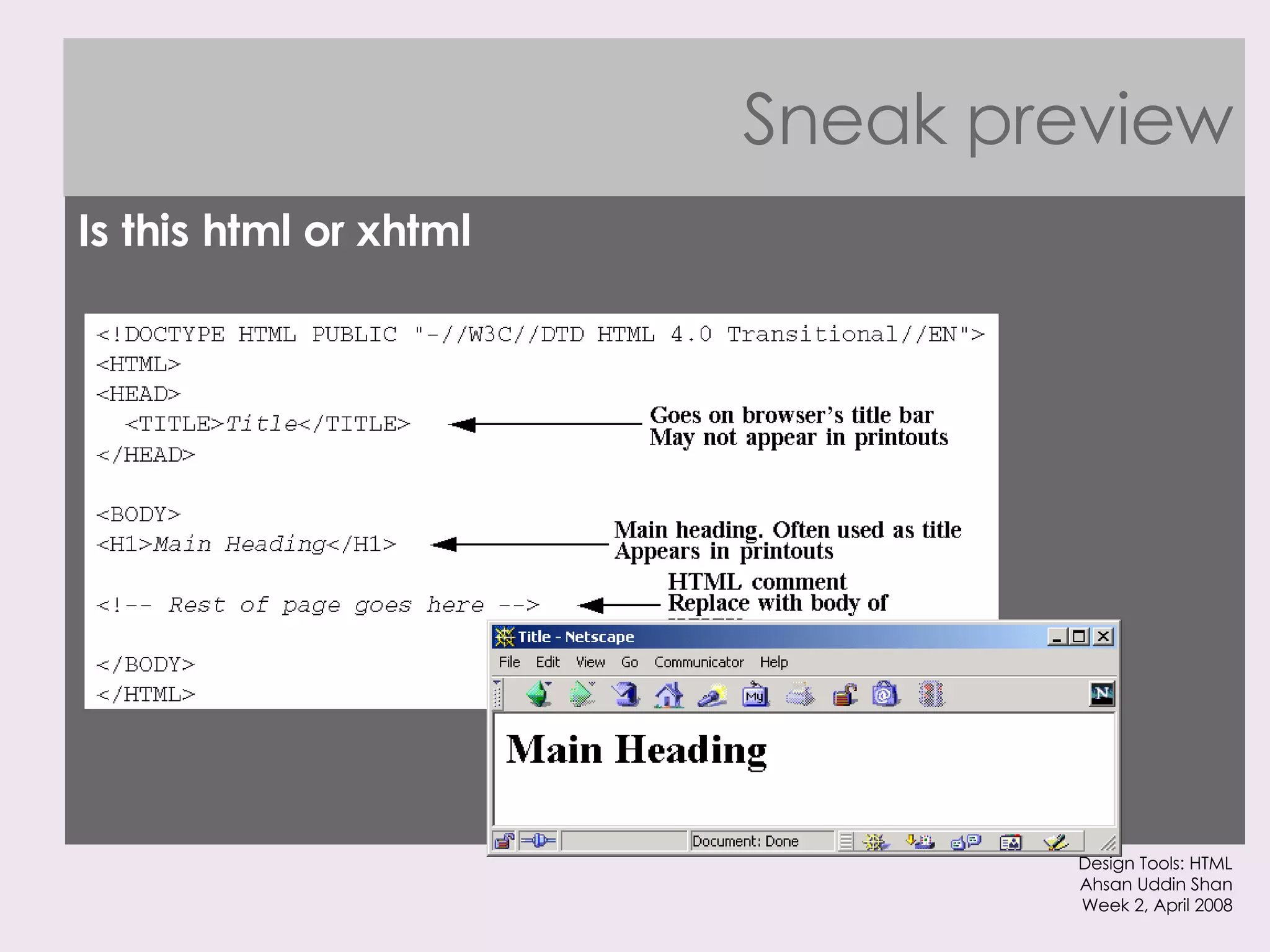
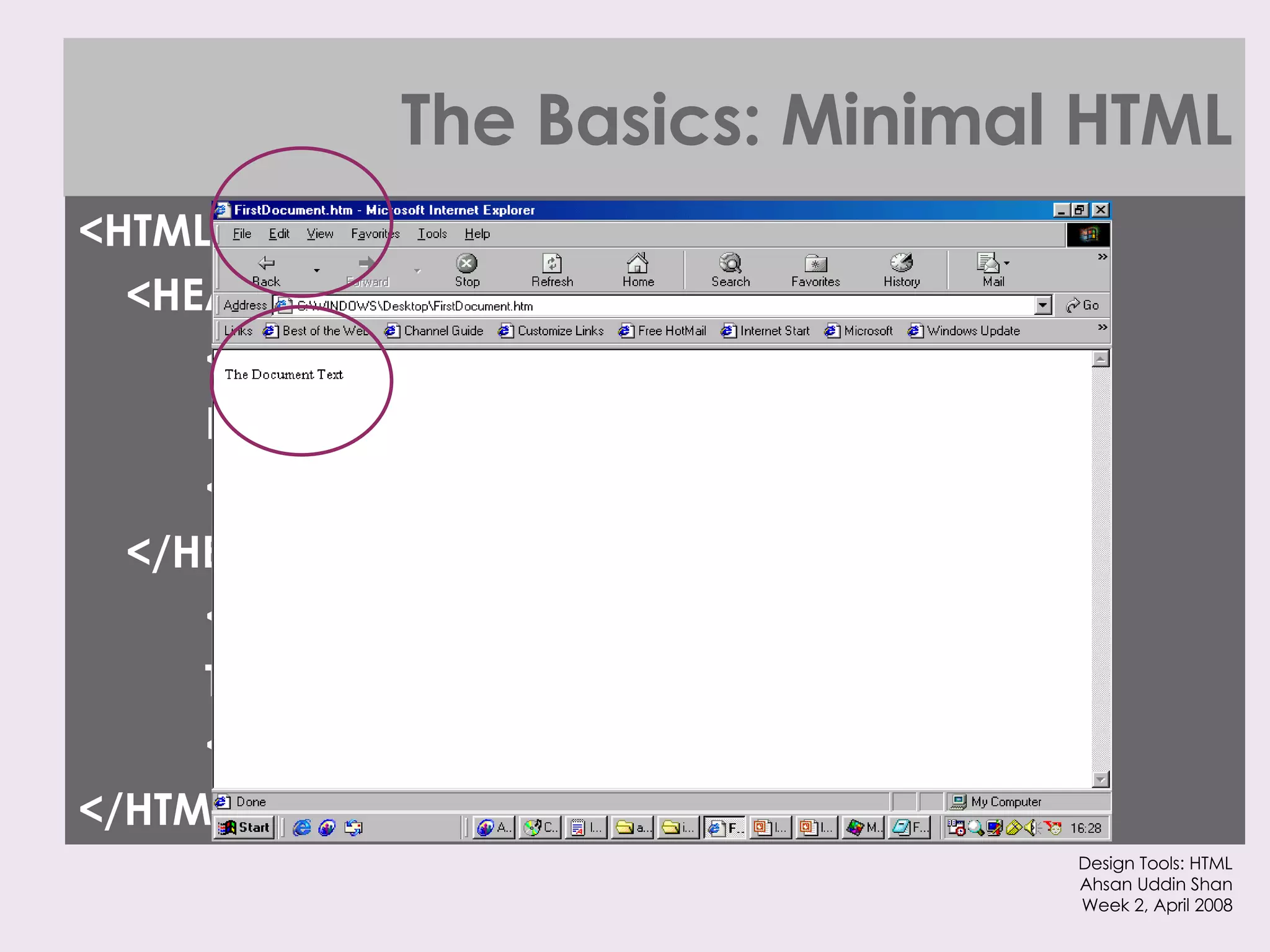
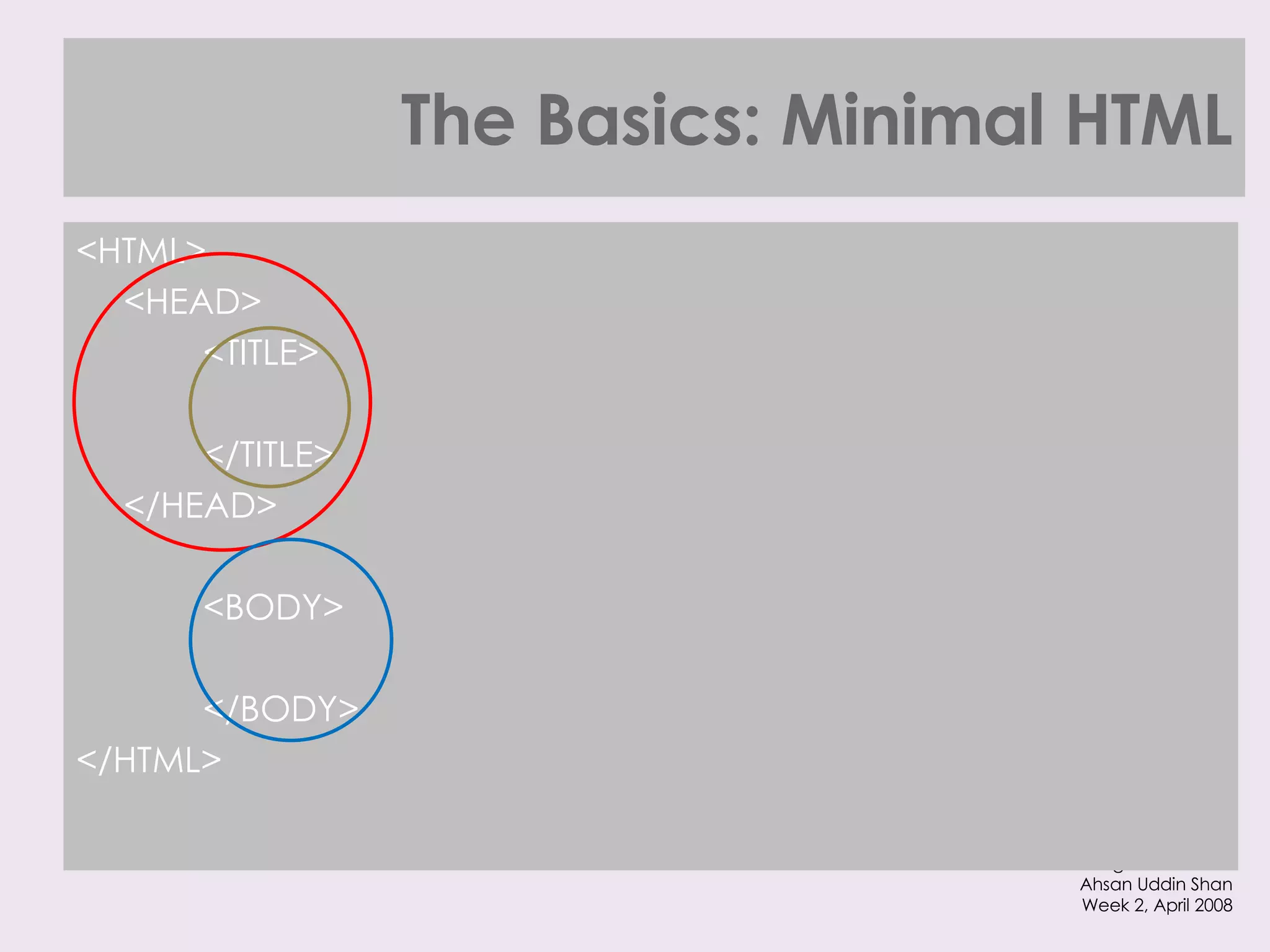
