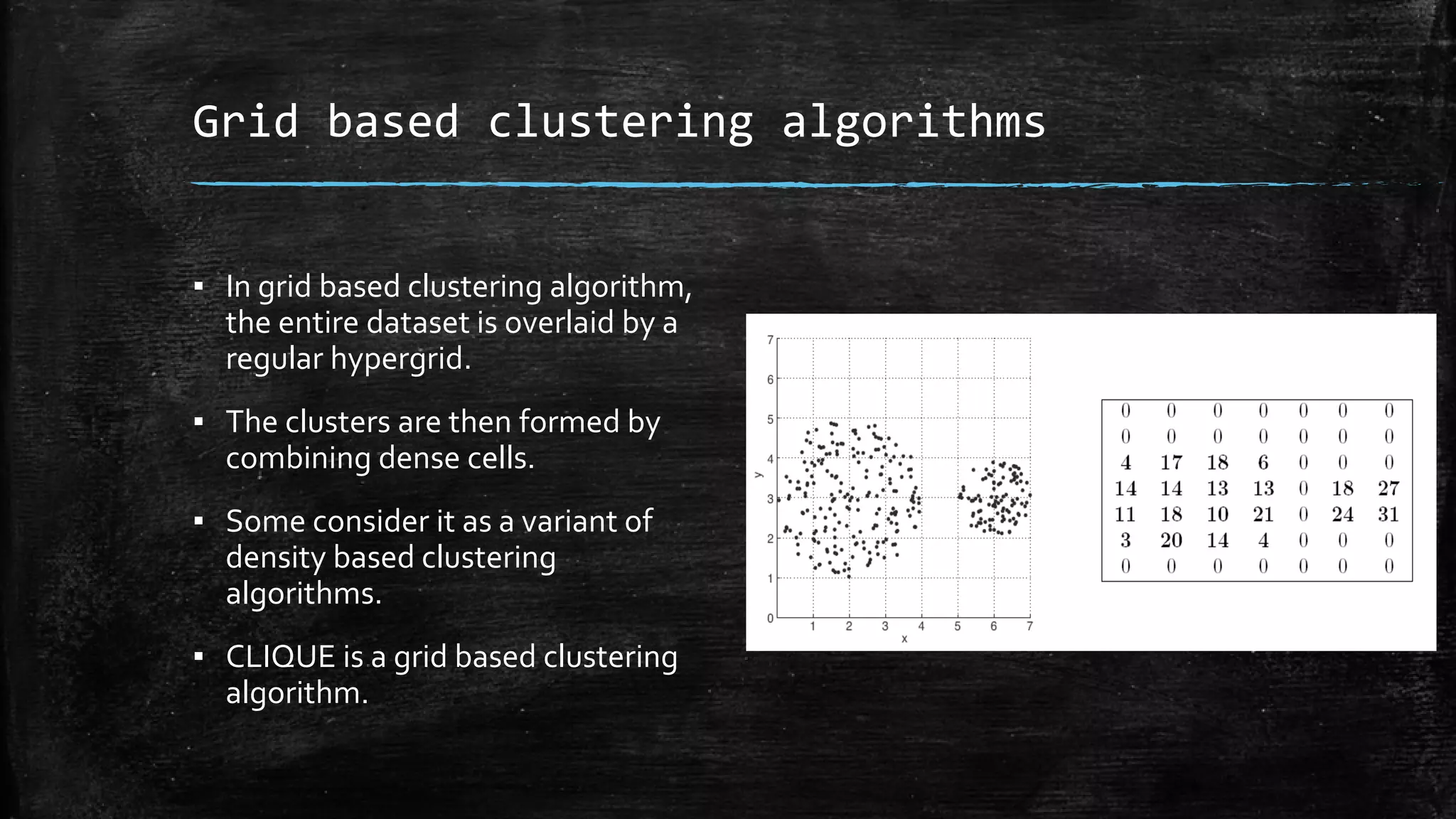
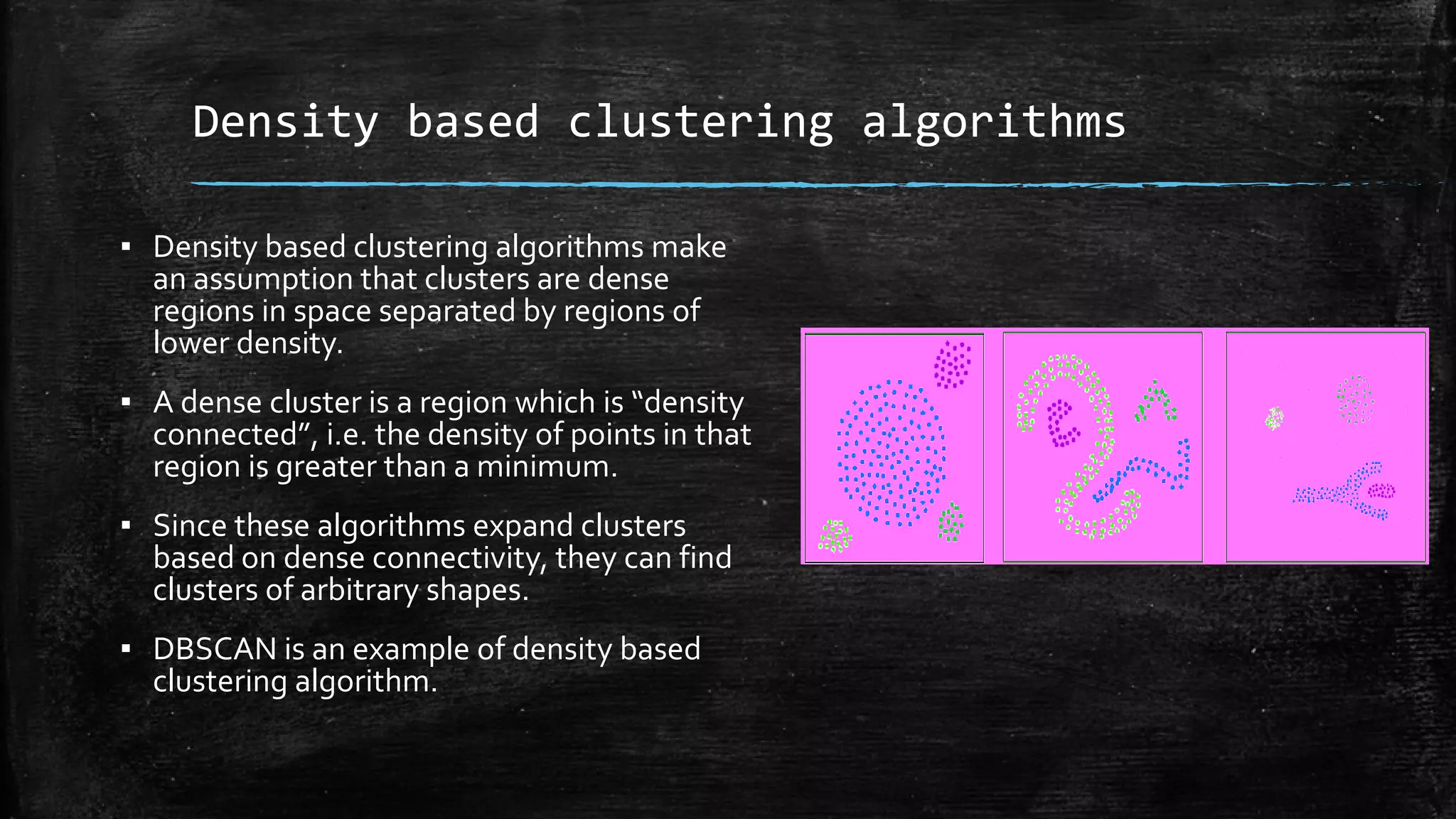
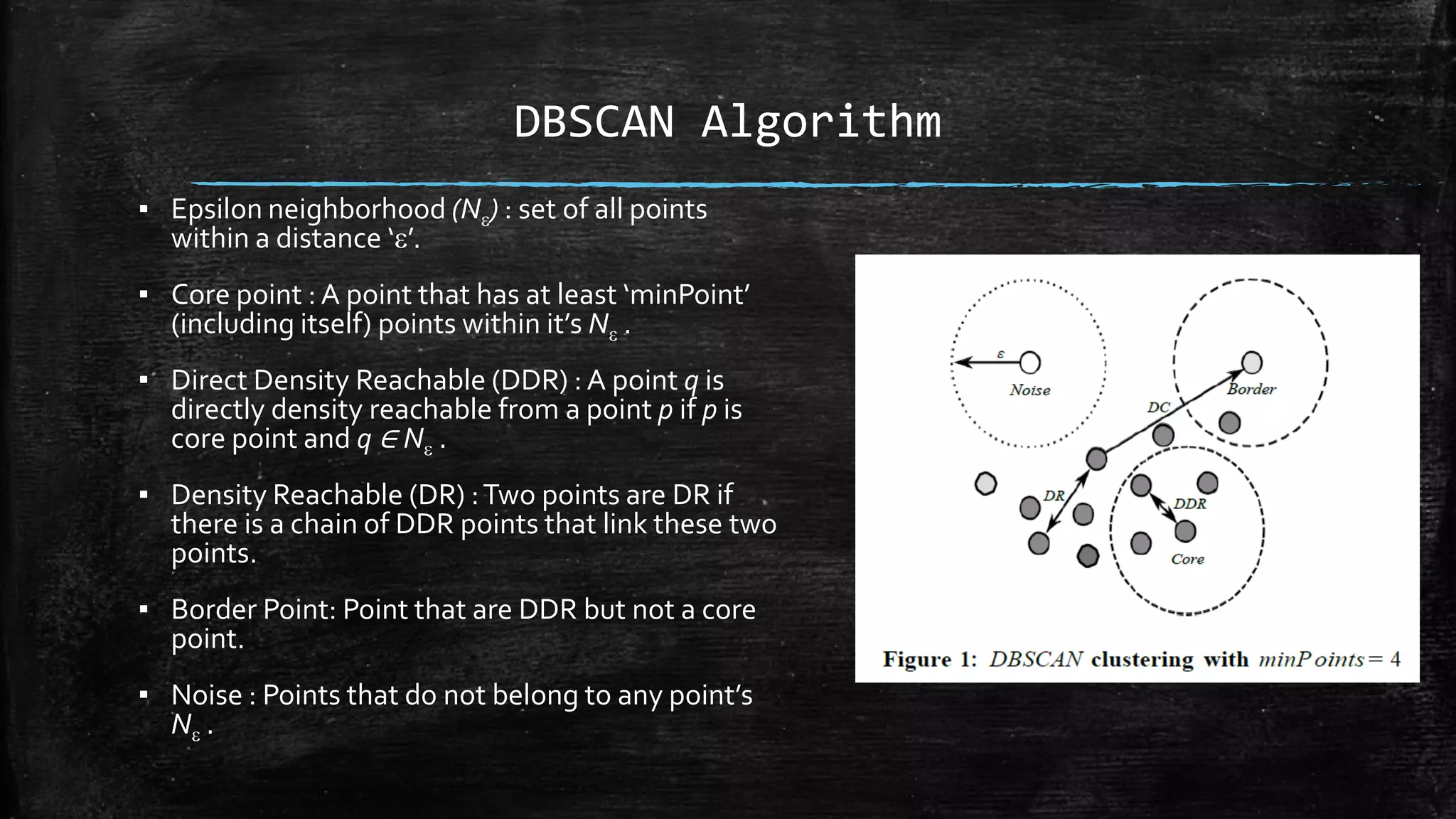
