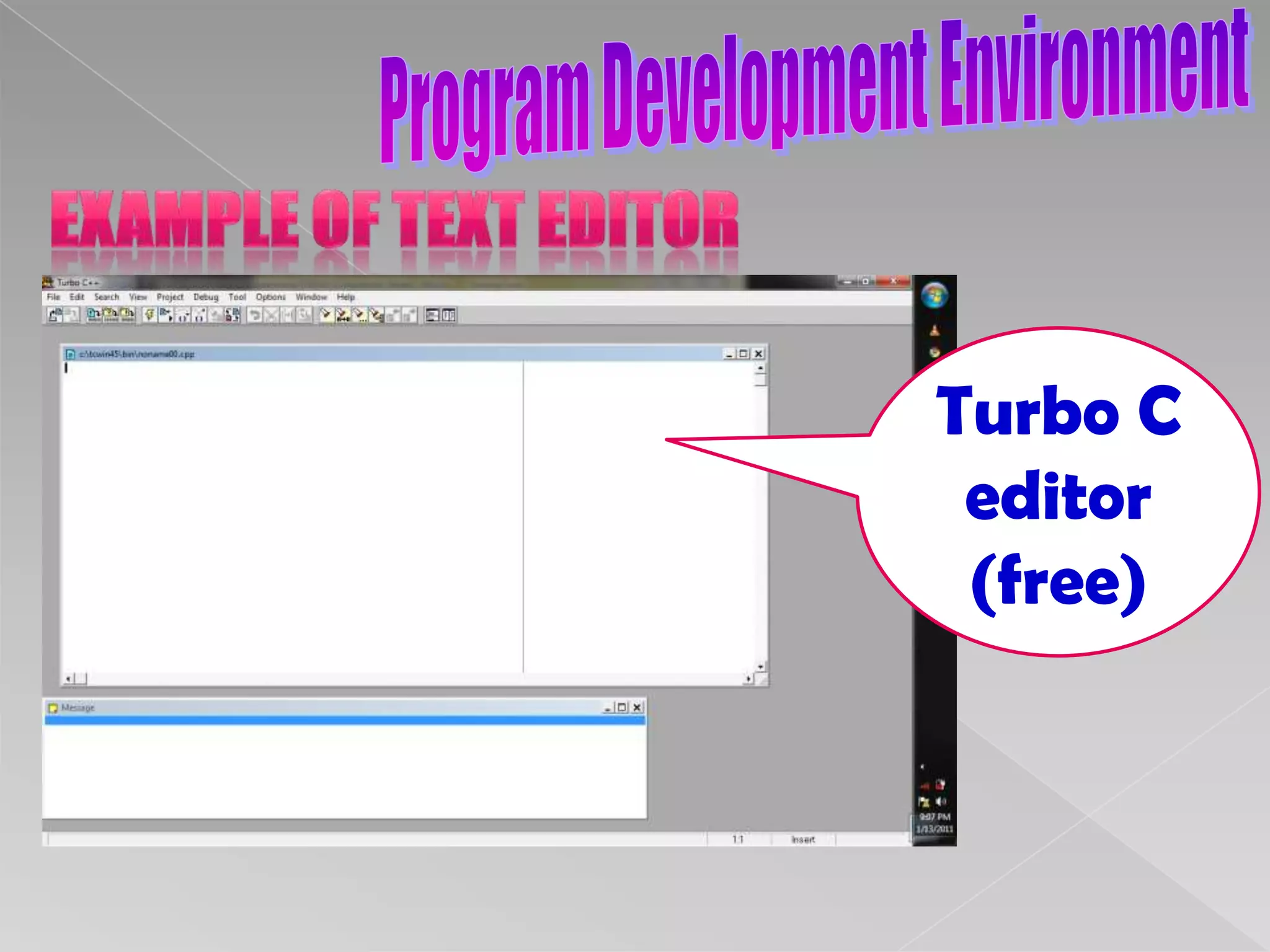
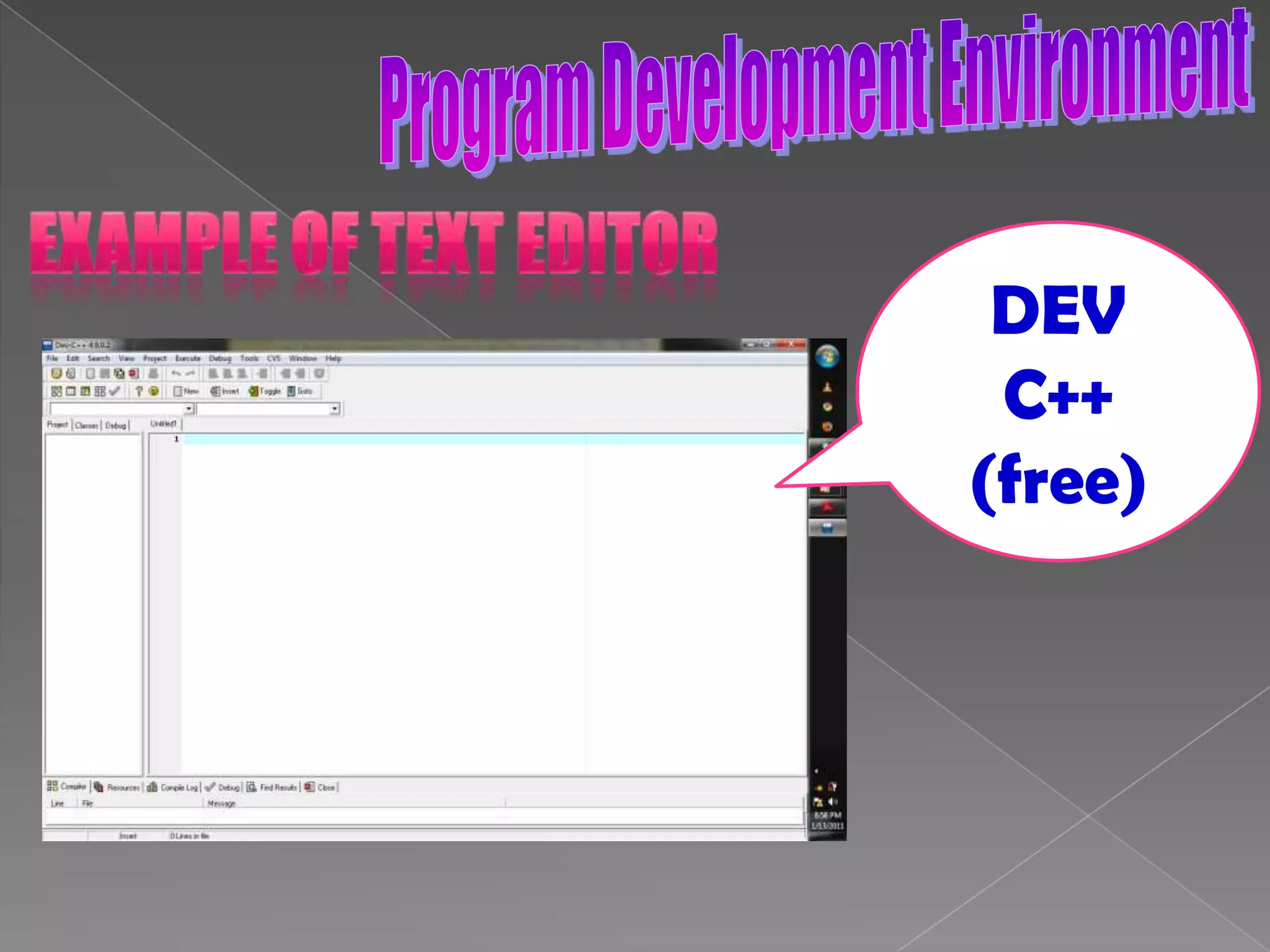
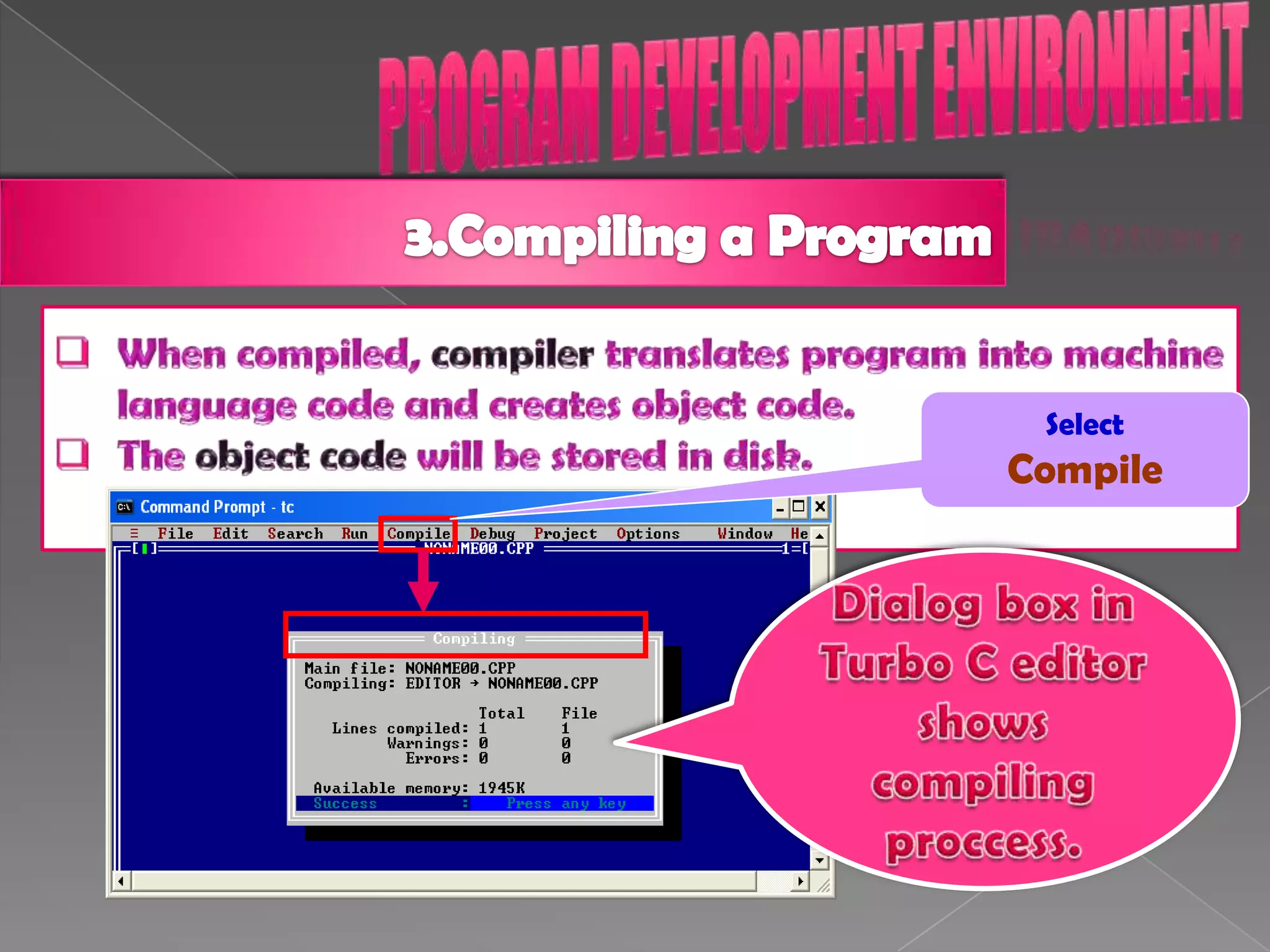
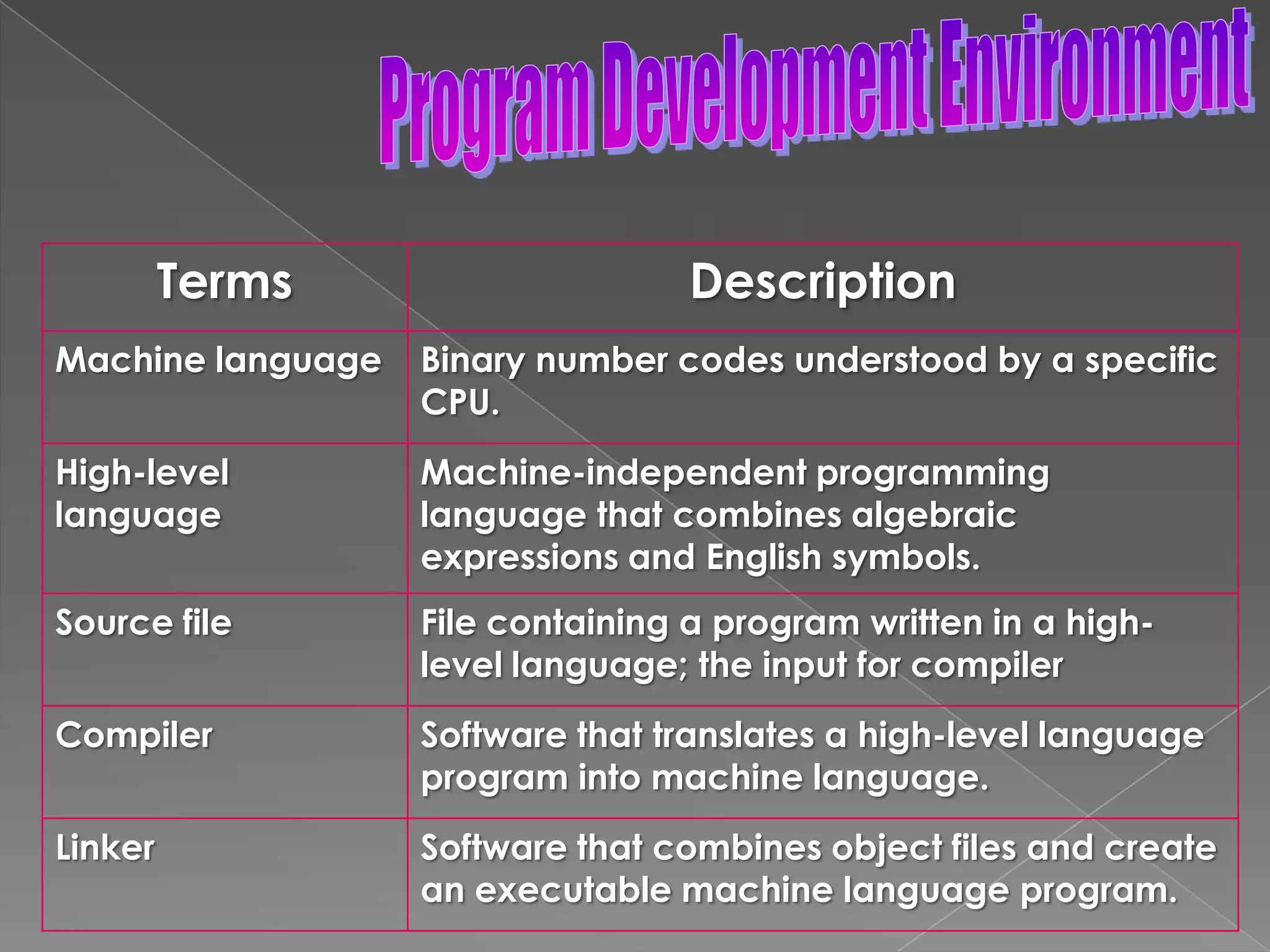
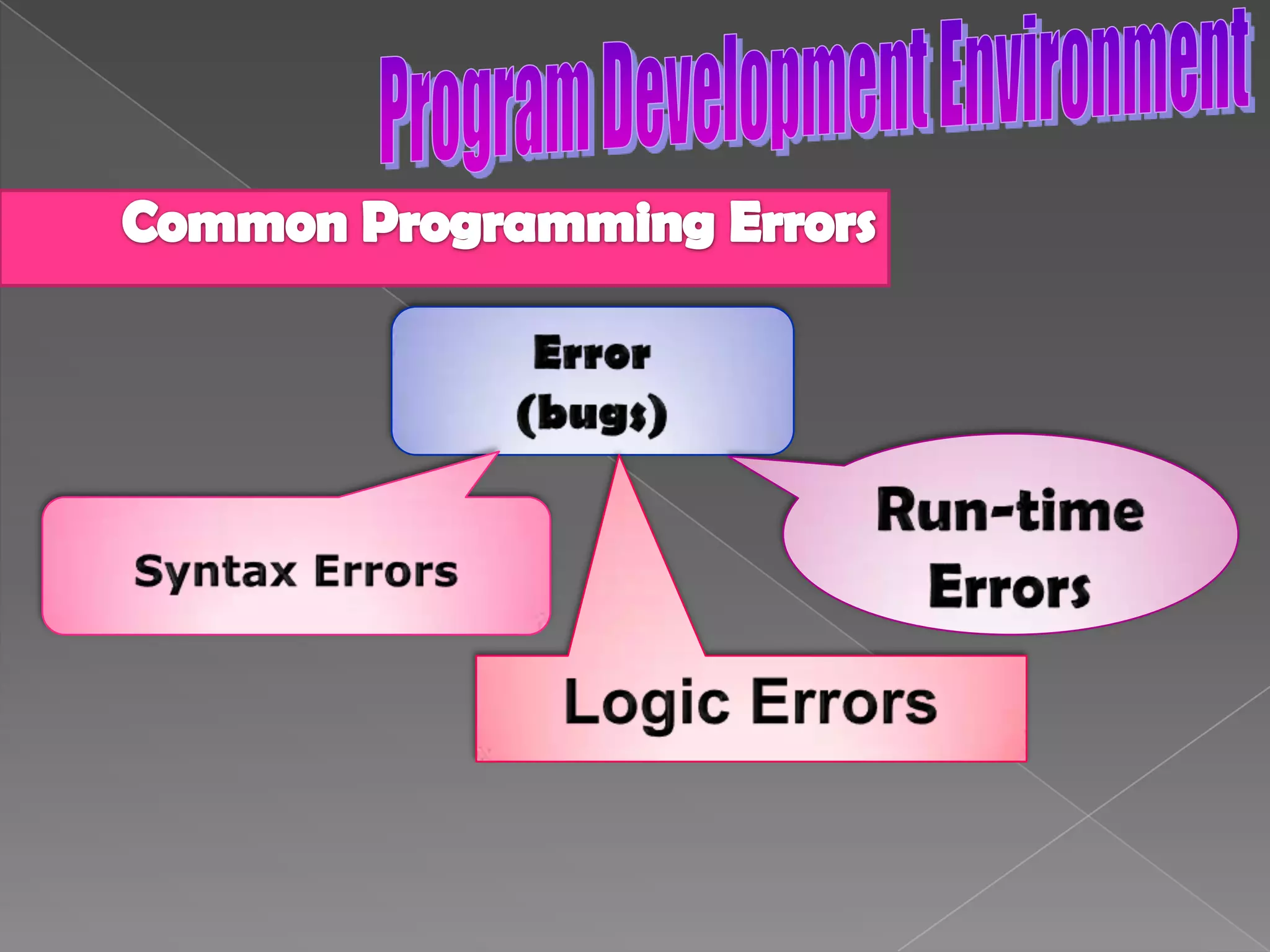