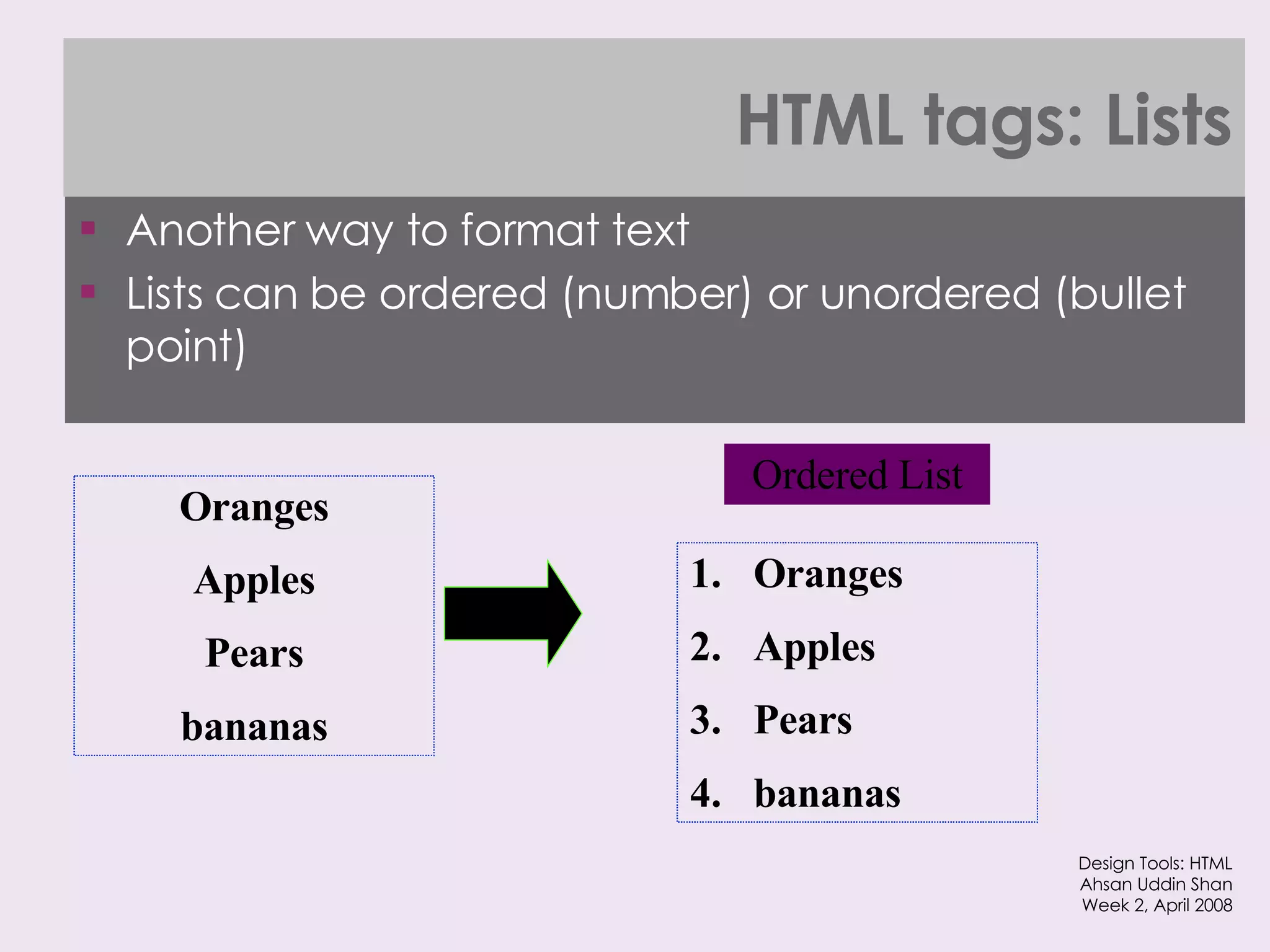
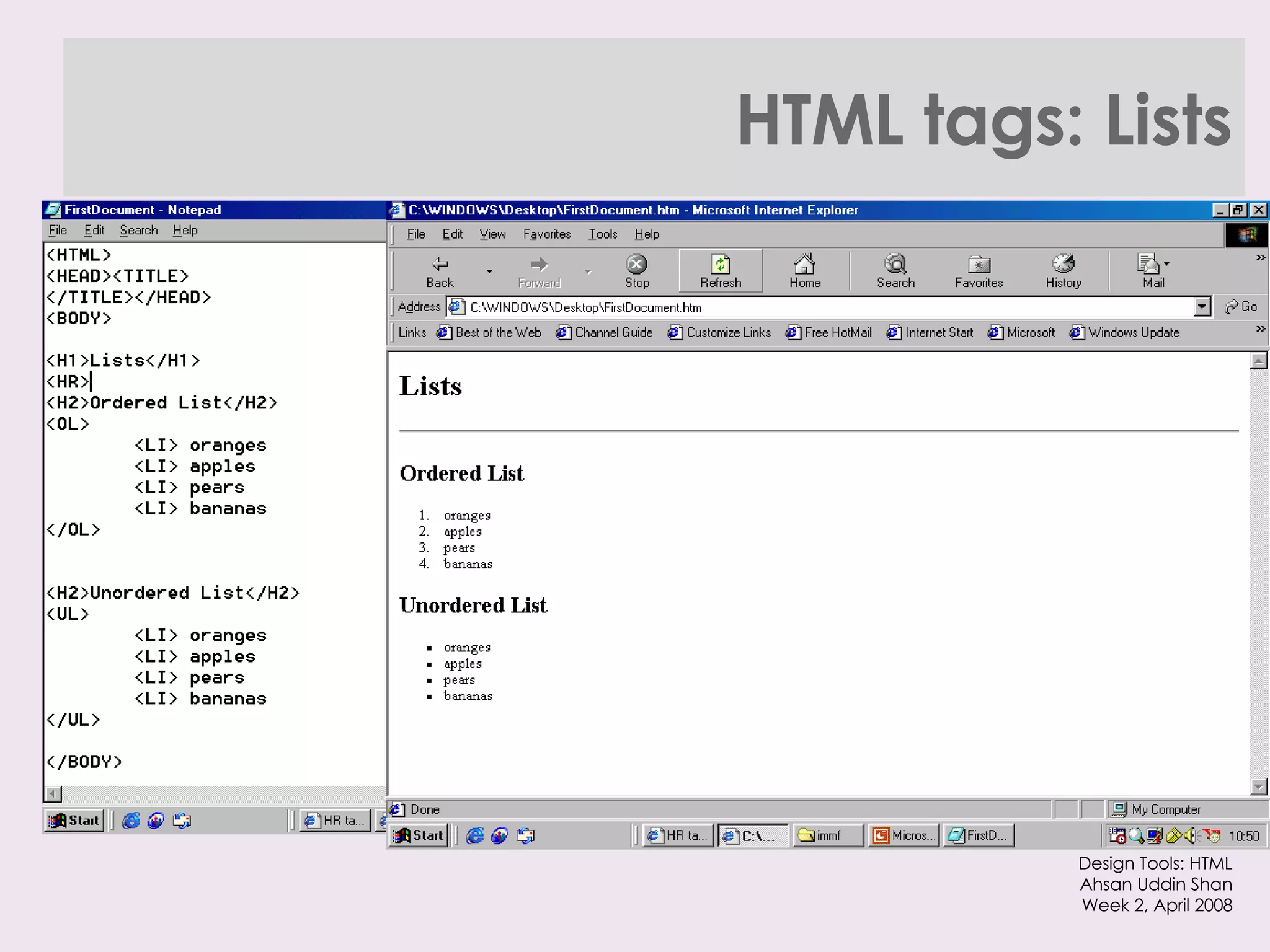
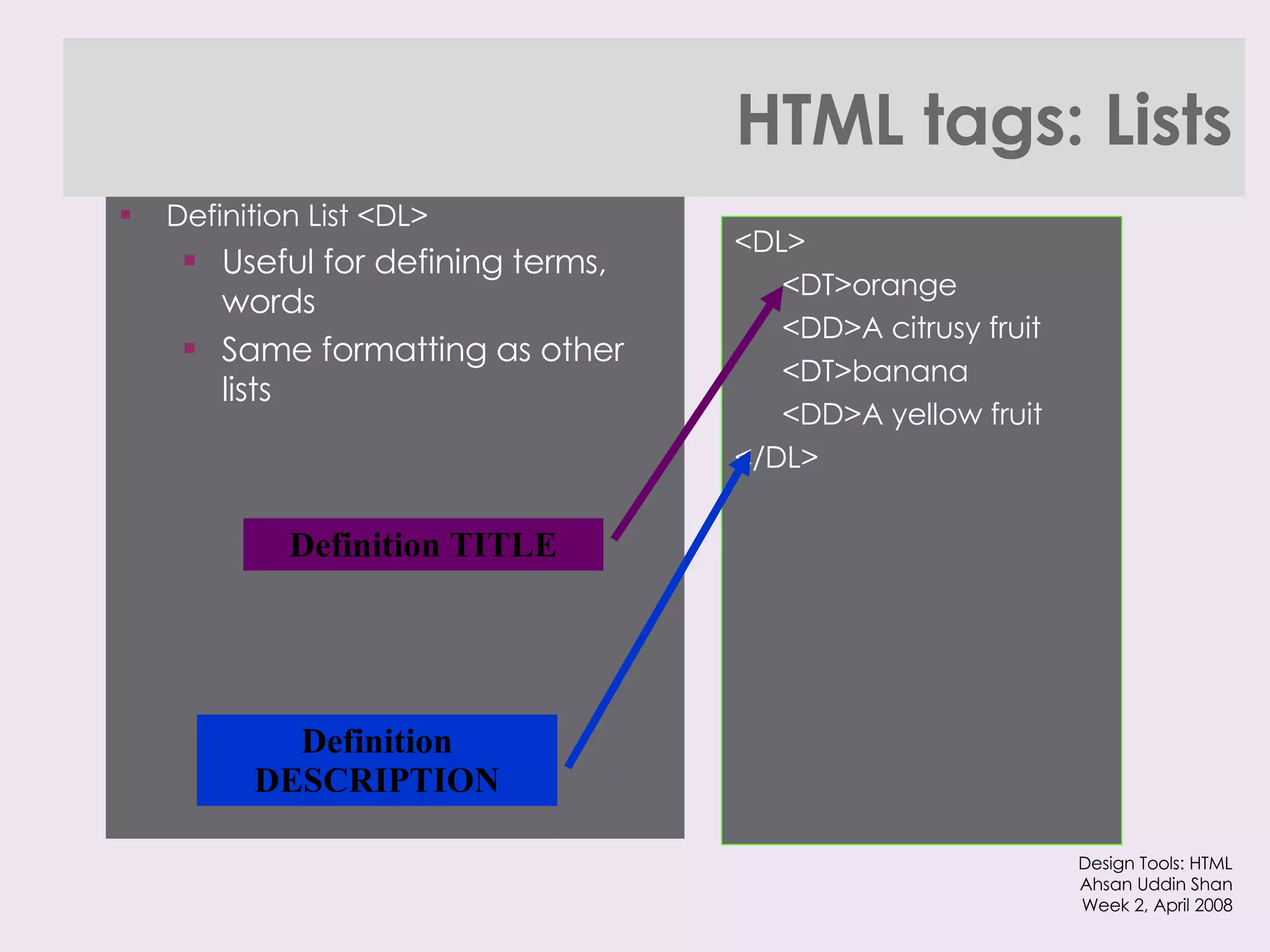
