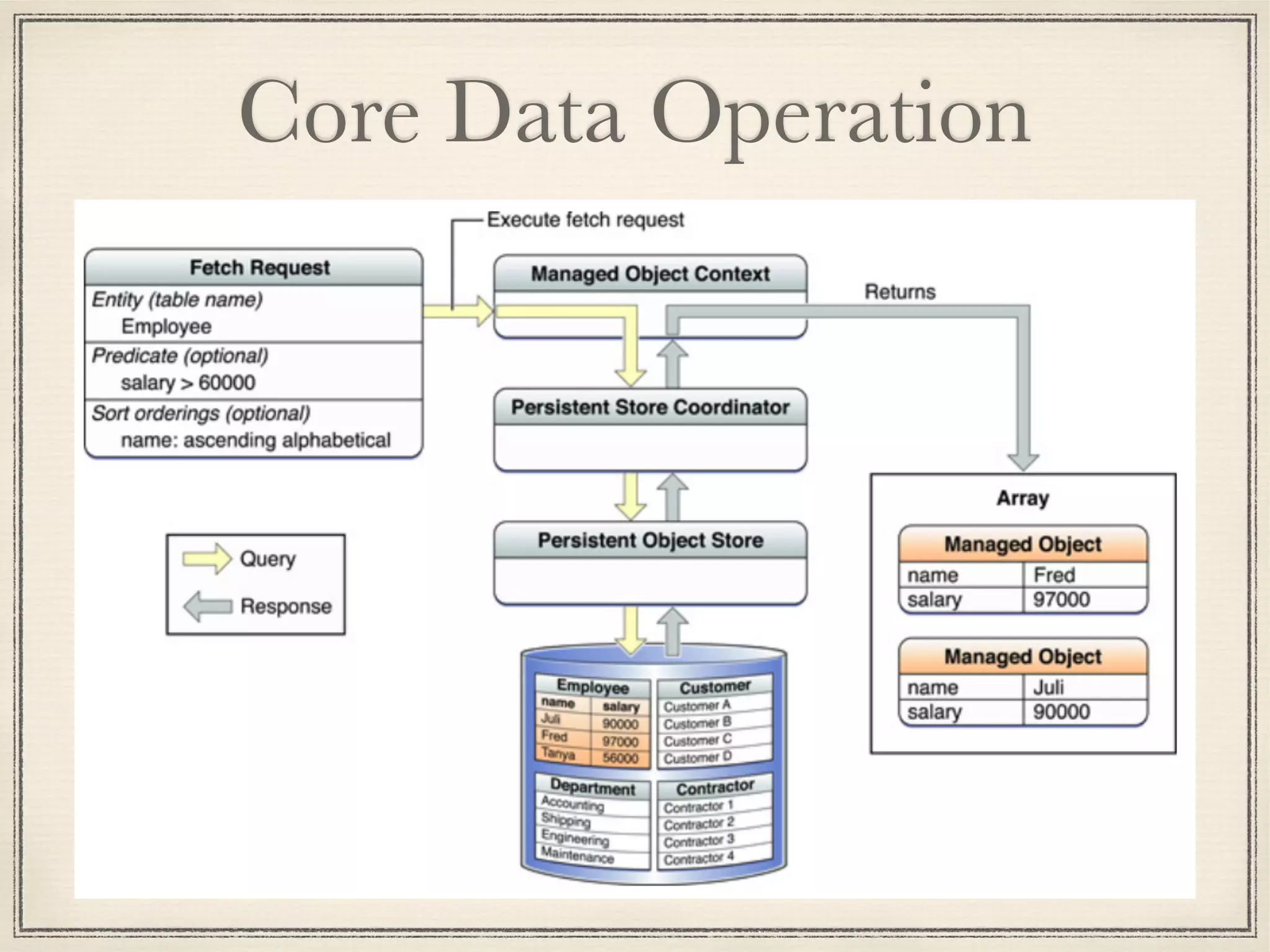
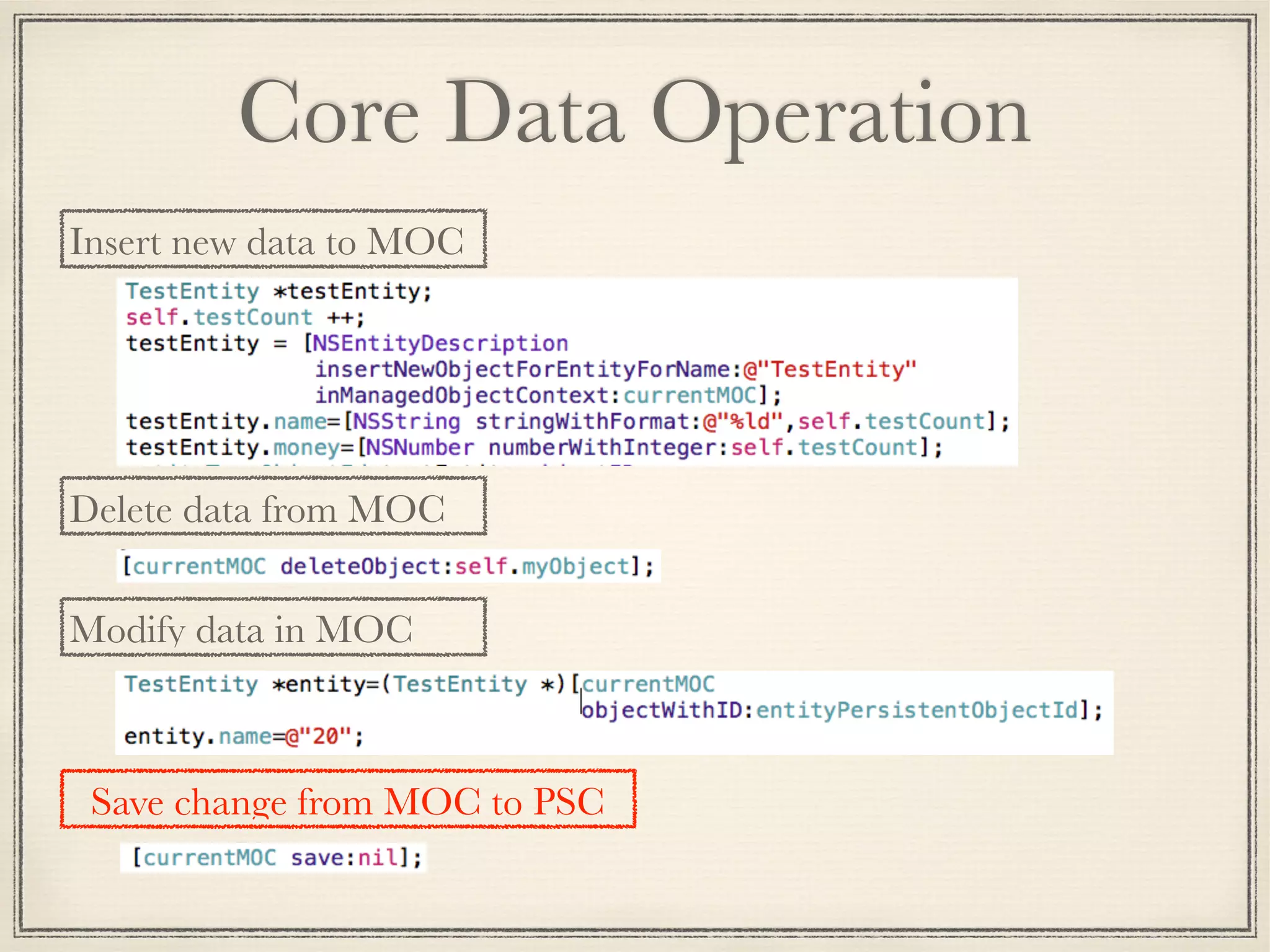
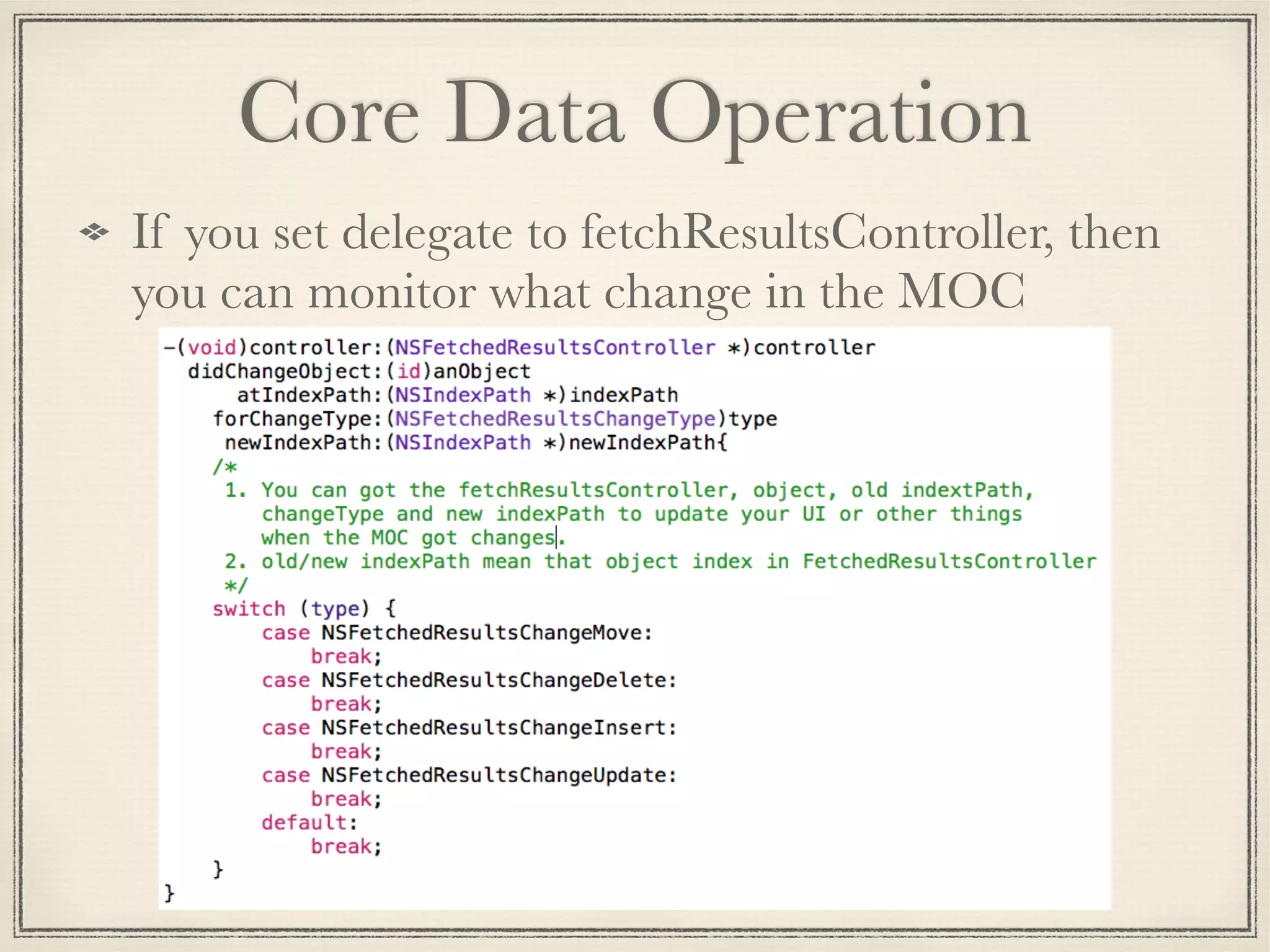
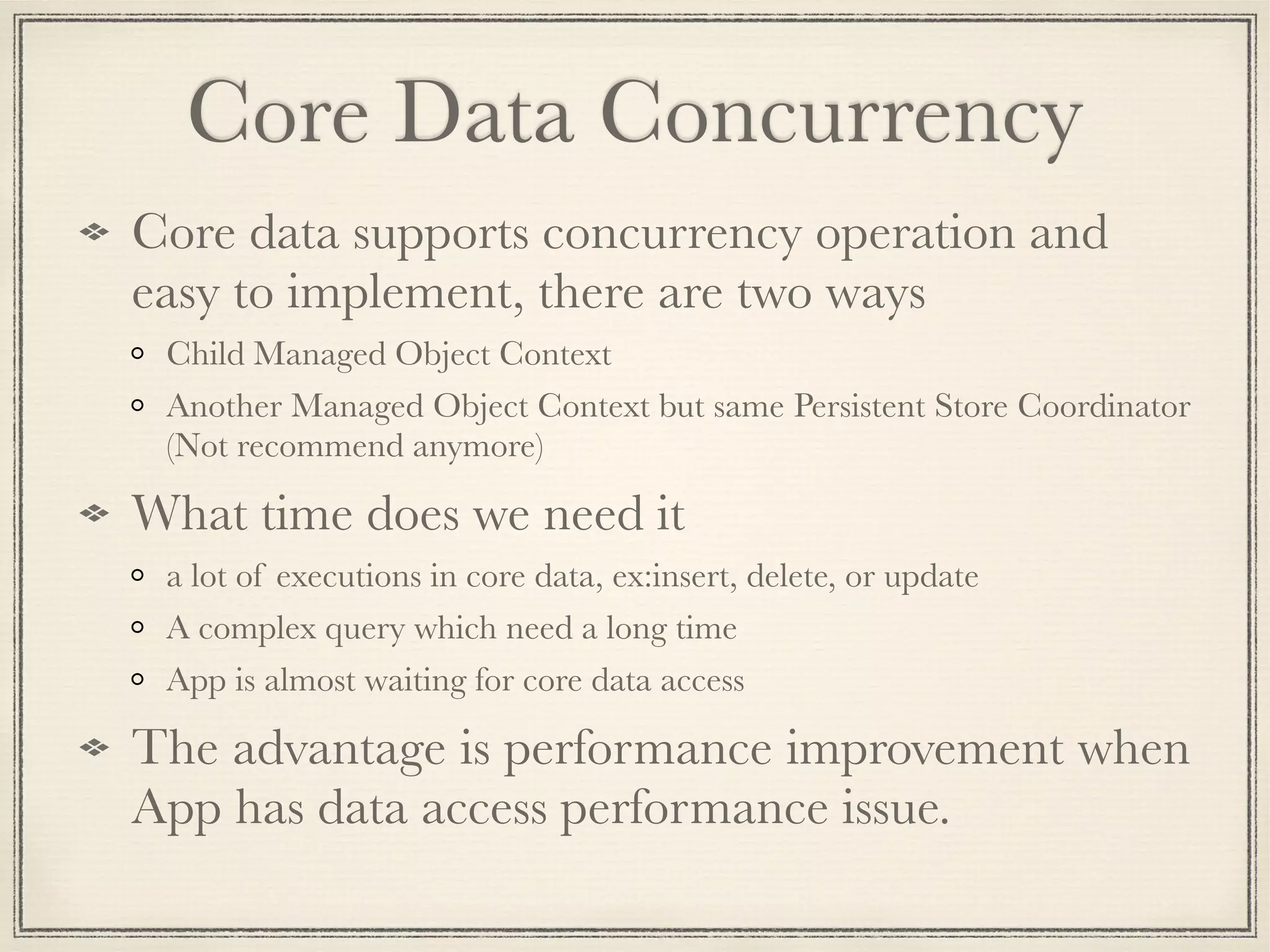
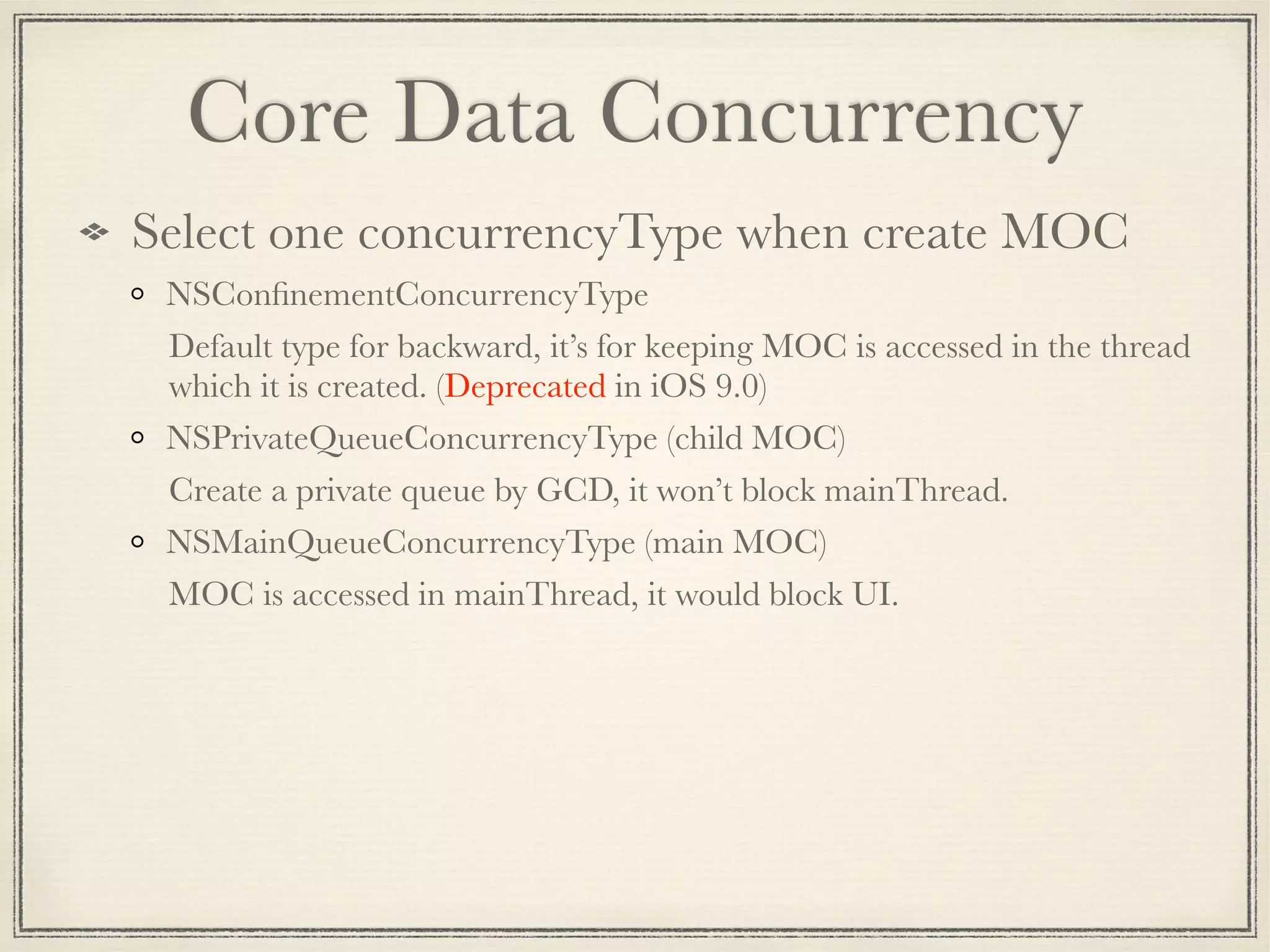
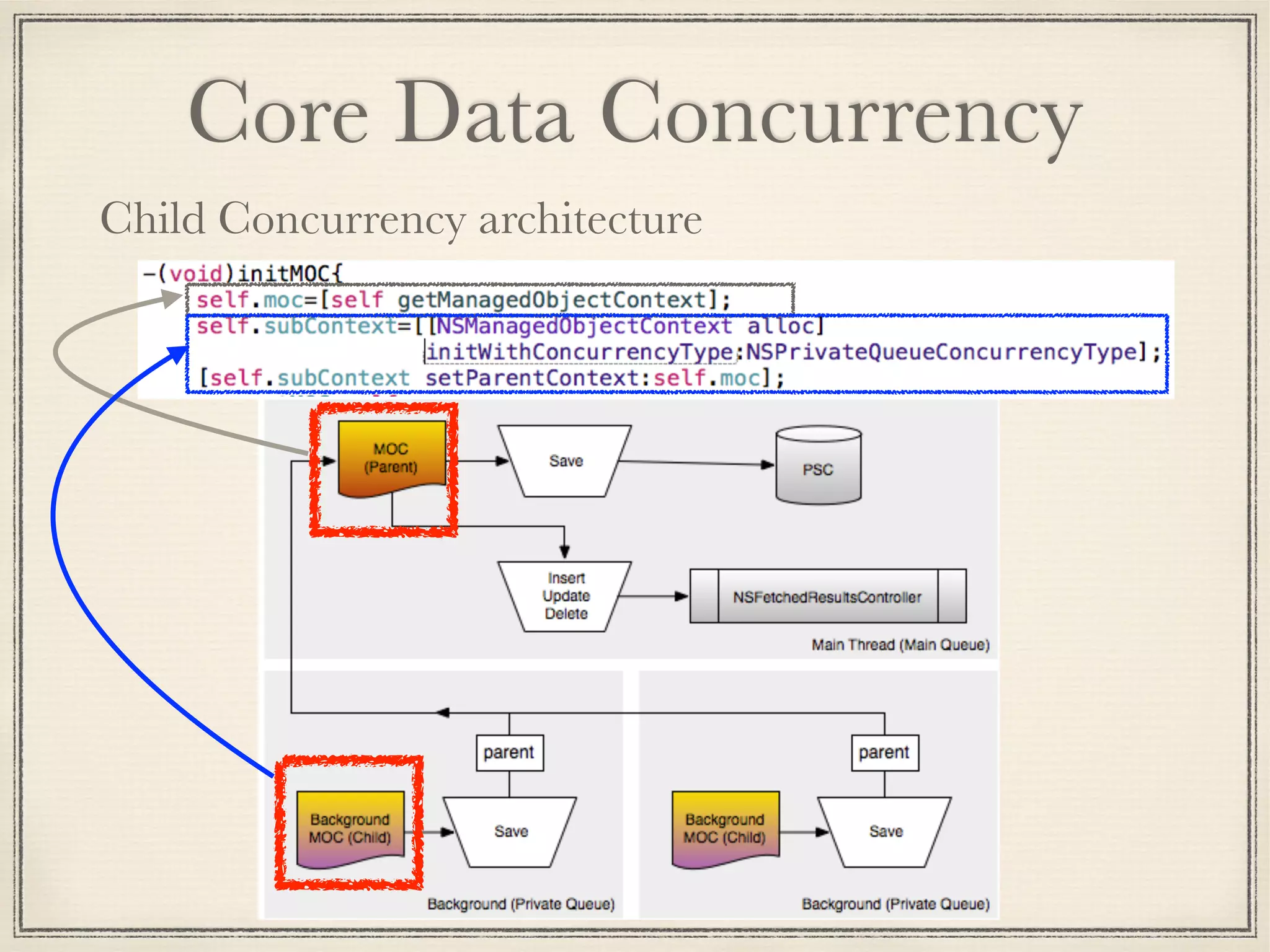
