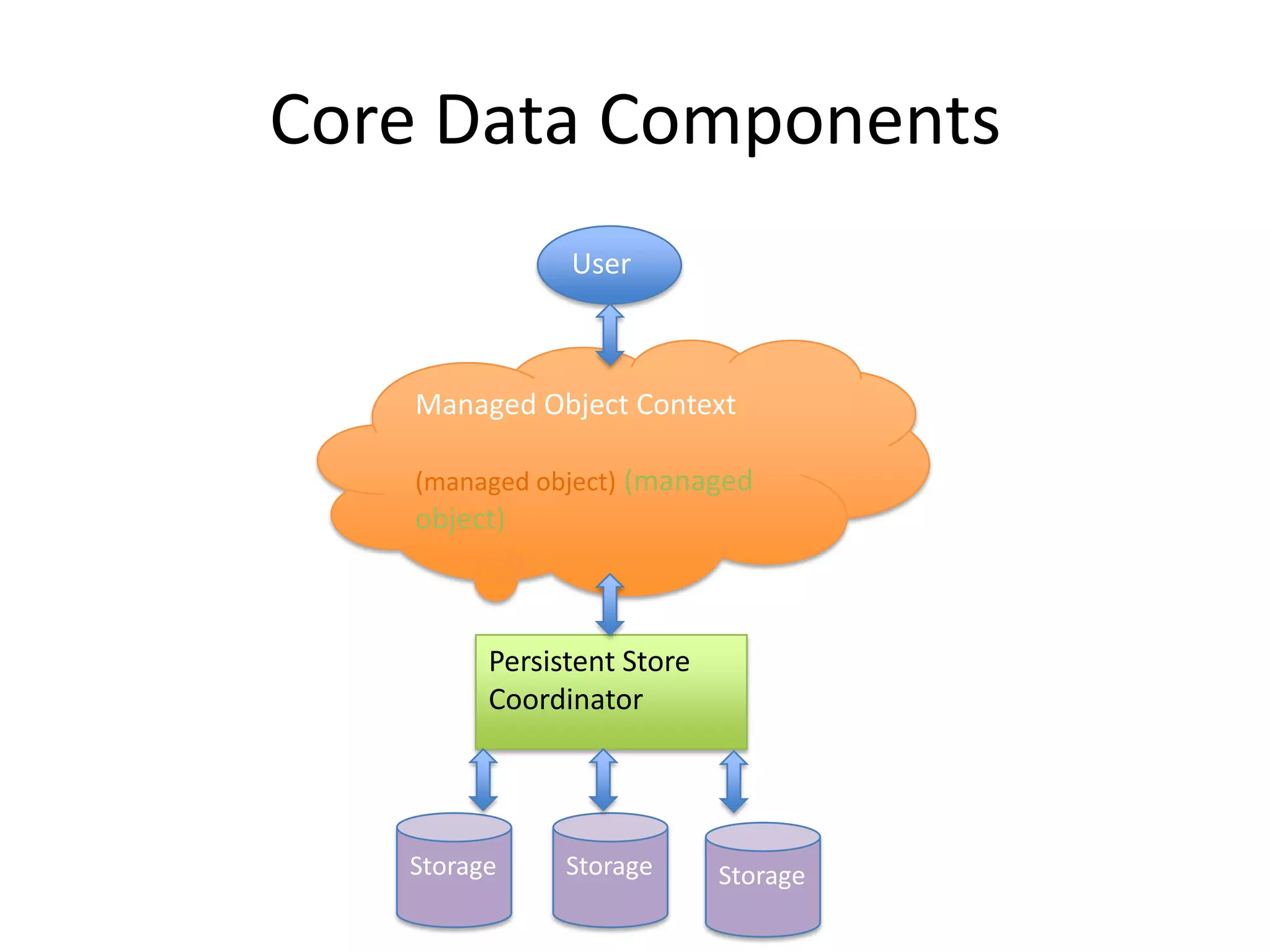
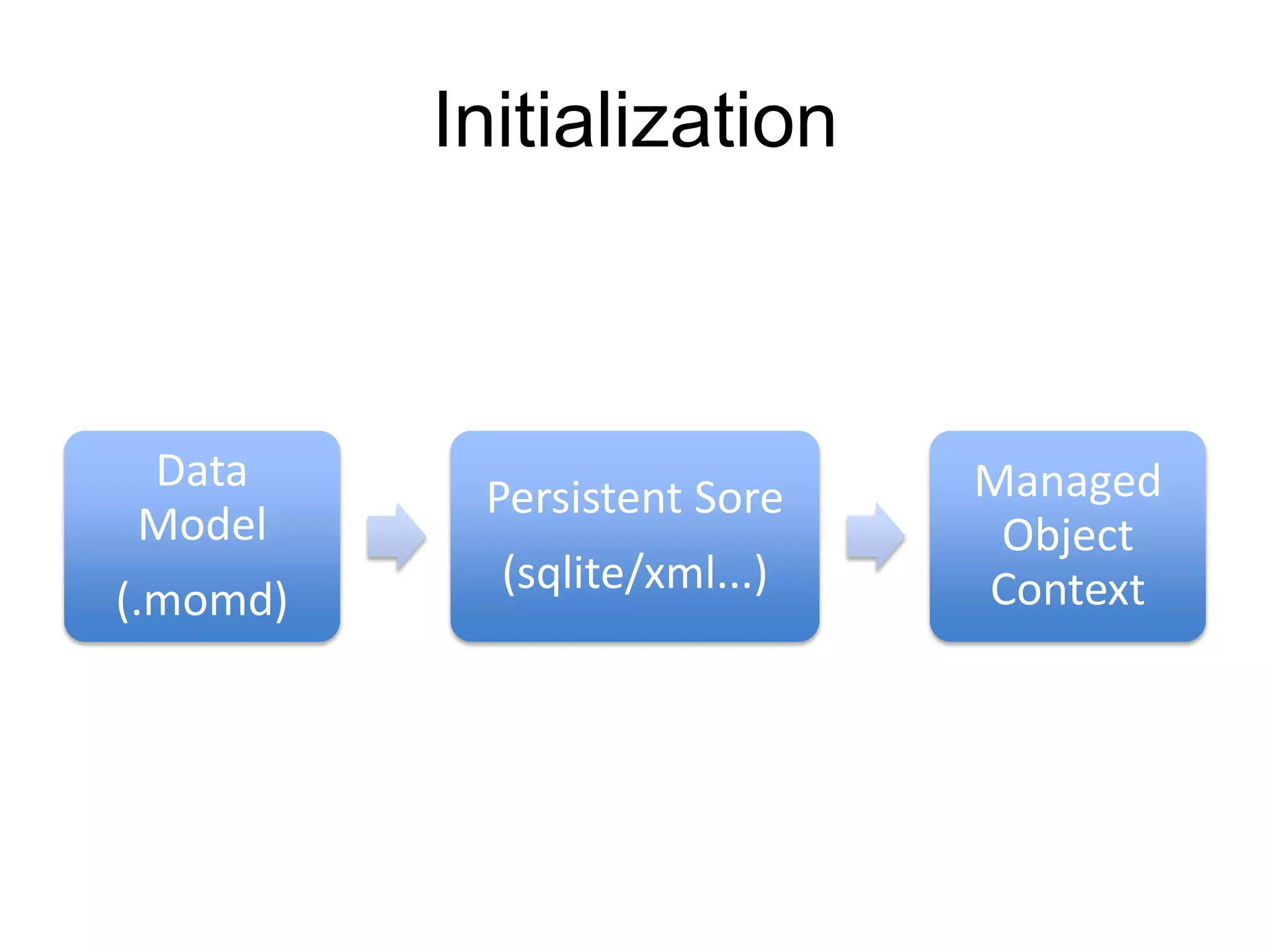
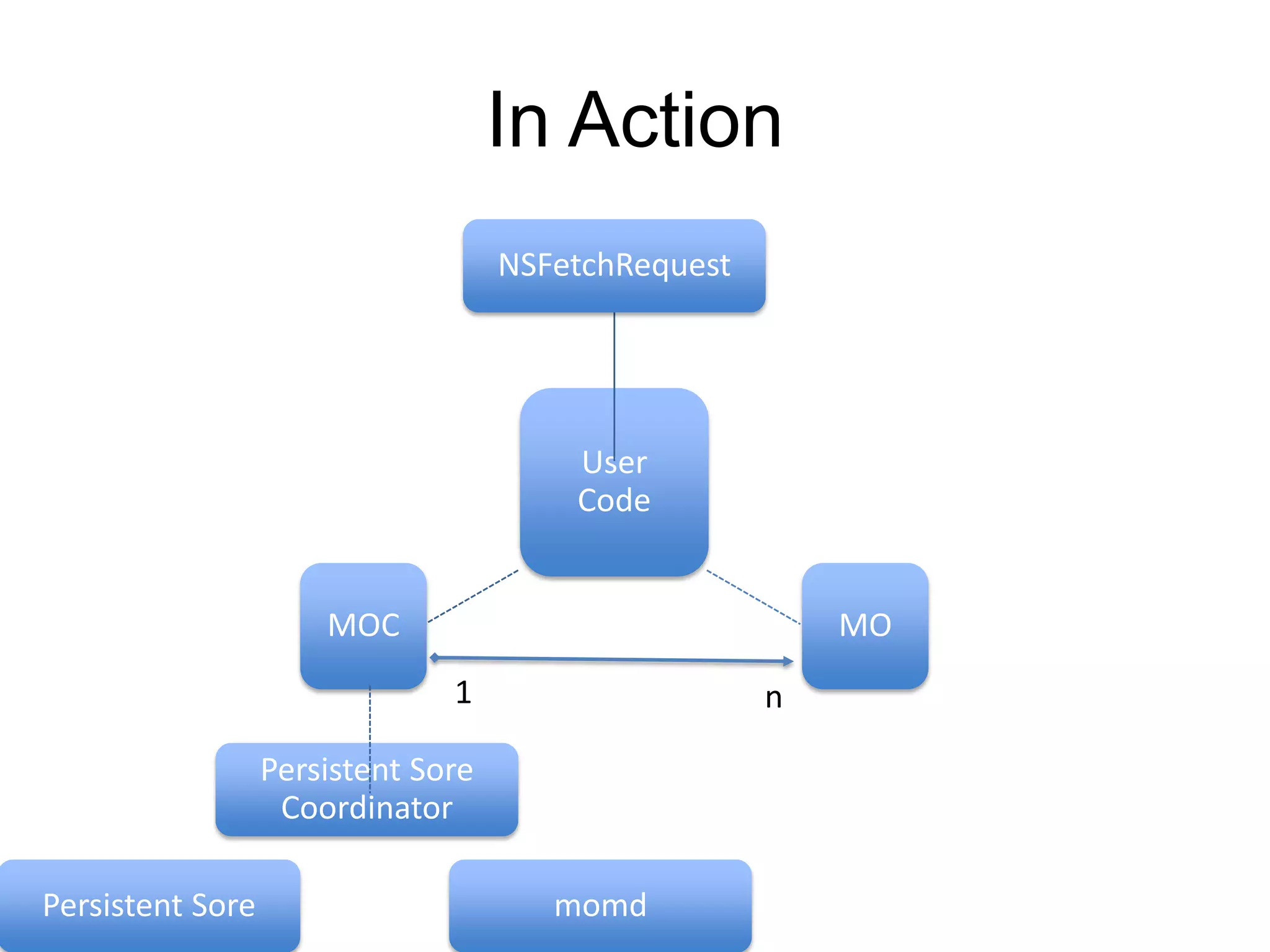
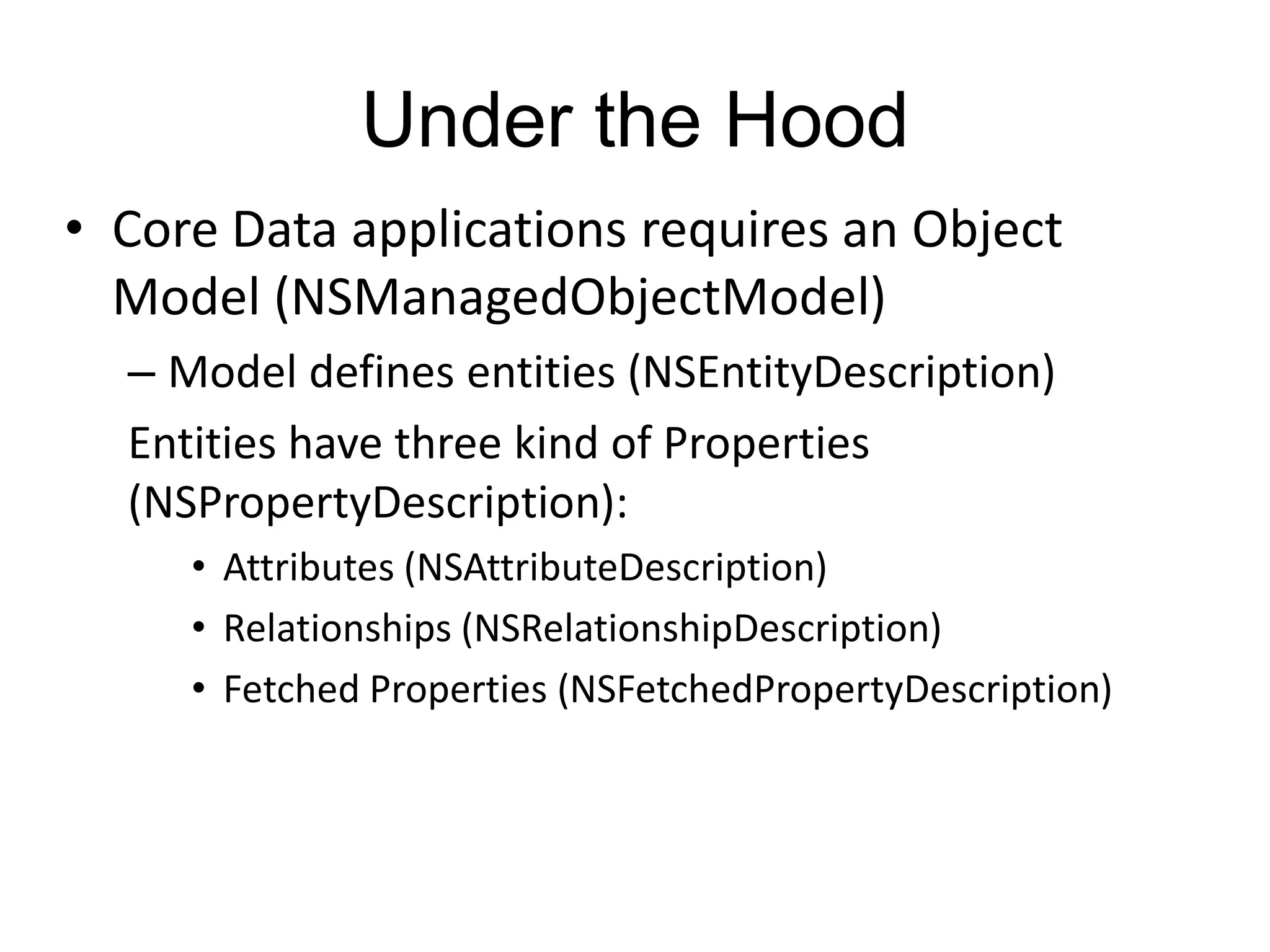
Core Data is Apple's object graph and persistence framework that allows developers to save model objects to files and retrieve them later. It provides automatic support for undo/redo operations and maintaining relationships between objects. Core Data uses a schema to describe model classes and their attributes and relationships. It allows managing just a subset of model objects in memory at once to conserve resources. Core Data has components like the managed object context, persistent store coordinator, and persistent store that work together to fetch, save, and manage model objects in an application's data layer.