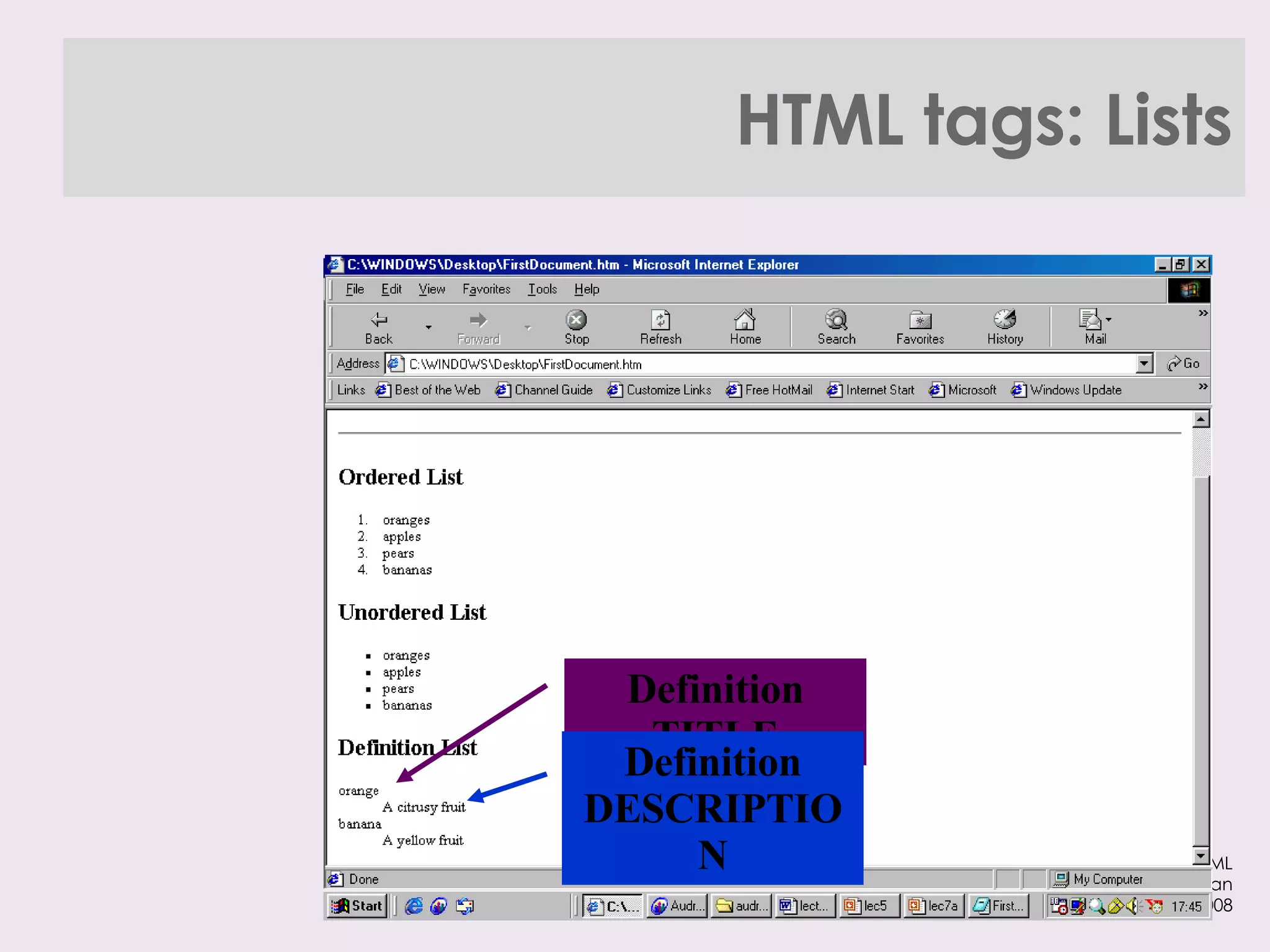
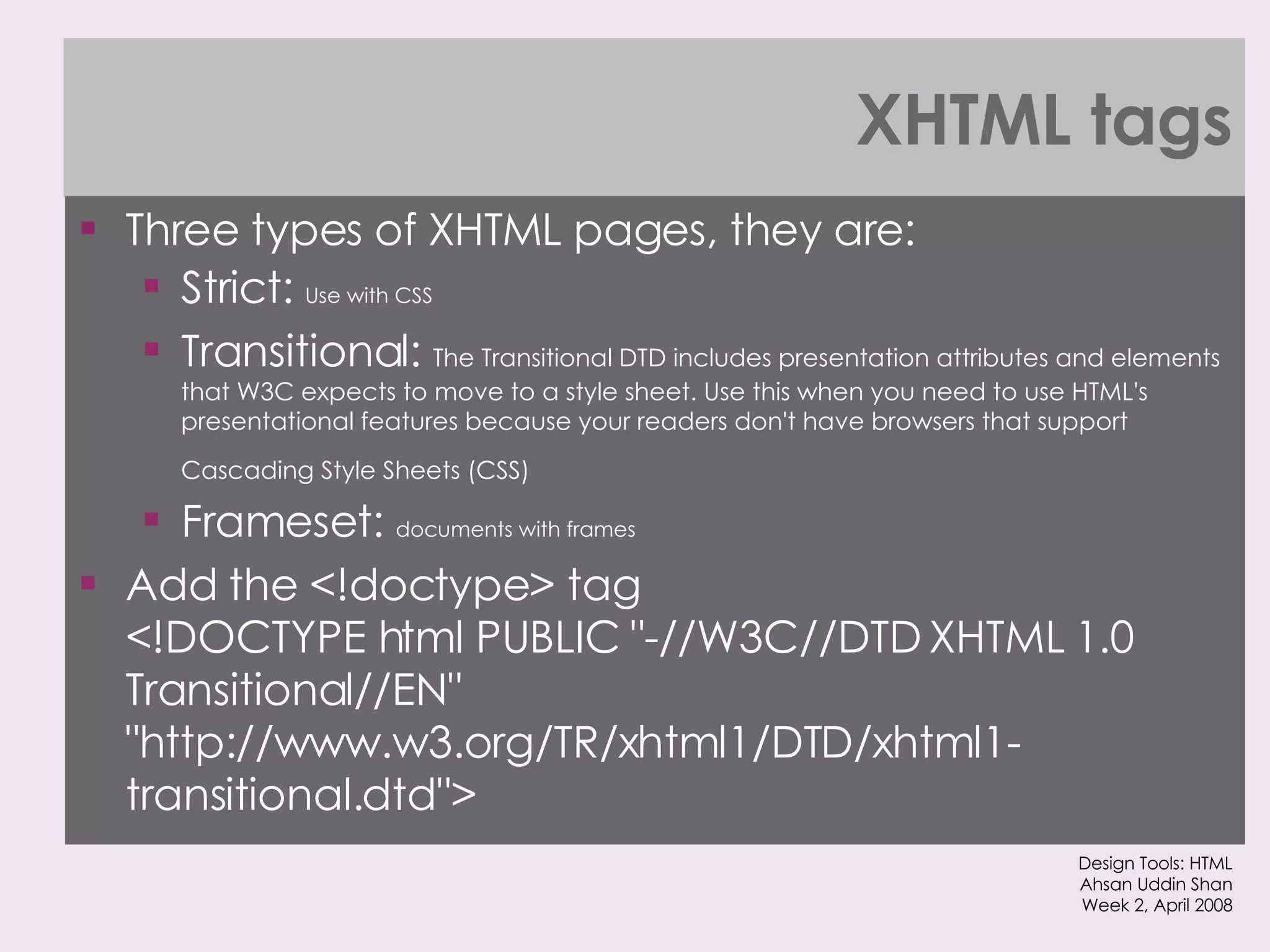
The document provides an overview of HTML and XHTML tags for formatting text and structuring web pages. It discusses basic HTML syntax and tags for headings, paragraphs, lists, breaks, and other text formatting. It also explains the differences between HTML and XHTML, with XHTML being a stricter combination of HTML and XML syntax.





![Basic HTML Syntax HTML documents are text documents that contain: formatting instructions, called tags Content [b/w body tag] Tags are enclosed in brackets [< >] <title> time management : so many boys so little time </title>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designtoolshtmlxhtml-1225443095810766-8/75/Design-Tools-Html-Xhtml-6-2048.jpg)