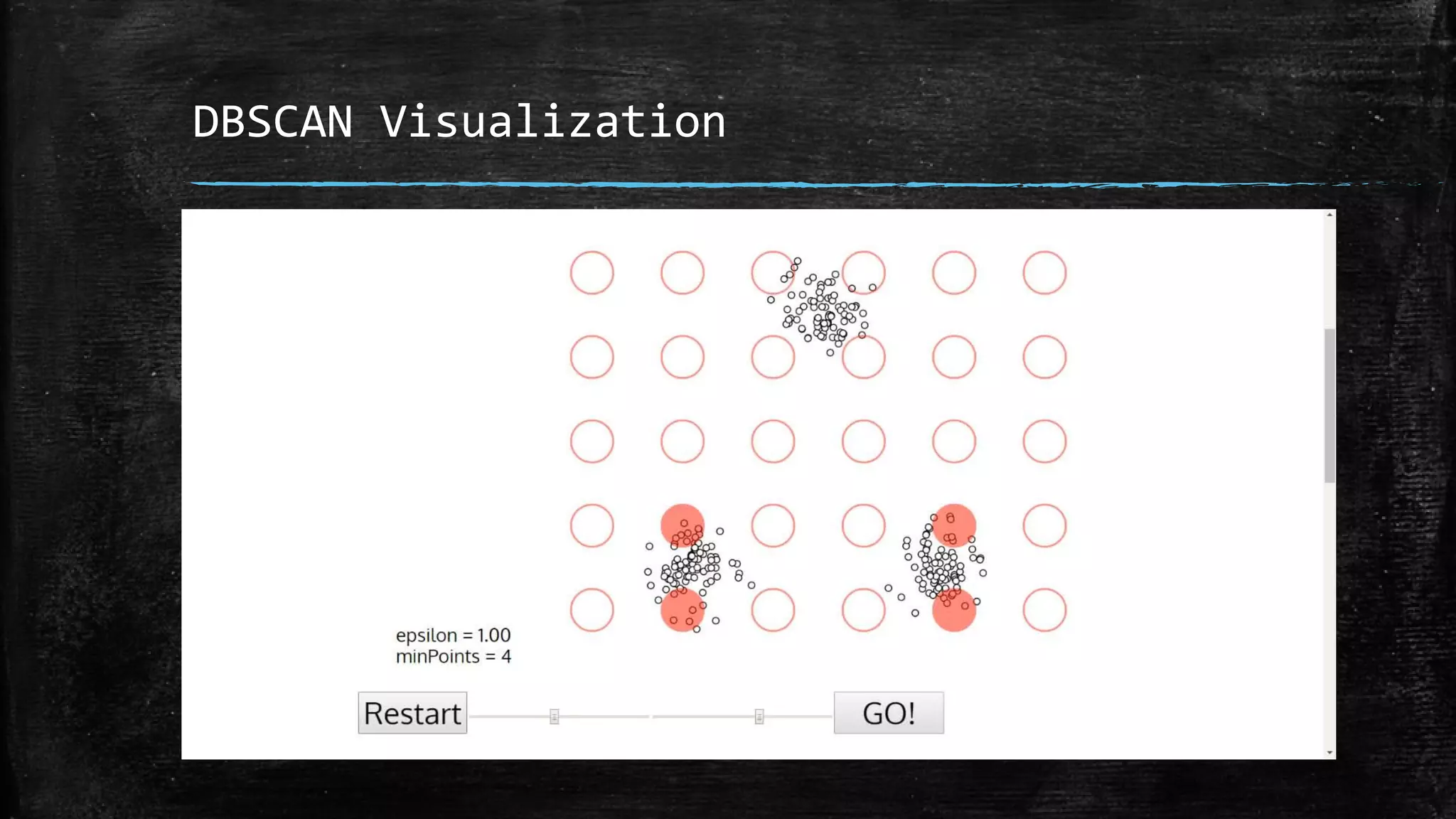
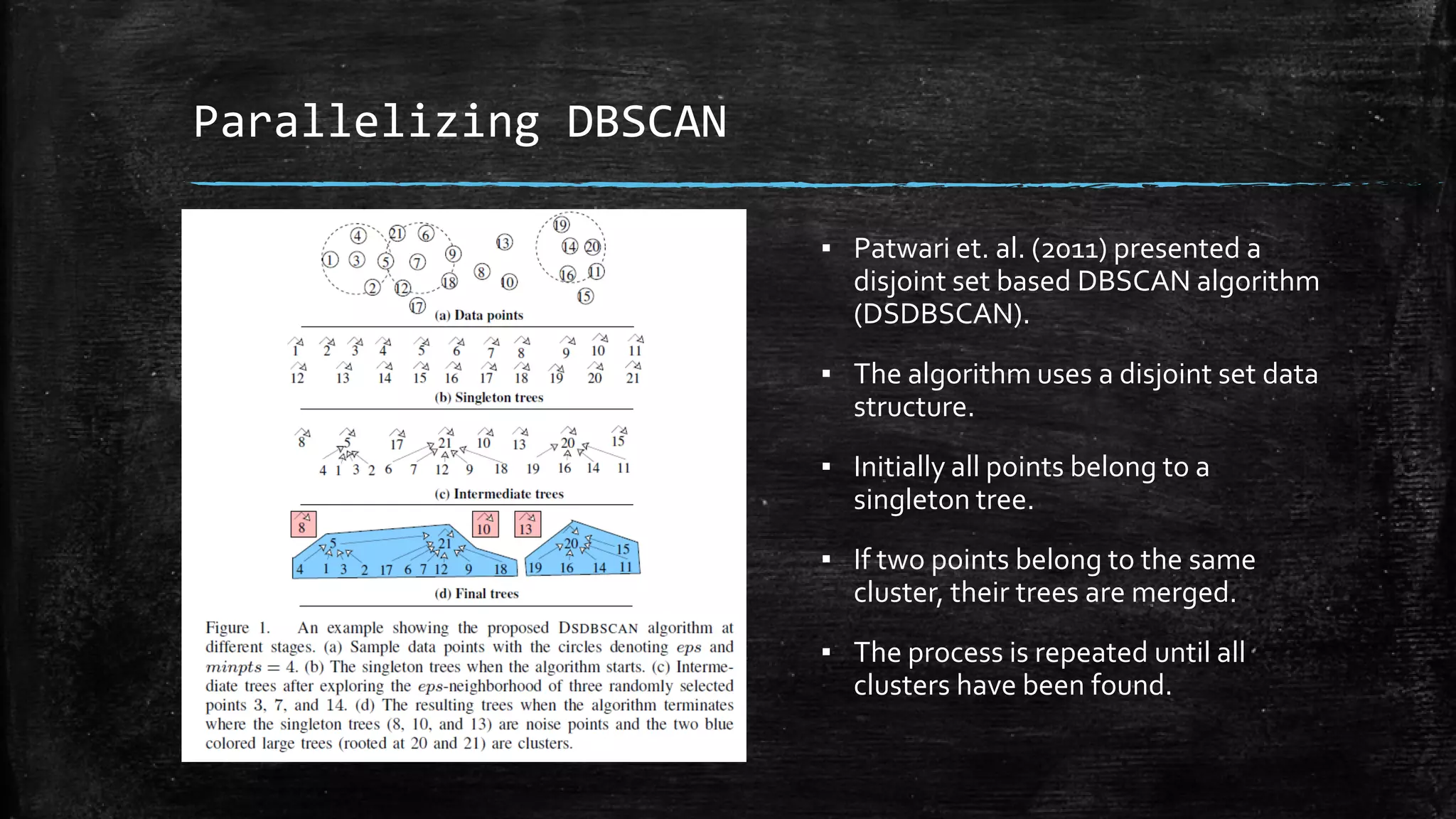
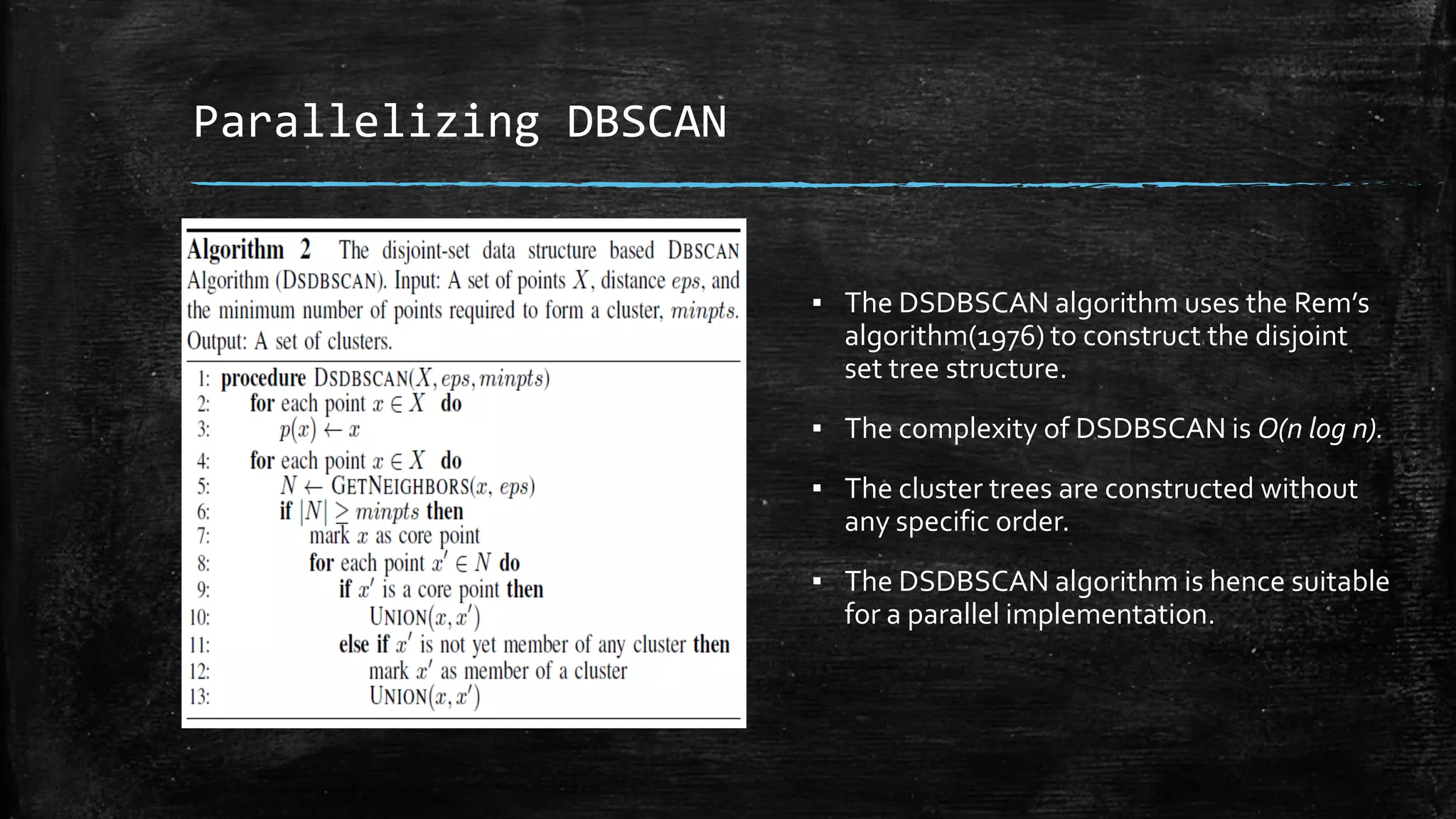
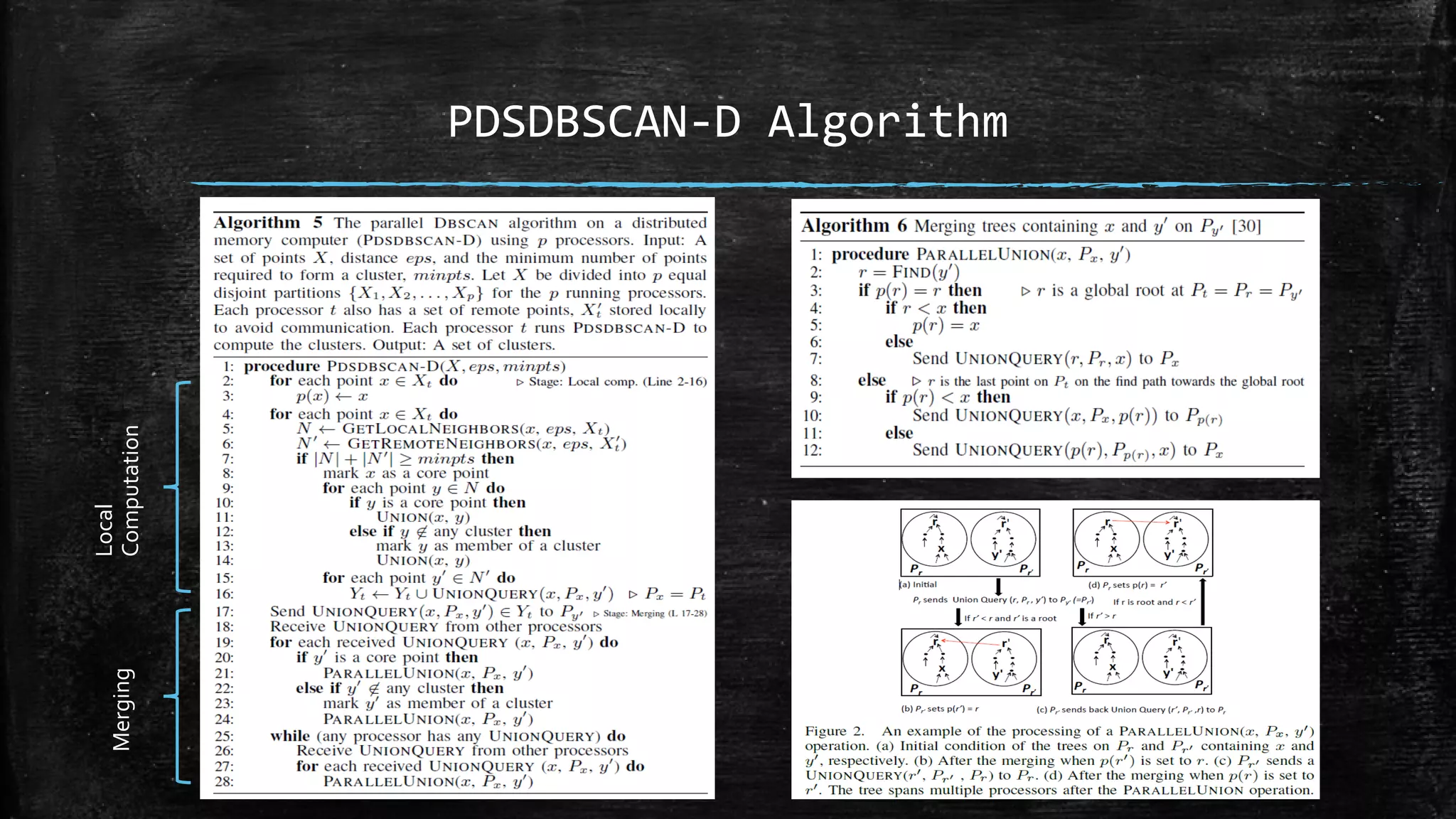
