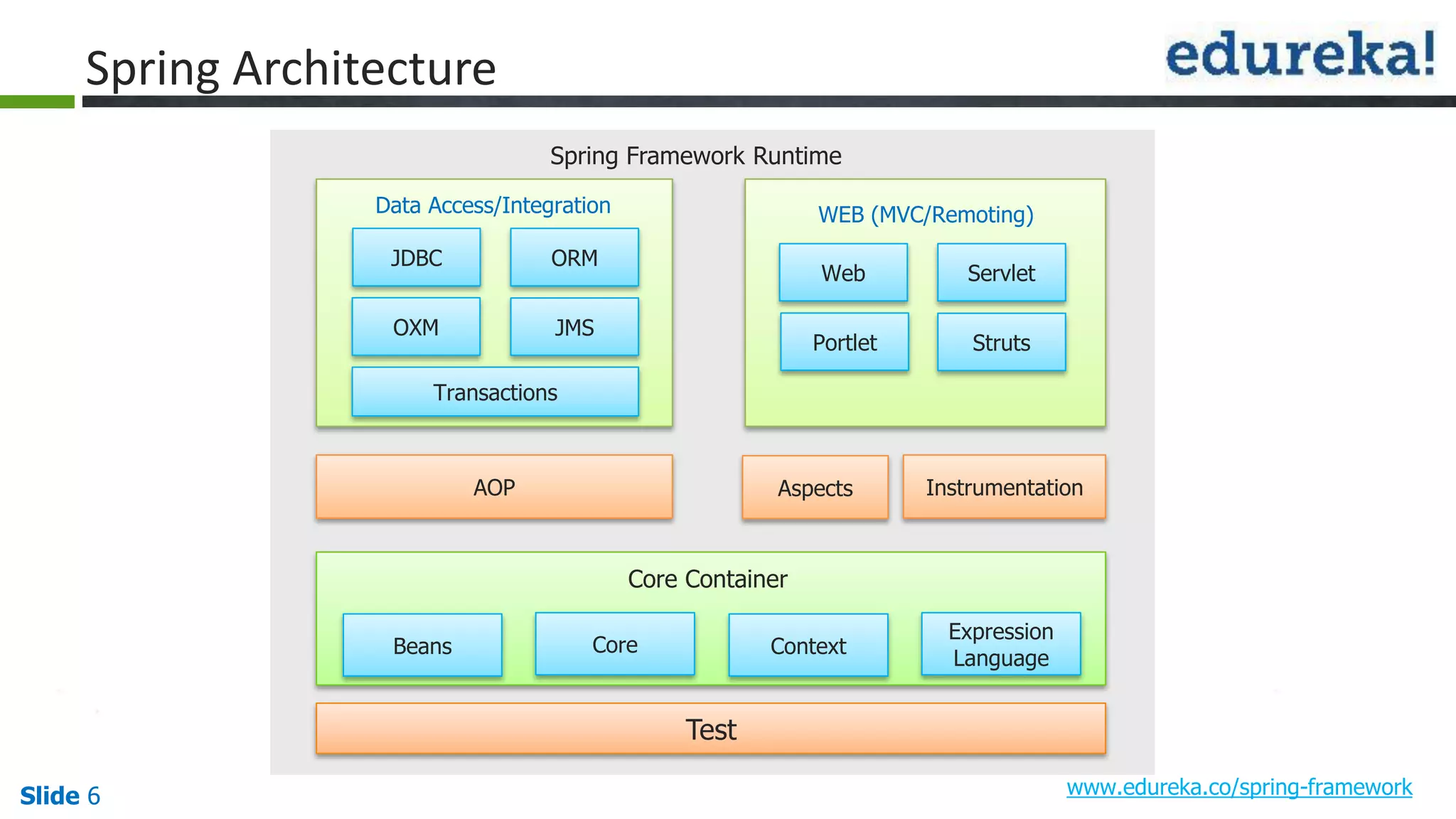
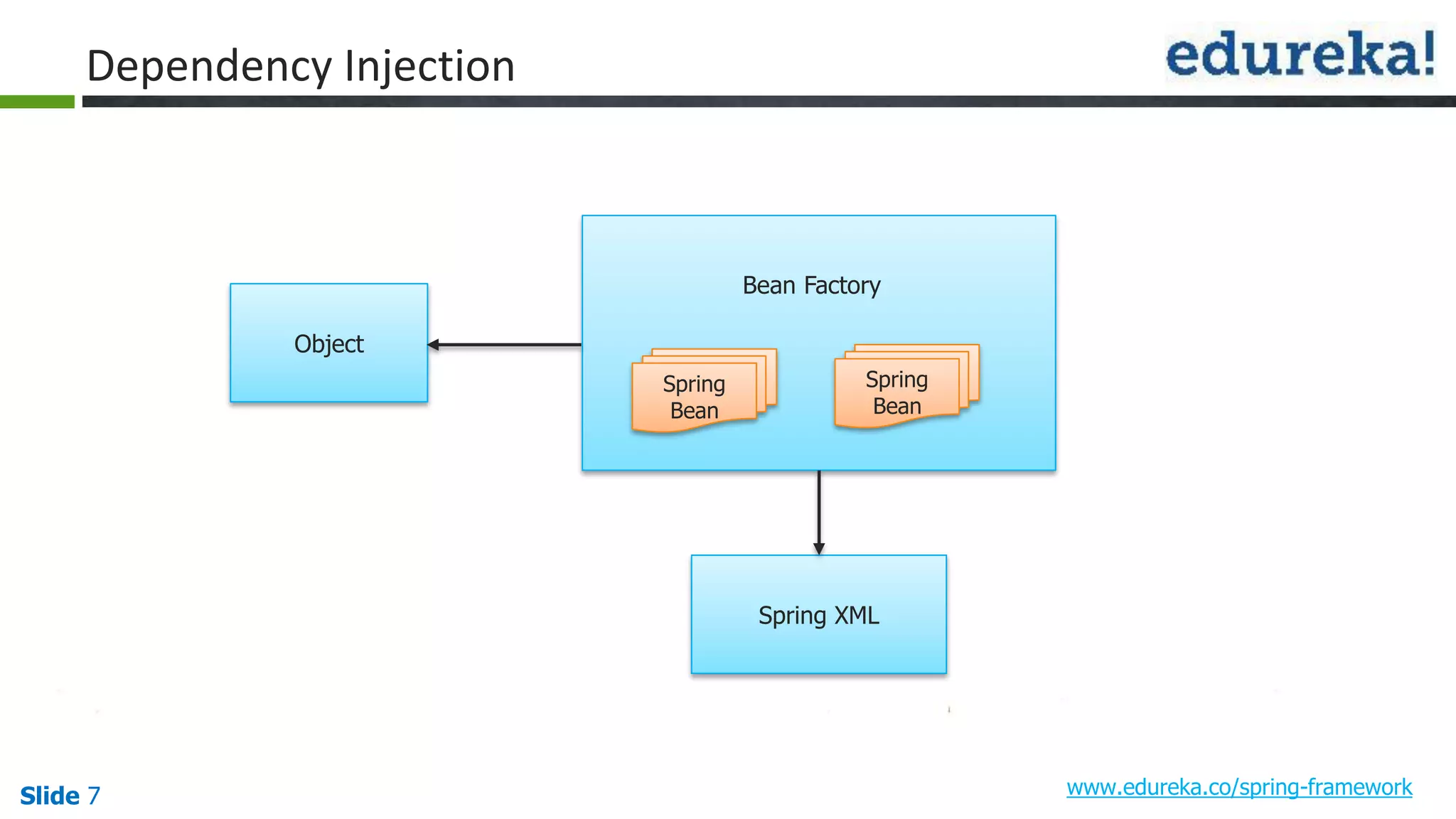