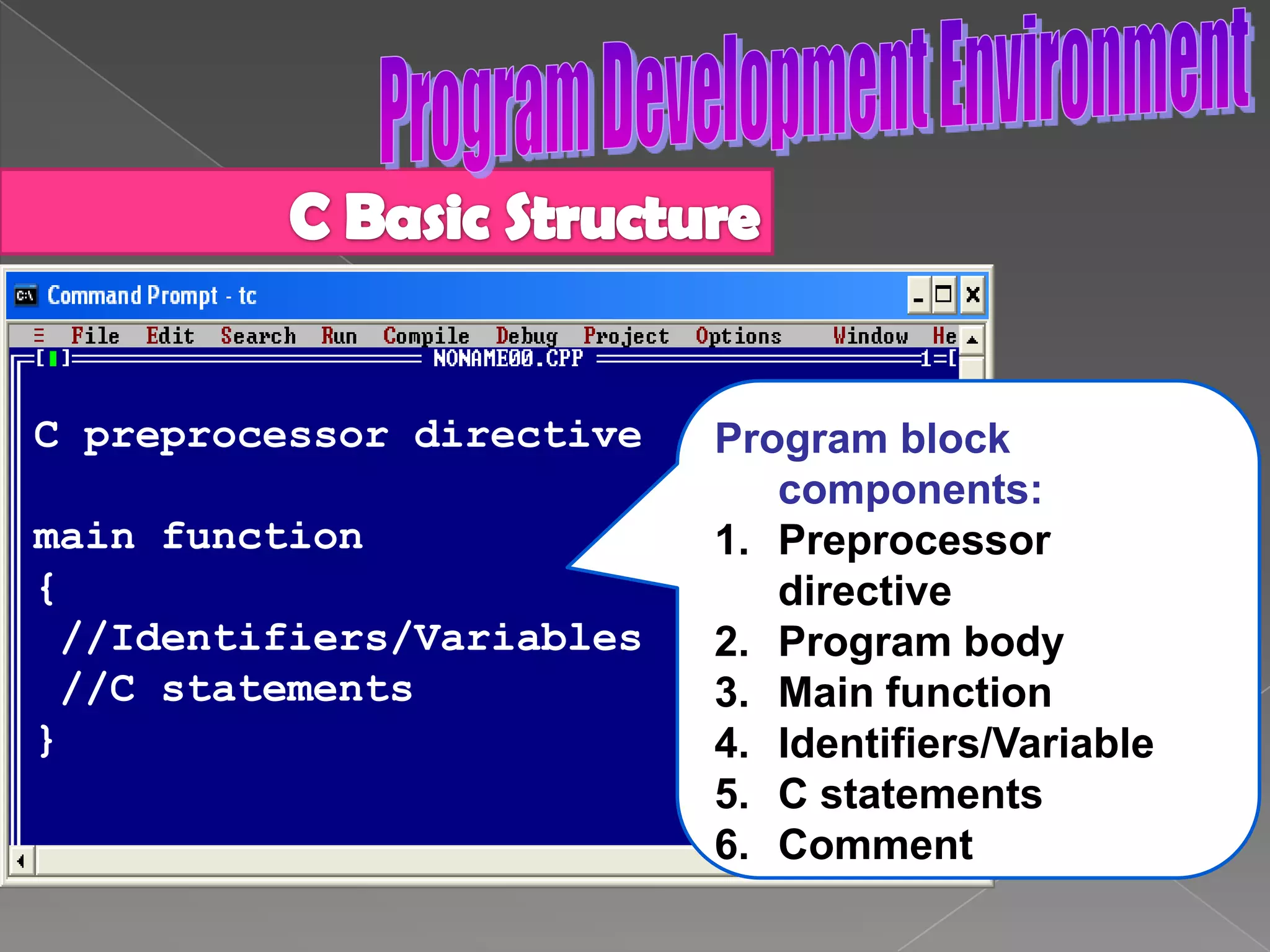
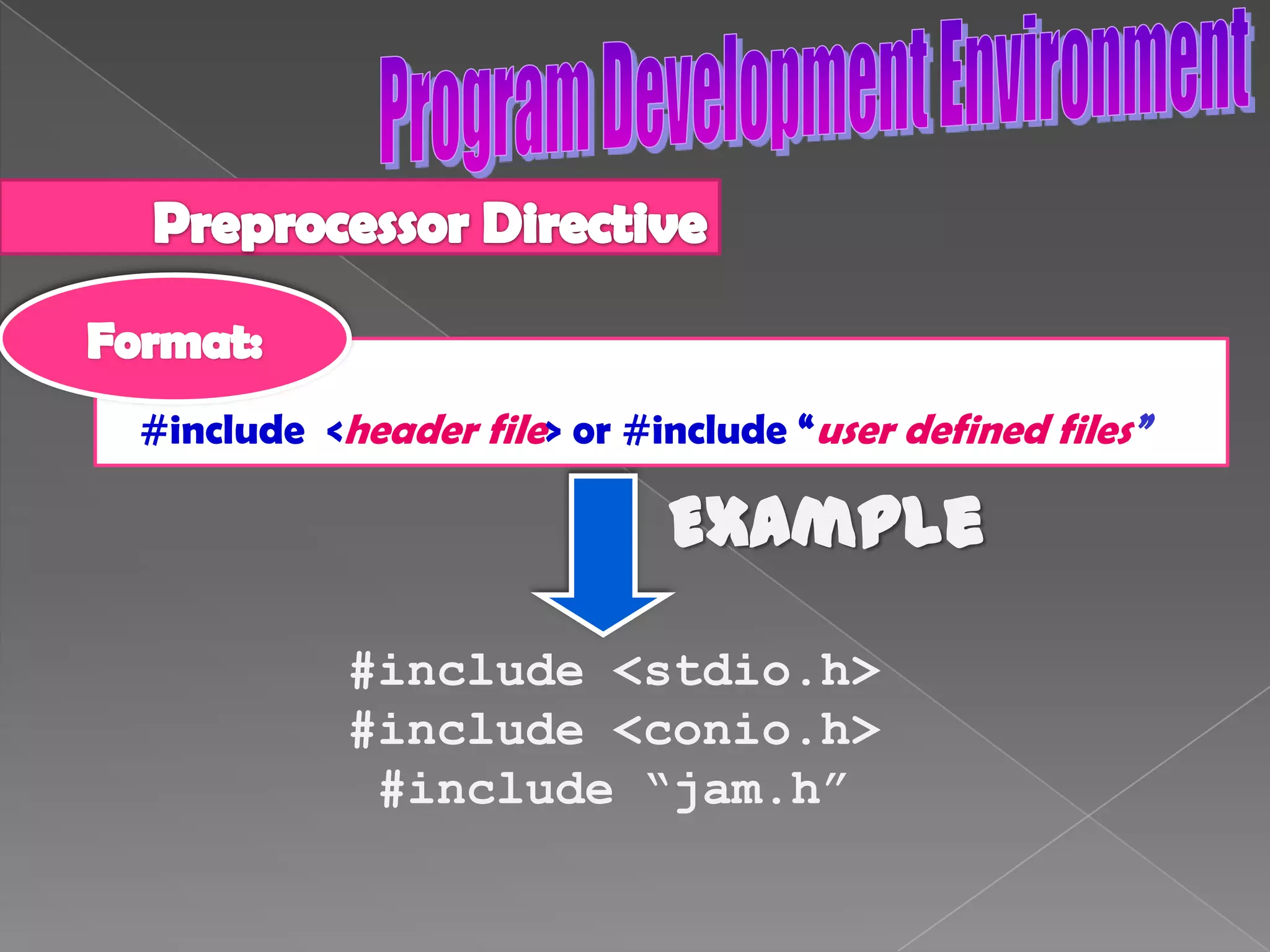
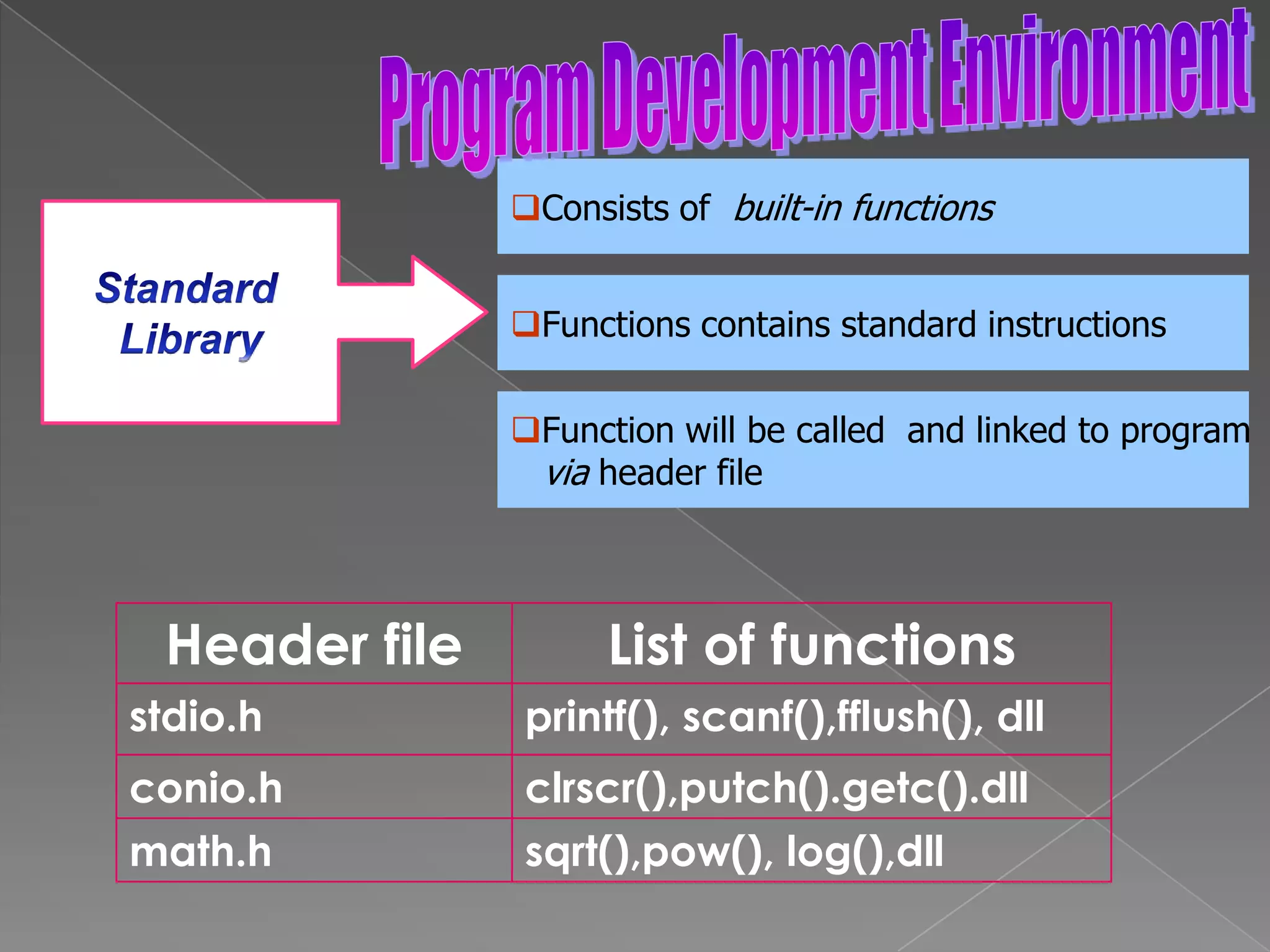
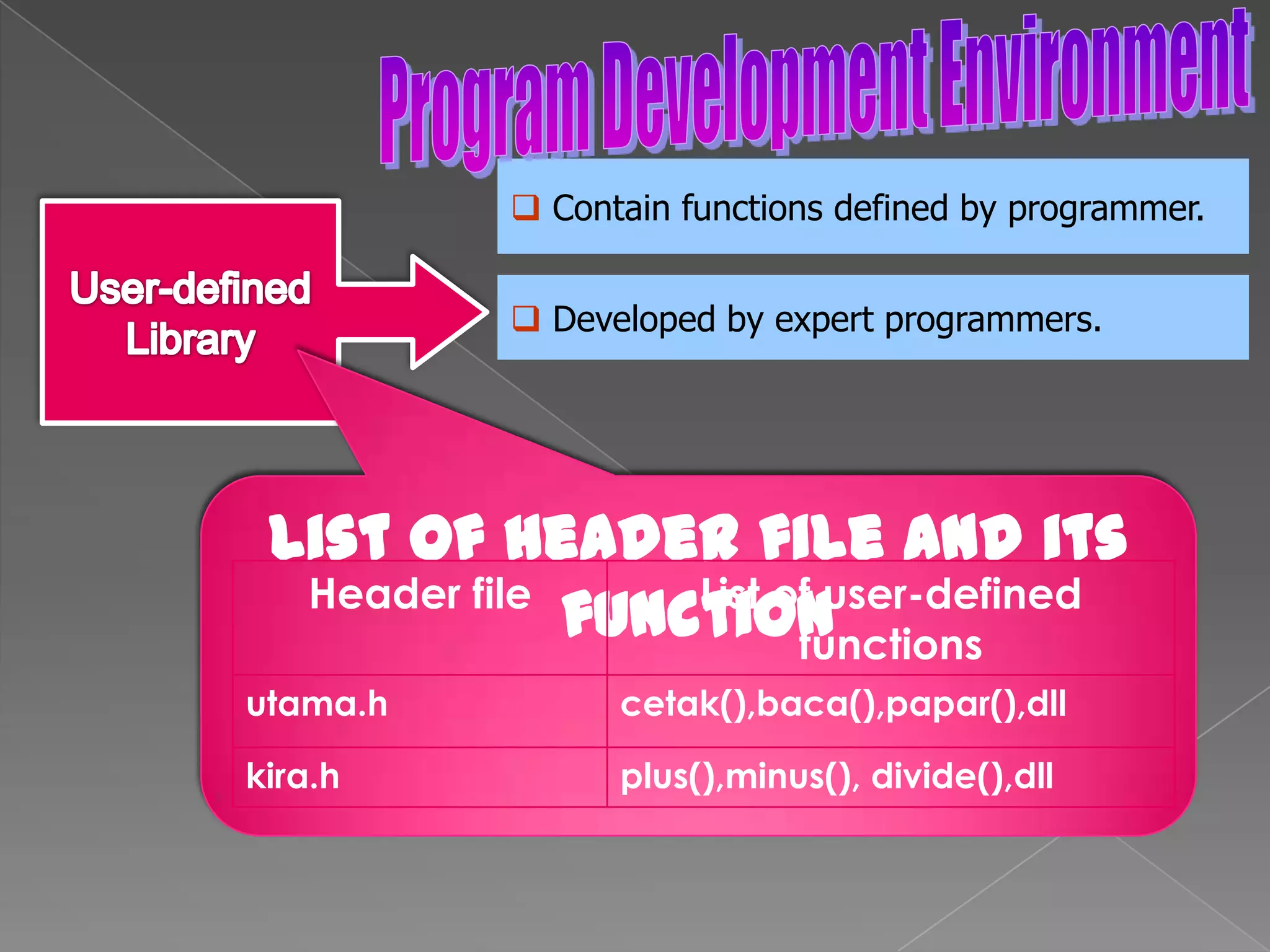
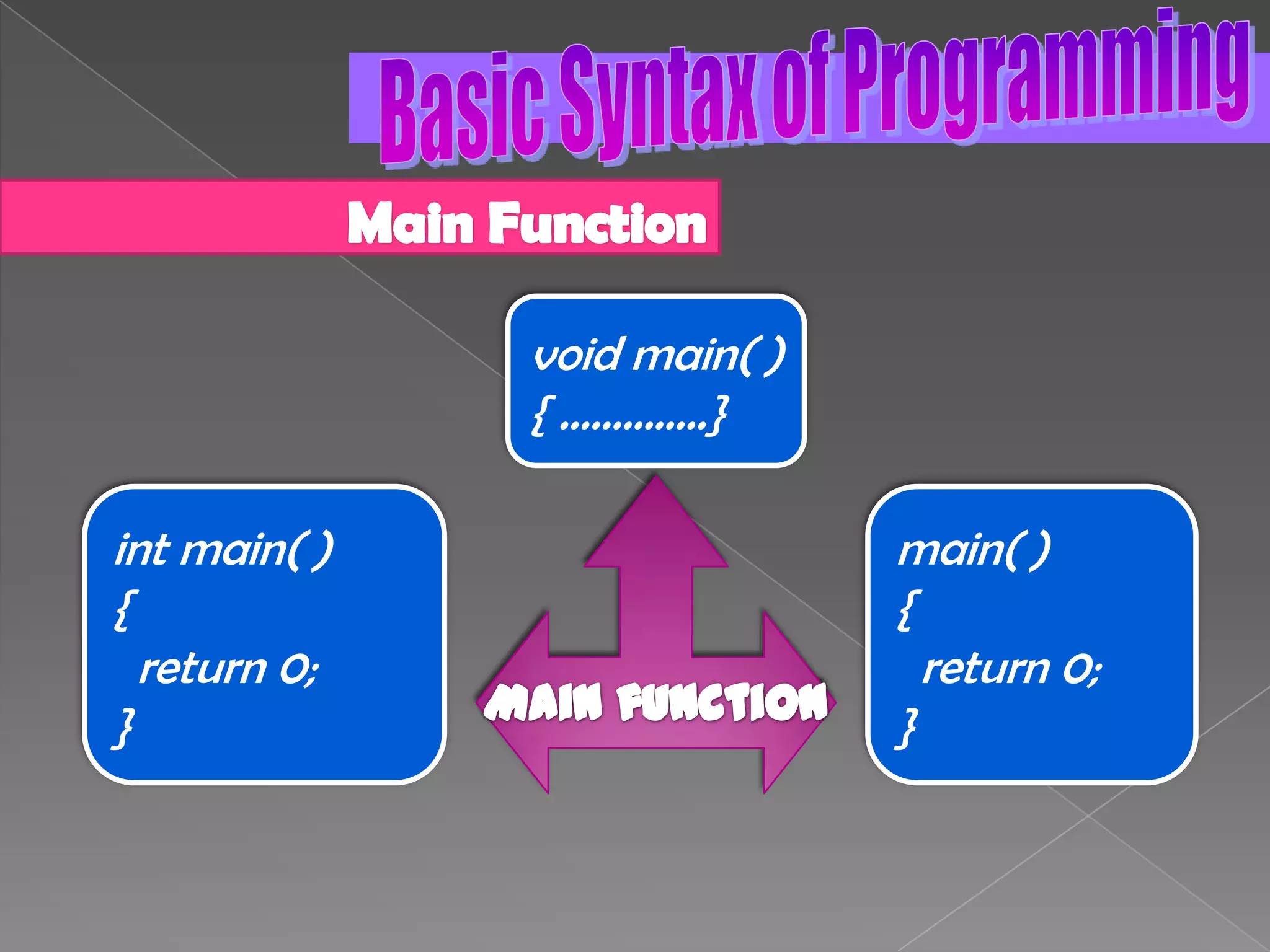
