Downloaded 1,649 times


























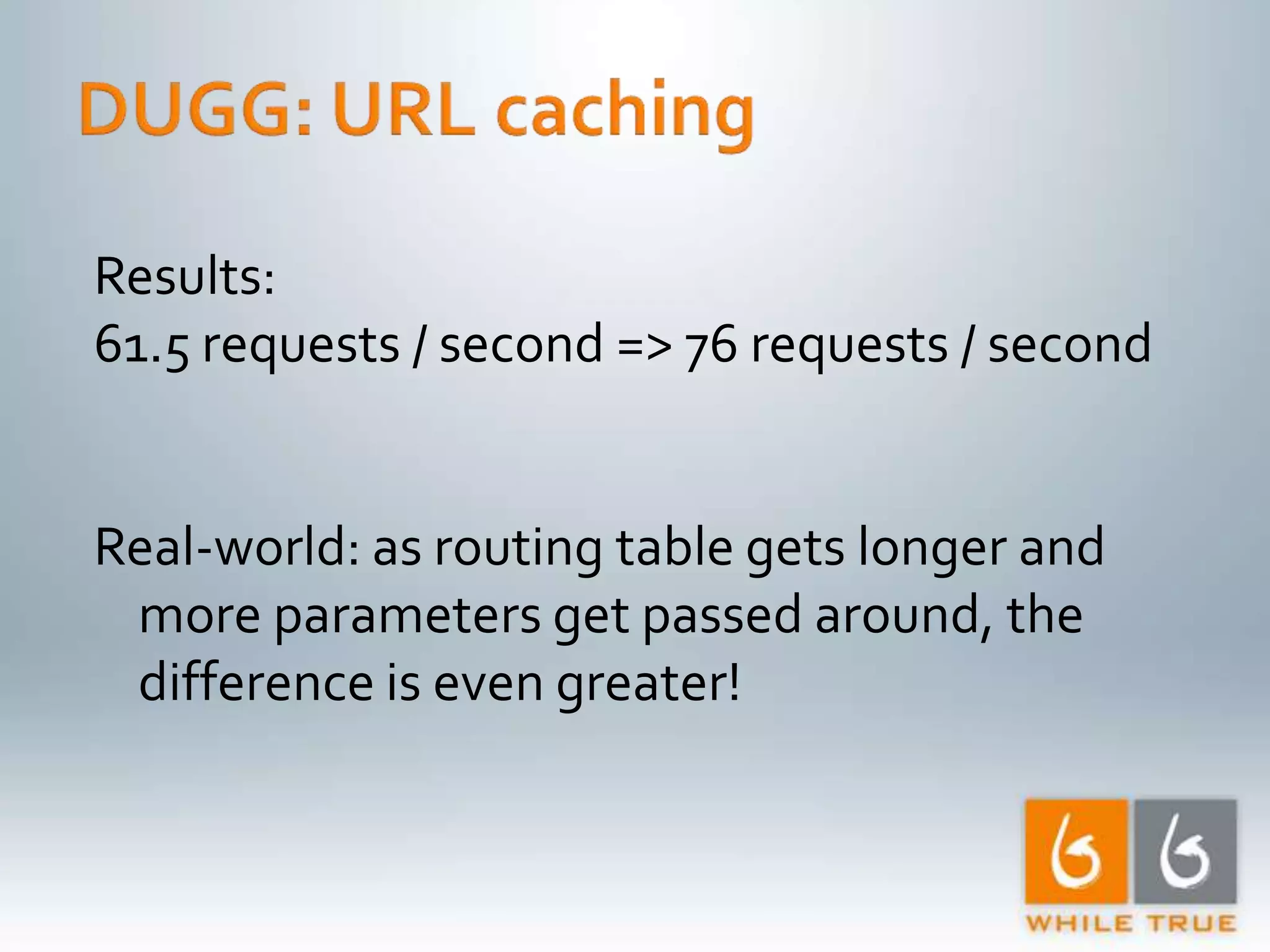
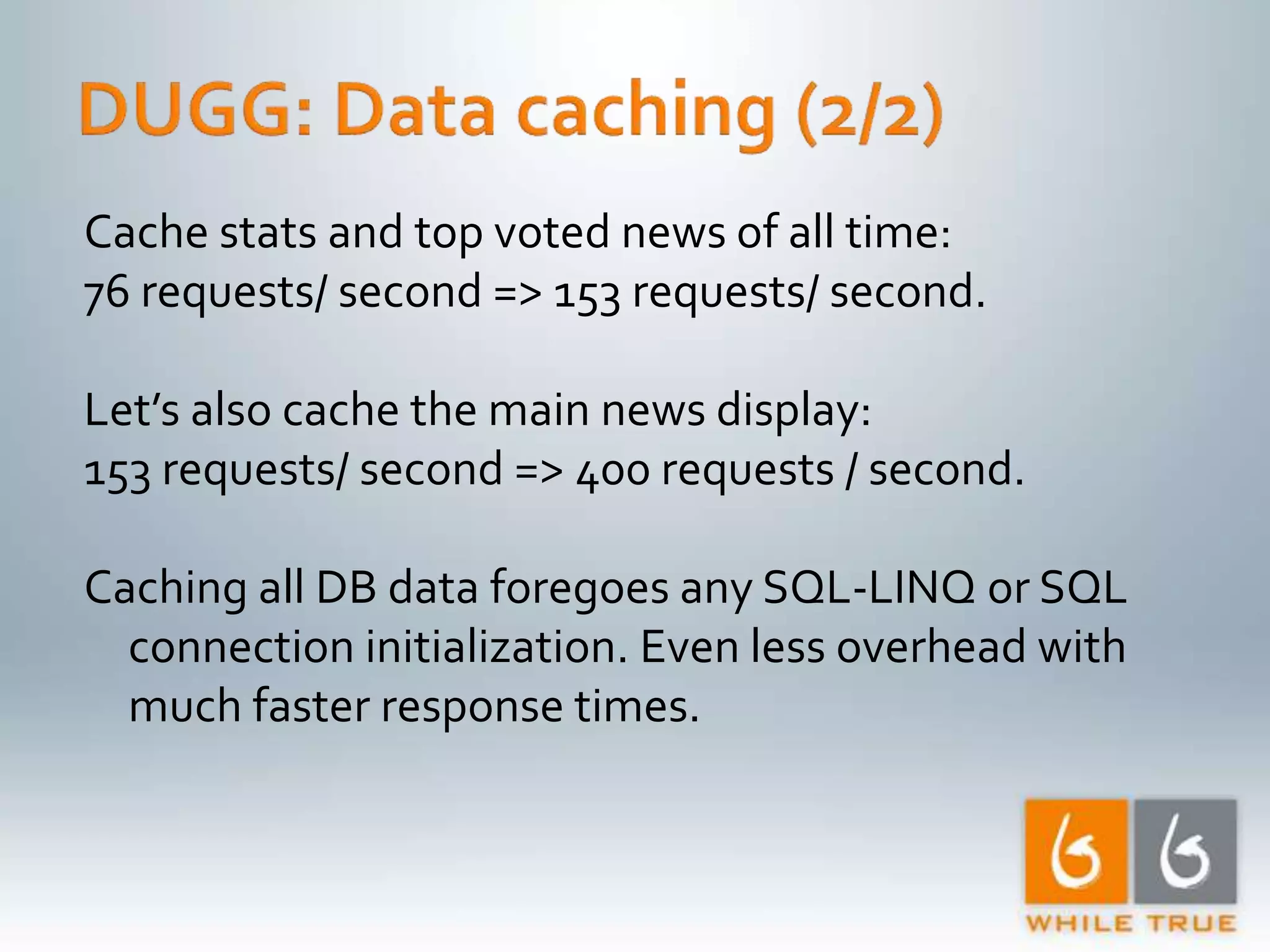
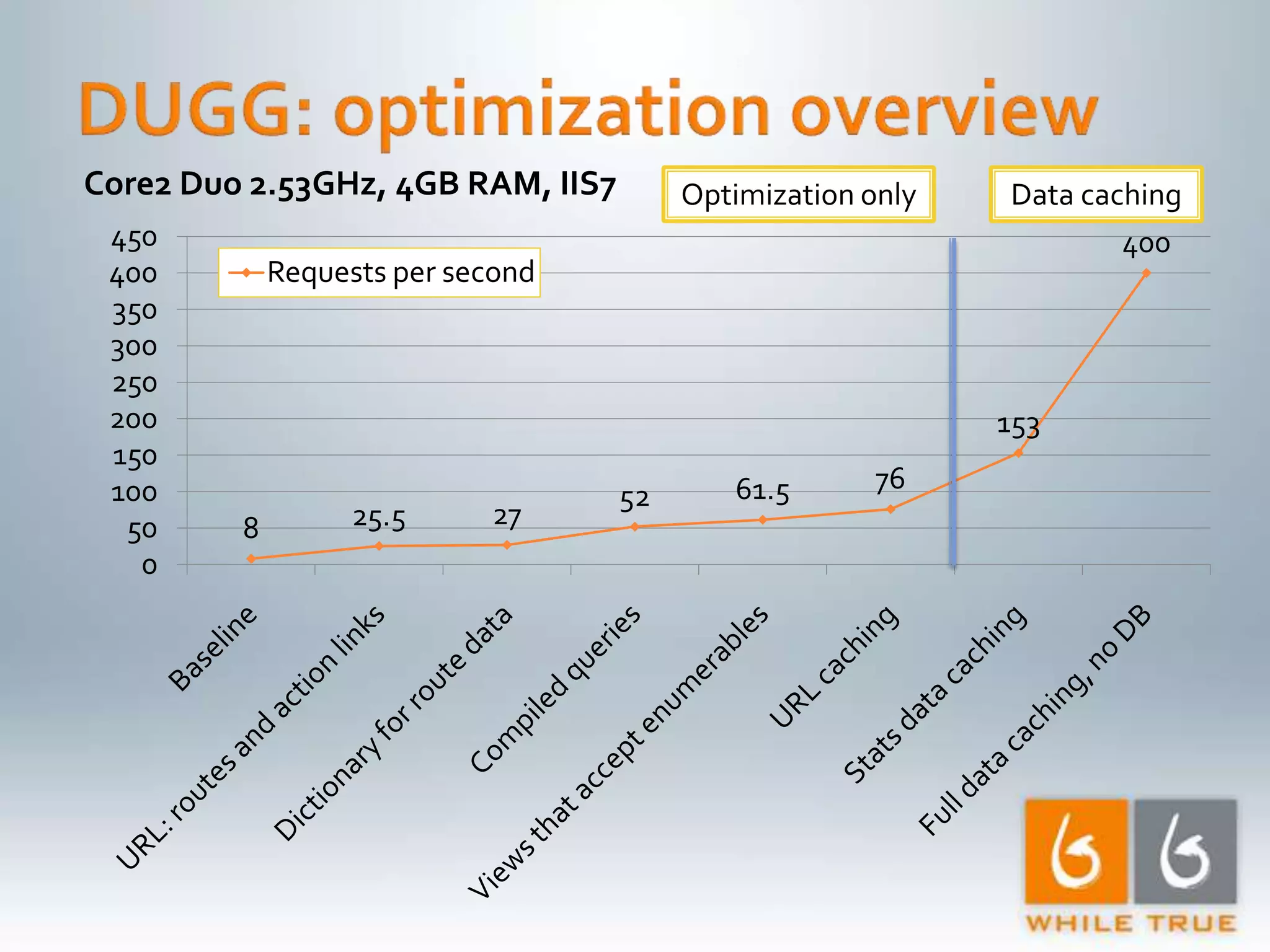



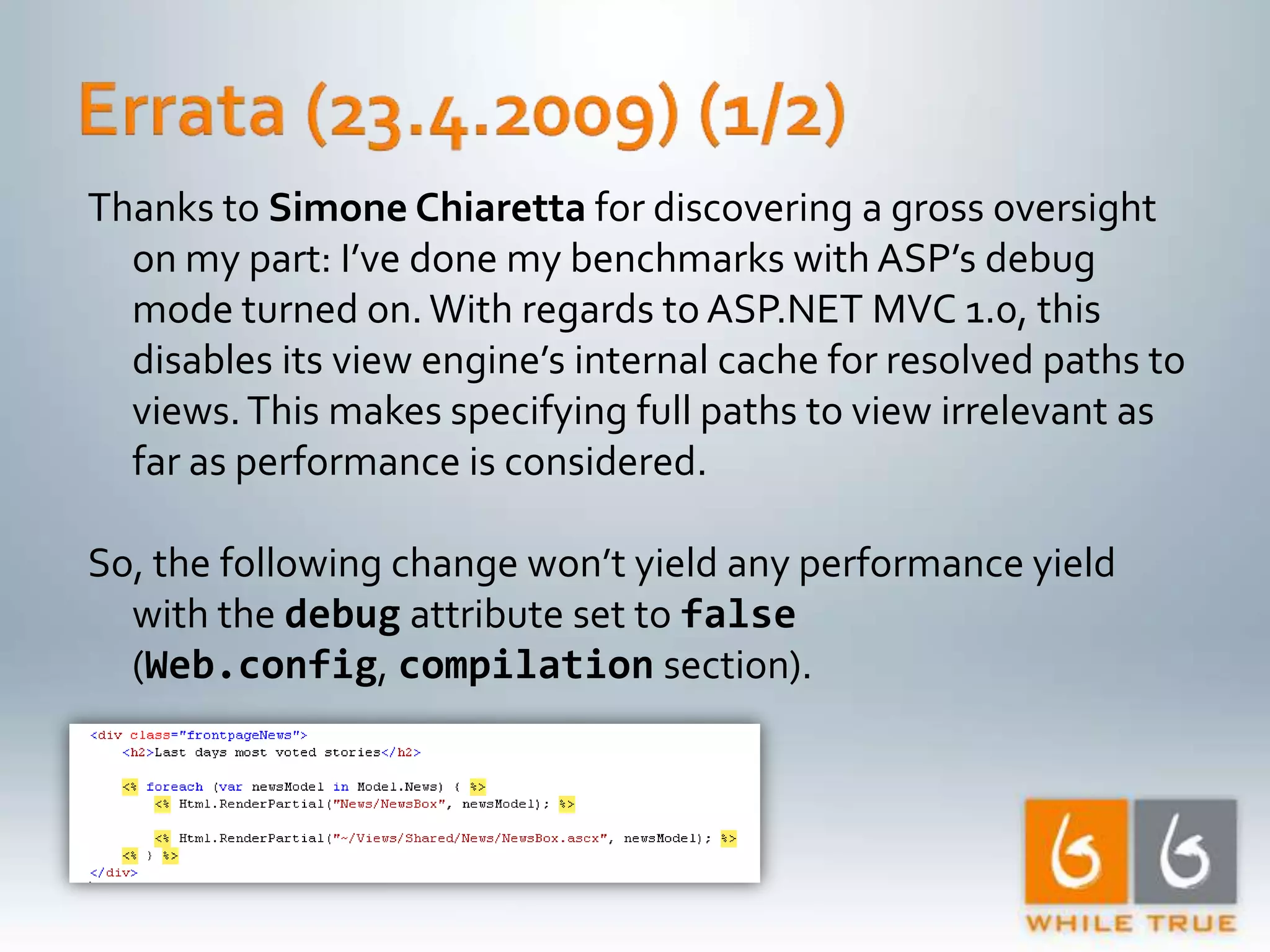
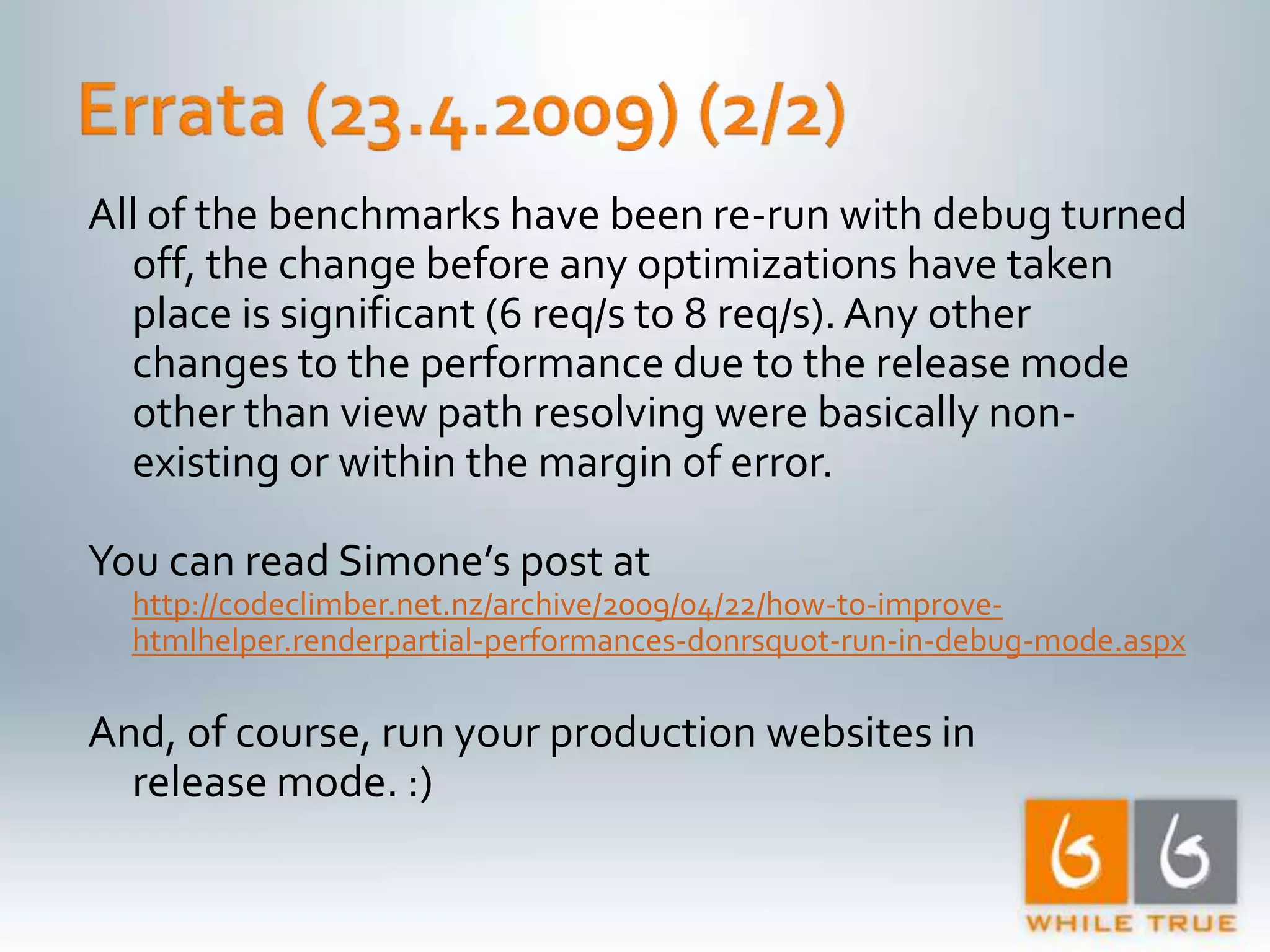
1. The document discusses various optimizations that can be made to an ASP.NET MVC application to improve performance, including compiled LINQ queries, URL caching, and data caching. 