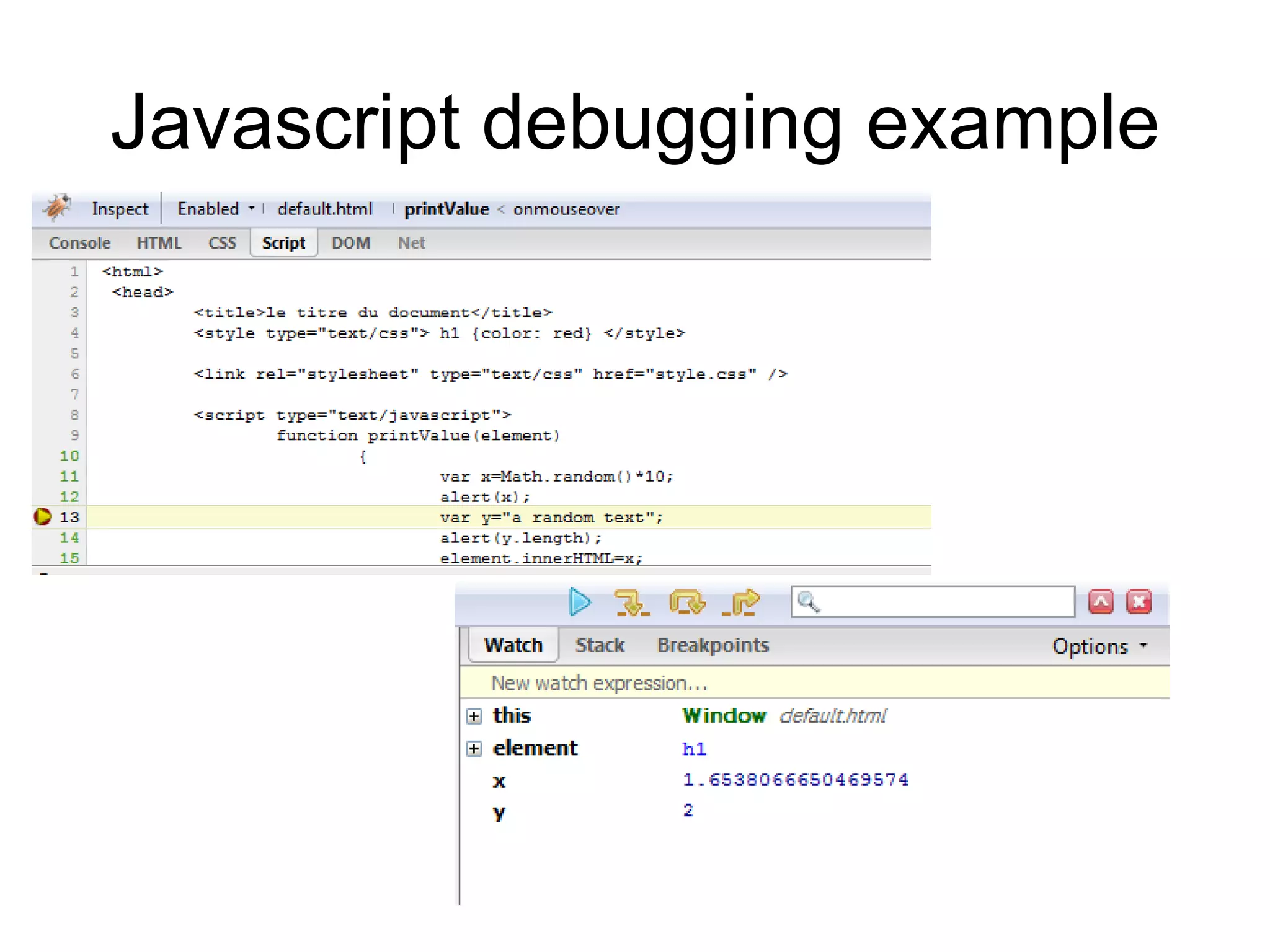
The document provides an introduction to JavaScript, including: 1) Why JavaScript was created, its syntax, and how to include it in HTML documents. 2) How JavaScript objects work and some predefined JavaScript objects like Math, String, and Array. 3) Examples of JavaScript functions, strings, and how to manipulate elements using the DOM. 4) JavaScript events and how code can run when events occur on HTML elements. 5) Methods for accessing and modifying DOM elements directly through properties, IDs, and collections.











