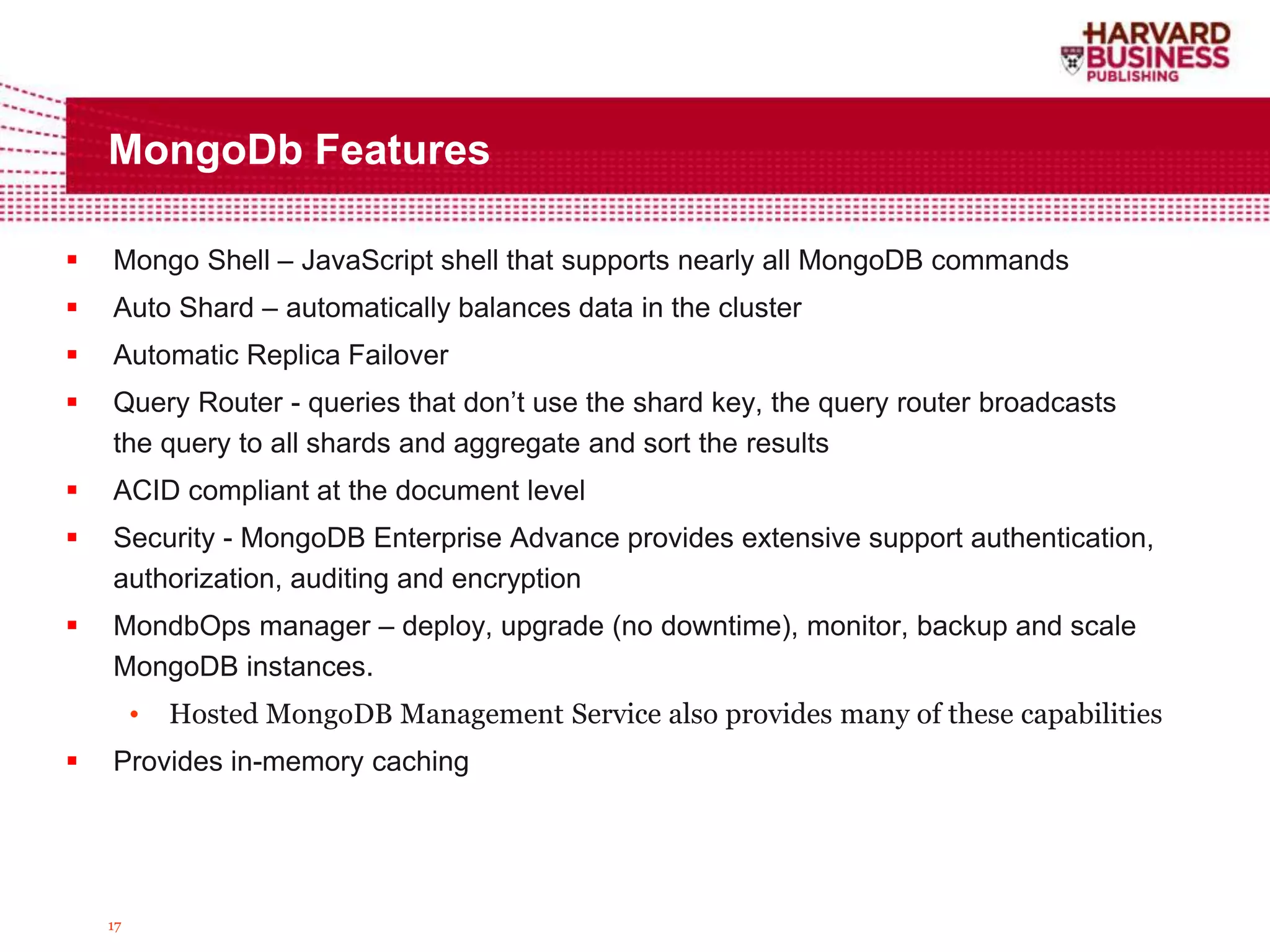
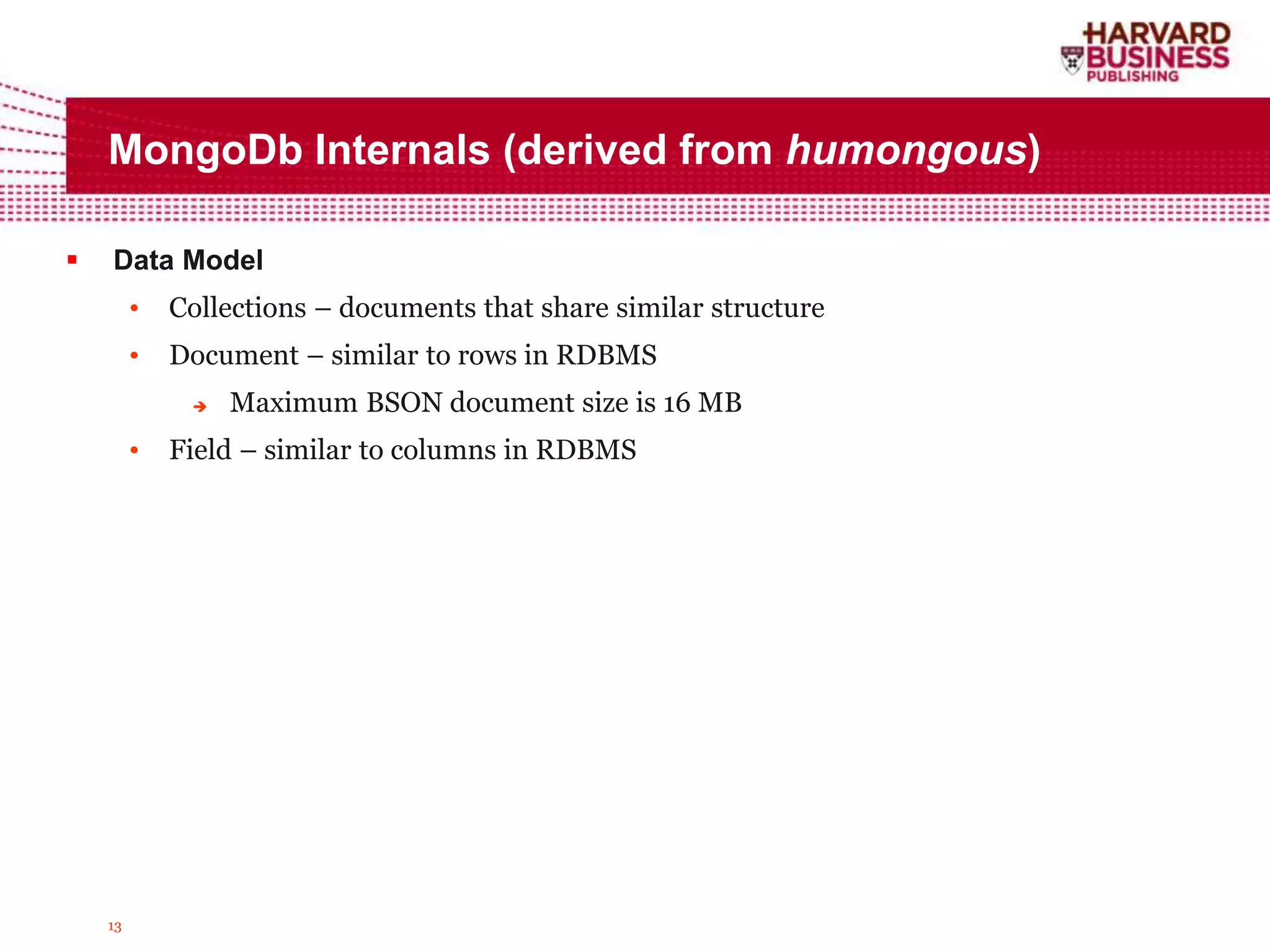
The document compares DynamoDB and MongoDB, focusing on their data structures, querying capabilities, and features for managing unstructured data. It details DynamoDB's key/value pair storage, throughput management, and automatic scaling, while highlighting MongoDB's document-oriented model, comprehensive querying, and ACID compliance at the document level. Additionally, both databases offer community support and integration options but differ in schema flexibility, indexing strategies, and performance under load.



![16 MongoDb – Sample Query Return states with populatin above 10 millions db.zipcodes.aggregate( [ { $group: { _id: "$state", totalPop: { $sum: "$pop" } } }, { $match: { totalPop: { $gte: 10*1000*1000 } } } ] )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamovsmongo-151010210646-lva1-app6892/75/Compare-DynamoDB-vs-MongoDB-16-2048.jpg)