2. Benchmark results show that optimizing partial view rendering, LINQ queries, and URL generation improved performance from 8 requests/second to 61.5 requests/second. Additional caching of URLs, statistics, and content improved performance to over 400 requests/second. 3. Turning off ASP.NET debug mode also provided a significant performance boost, showing the importance of running production sites in release mode.



























































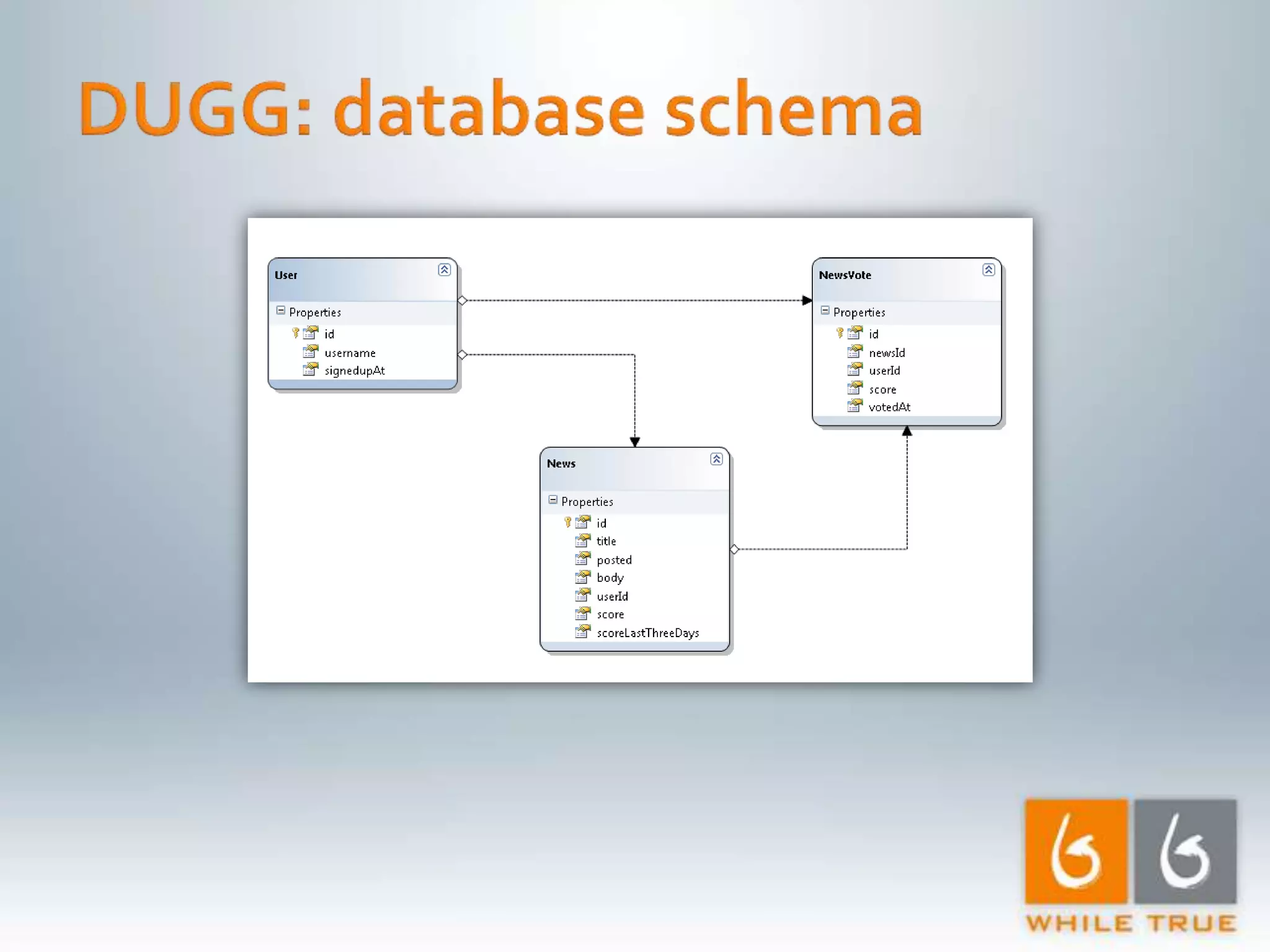
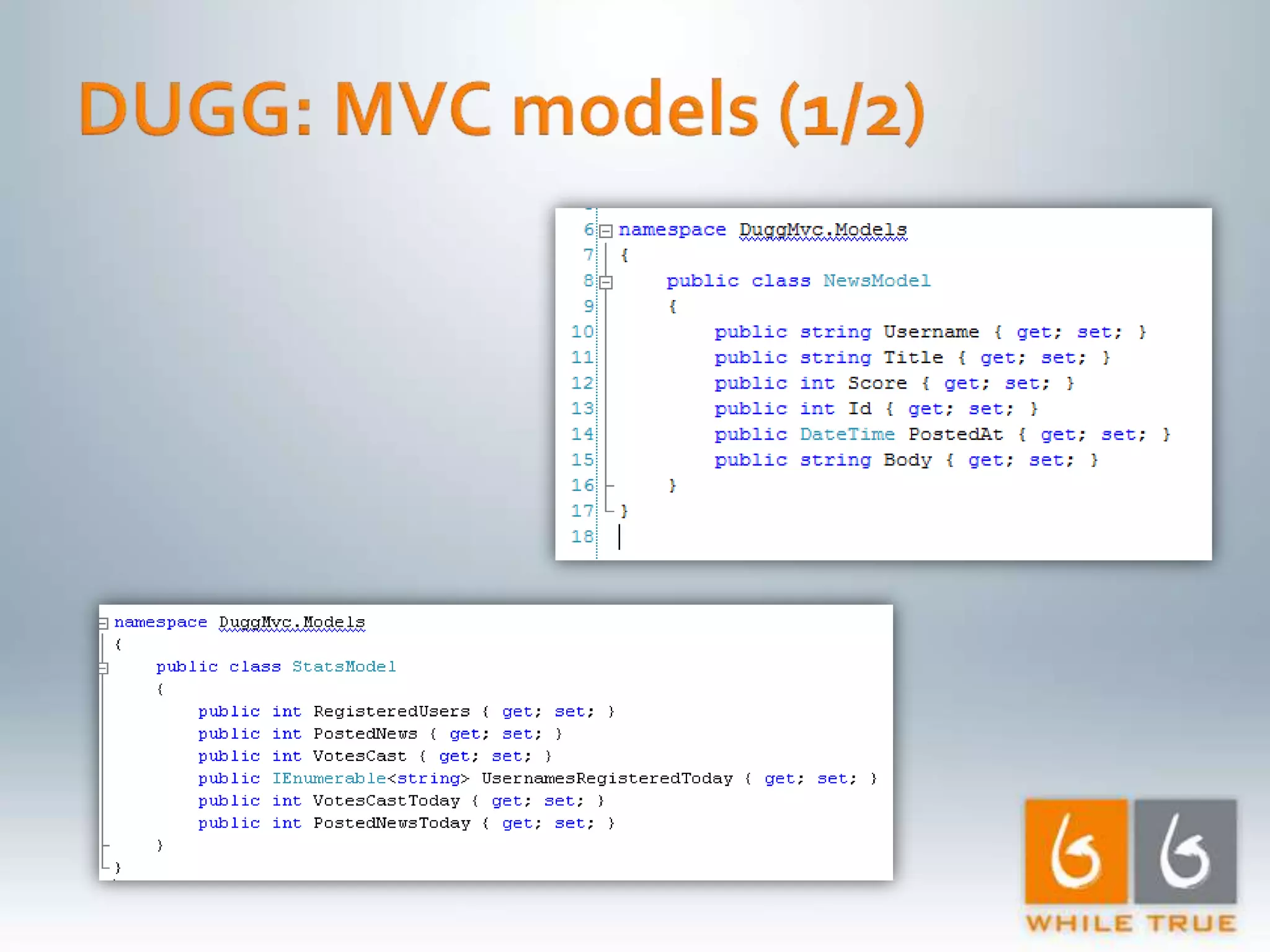
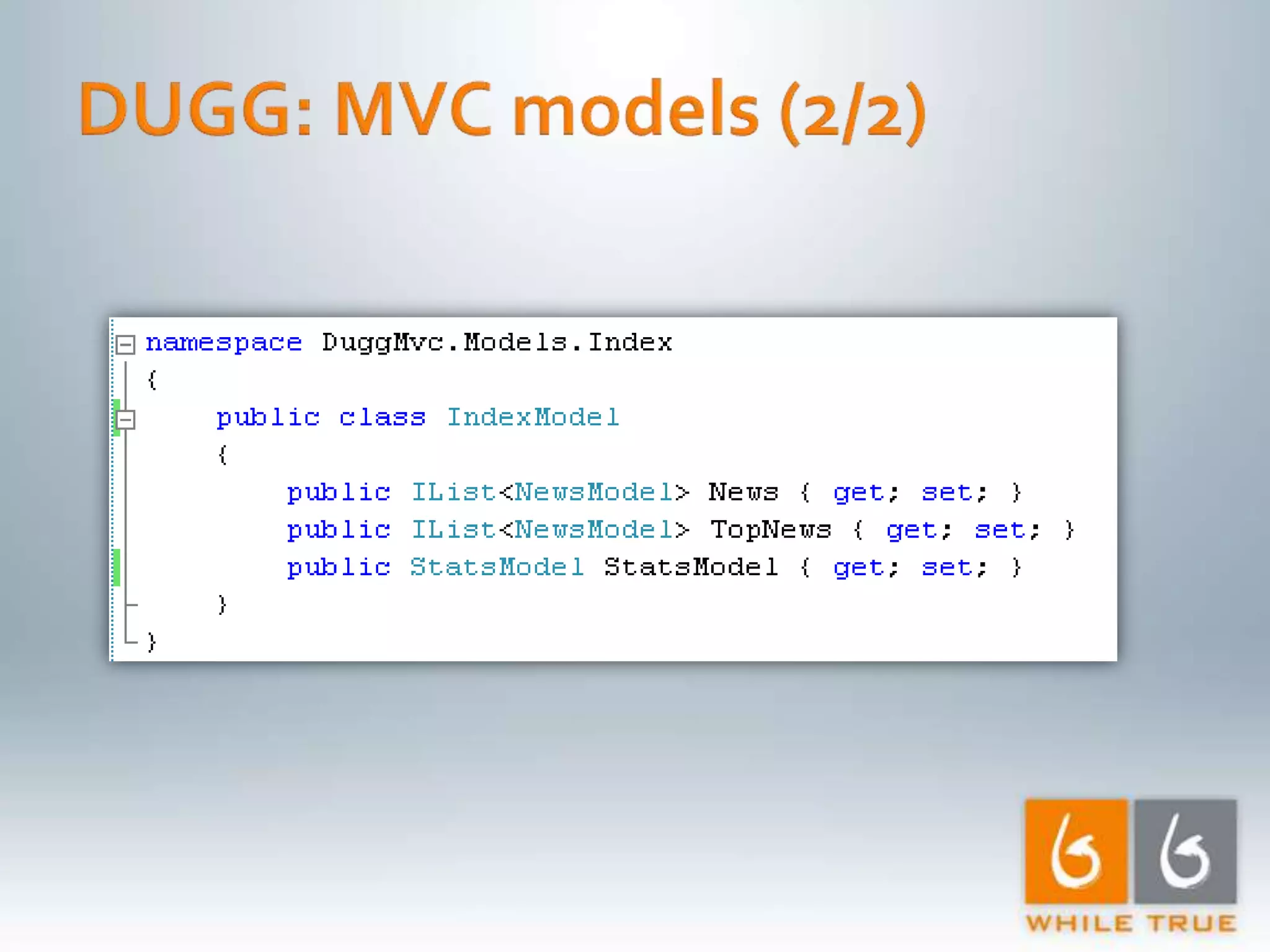
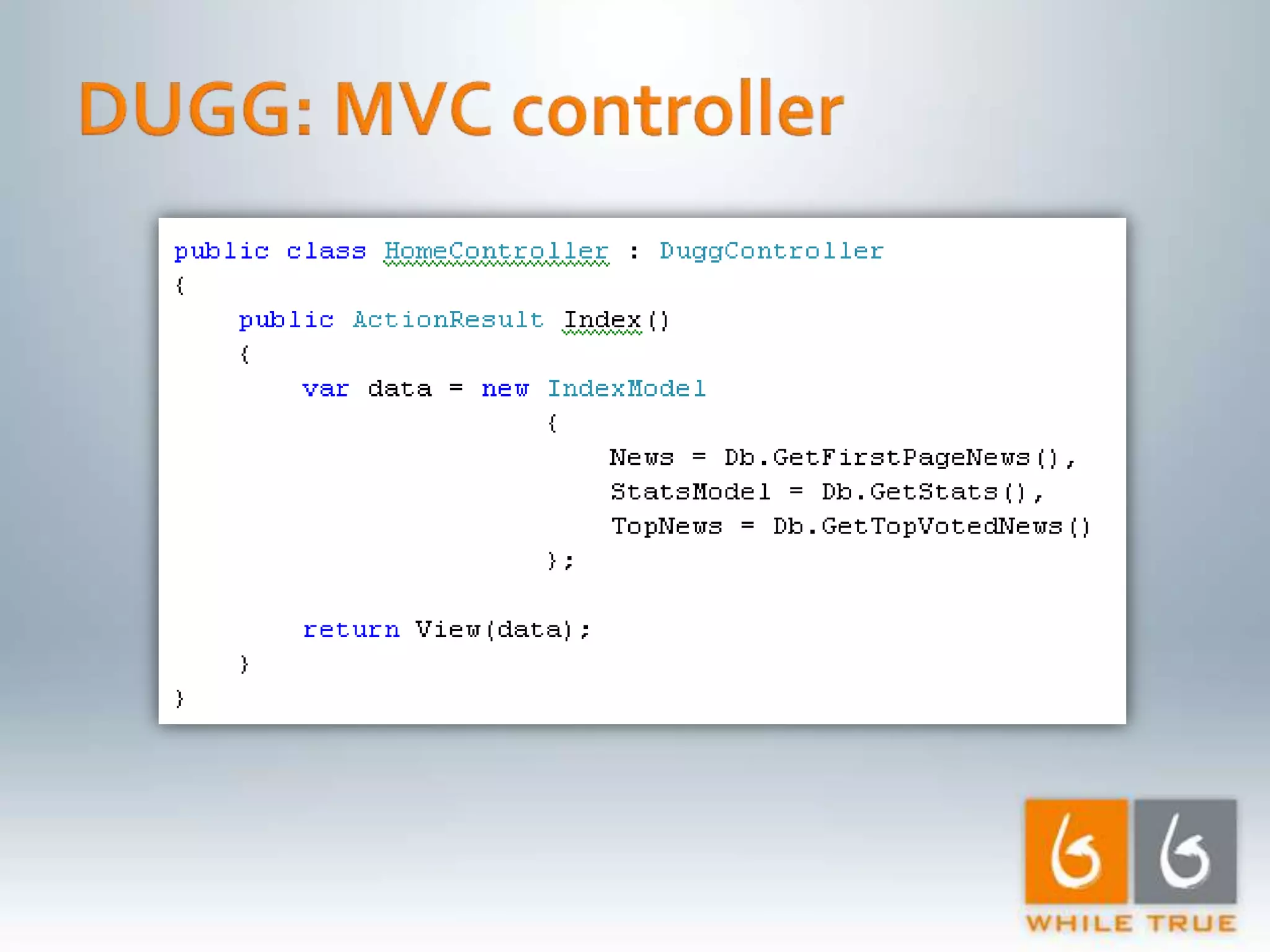
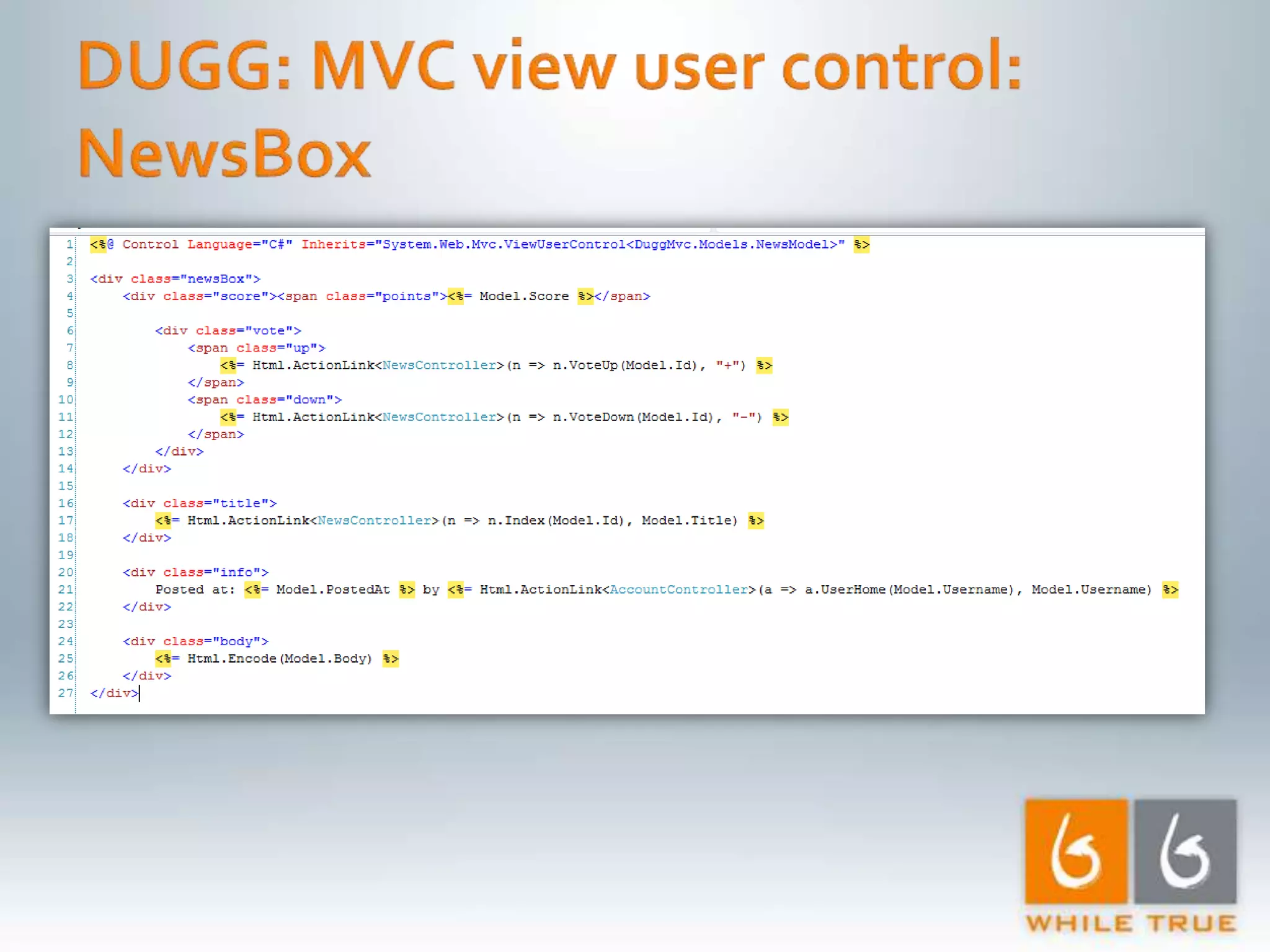
Introduction to a read-only MVC application with ASP.NET MVC 1.0, focusing on response time testing and tools.