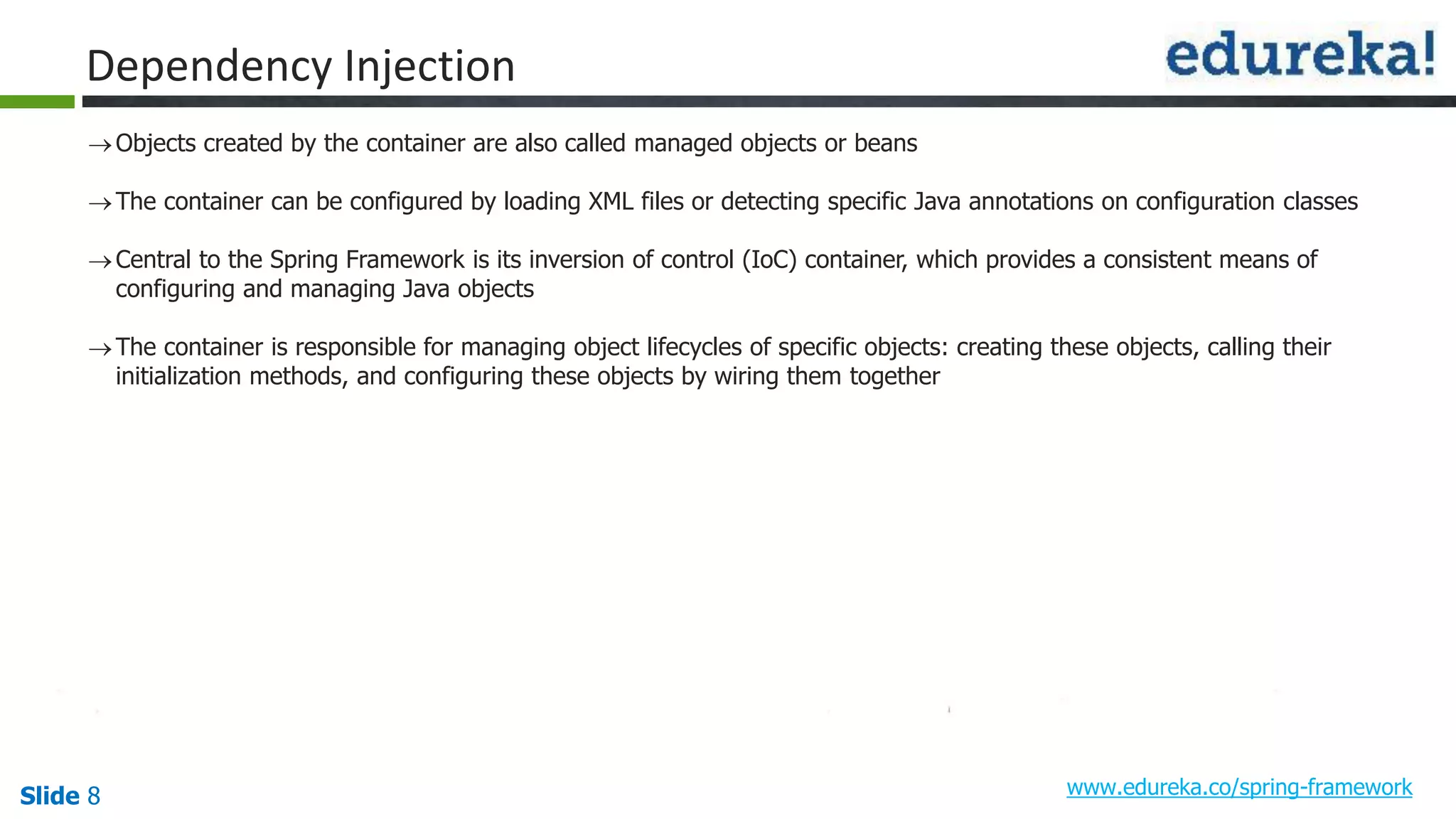
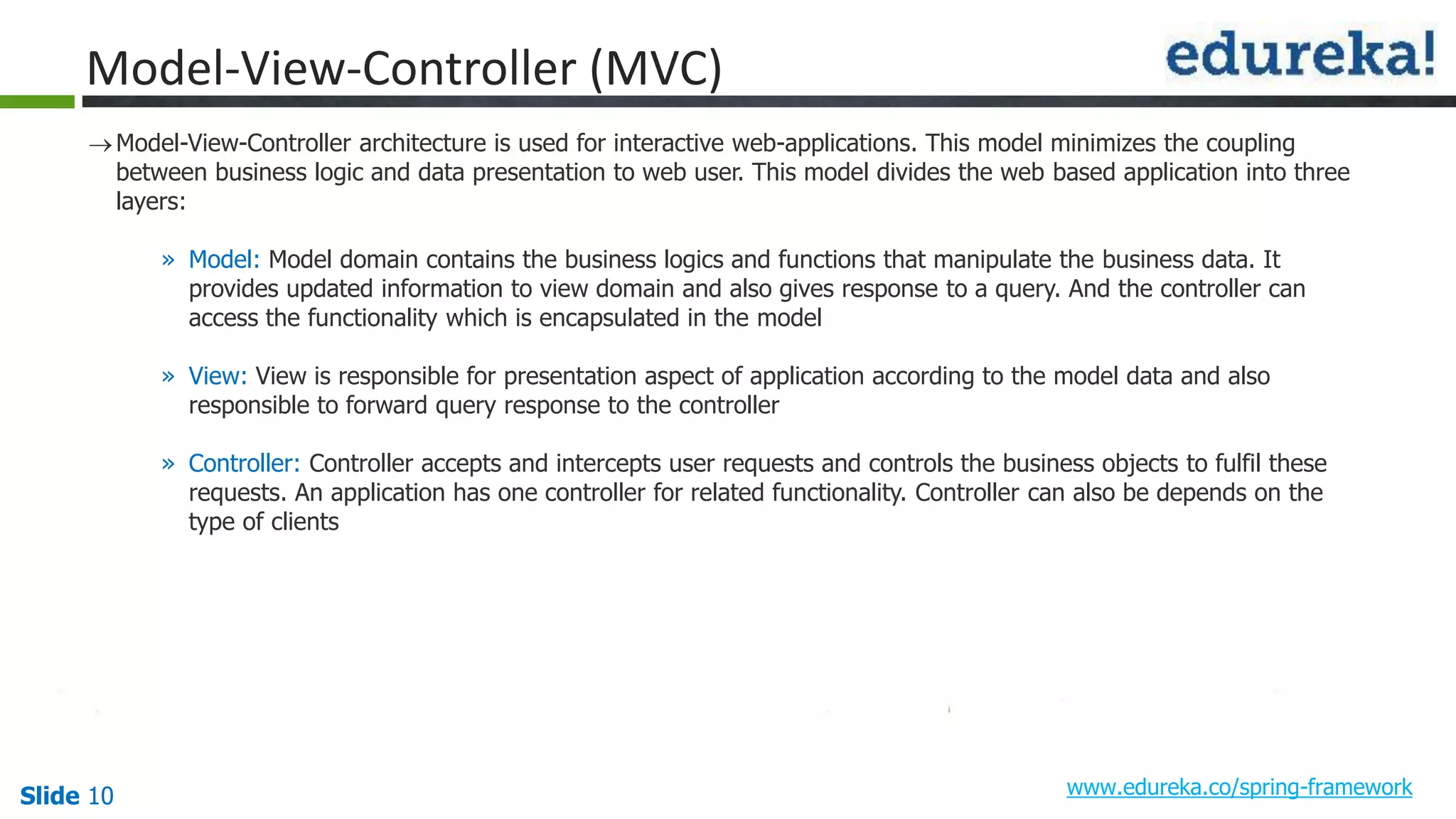
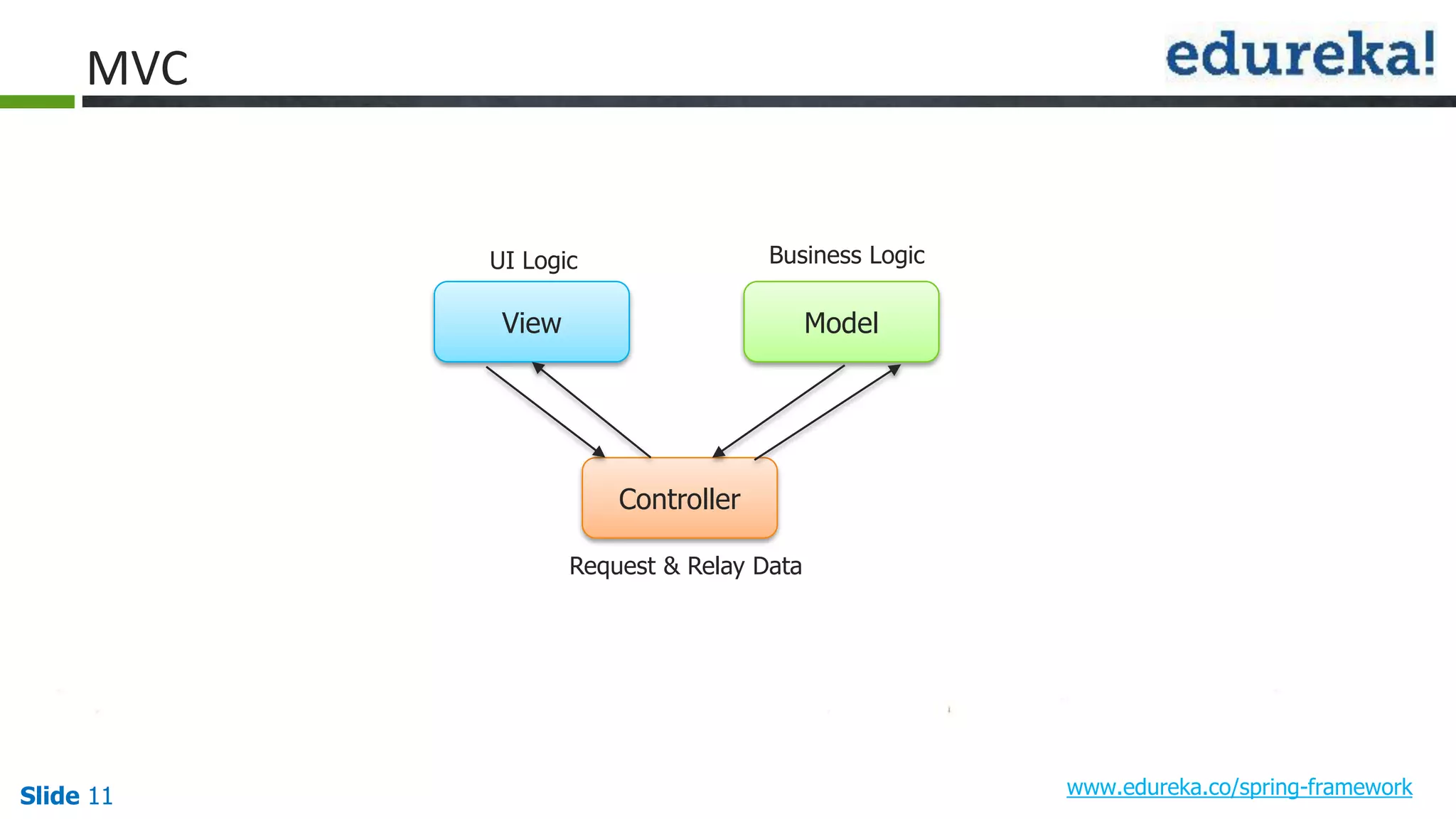
