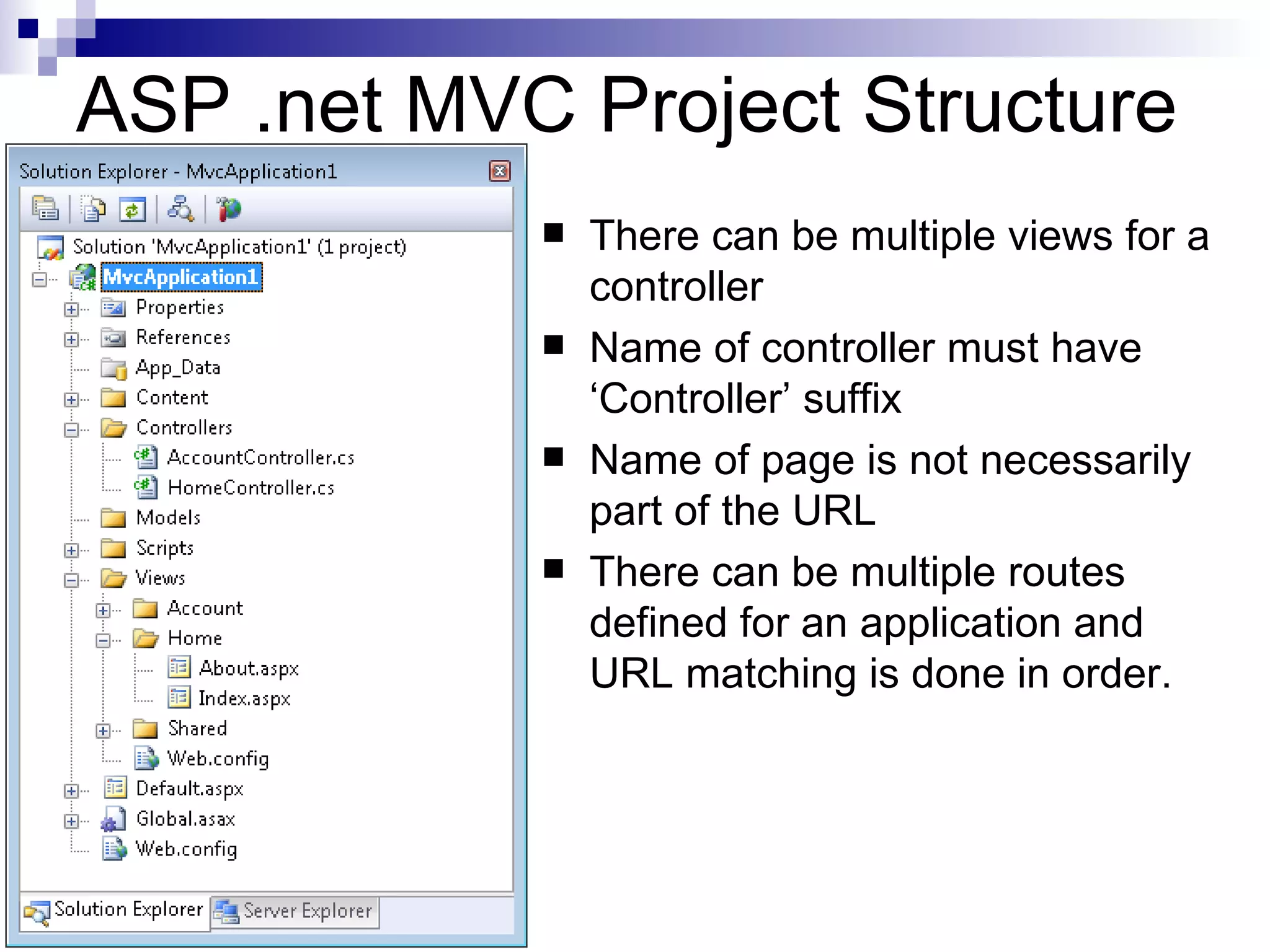
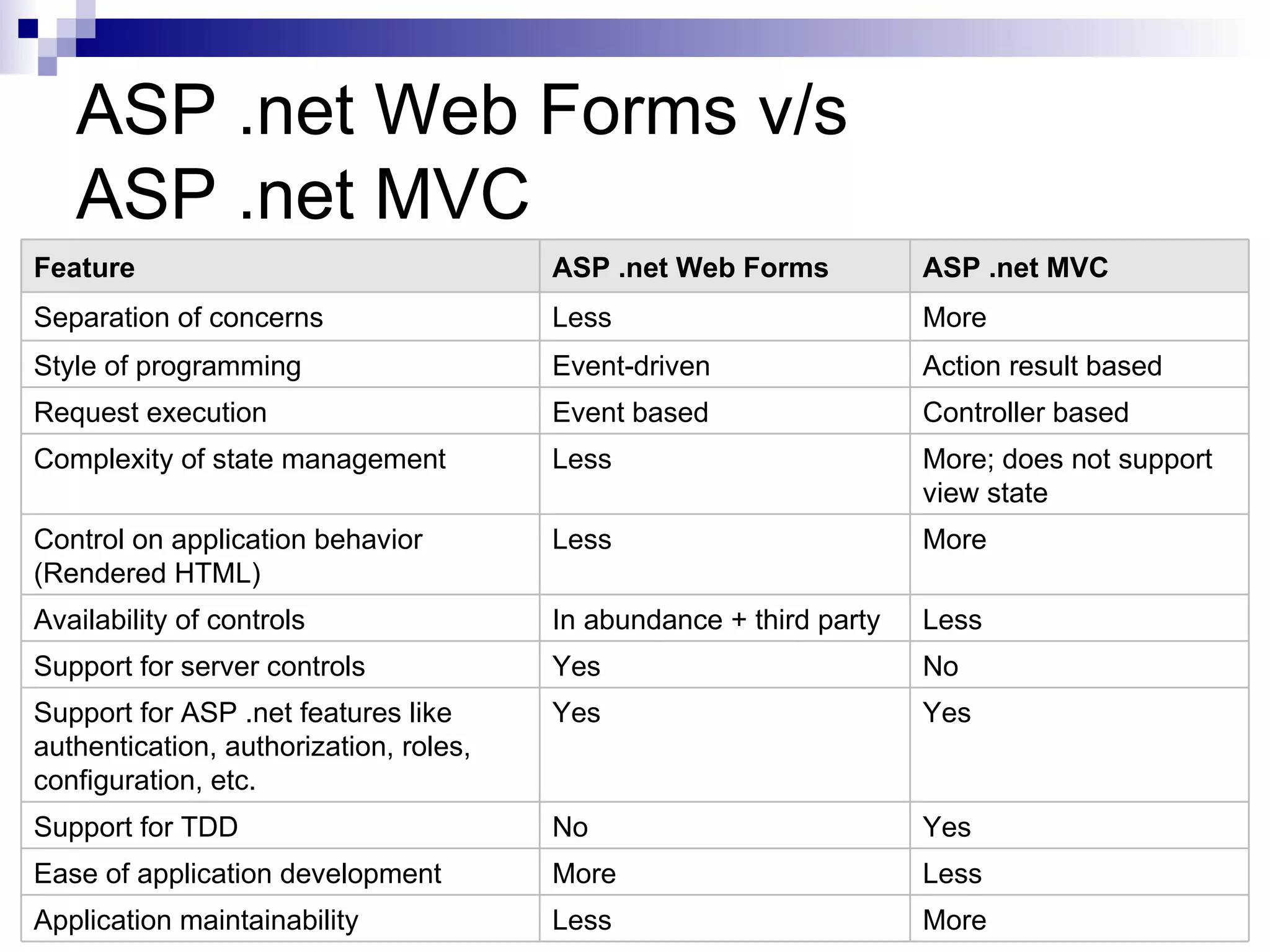
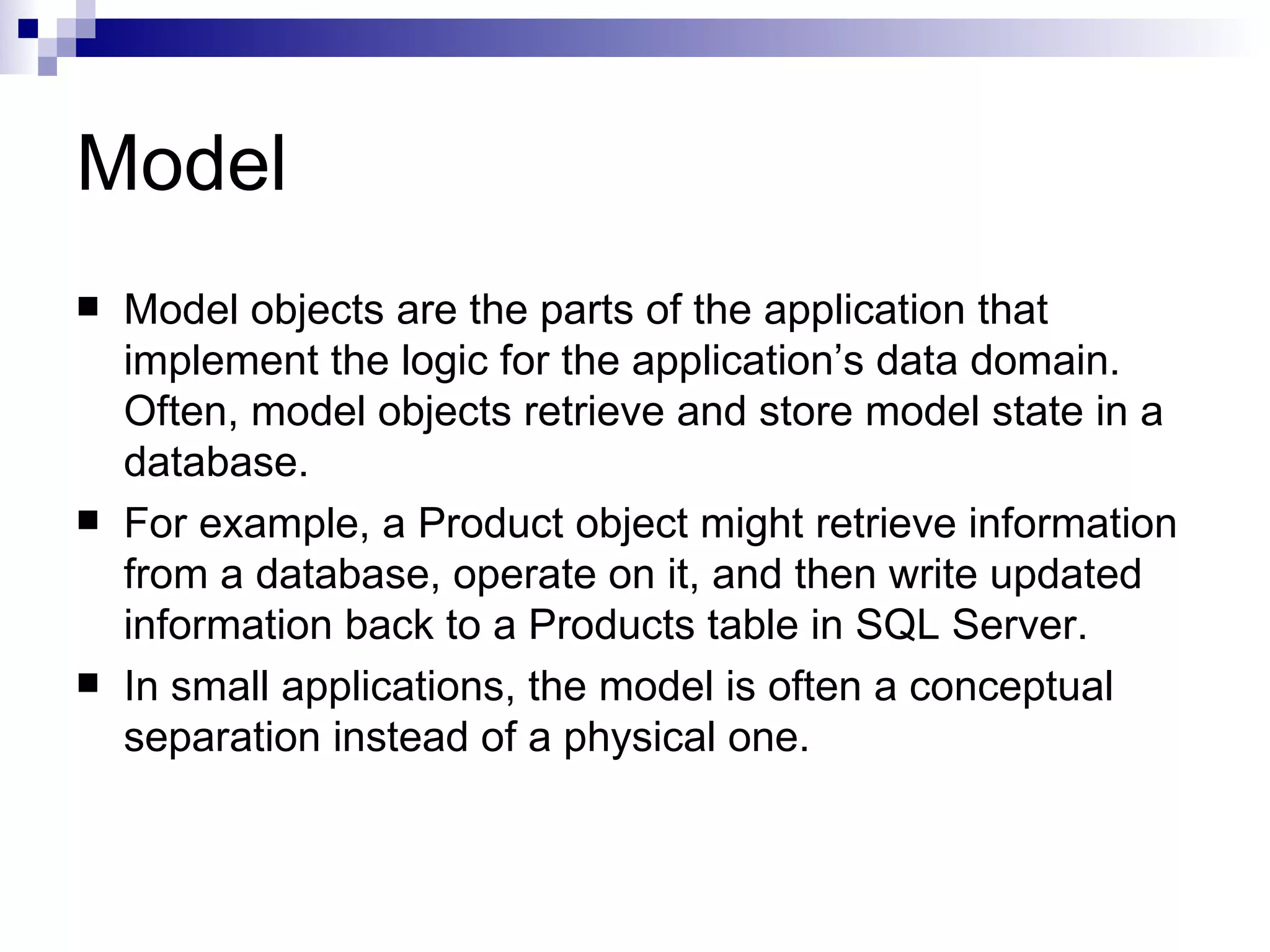
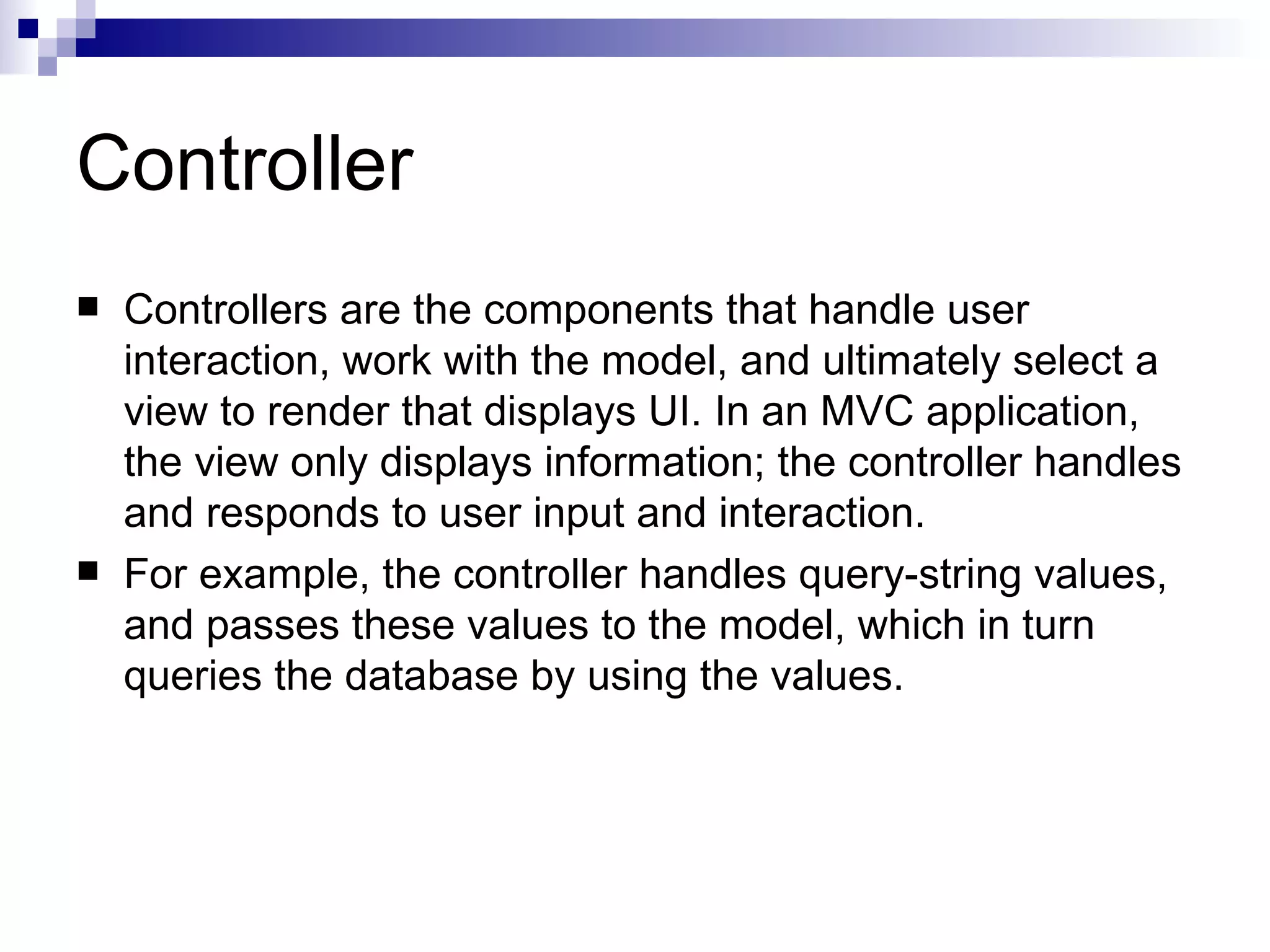
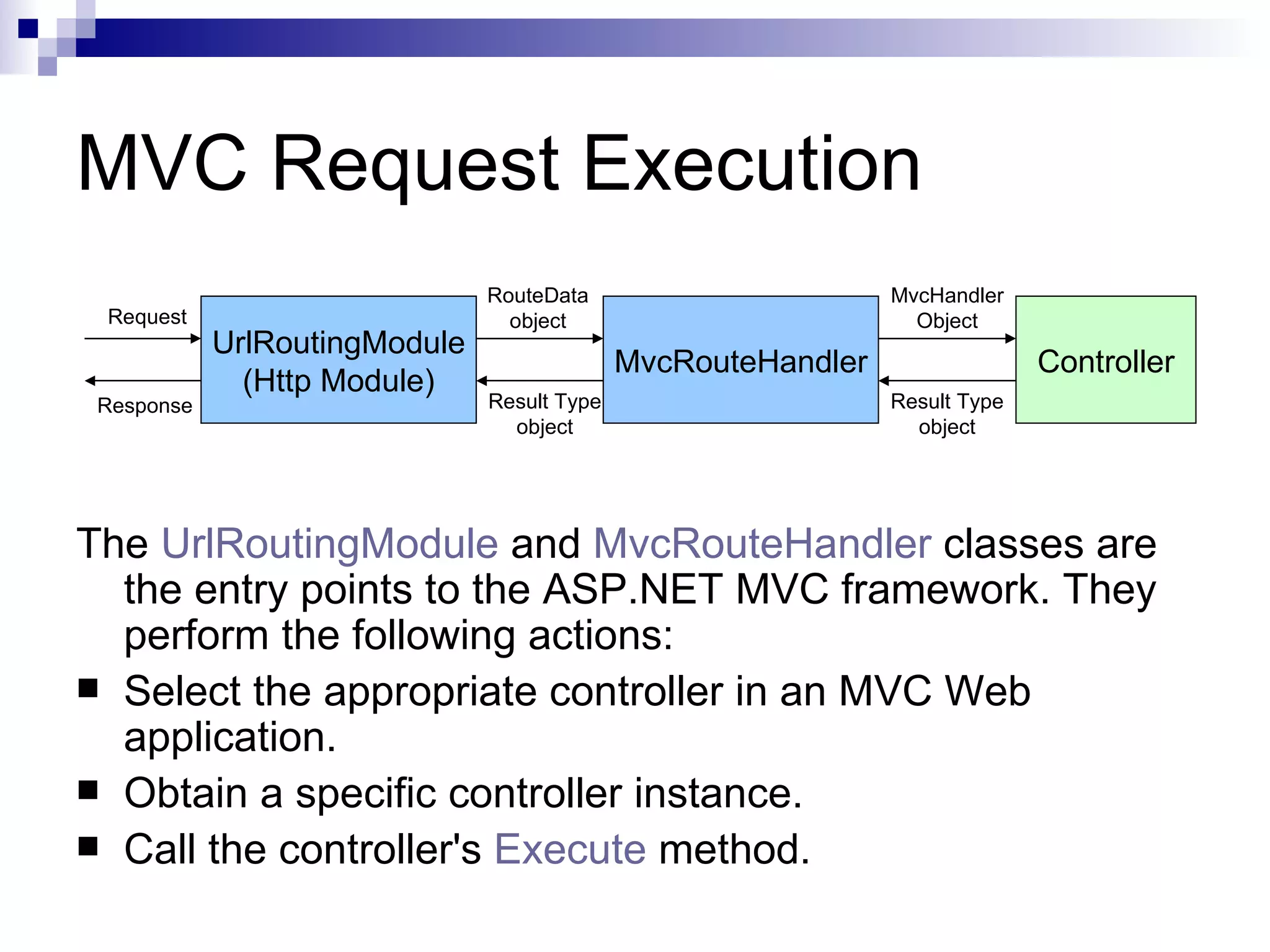
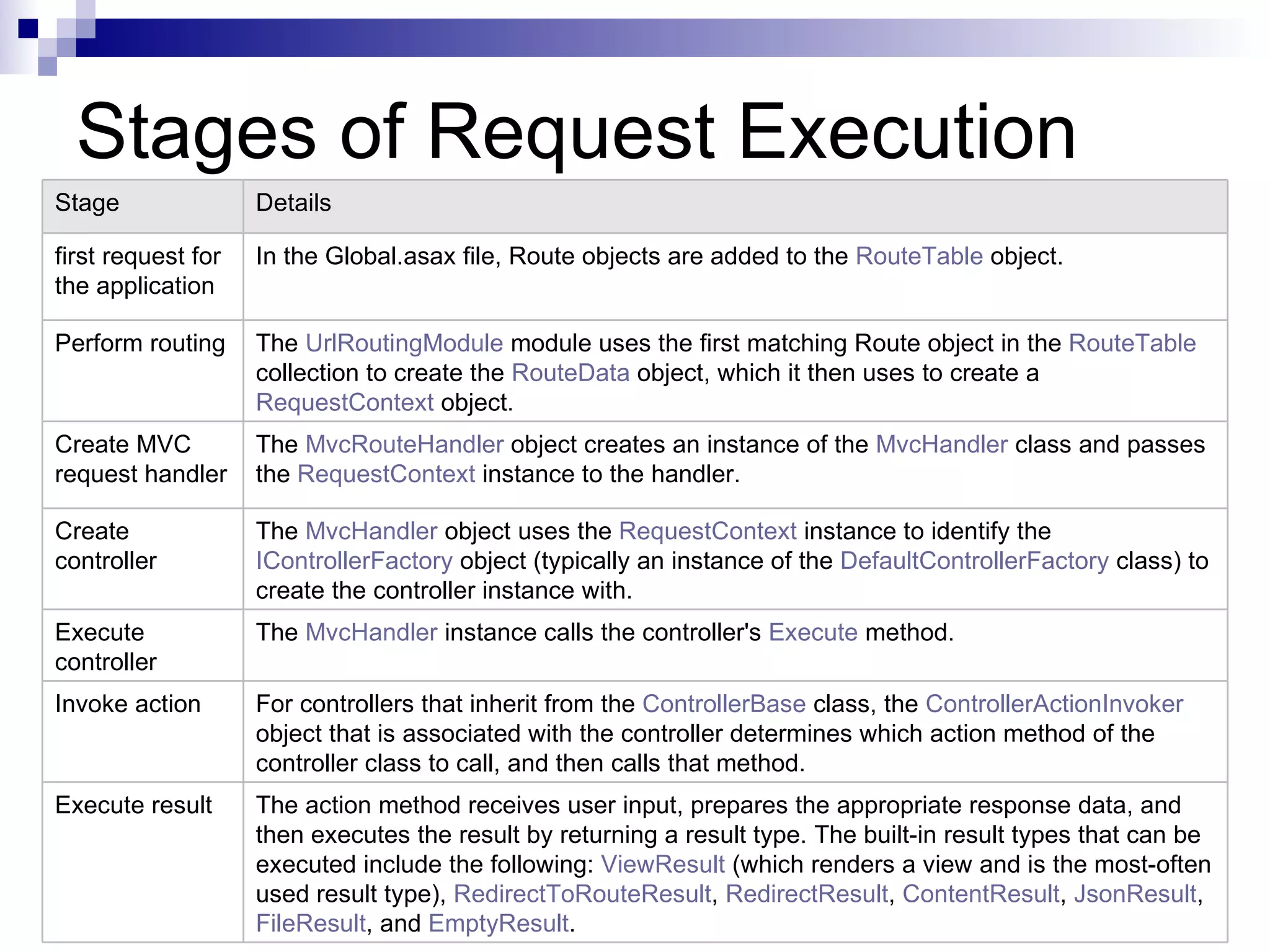
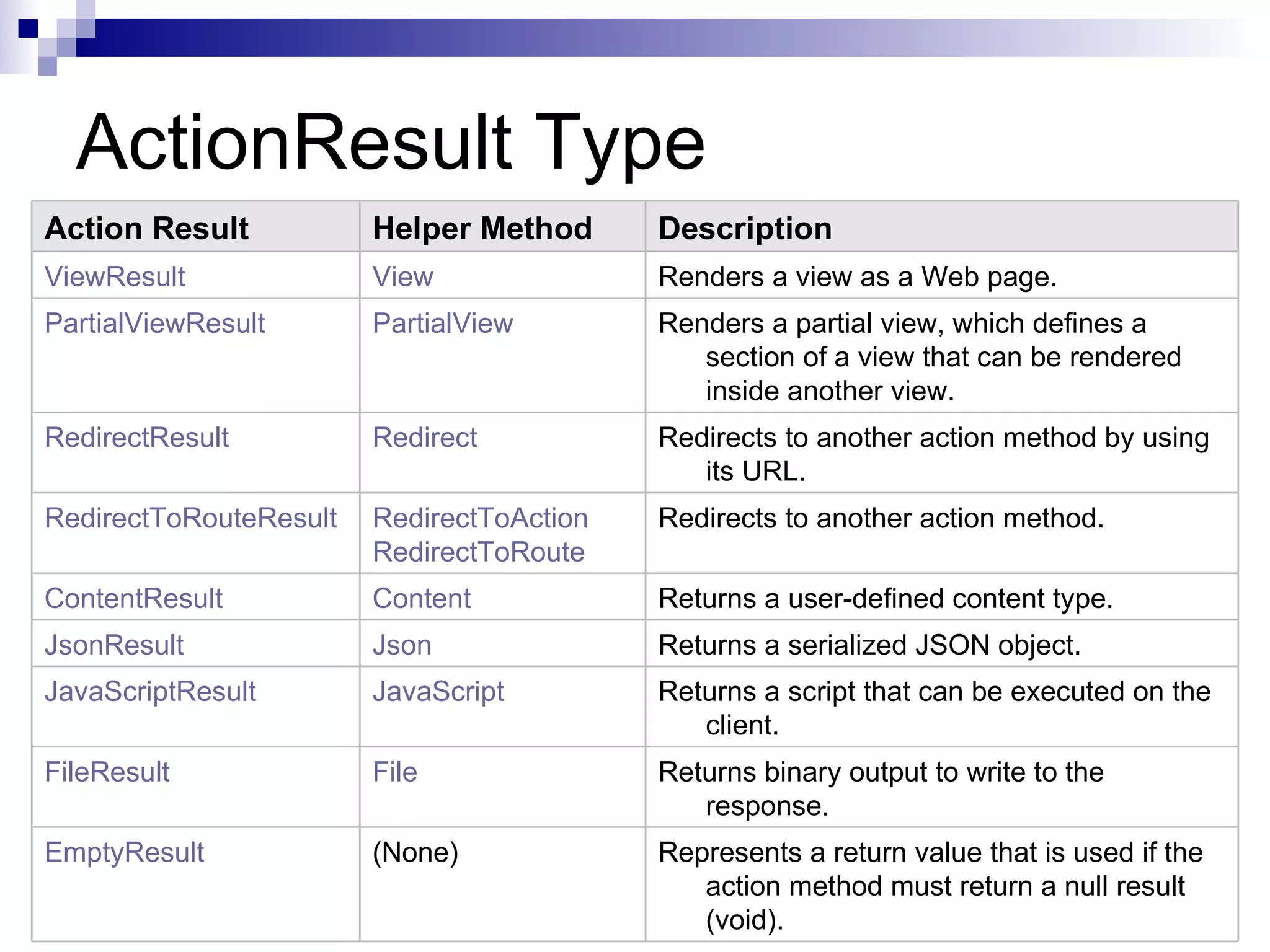