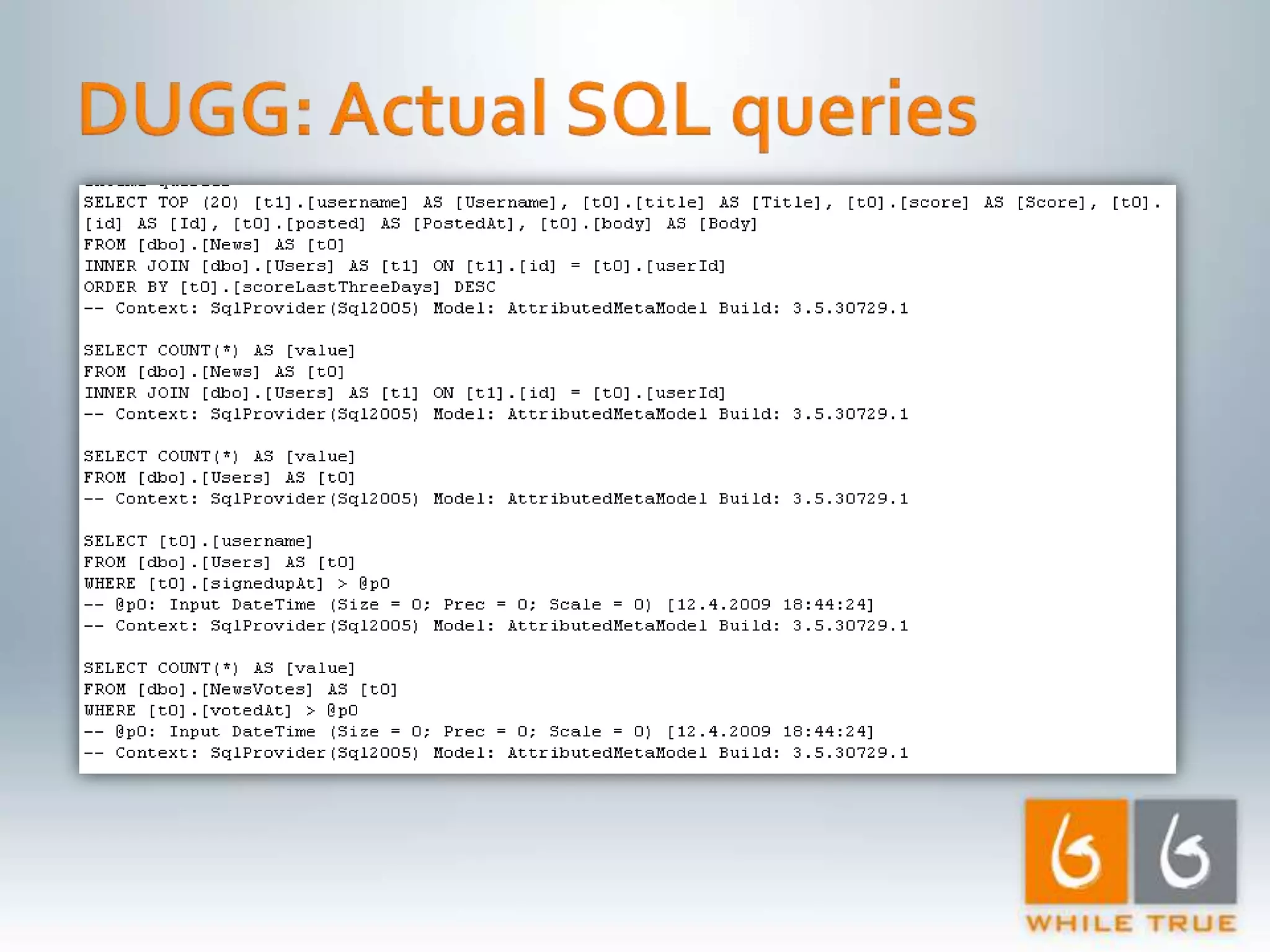
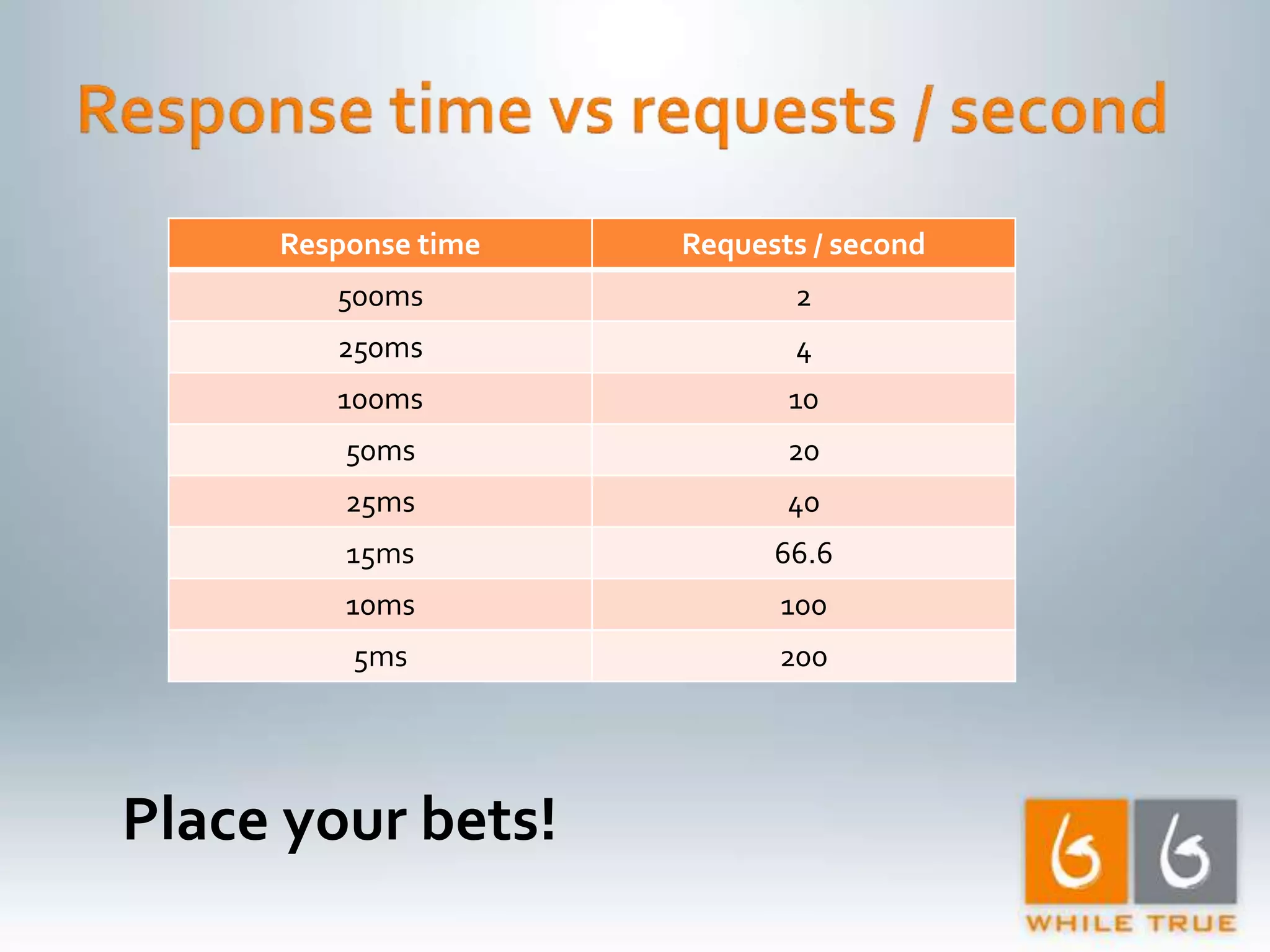
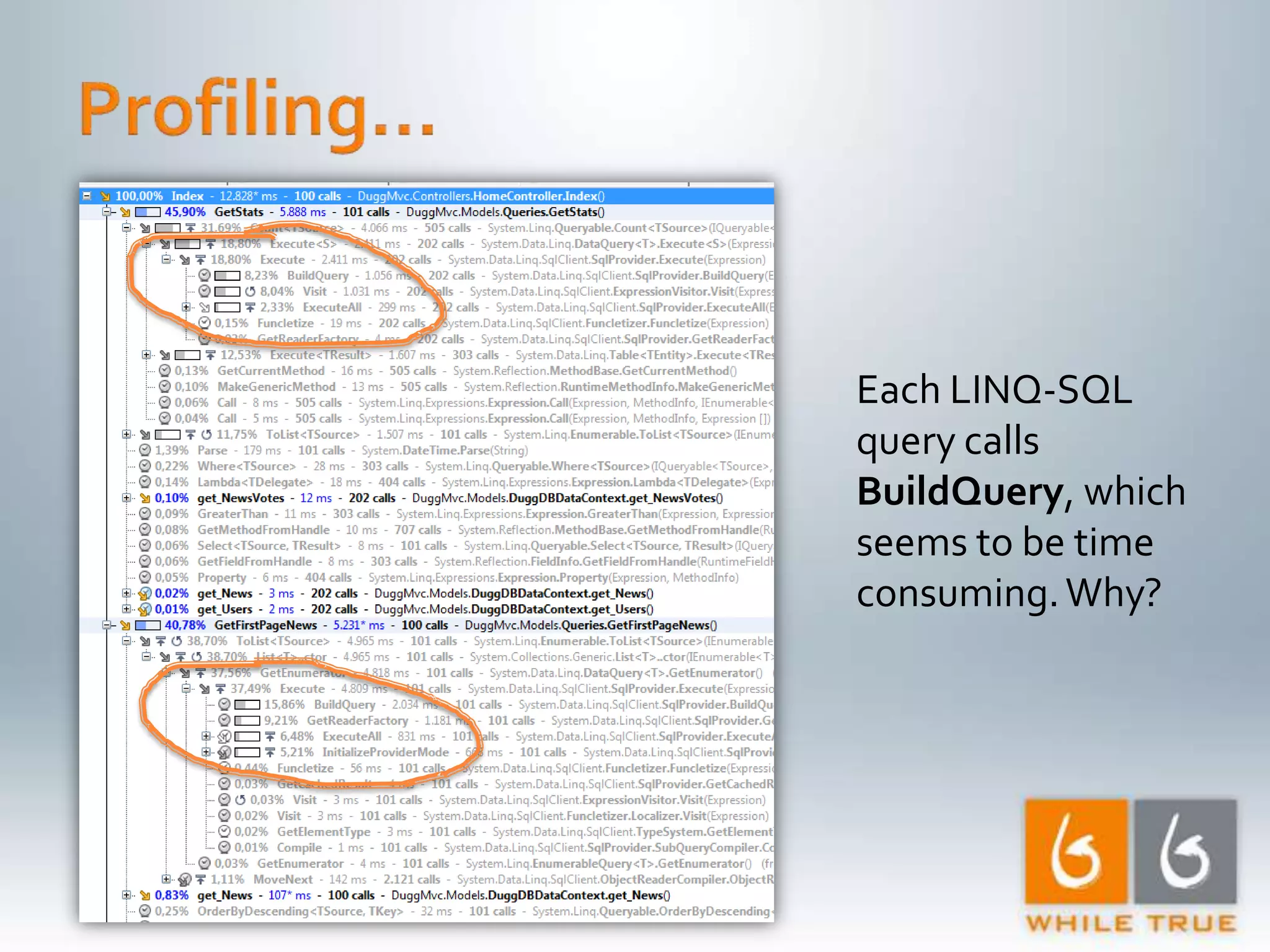
Testing response times using IIS7 and ApacheBench, demonstrating various response rates for concurrent requests.
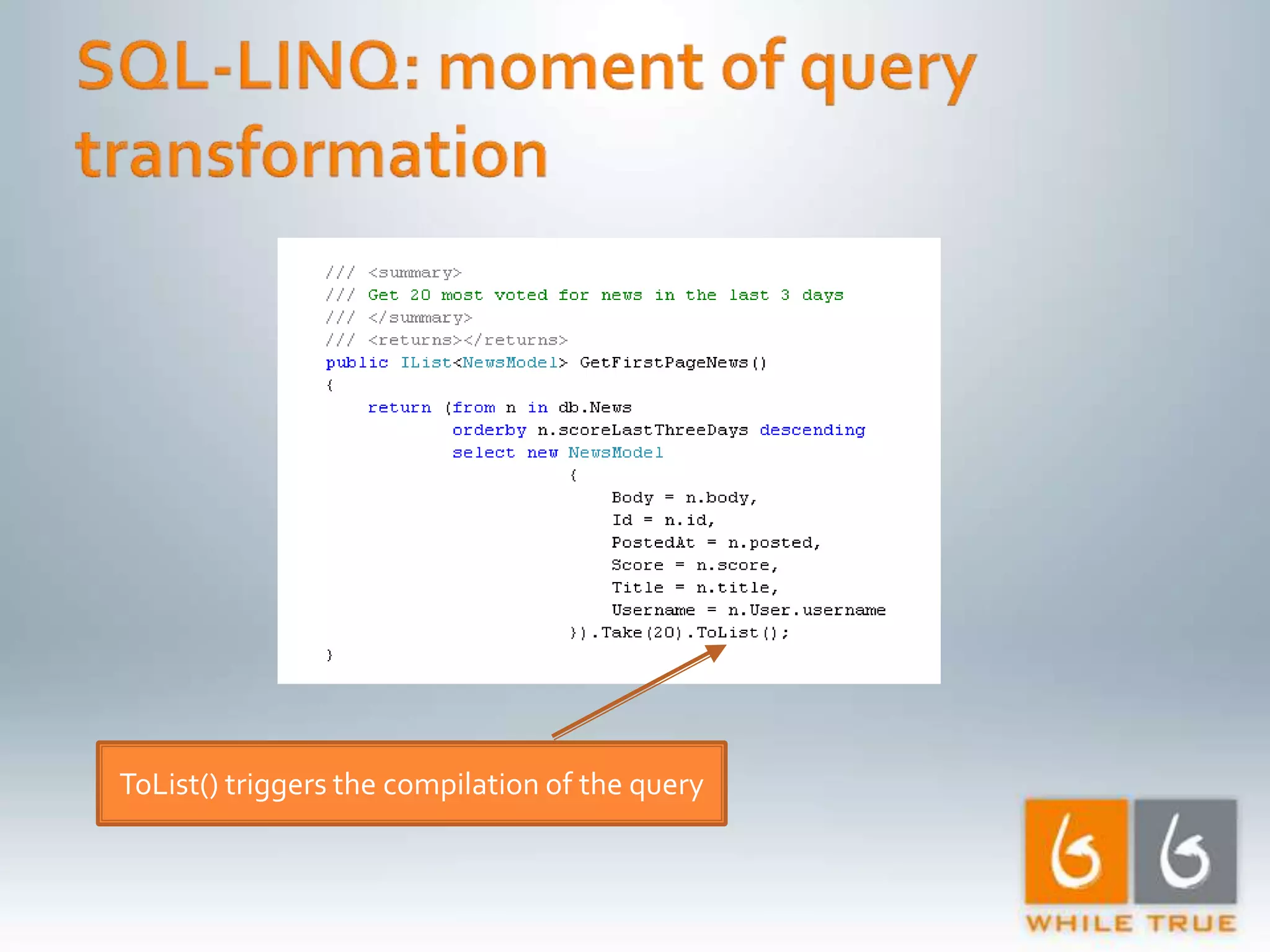