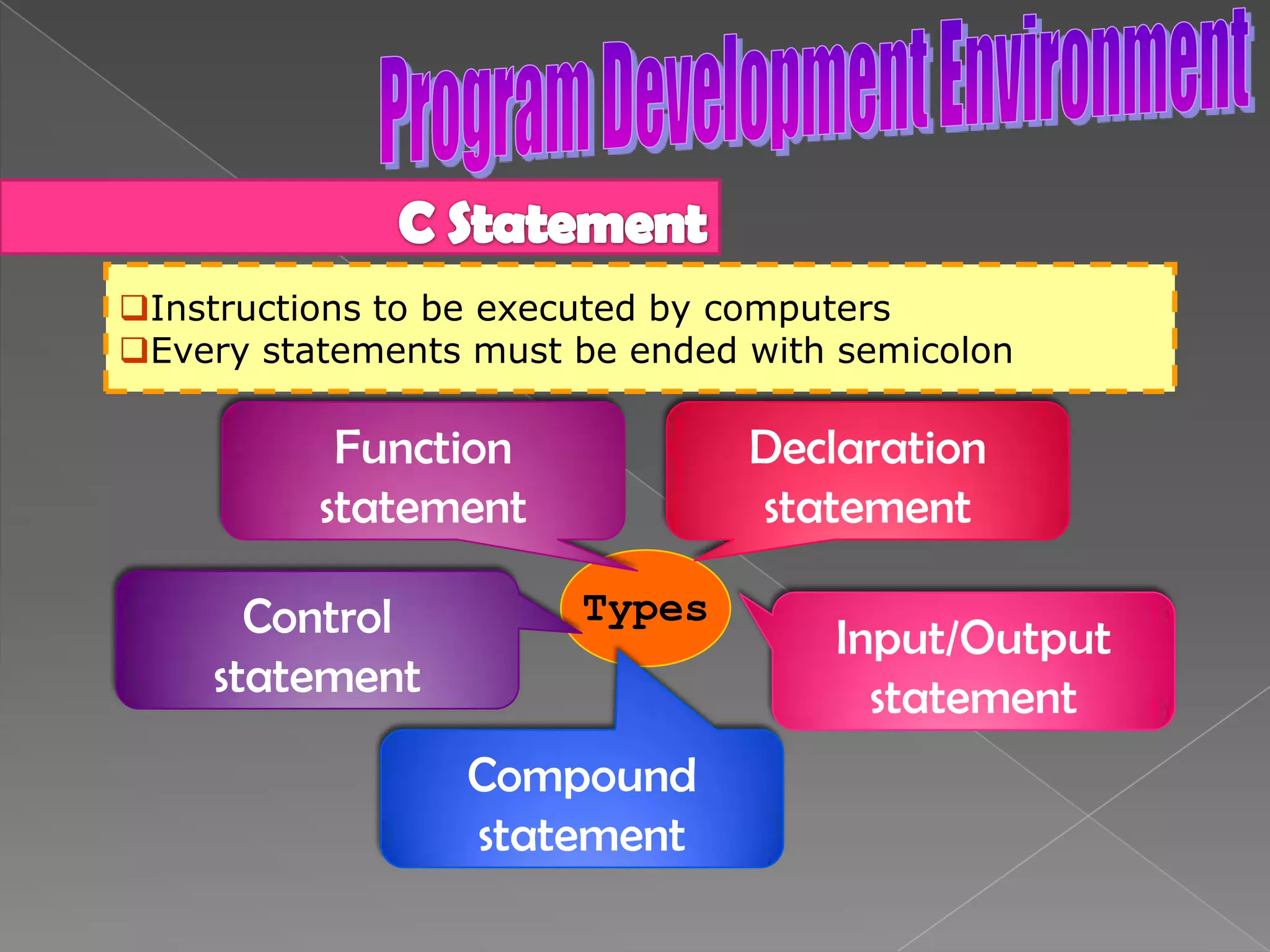
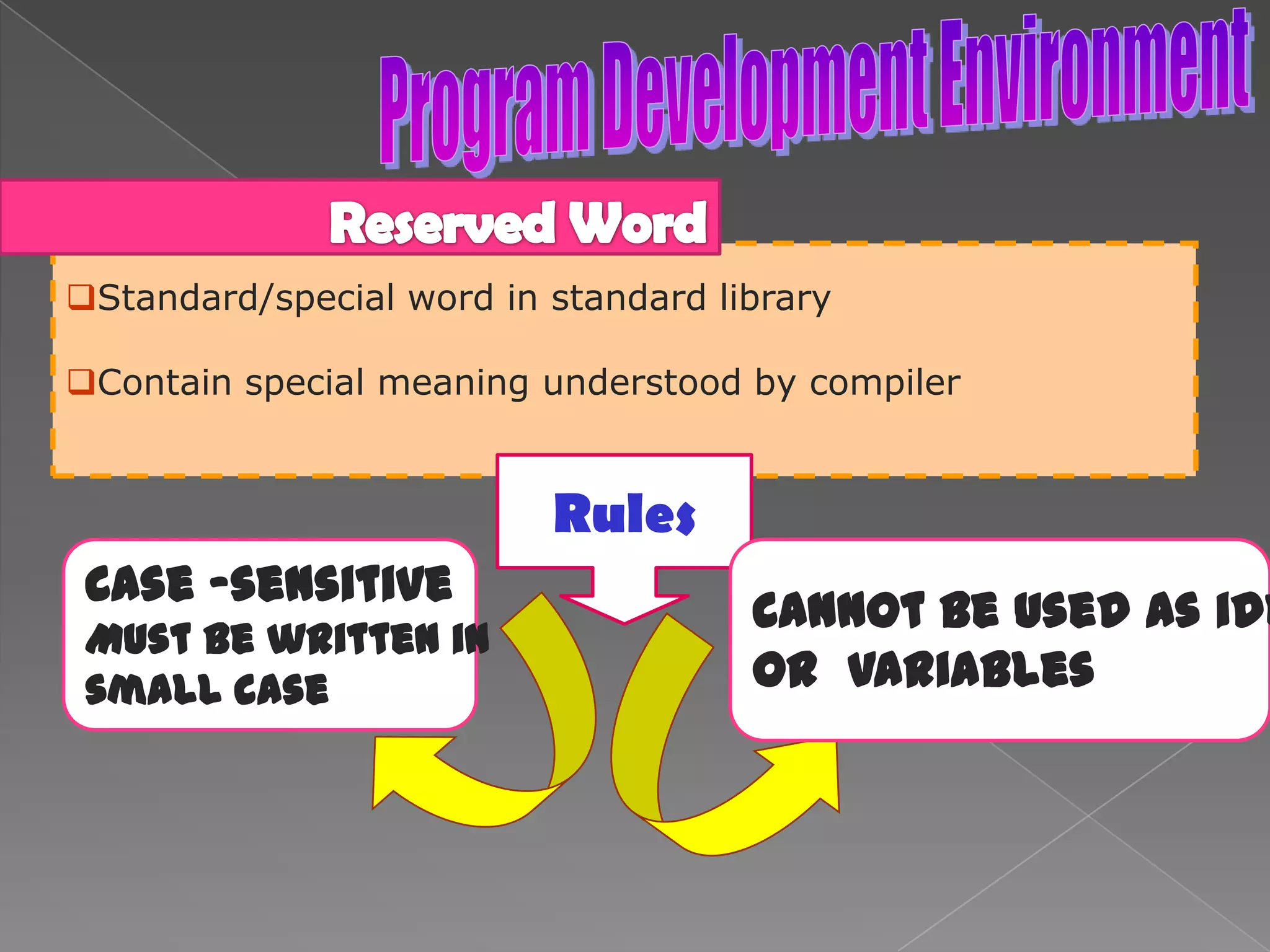
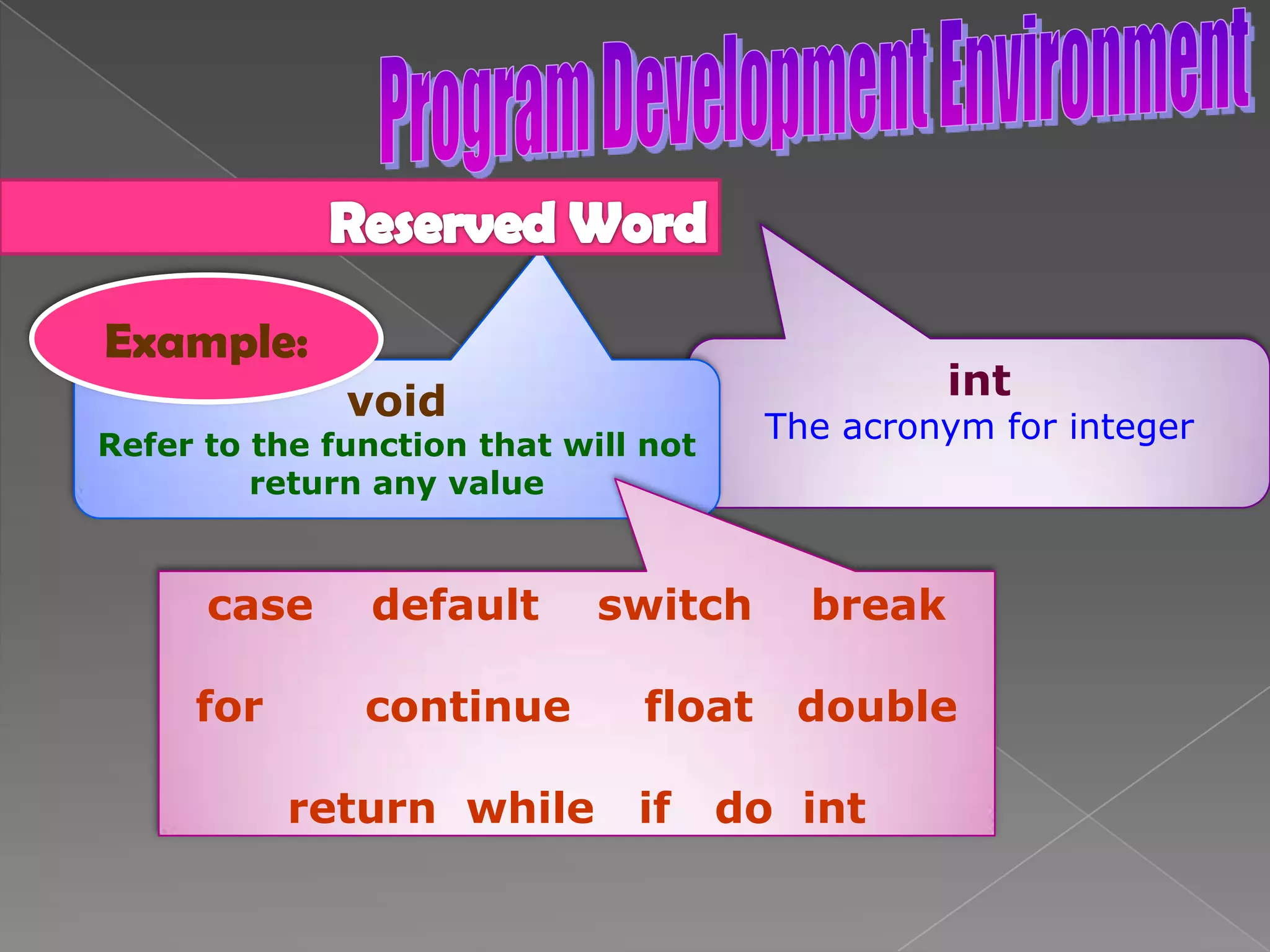
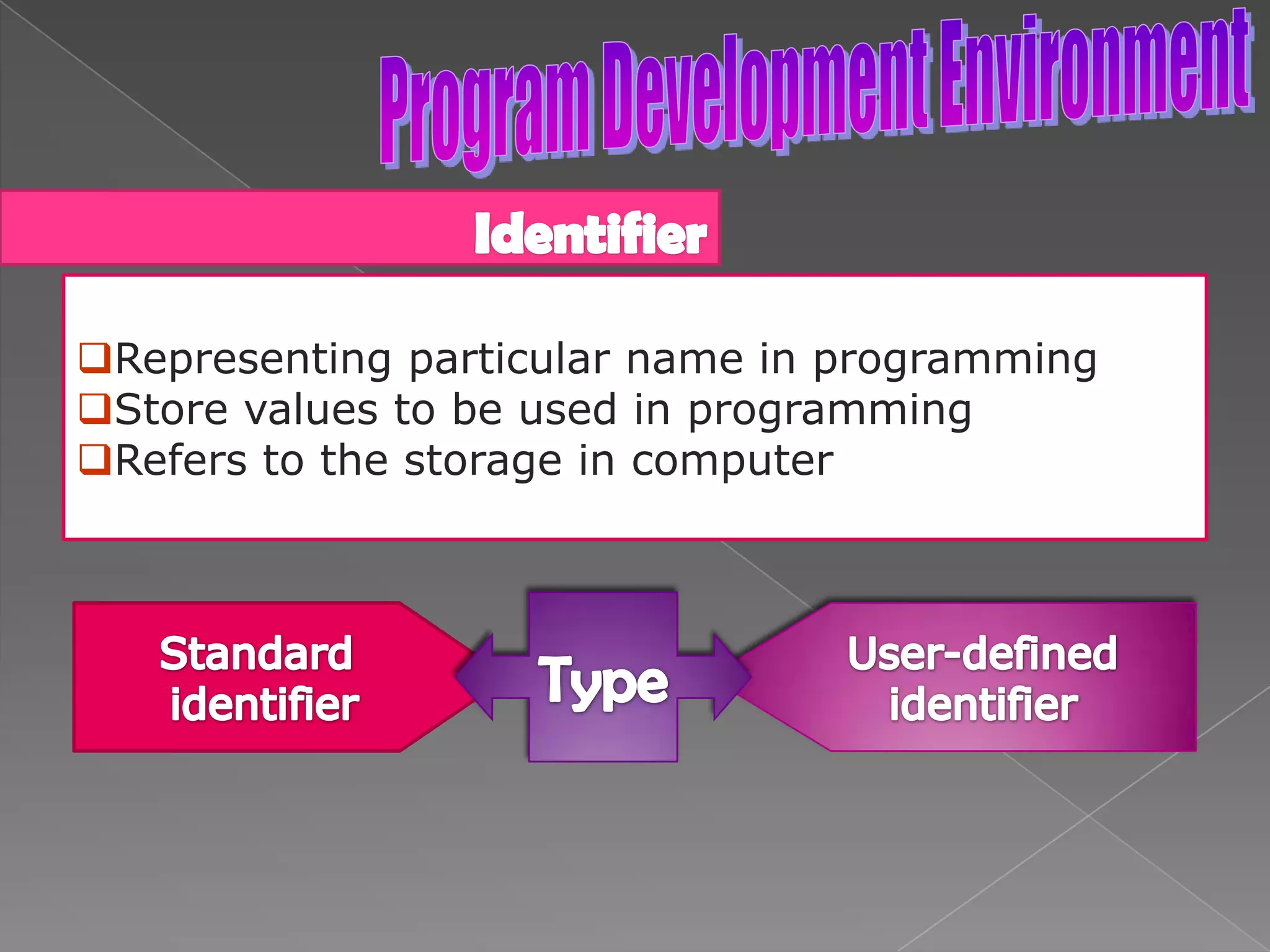
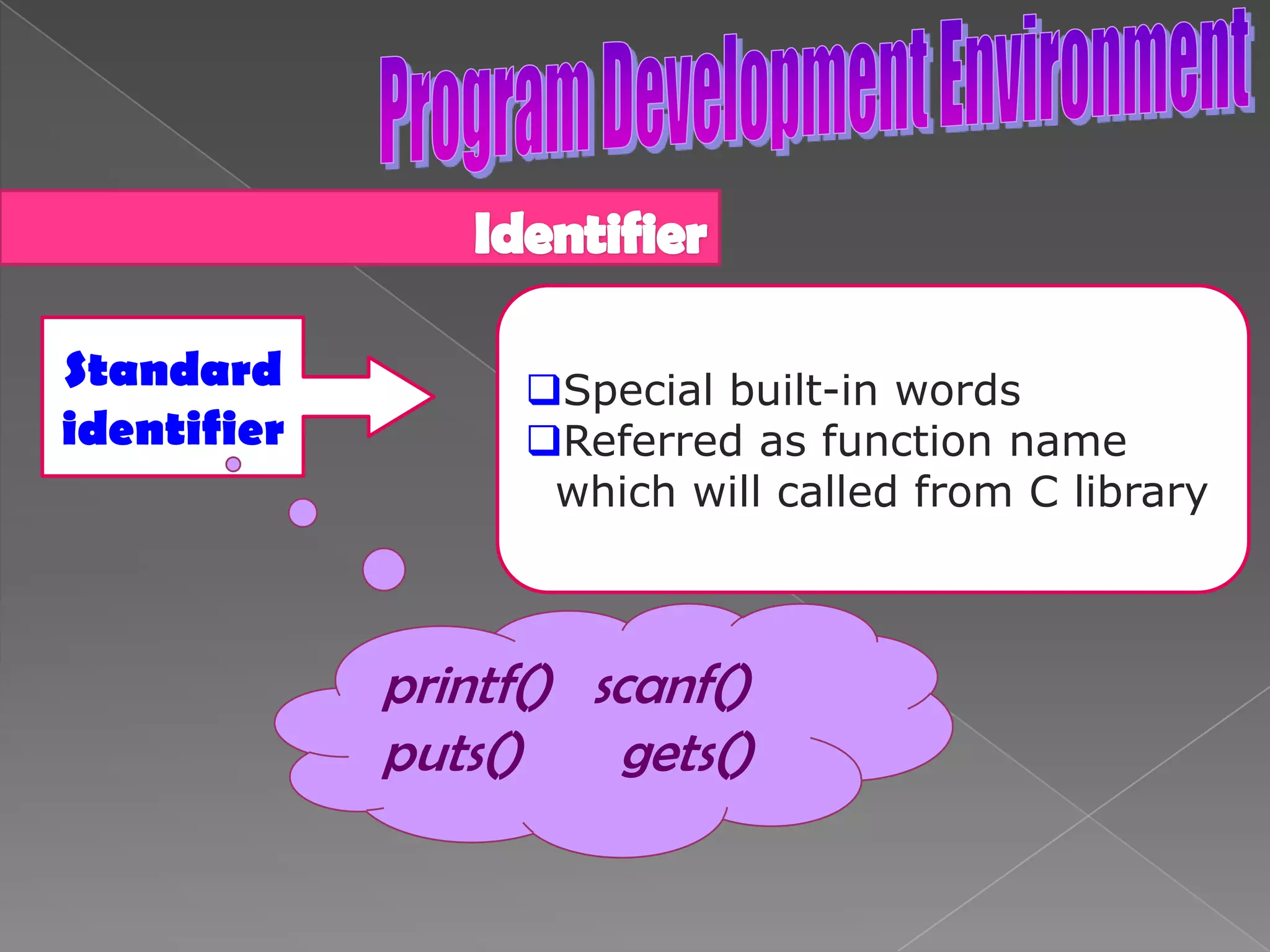
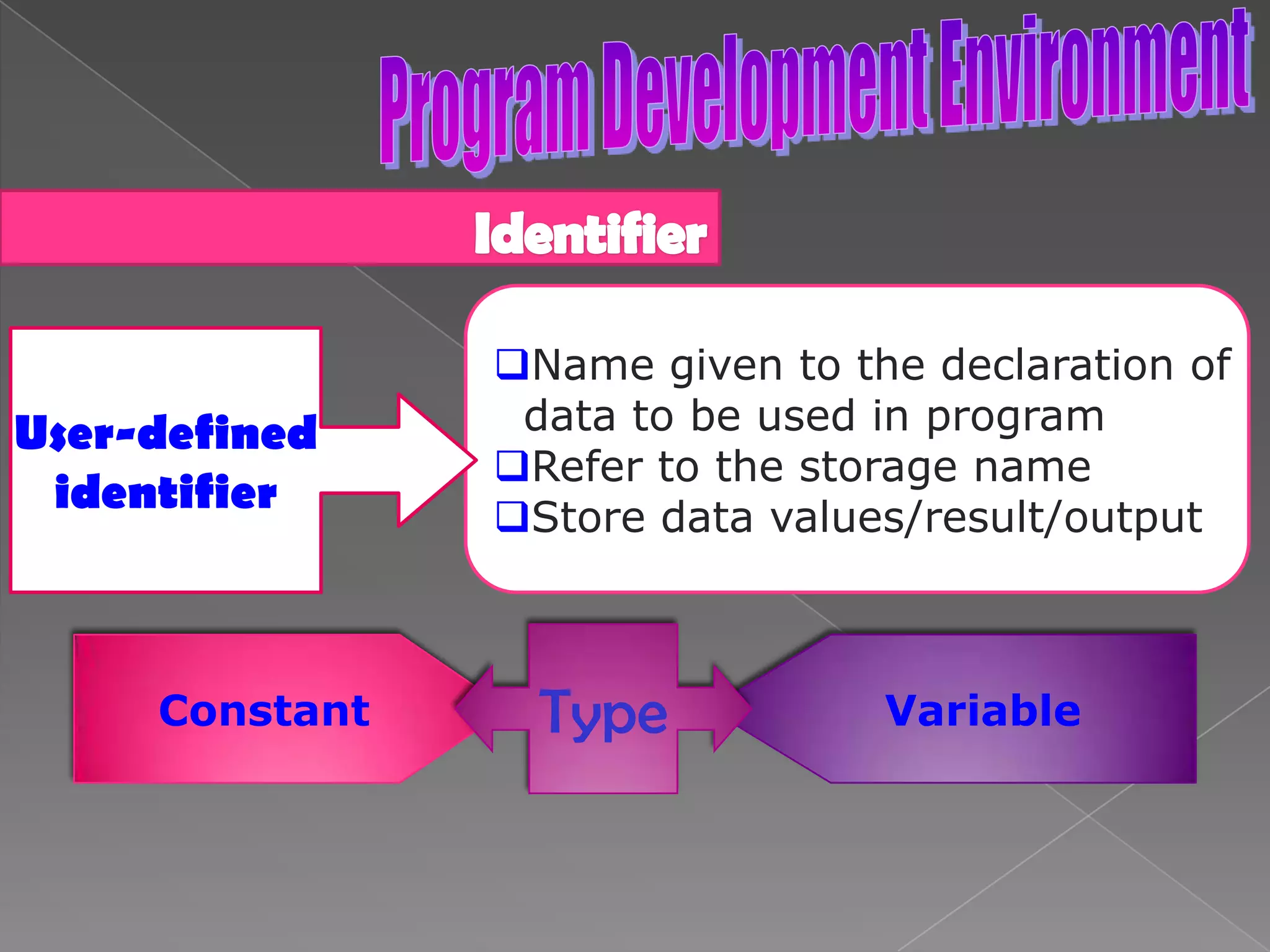