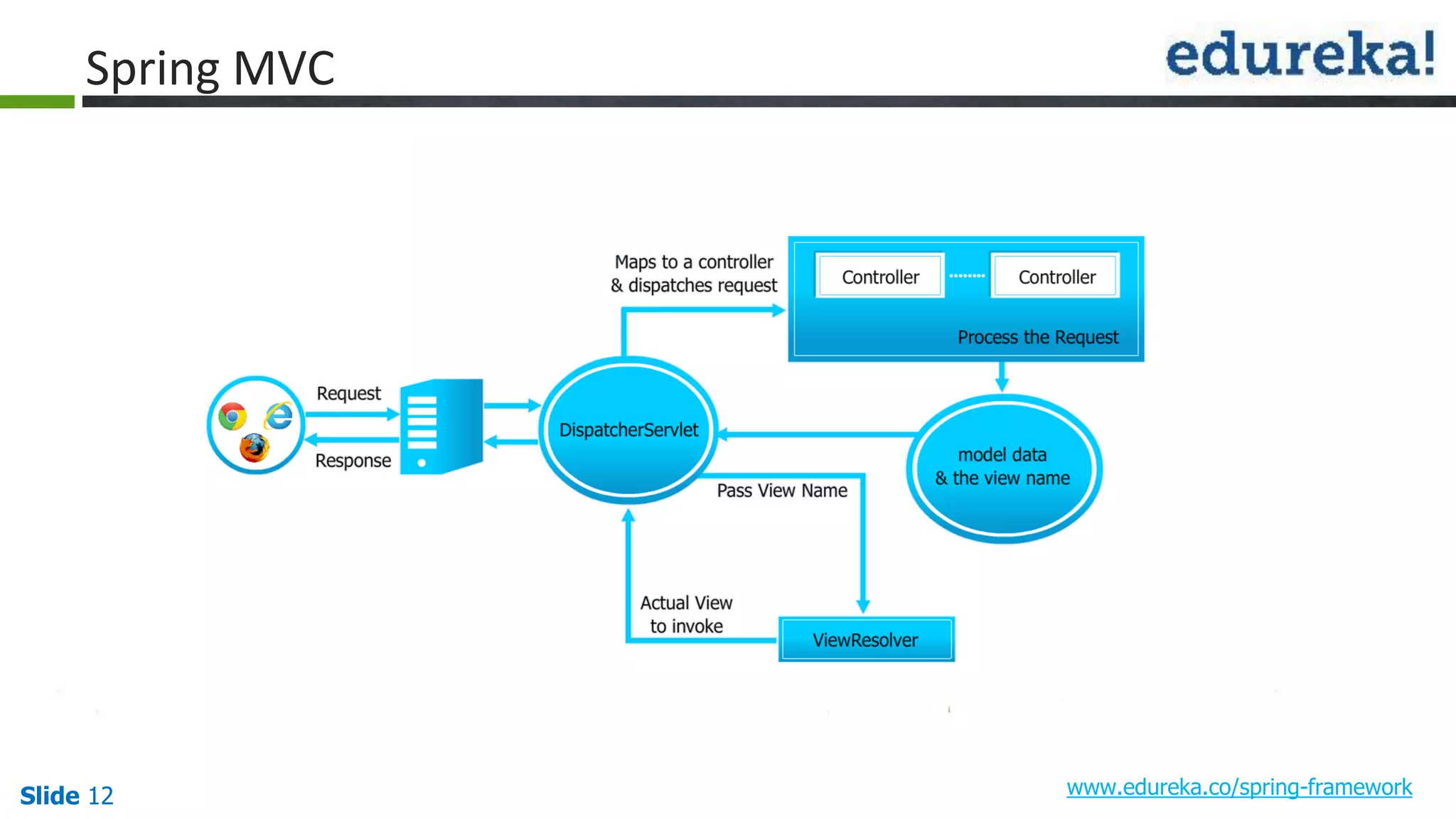
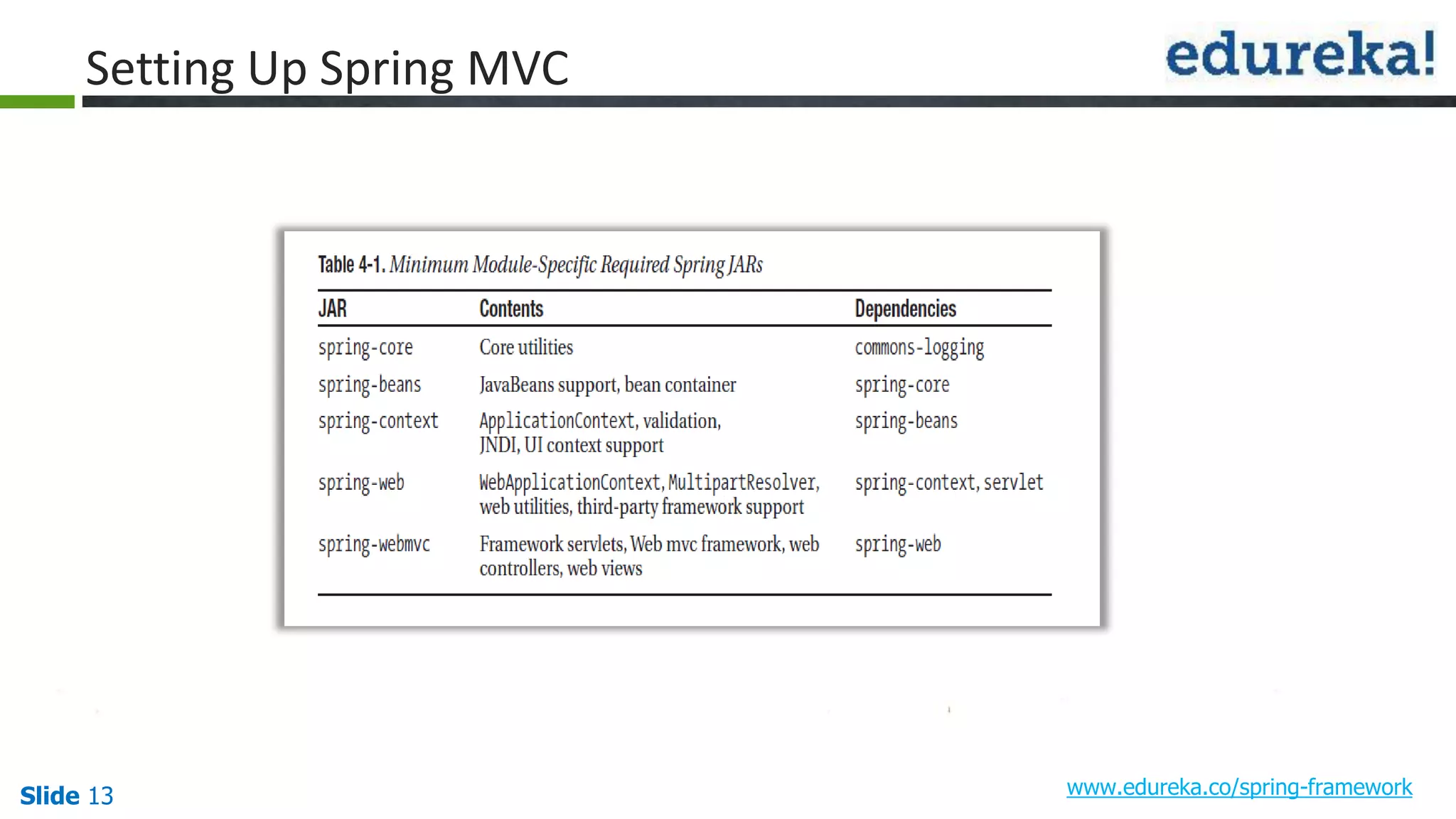