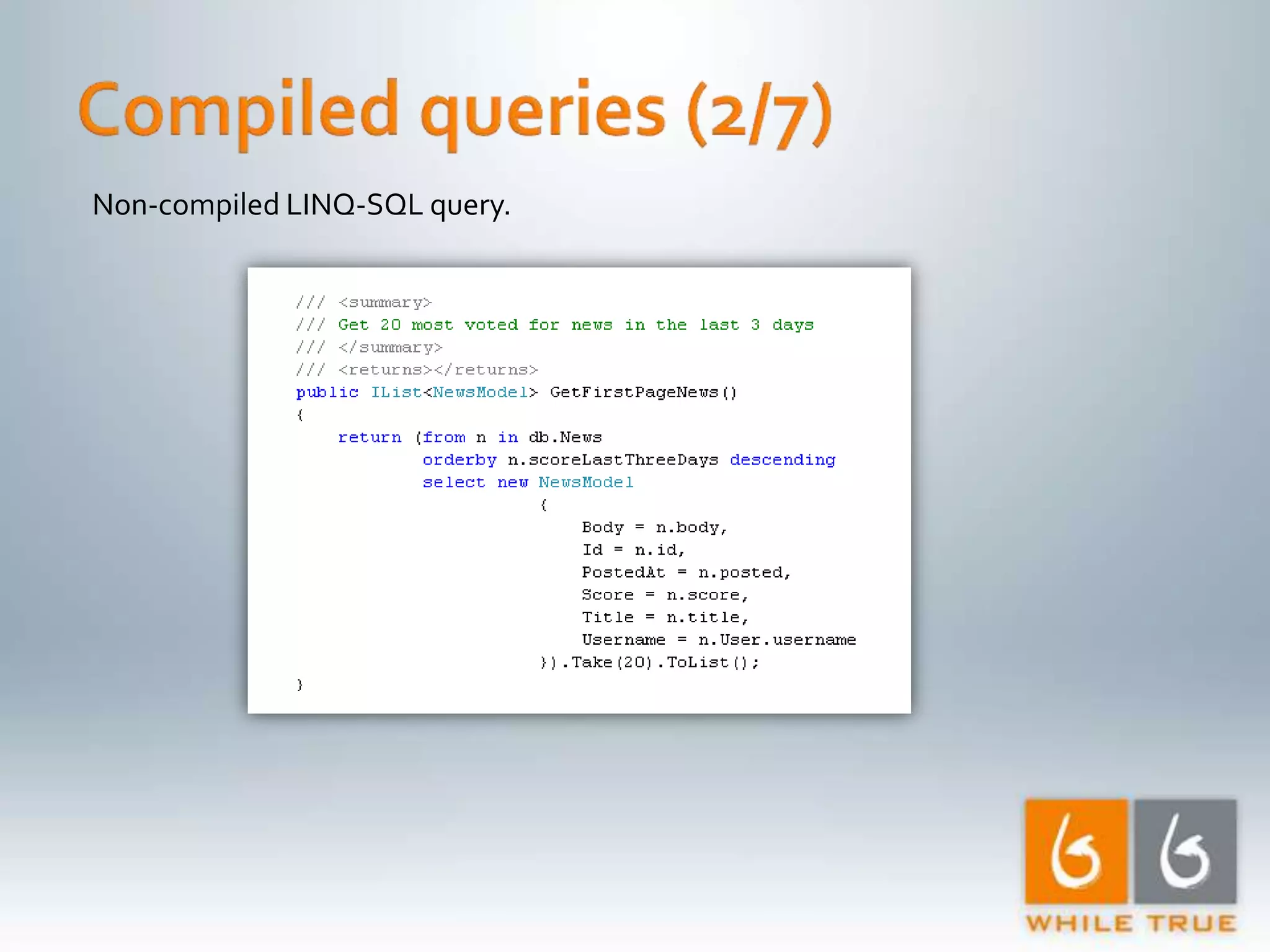
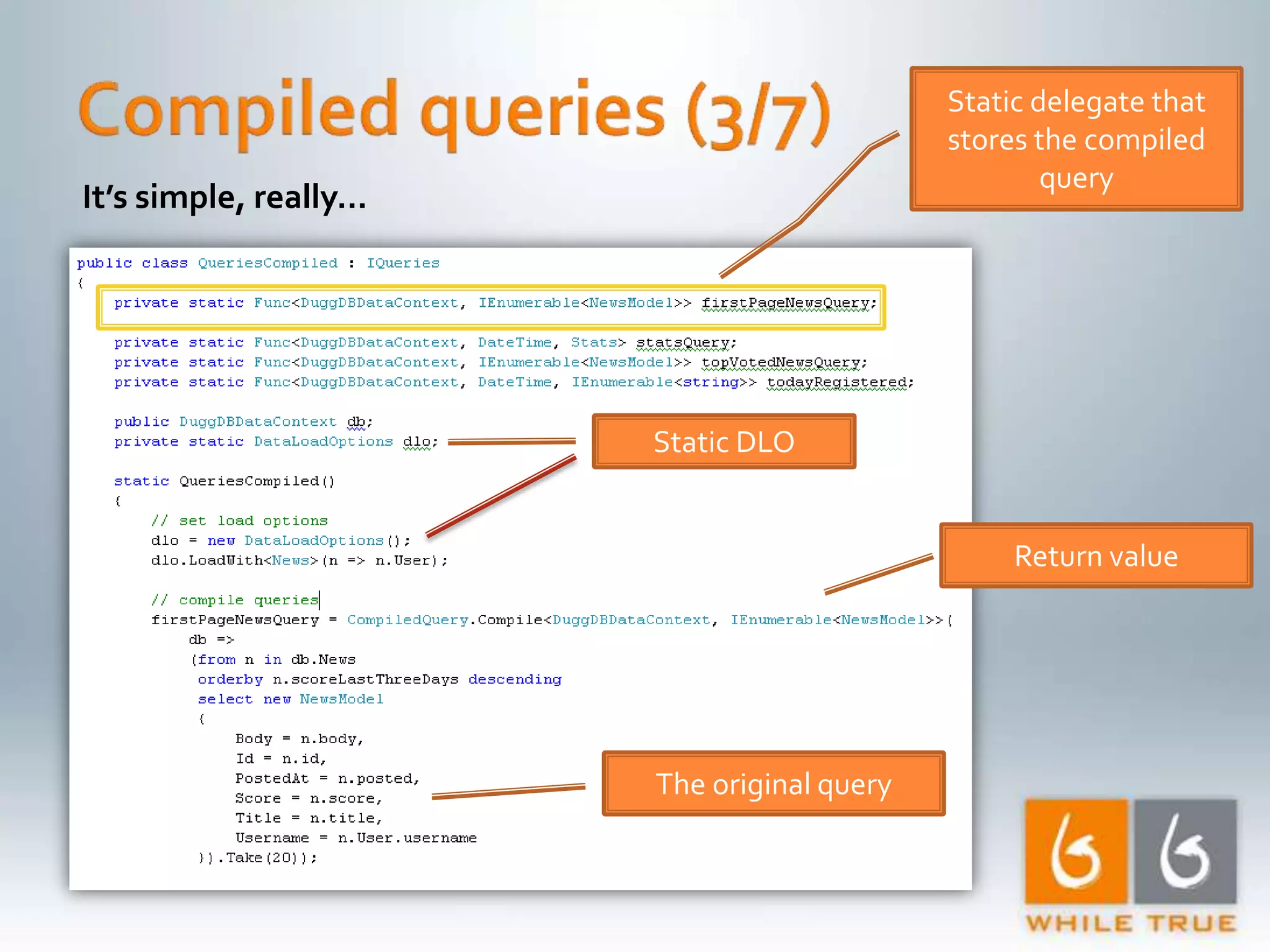
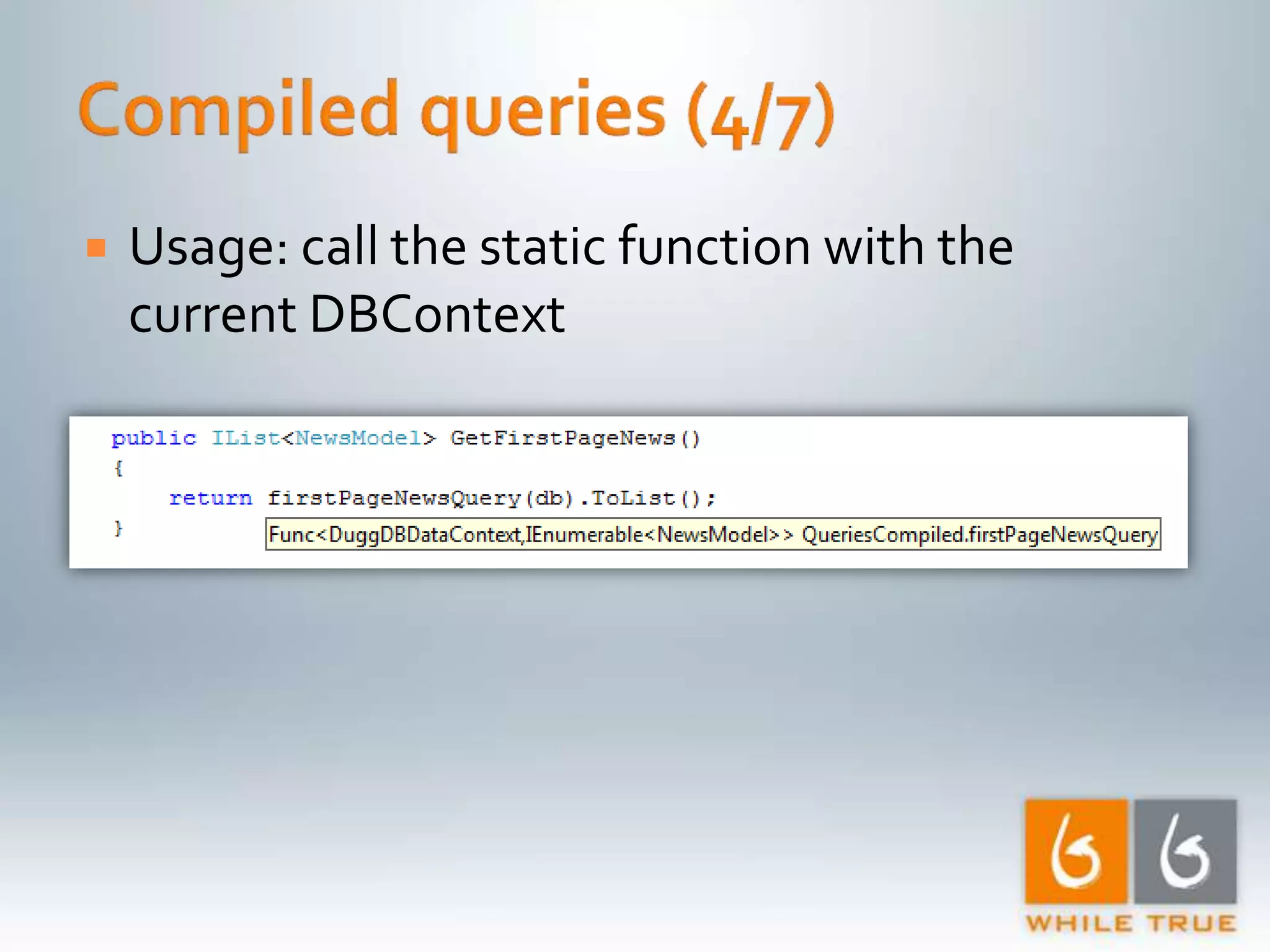
Highlighting the importance of responsive web applications, better user experience, and methods to enhance performance including LINQ-SQL optimizations.