This document provides an overview of ASP.net MVC, including what MVC is, how ASP.net MVC request execution works, details on controllers, routing, application development, differences from web forms, and when to use MVC. It describes MVC as separating applications into models, views, and controllers, and how ASP.net MVC implements the MVC pattern with controllers handling user input and selecting views. Request processing and controller lifecycles are also summarized at a high level.



![Controllers and ActionResult // action methods that render view pages // HelloWorld action method URL = Home/Index and Home/About with value for view data. URL = Home/HellowWorld [HandleError] public class public class HomeController : Controller HomeController : Controller { { public ActionResult Index() [ControllerAction] { public ActionResult ViewData["Msg"] = "Welcome" ; HelloWorld() return View(); { ViewData["Message"] = "Hello } World!"; public ActionResult About() return View(); { } return View(); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-netmvc-120511110101-phpapp01/75/ASP-net-MVC-10-2048.jpg)
![Controllers and ActionResult // non action method // optional arguments for action method e.g. URL = Products/ShowProduct/P1?23 or [NonAction] URL = Products/ShowProduct/P1?23 private void DoSomething() public ActionResult ShowProduct(string { category, int? id) // Method logic. { } if(!id.HasValue) { // use Request object to retrieve query string value id = 0; public void Detail() } { // ... int id = } Convert.ToInt32(Request["id "]); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-netmvc-120511110101-phpapp01/75/ASP-net-MVC-11-2048.jpg)