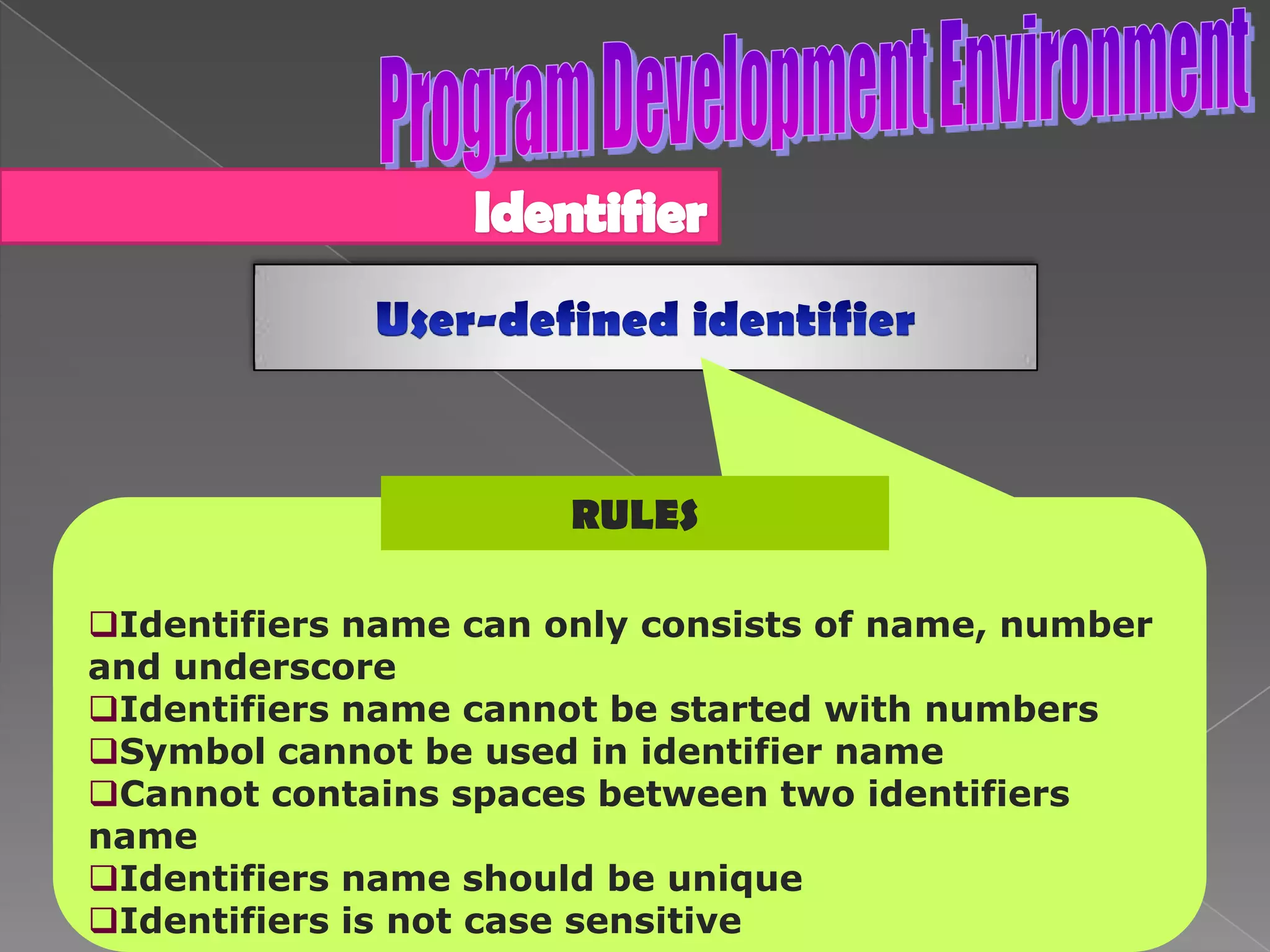
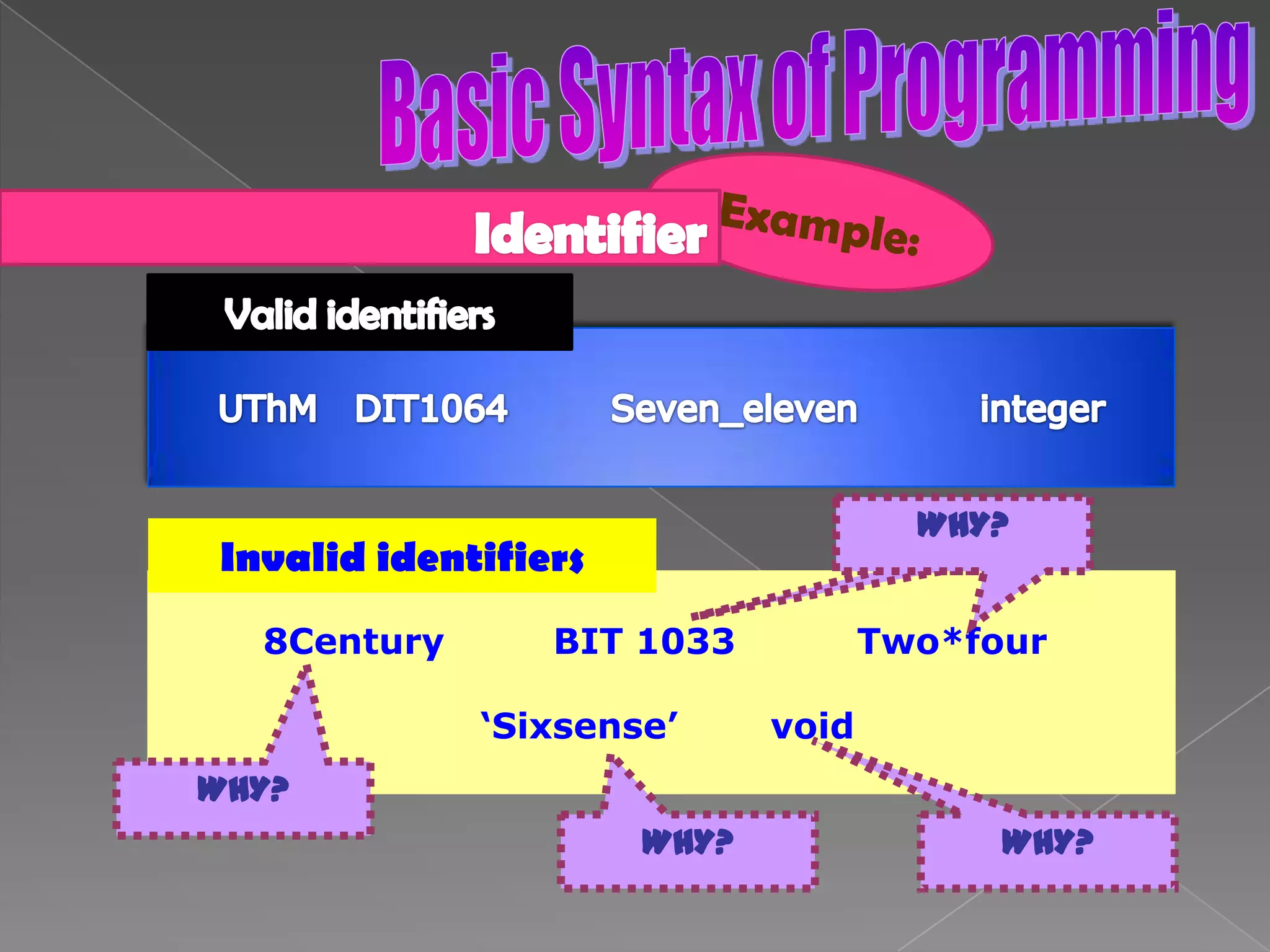
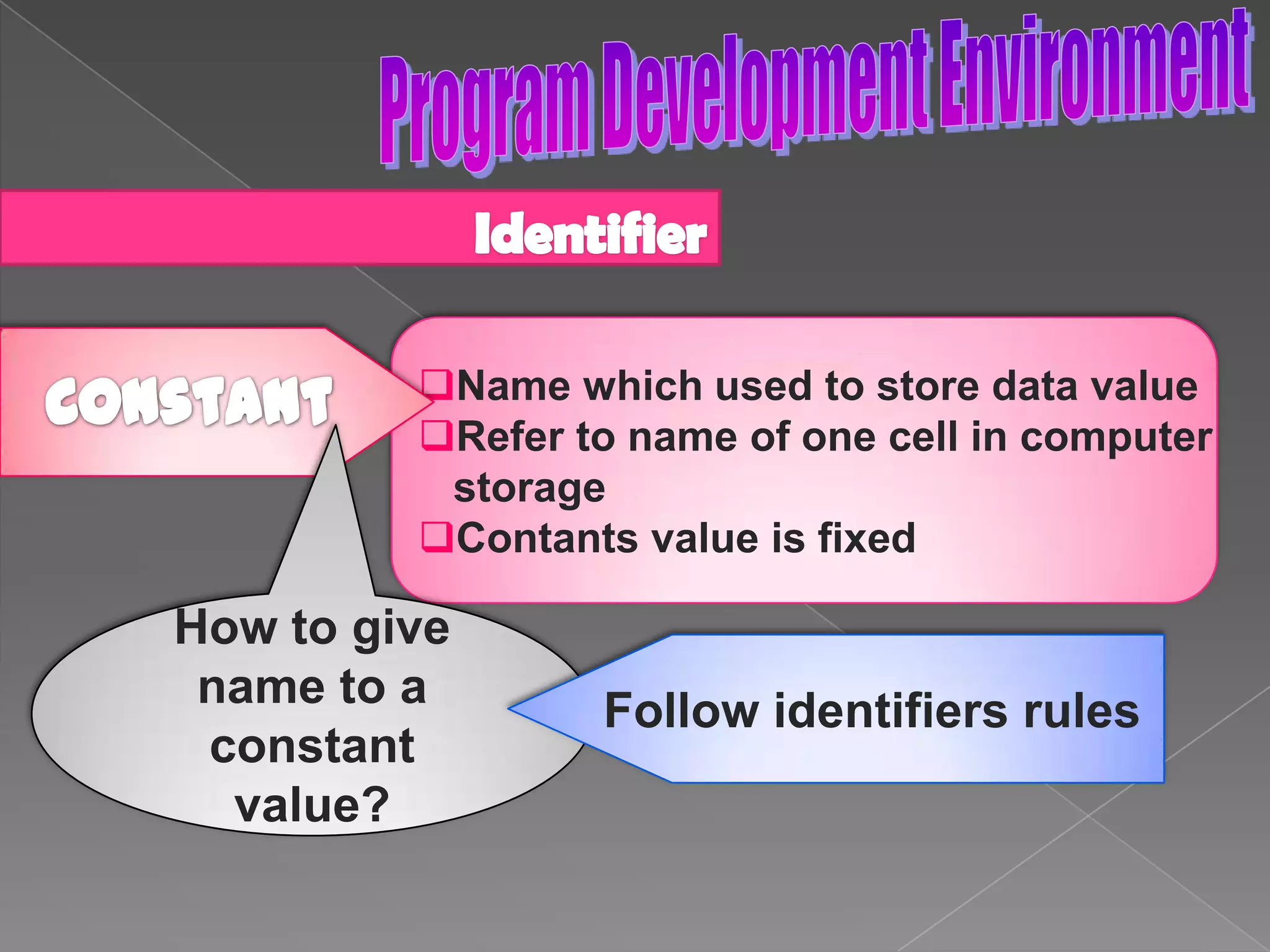
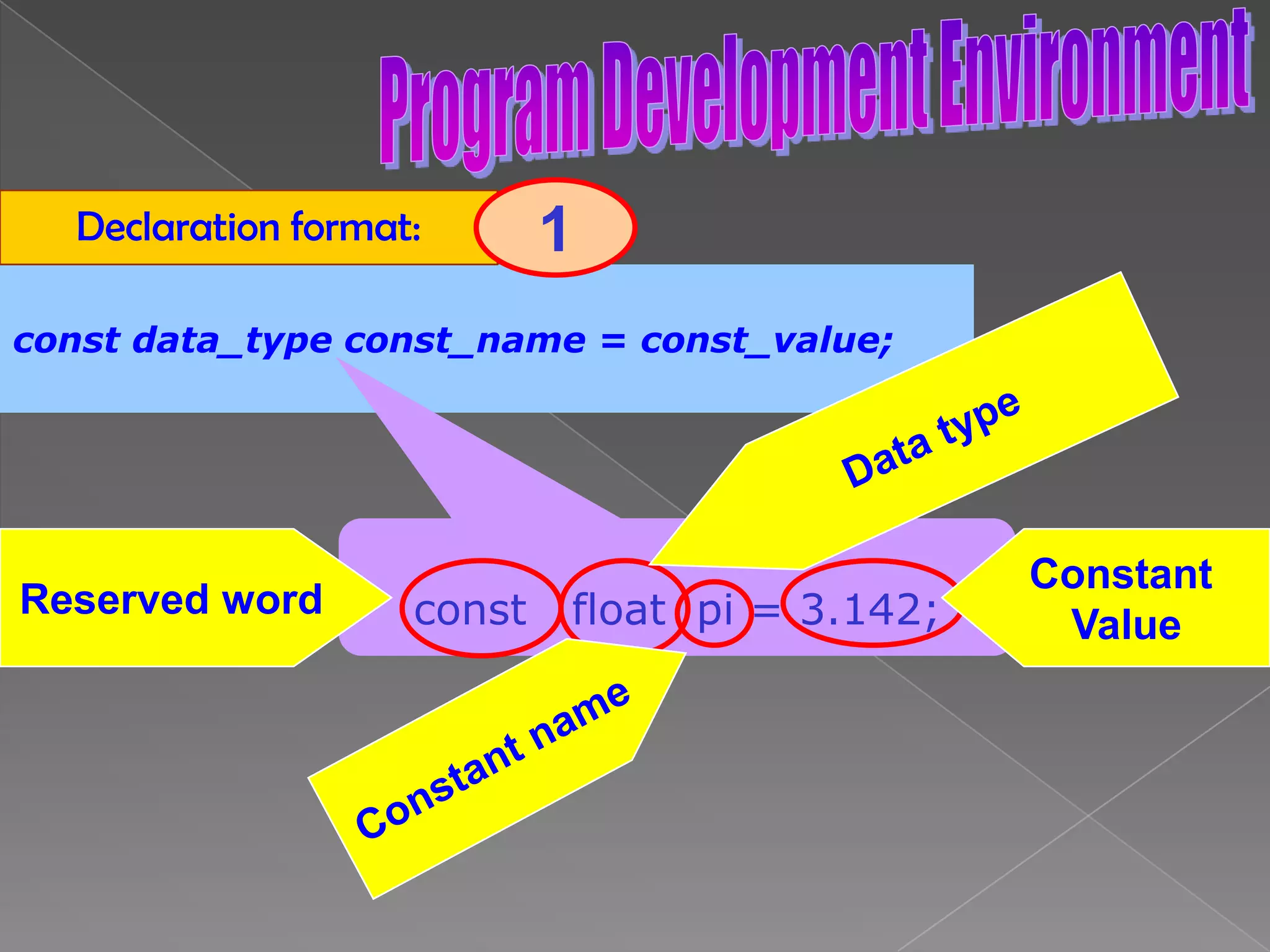
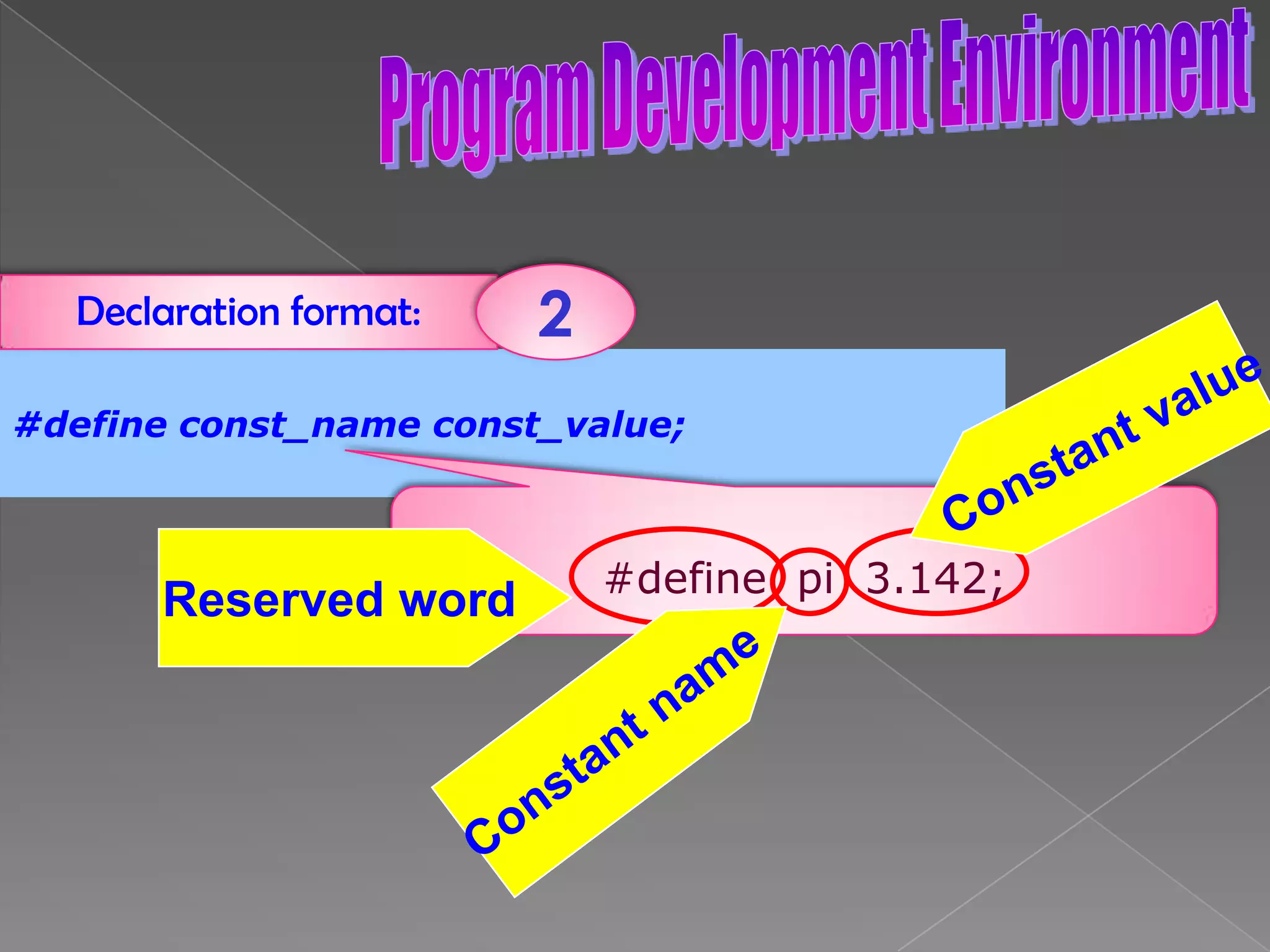