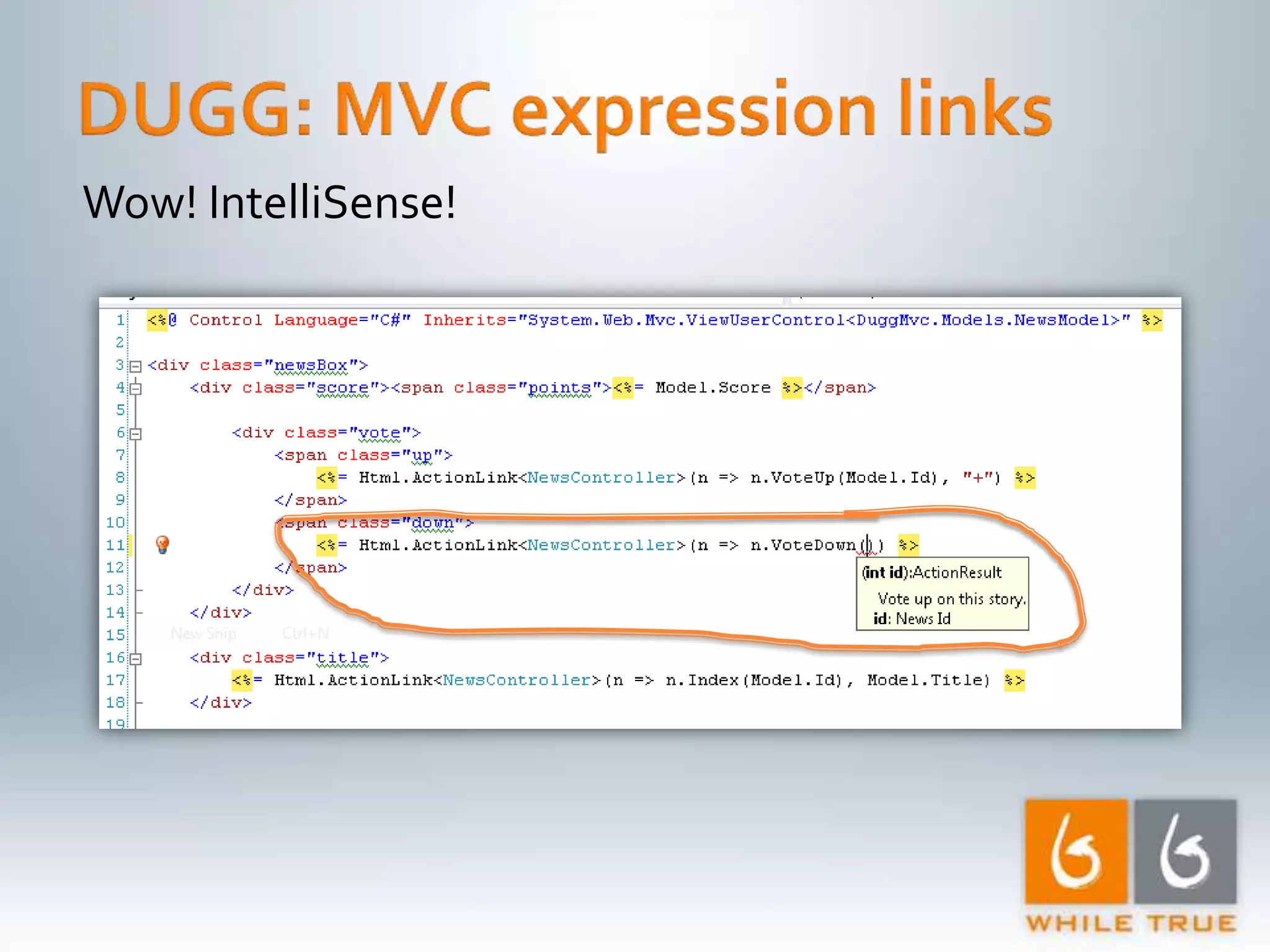
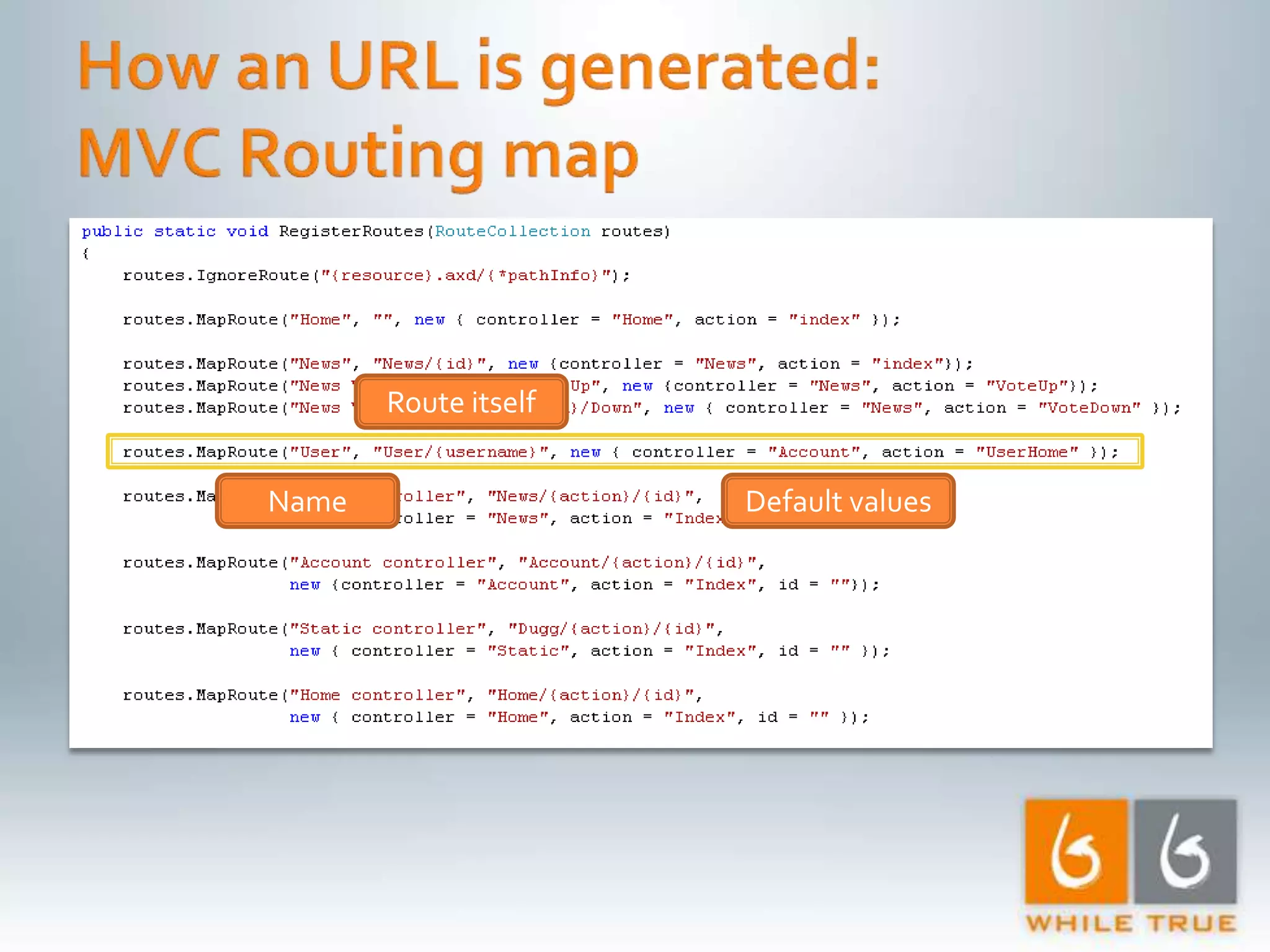
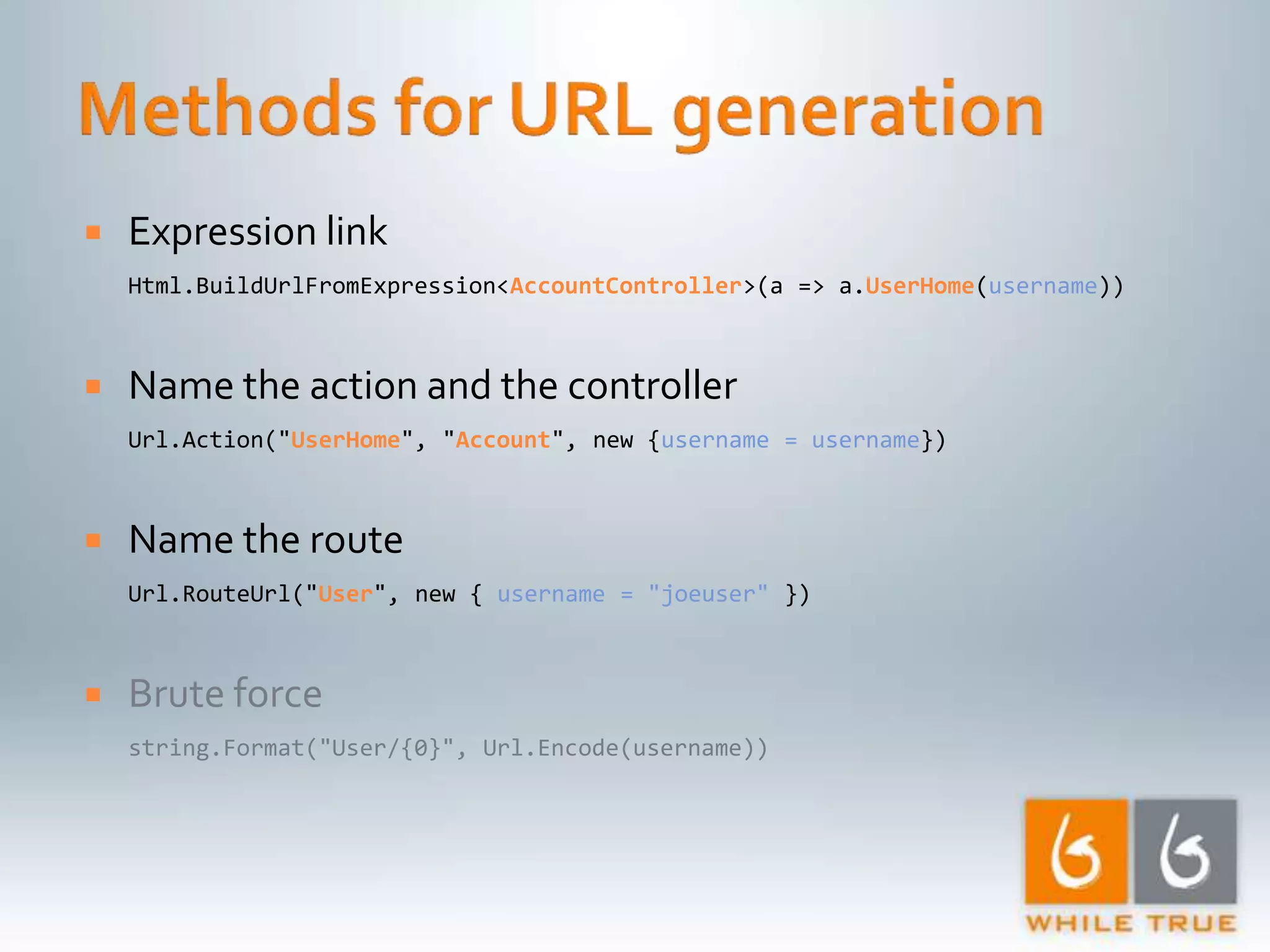
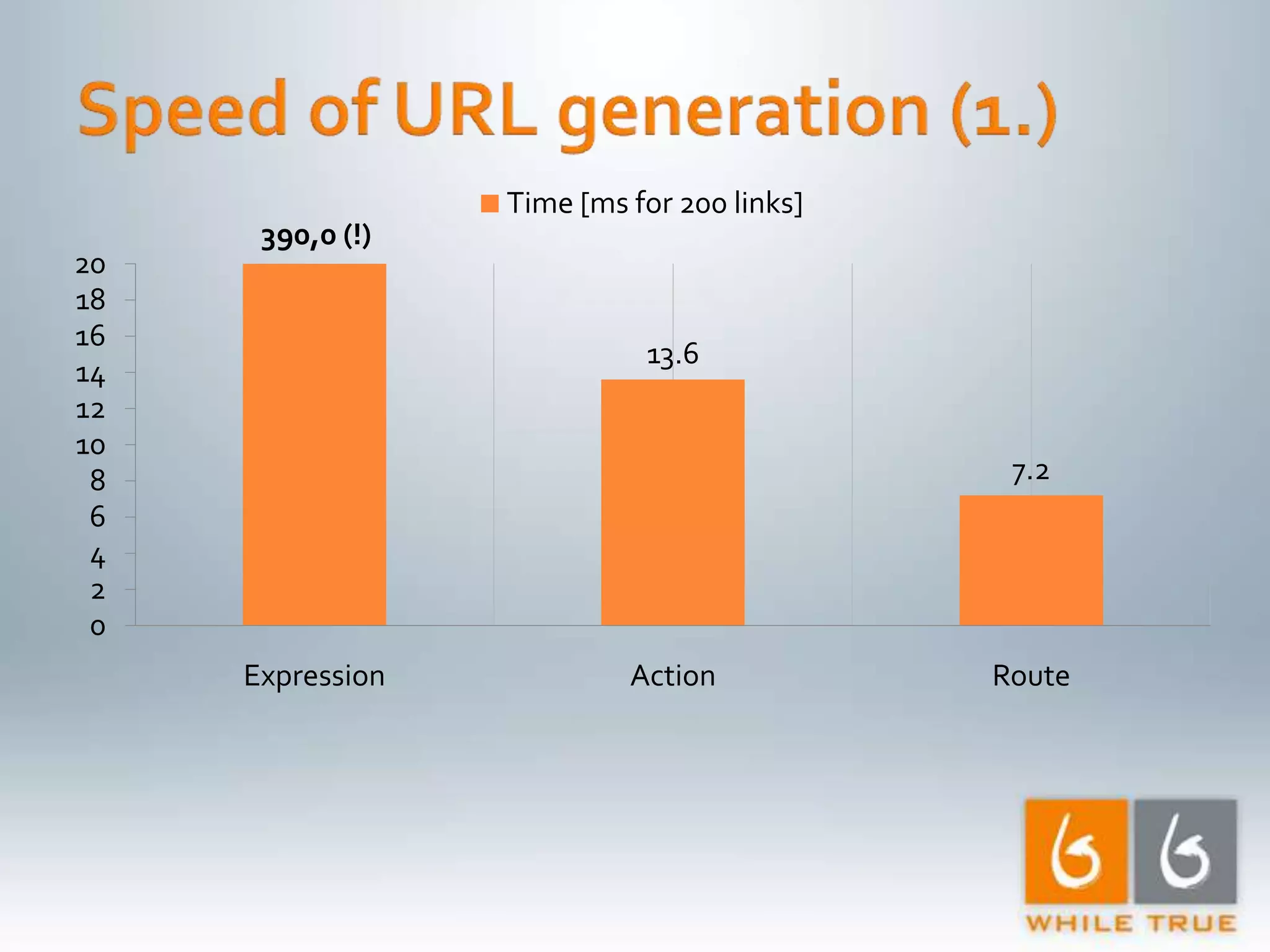
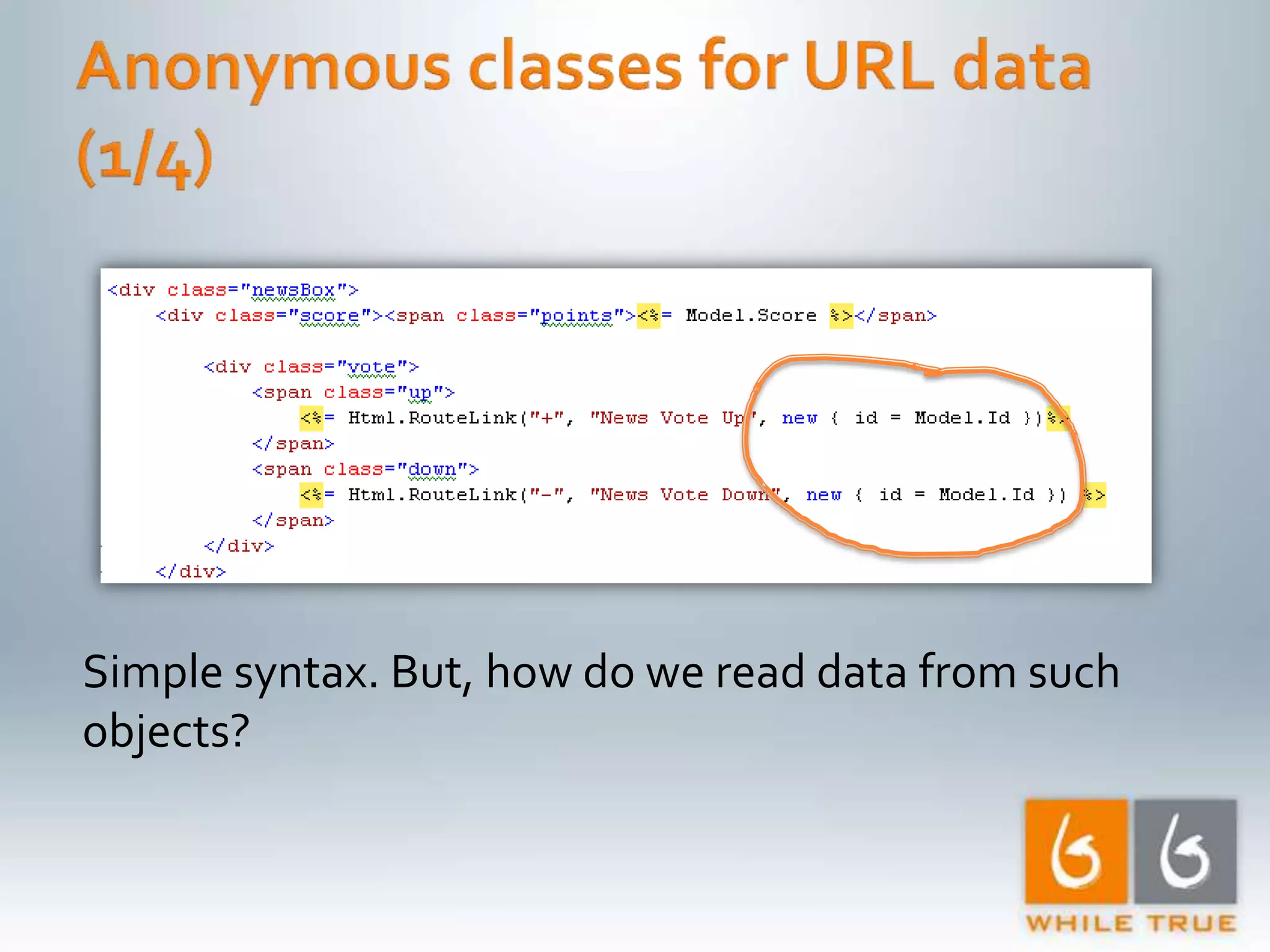
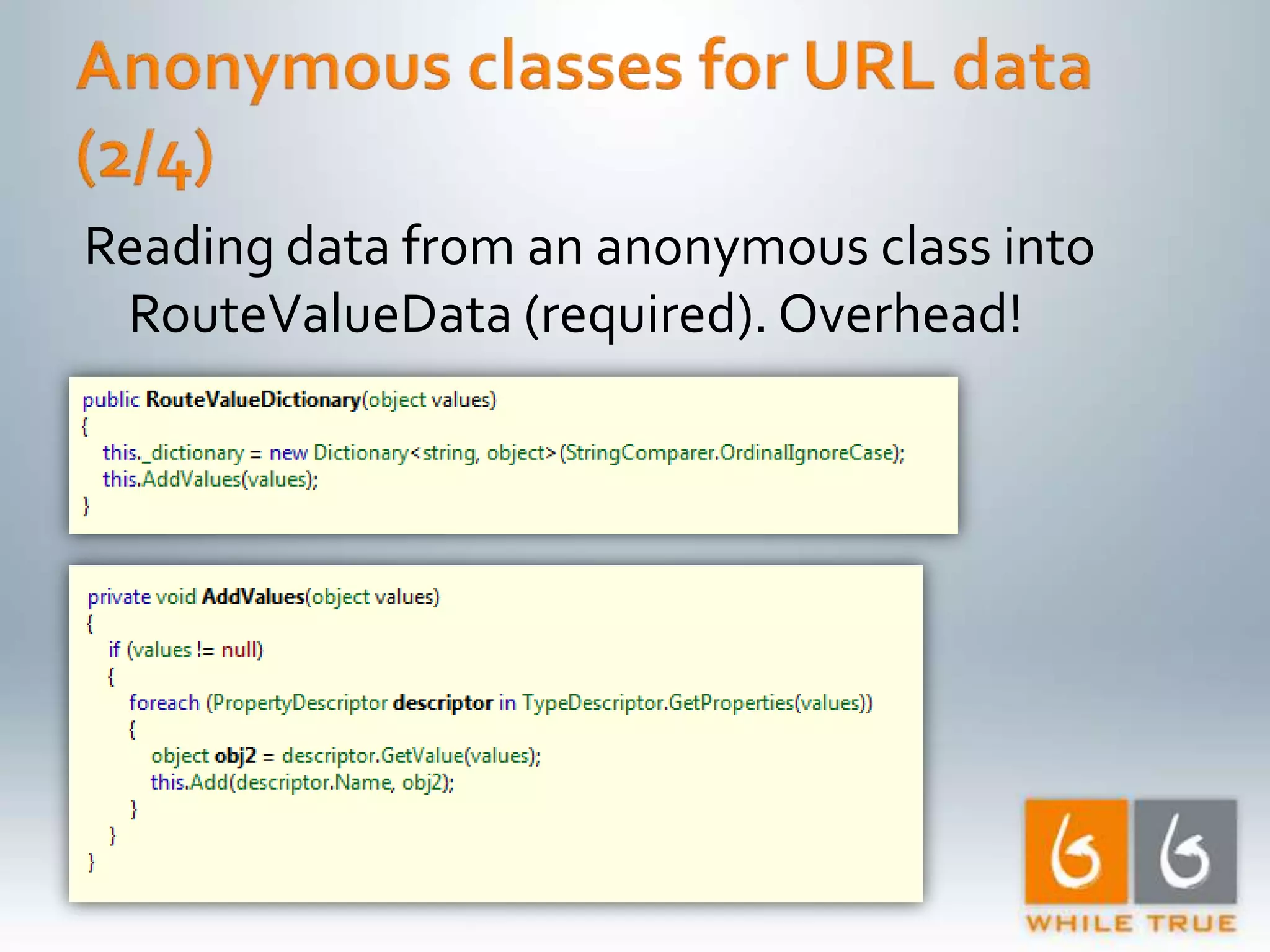