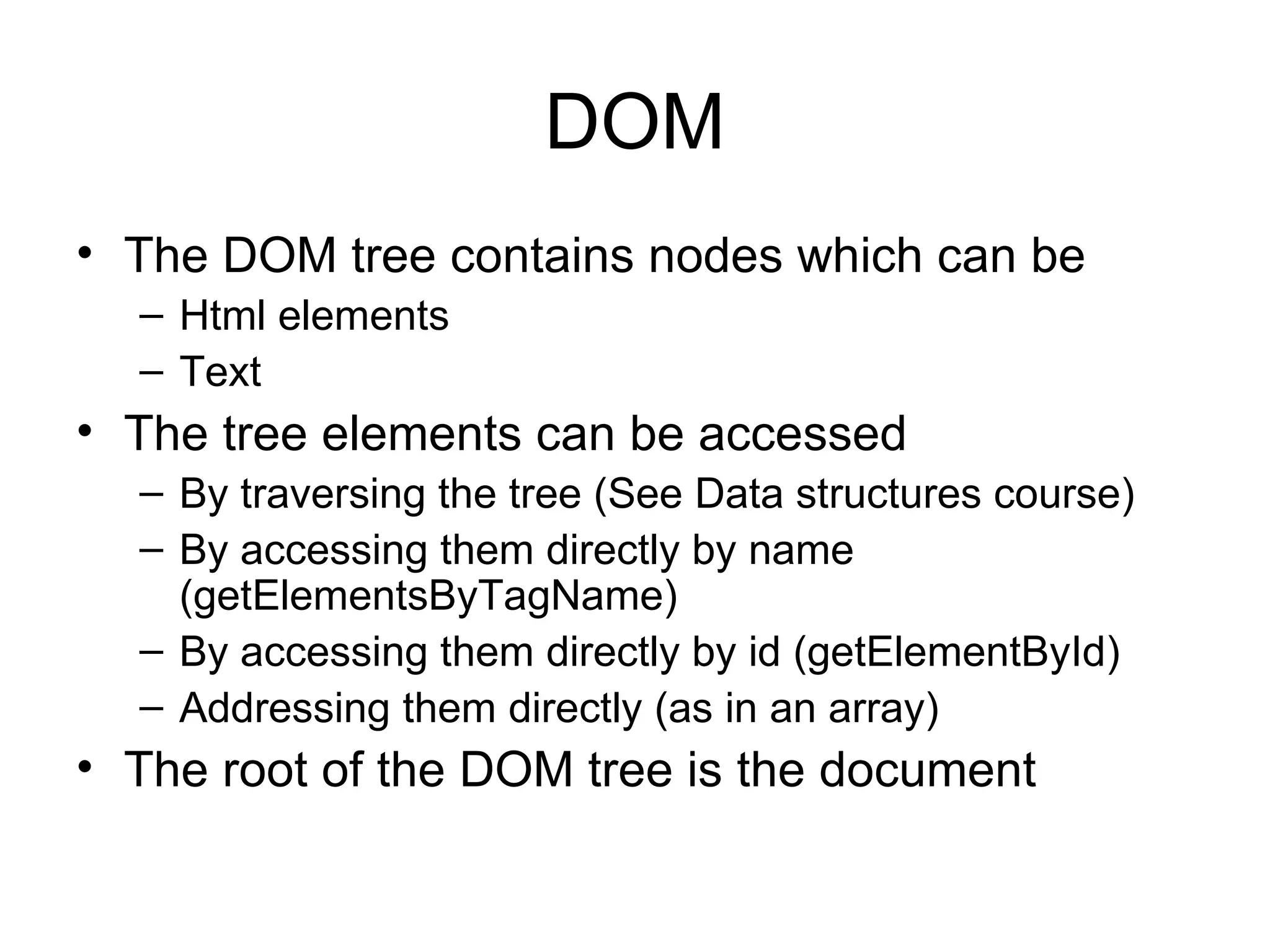

![DOM Methods and properties getElementsByTagName Returns an array of elements with a given name The we need to know the position of the element we need to modify inside the array function modifySecondH1() { var headersArray=document.getElementsByTagName("h1"); //retrieves all the elements whose names are h1 //elements’ numbering in the array starts at 0 headersArray[1].innerHTML=Math.random()*5; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c5-110405091639-phpapp02/75/C5-Javascript-17-2048.jpg)
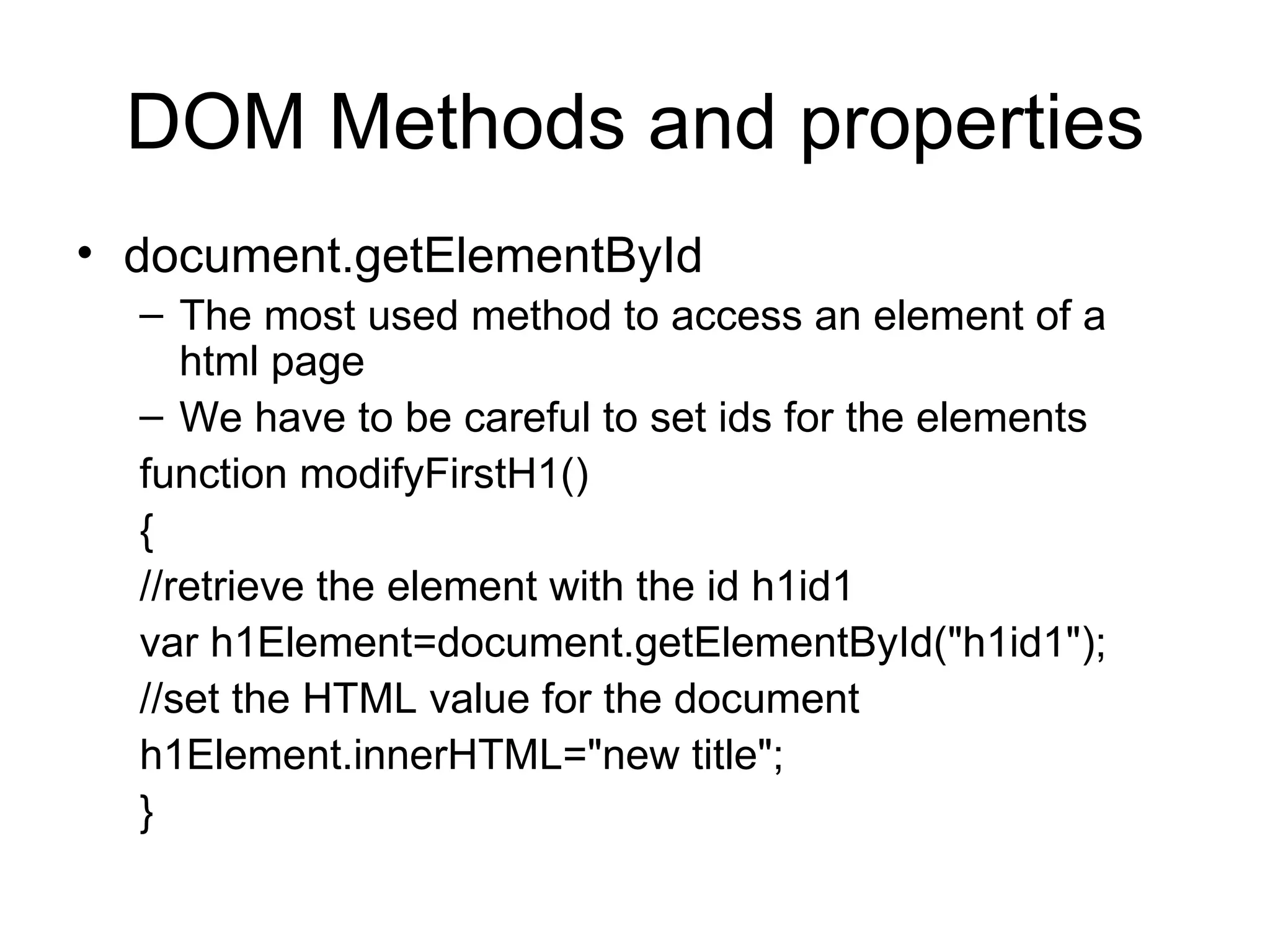
![DOM objects methods and properties Direct access to the element Predefined collections Forms Links Images document.forms[0].username.value – accesses the first form in the document and sets the value property for the username input](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c5-110405091639-phpapp02/75/C5-Javascript-19-2048.jpg)

![Validate forms with Javascript – example (I) function validateForm(){ var usernameElement=document.getElementById("username"); var passwordElement=document.getElementById("password"); var rePasswordElement=document.getElementById("repassword"); if(passwordElement.value!=rePasswordElement.value || passwordElement.value.length==0) {alert("please make sure the password is entered the same twice");return;} if (usernameElement.value.length<4) {alert("please make sure the username is longer than 4 letters");return; } document.forms[0].submit(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c5-110405091639-phpapp02/75/C5-Javascript-21-2048.jpg)