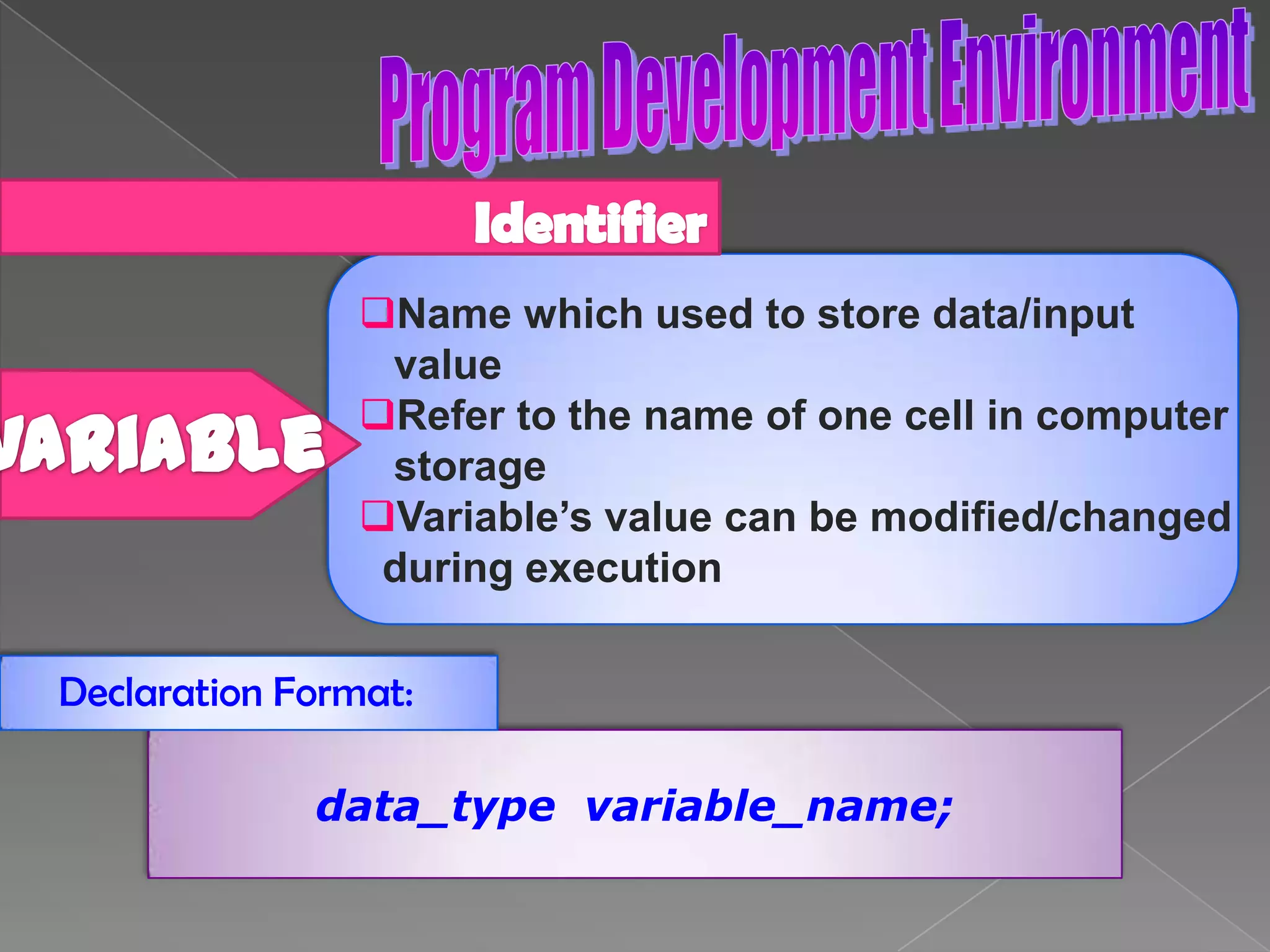
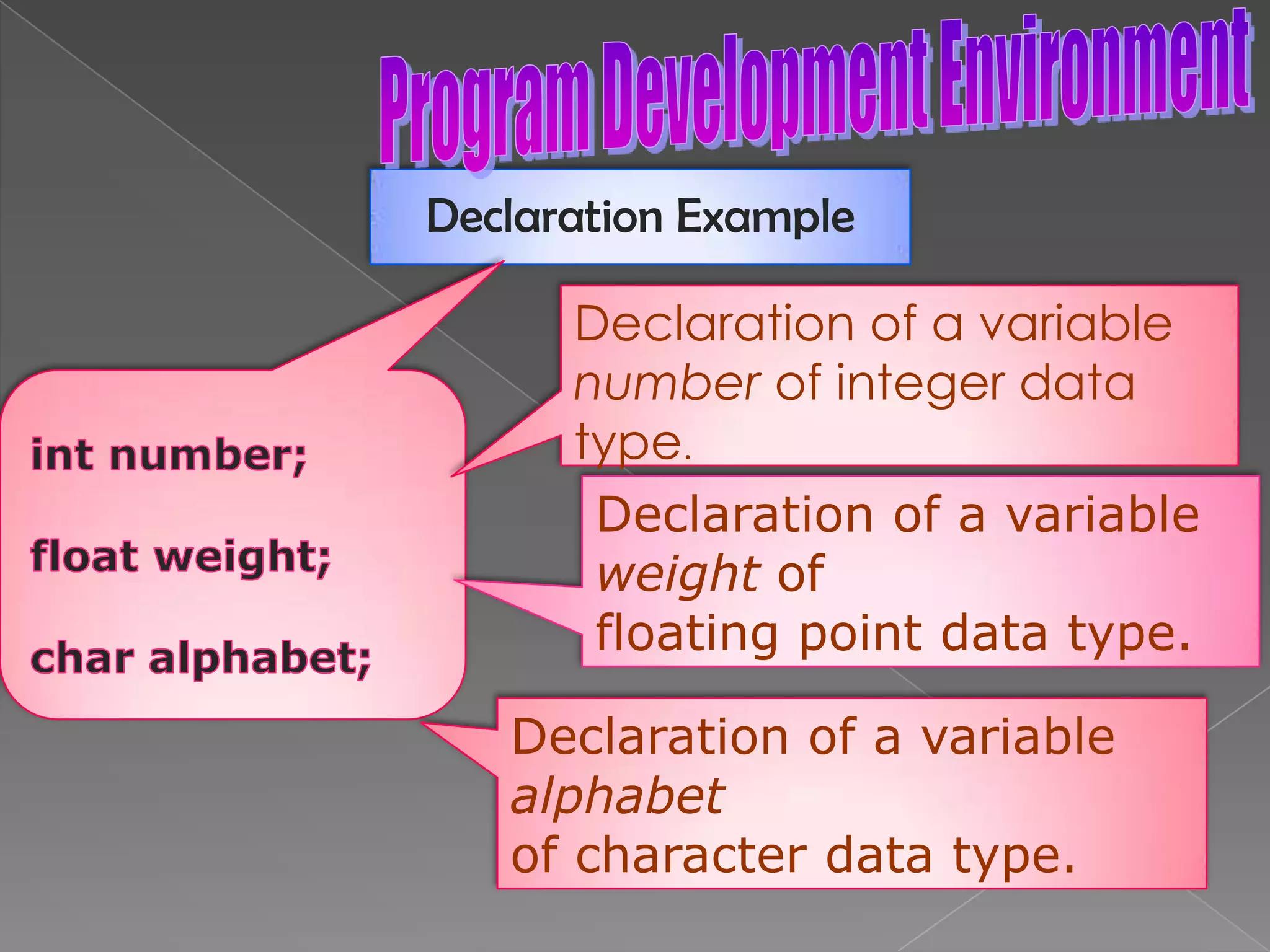
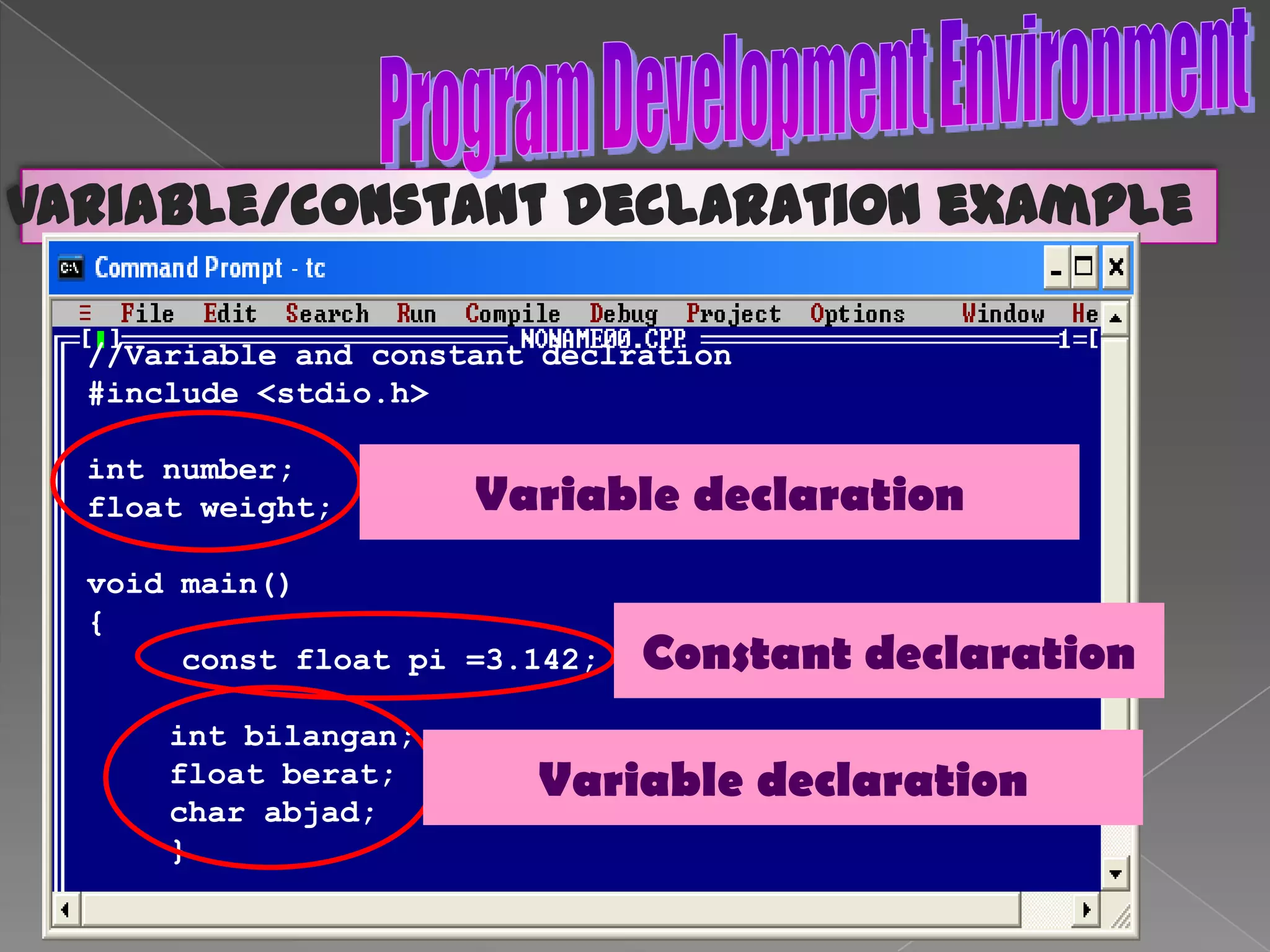
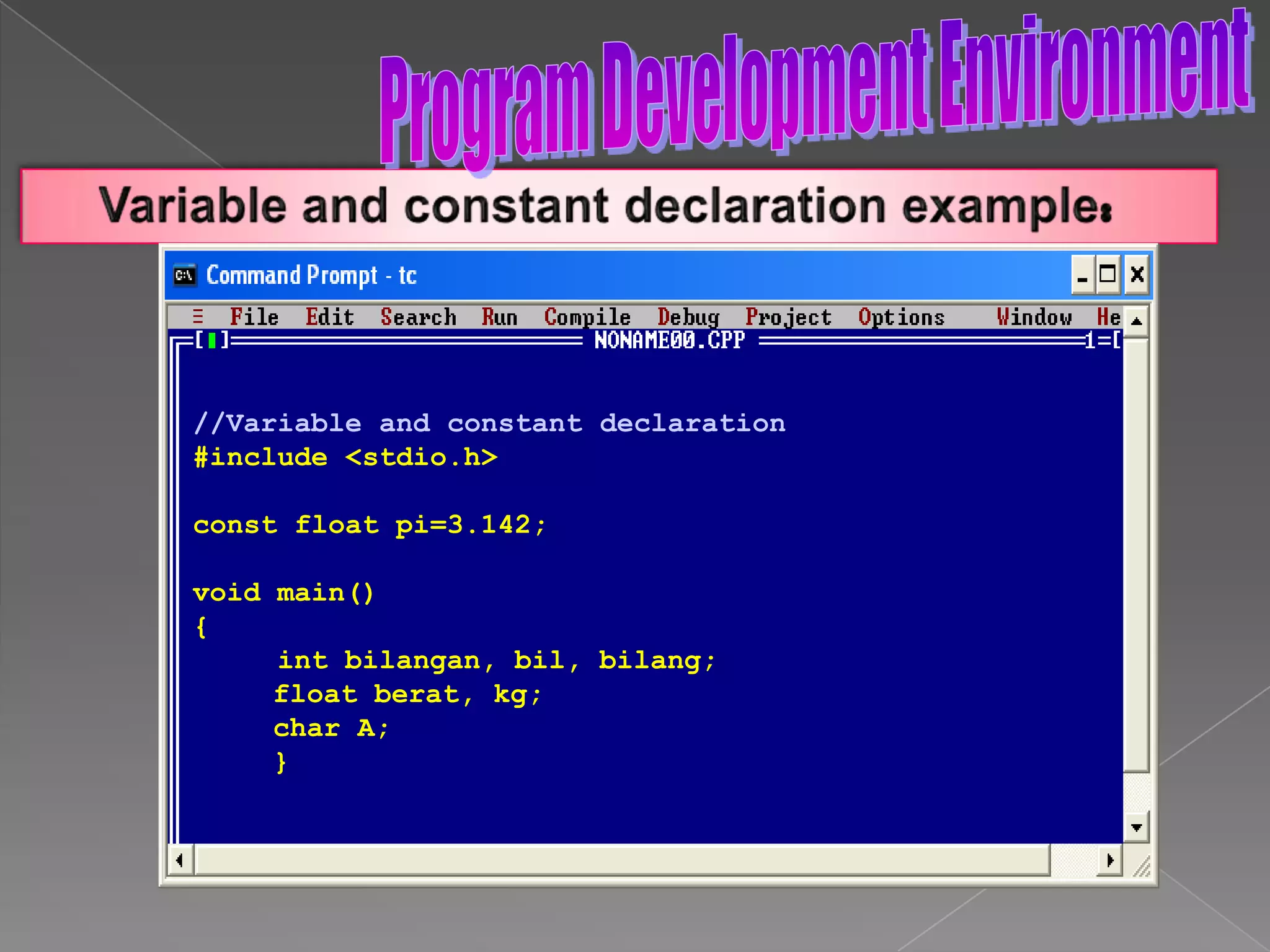
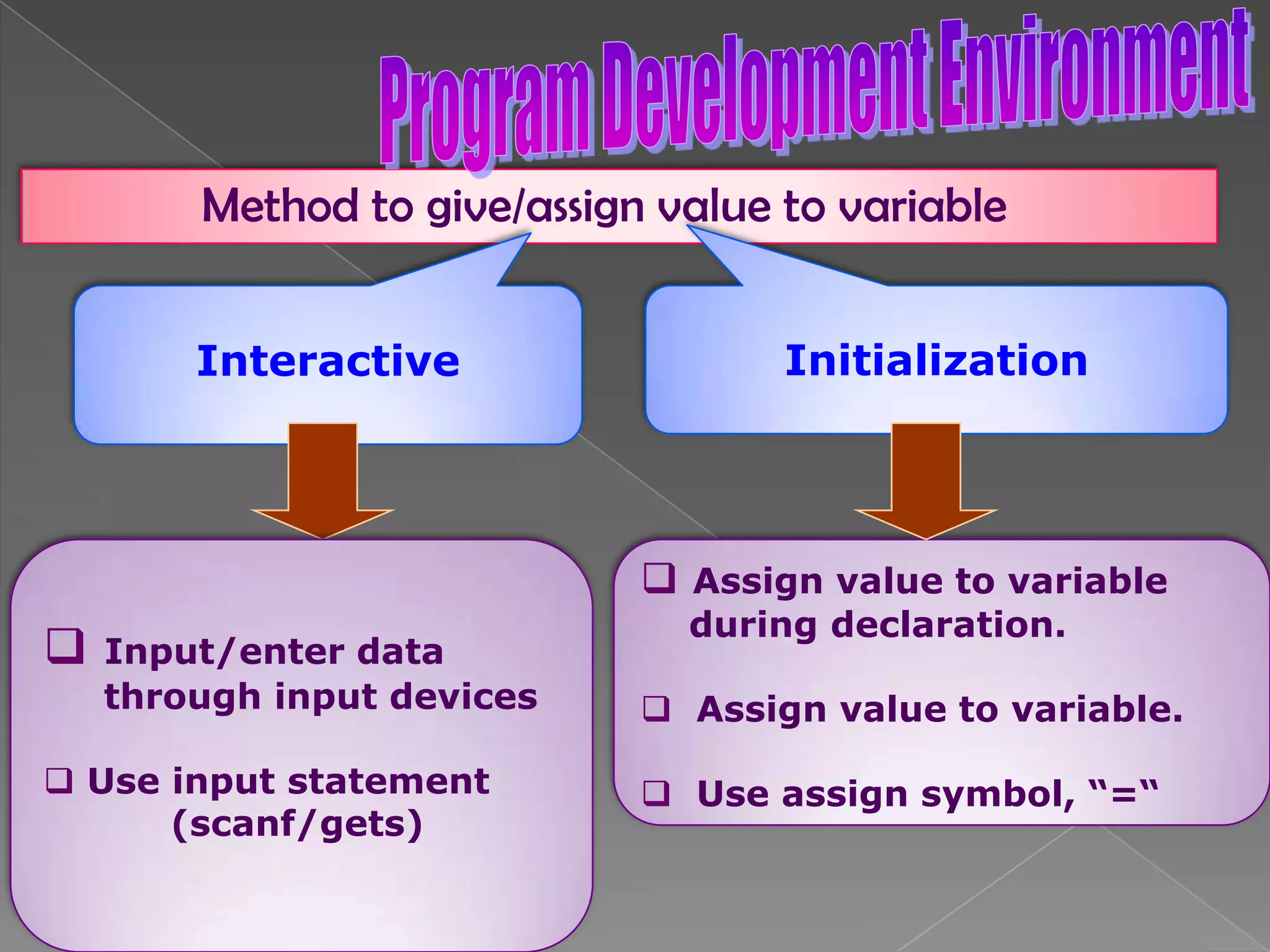