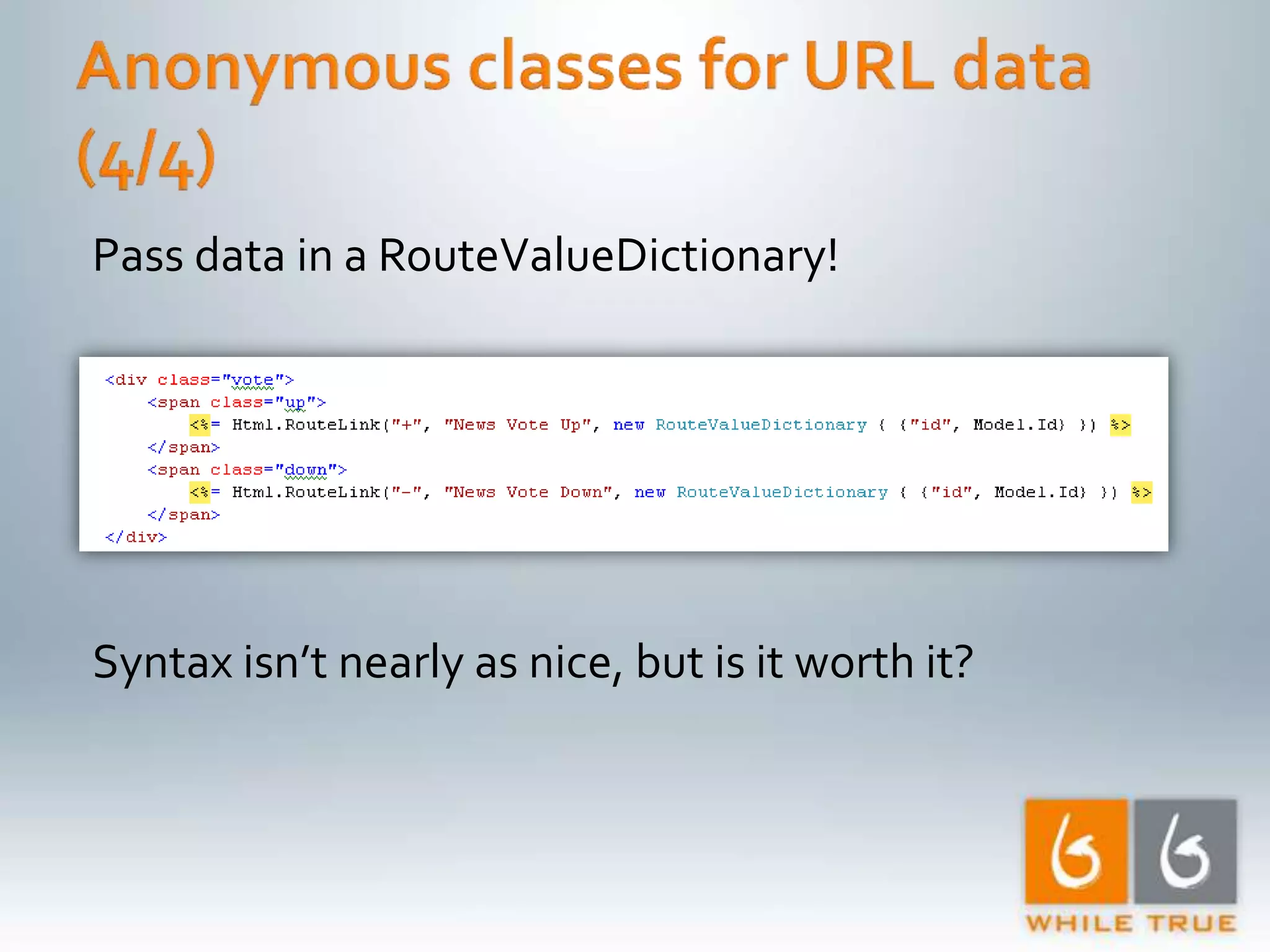
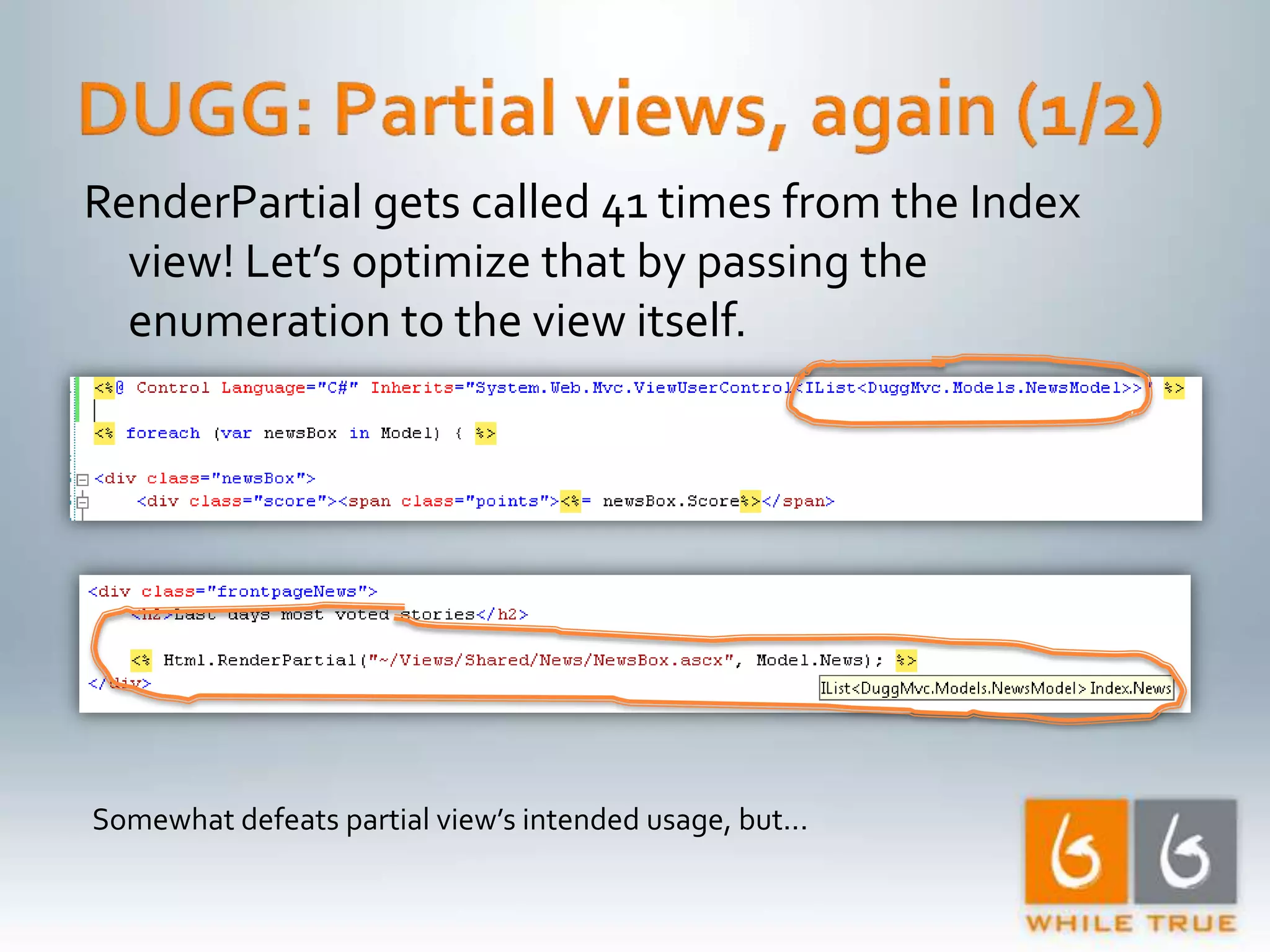
Demonstrating differences in performance between expressions and direct code paths in URL generation, showing efficiency and compilation impacts.