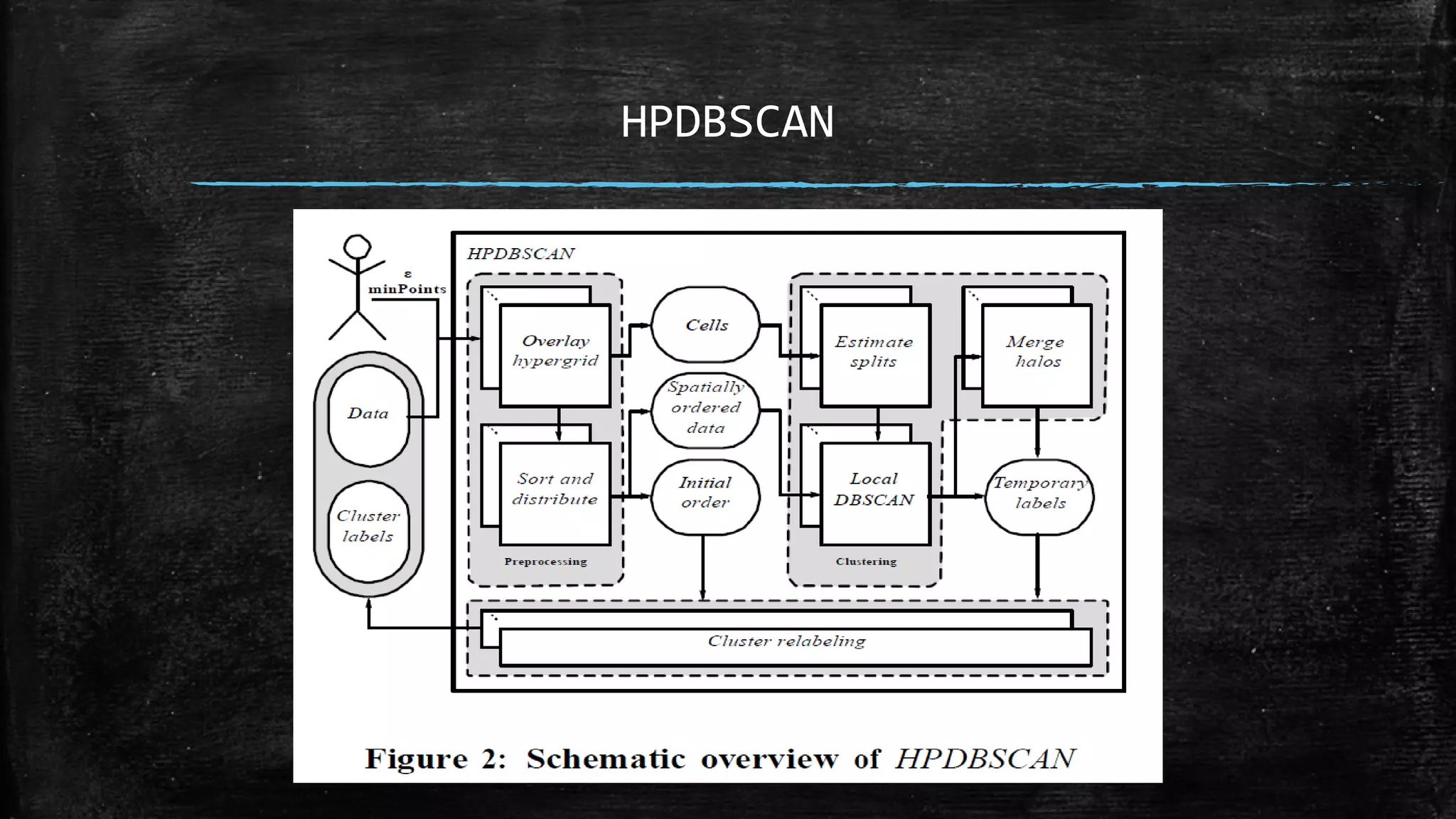
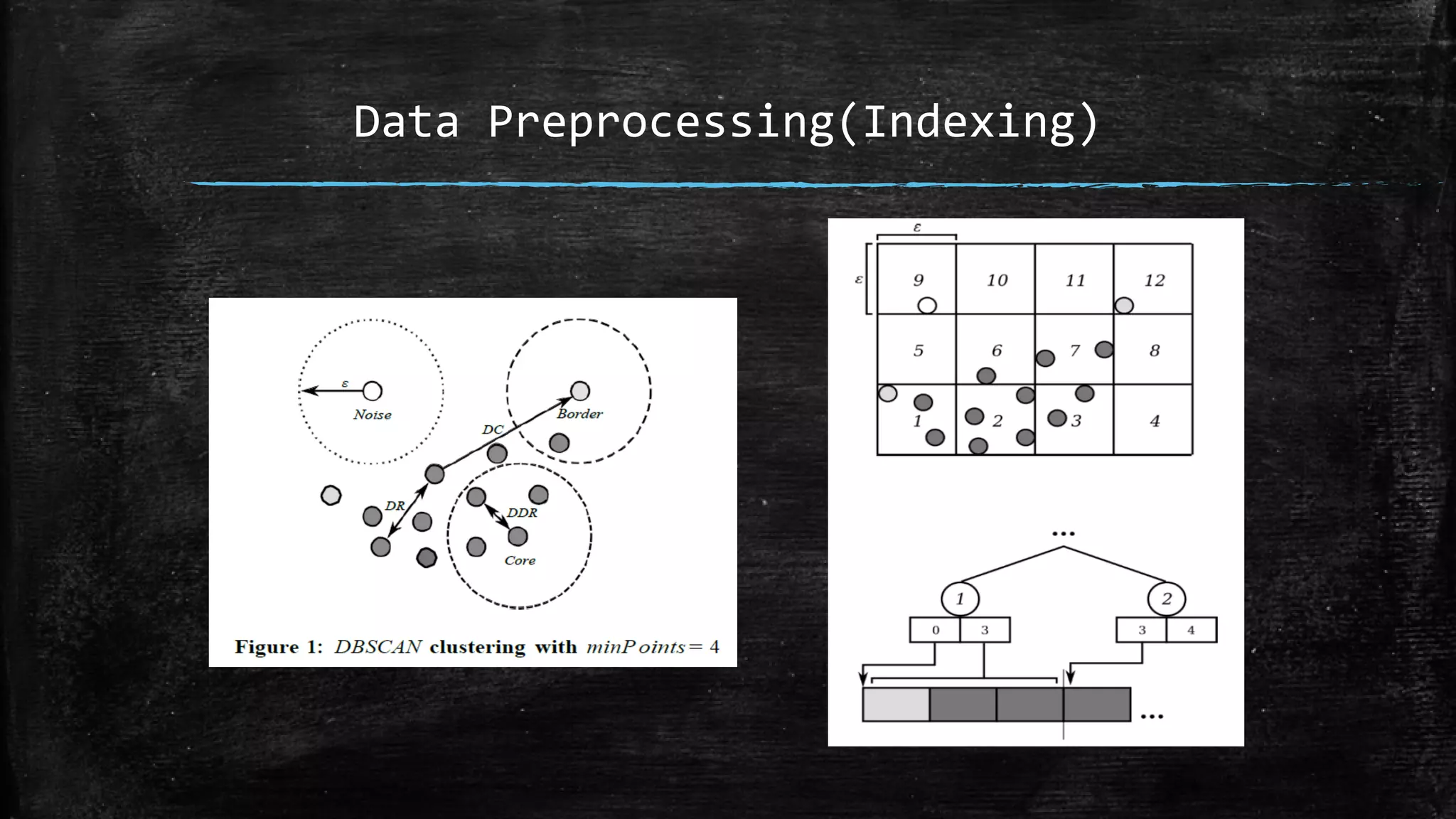
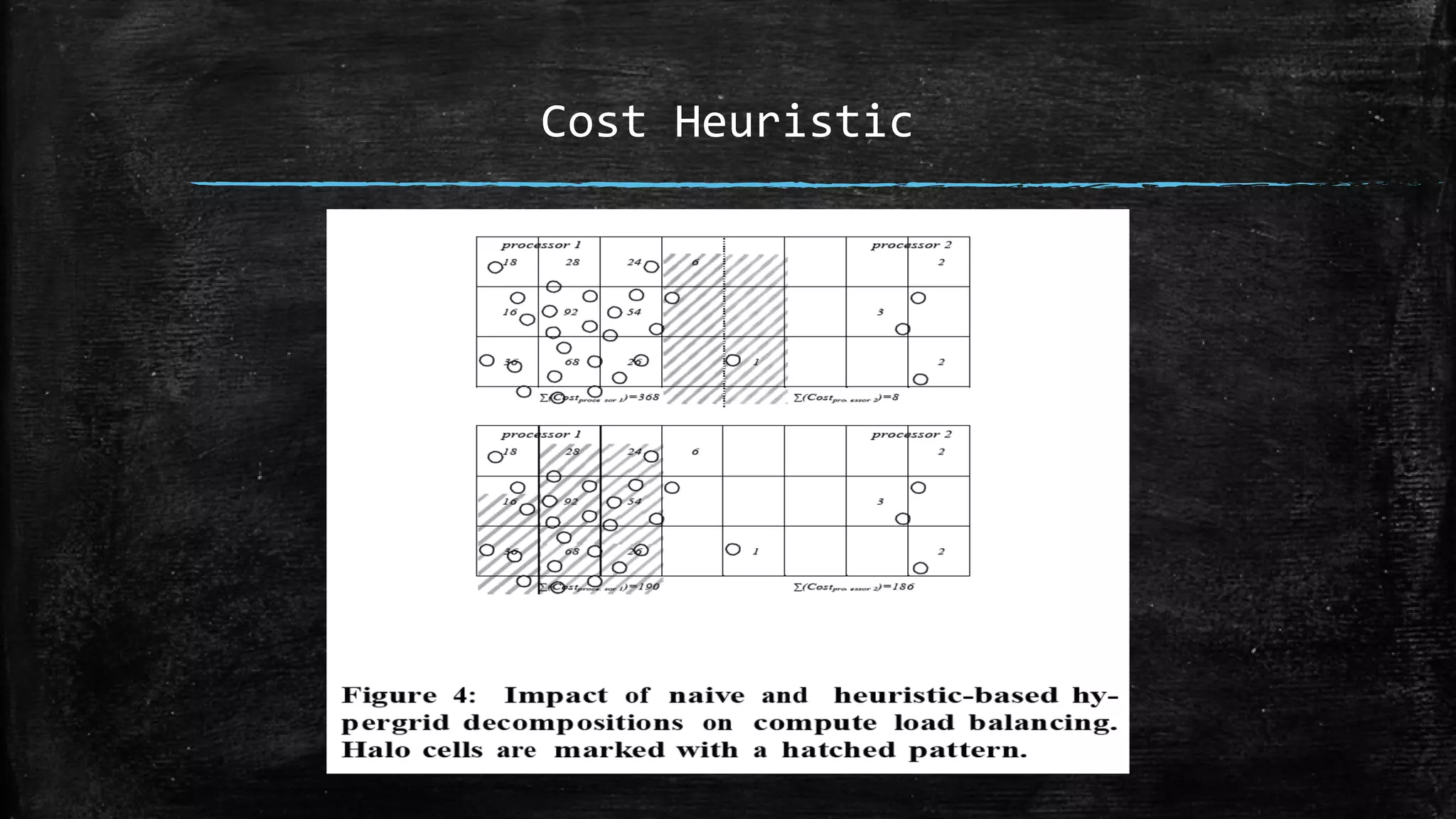