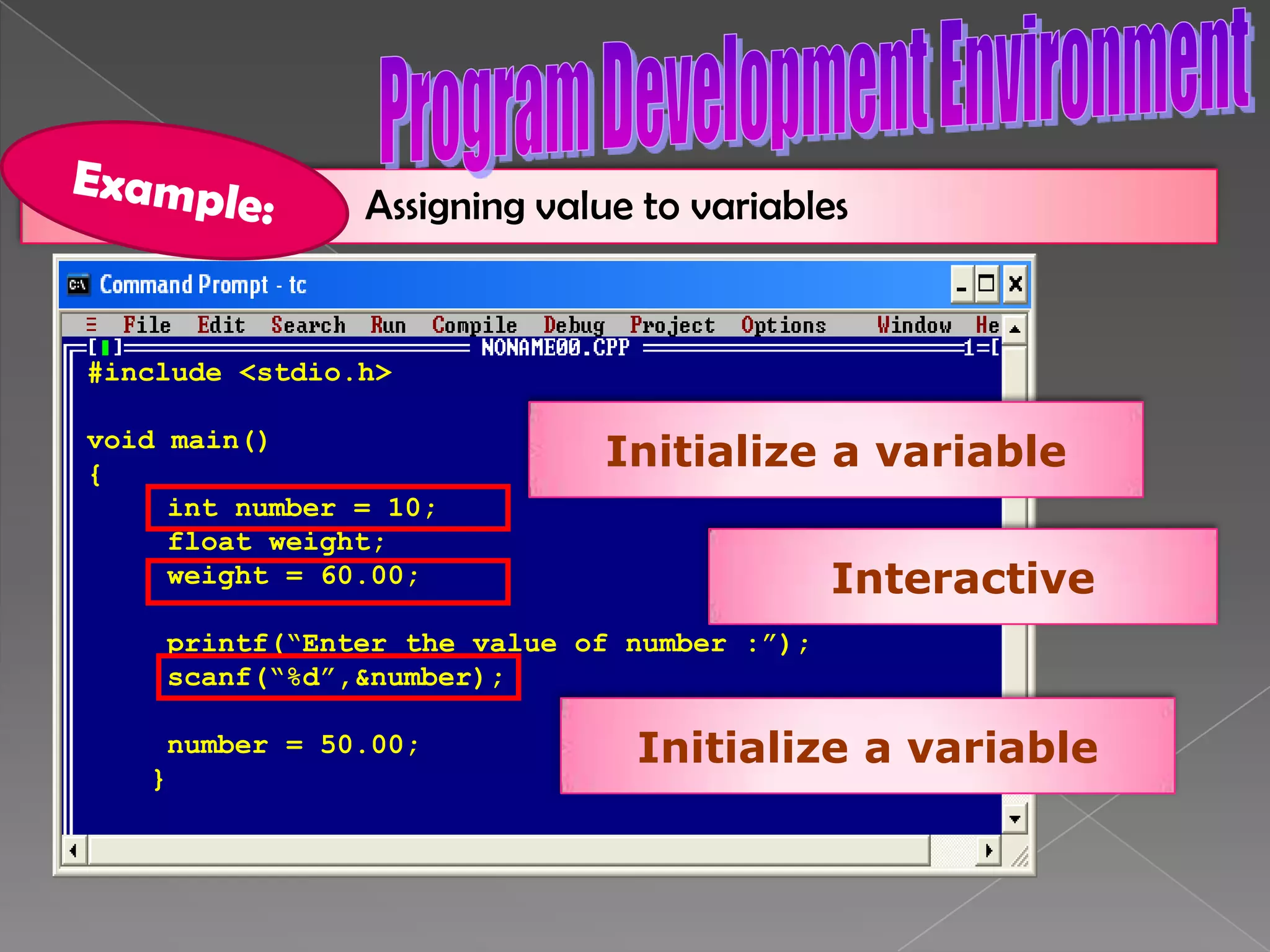
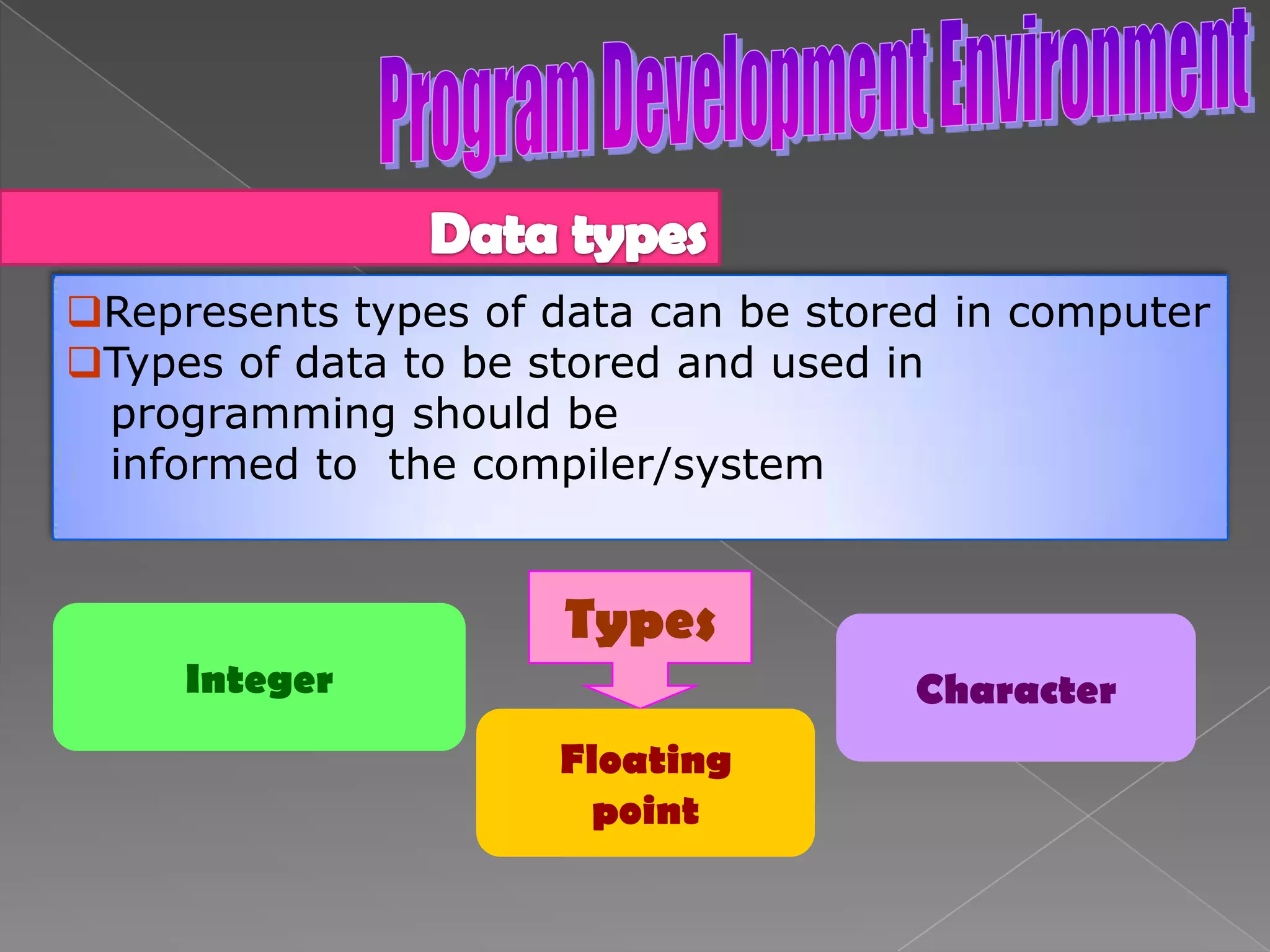
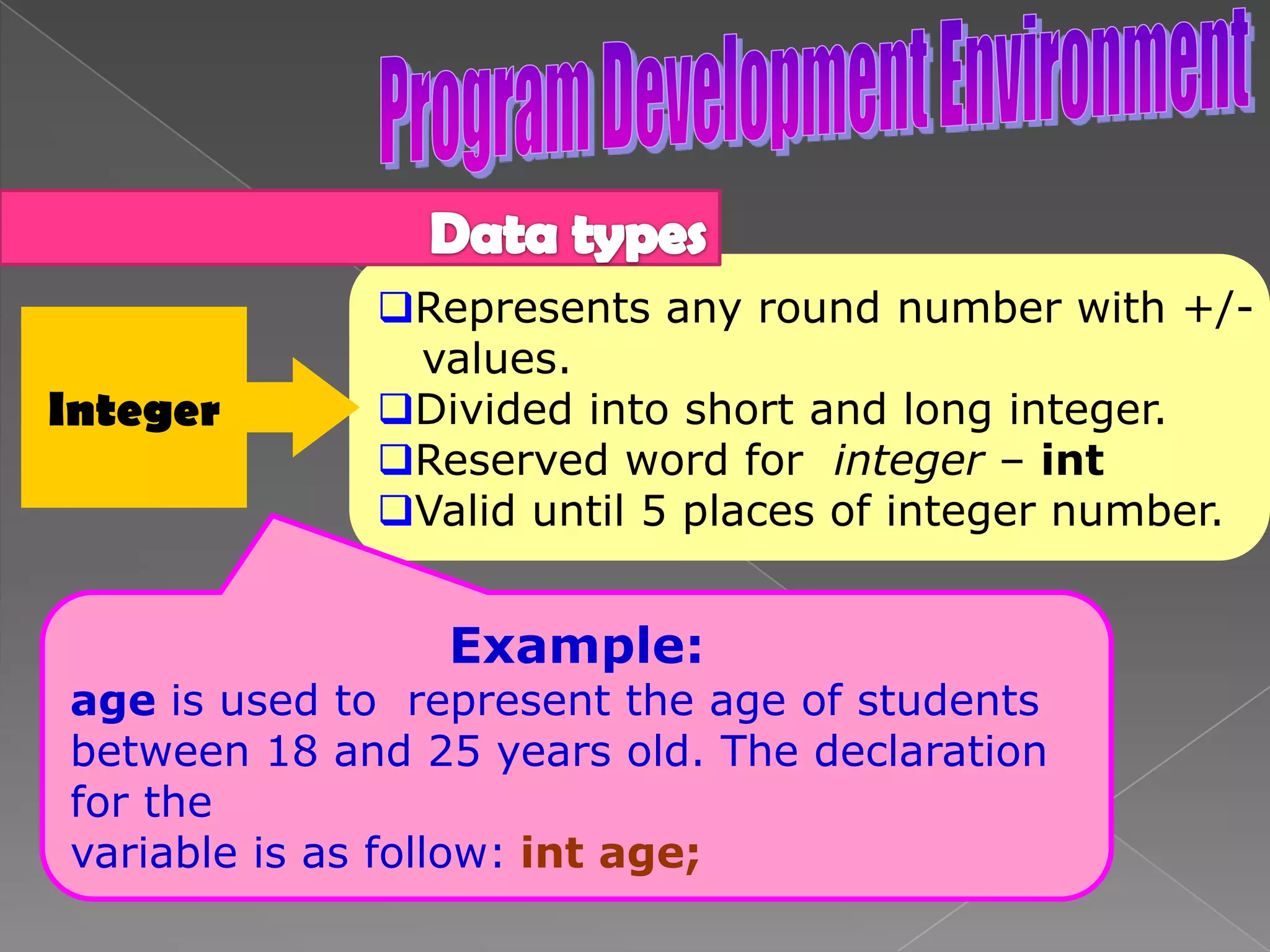
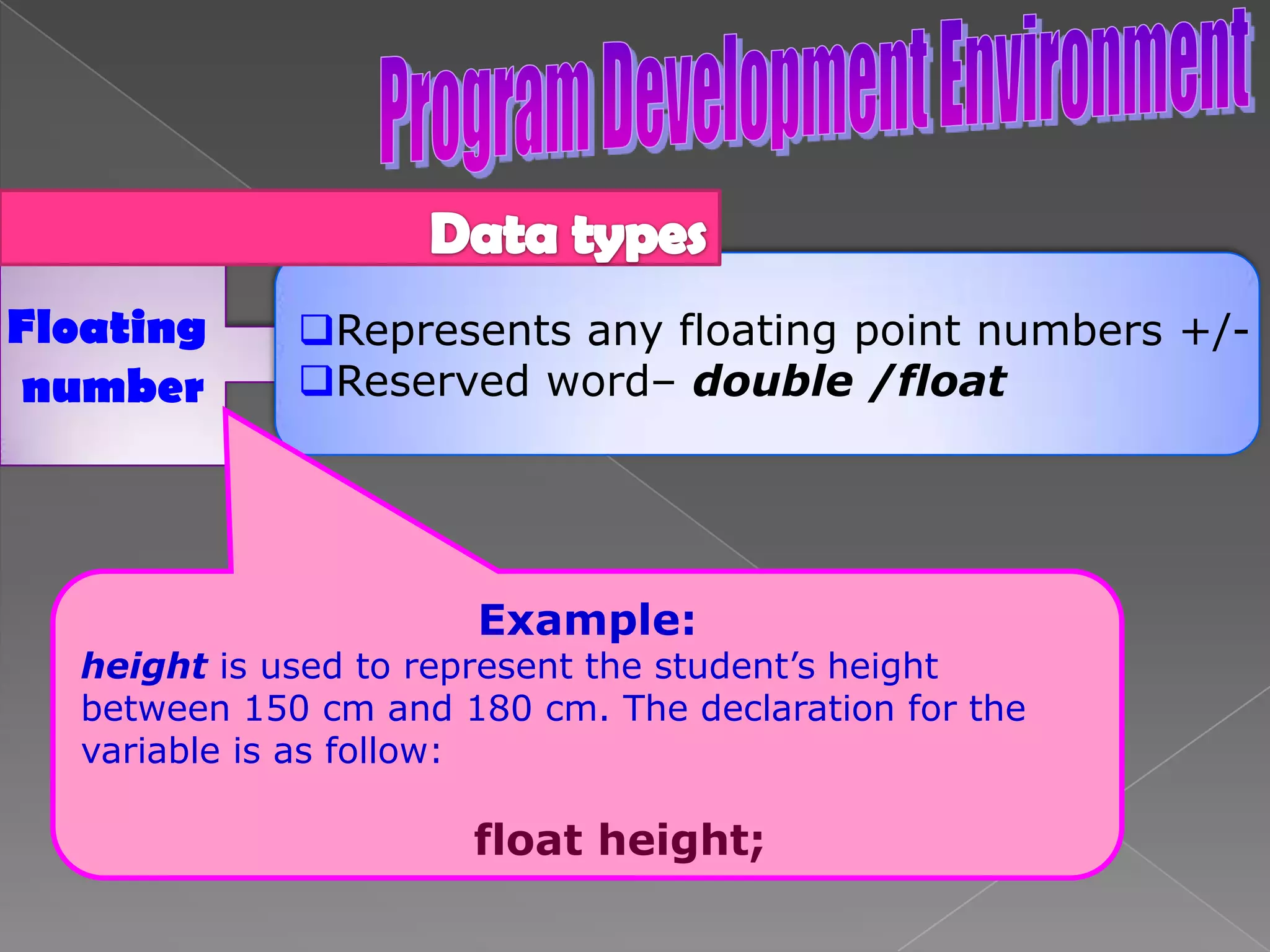
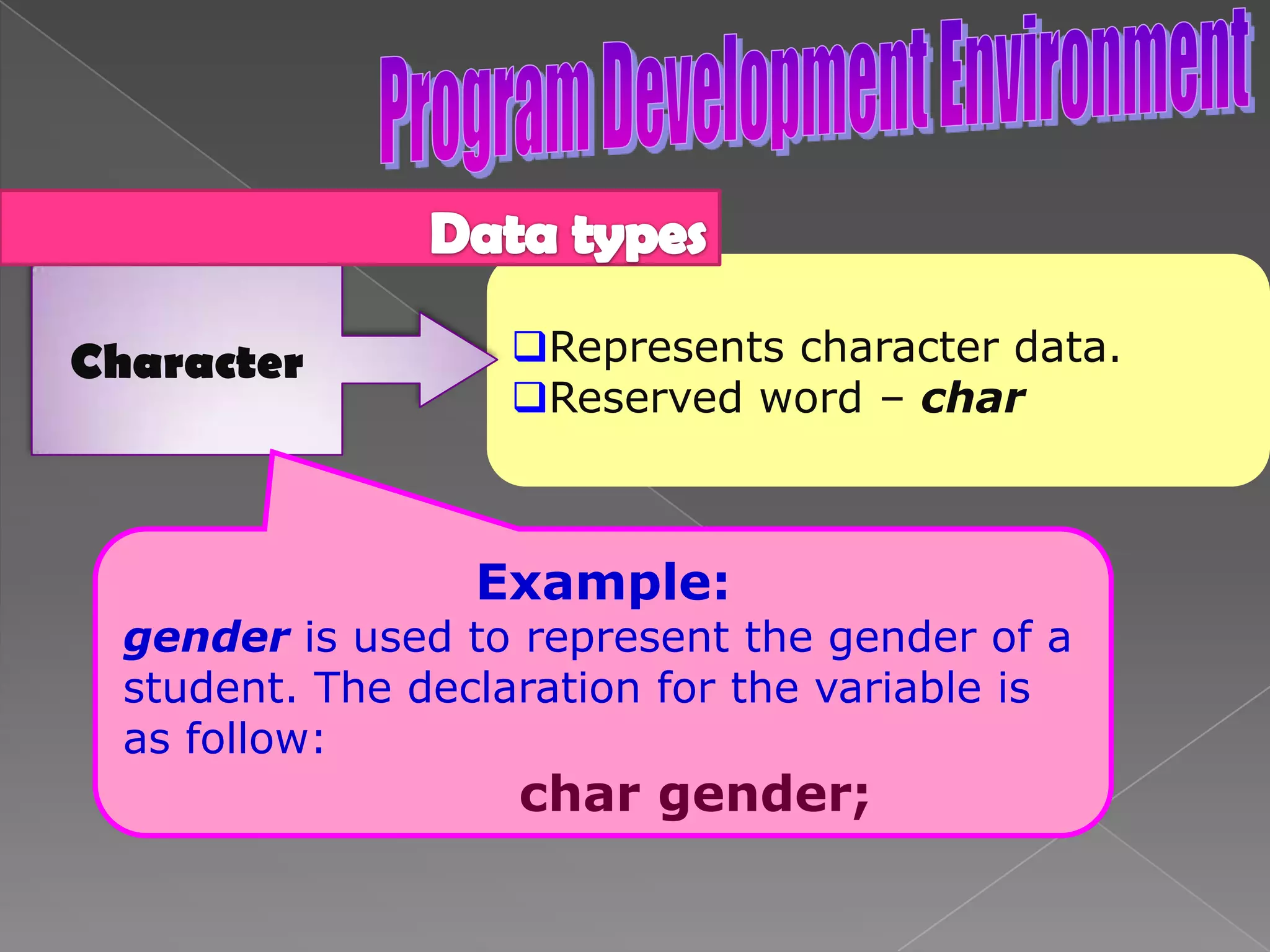
The document discusses the basic structure of computer programming, including the typical program development environment consisting of six phases: editing/writing, preprocessing, compiling, linking, loading, and executing. It also covers preprocessor directives, the main program structure, data types, variable declarations, common programming errors, and basic C syntax elements like identifiers, variables, constants, and comments.