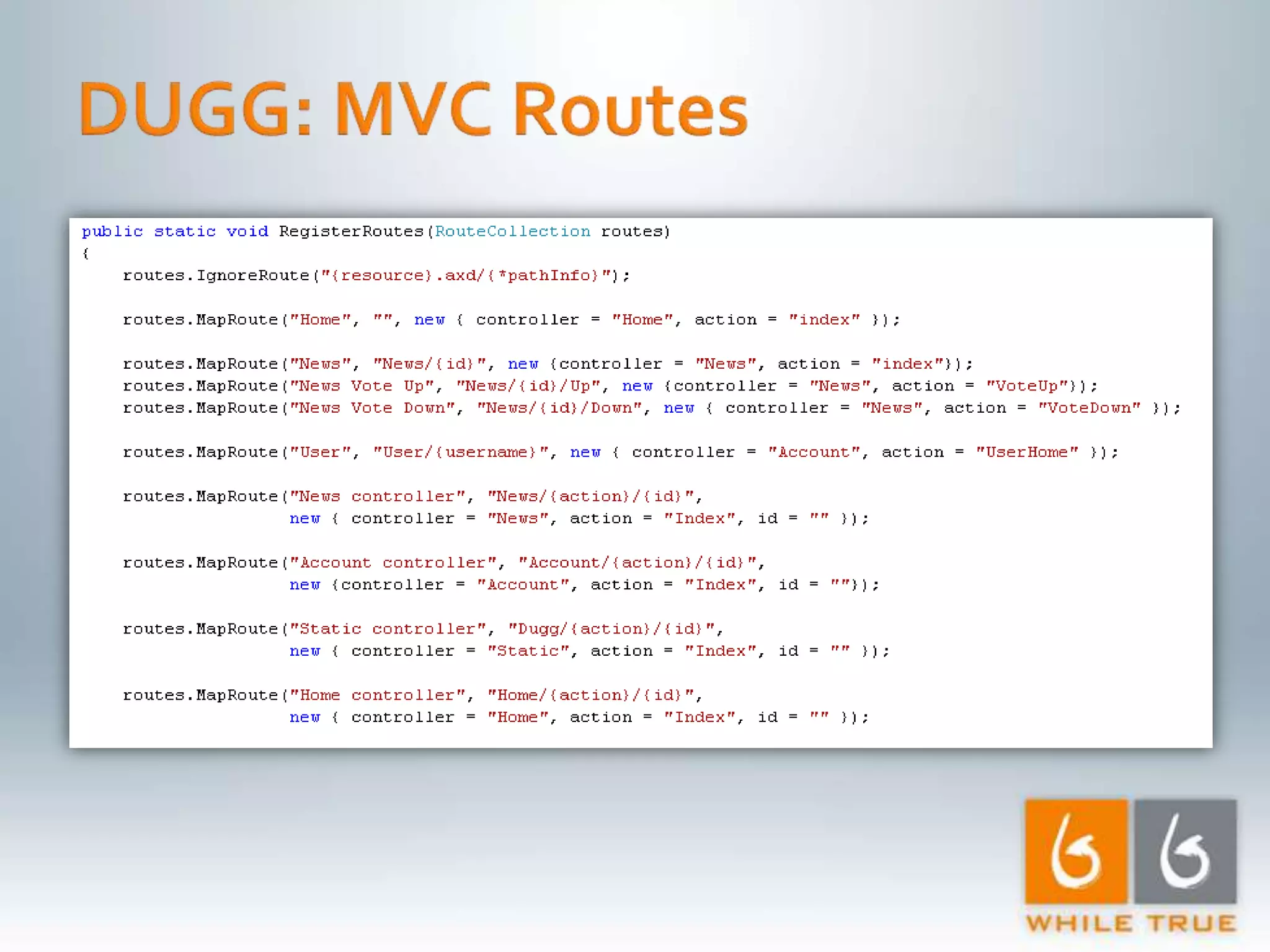
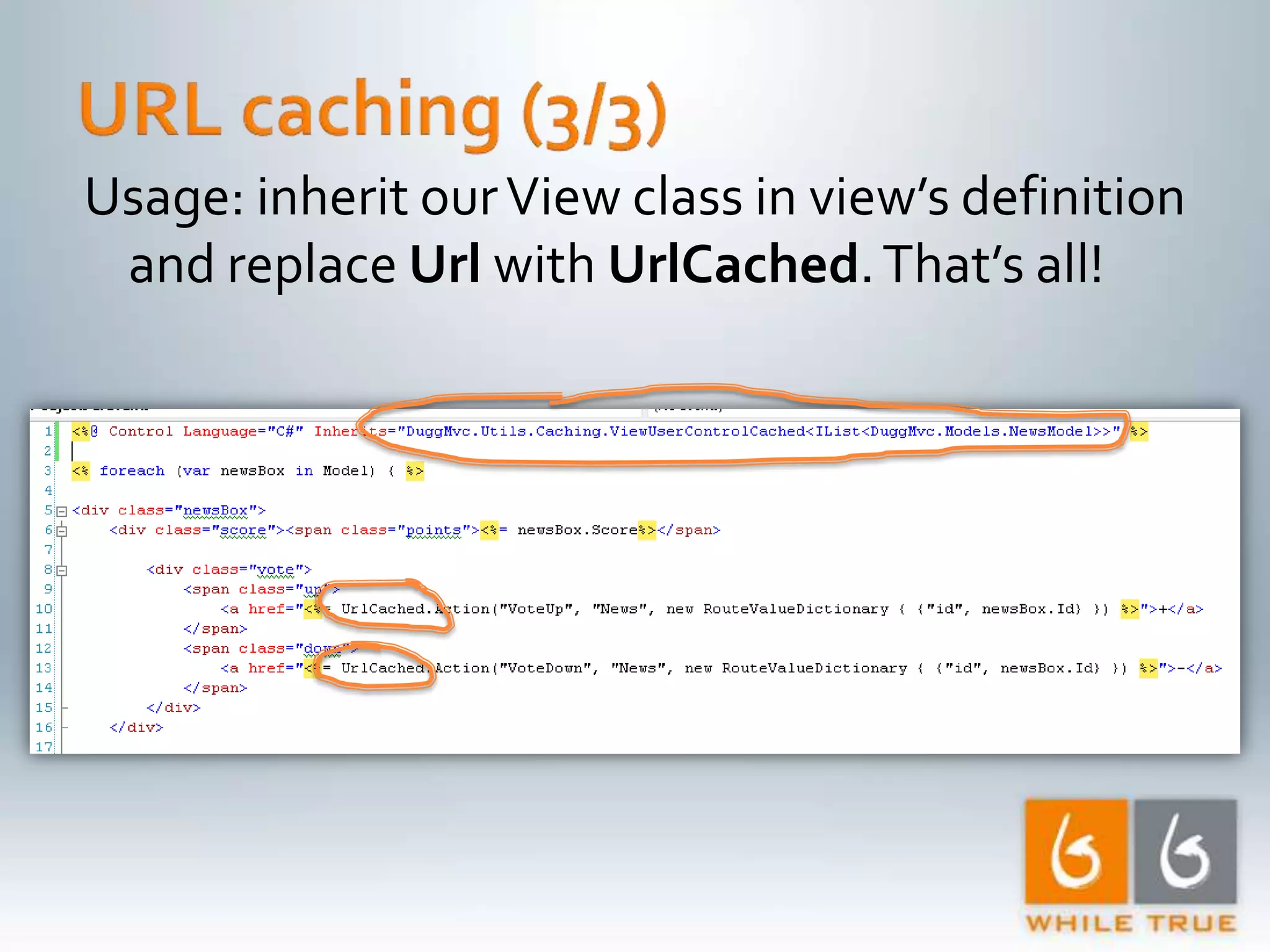
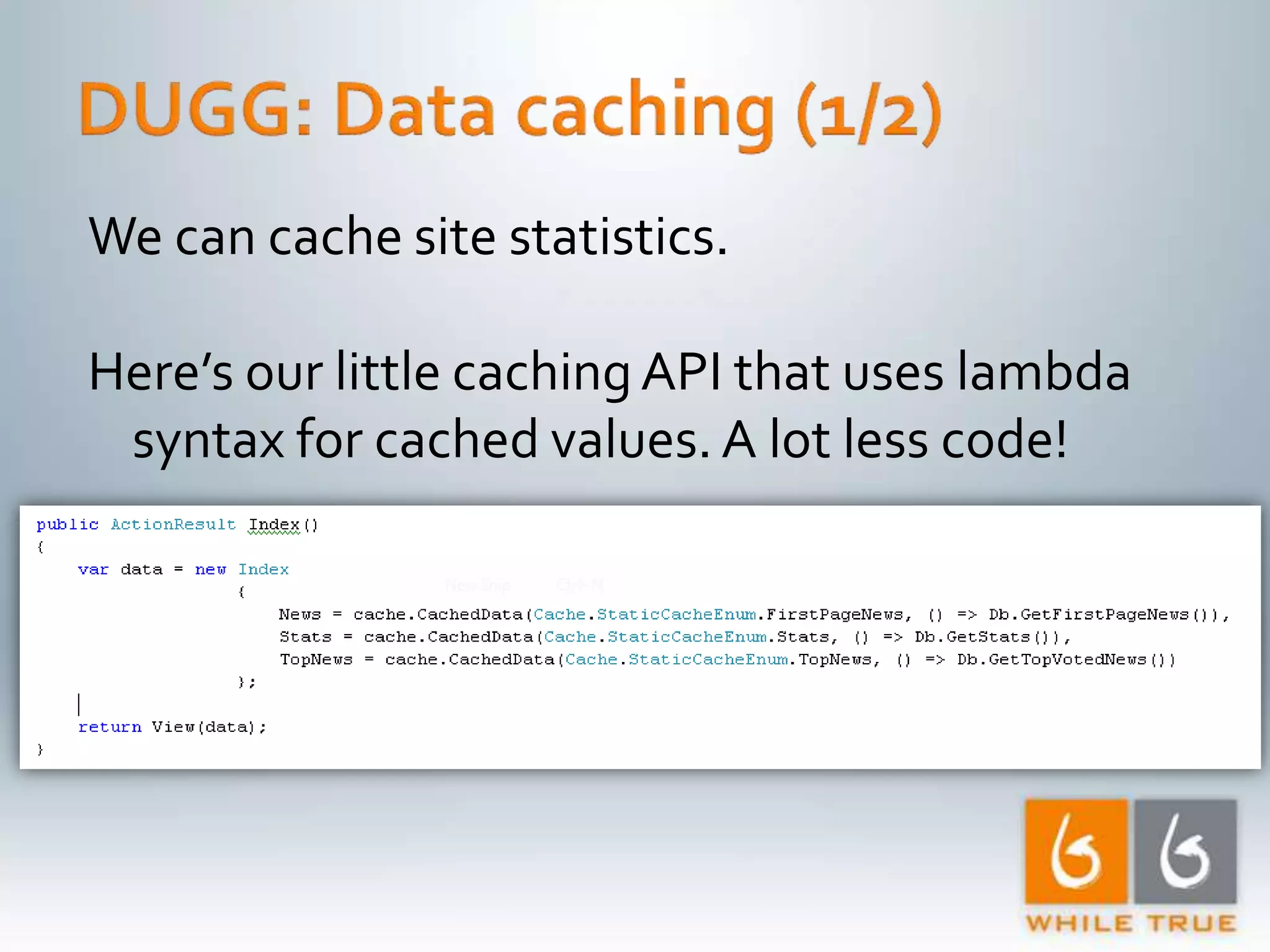
Implementation of caching strategies in MVC applications, discussing URL caching, data caching, and their impacts on request handling and performance.
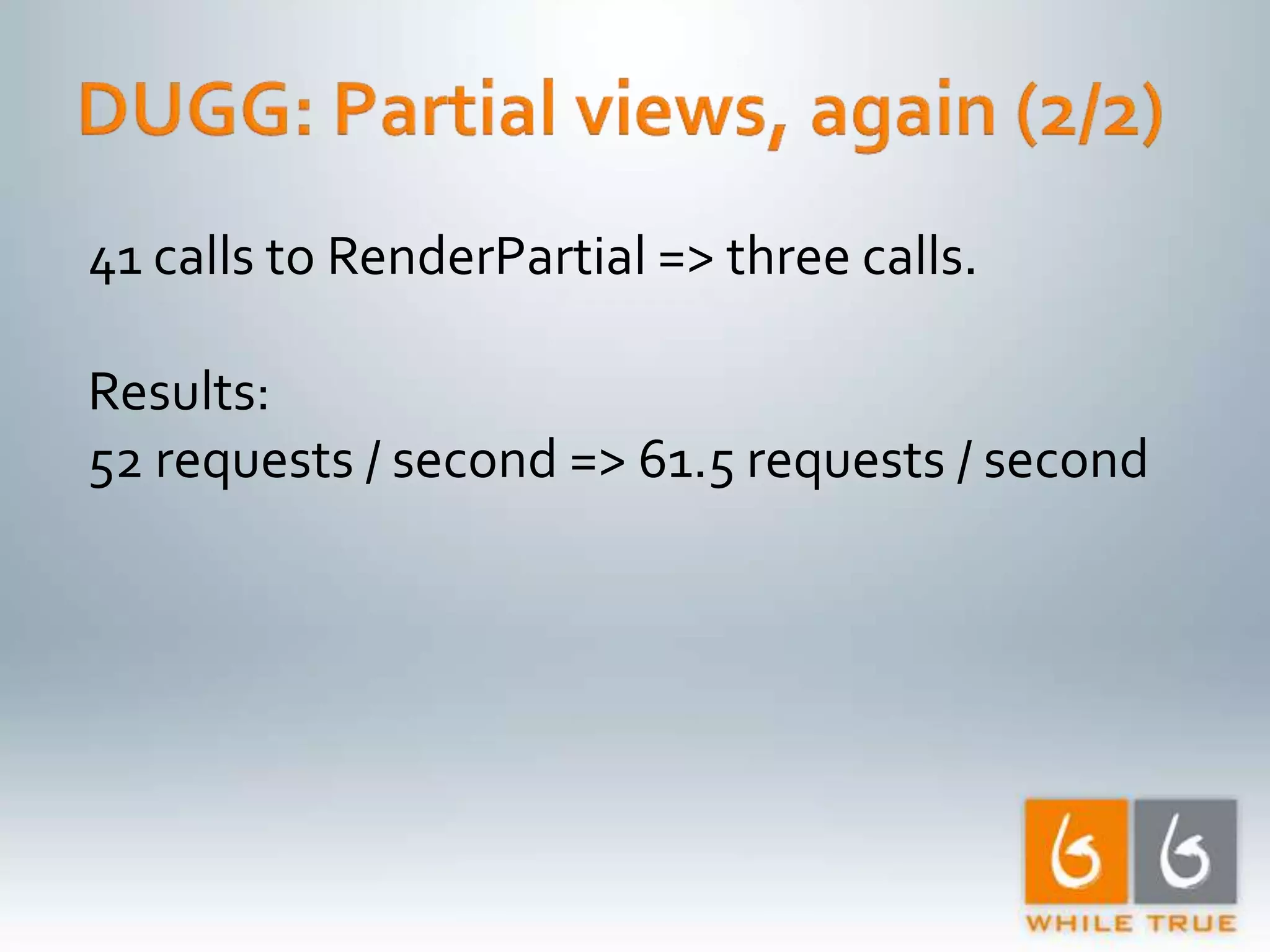
Overview of optimization methods leading to significant improvements, highlighting requests per second and the effectiveness of caching.
Suggestions for further optimizations, including smarter view compiling and builtin URL caching, highlighting benchmark observations.