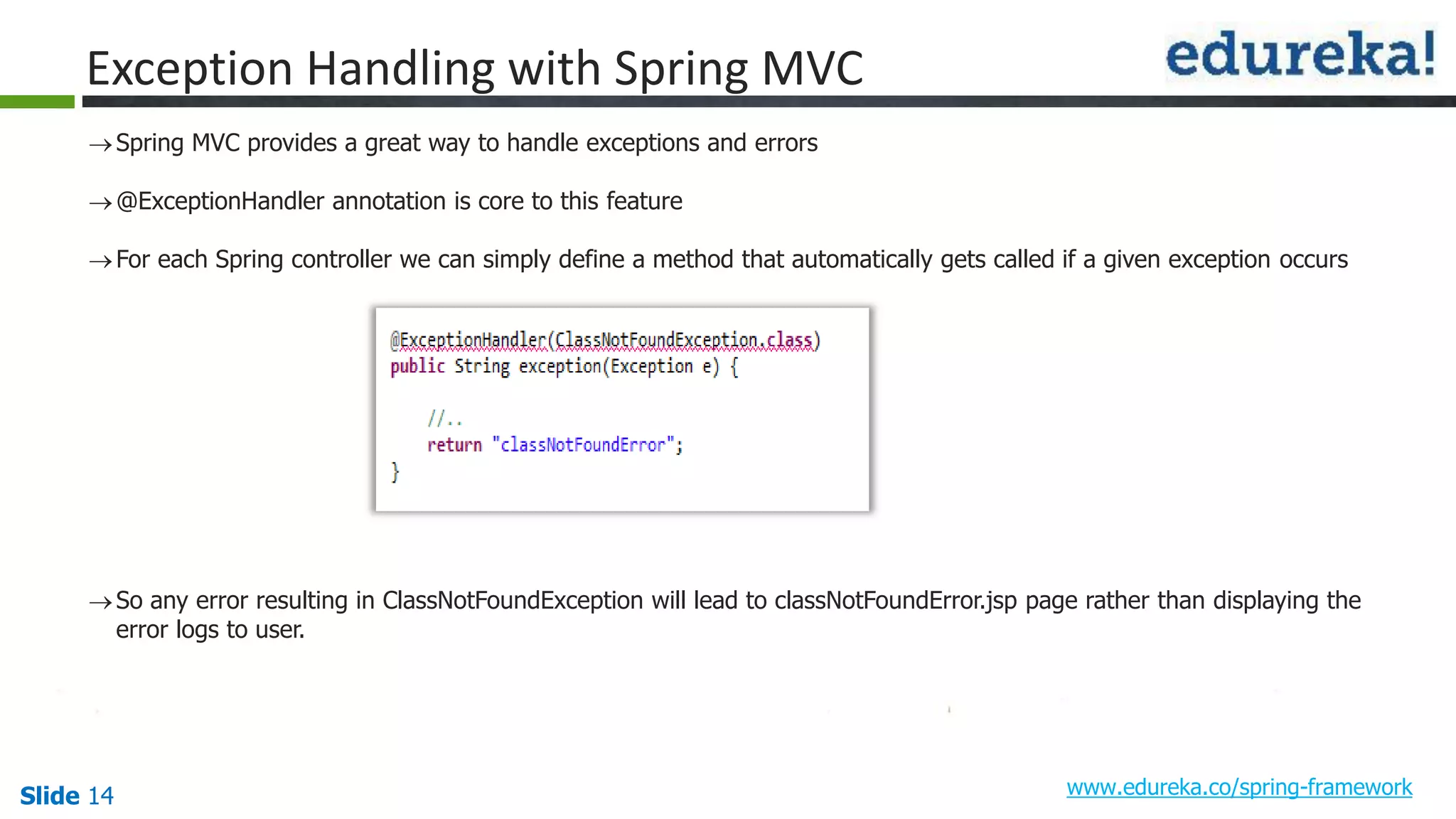
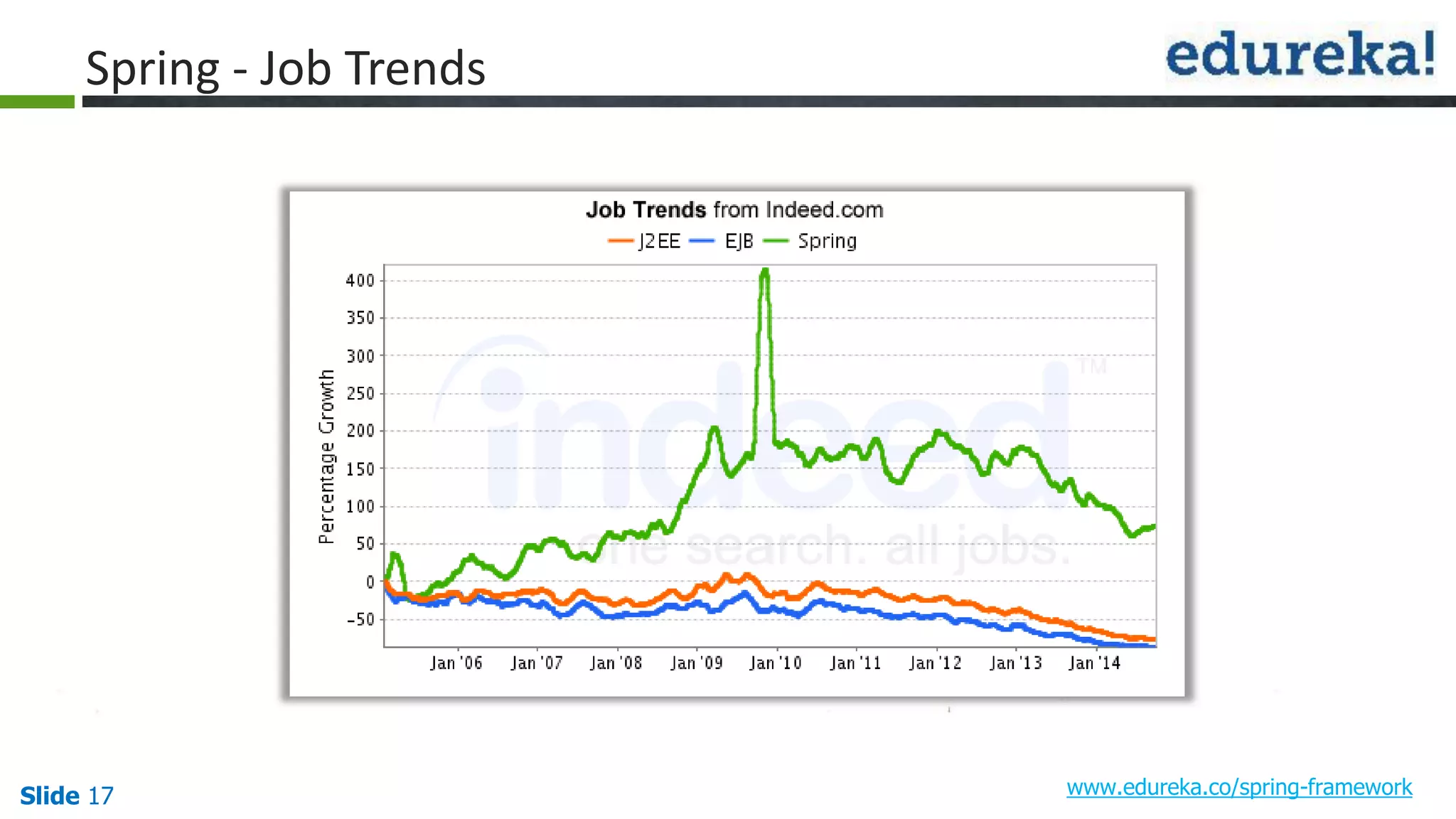
The document provides an overview of the Spring framework and how to build web applications using Spring. It discusses key Spring concepts like dependency injection, Spring MVC architecture, and exception handling. It also lists contact details for queries and the course objectives, which are to understand the Spring architecture, dependency injection, Spring MVC, exception handling, and how to build a web application with Spring.