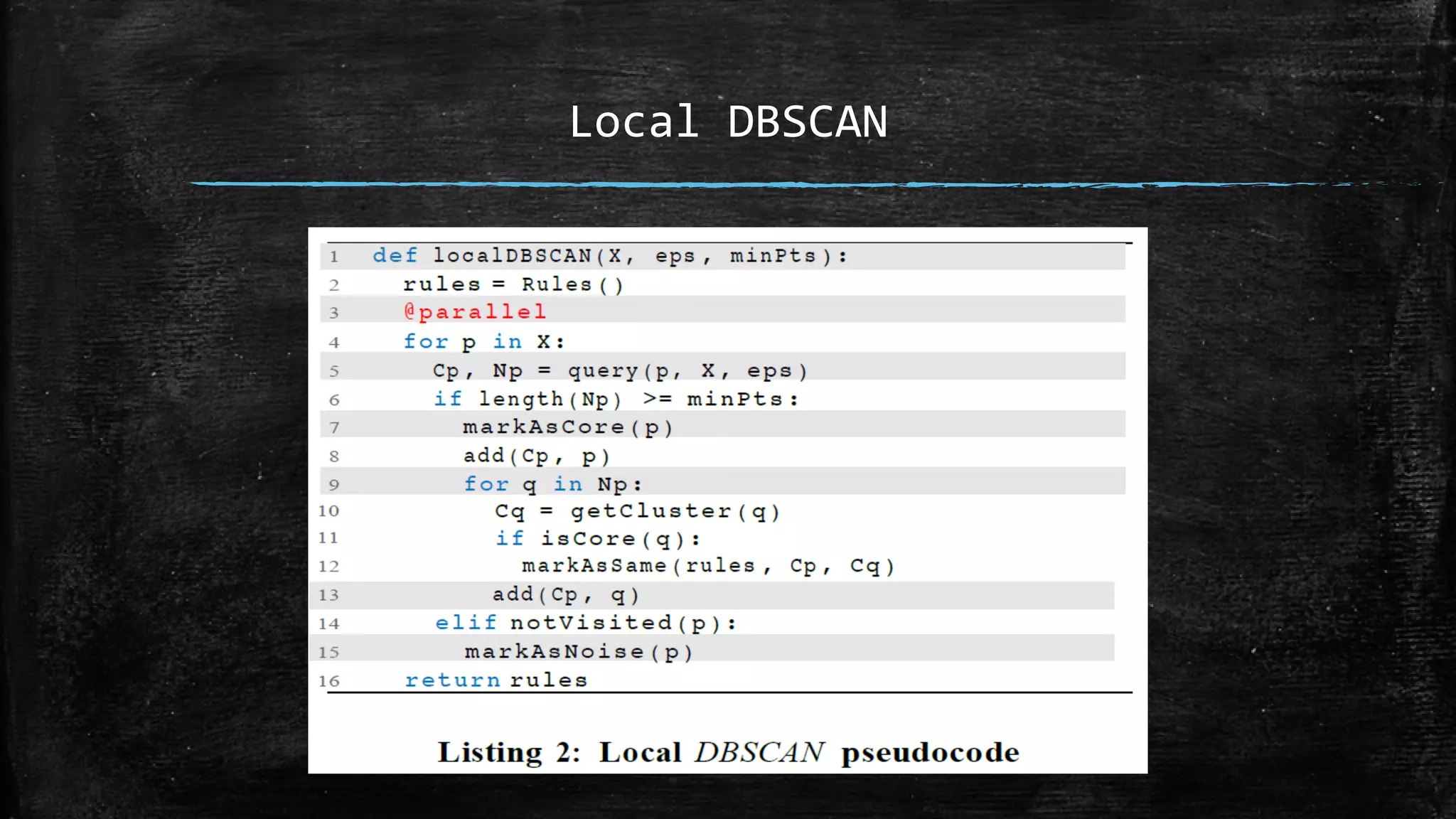
DBSCAN is a density-based clustering algorithm that groups together densely populated areas of points that are separated by low density areas. It has two parameters: epsilon, which defines neighborhood size, and minPoints, the minimum number of points required to form a cluster. It works by finding core points that have at least minPoints neighbors within epsilon distance, and recursively expanding clusters from these core points based on density connectivity. DBSCAN can find clusters of arbitrary shapes and handles noise well. The document discusses parallel versions of DBSCAN that improve its efficiency for large datasets by distributing the workload across multiple processors.