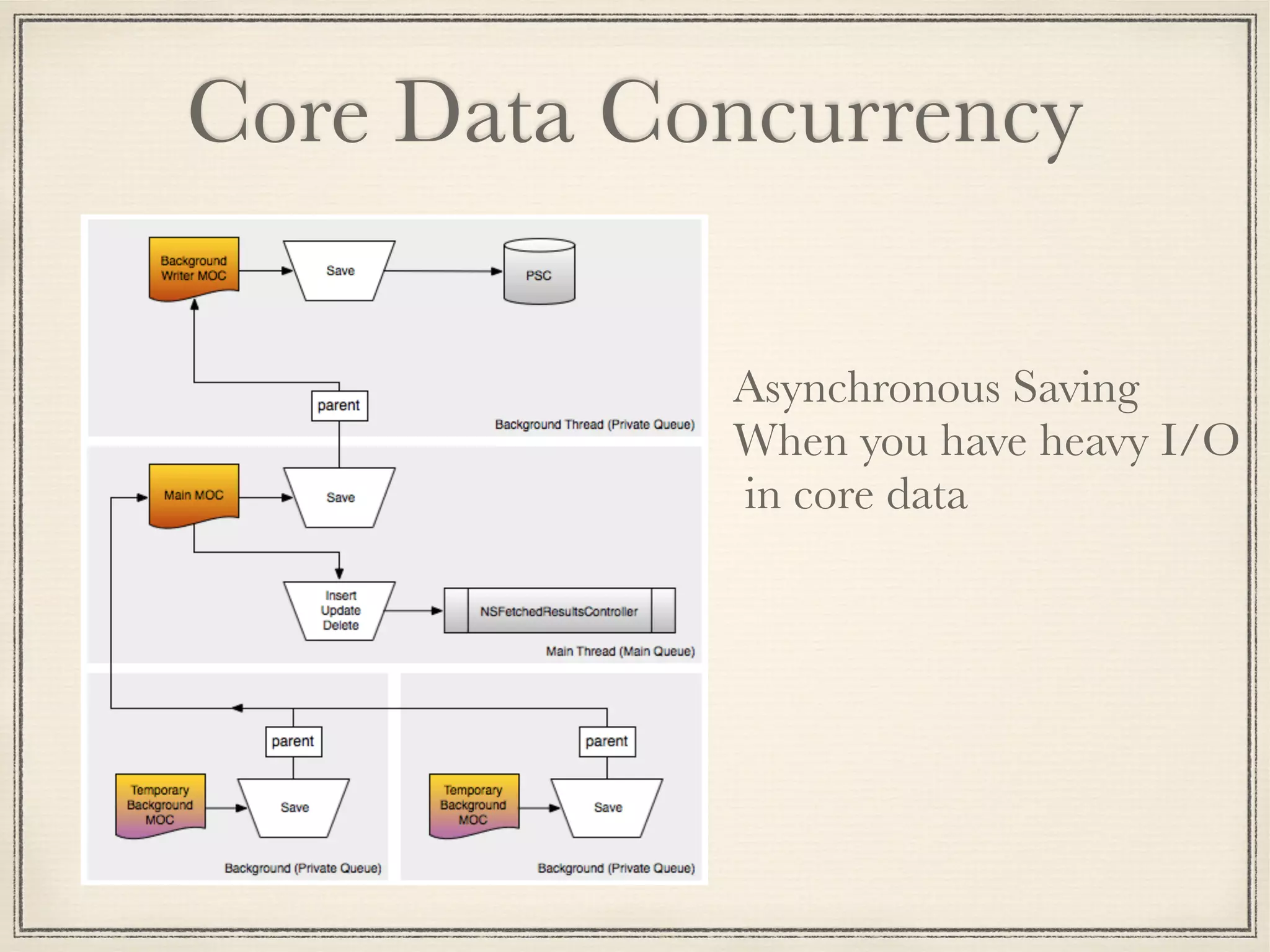
The document provides an overview of Core Data, outlining its role as an ORM framework for efficient data management and its advantages including lazy loading and schema migrations. It discusses the Core Data stack, operations for fetching, inserting, deleting, and modifying data, and highlights concurrency management with various concurrency types and their implications. The text also shares personal experiences related to data consistency, object states, and methods for accessing managed objects across contexts.










![Experience MO has some status properties isFault, isDeleted, faultingState, isInserted, isUpdated, isTemporaryID, hasChanges These status can be checked what they do in context These status would be reset after saved isDeleted If delete MO and it’s no saved before, then the MO would be nil directly If delete MO and it’s saved before, then only isDelete property would be changed
After deleted MO, it always existed if it was saved before!! Check MO is deleted Sometimes isDeleted can’t really know MO is deleted or not Using existingObjectWithID and managedObjectContext
Check condition should be: (MO.isDelete || ![MOC exist..ID:MOID] || ! MO.managedObjectContext)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coredatafundamentalslideshare-160628083929/75/Core-Data-Introduction-21-2048.jpg)