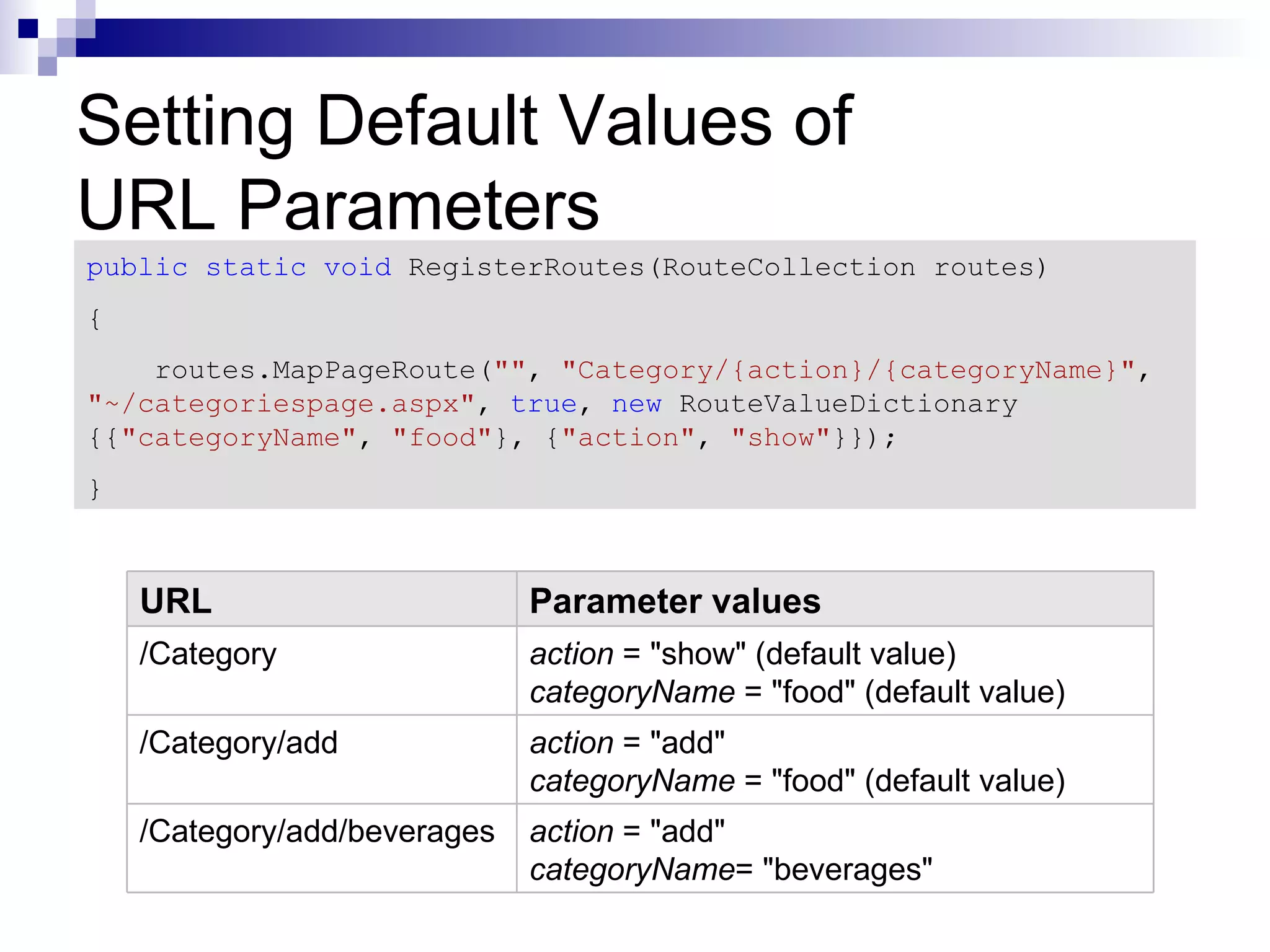
![Adding Constraints to Routes public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) { routes.MapPageRoute("", "Category/{action}/{categoryName}", "~/categoriespage.aspx", true, new RouteValueDictionary {{"categoryName", "food"}, {"action", "show"}}, new RouteValueDictionary {{"locale", "[a-z]{2}-[a-z]{2}"},{"year", @"d{4}"}} ); } URL Result /US No match. Both locale and year are required. /US/08 No match. The constraint on year requires 4 digits. /US/2008 locale = "US" year = "2008"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asp-netmvc-120511110101-phpapp01/75/ASP-net-MVC-16-2048.jpg)